Experimental study on the effect of surfactant on wettability of anthracite
-
摘要:
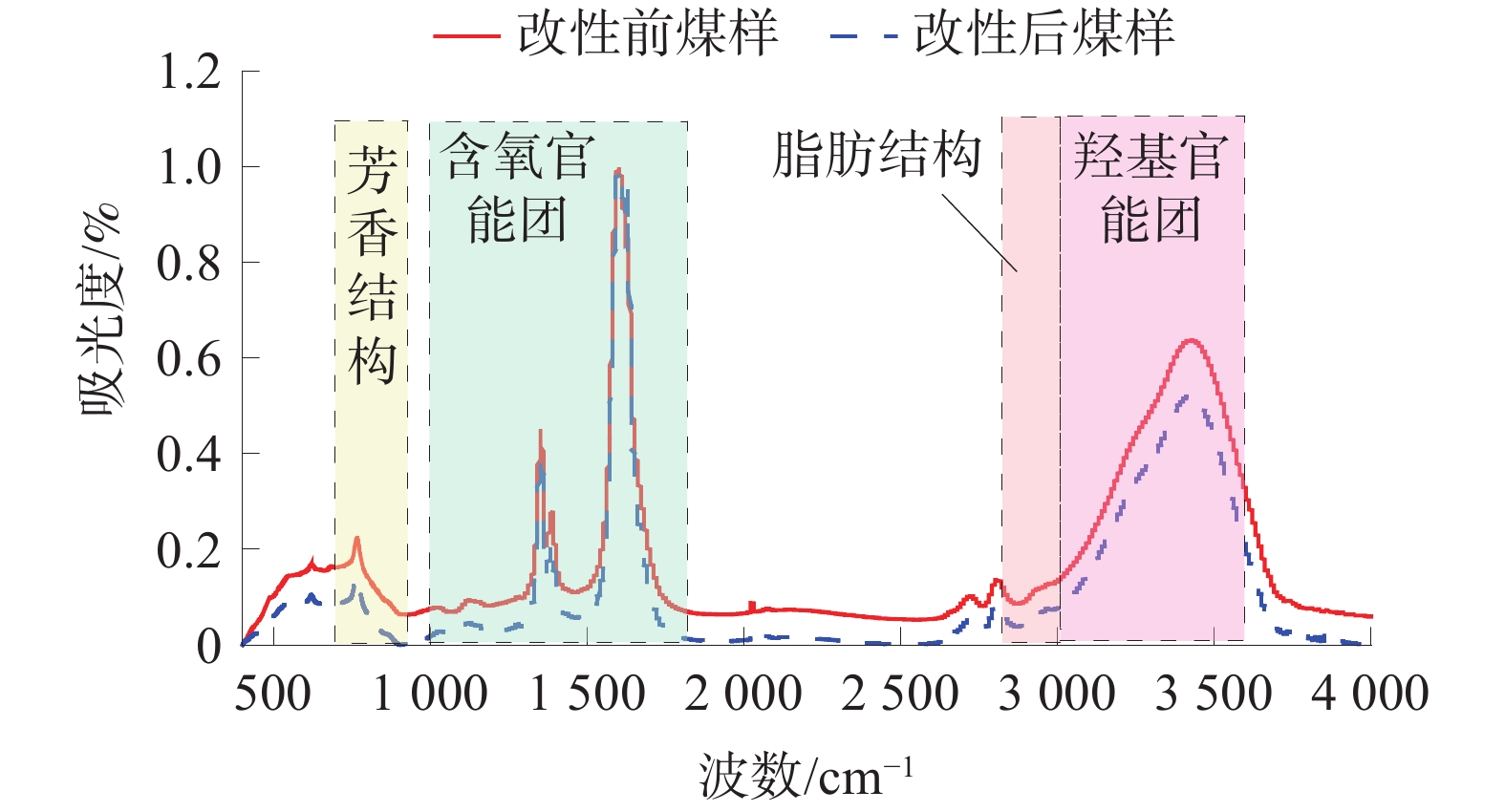
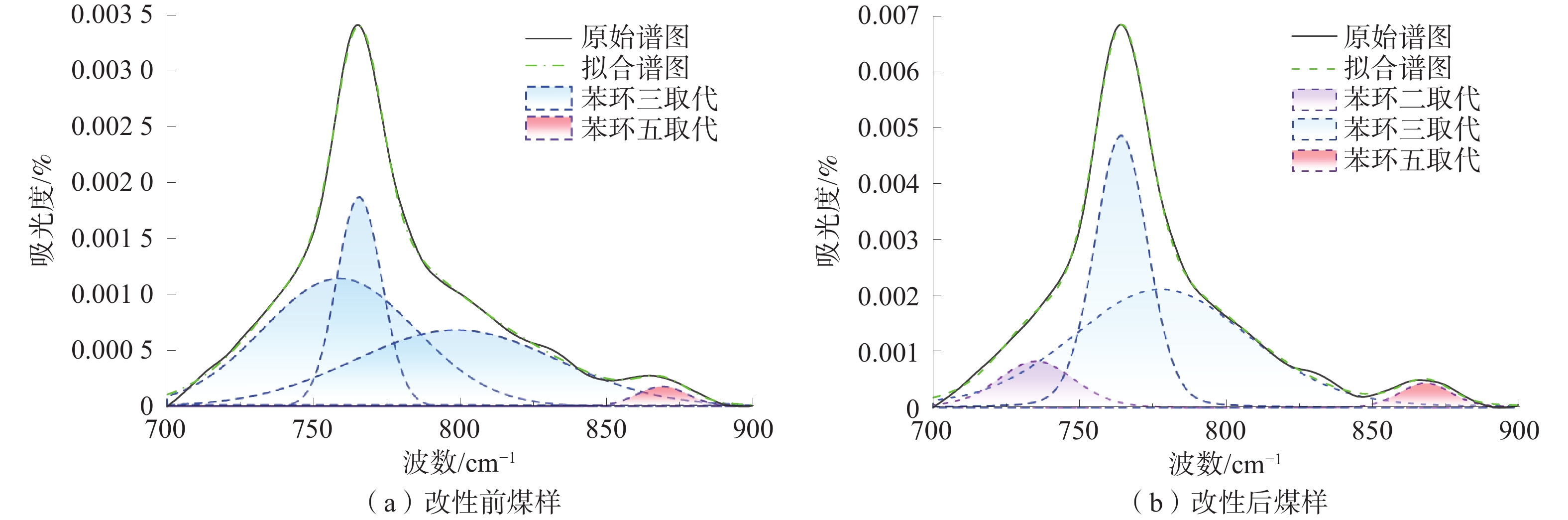
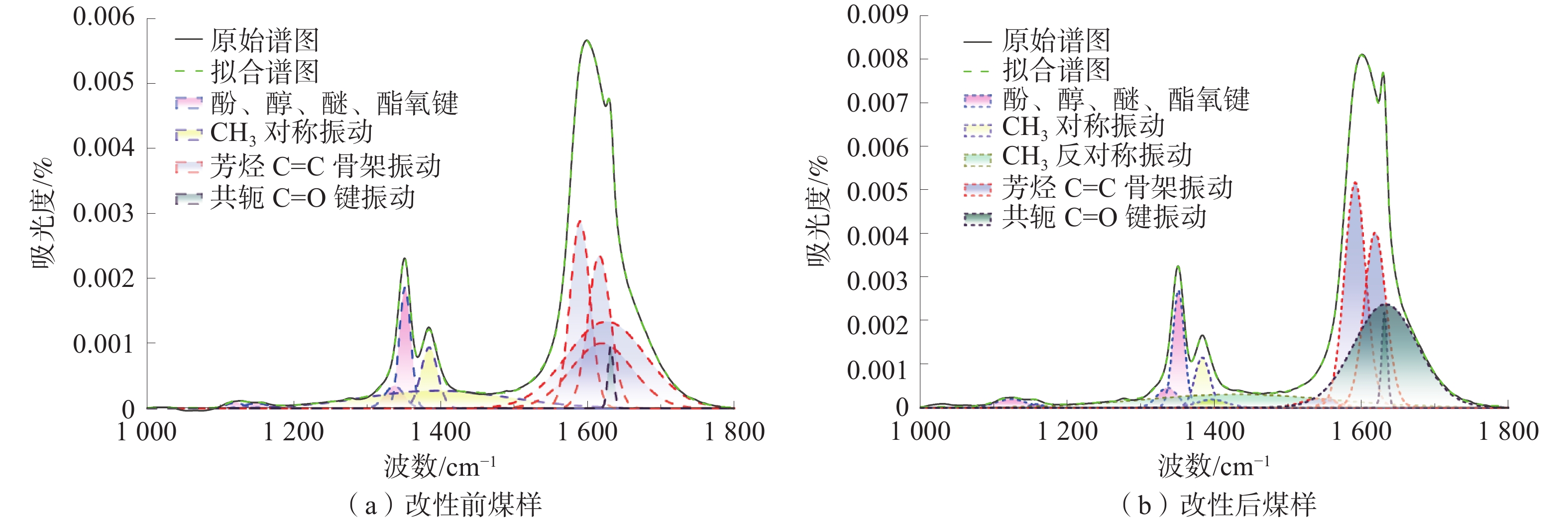
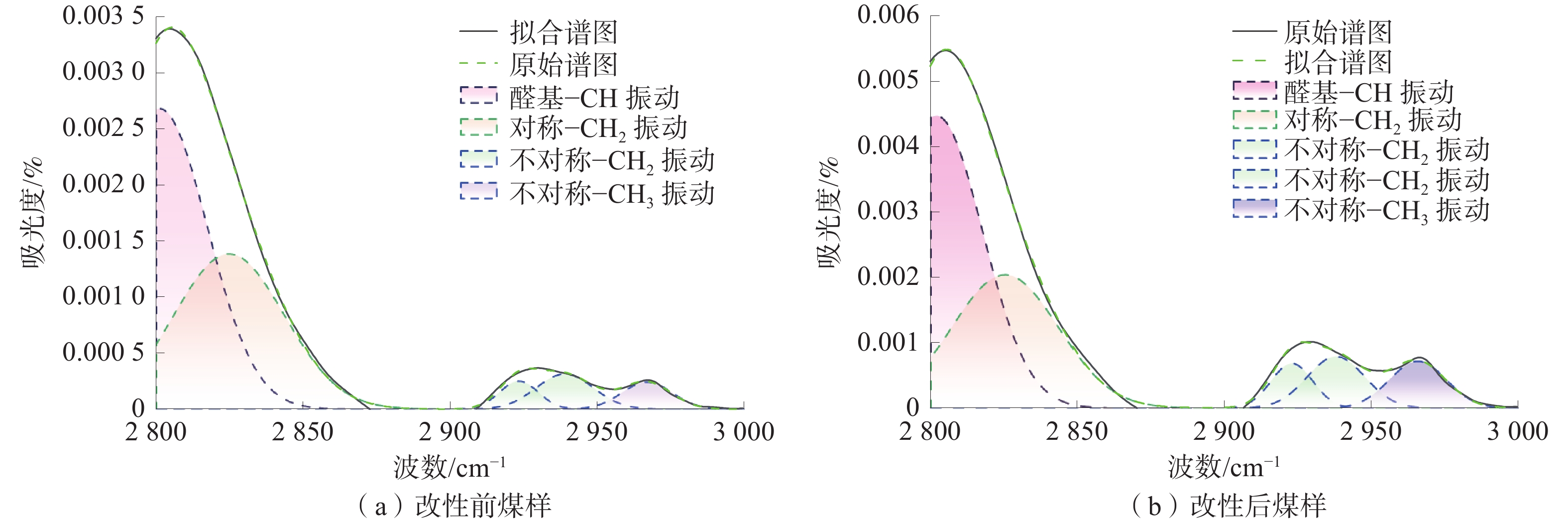
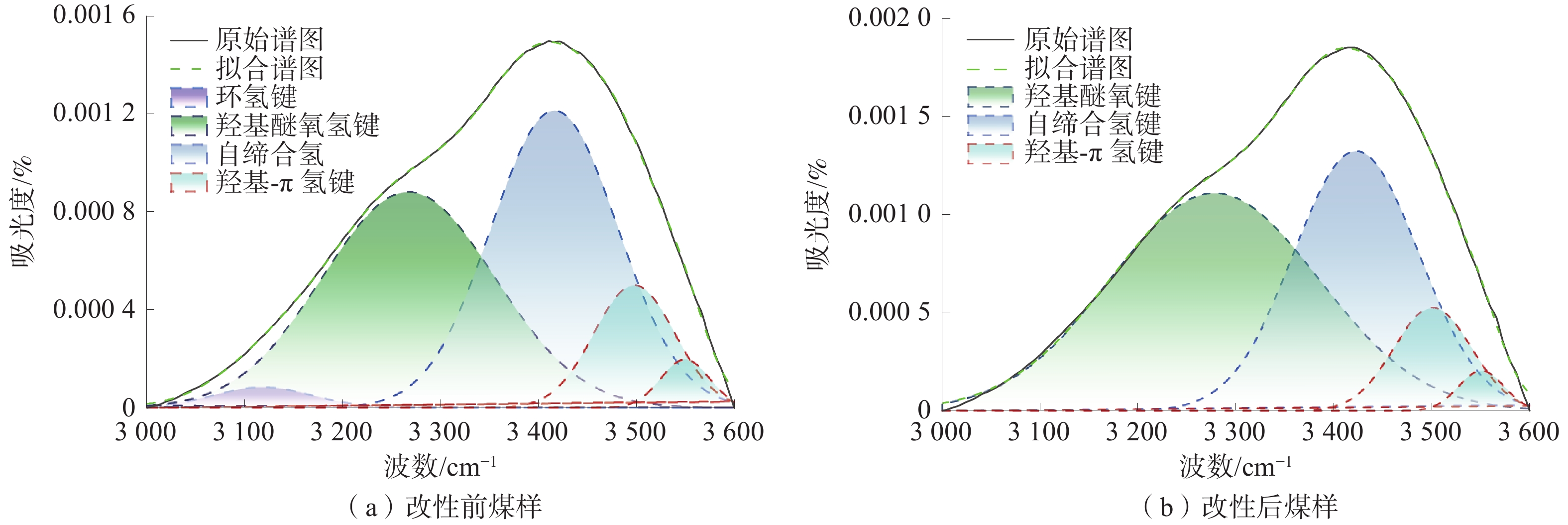
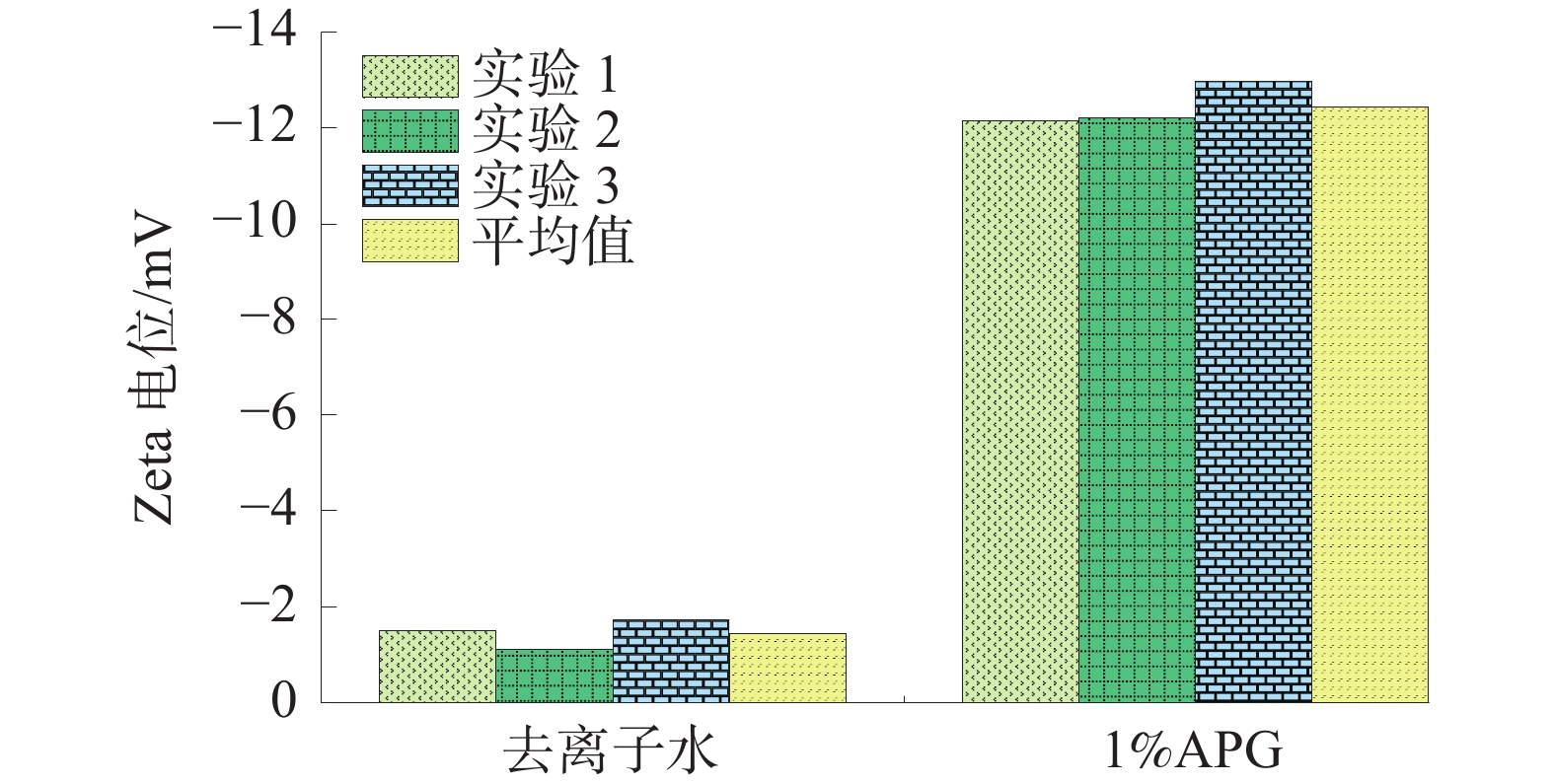
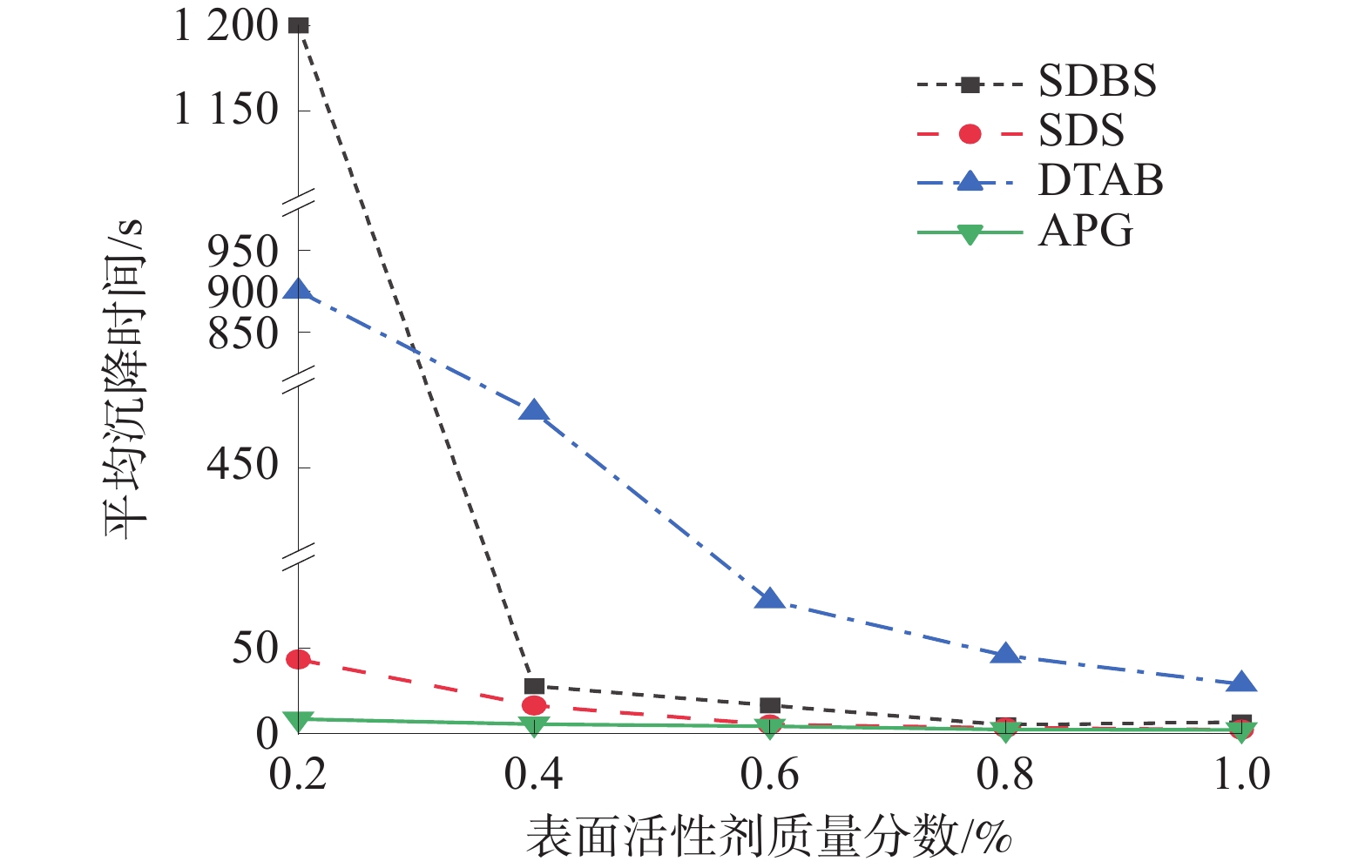
煤的润湿性对煤层注水及防尘有重要意义。为研究表面活性剂对煤尘表面润湿性的影响机理,以贵州矿区无烟煤为研究对象开展煤尘沉降实验,优选润湿实验煤样效果最佳的表面活性剂溶液,借助红外光谱实验及Zeta电位测定实验,探索表面活性剂作用下煤表面润湿性的变化规律。研究结果表明:实验所用4种表面活性剂均能大幅度提高煤尘润湿性;其中,质量分数为1%的APG润湿煤尘的效果最佳;改性后,实验煤样亲水基团和疏水基团均增加,但亲水基团增量明显大于疏水基团,说明表面活性剂改性对亲水基团的影响更显著,有利于提高煤尘表面的亲水性;改性后,实验煤样表面负电性增强约7.68倍,引起双电层中剪切面滑向液面,同时强化含氧官能团与水分子之间的偶极作用力,导致水化层增厚,煤样表面润湿性得以改善。
Abstract:The wettability of coal is of great significance to coal seam water injection and dust prevention. In order to study the influence mechanism of surfactant on the wettability of coal dust surface, the coal dust deposition experiment was carried out with the anthracite in Guizhou mining areas as the research object, and the surfactant solution with the best wetting effect was selected. With the help of infrared spectroscopy experiment and Zeta potential measurement experiment, the change law of coal surface wettability under the action of surfactants was explored. The results show that: the four surfactants used in the experiment can greatly improve the wettability of coal dust. Among them, 1% APG has the best wetting effect on coal dust; after modification, the hydrophilic groups and hydrophobic groups of the experimental coal samples increased, but the increase of hydrophilic groups was significantly greater than that of hydrophobic groups. It shows that the effect of surfactant modification on hydrophilic groups is more significant, which is beneficial to improve the hydrophilicity of coal dust surface; after modification, the surface negative charge of the experimental coal sample increased by about 7.68 times, causing the shear surface in the electric double layer to slide to the liquid surface, and strengthening the dipole force between the oxygen-containing functional groups and the water molecules, resulting in the thickening of the hydration layer and the improvement of the surface wettability of the coal sample.
-
-
-
[1] 陈喜阳,周程,王田. 多情景视角下中国能源消费和碳达峰路径[J]. 环境科学,2023,44(10):5464−5477. CHEN Xiyang, ZHOU Cheng, WANG Tian. China’s energy consumption and carbon peak path under different scenarios[J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(10): 5464−5477.
[2] 国家统计局. 中华人民共和国2022年国民经济和社会发展统计公报[N]. 人民日报,2023-03-01(9). [3] 仝晓波. 我国煤矿粉尘治理技术获重大突破[N]. 中国能源报,2022-11-21(3). [4] 孙光裕,杨付领,乞朝欣. 贵州省煤矿安全现状分析及对策研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2021,52(9):245−249. SUN Guangyu, YANG Fuling, QI Chaoxin. Analysis and countermeasures of coal mine safety in Guizhou Province[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021, 52(9): 245−249.
[5] 张迎新,吴强. 表面活性剂的强化喷雾降尘实验[J]. 黑龙江科技学院学报,2008,18(4):269−271. ZHANG Yingxin, WU Qiang. Efficiency of dust reduction by spraying using surfactants[J]. Journal of Heilongjiang Institute of Science and Technology, 2008, 18(4): 269−271.
[6] 林海飞,刘宝莉,严敏,等. 非阳离子表面活性剂对煤润湿性能影响的研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报,2018,28(5):123−128. LIN Haifei, LIU Baoli, YAN Min, et al. Research influence of non-cationic surfactant on wettability of coal[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2018, 28(5): 123−128.
[7] 许满贵,魏攀,何鹏程,等. 表面活性剂降尘效果试验研究[J]. 煤炭技术,2016,35(3):139−142. XU Mangui, WEI Pan, HE Pengcheng, et al. Experiment study on efficiency of reducing dust by using surfactants[J]. Coal Technology, 2016, 35(3): 139−142.
[8] 赵振保,杨晨,孙春燕,等. 煤尘润湿性的实验研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2011,36(3):442−446. ZHAO Zhenbao, YANG Chen, SUN Chunyan, et al. Experimental study of coal dust wettability[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2011, 36(3): 442−446.
[9] 杨静. 煤尘的润湿机理研究[D]. 青岛:山东科技大学,2008. [10] 陈松降,陶秀祥,何环,等. 油泡-低阶煤颗粒间的黏附特性[J]. 煤炭学报,2017,42(3):745−752. CHEN Songjiang, TAO Xiuxiang, HE Huan, et al. Attachment characteristics between oily bubbles and low rank coal particles[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2017, 42(3): 745−752.
[11] 孟筠青,夏捃凯,牛家兴,等. SDBS溶液对赵庄煤表面润湿作用机理的研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2021,50(2):381−388. MENG Junqing, XIA Junkai, NIU Jiaxing, et al. Study of the wetting mechanism of SDBS solution on Zhaozhuang coal surface[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2021, 50(2): 381−388.
[12] 阎杰,刘兴隆,单豆豆,等. 基于响应面法的无烟煤煤尘降尘剂配方优化[J]. 煤矿安全,2019,50(12):18−22. YAN Jie, LIU Xinglong, SHAN Doudou, et al. Optimization of formula of dust remover for anthracite coal dust based on response surface methodology[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2019, 50(12): 18−22.
[13] 李仲文,张志强,陈曦,等. 表面活性剂对无烟煤煤尘的抑尘效果研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2022,53(2):27−32. LI Zhongwen, ZHANG Zhiqiang, CHEN Xi, et al. Study on dust suppression effect of surfactant on anthracite coal dust[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(2): 27−32.
[14] 陈炫来,严国超,阳湘琳,等. SDS/SDBS对无烟煤润湿性影响的分子动力学模拟[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(12):185−193. CHEN Xuanlai, YAN Guochao, YANG Xianglin, et al. Molecular dynamics simulation of the effect of SDS/SDBS on the wettability of anthracite[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2022, 50(12): 185−193.
[15] 杨静,谭允祯,王振华,等. 煤尘表面特性及润湿机理的研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2007,32(7):737−740. YANG Jing, TAN Yunzhen, WANG Zhenhua, et al. Study on the coal dust surface characteristics and wetting mechanism[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2007, 32(7): 737−740.
[16] 赵璐,张蕾,文欣,等. 表面活性剂润湿低阶煤煤尘的性能及作用机理[J]. 西安科技大学学报,2021,41(2):323−330. ZHAO Lu, ZHANG Lei, WEN Xin, et al. Wetting ability of surfactants on low-rank coal and wetting mechanism[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Science and Technology, 2021, 41(2): 323−330.
[17] 郝盼云,孟艳军,曾凡桂,等. 红外光谱定量研究不同煤阶煤的化学结构[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2020,40(3):787−792. HAO Panyun, MENG Yanjun, ZENG Fangui, et al. Quantitative study of chemical structures of different rank coals based on infrared spectroscopy[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2020, 40(3): 787−792.
[18] 李娇阳,李凯琦. 煤表面润湿性的影响因素[J]. 煤炭学报,2016,41(S2):448−453. LI Jiaoyang, LI Kaiqi. Influence factors of coal surface wettability[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2016, 41(S2): 448−453.
[19] 赵孟浩,张守玉,郑红俊,等. 低阶煤中含氧官能团干燥前后的演变规律[J]. 煤炭学报,2016,41(2):483−489. ZHAO Menghao, ZHANG Shouyu, ZHENG Hongjun, et al. Transition of the oxygen-containing functional groups of low rank coal during drying process[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2016, 41(2): 483−489.
[20] 程卫民,薛娇,周刚,等. 基于红外光谱的煤尘润湿性[J]. 煤炭学报,2014,39(11):2256−2262. CHENG Weimin, XUE Jiao, ZHOU Gang, et al. Study of coal dust wettability based on FTIR[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2014, 39(11): 2256−2262.
[21] 康健婷. 无烟煤改性及其对吸附与润湿性影响的实验研究[D]. 太原:太原理工大学,2018. [22] 安文博,王来贵. 表面活性剂作用下煤体力学特性及改性规律[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(12):4074−4086. AN Wenbo, WANG Laigui. Mechanical properties and modification of coal under the action of surfactant[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(12): 4074−4086.
[23] 王超群,林柏泉,李庆钊,等. 煤尘表面含氧官能团对煤尘润湿性能的影响[J]. 煤矿安全,2014,45(5):173−176. WANG Chaoqun, LIN Baiquan, LI Qingzhao, et al. Effects of oxygen containing functional groups on coal dust wettability[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2014, 45(5): 173−176.
[24] 罗根华. 煤尘润湿性判别及难润湿煤尘控制技术研究[D]. 阜新: 辽宁工程技术大学,2016. [25] 唐纲,杨平,王吉白,等. 超导磁分离过程的混絮凝影响因素[J]. 环境科学与技术,2018,41(7):60−64. TANG Gang, YANG Ping, WANG Jibai, et al. Factors influencing flocculation of superconducting magnetic separation process[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 41(7): 60−64.
[26] 郭中雅. 表面活性剂在褐煤表面吸附特性及其对煤润湿性的影响[D]. 太原:太原理工大学,2016. [27] 魏帅,严国超,张志强,等. 晋城无烟煤的分子结构特征分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(2):555−562. WEI Shuai, YAN Guochao, ZHANG Zhiqiang, et al. Molecular structure analysis of Jincheng anthracite coal[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2018, 43(2): 555−562.
[28] 李树刚,闫冬洁,严敏,等. 烷基糖苷活性剂对煤体结构改性及甲烷解吸特性的影响[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(1):286−296. LI Shugang, YAN Dongjie, YAN Min, et al. Effect of alkyl glycoside on coal structure modification and methane desorption characteristics[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(1): 286−296.



 下载:
下载: