Study on overlying rock fissure and energy evolution law of high intensity mining working face adjacent to gob
-
摘要:
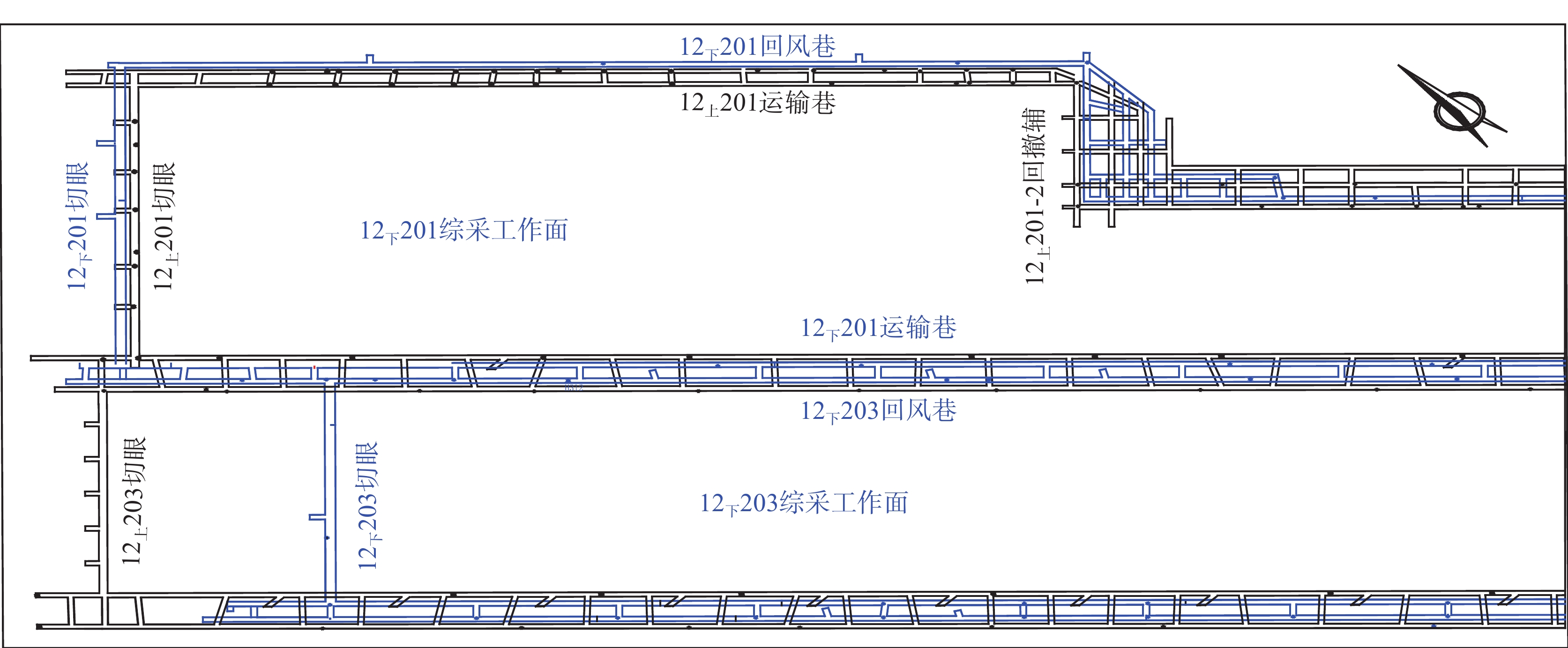
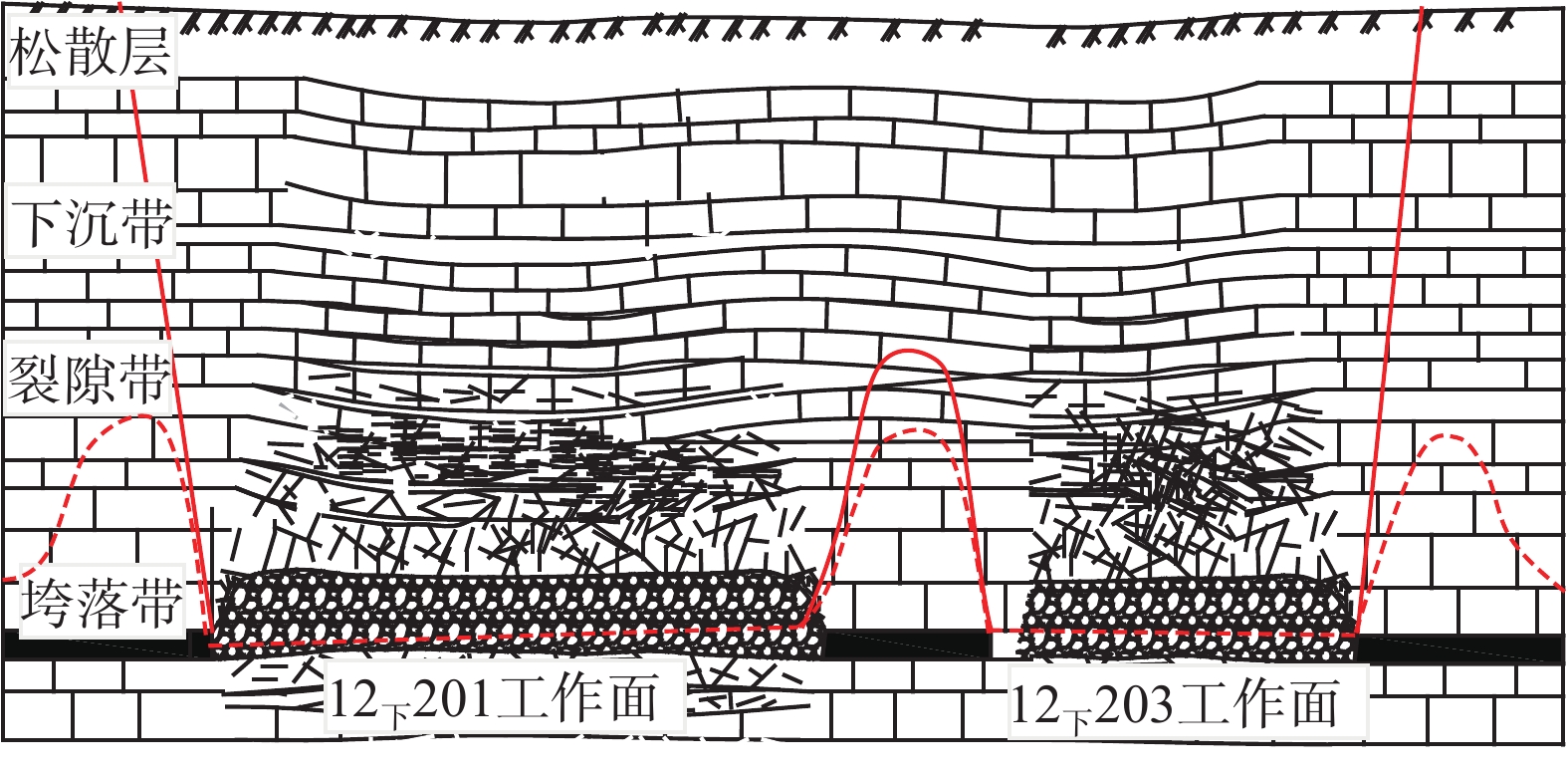
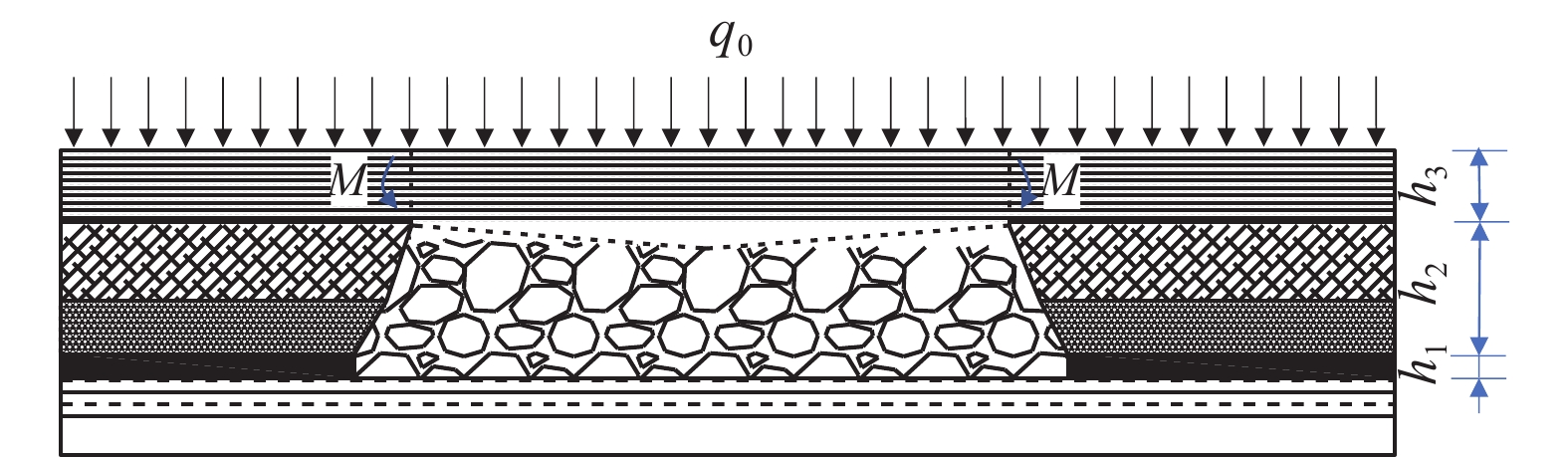
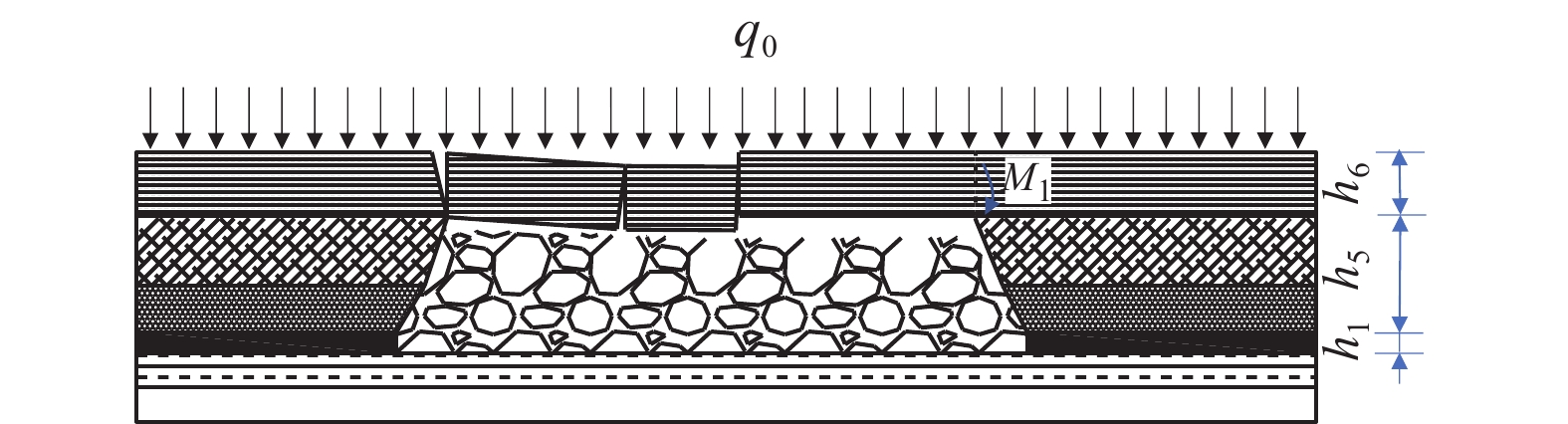
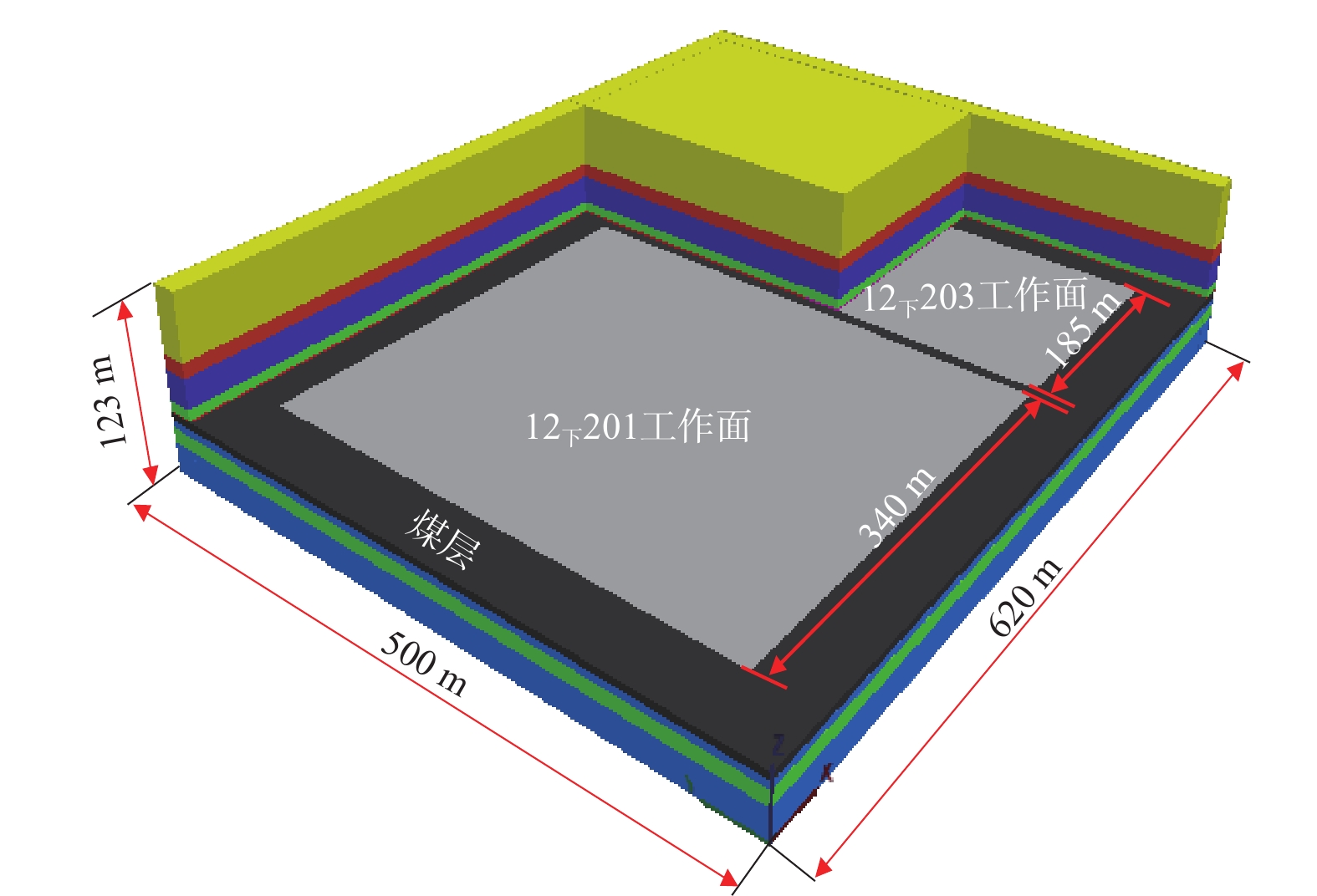
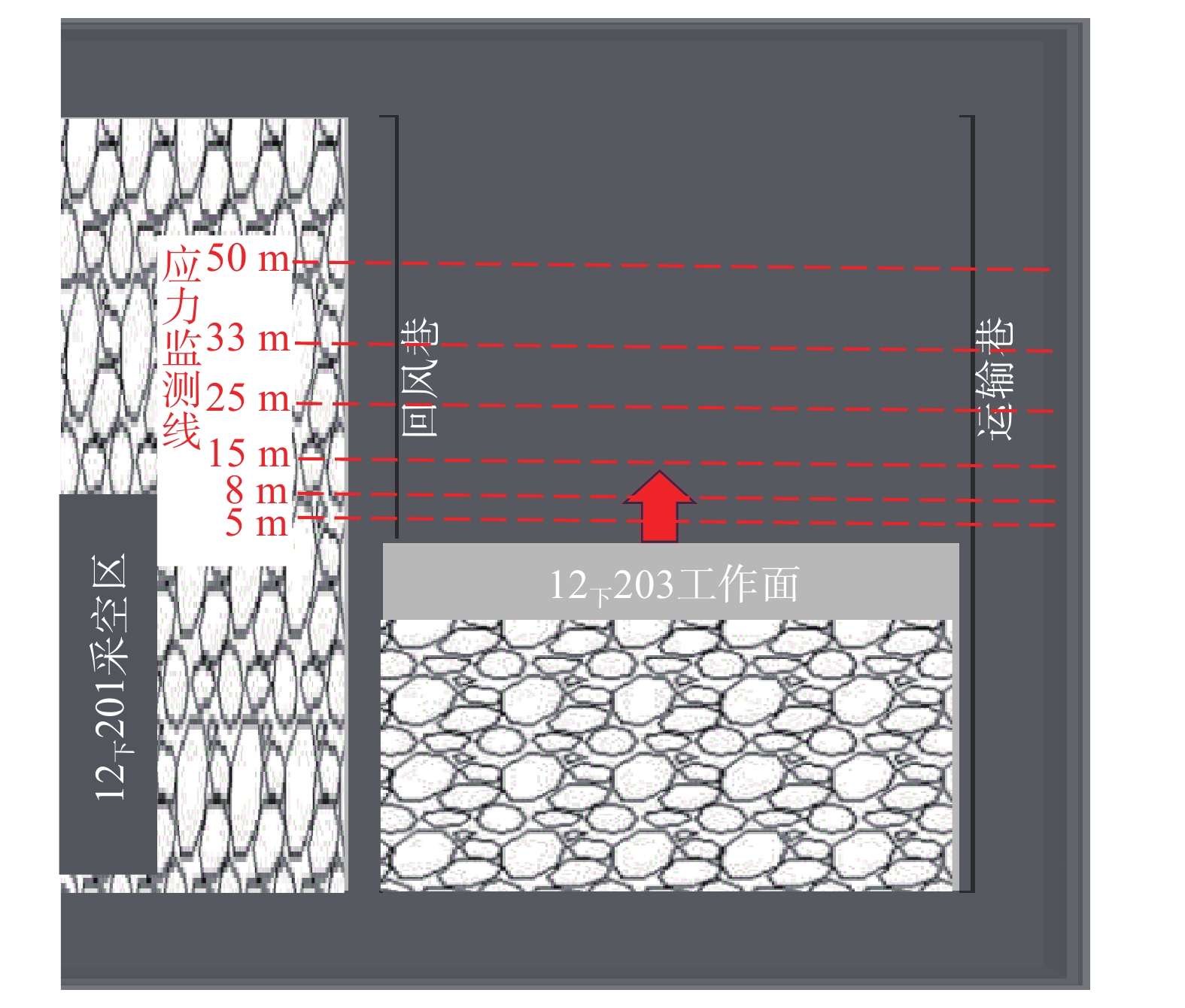
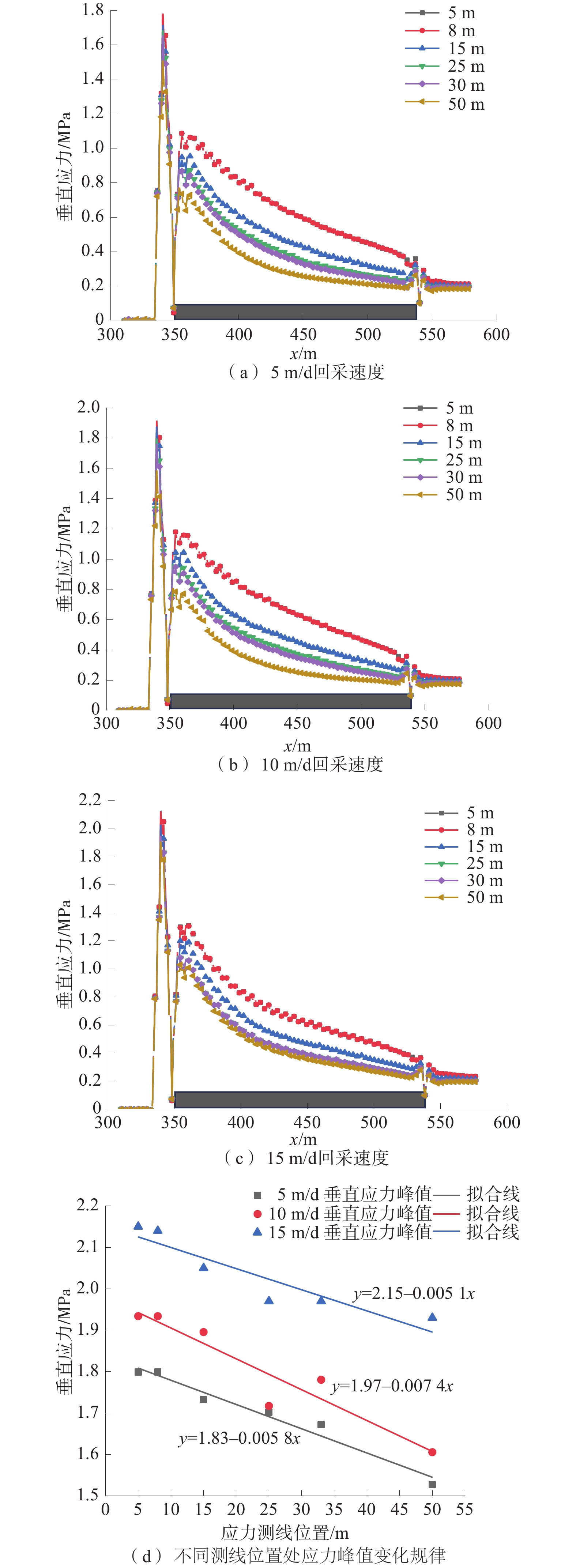
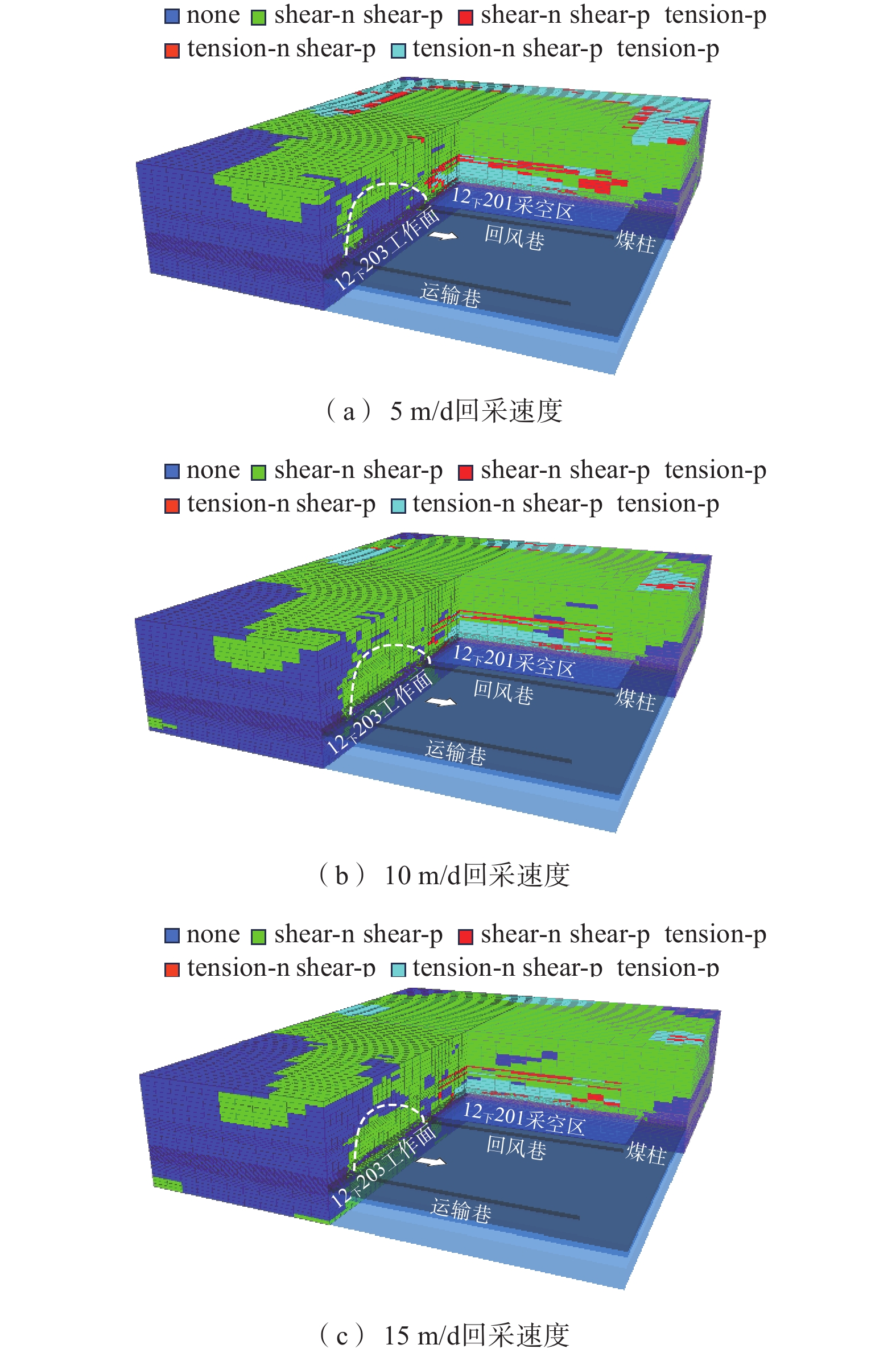
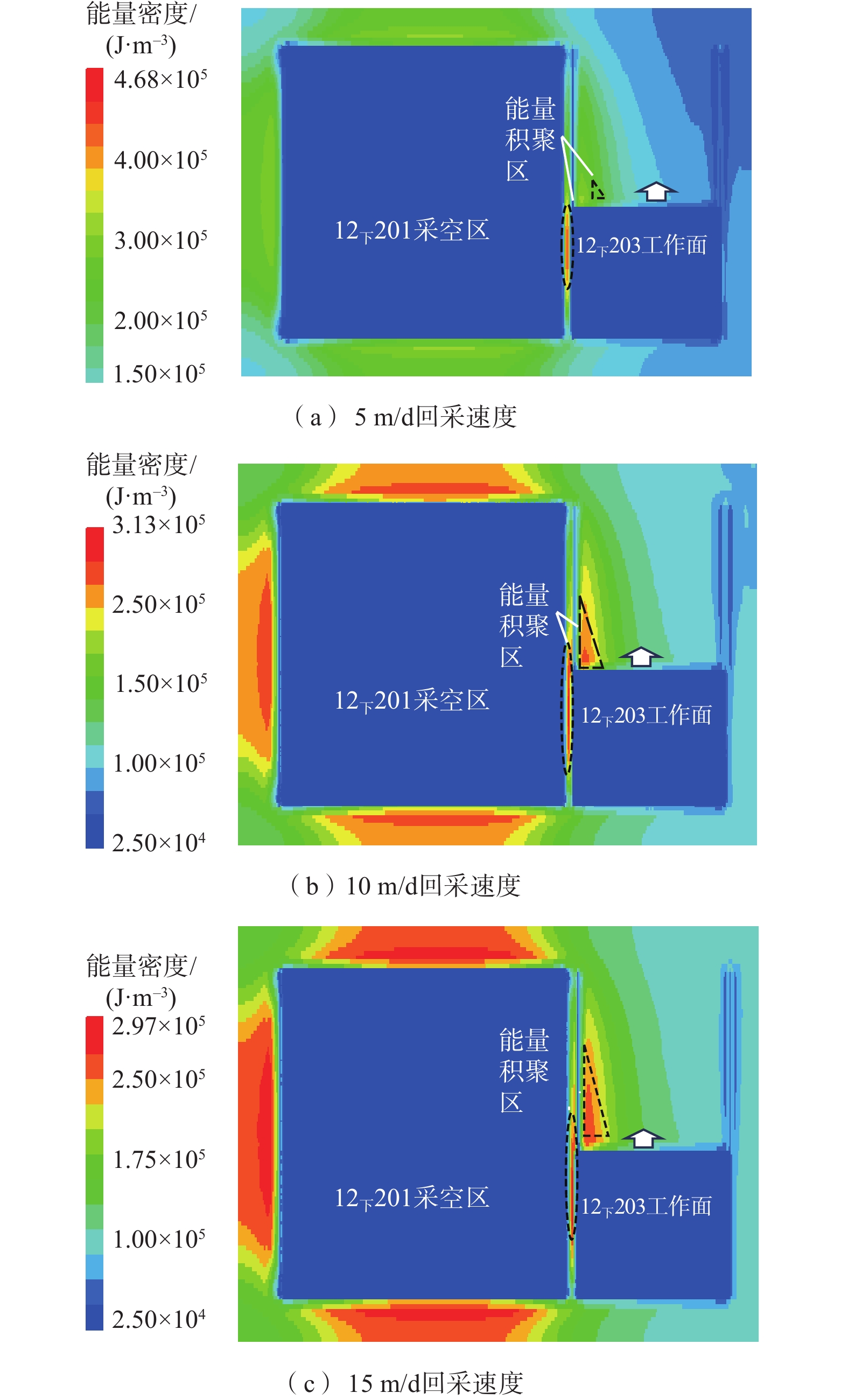
西部矿区高强度开采导致工作面上覆岩层结构及地表严重破坏,进而导致地表生态环境恶化。以大柳塔矿为工程背景,通过现场监测和理论分析研究了高强度开采邻空工作面覆岩裂隙及能量演化规律;采用FLAC3D数值模拟分析得出邻空12下203工作面垂直应力、覆岩破坏范围和能量积聚特征及不同回采阶段关键层能量演化规律。研究结果表明:初次来压后地表开裂并产生塌陷,裂缝可见深度为0.1~0.7 m,周期来压步距为7~17 m,平均步距12 m;12下203工作面上覆岩层破坏范围随回采速度增大,覆岩裂隙发育范围、地表破坏范围均与工作面推进速度呈正相关关系,回采速度对邻空工作面覆岩破坏范围影响较大;区段煤柱应力随回采速度增大而增大,工作面前方50 m仍受较高静载应力作用,巷道易冲击失稳;12下203工作面邻空端头处能量密度值及能量积聚区域,采场围岩扰动强烈,覆岩能量积聚来不及释放,易造成顶板围岩冲击失稳。
Abstract:The high-intensity mining in the western mining area has led to severe damage to the overlying rock structure and surface of the working face, resulting in the deterioration of the surface ecological environment. Taking Daliuta Mine as the engineering background, the study investigated the overlying rock fractures and energy evolution laws of high-intensity mining adjacent to the working face through on-site monitoring and theoretical analysis; using FLAC3D numerical simulation analysis, the vertical stress, range of overlying rock failure, and energy accumulation characteristics of the 12203 working face and the evolution law of key layer energy in different mining stages were obtained. The results showed that after the initial compaction, the surface cracked and collapsed, with visible depths ranging from 0.1 m to 0.7 m. The periodic compaction step distance was 7-17 m, with an average step distance of 12 m; the range of overlying rock damage on the 12203 working faces increases with the increase of mining speed. The development range of overlying rock fractures and the range of surface damage are positively correlated with the advancing speed of the working face. The mining speed has a significant impact on the range of overlying rock damage on adjacent working faces; the stress of the coal pillar in the section increases with the increase of the mining speed, and 50 m in front of the working face is still subjected to high static stress, and the roadway is prone to impact instability; the energy density value and energy accumulation area at the adjacent goaf end of the 12 lower 201 working face are strongly disturbed by the surrounding rock of the mining area, and the energy accumulation of the overlying rock cannot be released in time, which can easily cause instability of the roof surrounding rock due to impact.
-
矿山环境复杂、空间狭小、视觉环境差,并且存在部分易燃、易爆、易腐蚀等危险品,存在人工危险性大、巡检精确度不稳定和巡检效率低等问题。随着煤炭行业的智能化水平逐渐提高,巡检机器人采用耐腐蚀表面材料,可以在高温恶劣环境中保持良好工作状态,完成漏液检测、温度检测、有毒气体检测等巡检工作[1]。在巡检工作中,巡检机器人采集实时数据,将数据发送到智能运维平台,发现异常数据后发送警报信号。同时,巡检机器人还可以对数据先进行预处理,方便工作人员做出更科学的决策。
在巡检工作中,合理安全的路径规划对机器人至关重要。然而,由于工作人员走动、其他智能设备移动等,矿山环境动态随机变化,对巡检机器人的路径规划和动态避障提出了挑战。目前,移动机器人的传统路径规划方法有人工势场方法[2-3]、快速探索随机树算法[4](Rapidly-exploring Random Trees,RRT)和A*算法[5-6]等。然而,人工势场方法缺乏全局地图信息,不适用于全局路径规划;RRT算法需要庞大的搜索空间,路径规划的效率不高;A*算法在静态全局规划中很有效,但是不适用于动态随机的矿山环境。为了解决动态路径规划问题,有学者提出基于蚁群算法[7-8]、遗传算法[9]、粒子群算法[10]等启发式算法的路径规划方法。启发式算法可以根据部分信息进行自学习,但是容易陷入局部最优,而且收敛速度较慢。强化学习可以实时与环境交互,根据环境变化调整路径,已被广泛应用于机器人路径规划。文献[11]为了克服维度诅咒和降低历史数据关联性,避免陷入局部最优解,提出了一种重放回机制DQN(Deep Q-Network,深度Q网络)算法。但是使用一个策略采集完整轨迹的方差较大,学习效率较低。因此,提出一种结合策略梯度和时序差分学习的强化学习路径规划方法。
巡检机器人的能量非常重要,可以保障更长时间的工作。为了提高路径规划效率和提高机器人的工作时间,采用面向目标的转向角控制方法,并利用Actor-Critic算法选择巡检速度,根据动态随机的移动障碍物,以能量消耗最小化为目标规划巡检路线,实现机器人的无碰撞自主导航,在确保路线安全、合理的基础上,进一步降低巡检机器人的能量消耗。
1. 研究方法
矿山环境复杂多变,导致复杂多样的连续状态,传统离散化状态的方法不可取。为了在连续状态下产生合理高效的巡检路径,采用Actor-Critic深度强化学习算法。Actor-Critic算法包括策略网络和价值网络,可以进行单步更新,学习效率高。同时,为了解决传统深度Q-learning算法的过估计问题,考虑双策略网络和双价值网络,分别称为目标策略网络和目标价值网络,结构分别与策略网络和价值网络相同。
价值网络的Q值用$ Q\left( {s,a\left| {{w}} \right.} \right) $近似,策略网络的参数化策略用$ v\left( {s,a\left| {{\theta }} \right.} \right) $近似,其中:w、θ分别为表示价值网络和策略网络的参数,分别构成相应神经网络中激活函数的连接权值和偏差。为了减小样本之间的相关性,采用经验池存放历史样本。在每次训练中,从经验池中随机选择小批量的样本$ {\varPhi _{\mathrm{b}}} $更新策略网络的参数$ {{\theta }} $,更新公式为:
$$ {{\theta }} \leftarrow {{\theta }} + \frac{\alpha }{{\left| {{\varPhi _{\mathrm{b}}}} \right|}}{\nabla _{{\theta }}}v\left( {s,a\left| {{\theta }} \right.} \right){\nabla _{a'}}Q\left( {s,a'\left| {{w}} \right.} \right)\left| {_{a' = v\left( {s,a\left| {{\theta }} \right.} \right)}} \right. $$ (1) 式中:$ \alpha $为学习率;$ s $为矿山巡检环境的状态;$ a $为巡检机器人采取的动作;$ a' $为下一时隙机器人采取的动作。
价值网络的参数更新表达式为:
$$ {{w}} \leftarrow {{w}} - \frac{\alpha }{{\left| {{\varPhi _{\mathrm{b}}}} \right|}}{\sum\limits_{{\varPhi _{\mathrm{b}}}} {{\nabla _{{w}}}\left( {\xi - Q\left( {s,a\left| {{w}} \right.} \right)} \right)} ^2} $$ (2) 式中:$ \xi = R_{ss'}^a + C_{ss'}^a + \gamma Q\left( {s,v\left( {s,a\left| {{{\theta }}'} \right.} \right)\left| {{{w}}'} \right.} \right) $;$ R_{ss'}^a $为在状态$ s $采取动作$ a $后转移到状态$ s' $的奖赏;$ C_{ss'}^a $为在状态$ s $采取动作$ a $后转移到状态$ s' $的惩罚;$ \gamma $为奖赏折扣因子。
目标策略网络参数$ {{\theta }}' $和目标价值网络参数$ {{w}}' $更新公式为:
$$ {{w}}' \leftarrow \eta {{w}} + \left( {1 - \eta } \right){{w}}' $$ (3) $$ {{\theta }}' \leftarrow \eta {{\theta }} + \left( {1 - \eta } \right){{\theta }}' $$ (4) 式中:$ \eta $为远小于1的正值,保证算法稳定收敛。
2. 路径规划方法
2.1 巡检机器人坐标优化问题转化
在煤矿作业场景中,巡检机器人的巡检区域较大,直接应用强化学习优化巡检机器人的下一时隙坐标时,动作空间很大,导致学习效率比较低,路径规划的精度和效率难以权衡。当已知巡检机器人当前时隙坐标$ {{q}}\left( t \right) $和行进方向$ \varphi \left( t \right) $,以及下一时隙的转向角$ \Delta \left( {t + 1} \right) $和速度$ v\left( {t + 1} \right) $确定时,巡检机器人的行进方向和坐标可以更新为:
$$ \varphi \left( {t + 1} \right) = \varphi \left( t \right) + \Delta \left( {t + 1} \right) $$ (5) $$\begin{split} &\begin{gathered} {{q}}\left( {t + 1} \right) = \left( {x\left( t \right) + v\left( {t + 1} \right)\tau \cos\; \varphi \left( {t + 1} \right),} \right. \\ {\text{ }}\left. {y\left( t \right) + v\left( {t + 1} \right)\tau \sin\; \varphi \left( {t + 1} \right)} \right) \end{gathered}\\[-16pt]& \end{split}$$ (6) 式中:$ x\left( t \right) $为时隙$ t $巡检机器人的横坐标;$ y\left( t \right) $为时隙$ t $巡检机器人的纵坐标;$ \tau $为单个时隙的时长。
因此,巡检机器人的路径规划问题可看作马尔科夫过程,利用强化学习求解。首先根据巡检机器人的定位信息和巡检目标的位置信息,在机器人最大转向角约束和碰撞避免约束下计算巡检机器人每时隙的转向角,调整行进方向,然后利用Actor -Critic算法优化巡检机器人的速度。当机器人转向角和速度确定时,可以进一步计算巡检机器人各个时隙的坐标,进而得到巡检路线。
2.2 面向目标的转向角控制方法
巡检机器人配置感知模块和定位模块,可以感知周围环境信息和确定位置信息。当巡检机器人未感知到障碍物时,其决策模块根据自身坐标和巡检目标坐标计算转向角$\Delta \left( t \right) $为:
$$ \Delta \left( t \right) = \left\{ \begin{gathered} \min \left( {{\varphi _{\mathrm{r}}}\left( t \right) - \varphi \left( t \right),{\varphi _{\max }}} \right),{\varphi _{\mathrm{r}}}\left( t \right) \geqslant \varphi \left( t \right) \\ \max \left( {{\varphi _{\mathrm{r}}}\left( t \right) - \varphi \left( t \right), - {\varphi _{\max }}} \right),\qquad\;{\text{else}} \\ \end{gathered} \right. $$ (7) 式中:$ {\varphi _{\mathrm{r}}}\left( t \right) $为时隙$ t $时巡检机器人与巡检目标相对于$ x $正半轴的角度;$ {\varphi _{\max }} $为巡检机器人的最大转向角。
面向目标的避障转向角控制方法示意图如图1所示。
当巡检机器人感知到障碍物时,巡检机器人在障碍物边界上以最大感知角度和感知距离探测障碍物的边界点,并分别计算障碍物边界点B和C、巡检机器人A和巡检目标D的相对角度。根据正弦定理,选择相对角度最小的障碍物边界点作为行进目标,使行驶路径更短,从而最小化能量消耗。然后,巡检机器人根据其当前坐标和行进目标的坐标计算下一时隙的转向角。同时,根据Actor-Critic算法输出的速度行驶。在每时隙,巡检机器人感知更新障碍物的边界点,直至与障碍物之间的距离大于安全距离。
采用面向目标的转向角控制方法,巡检机器人将在避开障碍物的同时向巡检目标行进,从而大大提高轨迹规划的效率。
2.3 路径规划方法
在各个时隙初始确定巡检机器人的转向角后,采用Actor-Critic算法优化巡检机器人的速度。考虑速度约束、避障约束和巡检时间约束,巡检机器人的路径规划问题是带约束的马尔科夫决策过程,用元组$ \left\langle {S,A,R,C,T} \right\rangle $定义,其中:$ S $为状态集;$ A $为动作空间;$ R $、$ C $分别为即时奖赏和惩罚;$ T $为状态转移函数。
各个参数定义为:
1)状态。包括机器人的行进方向和坐标、机器人与障碍物的距离、机器人与基地的距离。
2)动作。机器人的速度。
3)奖赏。设置为机器人的能量消耗。
4)惩罚。当机器人与障碍物的距离小于安全距离,机器人与基地的距离大于剩余时间所能行驶的最大距离,给予1个很大的惩罚。
5)转移函数。机器人在状态$ s $执行动作$ a $后转移到状态$ s' $的概率。在本文,状态转移函数是未知的,所以采用Actor -Critic算法训练机器人。
基于转向角控制方法和Actor -Critic算法的路径规划训练框架如图2所示。
巡检机器人首先根据矿山巡检环境的状态$ s $,采用$ \varepsilon $贪婪算法选择动作$ a $。巡检机器人根据转向角调整行进方向并且执行动作$ a $,矿山巡检环境反馈奖赏和惩罚并转移到下一状态$ s' $。然后,将$ \left( {s,a,R,C,s'} \right) $作为1个样本存储在经验池中。每次训练时,从经验池中随机抽取部分样本更新策略网络的参数。另外,每隔$ \mu $个训练步骤,更新目标策略网络和目标价值网络的参数。
当算法收敛时,策略网络输出最优动作,使累积奖赏最小化,此时获得速度优化选择策略。根据不同的巡检环境,巡检机器人采用速度优化策略选择最优的速度,具有很好的迁移性。
3. 系统性能分析
为了验证基于Actor-Critic算法的巡检机器人路径规划方法的可行性和合理性,在Intel Xeon Gold 6226R CPU、256 RAM和NVIDIA Tesla P100-PCIE-16 GB GPU系统上使用Pytorch进行仿真实验。仿真中考虑1个长度为20 km、宽度为10 km的长方形巡检区域,区域中存在5个巡检目标、1个静态障碍物和1个动态障碍物。巡检机器人的最大转向角为20o,最大速度为20 m/s。巡检机器人从基地出发,要求在1 000个时隙内完成巡检,避免与其他障碍物发生碰撞,并返回基地。
在相同环境和参数条件下,巡检机器人的转向角选择都采用面向目标的转向角控制方法,各个时隙的速度分别利用Actor-Critic算法和DQN算法训练,完成轨迹规划。所提路径规划方法的收敛性如图3所示,所提路径规划方法的成功概率如图4所示,巡检机器人路径规划结果如图5所示,巡检机器人的速度和转向角如图6所示。
由图3可知,基于Actor-Critic算法和DQN算法的路径规划都可以收敛,由于巡检机器人在每个状态下都存在一定的概率选择1个随机动作进行探索,所以2种算法的能量消耗值是波动的。由于DQN算法容易陷入局部最优,因此DQN算法的能量消耗高于Actor-Critic算法。
对于每1个训练轮次中,如果巡检机器人能够在规定时间完成所有煤矿设备的检查,并且不发生碰撞地返回基地,则此轮次巡检成功。某一轮次的成功概率表示为当前成功总轮次数与当前总轮次数的比值。由图4可以看出:Actor-Critic算法的巡检成功概率可以达到98%。与DQN算法相比,Actor-Critic算法具有更高的成功概率,因为DQN算法采用1个深度学习网络,巡检机器人易陷入局部最优速度,无法在规定时间完成巡检作业,导致较低的成功概率和较高的能量消耗。因此,所提方法的路径寻优效率更高,能够更好地满足煤矿巡检作业要求。
图5中:红色圆表示静态障碍物,红色长方形表示动态障碍物,绿色圆表示可检测距离,蓝色圆表示安全距离。由图5可以看出:巡检机器人从基地出发,以巡检目标为行进方向,在探测到障碍物后改变转向角;巡检机器人可以在避开障碍物的同时向巡检目标行驶,完成所有目标设备的巡检作业,并返回基地。
由图6可以看出:机器人在600时隙内完成巡检作业,小于所要求的1 000个时隙;另外,机器人会尽量采用恒定的速度行驶,以减小能量消耗。所提路径规划方法不仅可以提高深度学习算法的学习效率,而且可以以更短的路径完成巡检作业,节省能量消耗。
4. 结 语
1)针对巡检任务区域大,路径规划精度和效率难以权衡的问题,提出了1种面向巡检目标和基于Actor-Critic算法的巡检机器人路径规划方法。该方法以巡检目标为行进方向,根据环境位置信息计算机器人的转向角,可以加快路径规划过程。Actor-Critic算法可以解决单深度学习网络的低估问题,设计安全可行的巡检路线,降低巡检机器人的能量消耗。
2)仿真结果表明,提出的路径规划算法能够实现合理可行的巡检路径规划,并且具有较高的作业成功概率和较低的巡检能量消耗,可以大幅提高煤矿巡检工作的效率。此训练模型可以很方便地迁移到不同的作业环境。
-
表 1 煤岩力学参数
Table 1 Physical and mechanical parameters of coal and rock mass
岩性 厚度/
m密度/
(kg·m−3)体积
模量/
GPa剪切
模量/
GPa黏聚力/
MPa内摩
擦角/
(°)抗拉
强度/
GPa细砂岩层 45 2 385 4.2 3.4 2.22 32.1 2.32 中砂岩层 10 2 650 5.4 4.3 1.82 32.4 1.45 粗砂岩层 20 2 200 6.0 5.0 2.05 37.2 1.13 粉砂岩层 7 2 350 4.4 5.5 1.77 35.3 1.82 煤层 6 1 340 0.4 0.5 1.20 30.1 0.84 泥岩层 5 2 470 2.0 4.8 2.26 35.3 1.75 粉砂岩层 10 2 350 3.7 4.5 1.77 30.2 1.82 砂质泥岩 20 2 480 5.2 4.9 2.28 34.3 1.75 -
[1] 王强民,董书宁,王皓,等. 西部风沙区采煤塌陷地裂缝影响下的土壤水分运移规律及调控方法[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(5):1532−1540. WANG Qiangmin, DONG Shuning, WANG Hao, et al. Influence of mining subsidence on soil water movement law and its regulation in blown-sand area of western China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(5): 1532−1540.
[2] 郭小铭,董书宁,刘英锋,等. 深埋煤层开采顶板泥砂溃涌灾害形成机理[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2019,36(5):889−897. GUO Xiaoming, DONG Shuning, LIU Yingfeng, et al. Formation mechanism of mud and sand inrush disaster during the mining of deep-buried coal seam[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2019, 36(5): 889−897.
[3] 郭文兵,白二虎,杨达明. 煤矿厚煤层高强度开采技术特征及指标研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(8):2117−2125. GUO Wenbing, BAI Erhu, YANG Daming. Study on the technical characteristics and index of thick coal seam high-intensity mining in coalmine[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2018, 43(8): 2117−2125.
[4] 黄庆享,李锋,贺雁鹏,等. 浅埋大采高工作面超前支承压力峰值演化规律[J]. 西安科技大学学报,2021,41(1):1−7. HUANG Qingxiang, LI Feng, HE Yanpeng, et al. Evolution law of the peak of front abutment pressure of large mining height working face in shallow buried[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Science and Technology, 2021, 41(1): 1−7.
[5] 周海丰,黄庆享,贺雁鹏. 8.8 m大采高综采工作面矿压规律[J]. 西安科技大学学报,2020,40(6):981−987. ZHOU Haifeng, HUANG Qingxiang, HE Yanpeng. Law of ground pressure in 8.8 m large mining height fully on mechanized face[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Science and Technology, 2020, 40(6): 981−987.
[6] 杨俊哲. 8 m大采高综采工作面关键回采技术研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2017,45(11):9−14. YANG Junzhe. Research on key mining technology of fully-mechanized working face with 8 m large mining height[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2017, 45(11): 9−14.
[7] 杨俊哲,张广伟,杨新林,等. 上湾煤矿超大采高工作面开采地表移动规律[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版),2022,41(2):109−113. YANG Junzhe, ZHANG Guangwei, YANG Xinlin, et al. Ground movement law of high seam longwall extraction in Shangwan Coal Mine[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University (Natural Science), 2022, 41(2): 109−113.
[8] 杨俊哲,雷少刚. 工作面开采强度对RUSLE坡度坡长因子的影响规律[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(1):192−197. YANG Junzhe, LEI Shaogang. The influence law of mining intensity on RUSLE slope gradient and length factor[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49(1): 192−197.
[9] 杨俊哲,何江,宋桂军,等. 布尔台煤矿42107工作面强矿压显现规律及其防治[J]. 煤炭工程,2021,53(1):71−74. YANG Junzhe, HE Jiang, SONG Guijun, et al. Law and control of strong rock pressure behavior in 42107 working face of Buertai Coal Mine[J]. Coal Engineering, 2021, 53(1): 71−74.
[10] 齐庆新,王守光,李海涛,等. 冲击地压应力流理论及其数值实现[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(1):172−179. QI Qingxin, WANG Shouguang, LI Haitao, et al. Stress flow theory for coal bump and its numerical implementation[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(1): 172−179.
[11] 魏江波,王双明,宋世杰,等. 浅埋煤层过沟开采覆岩裂隙与地表裂缝演化规律数值模拟[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2022,50(10):67−75. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.22.03.0134 WEI Jiangbo, WANG Shuangming, SONG Shijie, et al. Numerical simulation on evolution law of overburden fractures and surface cracks in crossing ditch mining of shallow coal seam[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2022, 50(10): 67−75. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.22.03.0134
[12] 张国华,李子波,李豫波,等. 煤厚变化区围岩能量积聚规律及开采方向对其影响[J]. 煤矿安全,2024,55(9):118−127. ZHANG Guohua, LI Zibo, LI Yubo, et al. Energy accumulation law of surrounding rock in coal thickness variation area and the influence of mining direction on it[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2024, 55(9): 118−127.
[13] 赵毅鑫,周金龙,刘文岗. 新街矿区深部开采邻空巷道受载特征及冲击失稳规律分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(5):1595−1606. ZHAO Yixin, ZHOU Jinlong, LIU Wengang. Characteristics of ground pressure and mechanism of coal burst in the gob side roadway at Xinjie deep mining area[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(5): 1595−1606.
[14] 焦振华,赵毅鑫,姜耀东,等. 采动诱发断层损伤滑移及其影响因素敏感性分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2017,42(S1):36−42. JIAO Zhenhua, ZHAO Yixin, JIANG Yaodong, et al. Fault damage induced by mining and its sensitivity analysis of influencing factors[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2017, 42(S1): 36−42.
[15] 张通,袁亮,赵毅鑫,等. 薄基岩厚松散层深部采场裂隙带几何特征及矿压分布的工作面效应[J]. 煤炭学报,2015,40(10):2260−2268. ZHANG Tong, YUAN Liang, ZHAO Yixin, et al. Distribution law of working face pressure under the fracture zone distribution characteristic of deep mining[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2015, 40(10): 2260−2268.
[16] 张村,任赵鹏,韩鹏华,等. 西部矿区厚基岩特大采高工作面导水裂隙带发育特征[J]. 矿业科学学报,2022,7(3):333−343. ZHANG Cun, REN Zhaopeng, HAN Penghua, et al. Characteristic of the water-conducting fracture zone development in thick overburden working face with extra-large mining height in western mining area[J]. Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2022, 7(3): 333−343.
[17] 何祥,张村,赵毅鑫,等. 基于覆岩损伤本构模型的高强度开采参数确定及减损效果评价[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2021,38(3):439−448. HE Xiang, ZHANG Cun, ZHAO Yixin, et al. Parameters determination of high-intensity mining and reduction effect evaluation based on damage constitutive model of overburden rock[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2021, 38(3): 439−448.
[18] 雷照源,赵茂平,李团结,等. 深埋大采高相邻工作面强矿压发生机理研究 [J/OL]. 煤炭科学技术,1−10[2024-07-10]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2402.td.20240611.1429.003.html. LEI Zhaoyuan, ZHAO Maoping, LI Tuanjie, et al. Strong mine pressure appearing mechanism and control at deep buried working face with large mining height[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 1−10[2024-07-10]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2402.td.20240611.1429.003.html.
[19] 钱鸣高,石平五,许家林. 矿山压力与岩层控制[M]. 2版. 徐州:中国矿业大学出版社,2010. [20] 冯龙飞,窦林名,王晓东,等. 回采速度对采场能量释放的影响规律研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2020,48(11):77−84. FENG Longfei, DOU Linming, WANG Xiaodong, et al. Study on influence law of mining speed on stope energy releasing[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48(11): 77−84.
[21] 来兴平,贾冲,崔峰,等. 急倾斜巨厚煤层开采深度影响的覆岩能量演化规律研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2023,42(2):261−274. LAI Xingping, JIA Chong, CUI Feng, et al. Study on the evolution law of overburden energy of steeply inclined extra-thick coal seam influenced by mining depth[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2023, 42(2): 261−274.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 程士宜. 不同温度-冲击载荷下煤的渗透率演化规律研究. 煤矿安全. 2024(08): 43-50 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 康俊强,简阔,傅雪海,申建,王一兵,段超超. 急倾斜煤储层水力压裂裂缝扩展研究. 煤矿安全. 2024(11): 49-60 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 熊冬,贺甲元,马新仿,曲兆亮,郭天魁,马诗语. 深部煤及顶底板不同射孔位置条件下的压裂模拟——以鄂尔多斯盆地某气田8号深部煤层为例. 煤炭学报. 2024(12): 4897-4914 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: