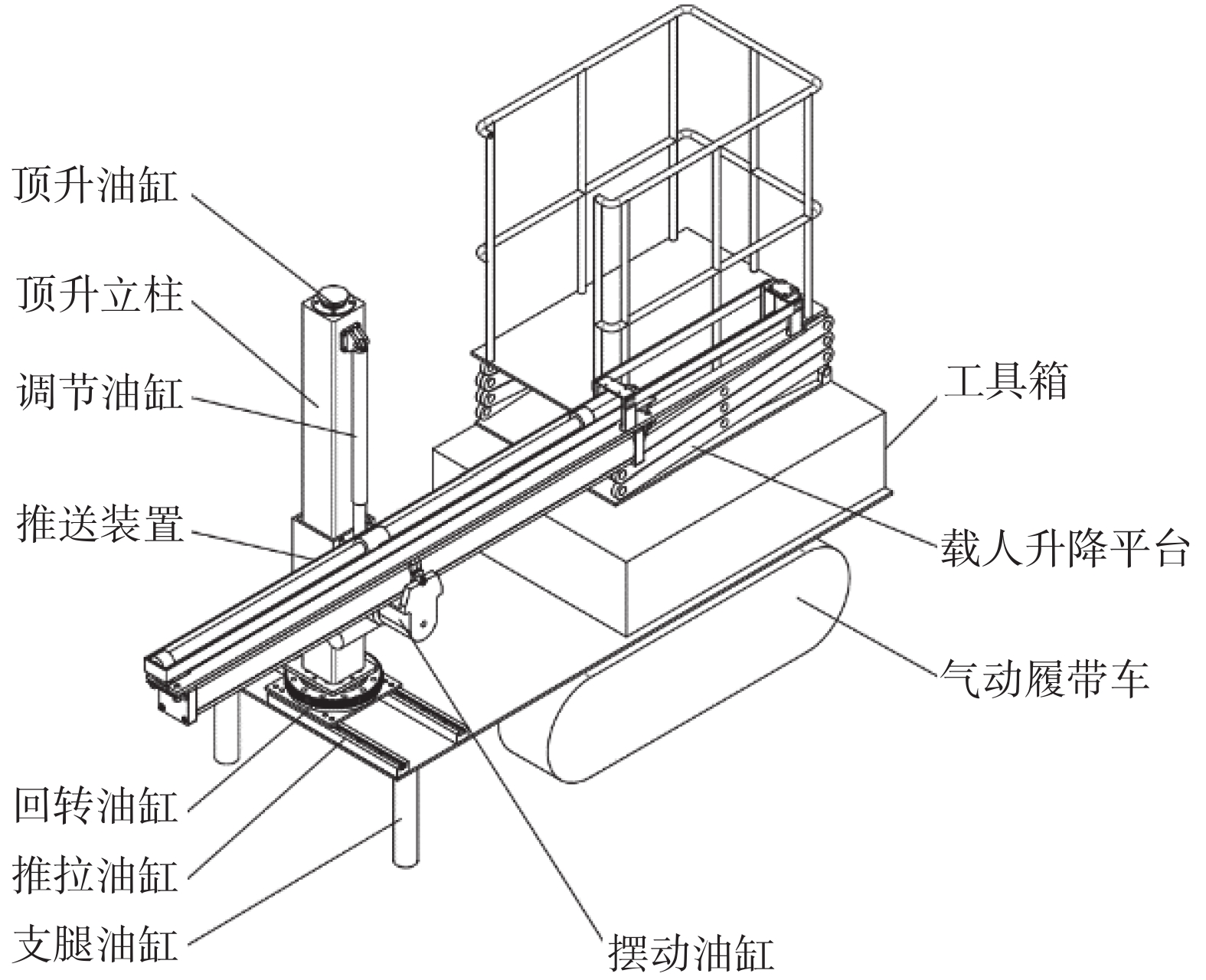
Practice of deep hole blasting and rapid charging technology for composite thick and hard roof
-
摘要:
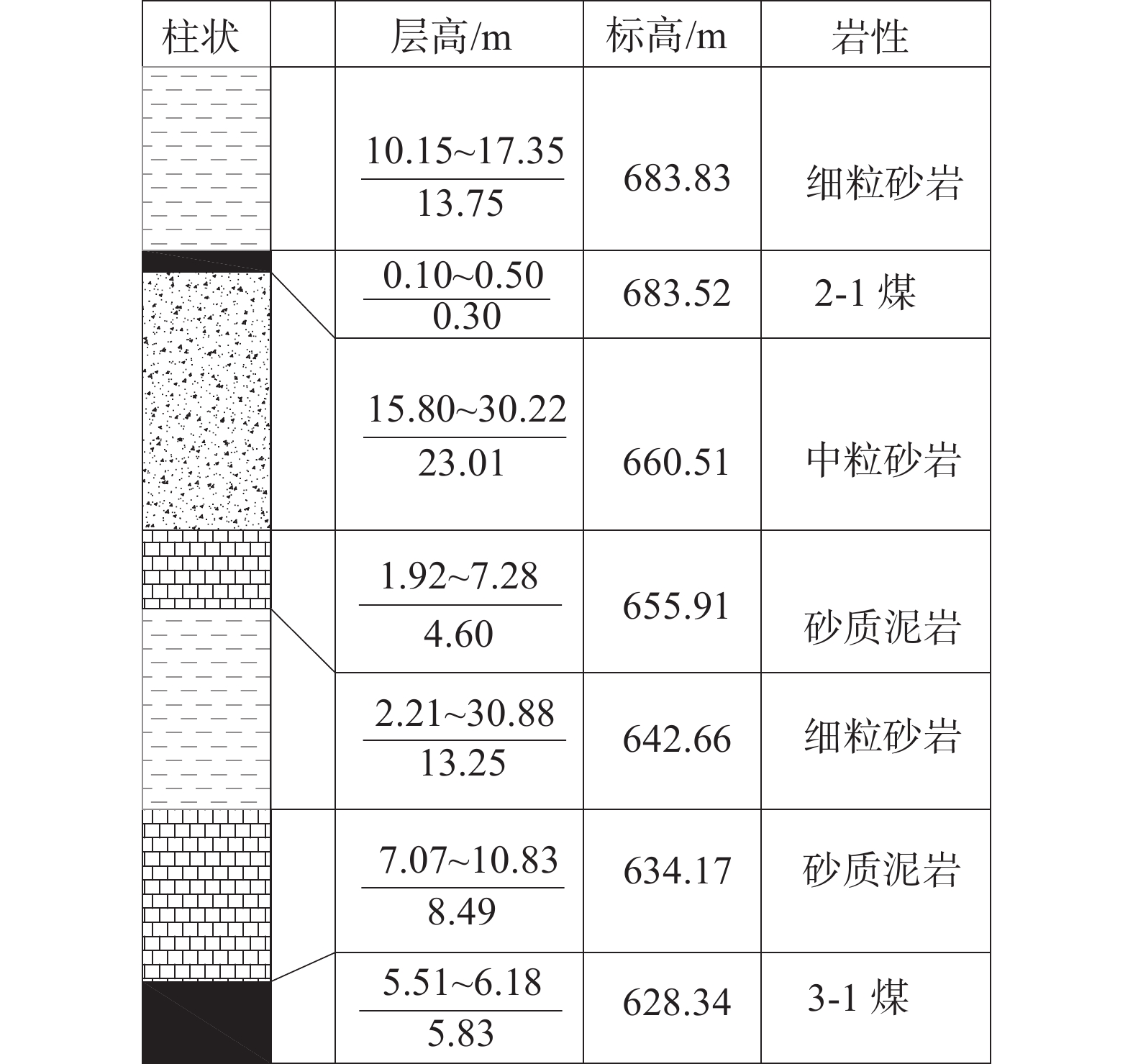
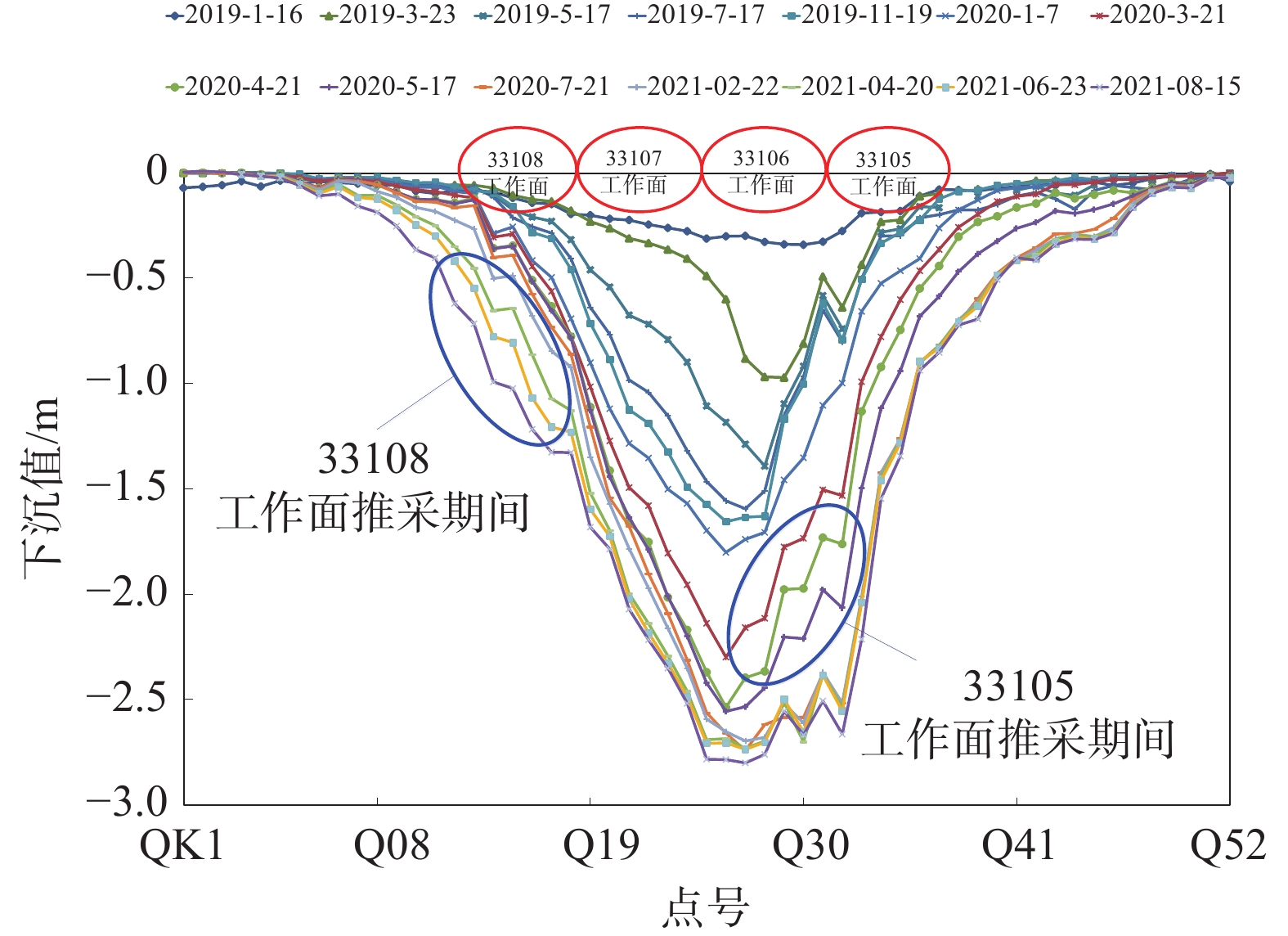
为控制复合厚硬顶板条件下工作面动压显现情况,以鄂尔多斯某矿为例,通过理论分析阐明厚硬顶板小煤柱巷道失稳主要分为变形失稳和冲击失稳,结合微震监测和地表岩移观测分析覆岩运动对动压显现的潜在影响,明确高位顶板预卸压的必要性,在此基础上设计顶板高低位加强爆破方案,并将机械化装药设备投入实践。结果表明:采用机械化装药后,单组装药人数由6人减为3人,超深孔单孔装药时长控制在50 min以内;33109工作面二次“见方”区域微震活动呈现低频低能的趋势,微震事件超前分布范围由238 m降低至168 m,超前影响区域缩小29.4%;支架末阻力整体呈降低趋势,尤其在工作面中部到回风巷一侧范围内下降较为明显;顶板垮落在回风巷一侧能够紧跟端头支架,在运输巷一侧悬顶长度一般不超过5 m。
Abstract:In order to control the dynamic pressure behavior of the working face under the condition of composite thick and hard roof, taking a mine in Ordos as an example, through theoretical analysis, it is clarified that the instability of small coal pillar roadway with thick and hard roof is mainly divided into deformation instability and impact instability. Combined with micro-seismic monitoring and surface rock movement observation, the potential impact of overlying rock movement on dynamic pressure manifestation is analyzed, and the necessity of pre-pressure relief of high roof is clarified. On this basis, a high-low reinforcement blasting scheme for the roof was designed, and mechanized charging equipment was put into practice. The results showed that after using mechanized charging, the number of people in a single group was reduced from 6 to 3, and the duration of single hole charging for ultra-deep holes was controlled within 50 minutes. The micro-seismic activity in the secondary “square” area of the 33109 working face showed a trend of low frequency and low energy. The distribution range of micro-seismic events in advance had decreased from 238 m to 168 m, and the affected area had decreased by 29.4%. The overall resistance at the end of the support showed a decreasing trend, especially within the range from the middle of the working face to the side of the return air channel, where the decrease was more significant. The collapse of the roof on one side of the return airway could closely follow the end support, and the length of the suspended roof on the transport roadway side was generally not more than 5 m.
-
粉尘危害普遍存在于矿山开采、金属加工、建筑材料、隧道挖掘等领域,随着机械化、自动化水平的不断提高,粉尘污染也日益严重[1-2]。目前粉尘治理的方法仍在不断改进[3],这些方法能够实现对全尘浓度的有效控制,但对于呼吸性粉尘等细微粉尘的防治效果不佳[4-5],呼吸性粉尘的监测技术滞后,无法实现呼吸性粉尘的实时监测[6]。通过各种粉尘治理方法煤矿企业一定程度上改善了作业环境,但是呼吸性粉尘浓度仍高于国家相关规定[7]。呼吸性粉尘具有粒径小、逸散能力强、表面积大、容易吸附毒害物质等特点,会随风流分布在作业环境中。并且传统的降尘方法不易使粉尘沉降,给安全生产带来诸多隐患。
目前,我国粉尘防治手段主要为:减尘、降尘、隔尘、排尘和个体防护,现在普遍采用多种防尘技术联合进行综合防尘[8]。其中喷雾降尘是最常用的技术手段[9],许多专家学者对喷雾降尘技术进行了大量的相关研究。传统的高压喷雾是较为常用的降尘方式,能够有效降低粉尘浓度,不过对压力要求较高[10-11]。邬高高等[12]、王健等[13]、马威[14]研究了喷雾压力改变的条件下,雾化角、雾滴粒径、有效射程、耗水量等雾化特性的变化规律,得出压力与降尘率的关系,并对喷雾降尘的压力进行了优化;秦波涛等[15]针对综采工作面高压喷雾降尘提出了活性磁化水雾化封闭尘源的降尘技术,构建了高效降尘工艺系统。
不过,传统喷雾降尘方式产生的雾滴粒径大,对呼吸性粉尘的降尘效果不佳。而雾化技术产生的雾滴粒径小,能够达到十几微米,耗水量相比传统喷雾显著减少、对设备和压力的要求低,对沉降细微粉尘具有很大优势。同时表面活性剂的加入能够降低水的表面张力,促进水雾化成粒径更小的雾滴;又有助于增强雾滴对粉尘颗粒的润湿性,增大对呼吸性粉尘的降尘率。将表面活性剂应用于超声雾化降尘技术,研究不同因素对雾化粒径及降尘效果的影响,对改善作业环境、减少生产危害、降低尘肺病发生率具有重要价值。
为此,设计了超声雾化喷雾实验平台,将阴离子型表面活性剂快渗T应用于超声雾化喷雾技术的研究,通过雾滴粒径实验研究表面活性剂溶液在不同压强组合下的粒径参数变化规律;为超声雾化喷雾降尘技术提供理论指导和依据。
1. 实验部分
1.1 实验平台
雾化粒度测量平台示意图如图1所示。
喷雾实验平台主要由喷雾系统和测量系统组成。喷雾系统主要由喷嘴、柱塞泵、空压机、喷雾管路、调压系统、压力表、流量计、实验架台和连接装置等组成,实验架台为实验室自行搭建,底部为边长1.5 m的正方形,整体尺寸为1.5 m×1.5 m×2.5 m,喷嘴通过支架固定在实验架台2.2 m高中心点处。测量系统主要由Winner318A激光粒度分析仪和计算机组成。
1.2 实验设备及仪器
1)实验采用东莞市华嶥喷雾技术有限公司生产的流体性超声雾化喷嘴,喷嘴型号SK508,喷雾角度为80°,喷嘴由喷头和底座2部分组成。在喷嘴底座的侧面和下部分别设有进水口和进气口,接口螺纹为G1/8和G1/4;喷头部分包含混合室和共振腔(超声波发生器),共振腔由钢丝支架连接混合室末端固定于喷嘴出口前方。该超声雾化喷嘴的雾化过程分为2个阶段:①在喷嘴内部液体与压缩空气混合在压力的作用下初步雾化,形成水喷雾喷出喷嘴;②喷出的高速雾滴撞击喷嘴前端的超声波发生器,雾滴在超声波的作用下再次发生破碎、雾化,形成的粒径更小也更为均匀雾滴。
2)激光粒度分析仪。实验采用济南微纳颗粒仪器股份有限公司生产的Winner318A工业激光粒度分析仪测量喷雾粒径。
3)柱塞泵和空压机。实验水压和气压范围均在0.1~0.6 MPa,调节间距为0.1 MPa。所选用高压柱塞泵可提供0~7 MPa的工作压力,空压机的使用压力为0.8 MPa,气罐容量为95 L,能够满足实验喷嘴的供气要求。
1.3 实验方案
实验所选用的表面活性剂为快渗T溶液,溶液浓度为0.07%,研究溶液在不同压强组合下超声雾化喷雾粒径参数的变化情况,使用Winner318A工业激光粒度分析仪对雾化粒度进行测量,测量的粒径参数有D10、D50、D90、VAD、SMD、NAD、Δs。其中:D10、D50、D90分别为粒径第10、第50、第90百分位数;VAD为体积加权平均粒径;SMD为表面积加权平均粒径;NAD为数量加权平均粒径;Δs(Δs=D90−D10)为雾滴粒径跨度,实质是雾滴粒径分布的极差,可表征雾滴粒径分散程度,Δs越小则雾滴粒径跨度越小,雾滴粒径分布越均匀。参照相关研究学者的测试参数,选取距离喷嘴口出下方60 cm处为喷雾雾滴粒径测点,激光发射仪和接收仪的距离为500 cm。喷雾实验参数为:①实验药品为快渗T;②溶液浓度0.07%;③气压0.1、0.2、0.3、0.4、0.5、0.6 MPa;④水压0.1、0.2、0.3、0.4、0.5、0.6 MPa;⑤测定参数D10、D50、D90、VAD、NAD、SMD、Δs;⑥风速0 m/s。
2. 实验结果
不同气压条件下超声雾化喷嘴雾滴粒径随水压变化情况如图2所示,不同气压条件下水压从0.1 MPa提高到0.6 MPa时粒径参数变化量见表1。
表 1 不同气压条件下水压从0.1 MPa提高到0.6 MPa时粒径参数变化量Table 1. Variation of particle size parameters when water pressure increases from 0.1 MPa to 0.6 MPa under different air pressure conditions气压/MPa ΔD10/μm ΔD50/μm ΔD90/μm ΔVAD/μm ΔSMD/μm ΔNAD/μm 0.1 16.034 19.082 24.307 19.364 18.780 17.633 0.2 23.005 19.348 10.123 17.704 20.820 25.927 0.3 31.121 32.447 29.928 31.189 33.537 36.804 0.4 25.883 40.069 61.325 42.276 37.971 30.479 0.5 22.614 35.494 54.751 37.441 33.625 26.908 0.6 5.0480 7.5890 11.260 7.9210 7.2630 6.0640 由图2可知:当气压为0.1、0.3、0.5 MPa时,D10、D50、D90、VAD、SMD、NAD均随着水压的增加而整体上呈现增大的趋势;当气压为0.2 MPa时,且水压为0.1~0.5 MPa的范围内,D50、D90、VAD、SMD均随着水压的增加而整体上呈现增大的趋势;同样地,当气压为0.6 MPa时,导致气压向相反变化趋势的水压拐点为0.4 MPa;此外,粒径参数D10、D50、VAD、SMD、NAD变化一致,Δs与D90变化一致。
由表1可知:在0.07 %表面活性剂状态下,当气压不变时,随着水压的增加D10、D50、D90、VAD、SMD、NAD值均增大;随着气压的增加,当水压从0.1 MPa提高到0.6 MPa时D10、D50、D90、VAD、SMD、NAD粒径增加量整体变化趋势相同,其中D10和NAD粒径增加量呈现高度一致,D50、VAD、SMD粒径增加量呈现高度一致。
不同水压条件下超声雾化喷嘴雾滴粒径随气压变化如图3所示,不同水压条件下气压从0.1 MPa提高到0.6 MPa时粒径参数变化量见表2。
表 2 不同水压条件下气压从0.1 MPa提高到0.6 MPa时粒径参数变化量Table 2. Variation of particle size parameters when air pressure increases from 0.1 MPa to 0.6 MPa under different water pressure conditions水压/MPa ΔD10/μm ΔD50/μm ΔD90/μm ΔVAD/μm ΔSMD/μm ΔNAD/μm 0.1 31.129 44.607 63.397 46.277 42.971 36.982 0.2 36.131 46.674 60.409 47.590 45.729 42.220 0.3 39.683 49.416 61.478 50.132 48.723 46.011 0.4 39.657 50.918 65.406 51.862 50.050 46.542 0.5 41.097 53.983 71.102 55.203 52.758 48.183 0.6 42.115 56.100 76.444 57.720 54.488 48.551 由图3可知:在0.07%表面活性剂状态下,当水压不变时,D10、D50、D90、VAD、SMD、NAD整体粒径均呈现出随着气压的增加而减少;各水压状态下,随气压的变化,D10、D50、D90、VAD、SMD、NAD几种参数粒径的变化呈现出一致性,且D10< NAD < SMD <D50< VAD <D90,Δs在气压较小时小于D10,随着气压的增大Δs呈现出先增大再减小的变化。
由表2可知:在0.07%表面活性剂状态下,当水压不变时,随着气压的增加D10、D50、D90、VAD、SMD、NAD值均减小;随着气压的增加,当水压从0.1 MPa提高到0.6 MPa时D10、D50、D90、VAD、SMD、NAD粒径增加量整体变化趋势相同,D90粒径减小量变化幅度最大,随着水压的增加呈现出先减小再增加的趋势,D10粒径减小量变化幅度最小,其中D10和NAD粒径减小量呈现高度一致,D50、VAD、SMD粒径减小量呈现高度一致。
3. 工程应用
华晋吉宁煤业有限责任公司大规模开采矿井的开采、开拓强度大,煤尘产生量及粉尘的危害严重,大型设备摩擦火花造成瓦斯煤尘的潜在危险性大,粉尘污染状况严重。高强度开采的综采工作面割煤机司机处粉尘浓度达800 mg/m3以上;工作面支架后6 m人行道粉尘浓度高达2 912 mg/m3,单呼吸性粉尘浓度也高达到1 146 mg/m3。此外,在大规模开采时,仅采煤工作面下巷各转载点所产生的粉尘就可使综采工作面粉尘达500 mg/m3。亟须解决生产过程中的粉尘防治问题。
综掘工作面粉尘浓度的测定操作步骤如下:①关闭综掘工作面所有的防尘设备,测定现场各工序的原始粉尘浓度,并以此结果作为计算除尘系统降尘率的基础;②开启喷雾降尘系统,测定现场各工序的粉尘浓度,并计算降尘效率。
华晋吉宁煤业在工作面现场对1#、2#、3#、4#、5#、6#测点(各测点相距离9 m,测点高度2.5 m,其中6#测点距掘进头45m)分别进行粉尘浓度测量,测量结果均为3次测量的平均值。未采取防尘措施时工作面现场各测点粉尘浓度数据见表3,采取喷雾降尘措施后工作面现场各测点粉尘浓度数据见表4。
表 3 未采取防尘措施时工作面现场各测点粉尘浓度数据Table 3. Dust concentration data of each measuring point in working face without dustproof measures测点 粉尘浓度/(mg·m−3) 全尘 呼尘 1# 1306.20 443.71 2# 1 121.73 369.56 3# 1 049.62 343.37 4# 1 093.79 375.54 5# 588.23 204.61 6# 467.31 148.69 表 4 采取喷雾降尘措施后工作面现场各测点粉尘浓度数据Table 4. Dust concentration data of each measuring point on working face after adopting spray dust-reduction measures测点 粉尘浓度/(mg·m-3) 全尘 呼尘 1# 81.23 80.26 2# 77.54 78.73 3# 78.26 77.85 4# 96.37 95.87 5# 82.59 82.36 6# 97.22 96.64 由表3和表4可知:对吉宁煤业某综掘工作面在未采取任何防尘措施时,掘进头处的粉尘浓度最高,该处全尘和呼尘浓度的平均值分别高达1 306.2 mg/m3和443.71 mg/m3,综掘工作面其余测点的粉尘浓度也较高,粉尘浓度最低的测点6#处(距掘进头处45 m左右),全尘和呼尘浓度的平均值也分别高达467.31 mg/m3和148.69 mg/m3;开启喷雾降尘系统后,工作面现场各测点的粉尘浓度相对于未采取任何防尘措施时均大大降低,喷雾后各测点全尘和呼尘的平均沉降率分别达到89.29%和67.86%,说明喷雾设备对巷道中漂浮粉尘捕捉沉降作用非常明显。
4. 结 语
分析了表面活性剂快渗T溶液浓度为0.07%时,不同气压和水压组合下,超声雾化喷雾粒径参数的变化情况。采用直观分析的方法分析了雾滴粒径与气压和水压的关系,得出各项参数变化规律。
1)粒径参数D10、D50、D90、VAD、SMD、NAD随着气压的增加而减小,减小幅度受到水压影响;随着水压的增加而增大,增大幅度也会受到气压影响,气压对雾滴粒径变化的影响程度大于水压,Δs随压力的改变无明显变化规律。
2)当压力改变时,粒径参数D10和NAD的变化趋势呈现高度一致,D50、VAD、SMD粒径增加量呈现高度一致,总体上D90变化幅度最大,D10变化幅度最小。
3)0.07%表面活性剂浓度时,随着气压的增加,当水压从0.1 MPa提高到0.6 MPa时,各粒径参数的增加量整体变化相同,且呈现出先增大再减小的趋势;随着水压的增加,各粒径参数的减少量变化趋势一致并呈现增大趋势,各粒径参数的减少量排序为D10< NAD < SMD<D50< VAD<D90。喷雾系统在工程应用时降尘效果显著,对巷道中漂浮粉尘捕捉沉降作用非常明显。
-
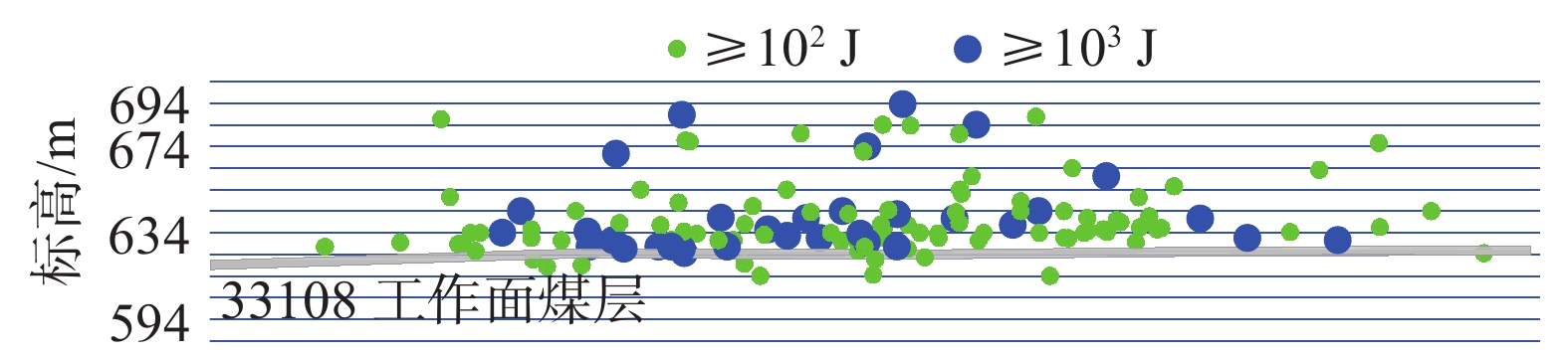
表 1 33109工作面微震监测统计
Table 1 Micro-seismic monitoring statistics of 33109 working face
区段/
m产量/
万t总能量/
kJ总频次 最大
能量/
kJ万吨
煤释放
能量/
kJ万吨
煤释放
频次0~550 105.0 1860 3410 7.5 18 32.5 550~650 19.2 350 300 6.6 18 19.6 -
[1] 赵善坤. 深孔顶板预裂爆破力构协同防冲机理及工程实践[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(11):3419−3432. ZHAO Shankun. Mechanism and application of force-structure cooperative prevention and control on rockburst with deep hole roof pre-blasting[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(11): 3419−3432.
[2] 赵善坤,赵阳,王寅,等. 采动巷道侧向高低位厚硬顶板破断模式试验研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(4):111−120. ZHAO Shankun, ZHAO Yang, WANG Yin, et al. Experimental study on fracture mode of lateral high and low thick and hard roof in mining roadway[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49(4): 111−120.
[3] 张广辉,蒋军军,邓志刚,等. 双巷掘进留小煤柱护巷下深浅孔组合爆破卸压技术研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(11):33−40. ZHANG Guanghui, JIANG Junjun, DENG Zhigang, et al. Research on pressure relief technology of deep and shallow hole combined blasting under retaining small coal pillar in double roadway excavation[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2023, 51(11): 33−40.
[4] 韩刚,窦林名,张寅,等. 沿空巷道动力显现影响机制与防治技术研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2021,38(4):730−738. HAN Gang, DOU Linming, ZHANG Yin, et al. Influence mechanism and prevention technology of dynamic manifestation of roadway along goaf[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2021, 38(4): 730−738.
[5] 毕慧杰,邓志刚,李少刚,等. 深孔爆破在小煤柱巷道顶板控制中的应用[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(3):85−91. BI Huijie, DENG Zhigang, LI Shaogang, et al. Application of deep hole blasting in roof control of small coal pillar roadway[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2022, 50(3): 85−91.
[6] 黄志增,高晓进,袁伟茗,等. 深孔预裂爆破沿空留巷技术及顶板应力分布规律[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(S2):88−96. HUANG Zhizeng, GAO Xiaojin, YUAN Weiming, et al. Stress distribution of cutting roof with deep borehole blasting for gob-side entry retaining techonolgy[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2022, 50(S2): 88−96.
[7] 张俊文,董续凯,柴海涛,等. 厚煤层一次采全高低位厚硬岩层垮落致冲机理与防治[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(2):734−744. ZHANG Junwen, DONG Xukai, CHAI Haitao, et al. The mechanism and prevention of rock burst caused by the collapse of low-level thick hard rock seam at full mining height in thick coal seam[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(2): 734−744.
[8] 解嘉豪,韩刚,孙凯,等. 邻空巷坚硬顶板预裂爆破防冲机理及效果检验[J]. 煤炭学报,2023,48(5):2078−2091. XIE Jiahao, HAN Gang, SUN Kai, et al. Rockburst prevention mechanism and effect test of blast presplitting of hard roof in gob-side roadway[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2023, 48(5): 2078−2091.
[9] 白俊杰. 回撤通道防冲断顶爆破设计方案优化及应用[J]. 煤炭工程,2022,54(11):73−78. BAI Junjie. Design optimization of roof-cutting blasting scheme in withdrawal channel for rockburst prevention[J]. Coal Engineering, 2022, 54(11): 73−78.
[10] 秦喜文,牟亮,韩刚,等. 双回撤通道冲击地压防治技术研究与应用[J]. 煤炭工程,2022,54(3):73−78. QIN Xiwen, MOU Liang, HAN Gang, et al. Research and application of rock burst prevention technology with double withdrawal channels[J]. Coal Engineering, 2022, 54(3): 73−78.
[11] 杨仁树,李成孝,陈骏,等. 我国煤矿岩巷爆破掘进发展历程与新技术研究进展[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(1):224−241. YANG Renshu, LI Chengxiao, CHEN Jun, et al. Development history and new technology research progress of rock roadway blasting excavation in coal mines in China[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2023, 51(1): 224−241.
[12] 何东升,刘旦龙,张洋. 复合顶板中厚煤层切顶卸压留巷无煤柱开采技术[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2018,46(9):126−132. HE Dongsheng, LIU Danlong, ZHANG Yang. Non-pillar mining technology of medium thick seam with roof cutting and pressure released retained gateway and complex roof[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2018, 46(9): 126−132.
[13] 杨战标,赵万里,丁坤朋,等. 定向爆破技术在沿空留巷中的应用[J]. 煤炭工程,2020,52(11):52−56. YANG Zhanbiao, ZHAO Wanli, DING Kunpeng, et al. Application of directional blasting in gob-side entry retaining[J]. Coal Engineering, 2020, 52(11): 52−56.
[14] 张选山,王海亮,孙中博,等. 单向荷载下不耦合装药预裂爆破效果研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2021,52(2):214−218. ZHANG Xuanshan, WANG Hailiang, SUN Zhongbo, et al. Study on effect of decoupling charge pre-splitting blasting under unidirectional load[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021, 52(2): 214−218.
[15] 胡亚超,熊祖强,王春,等. 煤层顶板深孔预裂爆破高效封孔材料及工艺研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(4):30−36. HU Yachao, XIONG Zuqiang, WANG Chun, et al. Research on high-efficiency sealing material and technology of coal roof deep-hole pre-splitting blasting[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2023, 51(4): 30−36.
[16] 路晓荣,李西凡,熊祖强,等. 新型深孔爆破快速封孔材料及封孔新工艺[J]. 煤矿安全,2020,51(9):148−152. LU Xiaorong, LI Xifan, XIONG Zuqiang, et al. New rapid sealing material of deep hole blasting and its process[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2020, 51(9): 148−152.
[17] 王恩元,冯俊军,张奇明,等. 冲击地压应力波作用机理[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(1):100−110. WANG Enyuan, FENG Junjun, ZHANG Qiming, et al. Mechanism of rockburst under stress wave in mining space[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(1): 100−110.
[18] 李鹏. 厚硬顶板冲击地压发生机理及防治实践[J]. 煤矿安全,2023,54(5):211−216. LI Peng. Mechanism and prevention practice of rock burst in thick and hard roof[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2023, 54(5): 211−216.




 下载:
下载: