Risk assessment of gas explosion based on fuzzy Bayesian network improved by entropy weight method
-
摘要:
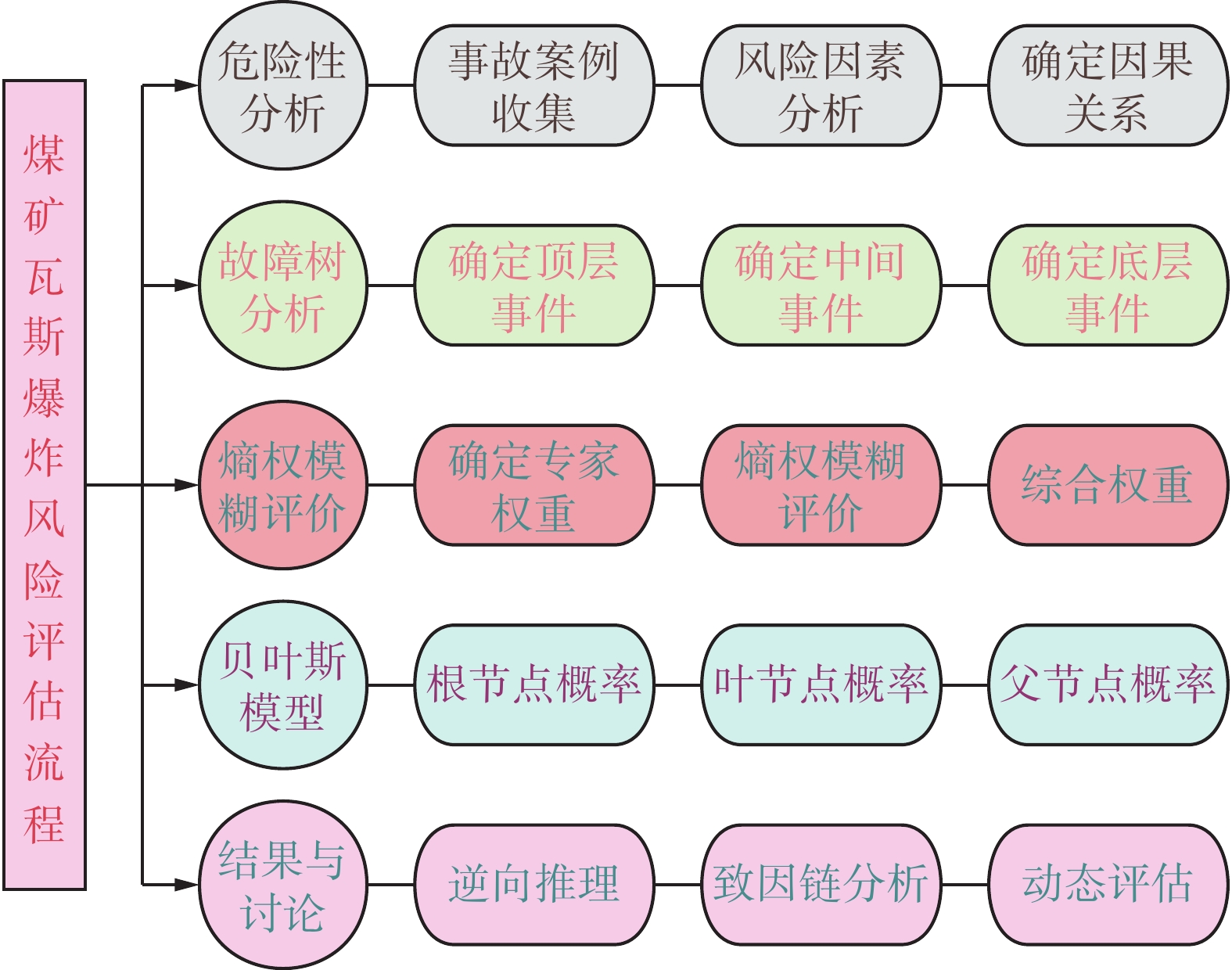
为了准确有效评估煤矿瓦斯爆炸风险,提出了基于熵权法改进的模糊贝叶斯网络瓦斯爆炸风险评估模型。首先,对瓦斯爆炸事故案例进行风险识别,提取出18个瓦斯爆炸主要风险因素;其次通过故障树模型,并根据映射规则建立出相应的贝叶斯网络模型;为减少专家判断的主观性,将熵权法结合模糊理论得到的组合权重作为贝叶斯网络的先验概率,然后通过此模型对贵州松林煤矿的瓦斯爆炸危险性进行了评估。结果表明:贵州松林煤矿瓦斯爆炸风险概率为25%,风险等级为一般风险;瓦斯积聚和煤炭自燃是导致瓦斯爆炸的主要风险因素;其中,通风阻力、瓦斯突出、防爆设备故障、违规爆破、煤自燃等因素是瓦斯爆炸的关键致因因素,评价结果与实际情况相符。
Abstract:In order to accurately and effectively evaluate the risk of gas explosion in coal mines, an improved fuzzy Bayesian network gas explosion risk assessment model based on entropy weight method is proposed. Firstly, the risk identification of gas explosion accident cases is carried out, and 18 main risk factors of gas explosion are extracted. Secondly, the fault tree model is established, and the corresponding Bayesian network model is established according to the mapping rules. In order to reduce the subjectivity of expert judgment, the combination weight obtained by entropy weight method combined with fuzzy theory is taken as the prior probability of Bayesian network, and then the risk of gas explosion in Songlin Coal Mine of Guizhou Province is evaluated by this model. The results show that the risk probability of gas explosion in Songlin Coal Mine in Guizhou is 25 %, and the risk level is general risk. Gas accumulation and coal spontaneous combustion are the main risk factors of gas explosion. Among them, ventilation resistance, gas outburst, explosion-proof equipment failure, illegal blasting, coal spontaneous combustion and other factors are the key causes of gas explosion, and the evaluation results are consistent with the actual situation.
-
Keywords:
- gas explosion /
- risk assessment /
- fault tree /
- fuzzy theory /
- entropy weight method /
- Bayesian network
-
-
表 1 模糊概率区间的划分
Table 1 Division of fuzzy probability interval
评语等级 三角模糊函数 评语等级 S1 (0.0,0.0,0.1) 非常低 S2 (0.0,0.1,0.3) 低 S3 (0.1,0.3,0.5) 较低 S4 (0.3,0.5,0.7) 中等 S5 (0.5,0.7,0.9) 较高 S6 (0.7,0.9,1.0) 高 S7 (0.9,1.0,1.0) 非常高 表 2 专家组的权重标准
Table 2 Weight standard of expert group
属性 描述 权重 专家职位 高级工程师 1.0 中级工程师 0.8 初级工程师 0.6 技术人员 0.4 工人 0.2 教育程度 博士 1.0 硕士 0.8 学士 0.6 大专 0.4 中专 0.2 工作年限 ≥20 年 1.0 15~<20 年 0.8 10~<15年 0.6 5~<10 年 0.4 <5 年 0.2 专业相关 非常相关 1.0 比较相关 0.8 一般相关 0.6 基本相关 0.4 不太相关 0.2 表 3 煤矿瓦斯爆炸因素
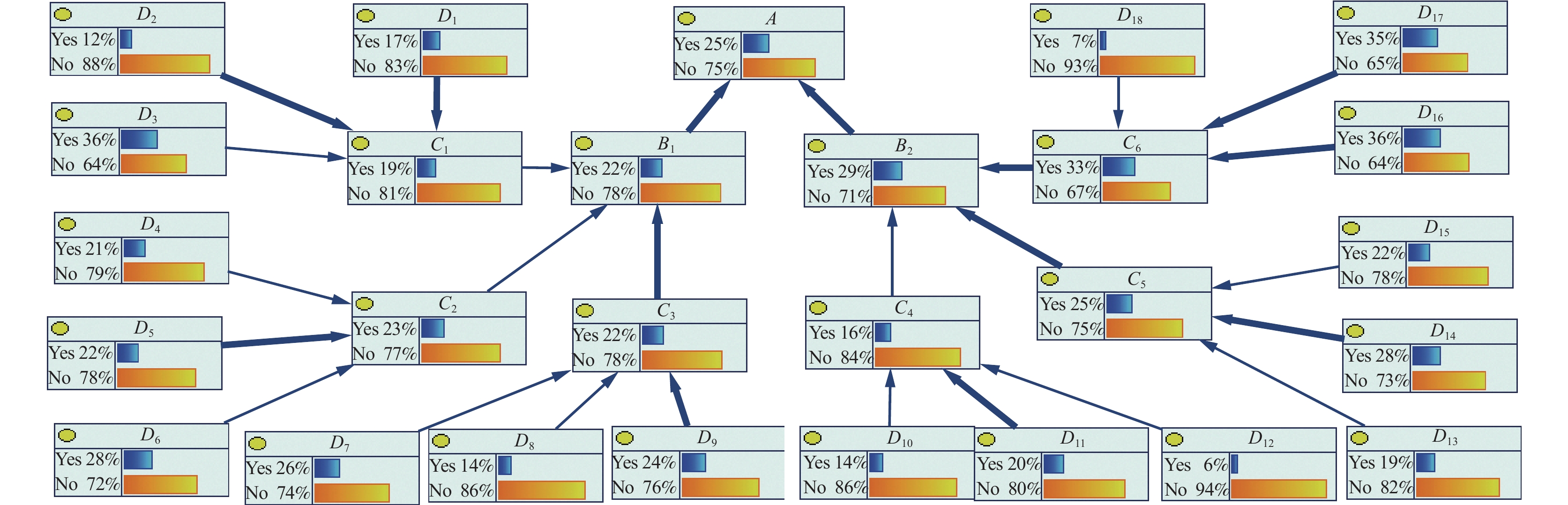
Table 3 Coal mine gas explosion factors
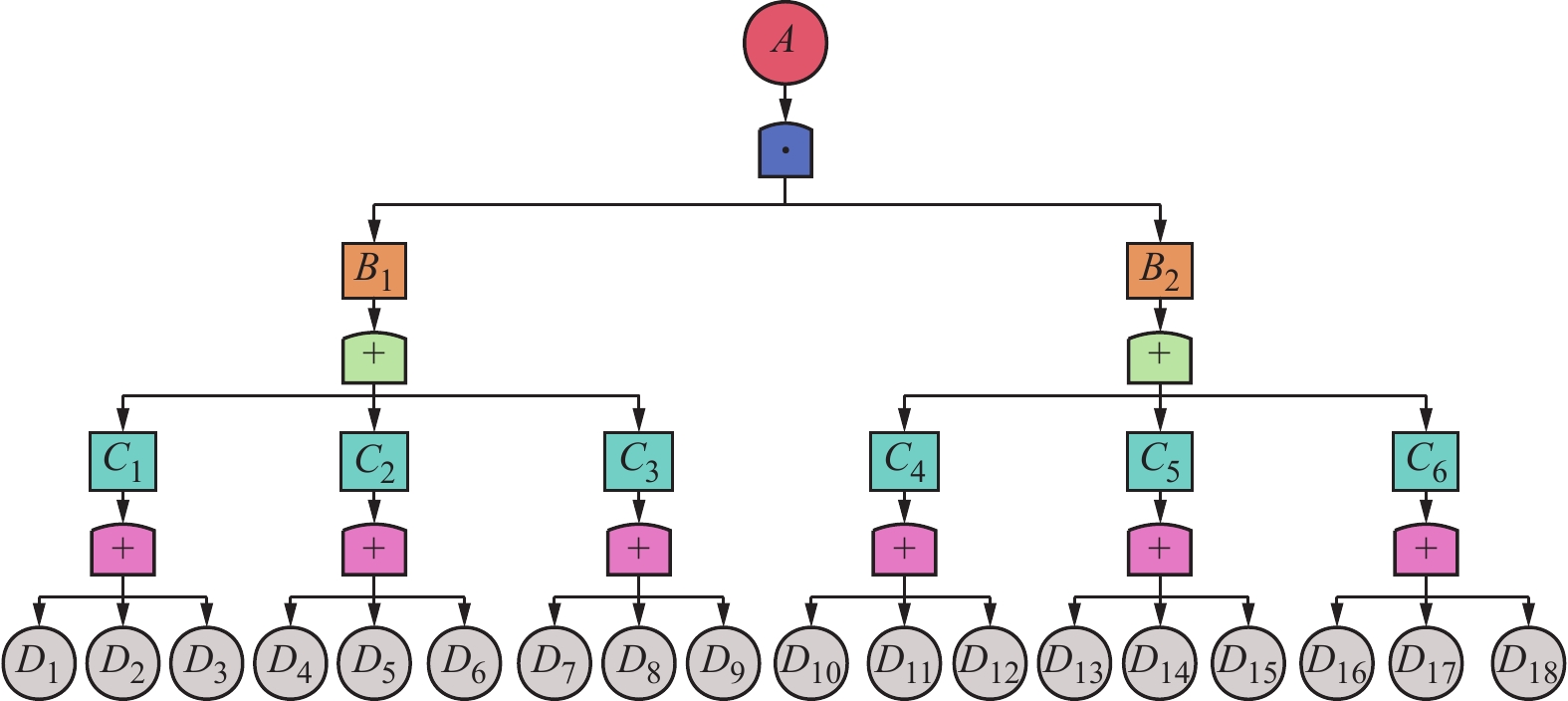
叶节点 根节点 事件描述 瓦斯措施C1 钻孔数量D1 钻孔的数量不够 密封质量D2 封孔质量差,导致密闭性不够 瓦斯抽采D3 没有进行瓦斯抽采;瓦斯抽采不达标 通风缺陷C2 通风不足D4 风量不足,不能满足矿井通风要求 通风阻力D5 巷道变形、巷道设计缺陷等 风机故障D6 没有通风设备;风机停止运行 浓度上升C3 瓦斯积聚D7 上隅角、盲巷、采空区出现瓦斯积聚 瓦斯涌出D8 瓦斯涌出量异常 瓦斯突出D9 瞬间释放大量瓦斯和煤 产生火花C4 摩擦火花D10 岩石,设备等摩擦产生火花 撞击火花D11 物体碰撞产生撞击火花 静电火花D12 物体接触产生静电火花 电气故障C5 电器故障D13 电气设备短路及故障等产生火花 防爆故障D14 防爆设备失效或没有防爆设备 设施故障D15 电缆老化、断裂产生火花 出现明火C6 违规爆破D16 爆破作业没有按照规范制度进行 煤炭自燃D17 煤体升温到着火点,与氧气反应燃烧 使用明火D18 人员吸烟,明火照明,焊接等 表 4 专家信息
Table 4 Expert information
序号 专家职位 工作年限/年 学历 专业相关 1 高级工程师 22 博士 非常相关 2 中级工程师 18 硕士 比较相关 3 初级工程师 12 本科 比较相关 4 技术人员 8 硕士 非常相关 表 5 专家打分表
Table 5 Expert scoring table
指标 专家 权重
均分信息熵 模糊
权重综合
权重1 2 3 4 D1 8 8 7 8 6.037 5 0.7809 0.2185 0.1706 D2 7 6 6 7 5.062 5 0.7044 0.1743 0.1228 D3 6 5 5 4 3.962 5 0.5980 0.6072 0.3631 D4 7 7 6 6 5.100 0 0.7076 0.2958 0.2093 D5 6 6 5 6 4.487 5 0.6520 0.3386 0.2208 D6 8 7 7 7 5.675 0 0.7540 0.3656 0.2757 D7 7 6 6 7 5.062 5 0.7044 0.3711 0.2614 D8 6 5 4 5 3.962 5 0.5980 0.2347 0.1404 D9 6 5 5 5 4.125 0 0.6154 0.3942 0.2426 D10 4 4 3 3 2.775 0 0.4433 0.3172 0.1406 D11 4 3 3 4 2.737 5 0.4374 0.4655 0.2036 D12 3 2 3 2 1.962 5 0.2928 0.2173 0.0636 D13 6 6 5 5 4.325 0 0.6360 0.2914 0.1853 D14 7 6 7 7 5.225 0 0.7181 0.3833 0.2752 D15 6 5 6 7 4.612 5 0.6639 0.3253 0.2160 D16 9 8 7 8 6.287 5 0.7985 0.4483 0.3580 D17 7 8 8 8 5.950 0 0.7745 0.4541 0.3517 D18 7 6 7 7 5.225 0 0.7181 0.0976 0.0701 表 6 节点的概率
Table 6 Probability of nodes
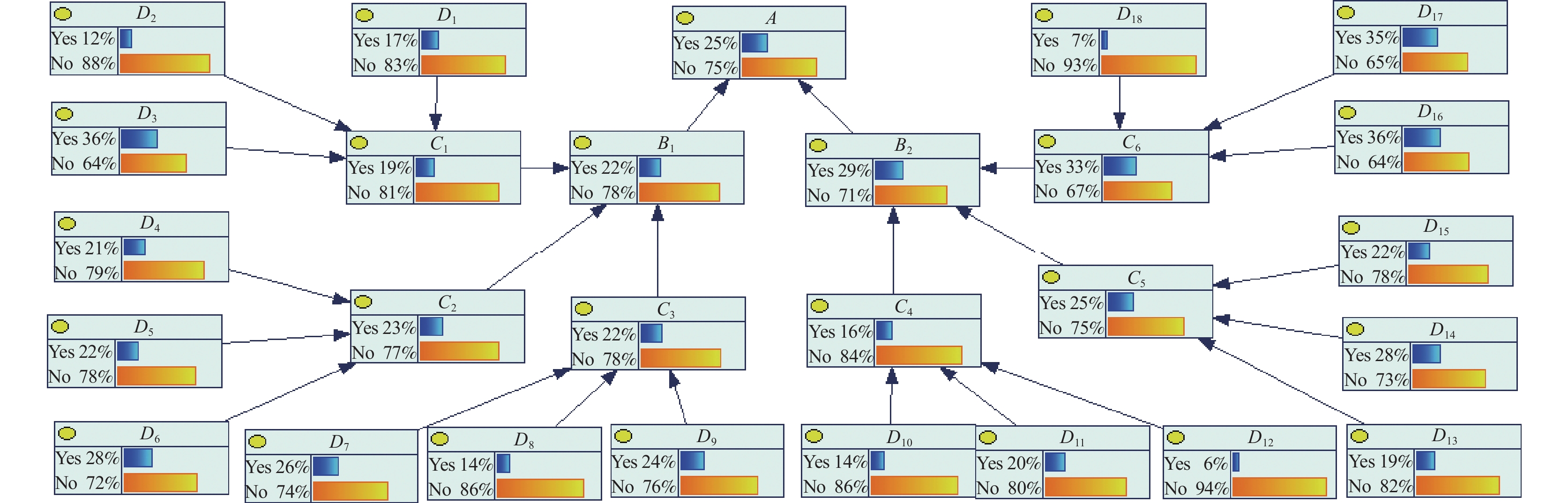
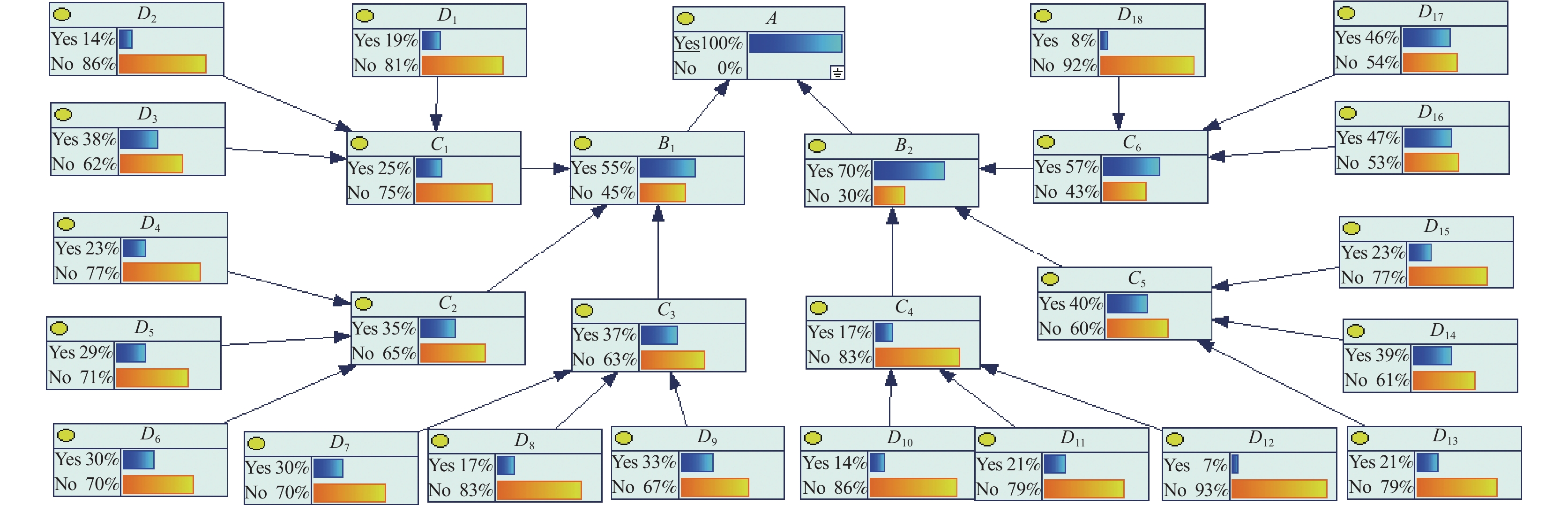
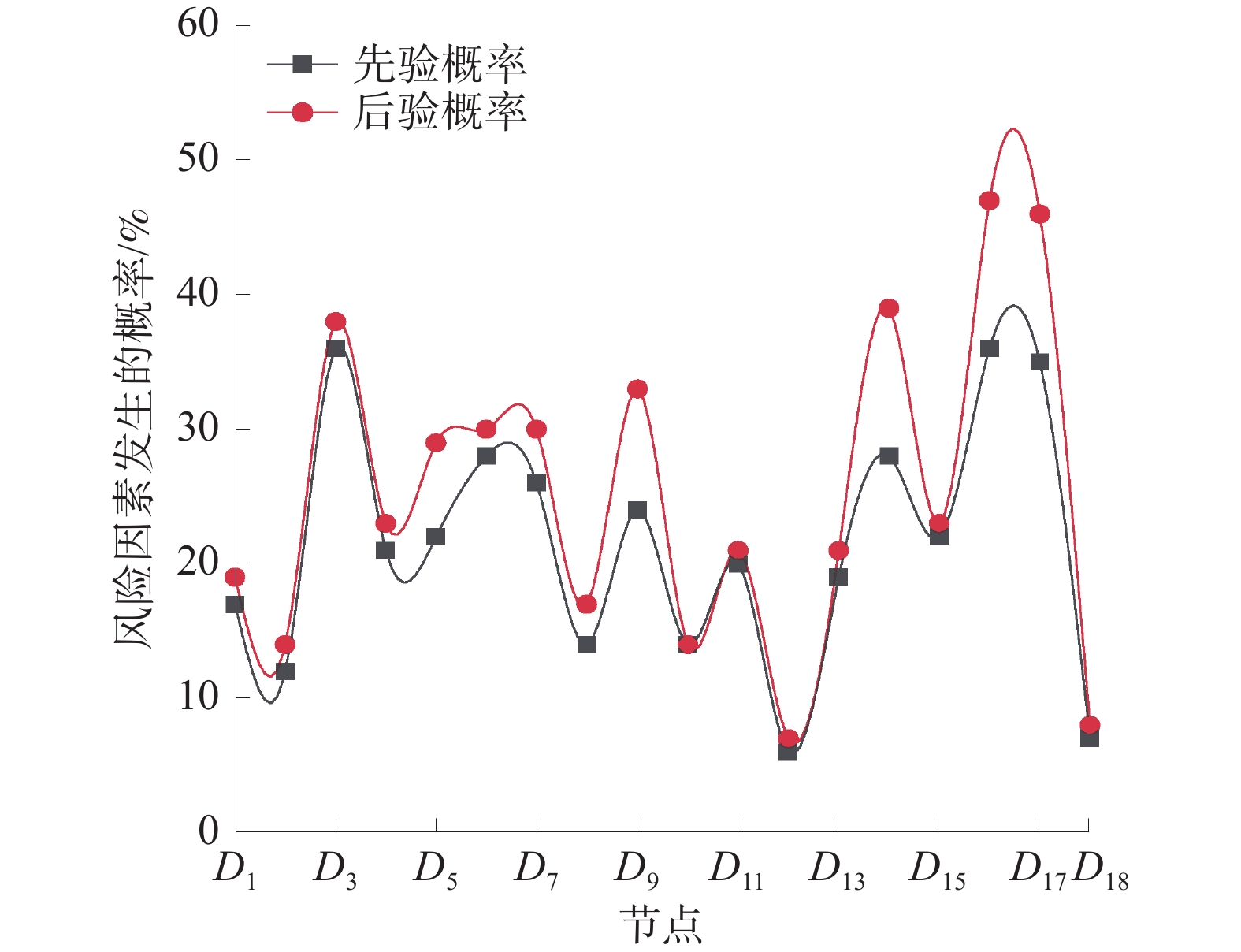
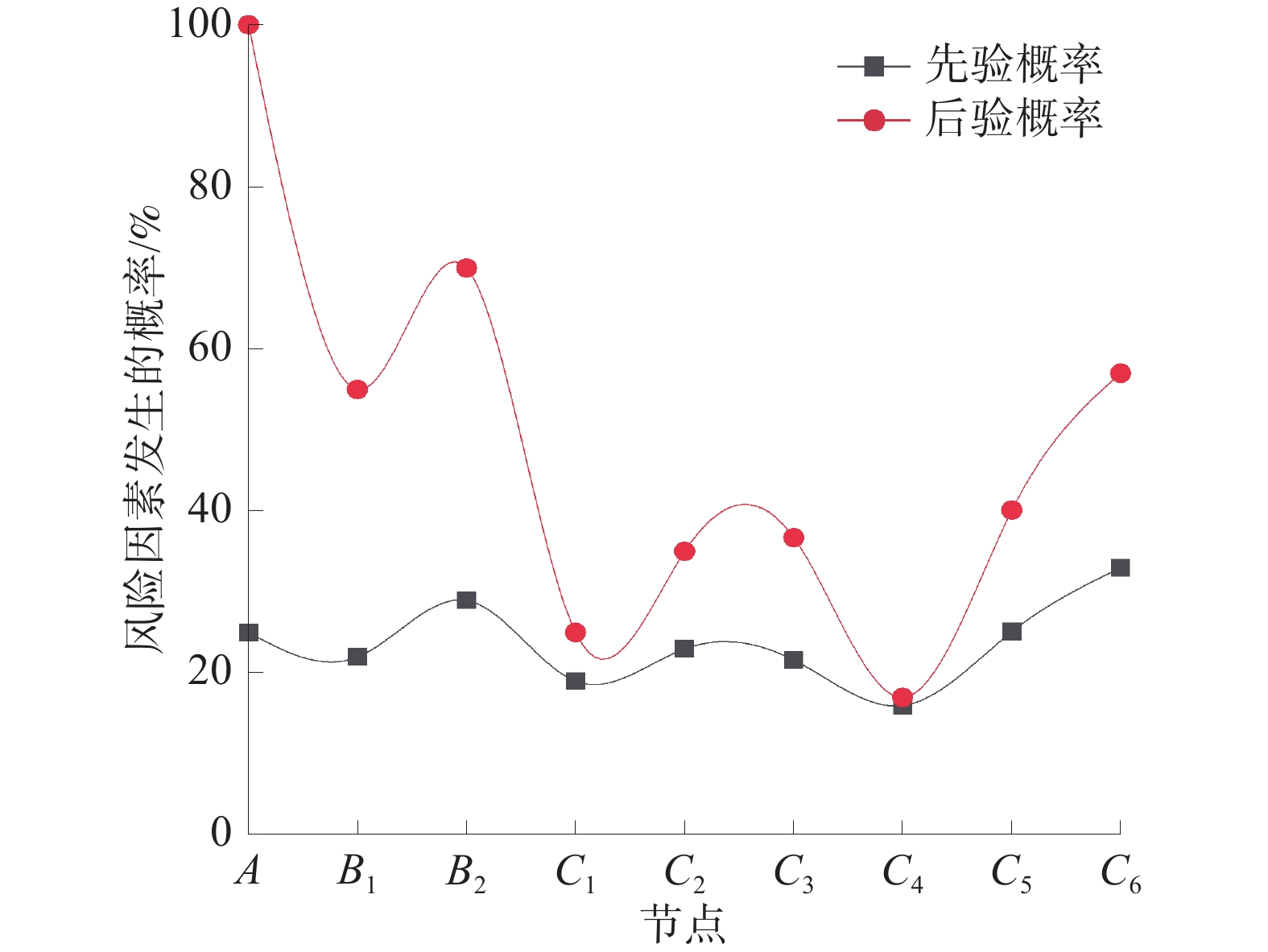
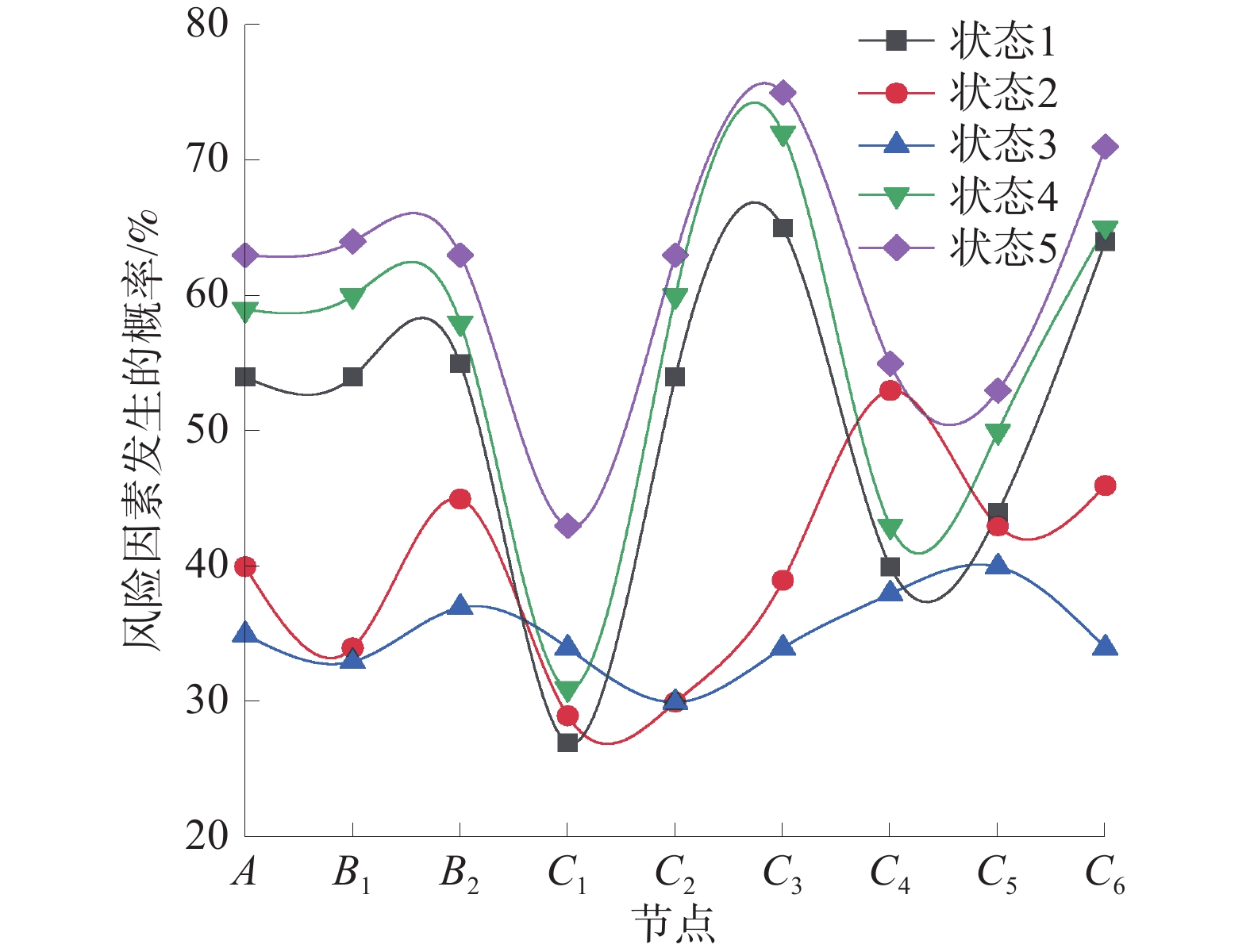
指标 概率 指标 概率 指标 概率 D1 0.171 D7 0.261 D13 0.185 D2 0.123 D8 0.140 D14 0.275 D3 0.363 D9 0.243 D15 0.216 D4 0.209 D10 0.141 D16 0.358 D5 0.221 D11 0.204 D17 0.352 D6 0.276 D12 0.065 D18 0.070 A 0.252 C1 0.190 C4 0.157 B1 0.215 C2 0.229 C5 0.251 B2 0.287 C3 0.216 C6 0.326 -
[1] 武强,涂坤,曾一凡,等. 打造我国主体能源(煤炭)升级版面临的主要问题与对策探讨[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(6):1625−1636. WU Qiang, TU Kun, ZENG Yifan, et al. Discussion on the main problems and countermeasures of building China’s main energy(coal) upgraded version[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2019, 44(6): 1625−1636.
[2] 赵佳佳,田世祥,杨家向,等. 基于知识图谱的煤矿热动力灾害可视化研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2023,54(3):33−39. ZHAO Jiajia, TIAN Shixiang, YANG Jiaxiang, et al. Study on visualization of thermodynamic disaster in coal mine based on knowledge map[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2023, 54(3): 33−39.
[3] 郭慧敏,成连华,李树刚. 基于DEMATEL-ISM-MICMAC的煤矿瓦斯爆炸致因研究[J]. 矿业安全与环保,2023,50(2):114−119. GUO Huimin, CHENG Lianhua, LI Shugang. Research on causal factors of coal mine gas explosion based on DEMATEL-ISM-MICMAC[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection, 2023, 50(2): 114−119.
[4] 解镕嘉,谢雄刚,殷涛,等. 基于熵权物元可拓模型的煤矿瓦斯爆炸危险性评价[J]. 化工矿物与加工,2023,52(8):32−38. XIE Rongjia, XIE Xionggang, YIN Tao, et al. The risk evaluation of gas explosion in coal mines by matter-element extension model based on entropy weight[J]. Industrial Minerals & Processing, 2023, 52(8): 32−38.
[5] 景国勋,陈纪宏. 基于SPA-VFS耦合模型的瓦斯爆炸风险评价[J]. 安全与环境学报,2023,23(7):2151−2158. JING Guoxun, CHEN Jihong. Risk assessment of gas explosion based on SPA-VFS coupling model[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2023, 23(7): 2151−2158.
[6] 李红霞,吴雪菲,谢谦. 综采工作面瓦斯爆炸风险评估[J]. 西安科技大学学报,2022,42(2):245−250. LI Hongxia, WU Xuefei, XIE Qian. Gas risk assessment of fully-mechanized mining face[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Science and Technology, 2022, 42(2): 245−250.
[7] 汪圣伟,李希建,代芳瑞,等. 基于改进AHP-SPA的煤矿瓦斯爆炸风险评价[J]. 矿业研究与开发,2021,41(4):113−117. WANG Shengwei, LI Xijian, DAI Fangrui, et al. Risk assessment of gas explosion based on improved AHP-SPA[J]. Mining Research and Development, 2021, 41(4): 113−117.
[8] 鲁锦涛,任利成,戎丹,等. 基于灰色-物元模型的煤矿瓦斯爆炸风险评估[J]. 中国安全科学学报,2021,31(2):99−105. LU Jintao, REN Licheng, RONG Dan, et al. Assessment of coal mine gas explosion risk based on grey-matter element model[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(2): 99−105.
[9] 李红霞,郑佳敏. 煤矿瓦斯爆炸模糊Bow-tie模型分析[J]. 矿业安全与环保,2020,47(5):119−126. LI Hongxia, ZHENG Jiamin. Analysis of fuzzy Bow-tie model of gas explosion in coal mine[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection, 2020, 47(5): 119−126.
[10] 皮子坤,贾宝山,贾廷贵,等. 基于前景理论和区间数的煤矿瓦斯爆炸风险评价[J]. 中国安全科学学报,2017,27(6):91−96. PI Zikun, JIA Baoshan, JIA Tinggui, et al. Assessment of risk of gas explosion in coal mine based on prospect theory and interval number[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2017, 27(6): 91−96.
[11] 张津嘉,许开立,王延瞳,等. 瓦斯爆炸事故风险耦合分析[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版),2017,38(3):414−417. ZHANG Jinjia, XU Kaili, WANG Yantong, et al. Analysis of risk coupling of gas explosion accidents[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 38(3): 414−417.
[12] LI M, WANG D M, SHAN H. Risk assessment of mine ignition sources using fuzzy Bayesian network[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2019, 125: 297−306. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2019.03.029
[13] 史晓娟,姚兵,顾华北. 基于模糊贝叶斯网络的矿井排水系统故障诊断[J]. 工矿自动化,2022,48(9):77−83. SHI Xiaojuan, YAO Bing, GU Huabei. Fault diagnosis of mine drainage system based on fuzzy Bayesian network[J]. Industry and Mine Automation, 2022, 48(9): 77−83.
[14] 李金蓉,杨玉中. DS理论-贝叶斯网络下的煤矿通风系统风险评估[J]. 中国安全科学学报,2022,32(8):146−153. LI Jinrong, YANG Yuzhong. Risk assessment of ventilation system in coal mines based on DS theory and Bayesian network[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(8): 146−153.
[15] 袁奇,张晓蕾,张兴凯,等. 地下工程火灾综合定量风险评估方法[J]. 安全与环境学报,2024,24(1):42−52. YUAN Qi, ZHANG Xiaolei, ZHANG Xingkai, et al. Integrated quantitative risk assessment method for underground engineering fires[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2024, 24(1): 42−52.
[16] 洪伟斌,盛武. 基于DEMATEL-ISM-BN的煤矿透水事故影响因素分析[J]. 工矿自动化,2022,48(12):116−122. HONG Weibin, SHENG Wu. Analysis of influencing factors of coal mine flooding accidents based on DEMATEL-ISM-BN[J]. Industrial and Mining Automation, 2022, 48(12): 116−122.
[17] 成连华,左敏昊. 基于扎根理论的瓦斯爆炸风险累积效应研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术,2021,17(10):53−59. CHENG Lianhua, ZUO Minhao. Research on cumulative effect of gas explosion risk based on grounded theory[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2021, 17(10): 53−59.
[18] 李敏,林志军,鲁义,等. 基于模糊贝叶斯网络的煤矿瓦斯爆炸风险评估[J]. 煤炭学报,2023,48(S2):626−637. LI Min, LIN Zhijun, LU Yi, et al. Risk assessment of gas explosion coal mines based on fuzzy Bayesian network[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2023, 48(S2): 626−637.
[19] 陈雍君,李晓健,张丽,等. 故障树和模糊贝叶斯网络在管廊运维风险评估中的应用研究[J]. 安全与环境学报,2024,24(3):857−866. CHEN Yongjun, LI Xiaojian, ZHANG Li, et al. Research on the application of fault tree and fuzzy Bayesian network in utility tunnel operation and maintenance risk assessment[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2024, 24(3): 857−866.
[20] 田文杰,徐吉辉,郝旭祥. 不确定条件下任务风险分析的贝叶斯网络方法[J]. 兵器装备工程学报,2023,44(1):152−158. TIAN Wenjie, XU Jihui, HAO Xuxiang. Bayesian network method for mission risk analysis under uncertainty[J]. Journal of Ordnance and Equipment Engineering, 2023, 44(1): 152−158.
[21] 姚成玉,陈东宁,王斌. 基于T-S故障树和贝叶斯网络的模糊可靠性评估方法[J]. 机械工程学报,2014,50(2):193−201. doi: 10.3901/JME.2014.02.193 YAO Chengyu, CHEN Dongning, WANG Bin. Fuzzy reliability assessment method based on T-S fault tree and Bayesian network[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 50(2): 193−201. doi: 10.3901/JME.2014.02.193
[22] 余磊,李波. 基于熵权的未确知测度理论的高层建筑火灾危险性评价[J]. 安全与环境工程,2017,24(1):115−120. YU Lei, LI Bo. Fire risk evaluation for high-rise buildings based on entropy weight and uncertainty measurement theory[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2017, 24(1): 115−120.
[23] 成连华,解萌玥,左敏昊,等. 基于ISM-BN的煤矿瓦斯爆炸风险评判方法及其应用[J]. 煤矿安全,2022,53(10):1−8. CHENG Lianhua, XIE Mengyue, ZUO Minhao, et al. Risk evaluation method of coal mine gas explosion based on ISM-BN and its application[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(10): 1−8.
[24] 司荣军,李润之. 低浓度含氧瓦斯爆炸动力特性及防控关键技术[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2020,48(10):17−36. SI Rongjun, LI Runzhi. Dynamic characteristics of low-concentration oxygen-containing gas explosion and key technologies for prevention and control[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48(10): 17−36.
[25] 赵佳佳,田世祥,李鹏,等. SiO2-H2O纳米流体强化煤尘润湿性的微观机理研究[J]. 化工学报,2023,74(9):3931−3945. ZHAO Jiajia, TIAN Shixiang, LI Peng, et al. Microscopic mechanism of SiO2-H2O nanofluids to enhance the wettability of coal dust[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3931−3945.
[26] 程方明,南凡,罗振敏,等. 瓦斯抑爆材料及机理研究进展与发展趋势[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(8):114−124. CHENG Fangming, NAN Fan, LUO Zhenmin, et al. Research progress and development trend of gas explosion suppression materials and mechanism[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49(8): 114−124.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 唐巨鹏,张昕,潘一山. 煤与瓦斯突出物理模拟试验研究现状及展望. 岩石力学与工程学报. 2024(03): 521-541 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张超林,王培仲,王恩元,许江,李忠辉,刘晓斐,彭守建. 我国煤与瓦斯突出机理70年发展历程与展望. 煤田地质与勘探. 2023(02): 59-94 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张文柯. 基于AHP-MCS的煤与瓦斯突出主控因素分析. 能源技术与管理. 2023(05): 126-127 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: