Formation mechanism of job burnout of coal mine safety managers based on JD-R model
-
摘要:
为探讨煤矿安全管理者职业倦怠形成机理,基于工作要求构建资源模型,运用扎根理论对煤矿安全管理者开展深度访谈,构建了煤矿安全管理者职业倦怠JD-R理论模型提出相关假设,通过对300名煤矿安全管理者开展问卷调查进行模型验证。结果表明:人口统计学变量中工龄、职位、工作时长会影响职业倦怠;工作要求和角色压力负向预测职业倦怠,工作资源和组织公平感正向预测煤矿安全管理者职业倦怠;角色压力在工作要求与职业倦怠之间中介效应值为0.276,组织公平在工作资源与职业倦怠间中介效应值为−0.365。
Abstract:In order to explore the formation mechanism of job burnout of coal mine safety managers, based on the job demand-resource model and grounded theory, the research conducted in-depth interviews with coal mine safety managers, built a JD-R theoretical model of coal mine safety managers’ job burnout and proposed relevant hypotheses. The results show that: among the demographic variables, working age, position and working time will affect job burnout; job demands and role pressure negatively predict job burnout, while job resources and organizational justice positively predict job burnout of coal mine safety managers. The mediating effect of role stress on job demand and job burnout was 0.276, and the mediating effect of organizational justice on job resource and job burnout was -0.365.
-
-
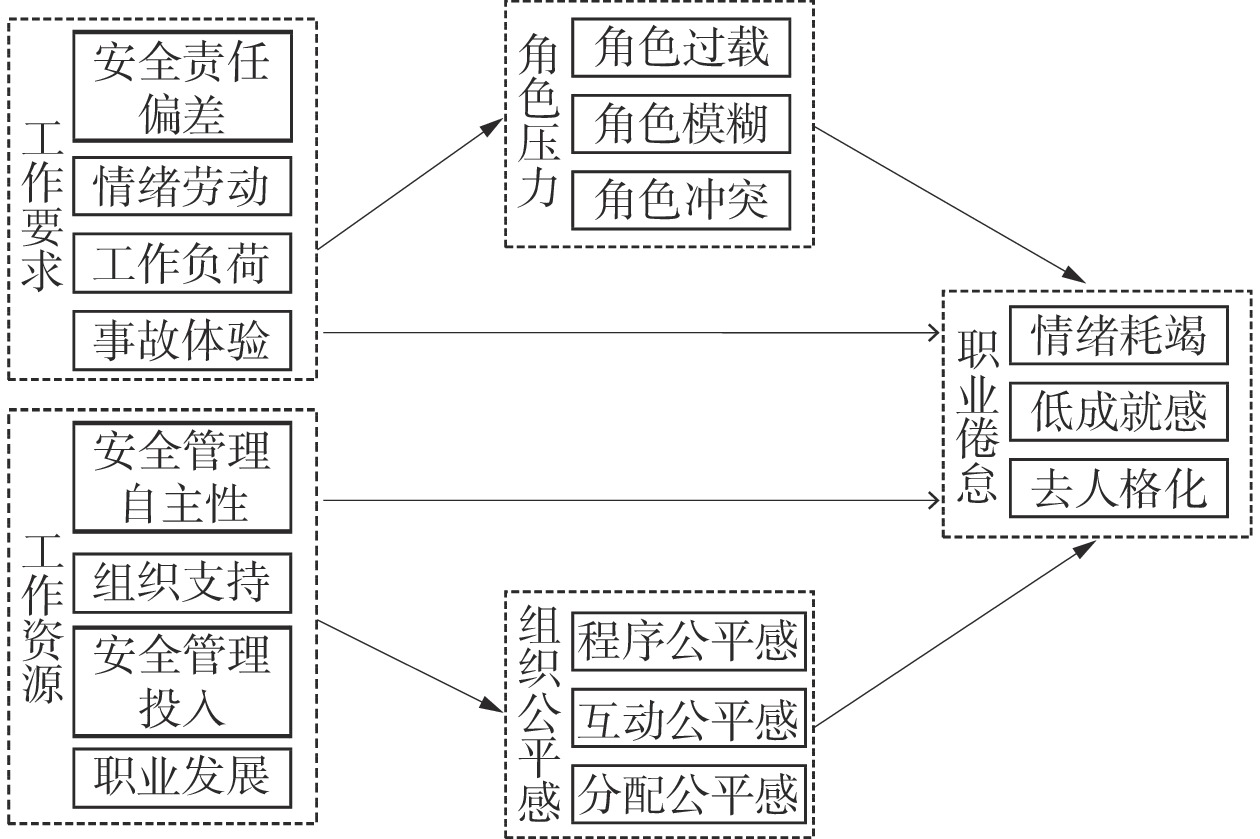
表 1 三级编码内容展示
Table 1 Displayed three-level coding content
选择编码 主轴编码 开放式编码
工作要求
↓
角色压力
↓
煤矿安全管理者
职业倦怠工作要求 安全责任感偏差 情绪劳动 工作负荷 事故体验 角色压力 角色过载 角色模糊 角色冲突 职业倦怠 情绪耗竭 低成就感 去人格化
工作资源
↓
组织公平感
↓
煤矿安全管理者
职业倦怠组织公平感 程序公平感 互动公平感 分配公平感 工作资源 安全管理自主性 组织支持 安全管理投入 职业发展 表 2 不同类型煤矿安全管理者职业倦怠差异性分析
Table 2 Analysis of the differences in job burnout of different types of coal mine safety managers
因素 变量 职业倦怠 T/F P 性别 男 3.310 −1.521 0.129 女 3.458 年龄 18~25 3.483 1.885 0.112 25~36 3.385 40以上 3.182 教育水平 中专及以下 3.854 1.219 0.303 大专 3.396 本科及以上 3.310 工龄/a ≤2 3.496 2.569 <0.05 3~10 3.316 11~20 3.185 ≥20 3.216 职位 基层 3.439 9.468 <0.001 中层 3.106 高层 3.235 工作时长/h ≤40 3.180 3.667 <0.01 40~50 3.230 50~60 3.423 >60 3.540 注:P为显著性水平;T为回归参数的显著性检验值;F为F检验的统计量。 表 3 直接预测效应检验结果表
Table 3 Direct prediction effect test results table
假设 因素 SE T β P R2 结果 H1 常量 0.229 7.050 — <0.001 0.425 成立 WL 0.043 2.310 0.123 <0.050 — 成立 AE 0.040 −0.437 −0.022 0.662 — 不成立 EL 0.049 5.547 0.293 <0.001 — 成立 SRD 0.044 2.580 0.139 <0.010 — 成立 H2 常量 0.126 38.630 — <0.001 0.575 成立 OS 0.043 −3.893 −0.225 <0.010 — 成立 CD 0.043 −6.197 −0.323 <0.010 — 成立 SMA 0.046 −0.557 −0.030 0.578 — 不成立 SMI 0.035 −2.860 −0.146 <0.010 — 成立 H3 常量 0.166 9.474 — <0.001 0.501 成立 RC 0.047 3.622 0.195 <0.010 — 成立 RA 0.035 4.420 0.216 <0.010 — 成立 RO 0.040 4.894 0.256 <0.010 — 成立 H4 常量 0.092 53.050 — <0.001 0.686 成立 DJ 0.039 −5.090 −0.260 <0.010 — 成立 PJ 0.038 −4.030 −0.220 <0.001 — 成立 IJ 0.037 −6.020 −0.320 <0.010 — 成立 -
[1] SCHAUFELI W B, TARIS T W. A critical review of the job demands-resources model: Implications for improving work and health[J]. Bridging Occupational Organizational & Public Health, 2014: 43-68.
[2] 周密,赵文红,姜玉洁. 基于工作要求—资源模型的新生代产业工人工作倦怠的研究−心理韧性的作用[J]. 软科学,2016,30(12):67−71. ZHOU Mi, ZHAO Wenhong, JIANG Yujie. Study on the new generation workers’ burnout based on job demands−resources model from the perspective of resilience[J]. Soft Science, 2016, 30(12): 67−71.
[3] 牛莉霞,刘谋兴,李乃文,等. 工作倦怠、安全注意力与习惯性违章行为的关系[J]. 中国安全科学学报,2016,26(6):19−24. NIU Lixia, LIU Mouxing, LI Naiwen, et al. Relationship among job burnout, safety attention and habitual violation behavior[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2016, 26(6): 19−24.
[4] 燕勇,栗继祖. 智能化变革背景下矿工工作压力对风险行为的影响研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2021,52(8):253−258. YAN Yong, LI Jizu. Study on influence of working pressure on risky behavior of miners under the background of intelligent change[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021, 52(8): 253−258.
[5] 于维英,张玮. 生产安全监督管理人员的胜任特征模型[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术,2011,7(7):133−137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-193X.2011.07.028 YU Weiying, ZHANG Wei. Development of competency model of manufacturing safety managers[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2011, 7(7): 133−137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-193X.2011.07.028
[6] 周梅华,李文唤,梅学聃. 煤矿工作资源对矿工工作倦怠的影响:心理资本和疲劳的中介作用[J]. 中国煤炭,2018,44(3):23−27. ZHOU Meihua, LI Wenhuan, MEI Xuedan. The relationship between coal miners job resources and job burnoutthe mediating effects of psychological capital and fatigue[J]. China Coal, 2018, 44(3): 23−27.
[7] 张叶馨,栗继祖,冯国瑞,等. 基于SEM矿工组织支持感与不安全行为关系研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2017,48(8):238−241. ZHANG Yexin, LI Jizu, FENG Guorui, et al. Research on relationship between miners’ perceived organizational support and unsafe behavior based on SEM[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2017, 48(8): 238−241.
[8] 唐咏,倪小琪. 医务社会工作者职业紧张、组织支持与离职意愿的关系研究[J]. 社会工作,2023(2):84−95. TANG Yong, NI Xiaoqi. Study on the relationship between ocupational stress, organization a support and turnover intention of medical social workers[J]. Journal of Social Work, 2023(2): 84−95.
[9] 吕威建,吕永卫. 角色压力对矿工不安全行为的影响研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2021,52(4):255−259. LYU Weijian, LYU Yongwei. Study on the influence of role stressors on miners’ unsafe behavior[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021, 52(4): 255−259.
[10] UM M Y, HARRISON D F. Role stressors, burnout, mediators, and job satisfaction: A stress-strain-outcome model and an empirical test[J]. Social Work Research, 1998, 22(2): 100−115. doi: 10.1093/swr/22.2.100
[11] 葛志鸿. 组织支持感与空管安全管理绩效的关联性研究[D]. 武汉:武汉理工大学,2012. [12] 李超平,时勘. 分配公平与程序公平对工作倦怠的影响[J]. 心理学报,2003,35(5):677−684. LI Chaoping, SHI Kan. The influence of distributive justice and procedural justice on job burnout[J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2003, 35(5): 677−684.
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 李润芝. 动压影响孤岛工作面巷道围岩“卸-支平衡”协同控制技术. 煤矿安全. 2024(03): 199-208 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 胡威,高志强. 基于薄板理论的覆岩导水裂隙带高度研究. 煤炭科技. 2024(03): 126-130 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李辉,宋宇航,毕健成,李强. 孤岛工作面侧向顶板结构及切顶卸压技术. 科学技术与工程. 2024(36): 15396-15403 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王鹏,王虎伟,王帅,王鹏程. 孤岛工作面回采巷道围岩破坏机理及差异化控制技术. 金属矿山. 2024(12): 96-105 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 秦忠诚,张国兴,詹召伟,王彦敏,高超. 1310孤岛工作面初采矿压特征与支架适应性评价. 矿业研究与开发. 2023(03): 147-153 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 杨旭,王涛. 孤岛工作面顶板条带弱化技术研究及应用. 矿业安全与环保. 2023(03): 111-116+123 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)



 下载:
下载:
