Study on the law of multi-fracture through-layer propagation of crushed soft coal seam roof by hydraulic fracturing
-
摘要:
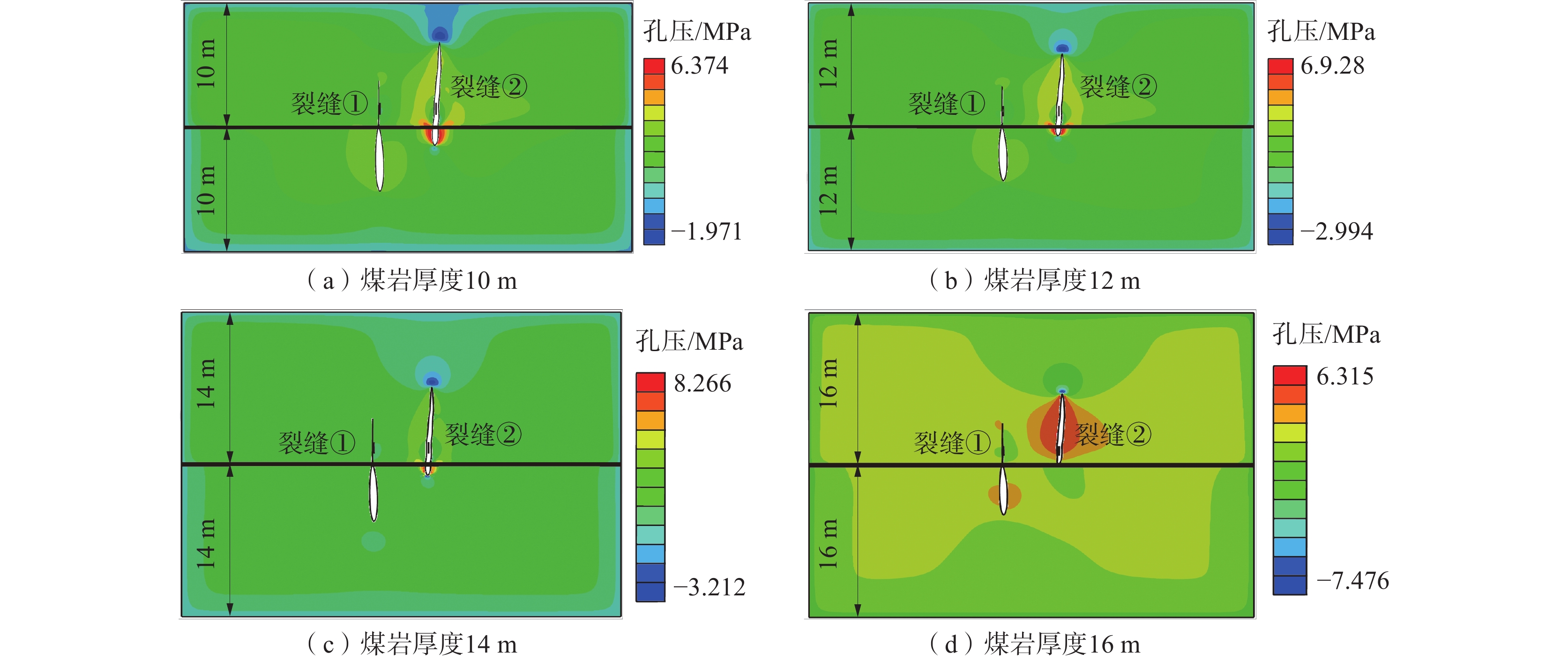
为了研究碎软煤层顶板水力压裂过程中多裂缝穿层扩展规律,应用扩展有限元方法,分析了间接压裂时不同地质参数、施工参数、压裂顺序等因素对多裂缝穿层扩展形态和缝间应力干扰的影响。结果表明:顶板岩层最小水平主应力越大,裂缝在煤层中扩展效果越好;煤岩层厚度越大,裂缝穿层扩展的可能性越小;压裂液注入速率越快,裂缝在煤层中长度增加,但缝间应力干扰范围不断变大;裂缝起裂角度越大,压裂裂缝转向距离增加,使裂缝主要在顶板内扩展;较大的裂缝间距能够保证压裂后多裂缝均匀扩展进入煤层;不同的起裂顺序下,多裂缝起裂顺序依次为左侧、右侧、中间时,压裂后在煤层中形成的水力裂缝长度和面积是起裂顺序依次为中间、左侧、右侧时的2倍;相比裂缝起裂顺序依次为左侧、中间、右侧时,同时起裂会增大应力干扰范围,裂缝起裂压力变高,在煤层中形成的面积更小。
Abstract:The effects of different geological parameters, construction parameters, fracturing sequence and other factors on the propagation patterns of multiple cracks and stress interference between cracks in indirect fracturing were analyzed by the extended finite element method (FEM) in order to study the law of multi-fracture through-layer propagation during hydraulic fracturing of crushed soft coal seam roof. The results show that the larger the minimum horizontal principal stress of the roof layer is, the better the spreading effect of the crack in the coal seam is. The greater the thickness of coal layer, the less the possibility of fracture propagation. As the injection rate increases, the length of crack in coal seam increases, but the interference range of stress between cracks increases continuously. The larger the fracture initiation angle, the larger the fracture turning distance, the fracture mainly spreads in the roof. The larger fracture spacing can ensure the uniform expansion of multiple fractures into the coal seam after fracturing. The length and area of hydraulic fractures formed in coal seam after fracturing are twice as long as those in middle, left and right fractures in different fracture initiation sequences. When the fracture initiation sequence is left side, middle side and right side, the stress interference range will be increased, the fracture initiation pressure will be higher, and the area formed in the coal seam will be smaller.
-
-
表 1 数值模型基本参数
Table 1 Numerical model parameters
岩层 抗拉强度/
MPa弹性模量/
GPa泊松比 孔隙比 垂向地应力/
MPa煤层 0.2 2 0.30 0.2 15 顶板 0.5 5 0.25 0.1 15 表 2 数值模拟方案
Table 2 Numerical simulation schemes
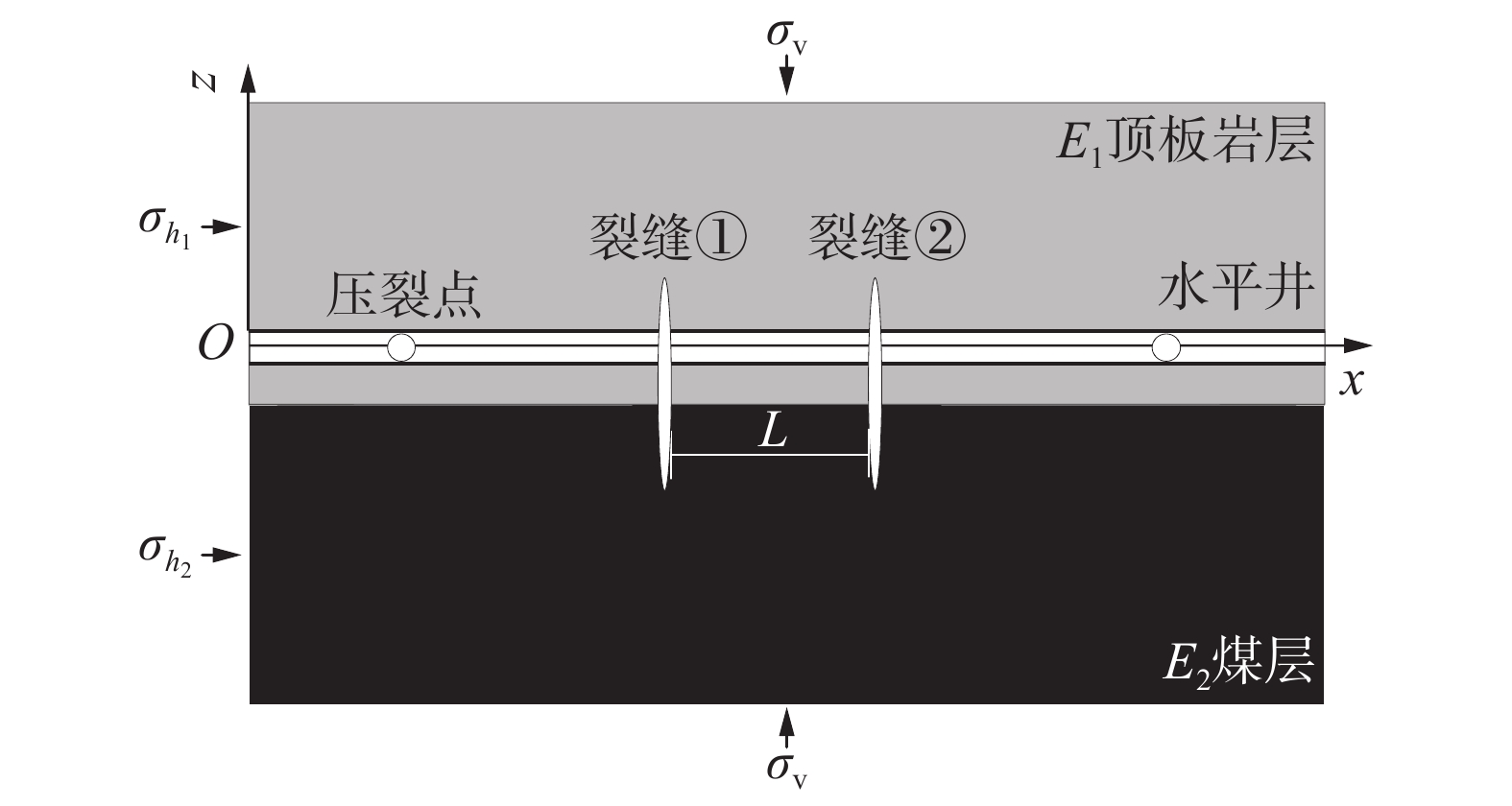
组号 顶板最小水平主应力/MPa 煤岩厚度/m 注入速率/(m3·min−1) 起裂角度/(°) 裂缝间距/m 裂缝起裂顺序 1 6、7、8、9 10 2 0 5 ①② 2 8 10、12、14、16 2 0 5 ①② 3 8 10 0.5、1、2、3 0 5 ①② 4 8 10 2 0、15、30、45 5 ①② 5 8 10 2 0 10、8、5、2 ①② 6 8 10 2 0 5 同步 7 8 10 2 0 5 ①②③ 8 8 10 2 0 5 ①③② 9 8 10 2 0 5 ②①③ -
[1] 姜在炳,李浩哲,方良才,等. 紧邻碎软煤层顶板水平井分段穿层压裂裂缝延展机理[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(S2):922−931. JIANG Zaibing, LI Haozhe, FANG Liangcai, et al. Fracture propagation mechanism of staged through-layer fracturing for horizontal well in roof adjacent to broken-soft coal seams[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(S2): 922−931.
[2] 郭德勇,张超,李柯,等. 松软低透煤层深孔微差聚能爆破致裂机理[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(8):2583−2592. GUO Deyong, ZHANG Chao, LI Ke, et al. Mechanism of millisecond-delay detonation on coal cracking under deephole cumulative blasting in soft and low permeability coal seam[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(8): 2583−2592.
[3] 曹代勇,占文锋,李焕同,等. 中国煤矿动力地质灾害的构造背景与风险区带划分[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(7):2376−2388. CAO Daiyong, ZHAN Wenfeng, LI Huantong, et al. Tectonic setting and risk zoning of dynamic geological disasters in coal mines in China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(7): 2376−2388.
[4] 张慧杰,张浪,汪东,等. 构造煤的瓦斯放散特征及孔隙结构微观解释[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(12):3404−3410. ZHANG Huijie, ZHANG Lang, WANG Dong, et al. Gas emission characteristics of tectonic coal and microscopic explanation of pore structure[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2018, 43(12): 3404−3410.
[5] 郑凯歌. 碎软低透煤层底板梳状长钻孔分段水力压裂增透技术研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2020,37(2):272−281. ZHENG Kaige. Permeability improving technology by sectional hydraulic fracturing for comb-like long drilling in floor of crushed and soft coal seam with low permeability[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2020, 37(2): 272−281.
[6] 冯仁俊. 煤层群分层水力压裂与多层综合压裂增透效果对比研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2021,52(12):21−28. FENG Renjun. Comparative study on permeability enhancement effect of separate-layer fracturing and multi-layers comprehensive fracturing in coal seam group[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021, 52(12): 21−28.
[7] 荆俊杰,于丽雅,延婧. 高瓦斯低渗煤层水力造穴增透技术优化研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2022,53(1):8−14. JING Junjie, YU Liya, YAN Jing. Research on optimization of hydraulic flushing and permeability enhancement technology in high gas and low permeability coal seam[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(1): 8−14.
[8] 张群,葛春贵,李伟,等. 碎软低渗煤层顶板水平井分段压裂煤层气高效抽采模式[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(1):150−159. ZHANG Qun, GE Chungui, LI Wei, et al. A new model and application of coalbed methane high efficiency production from broken soft and low permeable coal seam by roof strata-in horizontal well and staged hydraulic fracture[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2018, 43(1): 150−159.
[9] 姜在炳,李浩哲,许耀波,等. 煤层顶板分段压裂水平井地质适应性分析与施工参数优化[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2022,50(3):183−192. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.22.01.0037 JIANG Zaibing, LI Haozhe, XU Yaobo, et al. Geological adaptability analysis and operational parameter optimization for staged fracturing horizontal wells in coal seam roof[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2022, 50(3): 183−192. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.22.01.0037
[10] 许耀波,郭盛强. 软硬煤复合的煤层气水平井分段压裂技术及应用[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(4):1169−1177. XU Yaobo, GUO Shengqiang. Technology and application of staged fracturing in coalbed methane horizontal well of soft and hard coal composite coal seam[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2019, 44(4): 1169−1177.
[11] 许耀波,朱玉双,张培河. 紧邻碎软煤层的顶板岩层水平井开发煤层气技术[J]. 天然气工业,2018,38(9):70−75. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2018.09.009 XU Yaobo, ZHU Yushuang, ZHANG Peihe. Application of CBM horizontal well development technology in the roof strata close to broken-soft coal seams[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2018, 38(9): 70−75. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2018.09.009
[12] 巫修平,张群. 碎软低渗煤层顶板水平井分段压裂裂缝扩展规律及控制机制[J]. 天然气地球科学,2018,29(2):268−276. WU Xiuping, ZHANG Qun. Research on controlling mechanism of fracture propagation of multi-stage hydraulic fracturing horizontal well in roof of broken soft and low permeability coal seam[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2018, 29(2): 268−276.
[13] 张玉旗. 定向水力压裂裂纹扩展规律的模拟研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2019. [14] 李浩,梁卫国,李国富,等. 碎软煤层韧性破坏-渗流耦合本构关系及其间接压裂工程验证[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(3):924−936. LI Hao, LIANG Weiguo, LI Guofu, et al. Ductile failure-seepage coupling constitutive equations of broken soft coal and its verification in indirect fracturing engineering[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(3): 924−936.
[15] 宋晨鹏,卢义玉,贾云中,等. 煤岩交界面对水力压裂裂缝扩展的影响[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版),2014,35(9):1340−1345. SONG Chenpeng, LU Yiyu, JIA Yunzhong, et al. Effect of coal-rock interface on hydraulic fracturing propagation[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2014, 35(9): 1340−1345.
[16] 张智渊,朱传杰,刘思远,等. 复合储层层间窜流对瓦斯抽采的影响机制研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2022,53(2):1−8. ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Chuanjie, LIU Siyuan, et al. Influence of interlayer channeling of composite reservoir on gas drainage[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(2): 1−8.
[17] 庞涛,姜在炳,李浩哲,等. 碎软煤层顶板水平井空间位置对压裂裂缝扩展的影响[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(S1):196−203. PANG Tao, JIANG Zaibing, LI Haozhe, et al. Influence of the spatial position of horizontal well in roof strata of coal seam on the propagation of fracturing fractures[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(S1): 196−203.
[18] 刘立峰,冉启全,王欣,等. 致密储层水平井体积压裂段间距优化方法[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2015,37(3):84−87. LIU Lifeng, RAN Qiquan, WANG Xin, et al. Method of optimizing the spacing between volumetric fracturing stages in horizontal wells in tight reservoir[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2015, 37(3): 84−87.
[19] 李浩哲,姜在炳,舒建生,等. 水力裂缝在煤岩界面处穿层扩展规律的数值模拟[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2020,48(2):106−113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.02.017 LI Haozhe, JIANG Zaibing, SHU Jiansheng, et al. Numerical simulation of layer-crossing propagation behavior of hydraulic fractures at coal-rock interface[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2020, 48(2): 106−113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.02.017
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 孔令帅,栗继祖. 安全基地型领导对新生代矿工安全参与行为的影响研究. 煤炭经济研究. 2025(02): 170-176 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: