Study on crack propagation law of hydraulic fracturing of coal rock complex based on cohesive element
-
摘要:
为分析煤岩复合体中水力裂缝扩展路径及演化规律,从应力场、煤岩交界面强度以及煤层层理倾角出发,基于黏聚力单元法建立了煤岩复合体水力压裂模型,分析了不同工况下煤岩复合体水力裂缝扩展规律。研究结果表明:煤岩复合体水压裂缝在上覆岩层中起裂后,随着垂向与水平应力差的逐渐增大,水力压裂裂缝受应力场的控制作用越来越显著;煤岩交界面强度较小时,水力裂缝在交界面中难以形成水压聚集达到煤层的开裂条件,煤岩交界面强度较大时能够在煤岩交界面中扩展一定距离并完成憋压,当压力达到煤层开裂条件时水压裂缝穿越煤岩交界面并诱导煤层起裂扩展;在煤层层理倾角30°条件下水力裂缝沿主应力方向形成主裂缝并沿层理方向形成次生分支裂缝;在不同地质条件下,应力场、煤岩交界面和煤体层理对水力裂纹的控制作用不同,可结合三者对水力裂纹的控制作用使其形成复杂的裂纹网络结构。
Abstract:In order to further analyze the propagation path and evolution law of hydraulic fractures in coal rock complex, from the perspective of stress field, coal rock interface strength and coal seam bedding dip angle, a hydraulic fracture model of coal rock complex is established based on cohesion unit method, and the propagation law of hydraulic fractures in coal rock complex under different working conditions is analyzed. It is found that after the hydraulic fracture of coal rock complex cracks in the overlying strata, with the gradual increase of the stress difference between σy and σx, the hydraulic fracture is more and more significantly controlled by the stress field. When the strength of coal rock interface is small, it is difficult for hydraulic cracks to form water pressure accumulation in the interface to reach the cracking conditions of coal seams. When the strength of coal rock interface is large, it can expand a certain distance in the coal rock interface and complete pressure holding. When the pressure reaches the cracking conditions of coal seams, water pressure cracks pass through the coal rock interface and induce the crack initiation and expansion of coal seams. Under the condition of 30° dip angle of coal seam bedding, hydraulic fractures form main fractures along the direction of main stress and secondary branch fractures along the direction of bedding. Under different geological conditions, stress field, coal rock interface and coal bedding have different control effects on hydraulic cracks, so they can be effectively combined to form a complex crack network structure.
-
Keywords:
- coal rock complex /
- hydraulic fracturing /
- interface strength /
- cohesive element /
- crack propagation
-
随着煤炭和石油等资源开采深度的不断拓展,常规能源的开发程度随采深逐渐受限,煤层气和页岩油气等非常规油气资源开发利用具备广阔前景,成为当前国内外学者研究的重点[1]。煤层气等资源的开采主要针对煤岩储层裂纹网络改造,主要通过水力压裂工艺形成较为复杂的裂纹网络体系,从而提高煤层气资源的抽采效率[2-4]。
实际煤岩储层地质结构复杂,特别是复合体层状储层具有纵向岩性复杂、层间物性差异较大,具有非均质性强且天然裂隙发育等特点,需考虑水力裂缝在不同岩性介质中扩展特征的差异,采用穿层压裂技术综合开采煤层气资源具有重要意义[5]。由于复合体层间岩石力学性质、地应力、结构弱面及压裂工艺参数的不同,水压裂缝呈现的形态差异较大[6-7];针对水压裂缝在多岩性复合体储层中的延伸扩展方面,国内外学者进行了大量的研究。TAN等[8-9]对比研究了煤岩、砂岩及页岩不同组合条件下,水压裂缝从煤岩层顶底板起裂及跨界面穿层扩展规律,分析了结构面胶结强度对水压裂缝穿层扩展的影响作用,掌握了水压裂缝垂向非对称延伸特征;LIU等[10]在考虑分层介质中方位角、不同井斜角及射孔参数的情况下,对水压裂的起裂扩展规律进行了研究;马衍坤等[11-12]研究了跨界面水力压裂增渗作用机制,指出水力压裂通过引起岩体破碎膨胀而使得煤层卸压增透,提高煤层透气性;XING等[13]研究了裂缝垂直扩展行为,在考虑层间应力差、界面胶结强度、缝内净压力及垂向应力差的影响下,构建了多参数影响的控制模型;武鹏飞等[14]开展了大尺寸水力压裂试验,发现水压裂缝跨界面扩展时,容易在界面处形成偏转型、贯穿型、止裂型裂缝形态;付世豪等[15]开展了真三轴水力压裂物理模拟试验,研究了多因素对水力裂缝垂向扩展行为的影响,发现了水力裂缝在纵向上呈现非对称、非平面扩展特征,依据水力裂缝与岩性界面不同的作用方式,水力裂缝具有停止、转向、分叉、穿透等多种复杂扩展模式;GUO等[16]通过ABAQUS数值模拟软件对四川盆地砂岩-页岩相互组合的储层中裂缝与界面之间的相互作用行为进行了计算,发现提高压裂液注入压力和减小压裂液黏度更有利于使得水力裂缝克服不同岩性储层的阻力穿过界面形成穿层裂缝;ZOU等[17]通过实验室物理试验和数值模拟结合的方式,对渗透性层理和水力裂缝之间的相互作用进行了研究,发现处于较低压裂液黏度时在天然层理面的滤失作用会增强,大排量注入会有利于水力裂缝穿过层里面扩展;LI等[18]通过渗流-损伤-应力耦合程序对薄互层沉积岩组合储层进行了水力压裂模拟,发现水力裂缝在岩石交界面出的转折程度增加会减小渗流通道的开度。
综上,目前煤岩复合体水力压裂的研究多集中在煤岩组分和压裂参数等方面,水力裂缝在不同组合岩体条件下扩展的完整过程尚不明确,考虑煤岩复合体水力裂缝扩展过程中与煤岩交界面以及层理等天然裂缝的复杂相互作用行为还需要深入研究。为此,基于黏聚力单元法模拟煤岩内部基质缝网结构,结合ABAQUS数值模拟软件开展煤岩复合体水力压裂数值计算,针对应力场、煤岩交界面强度和煤层层理倾角等因素对煤岩复合体水力压裂裂纹扩展规律的影响进行研究,以期为煤岩复合体储层裂纹网络改造提供参考理论基础。
1. 黏聚力单元法
1.1 黏聚力单元简介
黏聚力指的是在同种物质内部相邻各部分之间的相互吸引力,这种相互吸引力是同种物质分子之间存在分子力的微观表现,只有在物质内分子间的距离十分接近时,一般为小于10−6 cm时,这种黏聚力才显现出来[19]。在水力压裂裂缝扩展模拟过程中,黏聚力单元本身并不代表任何材料,只是黏聚力单元中存在的黏聚力可以抵抗裂缝尖分离时产生的拉应力,正是因为黏聚力单元具有此特征,才使得在水力压裂裂缝扩展模拟过程中,基于黏聚力单元的各类模型得到了广泛的应用。
黏聚力单元嵌入在煤岩体实体单元内,当煤岩体发生破坏发生时,黏聚力单元张开从而引起裂缝的起裂及扩展。因此模拟水力裂缝的扩展主要是依赖于黏聚力单元的嵌入,而水力裂纹如何扩展,这取决于黏聚力单元的网格划分,其网格精度对数值模拟结果有着重要的影响[20]。
1.2 力学损伤破坏准则
在黏聚力单元破坏理论中,裂缝扩展过程是裂缝尖端克服黏聚力作用并发生分离断裂,裂缝起裂与扩展由牵引-分离准则控制。
1)初始损伤。裂缝牵引力的拉伸组分主要由裂缝流体压力引起,其剪切组分由地应力差和煤岩内部天然裂缝的存在引起的局部剪应力场所诱导。对于拉-剪混合破坏模式的裂缝,其初始损伤位移并不为定值,而是与具体荷载条件下的张拉-剪切混合方式及混合比例有关。采用拉-剪混合模式的二阶应力准则预测初始损伤,如式(1)[21]:
$$ \left(\frac{t_{{\rm{n}}}}{\sigma_{{\rm{t}}}}\right)^{2}+\left(\frac{t_{{\rm{s}}}}{\sigma_{{\rm{s}}}}\right)^{2}=1 $$ (1) 式中:σt、σs为拉伸强度和剪切强度,Pa;tn、ts为法向牵引力和切向牵引力,Pa。
2)损伤演化。通过引入损伤因子D来表征黏聚力单元的损伤程度,初始损伤发生后,D从0单调递增至1。则由损伤引起的应力变化可表示为:
$$ \left\{\begin{array}{*{20}{l}} t_{{\rm{n}}}=(1-D) \bar{t}_{{\rm{n}}}& \text { 拉伸状态 } \\ t_{{\rm{n}}}=\bar{t}_{{\rm{n}}}& \text { 压缩状态 } \\ t_{{\rm{n}}}=(1-D) \bar{t}_{{\rm{s}}}& \end{array}\right. $$ (2) 式中:tn为描述拉-剪混合模式下损伤演化;$ \overline{t_{{\rm{n}}}} $、$ \bar{t}_{{\rm{s}}} $为当前分离位移在线弹性法则下的应力组分。
1.3 流体流动准则
假设缝内压裂液选取为不可压缩的牛顿流体,符合牛顿黏性定律:
$$ \tau=\mu \frac{\mathrm{d} u}{\mathrm{~d} y} $$ (3) 式中:$ \tau $为剪应力,Pa;$ \dfrac{\mathrm{d} u}{\mathrm{d} y} $为剪切变形速率,m/s;$ \mu $为压裂液黏度,Pa·s。
缝内流体切向流动方程为:
$$ q_{{\rm{t}}} w=-\frac{w^{3}}{12 \mu} \nabla p_{{\rm{w}}} $$ (4) 式中:qt为单位面积压裂液流速,m/s;$ w $为裂缝宽度,m;$ \nabla p_{\text {w }} $裂缝方向的压力梯度,Pa/m;$ \dfrac{w^{3}}{12} $可以理解为渗透性或流动阻力。
缝内向煤岩多孔基质滤失行为的法向流定义如下:
$$ \left\{ \begin{gathered} {q_{\text{a}}} = {c_{\text{a}}}{\text{(}}{p_{\text{m}}}{{ - }}{p_{\text{a}}}{\text{)}} \\ {q_{\text{b}}} = {c_{\text{b}}}{\text{(}}{p_{\text{m}}}{{ - }}{p_{\text{b}}}{\text{)}} \\ \end{gathered} \right. $$ (5) 式中:qa、qb为单元顶面和底面的法向滤失流动速率,m/s;$ {c_{\text{a}}} $、$ {c_{\text{b}}} $为顶底面滤失系数,m/(Pa·s);$ {p_{\text{m}}} $为单元中面裂隙流压力,Pa;$ {p_{\text{a}}} $、$ {p_{\text{b}}} $为单元顶底面处的孔隙压力,Pa。
水力压裂黏聚力模型如图1,模型中的裂缝分为黏性断裂区与黏性非断裂区。
2. 煤岩复合体水力压裂数值模型及试验方案
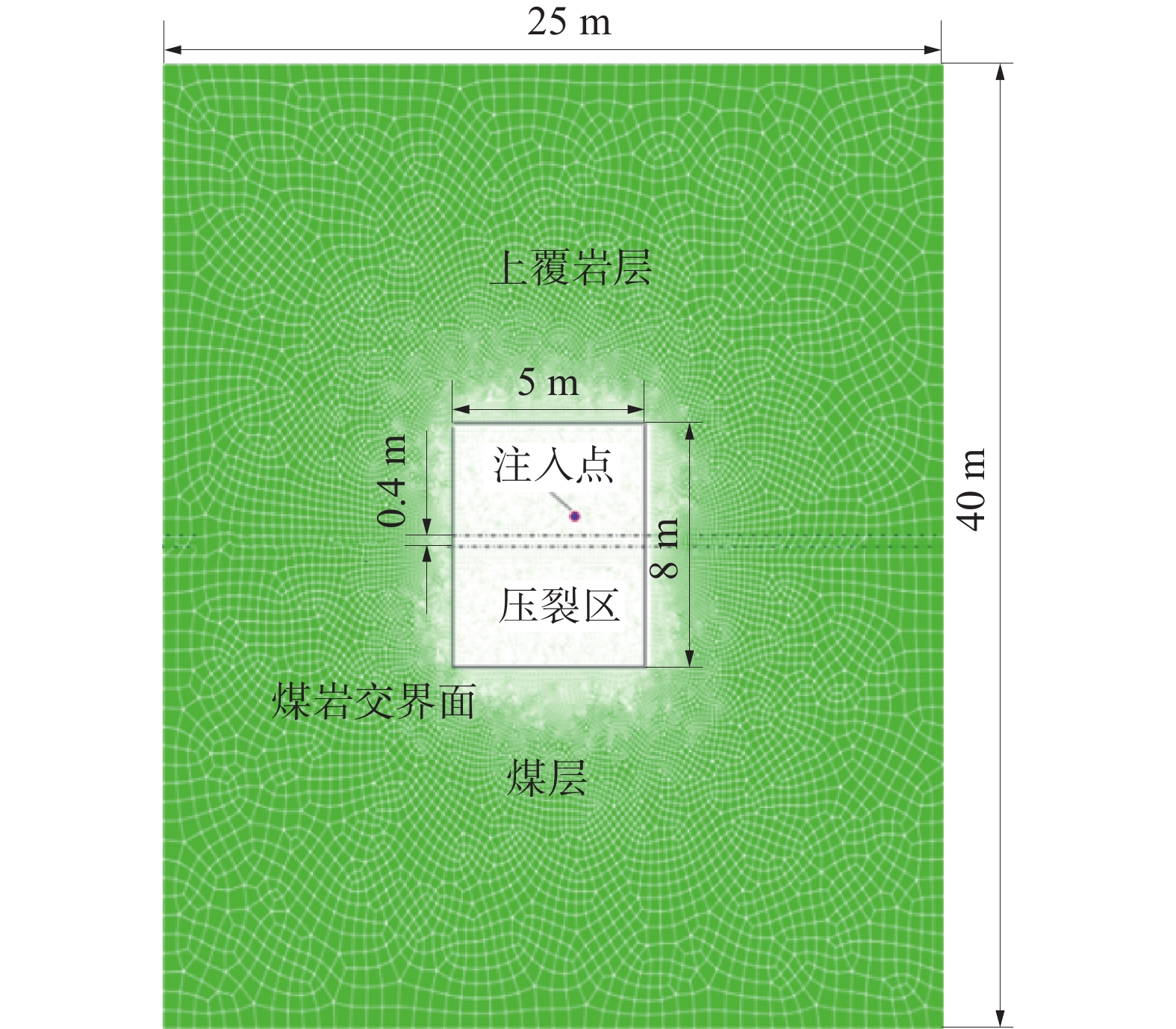
1)煤岩复合体水力压裂数值模型。煤岩复合体水力压裂数值计算模型如图2,整个模型尺寸与压裂区尺寸之比为5∶1,模型共划分46 857个单元,其中孔隙流体-应力耦合平面应变单元(类型CPE4P)为34 533个,黏聚力孔压单元(类型COH2D4P)为12 324个。模型边界节点自由度采用固支约束,即约束x方向和y方向自由度,xy平面内的转动自由度不被约束。模型物理力学参数见表1。
表 1 数值计算模型主要物理力学参数表Table 1. Table of physical and mechanical parameters of numerical calculation model岩体 弹性模
量/GPa泊松比 孔隙比 渗透率/
10−3μm2内摩擦
角/(°)抗拉强
度/MPa煤层 3.50 0.29 0.055 4 0.039 3 27 1.13 岩层 17.50 0.25 0.055 4 0.019 3 30 4.13 交界面 2.00 0.25 0.065 4 0.058 9 25 0.73 2)试验方案。将应力场、煤岩交界面强度和煤层层理作为单因素控制变量来研究不同条件下水压裂纹扩展规律,x水平方向和y垂直方向应力场(σx,σy)设置4组,分别为(5 MPa,2.5 MPa)、(5 MPa,5 MPa)、(5 MPa,7.5 MPa)、(5 MPa,10 MPa)、(5 MPa,12.5 MPa)、(5 MPa,15 MPa);煤岩交界面弹性模量分别为1.5、2.5、5 GPa;煤体层理倾角(层理与x水平方向)分别设置为0°、30°、60°;压裂液排量设置为0.006 m3/s。
3. 数值模拟结果
3.1 应力场对煤岩复合体水力压裂的影响
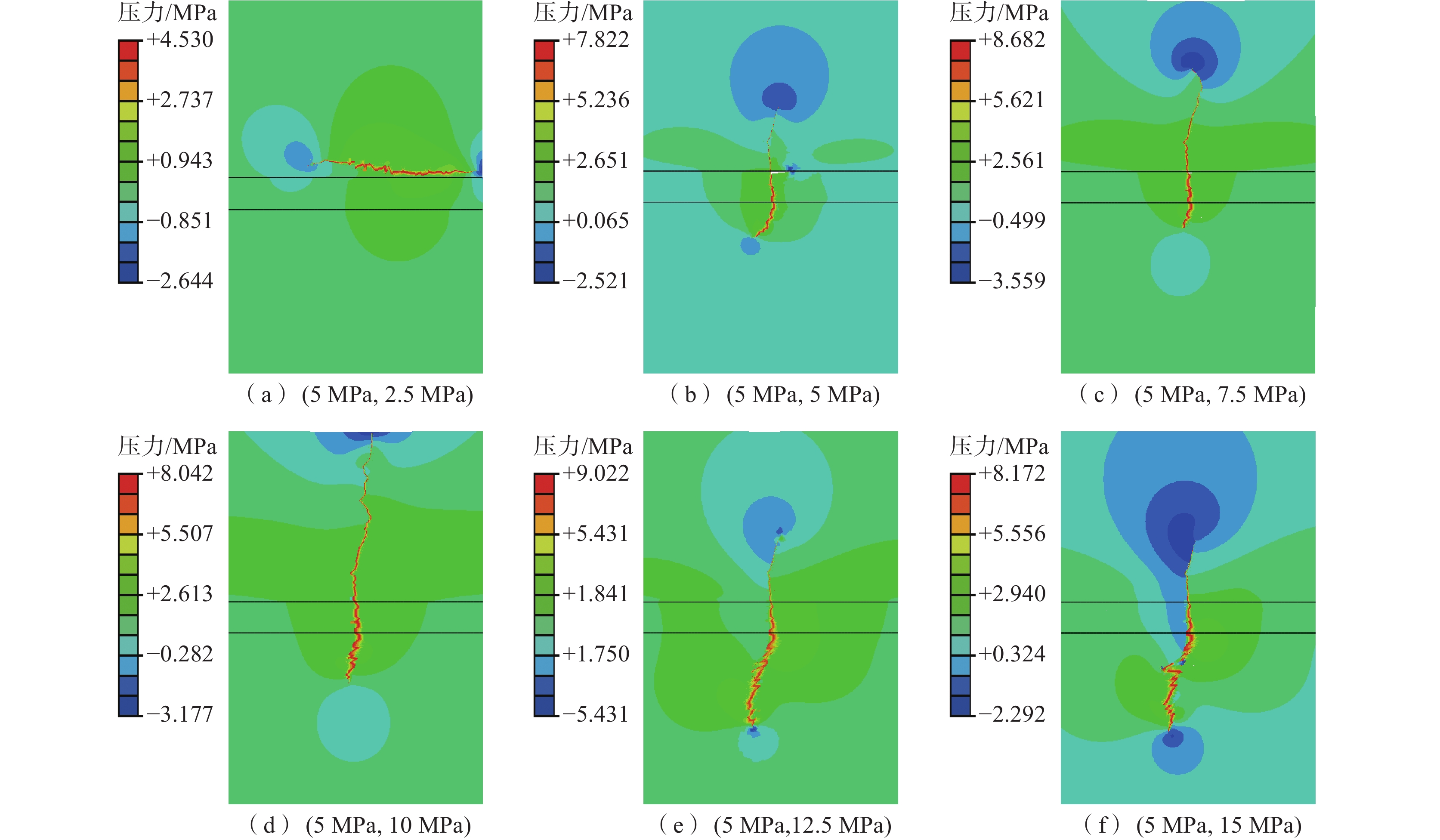
为了分析不同应力条件对煤岩复合体水力压裂裂纹扩展规律的影响,设置x方向应力σx为5 MPa不变,只改变y方向应力σy,间隔为2.5 MPa,进行对比水力压裂模拟试验研究。裂纹扩展过程中孔隙压力数值模拟结果如图3,水力压裂裂纹张开度结果对比云图如4,不同应力条件下注入压力全程变化对比曲线如图5。
由图3和图4可知:应力对水力裂纹的扩展过程和形态有重要影响作用。在应力场(σx,σy)=(5 MPa,2.5 MPa)的条件下,水压裂缝在上覆岩层中起裂并沿着最大主应力方向扩展,水力裂缝在上煤岩交界面水平平行扩展并未沿着煤岩交界弱面扩展,由于上覆岩力学特性较强且层脆性较大,所以水压裂缝张开度整体较小,裂缝传播速度较快;在应力场(σx,σy)=(5 MPa,5 MPa)的条件下,水压裂缝在上覆岩层中起裂,到达上煤岩交界面后形成了2条主裂缝,其中1条主裂缝直接穿过煤岩交界面到达煤层中并持续在煤体里边扩展,另1条主裂缝在达到上煤岩交界面后沿着上煤岩交界面上扩展延伸,在煤岩交界面处裂缝张开度最大;在应力场(σx,σy)=(5 MPa,7.5/10/12.5/15 MPa)的条件下,水压裂缝在上覆岩层中起裂后,随着应力差的逐渐增大,水力压裂裂缝受应力场的控制作用越来越显著,沿着最大主应力直接穿过煤岩交界面到达煤层后持续沿着此方向扩展。但随着应力差越来越大,水压裂缝在上覆岩层中扩展的距离越来越短,穿过交界面后在煤层中扩展越来越远。
由图5可知:σx应力为5 MPa,σy应力依次为2.5、5、7.5、10、12.5、15 MPa条件下的首次压裂压力分别为21.14、21.41、23.77、23.83、22.65、22.51 MPa;当应力差较低时,应力场难以控制水力压裂裂缝的扩展方向,只能在岩体内部产生扩展裂缝;随着应力差增大,水力压裂裂缝会沿着最大主应力方向,对煤岩复合体产生不同程度的孔隙压力,导致煤岩复合体内部产生水压裂缝;后期σy`应力为7.5 MPa和10 MPa注入压力平稳时相对较高,σy应力为12.5 MPa和15 MPa注入压力相对较小一些,是因为形成裂缝的大小不同差异导致卸压不同。
3.2 交界面强度对煤岩复合体水力压裂的影响
为分析交界面强度对煤岩复合体水力压裂裂纹扩展规律的影响,设置应力场在(σx,σy)=(5 MPa,10 MPa)条件下,改变煤岩交界面的弹性模量进行对比水力压裂模拟试验研究。不同交界面弹性模量条件下水力压裂模拟结果对比云图如图6。
如图6(a),煤岩交界面强度1.5 GPa,水力压裂裂缝从岩层扩展并贯穿交界面,但是由于交界面强度较弱难以形成水压聚集达到煤层的开裂条件,裂缝最终沿着煤层上表面向两侧扩展,此条件下水压裂缝不能诱导煤层出现裂缝。
如图6(b),煤岩交界面强度2 GPa和2.5 GPa水压裂缝能够穿越交界面并最终在煤层中扩展延伸,但是此时交界面强度较弱水压裂缝不仅穿越煤岩交界面并诱导煤层起裂扩展并且在煤层上表面也沿交界面扩展一定距离。
如图6(c),当交界面强度超过煤层时由于煤岩交界面强度较大破裂所需压力大于煤层,所以基本上不存在沿煤层上表面扩展的现象,裂缝直接穿越交界面并在煤层中扩展。
从水压裂缝在煤层中扩展的长度和缝宽来讲,相同应力条件下交界面强度越大在煤层中扩展的长度越长,同时界面强度越大,水压裂缝在煤层中的缝宽越宽。特别的,当交界面强度很大超过煤层时由于煤岩交界面强度大破裂所需破裂压力大于煤层,所以基本上不存在沿煤层上表面扩展的现象,裂缝直接穿越交界面并在煤层中扩展。同时从水压裂缝在煤层中扩展的长度和缝宽来讲,相同应力条件下交界面强度越大在煤层中扩展的长度越长,同时界面强度越大,水压裂缝在煤层中的缝宽越宽。
结合应力分析:煤岩复合体水力压裂裂缝穿过交界面并在煤层中扩展存在阈值,主应力差,交界面强度对此阈值存在重要的影响。主应力差相同时,煤岩交界面强度越大越容易形成水压聚集达到煤层破裂扩展的阈值,同时界面强度越大水力压裂裂缝穿越煤岩交界面后更容易在煤层中扩展。
3.3 交界面强度对煤岩复合体水力压裂的影响
为分析煤层层理倾角对煤岩复合体水力压裂裂缝扩展规律的影响,在(σx,σy)=(5 MPa,10 MPa)应力场条件下,改变煤层层理倾角进行对比水力压裂模拟试验研究。不同煤层层理倾角条件下水力压裂模拟结果对比云图如图7。
由图7可知:层理倾角为0°和30°条件下,主裂缝均穿过层理面并在层理处形成张开裂缝,其中层理倾角30°条件下在层理面扩展程度较为明显;层理倾角为60°条件下未能穿过层理面,但在层理面出现明显的裂缝张开滑移;层理倾角为0°时水力裂缝可以穿过煤岩交界面并在煤层中穿过层理扩展,在主裂缝与层理遭遇时形成一定数量的分值裂缝;层理倾角为30°时水力裂缝在穿过交界面时先在交界面中扩展一定距离后沿多个层里面延伸,最终贯穿层理面;层理倾角为60°时,主裂缝穿越交界面后在煤层中受层理约束沿层理扩展未能贯穿层理面压裂的作用范围仅在两相邻层理之内的煤层中,说明此条件下层理弱面对裂缝扩展方向的控制作用强于地应力。
4. 结 语
1)煤岩复合体水压裂缝在上覆岩层中起裂后,随着σy与σx应力差的逐渐增大,水力压裂裂缝受应力场的控制作用越来越显著,沿最大主应力方向持续扩展。在应力场(σx,σy)=(5 MPa,5 MPa)的条件下,水压裂缝在上覆岩层中起裂后在煤岩交界面和煤层中扩展形成了的2条主水力裂缝。
2)煤岩交界面强度较小时,在交界面中难以形成水压积聚达到煤层的开裂条件,裂缝最终沿着煤层上表面向两侧扩展,不能诱导煤层出现裂缝。煤岩交界面强度较大时水压裂缝能够穿越交界面并最终在煤层中扩展延伸,能够在煤岩交界面中扩展一定距离并完成憋压,当压力达到煤层开裂条件时水压裂缝穿越煤岩交界面并诱导煤层起裂扩展;煤岩交界面强度很大超过煤层强度时,水压裂缝基本上不沿煤层上表面扩展,而是裂缝直接穿越交界面并在煤层中扩展。同时从水压裂缝在煤层中扩展的长度和缝宽来讲,相同应力条件下交界面强度越大在煤层中扩展的长度越长,同时界面强度越大,水压裂缝在煤层中的缝宽越宽。
3)层理倾角为0°时水力裂缝可以穿过煤岩交界面并在煤层中穿过层理扩展,在主裂缝与层理遭遇时形成一定数量的分值裂缝;层理倾角为30°时水力裂缝在穿过交界面时先在交界面中扩展一定距离后沿多个层里面延伸,最终贯穿层理面;层理倾角为60°时,主裂缝穿越交界面后在煤层中受层理约束沿层理扩展未能贯穿层理面压裂的作用范围仅在两相邻层理之内的煤层中,说明此条件下层理弱面对裂缝扩展方向的控制作用强于地应力。
-
表 1 数值计算模型主要物理力学参数表
Table 1 Table of physical and mechanical parameters of numerical calculation model
岩体 弹性模
量/GPa泊松比 孔隙比 渗透率/
10−3μm2内摩擦
角/(°)抗拉强
度/MPa煤层 3.50 0.29 0.055 4 0.039 3 27 1.13 岩层 17.50 0.25 0.055 4 0.019 3 30 4.13 交界面 2.00 0.25 0.065 4 0.058 9 25 0.73 -
[1] 柳占立,庄茁,孟庆国,等. 页岩气高效开采的力学问题与挑战[J]. 力学学报,2017,49(3):507−516. LIU Zhanli, ZHUANG Zhuo, MENG Qingguo, et al. Problems and challenges of mechanics in shale gas efficient exploitation[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2017, 49(3): 507−516.
[2] 王耀锋,何学秋,王恩元,等. 水力化煤层增透技术研究进展及发展趋势[J]. 煤炭学报,2014,39(10):1945−1955. WANG Yaofeng, HE Xueqiu, WANG Enyuan, et al. Research progress and development tendency of the hydraulic technology for increasing the permeability of coal seams[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2014, 39(10): 1945−1955.
[3] 丁秀丽,张雨霆,张传健,等. 隧洞穿越活动断层应对措施及其适应性研究综述[J]. 隧道与地下工程灾害防治,2019,1(1):20−35. DING Xiuli, ZHANG Yuting, ZHANG Chuanjian, et al. Review on countermeasures and their adaptability evaluation to tunnels crossing active faults[J]. Hazard Control in Tunnelling and Underground Engineering, 2019, 1(1): 20−35.
[4] 种照辉,闫仑,高喜才,等. 天然裂隙储层水力裂缝扩展及渗流形态研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2020,37(6):1263−1273. CHONG Zhaohui, YAN Lun, GAO Xicai, et al. Mechanism of hydraulic fracture propagation and seepage pattern in naturally fractured reservoirs[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2020, 37(6): 1263−1273.
[5] 李五忠,孙斌,孙钦平,等. 以煤系天然气开发促进中国煤层气发展的对策分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2016,41(1):67−71. LI Wuzhong, SUN Bin, SUN Qinping, et al. Analysis on coal-bed methane development based on coal measure gas in China and its countermeasure[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2016, 41(1): 67−71.
[6] 谢英刚,孟尚志,万欢,等. 临兴地区煤系地层多类型天然气储层地质条件分析[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2015,43(9):71−75. XIE Yinggang, MENG Shangzhi, WAN Huan, et al. Analysis on geological conditions of multi type natural gas reservoir in coal measure strata of Linxing Area[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2015, 43(9): 71−75.
[7] 高杰,侯冰,陈勉,等. 岩性差异及界面性质对裂缝起裂扩展的影响[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2018,37(S2):4108−4114. GAO Jie, HOU Bing, CHEN Mian, et al. Effects of rock strength and interfacial property on fracture initiation and propagation[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(S2): 4108−4114.
[8] TAN P, Jin Y, HOU B, et al. Experiments and analysis on hydraulic sand fracturing by an improved true triaxial cell[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2017, 158: 766−774. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2017.09.004
[9] TAN P, Jin Y, HAN K, et al. Analysis of hydraulic fracture initiation and vertical propagation behavior in laminated shale formation[J]. Fuel, 2017, 206: 482−493. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.05.033
[10] LIU Z, JIN Y, CHEN M, et al. Analysis of non-planar multi-fracture propagation from layered-formation inclined-well hydraulic fracturing[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2016, 49: 1747−1758. doi: 10.1007/s00603-015-0872-1
[11] 马衍坤,刘泽功,周健,等. 基于孔壁应变发展规律的压裂孔三阶段起裂特征试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2016,36(8):2151−2158. MA Yankun, LIU Zegong, ZHOU Jian, et al. Study of tri-stage fracturing characteristic of borehole based on strain of hole-wall in hydraulic fracturing process[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2016, 36(8): 2151−2158.
[12] 马衍坤,刘泽功,田厚. 煤岩水力压裂过程中钻孔应变发展特征的试验研究[J]. 安全与环境学报,2015,15(4):47−51. MA Yankun, LIU Zegong, TIAN Houqiang. Experimental study of the features of the holeboring strain development in the hydraulic fracture process[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2015, 15(4): 47−51.
[13] XING P, YOSHIOKA K, ADACHI J. Lattice simulation of laboratory hydraulic fracture containment in layered reservoirs[J]. Computer and Geotechnics, 2018, 100: 62−75. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2018.03.010
[14] 武鹏飞,梁卫国,廉浩杰,等. 大尺寸煤岩组合体水力裂缝越界形成缝网机理及试验研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(5):1381−1389. WU Pengfei, LIANG Weiguo, LIAN Haojie, et al. Mechanism and experimental investigation of the formation of hydro-fracture system by fracturing through the interface of large-size coal-rock[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2018, 43(5): 1381−1389.
[15] 付世豪,侯冰,夏阳,等. 多岩性组合层状储层一体化压裂裂缝扩展试验研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(S1):377−384. FU Shihao, HOU Bing, XIA Yang, et al. Experimental research on hydraulic fracture propagation in integrated fracturing for layered formation with multi-lithology combination[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(S1): 377−384.
[16] GUO J C, LUO B, LU C, et al. Numerical investigation of hydraulic fracture propagation in a layered reservoir using the cohesive zone method[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2017, 186: 195−207. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2017.10.013
[17] ZOU Y S, MA X F, ZHOU T, et al. Hydraulic fracture growth in a layered formation based on fracturing experiments and discrete element modeling[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2017, 50(9): 2381−2395. doi: 10.1007/s00603-017-1241-z
[18] LI L C, XIA Y J, HUANG B, et al. The behaviour of fracture growth in sedimentary rocks: a numerical study based on hydraulic fracturing processes[J]. Energies, 2016, 169(9): 1−28.
[19] 牛钦环. 含水煤样剪切破坏损伤规律试验研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2017. [20] 王伸. 裂隙煤岩多级水力裂缝形成过程及机理研究[D]. 焦作: 河南理工大学, 2019. [21] WANG S, LI D, MITRI H, et al. Numerical simulation of hydraulic fracture deflection influenced by slotted directional boreholes using XFEM with a modified rock fracture energy model[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 193: 107375. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2020.107375
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 程士宜. 不同温度-冲击载荷下煤的渗透率演化规律研究. 煤矿安全. 2024(08): 43-50 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 康俊强,简阔,傅雪海,申建,王一兵,段超超. 急倾斜煤储层水力压裂裂缝扩展研究. 煤矿安全. 2024(11): 49-60 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 熊冬,贺甲元,马新仿,曲兆亮,郭天魁,马诗语. 深部煤及顶底板不同射孔位置条件下的压裂模拟——以鄂尔多斯盆地某气田8号深部煤层为例. 煤炭学报. 2024(12): 4897-4914 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: