Physical simulation and drilling optimization design of hydraulic cavitation and permeability enhancement in Wuhushan Coal Mine
-
摘要:
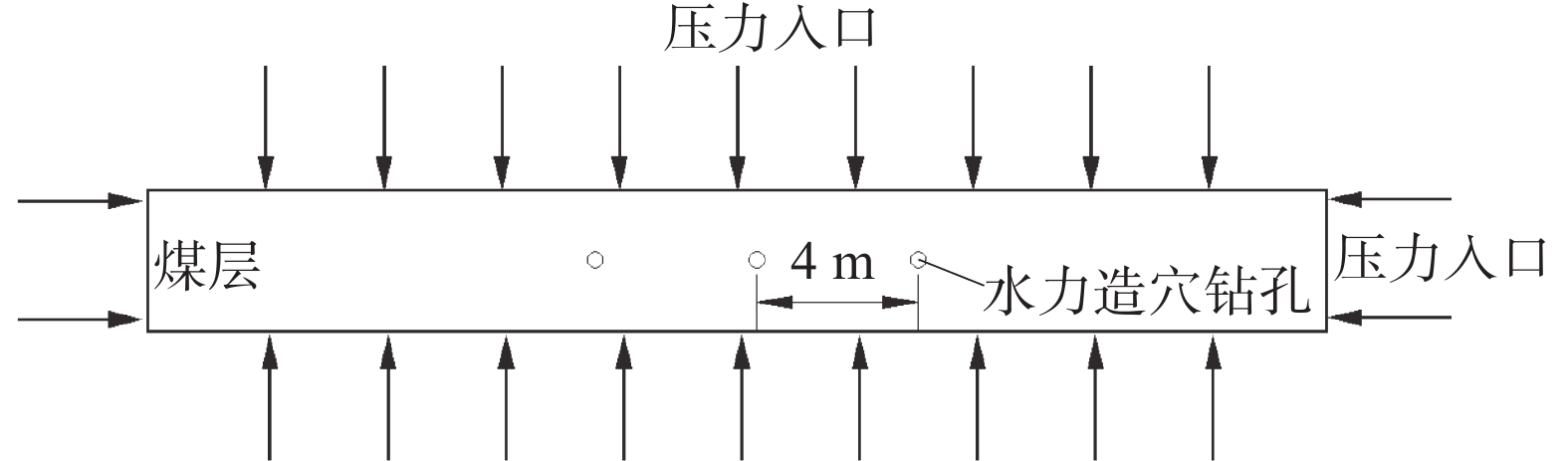
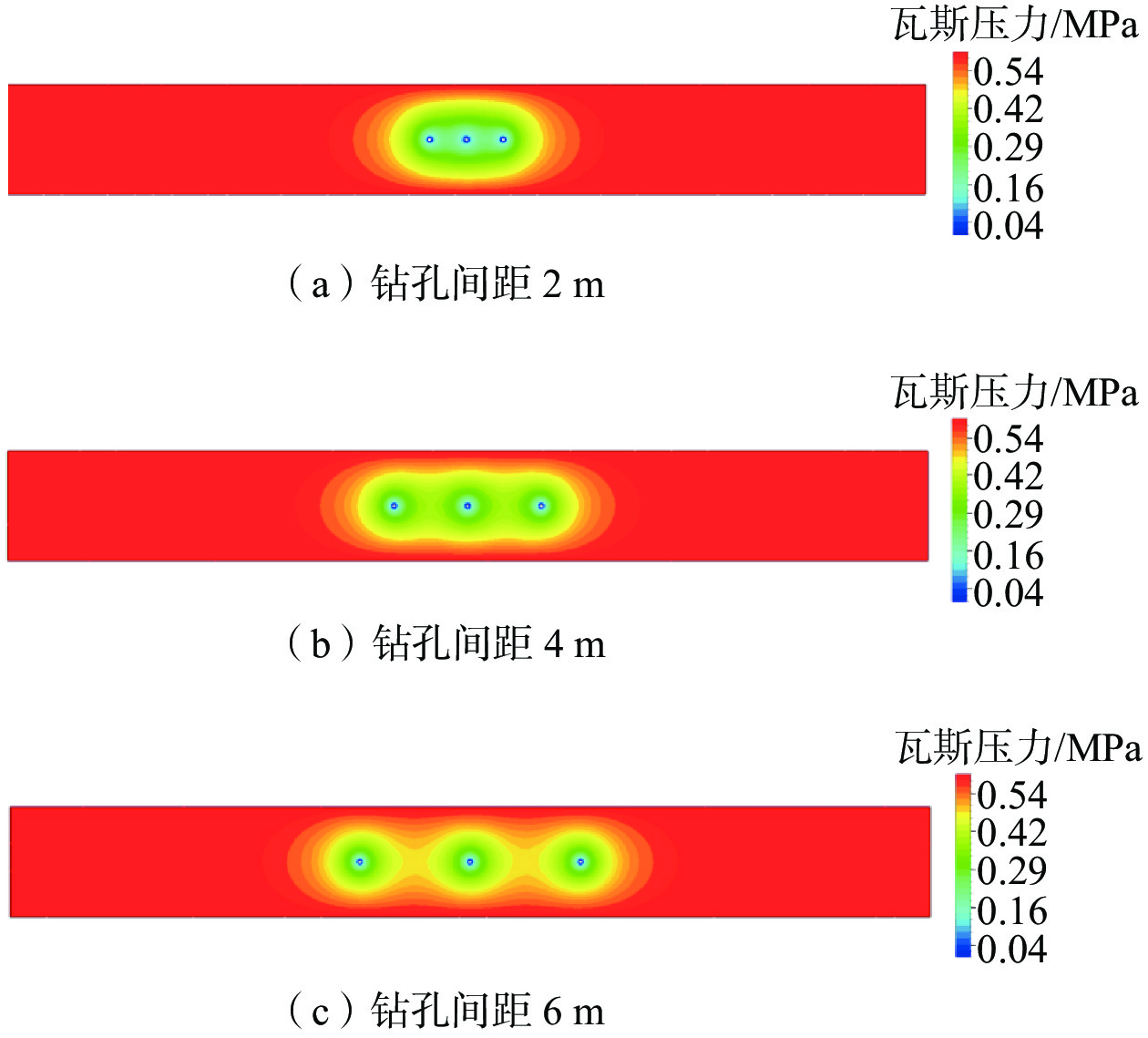
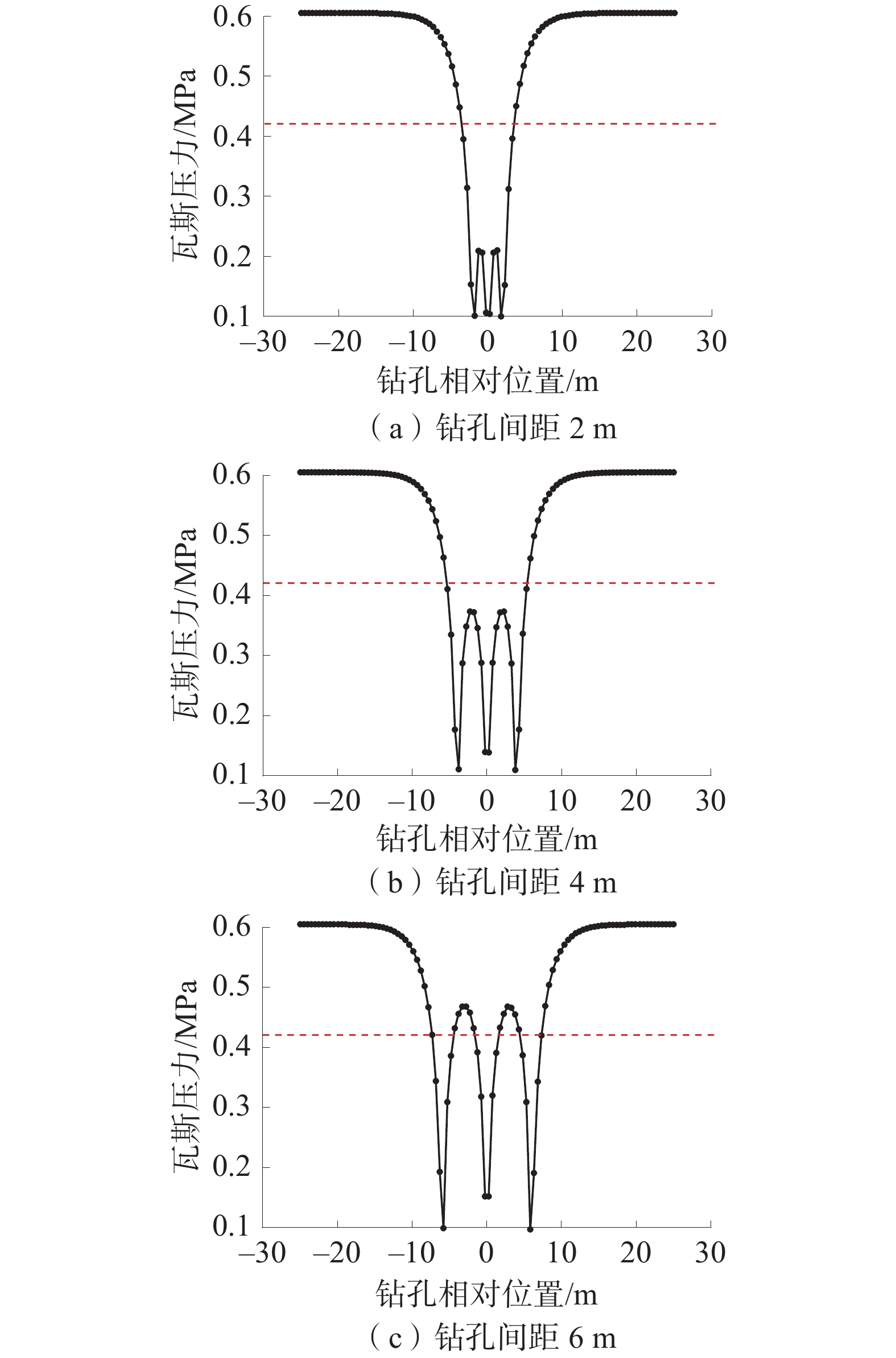
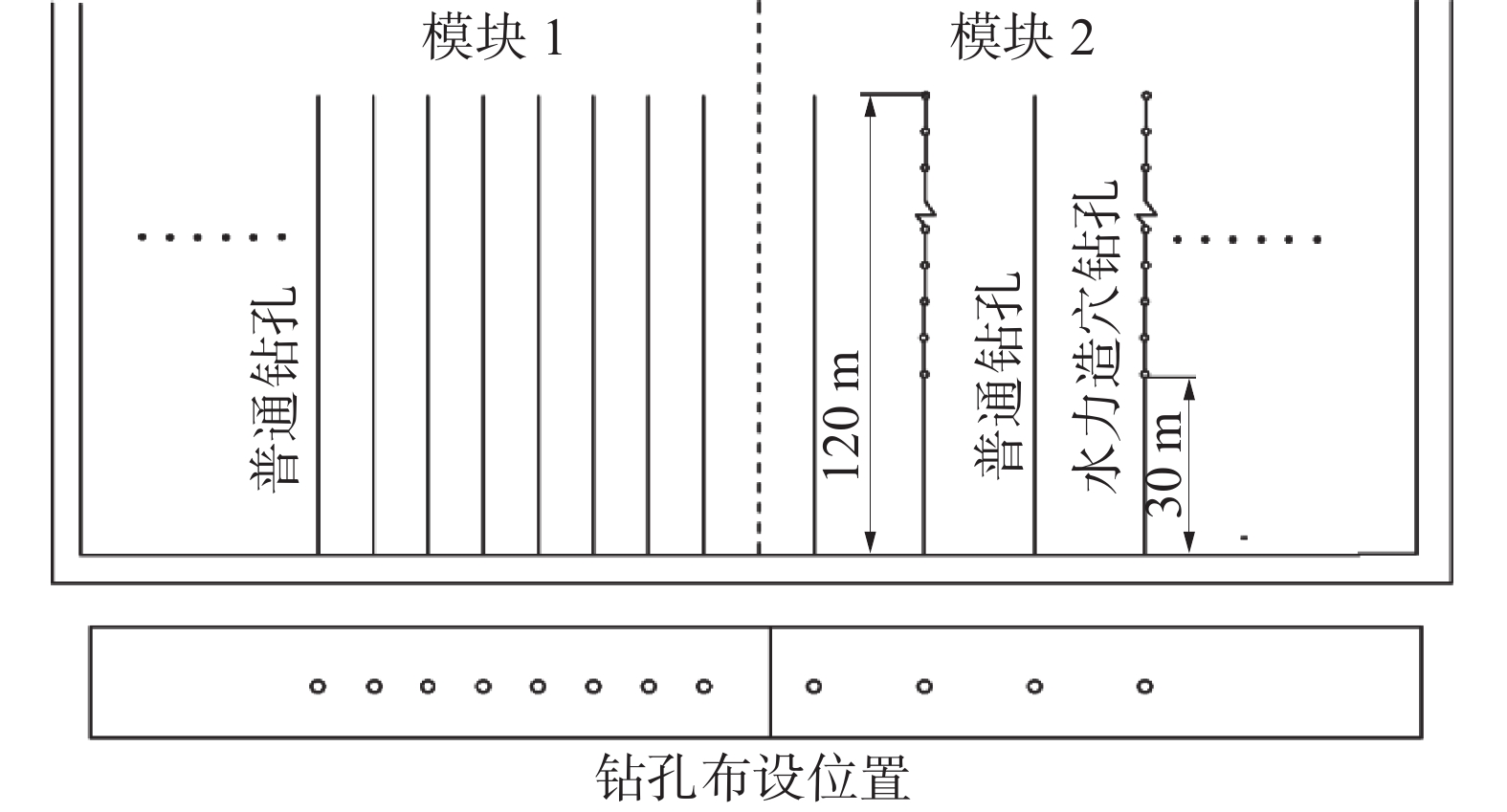
针对五虎山煤矿煤层透气性差、瓦斯吸附性强导致钻孔抽采效果差、抽采率低的问题,采用物理模拟和现场试验的方法,数值模拟水力造穴前后钻孔参数的变化特征,进而优化出适合该矿的瓦斯抽采钻孔布置方式。结果表明:五虎山煤矿011006工作面在符合矿上生产接续的情况下,水力造穴的最优钻孔造穴直径为0.5 m,合理布设间距为4 m;采用水力造穴工艺时瓦斯抽采体积分数平均为70.4%,达普通钻孔平均体积分数的3.8倍,抽采纯量是普通钻孔的3.5倍;采用水力造穴优化参数与普通钻孔间隔布置方式,可有效激活间隔的普通钻孔;通过对比钻孔施工卸压增透效果、瓦斯抽采效率、煤体扰动面积、体积及钻孔成孔率等评价指标,在相同面积模块下,采用间隔布设钻孔的模块2瓦斯抽采纯量达到模块1的1.8倍。
Abstract:For the problems that poor gas permeability and strong gas adsorption in the coal seams of Wuhushan Coal Mine leads to poor drilling and extraction efficiency and low extraction rate, physical simulation and on-site testing methods were used to numerically simulate the changes in drilling parameters before and after hydraulic drilling, and then optimize a suitable gas extraction drilling layout for the mine. The results show that under the condition that the 011006 working face of Wuhushan Coal mine is consistent with the production continuity in the mine, the optimal diameter of hydraulic cavitation is 0.5 m and the reasonable layout interval is 4 m; the average volume fraction of gas extraction is 70.4%, which is 3.8 times of the average volume fraction of ordinary borehole and 3.5 times of pure gas extraction; using the hydraulic cavitation optimization parameters and the arrangement of ordinary boreholes can effectively activate the ordinary boreholes at intervals; by comparing the evaluation indexes such as the pressure relief and permeability improvement effect of borehole construction, gas extraction efficiency, disturbed area of coal body, volume and hole formation rate of boreholes, under the same area module, the gas extraction pure quantity of module 2 using the spaced borehole arrangement is 1.8 times that of module 1.
-
Keywords:
- gas drainage /
- hydraulic cavitation /
- hydraulic punching /
- drilling optimization /
- coal seam /
- process parameters
-
-
表 1 模拟主要参数
Table 1 Main simulation parameters
参数名称 参数值 煤层原始瓦斯含量/(m3·t−1) 13 瓦斯压力/MPa 0.604 孔隙率/% 2.88 透气性系数/(m2·(MPa2·d)−1) 1.07~13.22 钻孔抽采负压/kPa −5.32 吸附常数a/(m3·t−1) 23.56 吸附常数b/MPa−1 1.09 煤密度/(t·m−3) 1.38 瓦斯衰减系数/d−1 0.265~0.244 煤的泊松比 0.25 瓦斯黏度系数/(Pa·s) 1.08×10−5 煤层温度/K 293 煤弹性模量/MPa 2 800 表 2 水力造穴钻孔与普通钻孔初始抽采纯量变化
Table 2 Changes in initial extraction net amount of hydraulic cavitation drilling and ordinary drilling
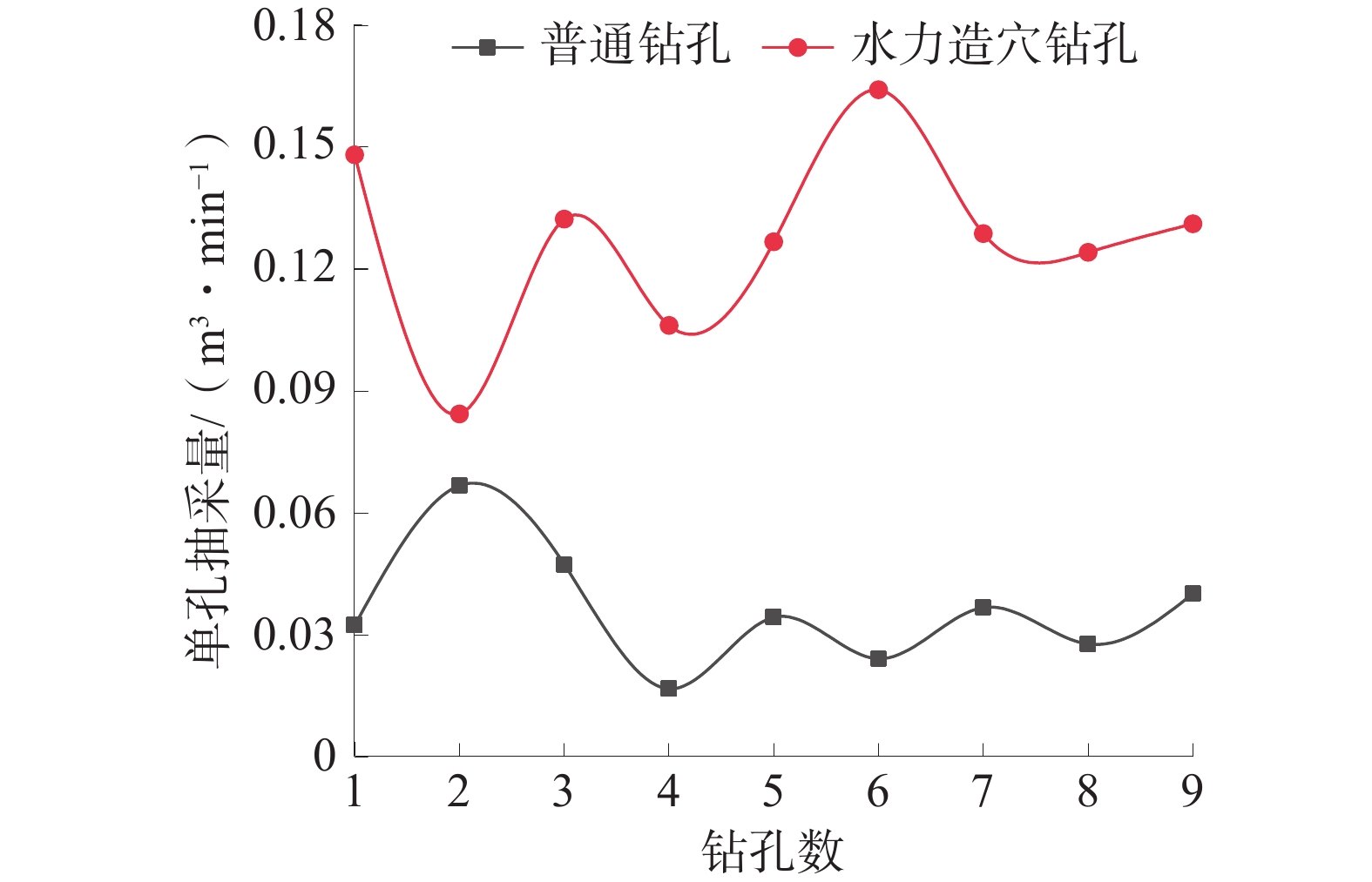
钻孔数 普通钻孔 水力造穴钻孔 瓦斯体积
分数/%纯量/
(m3·min−1)瓦斯体积
分数/%纯量/
(m3·min−1)1 18.6 0.032 4 76.2 0.148 2 2 32.8 0.066 8 58.4 0.084 4 3 20.4 0.047 4 74.6 0.132 4 4 8.2 0.016 8 56.2 0.106 2 5 18.4 0.034 4 66.4 0.126 8 6 10.2 0.024 2 80.2 0.164 2 7 19.8 0.036 8 74.4 0.128 8 8 16.2 0.027 8 70.6 0.124 2 9 19.4 0.040 2 76.6 0.131 2 平均值 18.2 0.036 3 70.4 0.127 4 表 3 水力造穴钻孔流量衰减系数
Table 3 Flow attenuation coefficient of hydraulic cavitation drilling
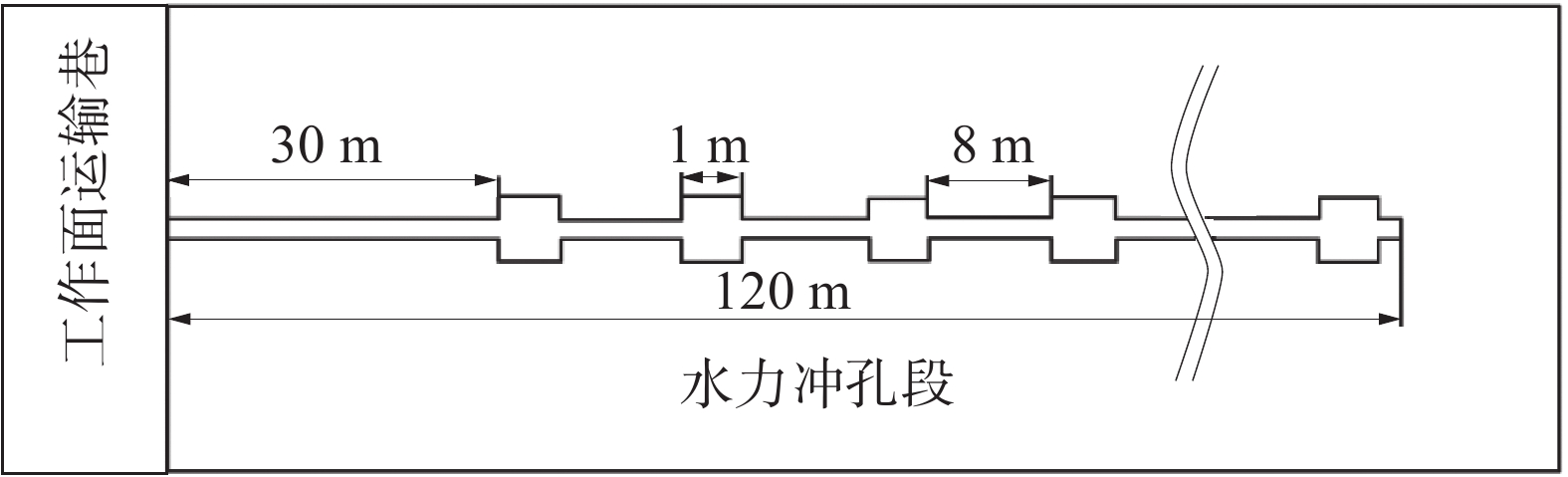
钻孔数 流量衰减系数/d−1 普通钻孔 水力造穴钻孔 1 0.034 8 0.015 30 2 0.045 2 0.039 40 3 0.025 4 0.016 40 4 0.040 2 0.009 40 5 0.026 8 0.010 60 6 0.036 6 0.017 20 平均值 0.034 8 0.018 05 表 4 011006运输巷不同工艺下基本抽采单元抽采纯量
Table 4 Net extraction volume of basic extraction units under different processes in 011006 transportation roadway
方案 钻孔类型 钻孔数 纯量/
(m3·min−1)小计/
(m3·min−1)合计/
(m3·min−1)1 普通钻孔 8 0.032 2 0.257 6 0.257 6 2 水力造穴钻孔 2 0.146 8 0.293 6 0.462 8 普通钻孔 2 0.084 6 0.169 2 -
[1] WANG Yajuan, LEI Dongji, ZHENG Yuanyuan. Study on response characteristics of surrounding rock rupture microseismic events during coal roadway excavation[J]. Shock and Vibration, 2021(9): 1−12.
[2] 雷东记,马涛,孟慧,等. 静电场对煤体瓦斯扩散特性影响研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报,2020,30(7):62−68. LEI Dongji, MA Tao, MENG Hui, et al. Influence of electrostatic field on coal gas diffusion characteristics in coal[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(7): 62−68.
[3] 王兆丰,李志强. 水力挤出措施消突机理研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2004,35(12):1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-496X.2004.12.001 WANG Zhaofeng, LI Zhiqiang. Study on removing outburst mechanism with hydraulic pressing measures[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2004, 35(12): 1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-496X.2004.12.001
[4] 李平. 水力挤出技术在突出煤层中的应用[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2007,35(8):45−47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2336.2007.08.012 LI Ping. Application of hydraulic squeezing technology in coal seams with outburst[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2007, 35(8): 45−47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2336.2007.08.012
[5] 杨海俊,胡宝军. 高突煤层水力挤出防突技术应用[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2007,35(6):31−33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2336.2007.06.008 YANG Haijun, HU Baojun. Practices on outburst control technology with hydraulic pressing in high outburst seam[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2007, 35(6): 31−33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2336.2007.06.008
[6] 白俊杰. 新景矿气相压裂与水力造穴相结合的增透效果研究[J]. 煤,2018,27(3):16−17. BAI Junjie. Research on the permeability enhancement of Xinjing gas and water combination with hydraulic caving in making[J]. Coal, 2018, 27(3): 16−17.
[7] 任仲久. 水力冲孔技术在低透气性突出煤层瓦斯抽采中的应用[J]. 煤炭工程,2019,51(3):65−70. REN Zhongjiu. Application of hydraulic punching technology in seam gas drainage in Yiwu Coal Mine[J]. Coal Engineering, 2019, 51(3): 65−70.
[8] 杨睿月,黄中伟,李根生,等. 煤层气水平井水力喷射分段造穴技术探索[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(9):3284−3297. YANG Ruiyue, HUANG Zhongwei, LI Gensheng, et al. Investigation of hydraulic jet multistage cavity completion in coalbed methane horizontal wells[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(9): 3284−3297.
[9] 张俊伟. 水力造穴卸压增透技术在底板岩巷中的应用研究[J]. 中国煤炭,2020,46(7):69−72. ZHANG Junwei. Application research on technology of hydraulic caving pressure-relief and permeability-enhancement in bottom rock roadway[J]. China Coal, 2020, 46(7): 69−72.
[10] 杨雷磊,徐腾飞. 五虎山煤矿010910工作面下隅角瓦斯治理[J]. 煤炭技术,2021,40(2):60−63. YANG Leilei, XU Tengfei. Gas control at lower corner of 010910 working face in Wuhushan coal mine[J]. Coal Technology, 2021, 40(2): 60−63.
[11] 杨宏民,邱向雷,吕晓来. 水力造穴“一孔多穴”模式的有效影响半径数值模拟[J]. 煤炭技术,2021,40(3):98−100. YANG Hongmin, QIU Xianglei, LYU Xiaolai. Numerical simulation of effective influence radius of hydraulic cavitation model of “one hole and multiple cavitation”[J]. Coal Technology, 2021, 40(3): 98−100.
[12] 吴仁伦,王继林,程辉,等. 五阳煤矿本煤层瓦斯超前采动卸压抽采试验[J]. 煤矿安全,2017,48(2):13−16. WU Renlun, WANG Jilin, CHENG Hui, et al. Experiment on advanced mining-included pressure relief gas extraction of current seam in Wuyang Coal Mine[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2017, 48(2): 13−16.
[13] 张波. 本煤层模块化水力造穴增透试验探究[J]. 煤,2022,31(11):95−97. ZHANG Bo. Experimental study on coal seam modularization hydraulic cavitation and permeability[J]. Coal, 2022, 31(11): 95−97.
[14] 荆俊杰,于丽雅,延婧. 高瓦斯低渗煤层水力造穴增透技术优化研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2022,53(1):8−14. JING Junjie, YU Liya, YAN Jing. Research on optimization of hydraulic flushing and permeability enhancement technology in high gas and low permeability coal seam[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(1): 8−14.
[15] 王建彬,魏宏超,高晓亮. 随钻水力造穴技术在低透性煤巷卸压孔中的应用[J]. 煤炭技术,2021,40(2):72−74. WANG Jianbin, WEI Hongchao, GAO Xiaoliang. Application by hydraulic flushing cavity technology while drilling in pressure relief hole of low-permeability coal roadway[J]. Coal Technology, 2021, 40(2): 72−74.
[16] 张亚鹤,魏风清,张永鹏,等. 大平煤矿穿层钻孔瓦斯抽采负压优化研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2019,50(5):158−161. ZHANG Yahe, WEI Fengqing, ZHANG Yongpeng, et al. Optimization of negative pressure for gas extraction in through beds hole of Daping Coal Mine[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2019, 50(5): 158−161.
[17] 贾秉义,陈冬冬,吴杰,等. 煤矿井下顶板梳状长钻孔分段压裂强化瓦斯抽采实践[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2021,49(2):70−76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.02.009 JIA Bingyi, CHEN Dongdong, WU Jie, et al. Practice of enhanced gas extraction by staged fracturing with comb-shaped long hole in coal mine roof[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2021, 49(2): 70−76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.02.009
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 李绪萍,李直,任晓鹏,张靖,刘艳青,周琛鸿. 煤矸石低温氧化官能团演化与气体相关性分析. 煤矿安全. 2024(06): 91-99 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: