Experimental study on inhibition effect of inert gas parameters on gas deflagration flame propagation
-
摘要:
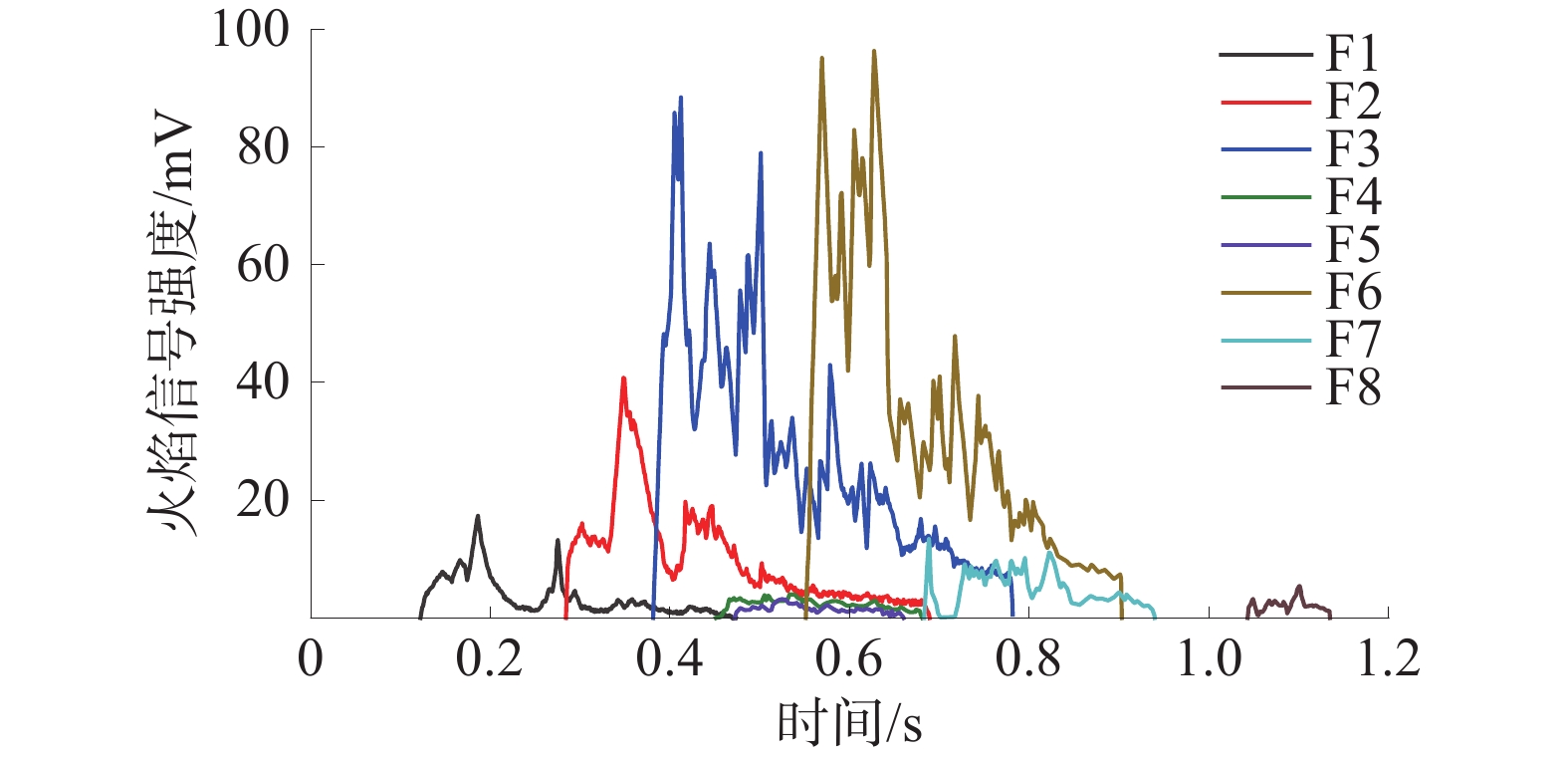
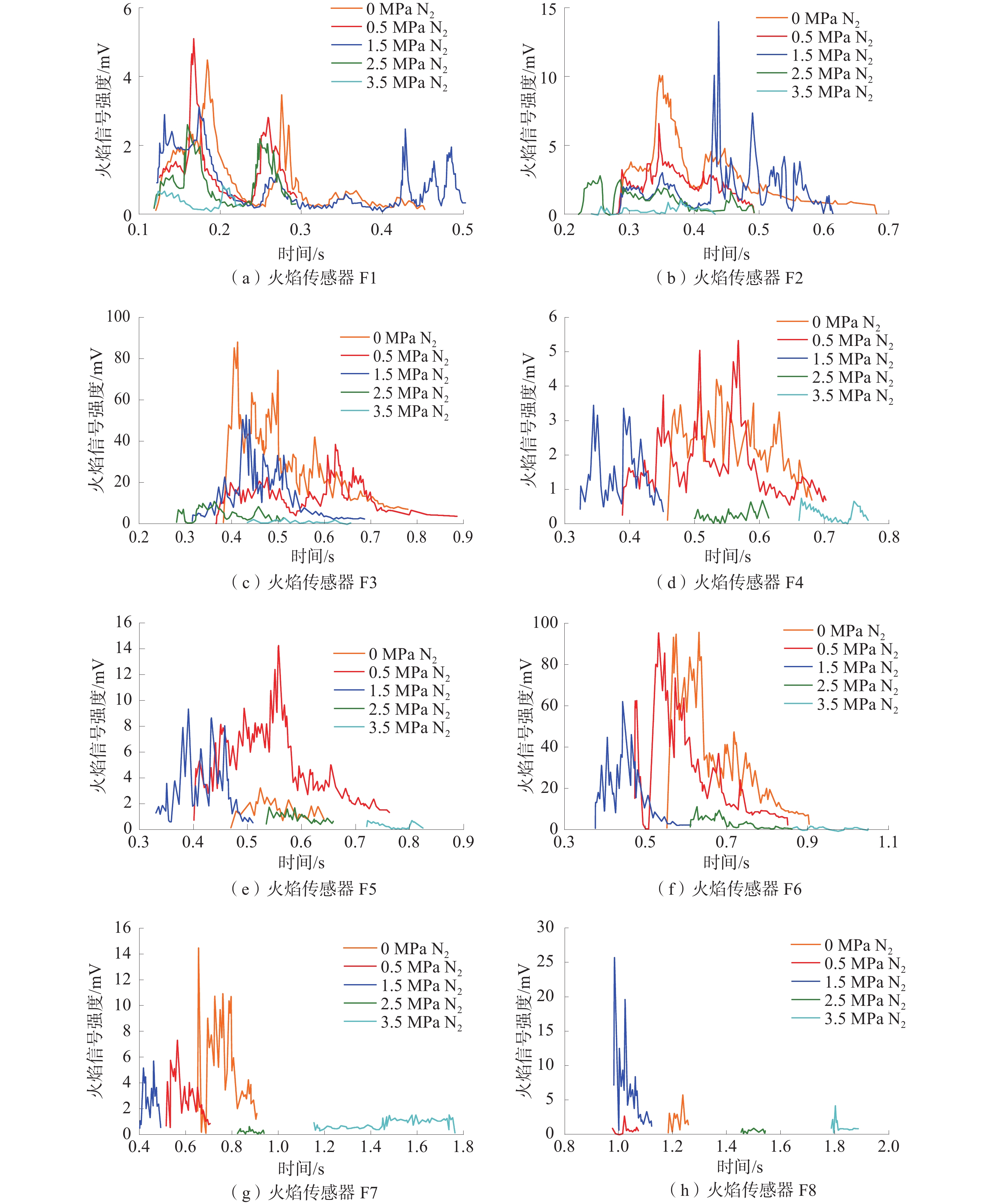
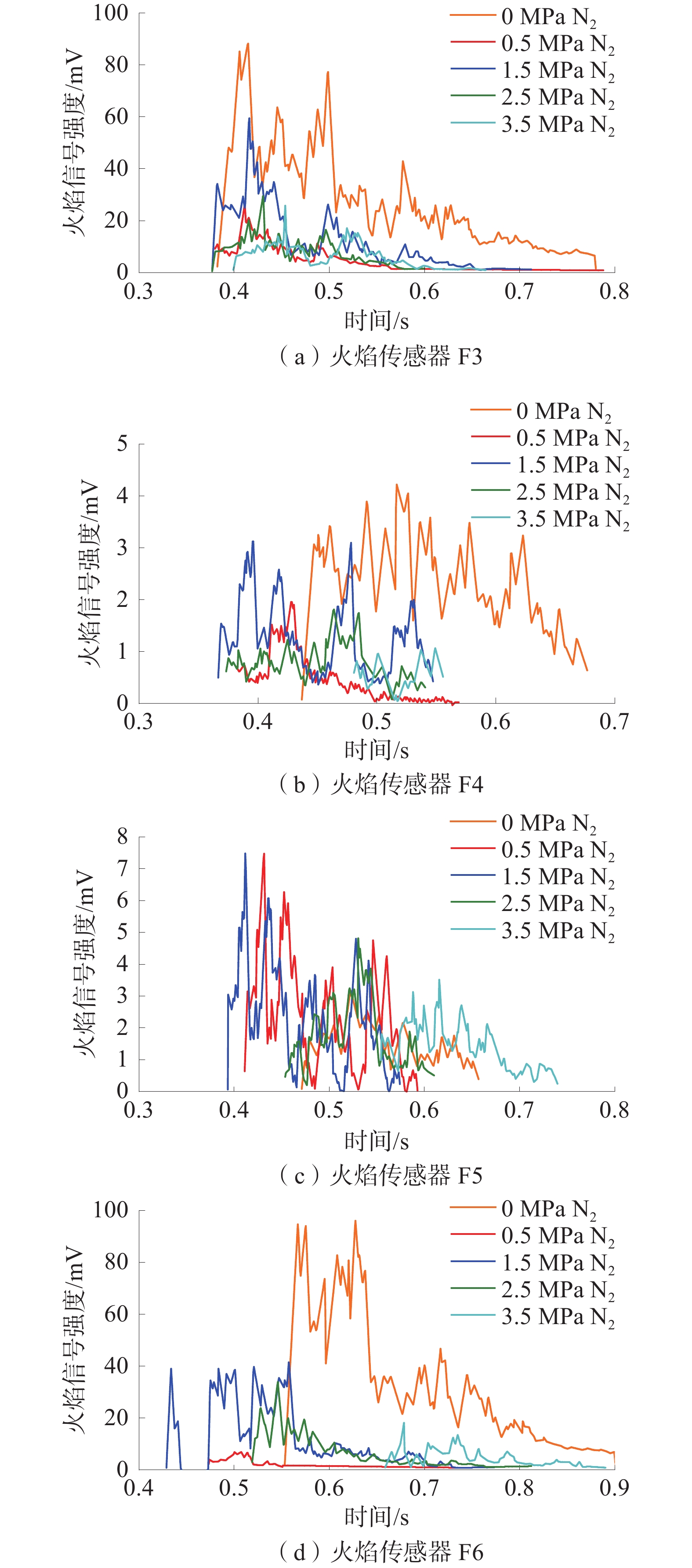
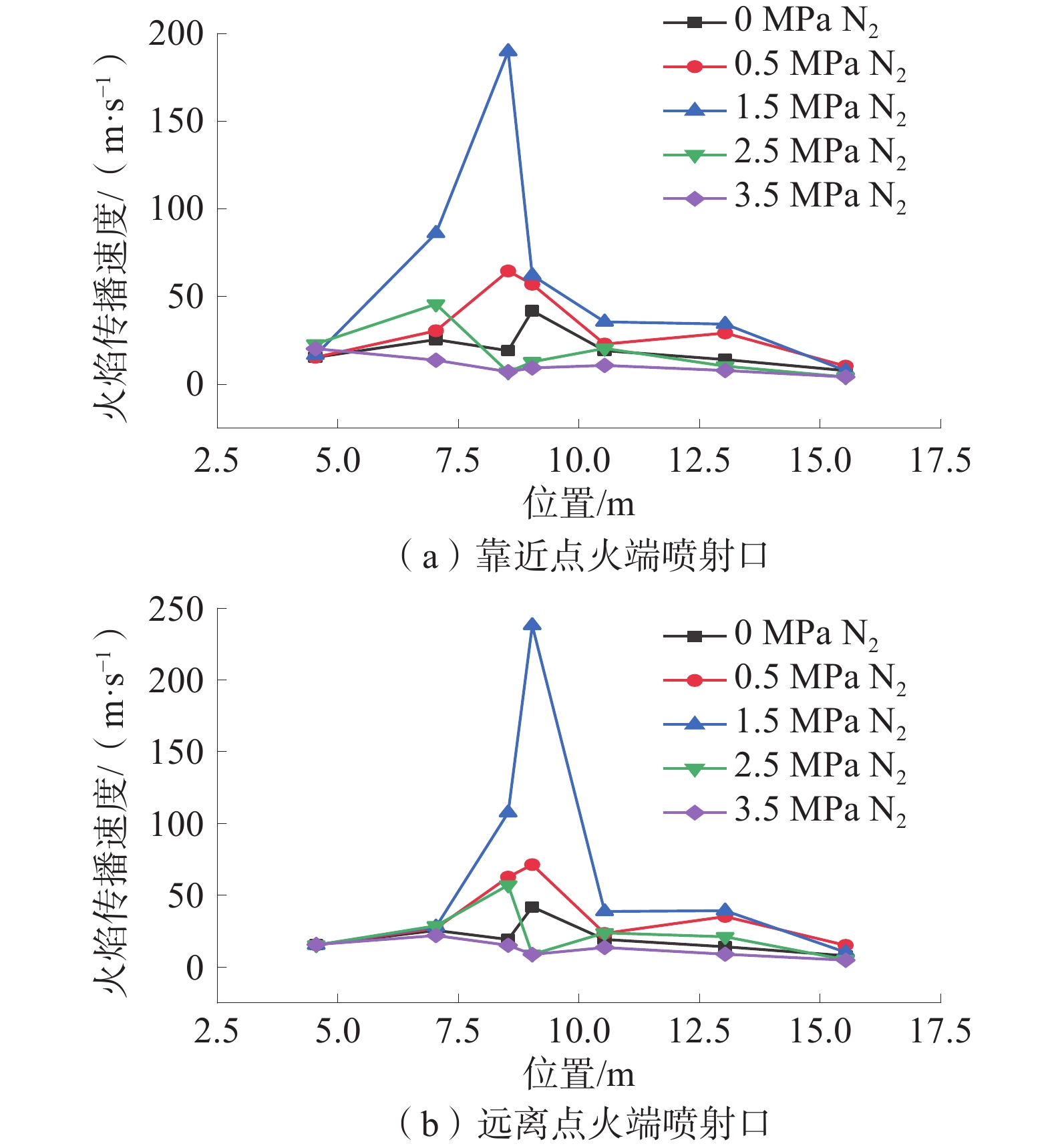
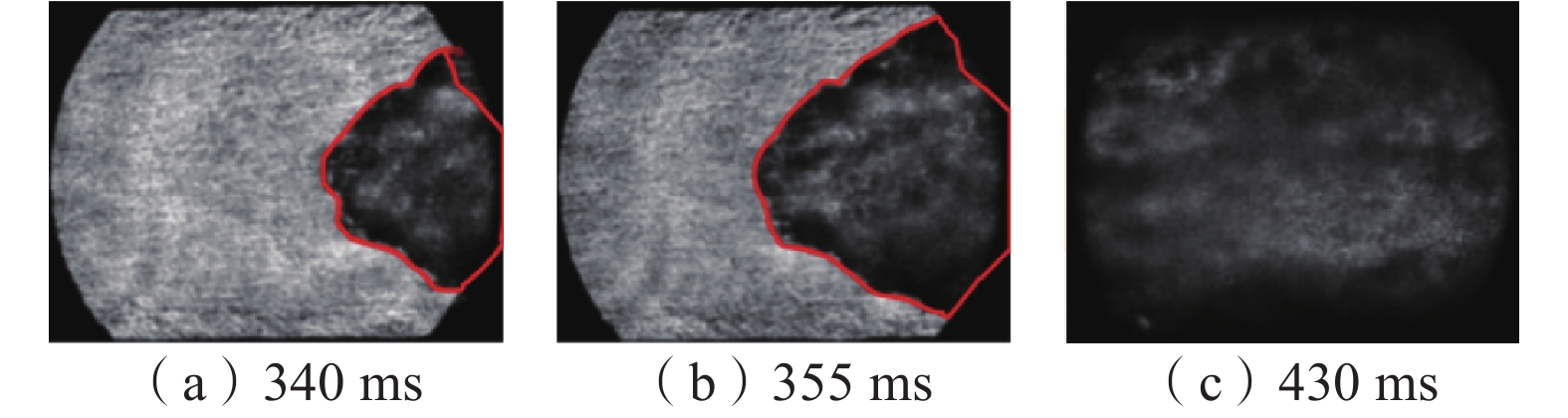
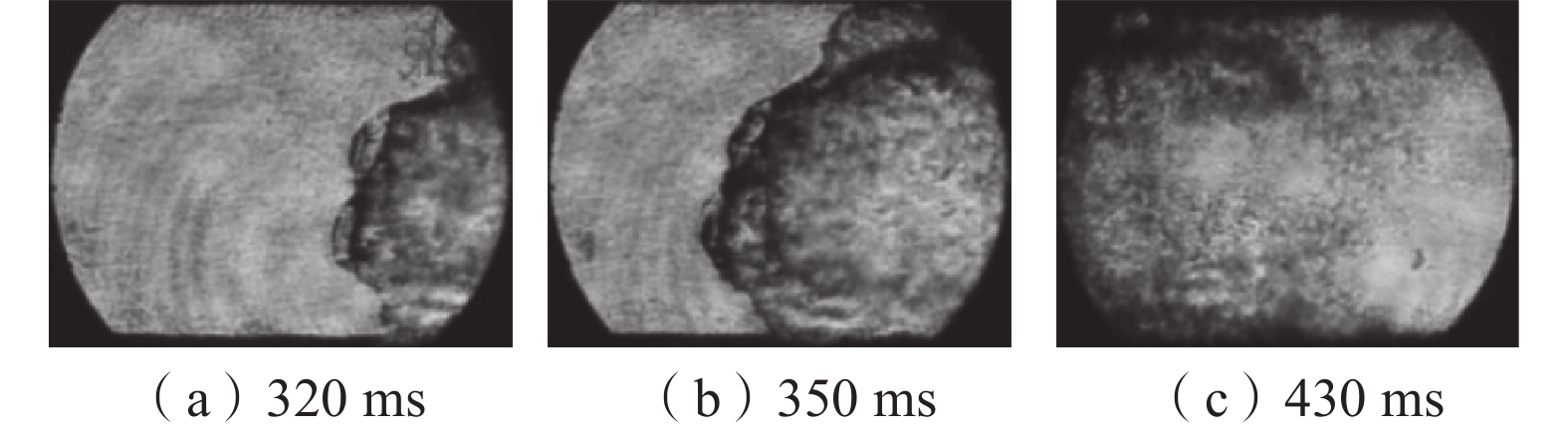
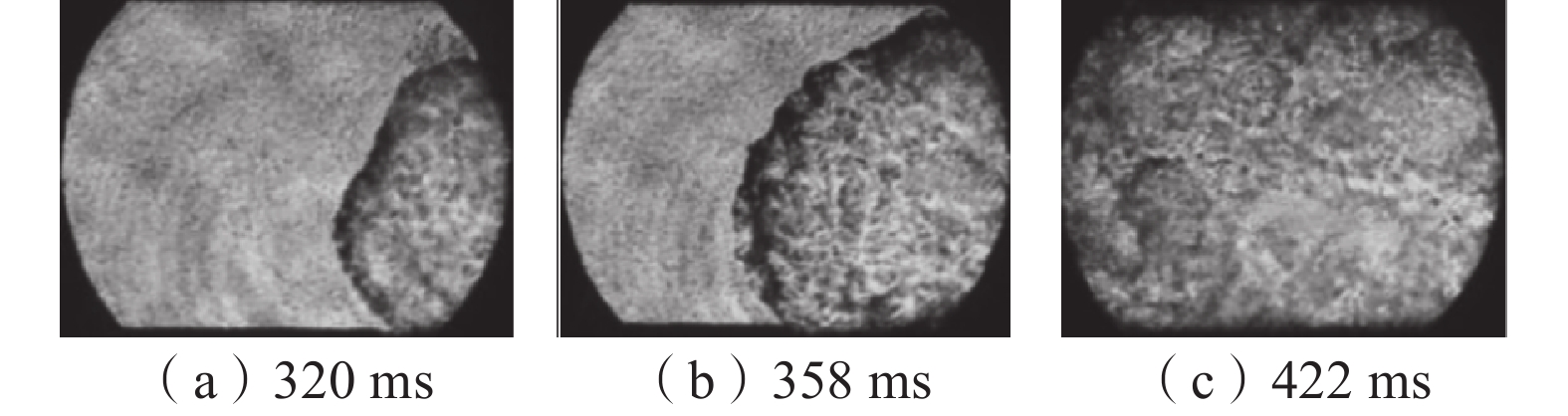
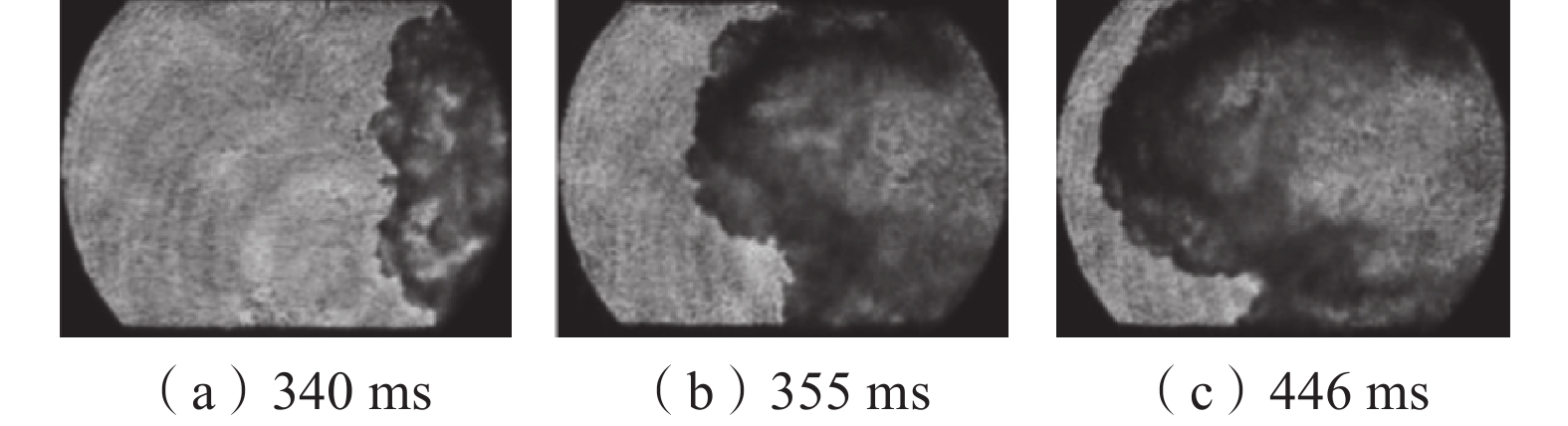
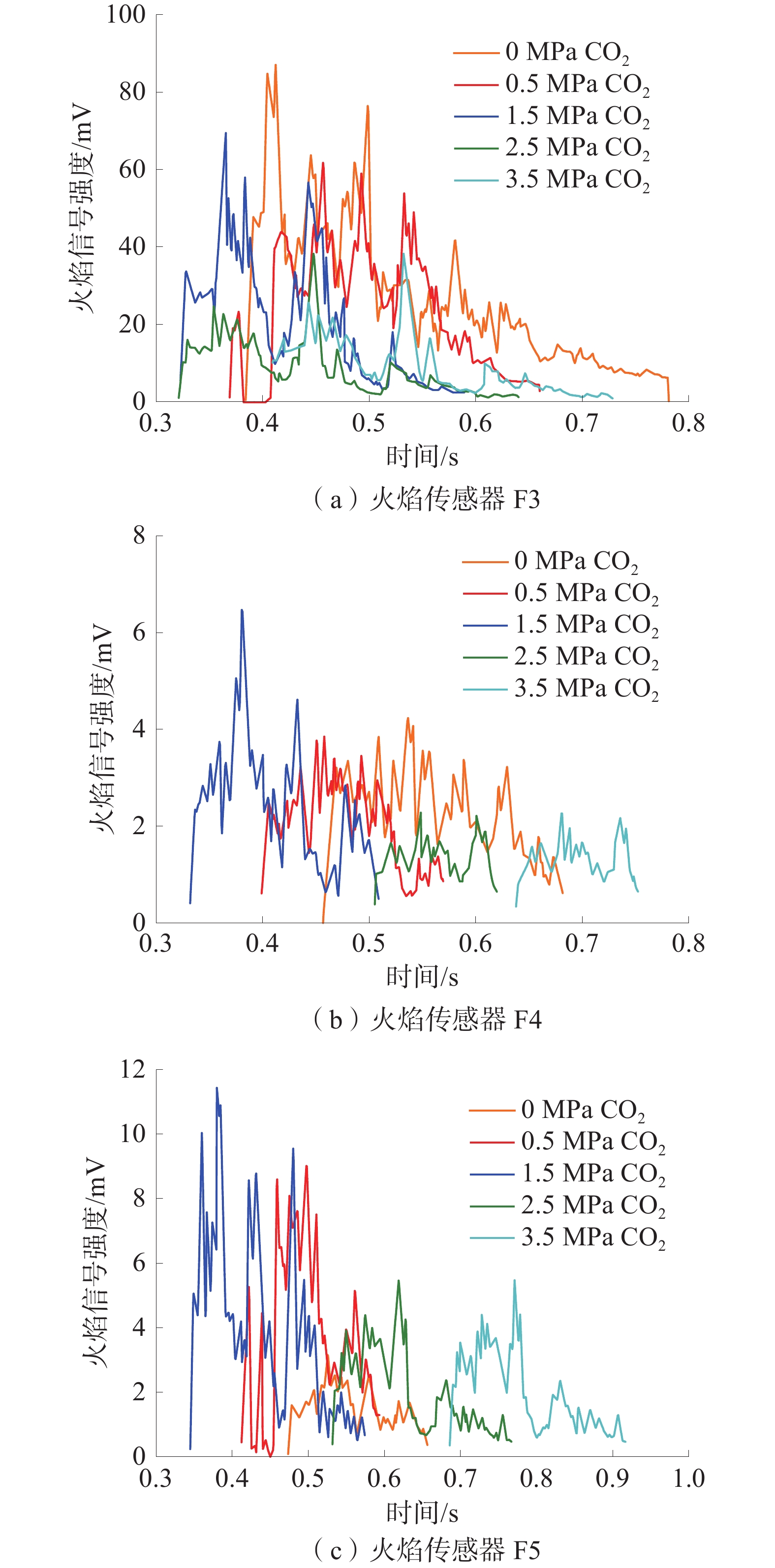
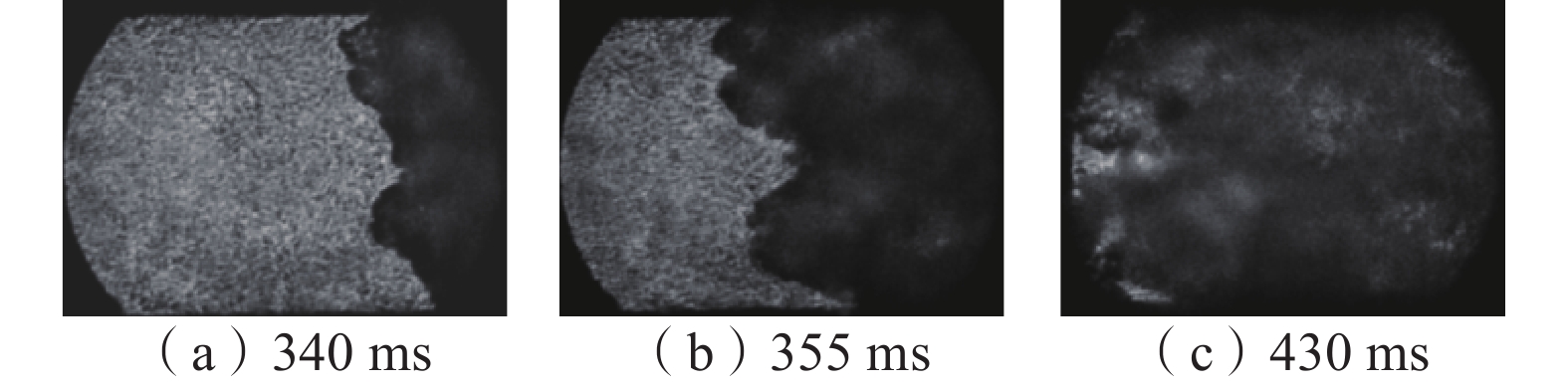
在自主搭建的中尺度爆炸管道上,构建超高速激光纹影测试系统,探究不同喷射位置和压力下N2和CO2抑制瓦斯/空气预混气体爆燃火焰传播特性。结果表明:在惰性气体抑制瓦斯/空气预混气体爆燃实验中,随着喷射压力的逐步增强,火焰传播速度呈现出先增大后减小的趋势,火焰形态也由指尖状逐渐拉伸变形,中部突出部分变小直至呈现近平面状;近点火端喷射CO2时比远离点火端喷射的最高火焰传播速度降低20.79%,喷射N2时降低20.25%,近点火端喷射CO2比远点火端的最低火焰速度低9.68%,喷射N2时降低12.86%;对比2种阻燃抑爆气体,近点火端喷射CO2比喷射N2的最高火焰传播速度低21.78%,最低速度比N2低1.82%;远点火端喷射CO2时的最高火焰速度比N2低21.25%,最低火焰速度比N2低5.27%。
Abstract:In this paper, we continue to build an ultra-high speed laser schlieren testing system on the self-developed mesoscale explosion pipeline to explore the flame propagation characteristics of nitrogen and carbon dioxide inhibiting gas/air premixed gas deflagration under different injection positions and pressures. The results show that: in the experiment of inert gas inhibiting gas/air premixed gas deflagration, with the gradual increase of injection pressure, the flame propagation speed shows a trend of first increasing and then decreasing, the flame shape also gradually stretches and deforms from fingertip shape, and the middle protruding part becomes smaller until it is nearly flat; the maximum flame propagation speed of CO2 injection near the ignition end is 20.79% lower than that of N2 injection far away from the ignition end, and 20.25% lower than that of N2 injection; when CO2 is injected far from the ignition end, the minimum flame speed is 9.68% lower than that of CO2 injection, and 12.86% lower than that of N2 injection; compared with the two kinds of flame retarding and explosion inhibition gases, the highest flame propagation speed of CO2 sprayed near the ignition end is 21.78% lower than that of N2, and the lowest flame propagation speed is 1.82% lower than that of N2. The highest flame velocity and the lowest flame velocity are 21.25% and 5.27% lower than N2 when CO2 is sprayed at the far ignition end.
-
-
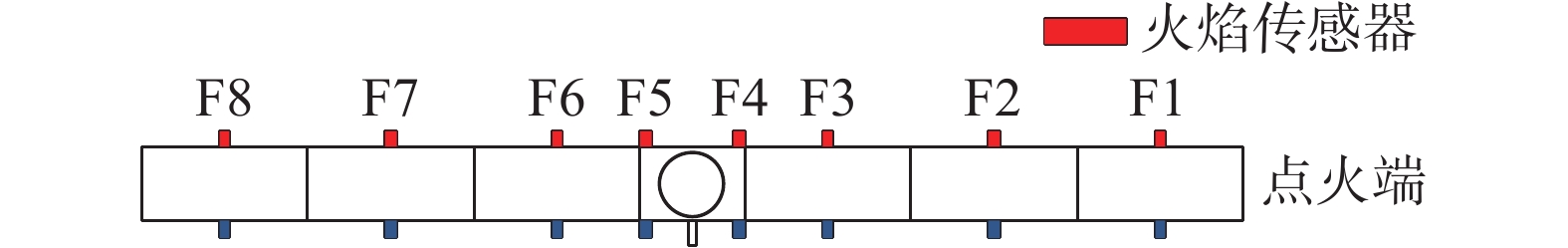
表 1 火焰传感器距点火端的位置
Table 1 Position of flame sensors from ignition end
火焰传感器 距点火端距离/m F1 2.03 F2 4.53 F3 7.03 F4 8.53 F5 9.03 F6 10.53 F7 13.03 F8 15.53 表 2 实验工况设计
Table 2 Design of experimental conditions
实验组 气体喷射压力/MPa 喷射口位置 1 0.5 近点火端 2 0.5 远点火端 3 1.5 近点火端 4 1.5 远点火端 5 2.5 近点火端 6 2.5 远点火端 7 3.5 近点火端 8 3.5 远点火端 -
[1] 徐腾飞,王学兵. 近十年我国低瓦斯煤矿瓦斯爆炸事故统计与规律分析[J]. 矿业安全与环保,2021,48(3):126−130. XU Tengfei, WANG Xuebing. Statistics and regularity analysis of gas explosion accidents in domestic low-gas coal mines in recent ten years[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection, 2021, 48(3): 126−130.
[2] 张培森,牛辉,朱慧聪,等. 2019-2020年我国煤矿安全生产形势分析[J]. 煤矿安全,2021,52(11):245−249. ZHANG Peisen, NIU Hui, ZHU Huicong, et al. Analysis of coal mine safety production situation in China from 2019 to 2020[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021, 52(11): 245−249.
[3] 葛瑛,傅贵. 特别重大瓦斯爆炸事故行为原因及预防策略研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2018,49(10):234−236. GE Ying, FU Gui. Special serious gas explosion accidents and prevention strategy[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2018, 49(10): 234−236.
[4] 朱云飞,王德明,李德利,等. 2000-2016年我国煤矿重特大事故统计分析[J]. 能源与环保,2018,40(9):40−43. ZHU Yunfei, WANG Deming, LI Deli, et al. Statistics analysis of serious coal mine disasters from 2000 to 2016 in China[J]. China Energy and Environmental Protection, 2018, 40(9): 40−43.
[5] 孙超伦,张一民,裴蓓,等. 惰气/赤泥两相抑爆剂抑制瓦斯爆炸试验研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报,2020,30(10):112−118. SUN Chaolun, ZHANG Yimin, PEI Bei, et al. Experimental study on suppression effects of inert gas/red mud two-phase inhibitors on gas explosion[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(10): 112−118.
[6] 王燕,林森,李忠,等. 惰性气体对 KHCO3冷气溶胶甲烷抑爆性能的影响研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(2):145−152. WANG Yan, LIN Sen, LI Zhong, et al. Research on synergistic effect of inert gas on methane explosion suppression performance of KHCO3 cold aerosol[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49(2): 145−152.
[7] 张江,罗振敏,杨忠民. 不同可燃气体影响氮气惰化甲烷爆炸的试验[J]. 安全与环境学报,2019,19(2):494−501. ZHANG Jiang, LUO Zhenmin, YANG Zhongmin. Experimental approach to testing the impact of different flammable gases on the inertion of methane explosion via nitrogen[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2019, 19(2): 494−501.
[8] KRISTOFFERSEN K, VAAGSAETHER K, BJERKETVEDT D, et al. Propane–air pipe explosion experiments. Data for estimation of 1-D burning velocity in slow regimes[J]. Experimental thermal and fluid science, 2004, 28(7): 723−728. doi: 10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2003.12.009
[9] THOMAS G, BAMBREY R, BROWN C. Experimental observations of flame acceleration and transition to detonation following shock-flame interaction[J]. Combustion Theory and Modelling, 2001, 5(4): 573−594. doi: 10.1088/1364-7830/5/4/304
[10] 杨春丽. 受限空间内惰性气体对CH4爆炸抑制特性研究[J]. 安全,2020,41(2):48−54. YANG Chunli. Study on suppression characteristics of methane explosion by inert gases in confined space[J]. Safety & Security, 2020, 41(2): 48−54.
[11] LI Manhou, XU Jingchao, WANG Changjian, et al. Thermal and kinetics mechanism of explosion mitigation of methane-air mixture by N2/CO2 in a closed compartment[J]. Fuel, 2019, 255: 115747. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.115747
[12] 陆卫东,贾宝山,李守国,等. CO2气体对瓦斯爆炸的阻尼效应研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2016,47(9):1−3. LU Weidong, JIA Baoshan, LI Shouguo, et al. Study on damping effect of CO2 on gas explosion[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2016, 47(9): 1−3.
[13] 胡洋,尹尚先,Bjørn J ARNTZEN,等. 瓦斯/空气预混气体爆燃流场测试系统多参数耦合同步控制实验方法[J]. 爆炸与冲击,2019,39(9):121−127. HU Yang, YIN Shangxian, Bjørn J ARNTZEN, et al. Experimental study of multi-objective coupling synchronous control in gas/air premixed gas deflagration flow test system[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2019, 39(9): 121−127.
[14] 胡洋,秦汉圣,庞磊,等. 阻燃剂抑制瓦斯爆燃光学测试实验方案设计[J]. 煤矿安全,2020,51(10):208−212. HU Yang, QIN Hansheng, PANG Lei, et al. Design of optical test experimental scheme for flame retardant to suppress gas deflagration[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2020, 51(10): 208−212.
[15] 胡洋,吴秋遐,张延炜,等. 激光纹影技术在煤矿瓦斯爆燃研究中的应用[J]. 煤矿安全,2021,52(5):66−71. HU Yang, WU Qiuxia, ZHANG Yanwei, et al. Application of laser schlieren technology in the study of gas deflagration in coal mines[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021, 52(5): 66−71.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 唐巨鹏,张昕,潘一山. 煤与瓦斯突出物理模拟试验研究现状及展望. 岩石力学与工程学报. 2024(03): 521-541 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张超林,王培仲,王恩元,许江,李忠辉,刘晓斐,彭守建. 我国煤与瓦斯突出机理70年发展历程与展望. 煤田地质与勘探. 2023(02): 59-94 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张文柯. 基于AHP-MCS的煤与瓦斯突出主控因素分析. 能源技术与管理. 2023(05): 126-127 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: