Multi-physical field parameter response in the whole process of coal and gas outburst under deep high stress
-
摘要:
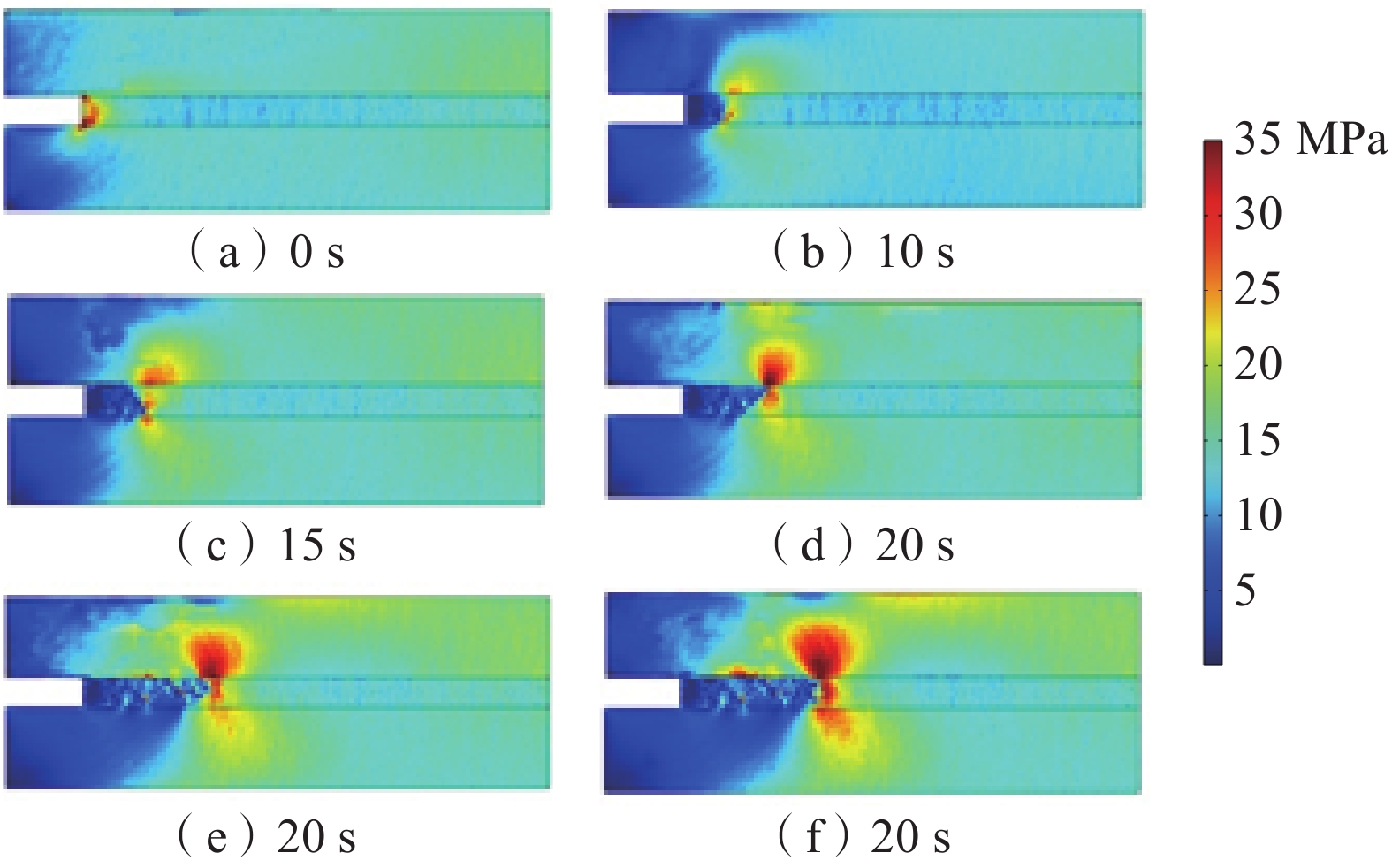
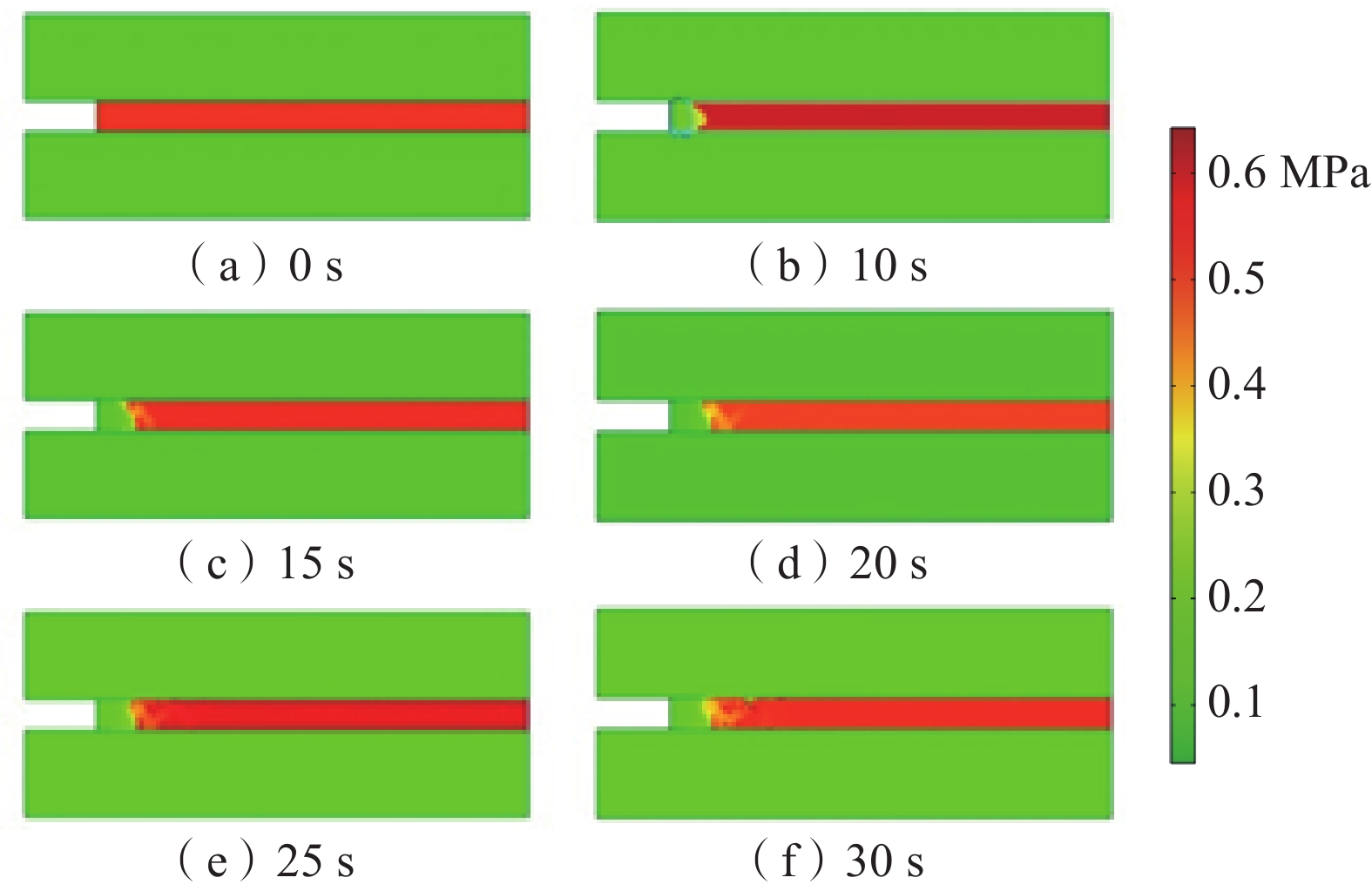
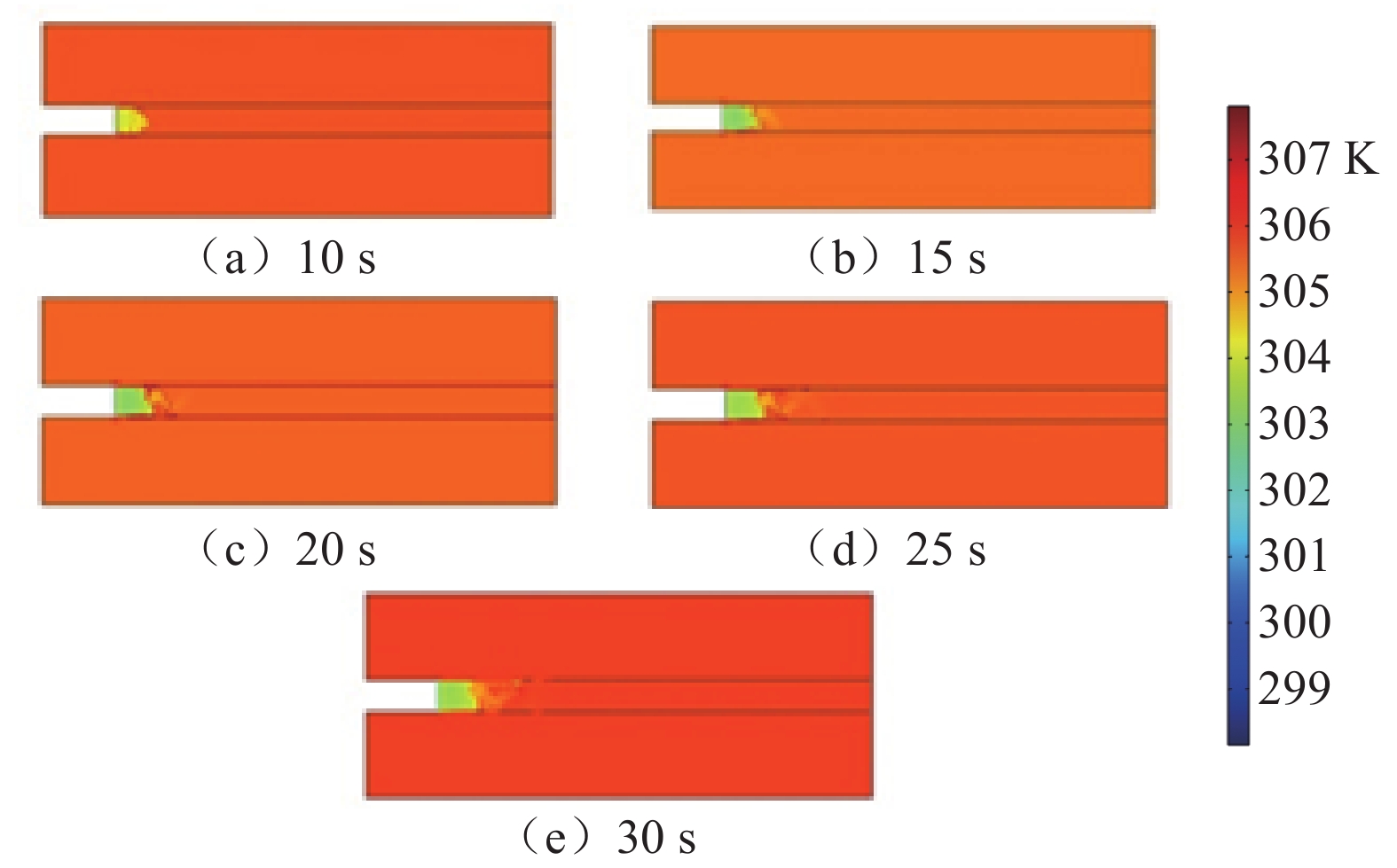
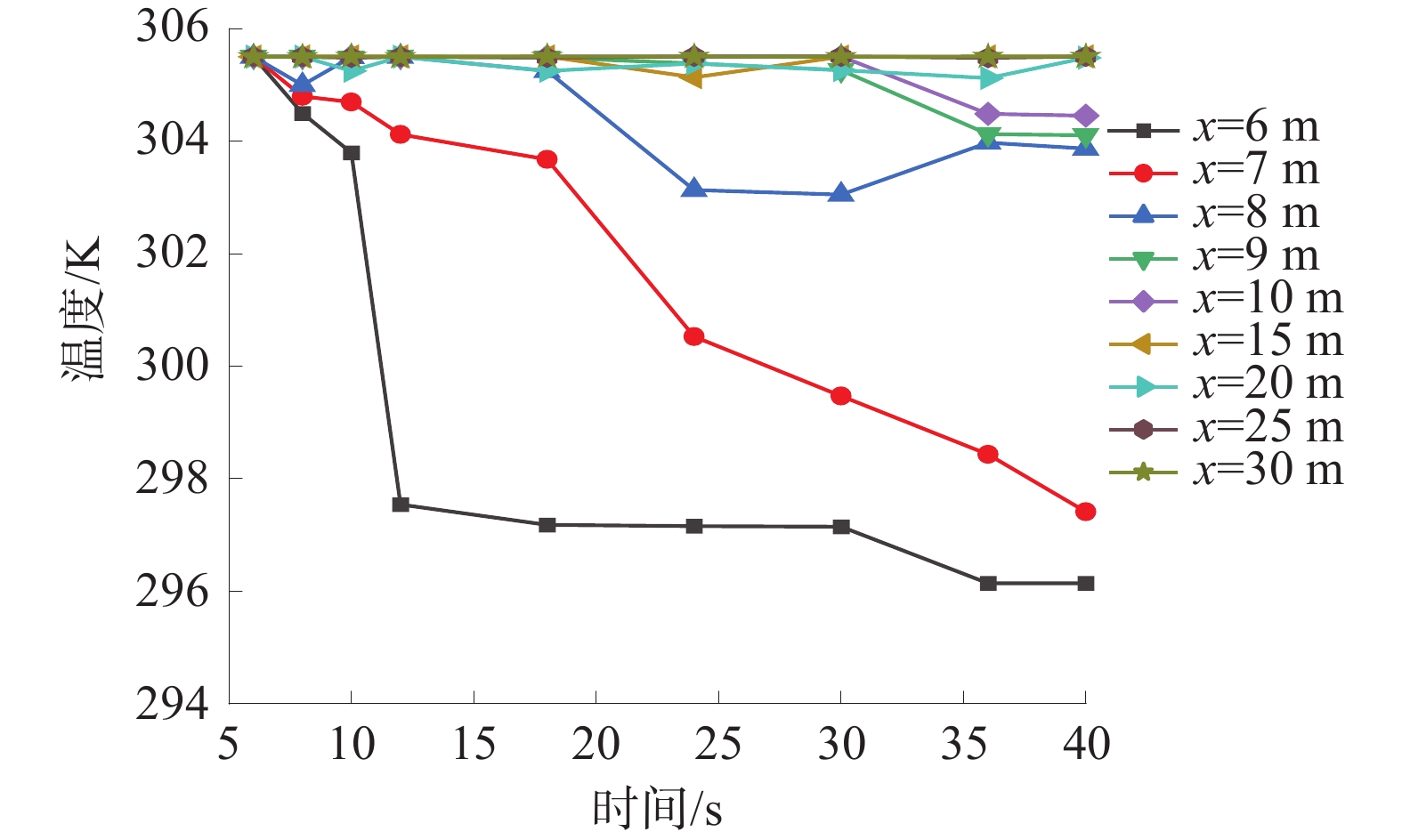
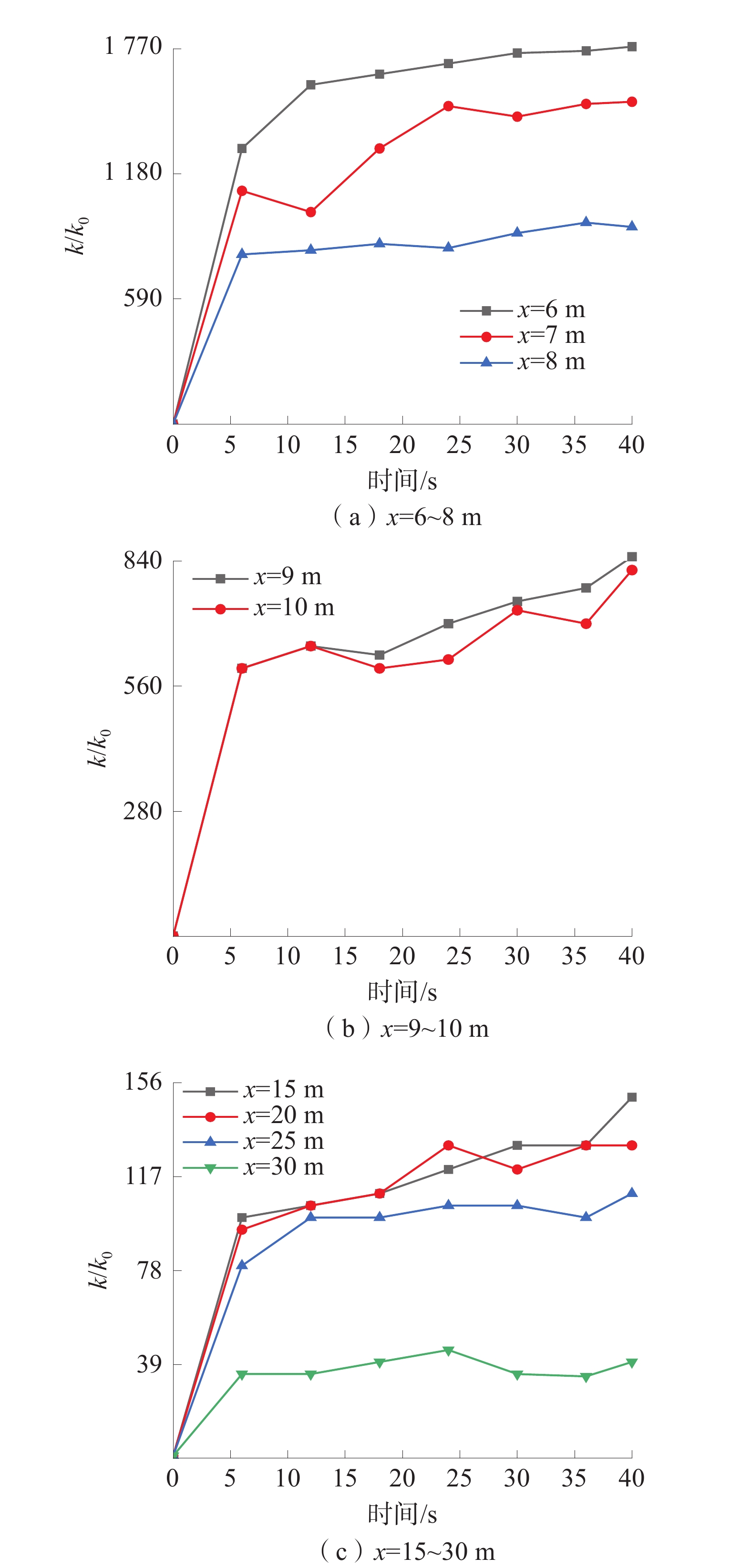
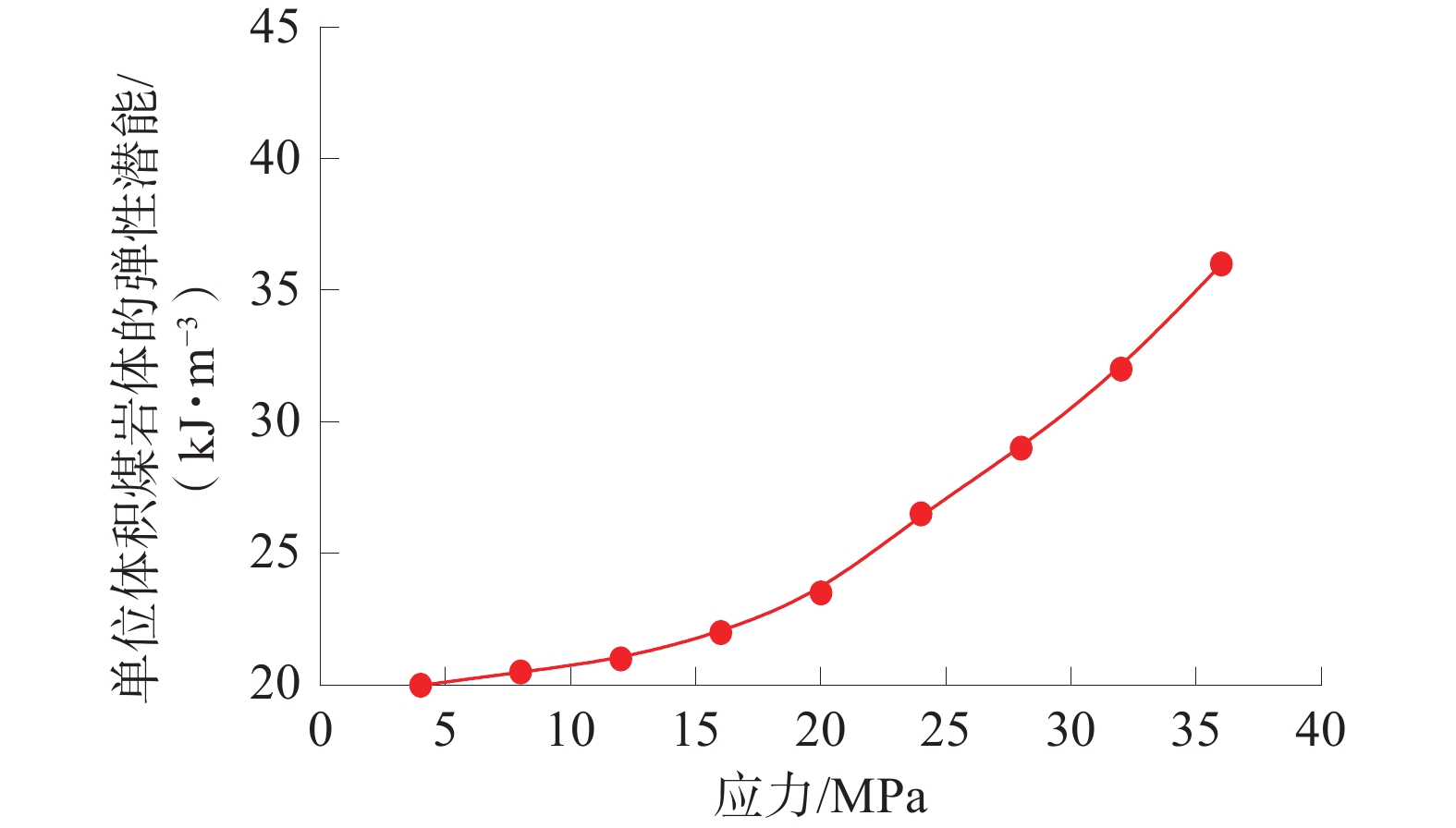
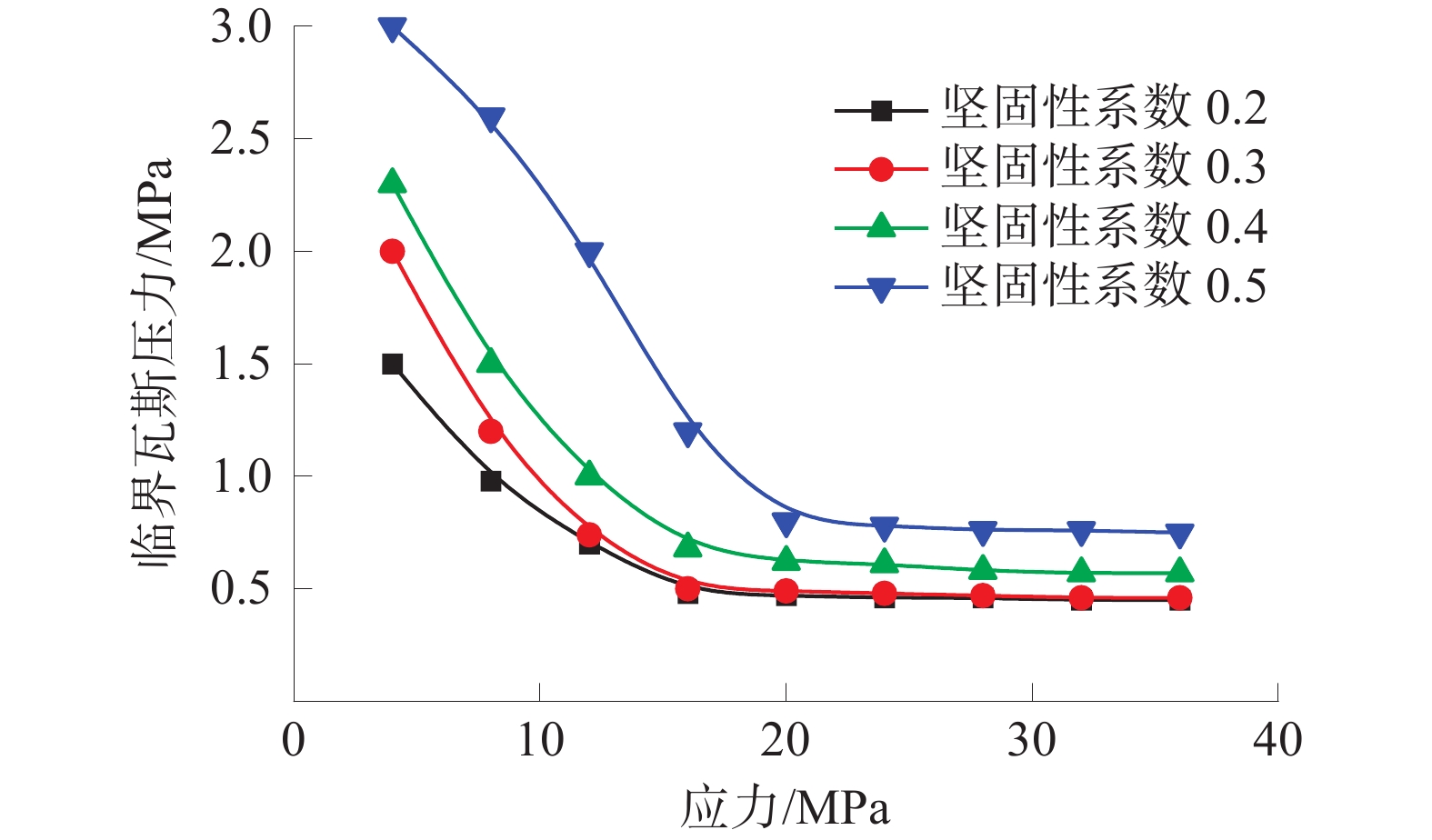
基于深部煤与瓦斯突出全过程的热−流−固耦合规律,建立了煤与瓦斯突出数值模型,分析了深部高应力条件下突出全过程中多物理场参数响应。研究结果表明:突出孔洞周围煤岩体应力场的响应规律为初始振动−突然衰减−后期稳定;瓦斯压力的下降速率与距离突出口的长度呈负相关关系;突出过程中,破碎煤所包含的吸附瓦斯迅速解吸并且膨胀做功,导致温度降低;突出发生后,渗透率发生显著变化的区域可分为突增区、中等增长区和增长区;随着应力的增加,弹性潜能占煤与瓦斯突出总能量的比例不断增加,弹性潜能占比与应力呈正相关关系。
Abstract:Based on the thermo-fluid-solid coupling law of coal and gas outburst in deep mining, a numerical model of coal and gas outburst is established, and the response of multi-physical parameters in the whole process of coal and gas outburst under high stress condition is analyzed. The results show that the response rule of the stress field around the outburst hole is initial vibration-sudden attenuation-late stability. The decreasing rate of gas pressure is negatively correlated with the length of the outburst hole. In the outburst process, the adsorbed gas contained in the crushed coal quickly desorbed and expanded to do work, resulting in a decrease in temperature; the areas with significant changes in permeability after outburst can be divided into sudden increase area, medium increase area and increase area. With the increase of stress, the proportion of elastic potential in total coal and gas outburst energy increases, and the proportion of elastic potential is positively correlated with stress.
-
Keywords:
- deep mining /
- coal and gas outburst /
- stress /
- multiple physical fields /
- energy condition
-
-
表 1 基础参数
Table 1 Basic parameters
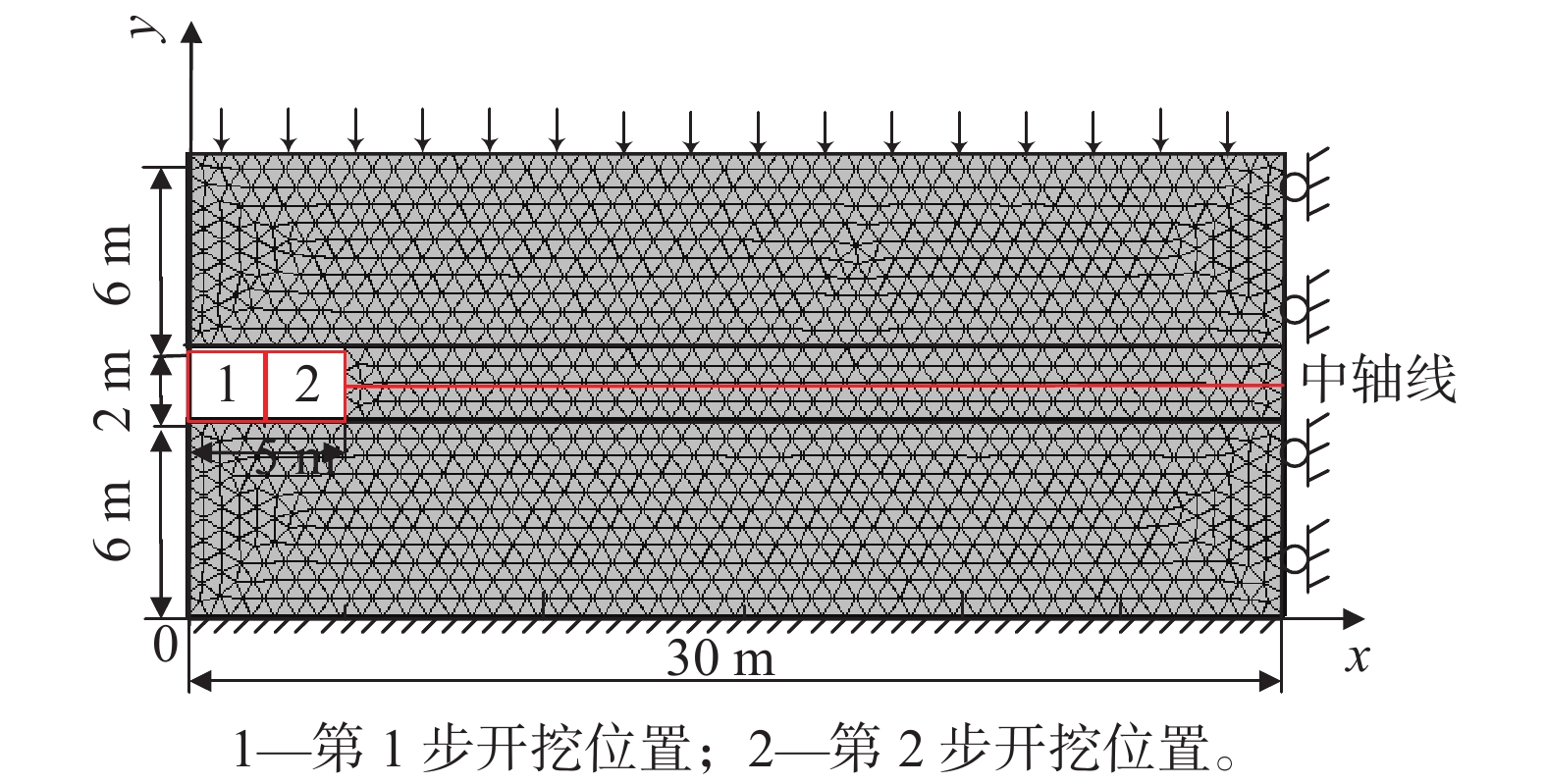
参数 取值 顶底板的弹性模量/GPa 21 顶底板的泊松比 0.40 顶底板的密度/(kg·m−3) 2.5×103 顶底板的黏聚力/ MPa 20 顶底板的内摩擦角/(°) 40 煤体的弹性模量/GPa 2.3 工作面气压/MPa 0.1 煤的泊松比 0.19 煤的传热系数/(W·m−1·K−1) 0.1 煤的密度/(kg·m−3) 1.41×103 煤层初始孔隙率/% 5.61 煤的黏聚力/MPa 20 煤的内摩擦角/(°) 40 气体动力黏度系数/(Pa·s) 11.124 气体的密度/(kg·m−3) 0.716 初始气体压力/MPa 0.50 煤体的初始温度/K 304.4 煤的渗透率/m2 3.1×10−12 -
[1] 袁亮. 煤及共伴生资源精准开采科学问题与对策[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(1):1−9. YUAN Liang. Scientific problem and countermeasure for precision mining of coal and associated resources[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2019, 44(1): 1−9.
[2] 徐筝峥,杨玉贵,陈勇,等. 深部大采高沿空留巷围岩应力分布与变形规律研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2022,53(5):59−66. XU Zhengzheng, YANG Yugui, CHEN Yong, et al. Research on stress distribution and deformation law of surrounding rock of deep and large mining height gob-side entry retaining[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(5): 59−66.
[3] 秦玉金,陈煜朋,姜文忠,等. 深部煤层瓦斯赋存机制研究现状及展望[J]. 煤矿安全,2020,51(5):10−15. QIN Yujin, CHEN Yupeng, JIANG Wenzhong, et al. Research status and prospect of gas occurrence mechanism in deep coal seam[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2020, 51(5): 10−15.
[4] 王宁. 深部急倾斜煤层开采灾害防控及力学行为研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2020,51(9):205−210. WANG Ning. Study on prevention and control of mining disaster and mechanical behavior of deep steep coal seam[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2020, 51(9): 205−210.
[5] 王恩元,张国锐,张超林,等. 我国煤与瓦斯突出防治理论技术研究进展与展望[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(1):297−322. WANG Enyuan, ZHANG Guorui, ZHANG Chaolin, et al. Research progress and prospect on theory and technology for coal and gas outburst control and protection in China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(1): 297−322.
[6] 袁亮. 深部采动响应与灾害防控研究进展[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(3):716−725. YUAN Liang. Research progress of mining response and disaster prevention and control in deep coal mines[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(3): 716−725.
[7] 赵训,李绍泉,李树清,等. 贵州煤与瓦斯突出鉴定与区域预测存在的问题及对策探讨[J]. 煤矿安全,2019,50(3):167−171. ZHAO Xun, LI Shaoquan, LI Shuqing, et al. Problems of coal and gas outburst identification and regional prediction in Guizhou Province[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2019, 50(3): 167−171.
[8] 梁冰. 煤和瓦斯突出固流耦合失稳理论[M]. 北京:地质出版社,2000:492−496. [9] 梁冰,章梦涛,王泳嘉. 煤层瓦斯渗流与煤体变形的耦合数学模型及数值解法[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,1996,15(2):135−142. LIANG Bing, ZHANG Mengtao, WANG Yongjia. Coupling mathematical model and numerical solution of coal seam gas seepage and coal deformation[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 1996, 15(2): 135−142.
[10] 张国华,梁冰. 煤岩渗透率与煤与瓦斯突出关系理论探讨[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版),2002,21(4):414−417. ZHANG Guohua, LIANG Bing. Aretical discussion of retationship between penetrate-rate of coal-rock and breaking out of coal and gas[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University (Natural Science), 2002, 21(4): 414−417.
[11] 何学秋. 含瓦斯煤流变特性及其对煤和瓦斯突出的影响[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,1990. [12] 王恩元,李忠辉,何学秋,等. 煤与瓦斯突出电磁辐射预警技术及应用[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2014,42(6):53−57. WANG Enyuan, LI Zhonghui, HE Xueqiu, et al. Application and pre-warning technology of coal and gas outburst by electromagnetic radiation[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2014, 42(6): 53−57.
[13] 蒋承林,俞启香,张超杰. 煤巷突出预测敏感指标及临界值的实验室测定方法及应用[J]. 煤矿安全,2021,52(10):24−29. JIANG Chenglin, YU Qixiang, ZHANG Chaojie. Laboratory determination method and application of sensitive index and critical value for coal roadway outburst prediction[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021, 52(10): 24−29.
[14] 吴爱军,蒋承林,唐俊. 瓦斯突出作用下煤岩体中冲击波传播规律的研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2010,35(10):1644−1648. WU Aijun, JIANG Chenglin, TANG Jun. Study on propagation laws of shock wave in coal-rock mass under the effect of gas outburst[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2010, 35(10): 1644−1648.
[15] 胡千庭,周世宁,周心权. 煤与瓦斯突出过程的力学作用机理[J]. 煤炭学报,2008,33(12):1368−1372. HU Qianting, ZHOU Shining, ZHOU Xinquan. Mechanical mechanism of coal and gas outburst process[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2008, 33(12): 1368−1372.
[16] 胡千庭,文光才. 煤与瓦斯突出的力学作用机理[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2013. [17] 胡千庭,邹银辉,文光才,等. 瓦斯含量法预测突出危险新技术[J]. 煤炭学报,2007,32(3):276−280. HU Qianting, ZOU Yinhui, WEN Guangcai, et al. New technology of outburst danger prediction by gas content[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2007, 32(3): 276−280.
[18] 张伟,郑春山,薛生,等. 基于煤体渗透率各向异性的瓦斯抽采特性研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2020,51(7):6−11. ZHANG Wei, ZHENG Chunshan, XUE Sheng, et al. Study on gas drainage characteristics based on permeability anisotropy of coal[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2020, 51(7): 6−11.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 唐巨鹏,张昕,潘一山. 煤与瓦斯突出物理模拟试验研究现状及展望. 岩石力学与工程学报. 2024(03): 521-541 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张超林,王培仲,王恩元,许江,李忠辉,刘晓斐,彭守建. 我国煤与瓦斯突出机理70年发展历程与展望. 煤田地质与勘探. 2023(02): 59-94 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张文柯. 基于AHP-MCS的煤与瓦斯突出主控因素分析. 能源技术与管理. 2023(05): 126-127 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: