Study on microcrystalline structure of medium and low rank coals in Xinjiang
-
摘要:
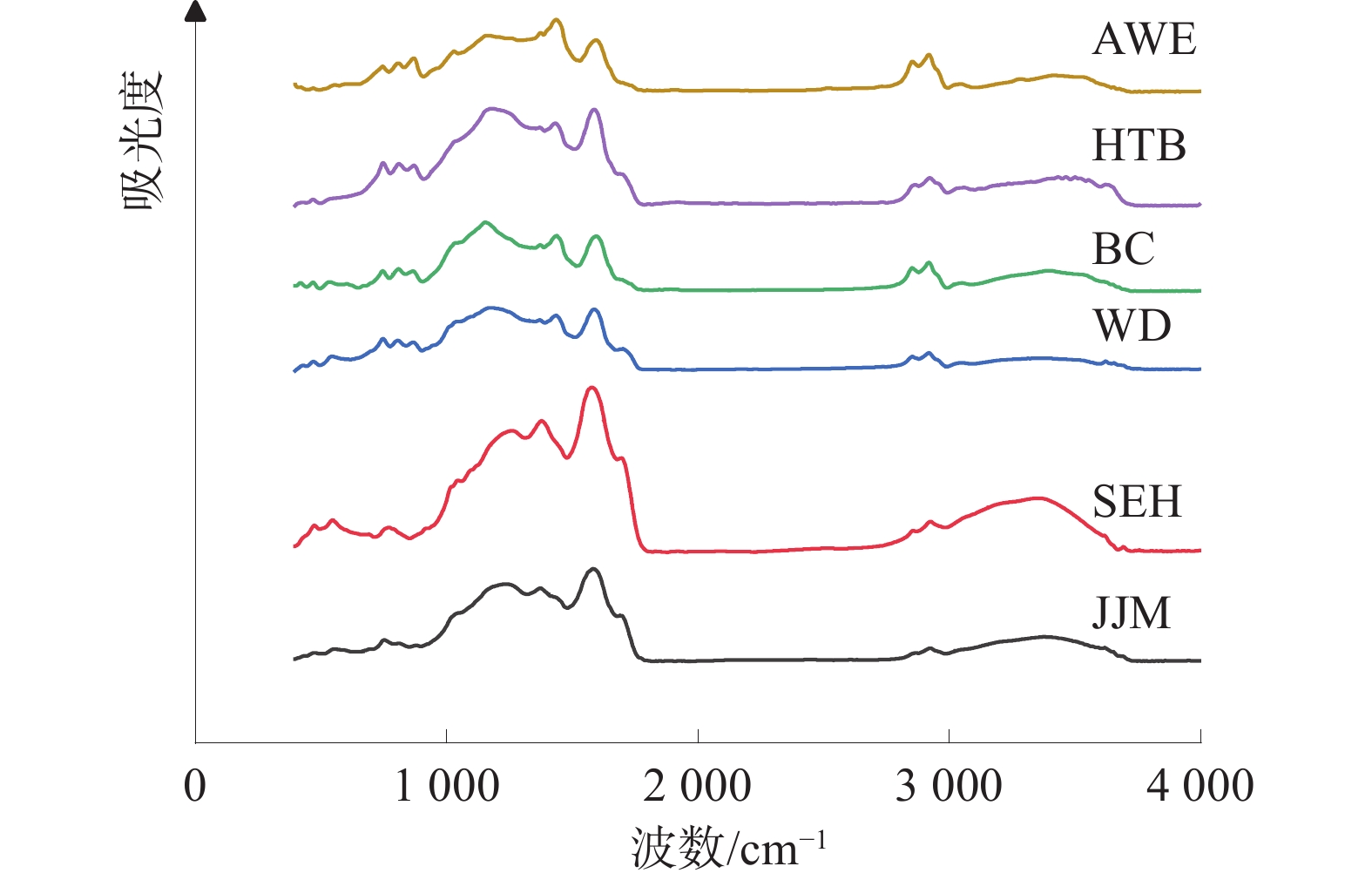
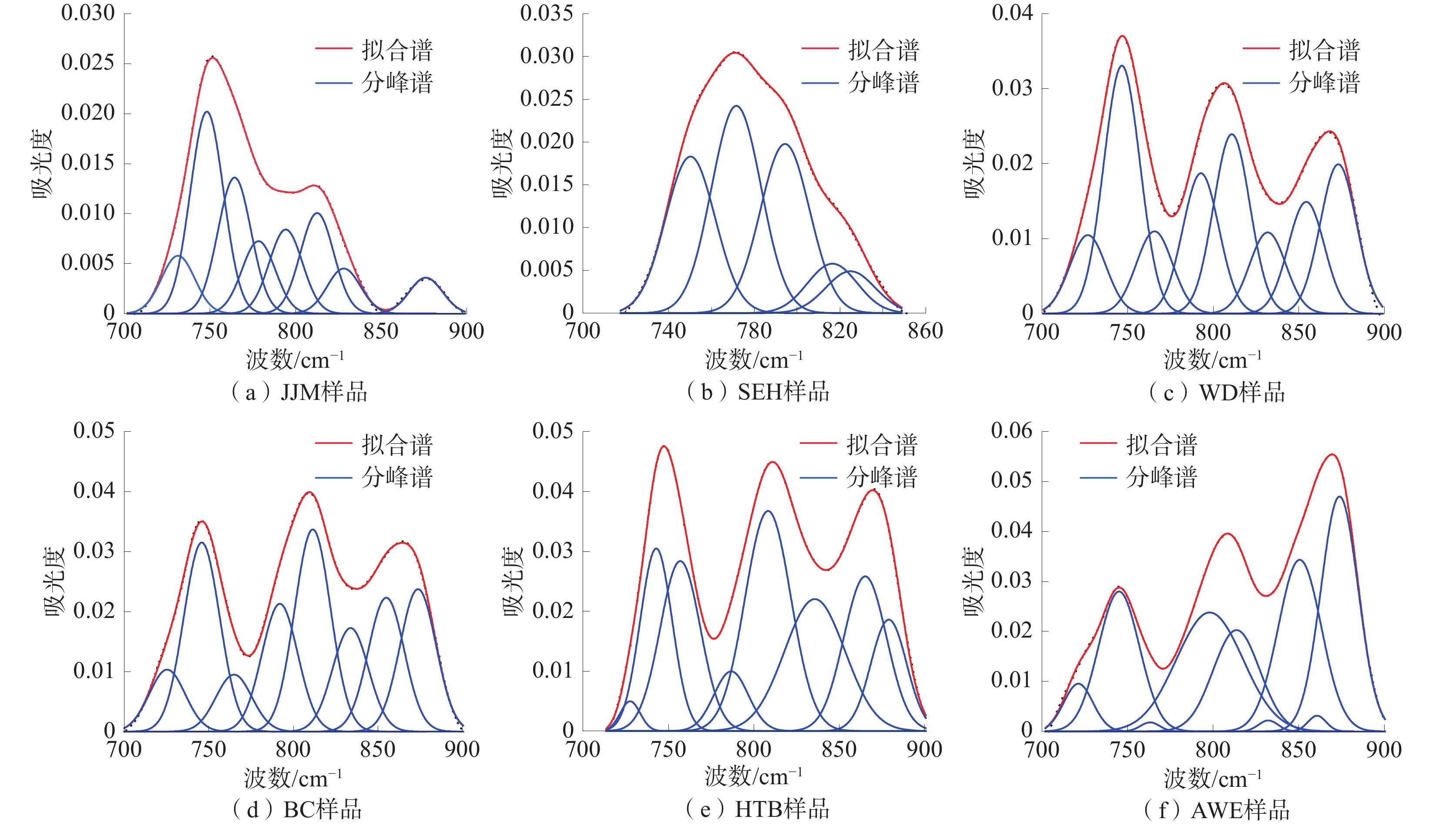
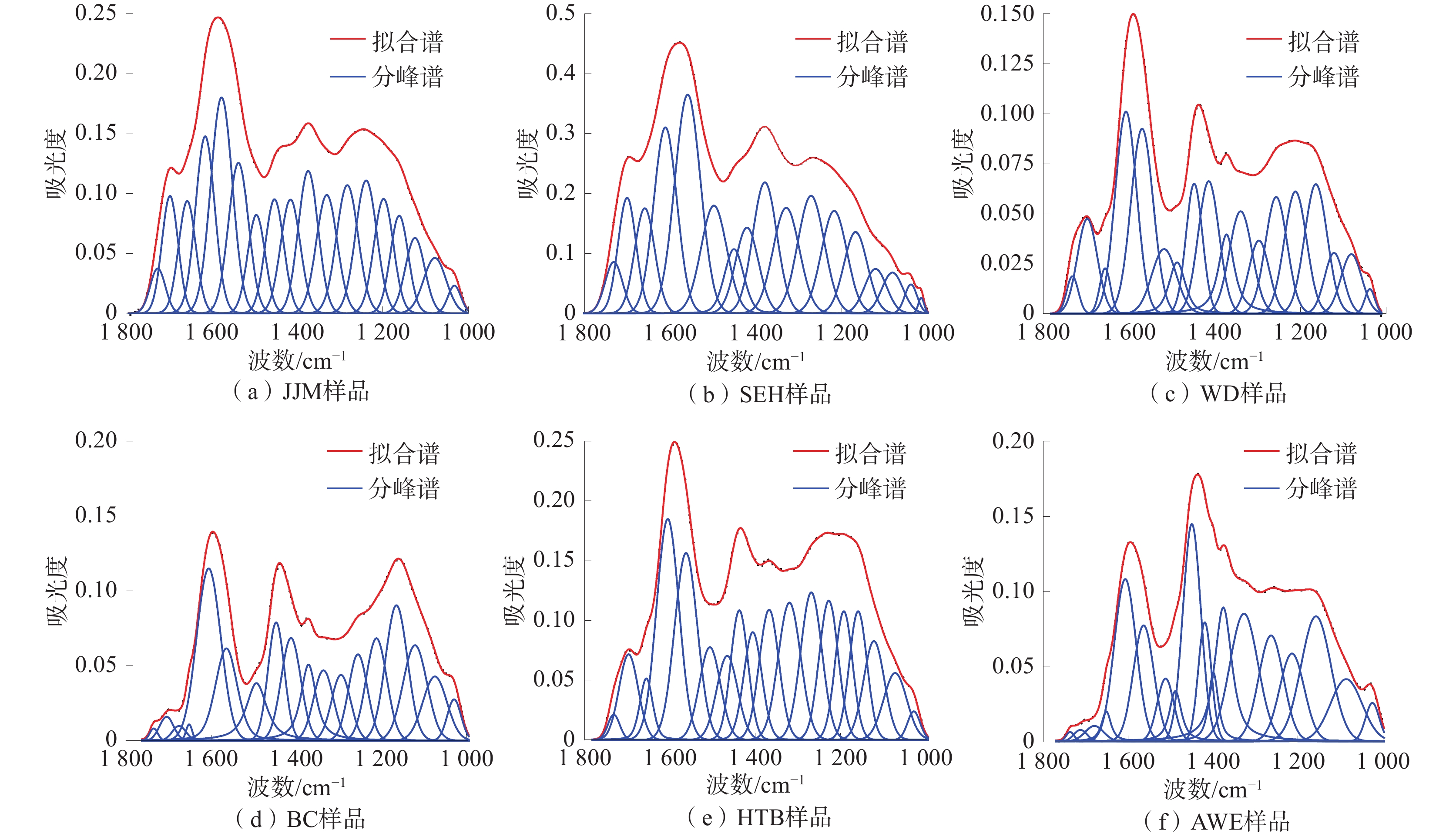
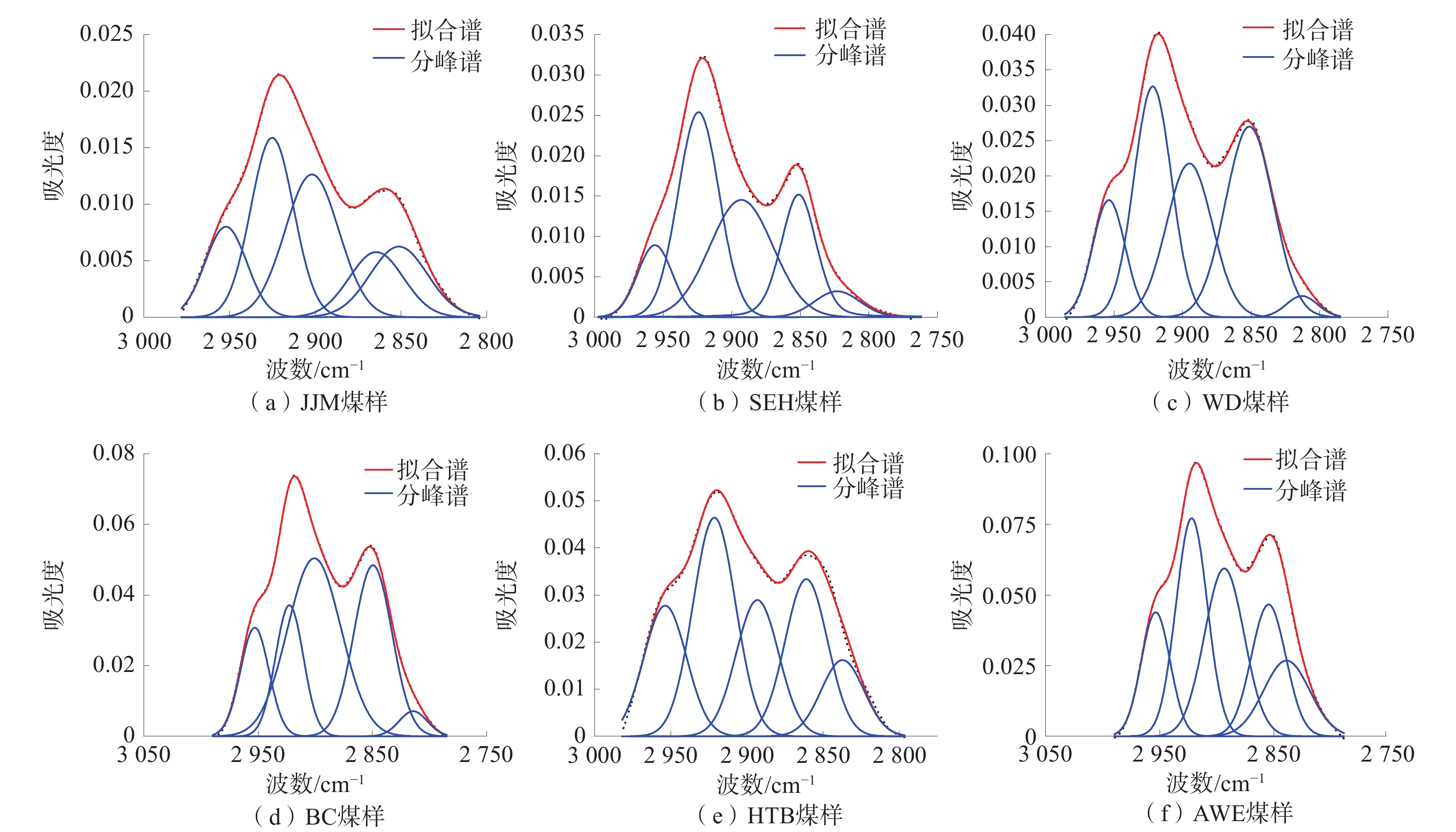
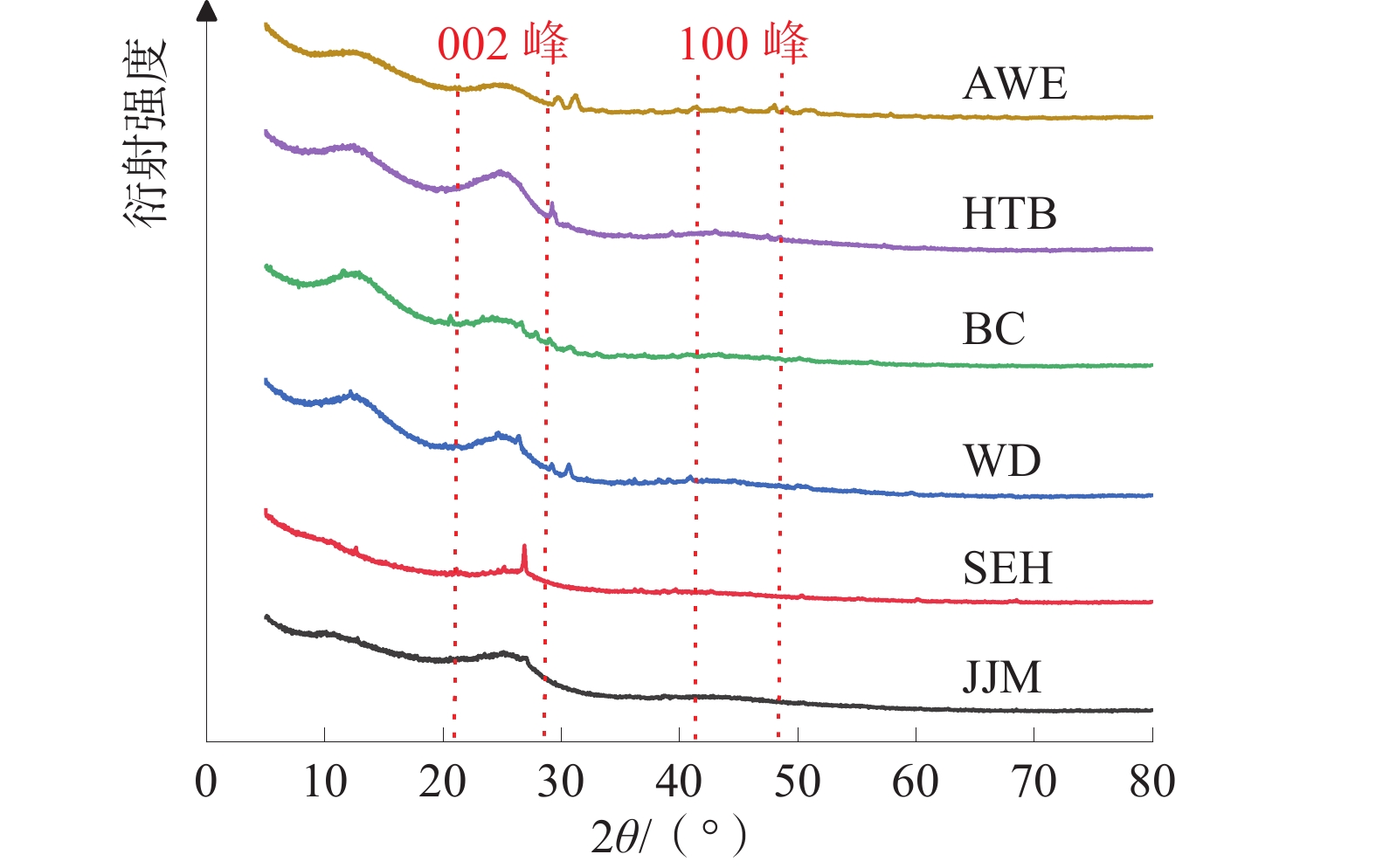
基于X射线衍射实验和傅里叶红外光谱实验,探讨了新疆准东、准南、吐哈及库拜煤田6组煤样的微晶结构特征及演化规律。结果表明:低阶煤中,002峰和100峰均峰形平缓,002峰随煤阶的增高逐渐尖锐,且“对称性”变好,100峰高度逐渐增高,但峰宽逐渐变窄;随着煤样变质程度的增大,芳香层片堆砌高度、延展度及其数量逐渐增大,芳香层片间距整体上呈下降趋势,煤中芳香结构的缩合程度逐渐增大;芳香族化合物和含氧官能团波段峰形尖锐,脂肪烃类物质和羟基官能团波段峰形平缓,均随着煤阶的升高而逐渐宽缓;随着煤阶的升高,芳香度、脂肪链长及其支链化程度、成熟度逐渐减小,而缩聚程度、生烃(油)能力逐渐增大;煤的演化过程以含氧官能团的脱落、脂肪烃类的富集、部分芳烃的缩聚为特征。
Abstract:Based on X ray diffraction and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, the microcrystalline structure characteristics and evolution patterns of a total of 6 coal samples from the eastern Junggar, southern Junggar, Tuha, and Kubai coalfields in Xinjiang were investigated. The peak shape of 002 and 100 peaks in low-rank coal is gentle, the peak 002 becomes sharper and the “symmetry” becomes better with the increase of coal rank, and the peak height of the peak 100 gradually increases but the peak width gradually shrinks. The height of the peak 100 gradually increases but the width gradually narrows; with the increase of coal sample metamorphism, the stacking height, elongation and quantity of aromatic laminates increase gradually, the spacing of aromatic laminates decreases on the whole, and the condensation degree of aromatic structures in coal increases gradually; the peak shape of aromatic compounds and oxygen-containing functional groups is sharp, and the peak shape of aliphatic hydrocarbons and hydroxyl functional groups is gentle, which gradually widens and slows down with the rise of coal rank; with the increase of coal rank, the aromaticity, fat chain length, branched chain degree and maturity gradually decrease, while the polycondensation degree and hydrocarbon (oil) generation ability gradually increase. The evolution process of coal is characterized by the shedding of oxygen-containing functional groups, the enrichment of aliphatic hydrocarbons, and the condensation of some aromatics.
-
-
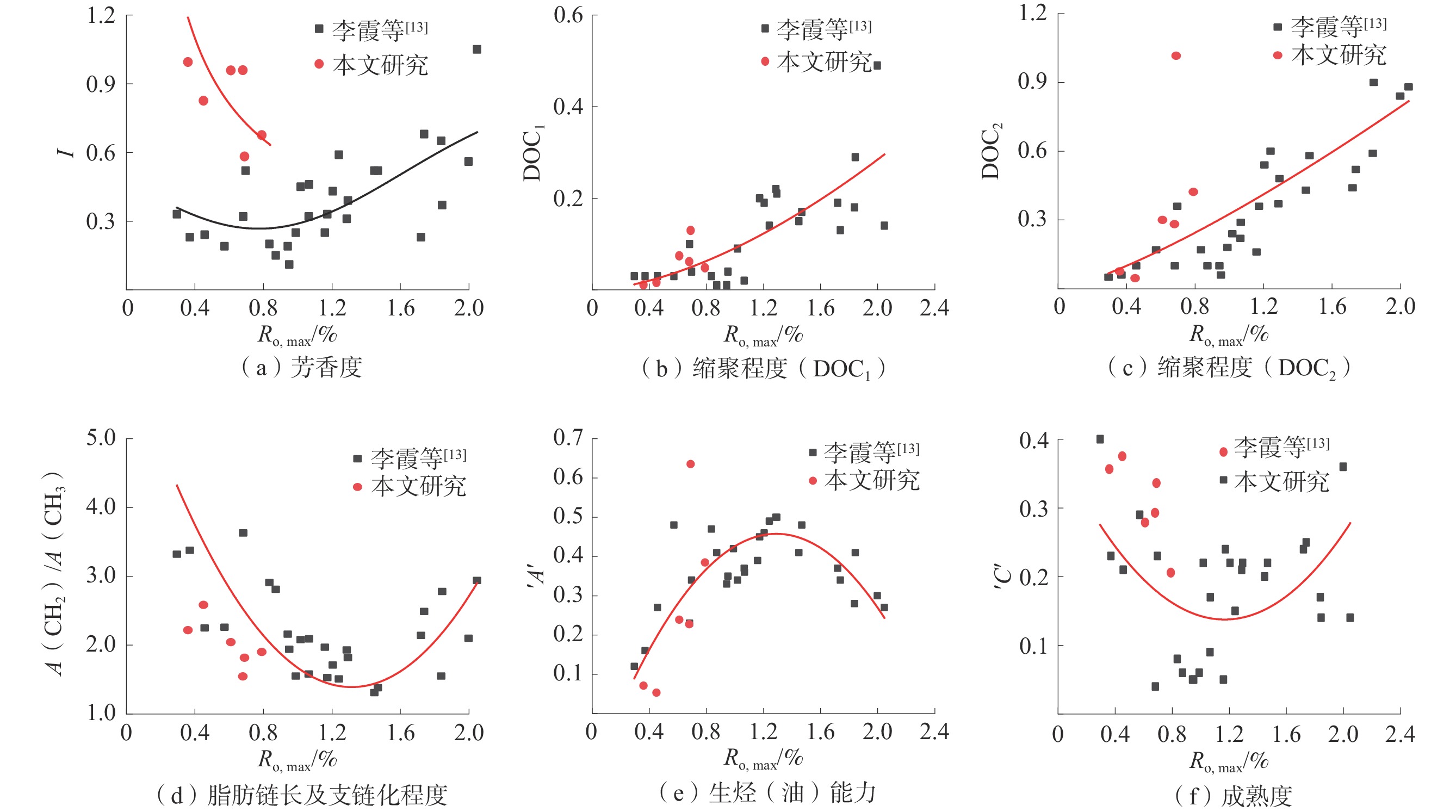
图 8 FTIR微晶结构参数与Ro, max的关系[12]
Figure 8. Relationship between FTIR microcrystalline structure parameters and Ro, max
表 1 煤样的XRD微晶结构参数
Table 1 XRD microcrystalline structure parameters of coal samples
煤样 Ro,max/% d002/nm Lc/nm La/nm Nc La/Lc JJM 0.36 0.3550 1.10 0.92 4.11 0.83 SEH 0.45 0.3561 1.16 1.01 4.27 0.86 WD 0.61 0.3521 1.40 1.27 4.99 0.90 BC 0.68 0.3408 1.46 1.35 5.28 0.92 HTB 0.69 0.3362 1.47 1.36 5.37 0.93 AWE 0.79 0.3301 1.53 1.46 5.63 0.95 表 2 煤样的FTIR微晶结构参数
Table 2 FTIR microcrystalline structure parameters of coal samples
煤样 A(CH2)/A(CH3) I DOC1 DOC2 ${'}A{'} $ ${'}C{'} $ JJM 2.22 0.99 0.01 0.08 0.07 0.36 SEH 2.58 0.83 0.02 0.05 0.05 0.38 WD 2.04 0.96 0.07 0.30 0.24 0.28 BC 1.90 0.68 0.05 0.42 0.38 0.21 HTB 1.55 0.96 0.06 0.28 0.23 0.29 AWE 1.82 0.58 0.13 1.02 0.64 0.34 -
[1] 李瑞明,周梓欣. 新疆煤层气产业发展现状与思考[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2022,50(3):23−29. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.21.11.0640 LI Ruiming, ZHOU Zixin. Development status and thoughts on coalbed methane industry in Xinjiang[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2022, 50(3): 23−29. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.21.11.0640
[2] 李帅魁,姜文忠,田富超. 不同温度下气体竞争吸附特性对煤微观结构响应研究进展[J]. 煤矿安全,2022,53(11):167−175. LI Shuaikui, JIANG Wenzhong, TIAN Fuchao. Research progress on response of gas competitive adsorption characteristics on coal microstructure at different temperatures[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(11): 167−175.
[3] 戴广龙. 煤低温氧化过程中微晶结构变化规律研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2011,36(2):322−325. DAI Guanglong. Research on microcrystalline structure change regularity in the coal low temperature oxidation process[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2011, 36(2): 322−325.
[4] LU L, SAHAJWALLA V, KONG C, et al. Quantitative X-ray diffraction analysis and its application to various coals[J]. Carbon, 2001, 39(12): 1821−1833. doi: 10.1016/S0008-6223(00)00318-3
[5] SAIKIA B K, BORUAH R K. X-Ray structural analysis of some Indian coals[J]. Aip Conference Proceedings, 2010, 1202(1): 112−116.
[6] 周贺,潘结南,李猛,等. 不同变质变形煤微晶结构的XRD试验研究[J]. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2019,38(1):26−35. ZHOU He, PAN Jienan, LI Meng, et al. Study on microcrystalline structures of different metamorphic and deformed coals based on XRD experiments[J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University (Natural Science), 2019, 38(1): 26−35.
[7] LI Z S, FREDERICKS P M, RINTOUL L, et al. Application of attenuated total reflectance micro-Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy to the study of coal macerals: Examples from the Bowen Basin, Australia[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2007, 70(1−3): 87−94.
[8] 郝盼云,孟艳军,曾凡桂,等. 红外光谱定量研究不同煤阶煤的化学结构[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2020,40(3):787−792. HAO Panyun, MENG Yanjun, ZENG Fangui, et al. Quantitative study of chemical structures of different rank coals based on infrared spectroscopy[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2020, 40(3): 787−792.
[9] 贾廷贵,李璕,曲国娜,等. 不同变质程度煤样化学结构特征FTIR表征[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2021,41(11):3363−3369. JIA Tinggui, LI Xun, QU Guona, et al. FTIR characterization of chemical structures characteristics of coal samples with different metamorphic degrees[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2021, 41(11): 3363−3369.
[10] 傅雪海,秦勇,韦重韬. 煤层气地质学[M]. 徐州:中国矿业大学出版社,2007. [11] 李霞,曾凡桂,王威,等. 低中煤级煤结构演化的XRD表征[J]. 燃料化学学报,2016,44(7):777−783. LI Xia, ZENG Fangui, WANG Wei, et al. XRD characterization of structural evolution in low-middle rank coals[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2016, 44(7): 777−783.
[12] 李霞,曾凡桂,王威,等. 低中煤级煤结构演化的FTIR表征[J]. 煤炭学报,2015,40(12):2900−2908. LI Xia, ZENG Fangui, WANG Wei, et al. FTIR characterization of structural evolution in low-middle rank coals[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2015, 40(12): 2900−2908.
[13] 相建华,曾凡桂,梁虎珍,等. 不同变质程度煤的碳结构特征及其演化机制[J]. 煤炭学报,2016,41(6):1498−1506. XIANG Jianhua, ZENG Fangui, LIANG Huzhen, et al. Carbon structure characteristics and evolution mechanism of different rank coals[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2016, 41(6): 1498−1506.
[14] 苏现波,司青,王乾. 煤变质演化过程中的XRD响应[J]. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2016,35(4):487−492. SU Xianbo, SI Qing, WANG Qian. The XRD response during the coalification process[J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University (Natural Science), 2016, 35(4): 487−492.
[15] 郝长胜,袁迎春,贾廷贵,等. 不同变质程度煤的化学结构红外光谱研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2022,53(11):15−22. HAO Changsheng, YUAN Yingchun, JIA Tinggui, et al. Infrared spectral research on chemical structure of coal with different levels of metamorphism[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(11): 15−22.
[16] 田继军,杨曙光. 准噶尔盆地南缘下-中侏罗统层序地层格架与聚煤规律[J]. 煤炭学报,2011,36(1):58−64. TIAN Jijun, YANG Shuguang. Sequence strata and coal accumulation of lower and middle Jurassic Formation from southern margin of Junggar Basin, Sinkiang, China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2011, 36(1): 58−64.
[17] 谭凯丽,宋燕莉,牛江露. 强氧化处理和微生物作用对煤样结构和成气的影响[J]. 贵州大学学报(自然科学版),2018,35(6):58−61. TAN Kaili, SONG Yanli, NIU Jianglu. The effects of strong oxidation treatment and microbial action on coal sample structure and gas formation[J]. Journal of Guizhou University (Natural Sciences), 2018, 35(6): 58−61.
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: