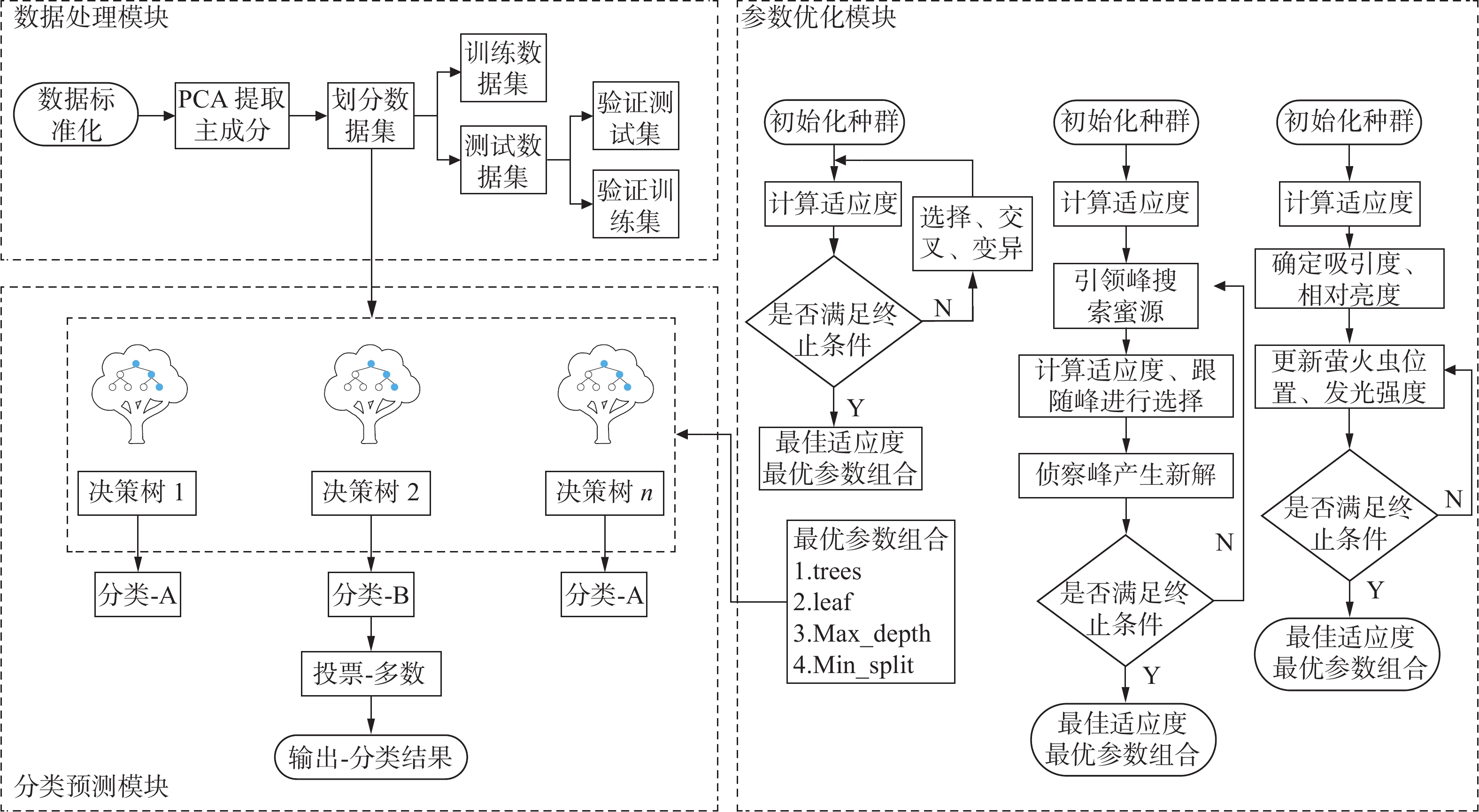
Mine water inrush source identification model based on PCA-GA-RF
-
摘要:
矿井突水已成为影响矿山安全生产的主要危害之一,快速准确识别突水水源类型是矿井突水灾害治理的关键步骤。提出了1种基于PCA-GA-RF的矿井突水水源识别模型;基于安徽省颍上县谢桥煤矿的88组水样实测数据,遵循分层随机抽样的原则,按照7∶3的比例将其分为62组训练样本和26组预测样本,经PCA提取4个主成分,构建PCA-GA-RF模型,并与PCA-RF、PCA-ABC-RF和PCA-FA-RF模型对比。结果表明:PCA-GA-RF模型判别结果准确率为96.153 8%,与其他模型相比准确率、精确率、召回率和F1值(精确召回率)最高,具有优越性。
-
关键词:
- 矿井突水 /
- 水源识别 /
- 主成分分析(PCA) /
- 随机森林(RF) /
- 遗传算法(GA)
Abstract:Mine sudden water has become one of the main hazards affecting the safety production of mines, and rapid and accurate identification of the type of sudden water source is a key step in the management of mine sudden water disaster, so a PCA-GA-RF-based mine sudden water source identification model is proposed. Based on the measured data of 88 groups of water samples from Xieqiao Coal Mine in Yingshang County, Anhui Province, and following the principle of stratified random sampling, it was divided into 62 groups of training samples and 26 groups of prediction samples according to the ratio of 7:3, and the four principal components were extracted by PCA to construct the PCA-GA-RF model, and compare it with the PCA-RF, PCA-ABC-RF and PCA-FA-RF models. The results show that the PCA-GA-RF model discriminates the results with an accuracy of 96.153 8%, which is superior with the highest accuracy, precision, recall and F1 value compared with other models.
-
-
表 1 谢桥煤矿水样实测数据(训练集)
Table 1 Actual measurement data of water samples in Xieqiao Coal Mine (training set)
编号 Na++K+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− SO42− HCO3− CO32− pH TDS 水样类型 1 890.85 12.83 0 535.30 46.11 1 220.40 6.00 8.46 2 101.29 Ⅰ 2 920.87 12.83 1.94 545.93 73.01 1 116.67 72.01 8.78 2 184.93 Ⅰ 3 883.85 11.22 0 574.29 0 1202.09 0 8.46 2 070.41 Ⅰ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ 24 920.29 30.26 17.88 777.06 281.12 844.52 42.01 8.41 2 493.70 Ⅱ 25 782.12 57.97 25.12 1 045.25 233.32 282.52 0 7.80 2 285.08 Ⅱ 26 785.43 47.33 20.64 1 027.54 228.38 260.86 6.00 7.90 2 245.79 Ⅱ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ 61 136.21 55.61 19.30 59.85 214.26 140.73 55.36 9.38 611.09 Ⅲ 62 568.98 6.01 0 111.67 57.64 921.40 108.02 9.57 1 313.02 Ⅲ 表 2 谢桥煤矿水样实测数据(测试集)
Table 2 Actual measurement data of water samples in Xieqiao Coal Mine(prediction set)
编号 Na++K+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− SO42− HCO3− CO32− pH TDS 水样类型 1 1 091.69 12.83 13.61 1 212.39 188.28 408.23 18.00 8.56 2 740.910 Ⅰ 2 933.64 14.43 9.72 967.79 57.64 631.56 0 8.34 2 299.000 Ⅰ 3 667.86 14.43 9.24 748.41 83.55 410.64 28.50 8.23 1 761.250 Ⅰ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ 11 897.75 14.01 7.30 1 064.58 226.70 306.47 18.45 8.36 2 382.890 Ⅱ 12 1 001.14 49.70 22.37 1 120.22 345.82 338.66 0 8.66 2 708.580 Ⅱ 13 869.94 50.90 19.94 1 064.92 317.55 327.68 0 8.26 2 487.590 Ⅱ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ ︙ 24 226.83 21.47 11.86 125.67 249.76 168.87 12.30 8.33 732.545 Ⅲ 25 85.65 23.05 10.94 19.50 129.68 99.16 18.00 9.67 336.400 Ⅲ 26 1 009.49 7.62 4.38 823.86 1.85 1304.00 0 8.00 2 500.200 Ⅲ 表 3 水化学成分指标相关系数矩阵
Table 3 Correlation coefficient matrix of water chemical composition indexes
相关性 Na++K+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− SO42− HCO3− CO32− pH TDS Na++K+ 1.000 Na++K+ −0.257 1.000 Mg2+ −0.233 0.699 1.000 Cl− 0.824 0.121 0.142 1.000 SO42− 0.072 0.661 0.560 0.401 1.000 HCO3− 0.406 −0.629 −0.623 −0..139 −0.663 1.000 CO32− 0.234 −0.454 −0.403 −0.189 −0.388 0.621 1.000 pH −0.055 −0.445 −0.399 −0.322 −0.272 0.254 0.481 1.000 TDS 0.975 −0.095 −0.106 0.896 0.236 0.258 0.124 −0.180 1 表 4 模型参数和训练结果
Table 4 Model parameters and training results
PCA-RF PCA-GA-RF PCA-ABC-RF PCA-FA-RF 参数
范围Trees=10∶10∶100 Pop=20∶10∶100 Pop=10∶5∶50 Pop=10∶5∶50 Leaf=1:1∶10 Max_iter=20∶10∶100 Max_iter=10∶10∶100 Max_iter=10∶10∶100 Max_depth=2∶1∶20 Pc=0.4∶0.1∶0.9 Nonlooker=1∶1∶10 Gamma=0.1∶0.1∶0.9 Min_split=1∶1∶10 Pm=0.0001∶0.004995∶0.1 L=1∶1∶10 — 超
参
组
合Trees=20 Trees=20 Pop=20 Trees=50 Pop=20 Trees=25 Pop=15 Leaf=2 Leaf=2 Max_iter=30 Leaf=1 Max_iter=10 Leaf=1 Max_iter=10 Max_depth=5 Max_depth=13 Pc=0.7 Max_depth=12 Nonlooker=2 Max_depth=9 Gamma=0.9 Min_split=6 Min_split=10 Pm=0.0301 Min_split=13 L=3 Min_split=7 — 验
证
集92.3077% 100.0000% 94.7368% 100.0000% 89.4737% 84.2105% 84.2105% 84.2105% 94.7368% 94.7368% 94.7368% 94.7368% 训
练
集100.0000% 100.0000% 100.0000% 100.0000% 测
试
集92.3077% 96.1538% 92.3077% 92.3077% 表 5 谢桥煤矿突水水源预测结果
Table 5 Prediction results of water inrush source in Xieqiao Coal Mine
编号 Na++K+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− SO42− HCO3− CO32− pH TDS 实际
类型预测类型 1 894.60 3.21 1.46 912.84 14.41 573.59 18.00 8.55 2 131.32 Ⅰ Ⅰ 2 940.39 16.03 7.29 918.16 38.42 750.55 0 8.44 2 295.56 Ⅰ Ⅰ 3 952.39 9.62 5.83 985.51 11.53 622.40 24.00 8.87 2 300.08 Ⅰ Ⅰ 4 911.12 10.01 7.30 1062.08 238.60 331.49 12.30 8.19 2 408.02 Ⅰ Ⅰ 5 887.66 54.09 15.83 1407.12 357.18 343.66 0 8.10 2 559.71 Ⅱ Ⅱ 6 896.13 56.99 14.36 1066.69 360.47 302.96 13.35 8.00 2 481.54 Ⅱ Ⅱ 7 867.47 46.83 22.44 1037.33 343.60 317.30 9.00 8.50 2 287.44 Ⅱ Ⅱ 8 820.74 33.07 17.02 965.03 232.55 408.20 0 7.50 2 272.51 Ⅱ Ⅱ 9 258.77 31.26 15.55 76.22 219.02 317.30 38.38 9.35 797.85 Ⅲ Ⅲ 10 143.61 37.85 16.94 67.63 115.27 281.45 18.45 8.35 540.62 Ⅲ Ⅲ 11 143.59 29.88 15.73 75.15 100.86 268.95 12.30 8.35 512.12 Ⅲ Ⅲ 12 208.02 33.86 12.10 75.15 220.94 293.96 6.15 8.49 703.40 Ⅲ Ⅲ -
[1] 武强. 我国矿井水防控与资源化利用的研究进展、问题和展望[J]. 煤炭学报,2014,39(5):795−805. WU Qiang. Progress, problems and prospects of prevention and control technology of mine water and reutilization in China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2014, 39(5): 795−805.
[2] 刘德民,顾爱民. 基于Fisher判别法的岱庄矿涌(突)水水源识别[J]. 煤炭技术,2023,42(4):94−97. LIU Demin, GU Aimin. Source of Daizhuang mine water inflow or inrush based on Fisher discrimination[J]. Coal Technology, 2023, 42(4): 94−97.
[3] 施龙青,杨晓,徐东晶,等. 基于灰色关联模型的矿井突水水源分析方法[J]. 中国科技论文,2020,15(9):1026−1030. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2020.09.009 SHI Longqing, YANG Xiao, XU Dongjing, et al. Discrimination on mine water inrush source by gray correlation analysis method[J]. China Sciencepaper, 2020, 15(9): 1026−1030. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2020.09.009
[4] 马雷,钱家忠,赵卫东. 基于GIS和水质水温的矿井突水水源快速判别[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2014,42(2):49−53. MA Lei, QIAN Jiazhong, ZHAO Weidong. An approach for quickly identifying water-inrush source of mine based on GIS and groundwater chemistry and temperature[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2014, 42(2): 49−53.
[5] 曾一凡,梅傲霜,武强,等. 基于水化学场与水动力场示踪模拟耦合的矿井涌(突)水水源判识[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(12):4482−4494. ZENG Yifan, MEI Aoshuang, WU Qiang, et al. Source discrimination of mine inflow or inrush using hydrochemical field and hydrodynamic field tracer simulation coupling[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(12): 4482−4494.
[6] 李垣志,牛国庆,刘慧玲. 改进的GA-BP神经网络在矿井突水水源判别中的应用[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术,2016,12(7):77-81. LI Yuanzhi, NIU Guoqing, LIU Huiling, Application of improved GA-BP neural network on identification of water inrush source in mine[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2016, 12(7): 77-81.
[7] 华星月,邵良杉. 基于KPCA-GWO-SVM的矿井突水水源识别[J]. 煤矿安全,2023,54(2):195−200. HUA Xingyue, SHAO Liangshan. Mine water inrush source identification model based on KPCA-GWO-SVM[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2023, 54(2): 195−200.
[8] 于小鸽,刘燚菲,翟培合. 基于PCA-AWOA-ELM模型的矿井突水水源识别[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(3):182−189. YU Xiaoge, LIU Yifei, ZHAI Peihe. Identification of mine water inrush source based on PCA-AWOA-ELM model[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2023, 51(3): 182−189.
[9] 董东林,张陇强,张恩雨,等. 基于PSO-XGBoost的矿井突水水源快速判识模型[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(7):72−82. DONG Donglin, ZHANG Longqiang, ZHANG Enyu, et al. A rapid identification model of mine water inrush based on PSO-XGBoost[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2023, 51(7): 72−82.
[10] 王怀秀,冯思怡,刘最亮. 基于改进随机森林算法的地质构造识别模型[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(4):149−156. WANG Huaixiu, FENG Siyi, LIU Zuiliang. Geological structure recognition model based on improved randomforest algorithm[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2023, 51(4): 149−156.
[11] 郝帅,王怀秀,刘最亮. 基于K-means SMOTE和随机森林算法的陷落柱识别模型[J]. 煤矿安全,2023,54(2):174−180. HAO Shuai, WANG Huaixiu, LIU Zuiliang. Collapsed column identification model based on K-means SMOTE and random forest algorithm[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2023, 54(2): 174−180.
[12] 黄敏,毛岸,路世昌,等. 矿井突水水源识别的主成分分析-混沌麻雀搜索-RF模型[J]. 安全与环境学报,2023,23(8):2607−2614. HUANG Min, MAO An, LU Shichang, et al. Identification of mine water inrush source based on PCA CSSA RF model[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2023, 23(8): 2607−2614.
[13] KARABOGA D, BASTURK B. On the performance of artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2008, 8(1): 687−697. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2007.05.007
[14] 宁永香,崔希民,崔建国. 基于ABC-GRNN组合模型的露天矿边坡变形预测[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2023,51(3):65−72. NING Yongxiang, GUI Ximin, GUI Jianguo. Deformation prediction of open-pit mine slope based on ABC-GRNN combined model[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2023, 51(3): 65−72.
[15] TILAHUN S L, ONG H C. Modified firefly algorithm[J]. Journal of Applied Mathematics, 2012(pt.12): 467631.
[16] 陈陆望,任星星,张杰,等. 淮北煤田太原组灰岩水水文地球化学形成作用及反向模拟研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(12):3999−4009. CHEN Luwang, REN Xingxing, ZHANG Jie, et al. Hydrogeochemical formation and inverse simulation of limestone groundwater in Carboniferous Taiyuan Formation of Huaibei coalfield[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(12): 3999−4009.
[17] 陈绍杰,刘久潭,汪锋,等. 基于PCA-RA的滨海矿井水源识别技术研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(2):217−225. CHEN Shaojie, LIU Jiutan, WANG Feng, et al. Technological research on water source identiftcation of coastal coal mines based on PCA-RA[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49(2): 217−225.
[18] 熊欣标,谢雄刚,杨培君,等. 基于PCA-Logistic回归模型的矿井底板突水危险性研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2023,54(10):176−181. XIONG Xinbiao, XIE Xionggang, YANG Peijun, et al. Research on water inrush risk of mine floor based on PCA-Logistic regression model[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2023, 54(10): 176−181.
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 李润芝. 动压影响孤岛工作面巷道围岩“卸-支平衡”协同控制技术. 煤矿安全. 2024(03): 199-208 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 胡威,高志强. 基于薄板理论的覆岩导水裂隙带高度研究. 煤炭科技. 2024(03): 126-130 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李辉,宋宇航,毕健成,李强. 孤岛工作面侧向顶板结构及切顶卸压技术. 科学技术与工程. 2024(36): 15396-15403 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王鹏,王虎伟,王帅,王鹏程. 孤岛工作面回采巷道围岩破坏机理及差异化控制技术. 金属矿山. 2024(12): 96-105 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 秦忠诚,张国兴,詹召伟,王彦敏,高超. 1310孤岛工作面初采矿压特征与支架适应性评价. 矿业研究与开发. 2023(03): 147-153 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 杨旭,王涛. 孤岛工作面顶板条带弱化技术研究及应用. 矿业安全与环保. 2023(03): 111-116+123 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)



 下载:
下载: