Research on directional control blasting technology around the rock roadway of Fangezhuang Mine
-
摘要:
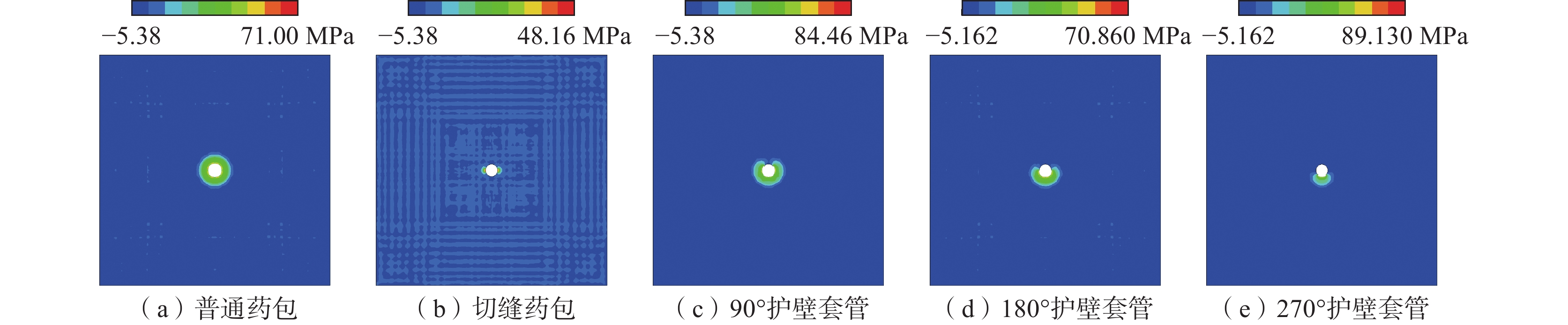
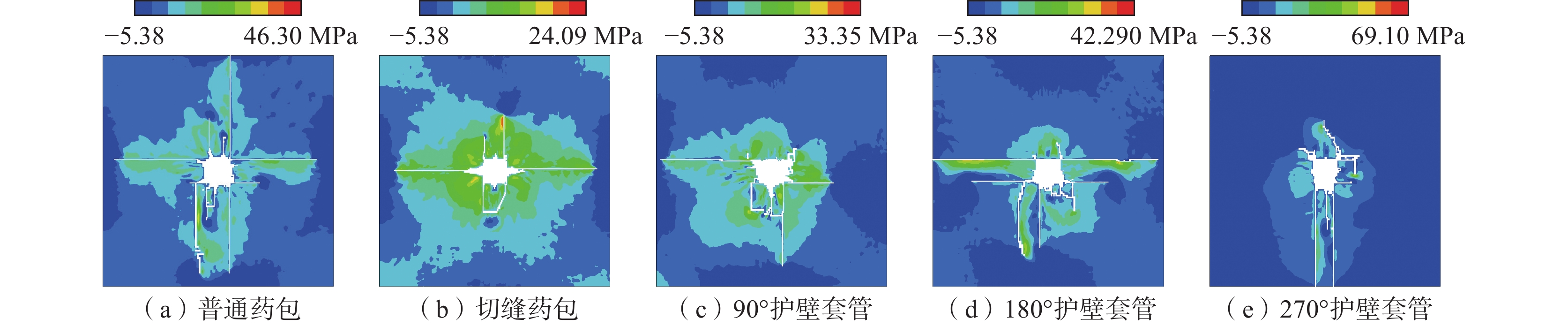
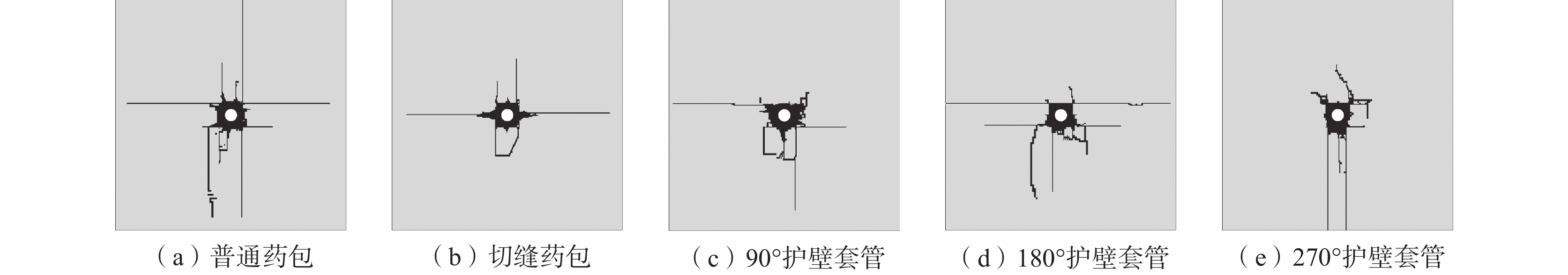
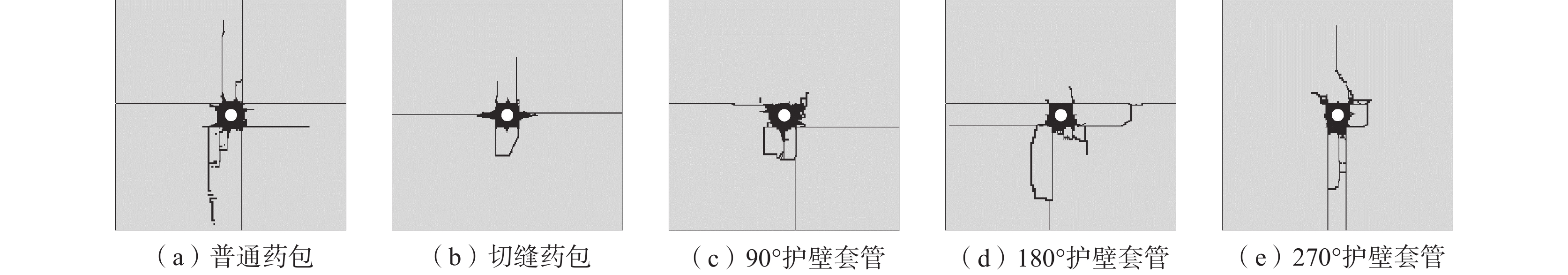
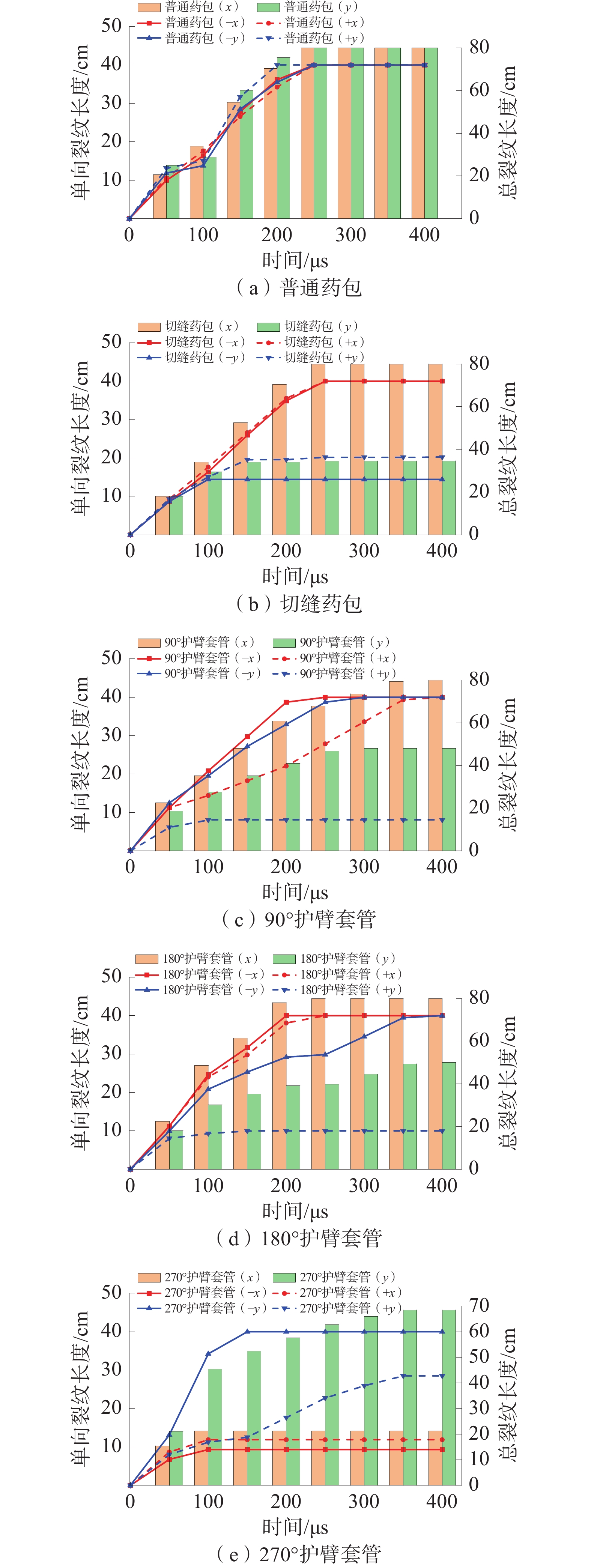
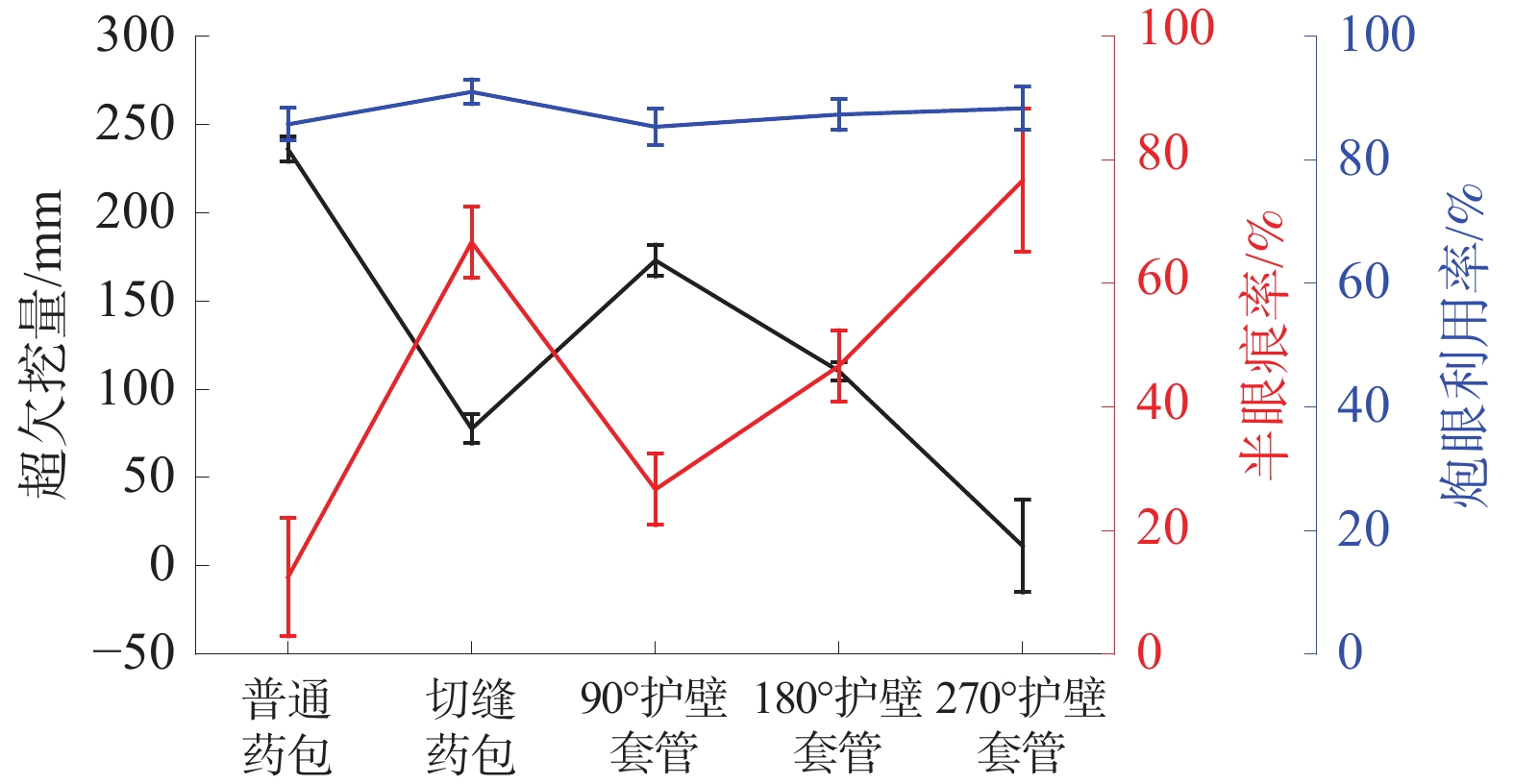
为解决范各庄矿岩巷钻爆法掘进过程中超挖、周边成型效果较差的问题,通过室内试验测定了围岩的物理力学参数并标定了HJC本构模型参数,通过数值模拟对比了岩石在普通药包、切缝药包、90°、180°、270°护壁套管作用下的爆生裂纹扩展规律,通过工程试验对比了不同控制爆破技术在周边眼的应用效果。数值模拟结果表明:切缝药包在切缝方向可以较好地实现定向断裂爆破,非切缝方向的裂纹长度减小了56.71%;护壁套管的弧度对粉碎区和径向裂纹的分布有较大影响,90°、180°护壁套管的护壁侧裂纹长度分别减小了79.9%和75.1%,270°护壁套管的护壁侧裂纹平均长度减小了58.57%;爆炸荷载对临空侧的岩石产生了更多损伤。工程试验结果表明:切缝药包和护壁套管均能在一定程度上起到定向控制爆破的作用;与普通药包相比,使用切缝药包的平均超挖量减少158.33 mm,3种弧度护壁套管对应的平均超挖量分别减少63.00、125.67、224.67 mm;半眼痕率随着护壁套管弧度的增大而提高,通过调整护壁套管的弧度可以改善周边眼的成型效果。
Abstract:In order to solve the problem of over excavation and poor surrounding shaping effect during the drilling and blasting of the rock roadway in Fangezhuang Mine, through indoor experiments, the physical and mechanical parameters of the surrounding rock were determined, and the HJC constitutive model parameters were calibrated. Through numerical simulation, the crack propagation laws of the rock under the action of ordinary explosives, slotted cartridge, 90°, 180°, and 270° protective wall casings were compared. The application effects of different control blasting techniques on peripheral eyes were compared through engineering experiments. The numerical simulation results show that the slotted cartridge can achieve directional fracture blasting well in the cutting seam direction, and the crack length in the non cutting seam direction is reduced by 56.71%. The curvature of the protective casing has a significant impact on the distribution of crushing zone and radial cracks. The crack length on the protective wall side of the 90° and 180° protective sleeves is decreased by 79.9% and 75.1%. The average length of cracks on the protective wall side of the 270° protective sleeve is decreased by 58.57%. The explosion load caused more damage to the rocks on the side of goaf. The engineering test results show that both the slotted cartridge and the protective wall casing can play a role in directional control blasting to a certain extent. Compared with ordinary explosives, the use of slotted cartridge reduces the amount of average over excavation by 158.33 mm. The average over excavation amount corresponding to the three types of curved wall protection sleeves is reduced by 63 mm, 125.67 mm, and 224.67 mm. The half eye mark rate increases with the curvature of the protective wall sleeve, and adjusting the curvature of the protective wall sleeve can improve the forming effect of the peripheral eyes.
-
采动诱发覆岩裂隙贯穿覆岩隔水层,极易造成生态水资源破坏和矿井水害,对生态环境的破坏尤为明显。钱鸣高[1]提出了煤矿绿色开采的理念,认为保水开采是绿色开采中的一项重要内容。目前相关学者对导水裂隙带发育规律进行了大量的研究,提出了隔水层隔水性不受破坏是保水开采的关键[2-5],揭示了煤层赋存条件、开采方法、开采参数及关键层位置对导水裂隙带发育高度的影响[6-18],通过理论分析、数学软件模拟及对大量实测数据的分析,总结了多种导水裂隙带发育高度理论预计方法,构建了导水裂隙带发育高度预测模型[15-21]。覆岩导水裂隙带发育高度与覆岩移动变形息息相关,虽然前人已对导水裂隙带发育高度进行了大量研究,但将覆岩移动变形与覆岩导水裂隙带发育高度有机结合方面研究相对较少。为此,基于前人研究成果,以小保当矿区2−2号煤层为研究对象,通过理论分析、相似模拟实验和实例验证的方法研究导水裂隙带动态发育高度,借助概率积分法预计导水裂隙带上部岩层的曲率变形,给出1种导水裂隙带动态发育高度的理论预计方法,为进一步分析采动过程中导水裂隙带发育高度动态演化规律和预计导水裂隙带发育高度提供理论依据。
1. 导水裂隙带发育高度动态演化理论
1.1 导水裂隙带发育高度与曲率变形的关系
采动诱发的覆岩移动破坏具有明显分带性,根据移动破坏特征将覆岩分为“三带”,其中垮落带和裂隙带共同组成导水裂隙带,导水裂隙带上部至地表范围内的岩层为弯曲下沉带。导水裂隙带上部岩层作为导水裂隙带与弯曲下沉带分界岩层,其是否破断对导水裂隙带发育高度有重要影响,因此对导水裂隙带发育高度的研究以分析导水裂隙带上部岩层变形破坏为主。
采动后覆岩发生弯曲,其弯曲程度随工作面推进长度增大逐渐加剧,当导水裂隙带上部岩层弯曲程度超过自身极限时,裂缝沿其法线方向向上发育,发育高度取决于导水裂隙带上部岩层曲率变形Ki大小[22]。地表与导水裂隙带上部岩层分别为弯曲下沉带上部与下部边界,其移动变形属于同一问题的2方面,移动变形规律相似,采用概率积分法可对导水裂隙带上部岩层移动变形进行分析[23]。导水裂隙带发育高度形态如图1。
图1中:hs为导水裂隙带发育高度,m;δ为移动角,(°);φ为采动角,(°);Ki为导水裂隙带上部岩层曲率变形,10−3/m;H为开采煤层埋藏深度,m;z为导水裂隙带上部岩层埋深,m;ri为导水裂隙带上部岩层主要影响半径,m;li为导水裂隙带上部岩层平底点距开采边界距离,m。
导水裂隙带上部岩层各点曲率变形值Ki表达式为:
$$ {K_i} = - 2{\text{π }}\frac{{{\eta _i}m\;\cos\; \alpha }}{{r_i^3}}x{{\mathrm{e}}^{ - {\text{π }}\frac{{{x^2}}}{{r_i^2}}}} $$ (1) 式中:ηi为导水裂隙带上部岩层下沉系数;m为煤层开采高度,m;α为煤层倾角,(°);x为导水裂隙带上部岩层任一点位置。
煤层开采后覆岩发生破断,破断岩层在采空区发生堆积,由于岩石具有碎胀性,导水裂隙带上部岩层下沉值一般小于煤层开采高度m,其下沉系数ηi表达式为:
$$ {\eta _i} = \frac{{{w_i}}}{{m\;\cos \;\alpha }} $$ (2) 式中:wi为导水裂隙带上部岩层下沉值,m。
导水裂隙带上部岩层最大曲率变形值相应点位置x的表达式为:
$$ x = \frac{{{r_i}}}{{\sqrt {2{\text{π }}} }} = 0.4{r_i} $$ (3) 将式(3)代入式(1)中,可得导水裂隙带上部岩层最大曲率变形值Kimax表达式为:
$$ {K_{i\max }} = \pm 1.52\frac{{{\eta _i}m\;\cos\; \alpha }}{{r_i^2}} $$ (4) 采动诱发覆岩移动破坏是1个随工作面推进长度改变动态变化的过程,工作面推进长度增大,覆岩破坏发育高度、导水裂隙带上部岩层层位及曲率变形均发生变化,分析采动过程中覆岩动态破断规律,确定导水裂隙带上部岩层层位及曲率变形大小是预计导水裂隙带动态发育高度的关键。
1.2 采动覆岩动态破断规律
煤层采出后采空区上覆岩层失去支撑出现悬露,悬露长度lxi随工作面推进长度L增大而增大,工作面推进长度L与岩层悬露长度lxi的关系如图2。
图2中:lxi为岩层悬露长度,m;θ1、θ2分别为开切眼与工作面侧覆岩破断角,(°);L为工作面推进长度,m。由图2可知,工作面推进长度L与岩层悬露长度lxi存在如下关系:
$$ {l_{xi}} = L - \left( {H - z} \right)\left( {\cot \;{\theta _1} + \cot \;{\theta _2}} \right) $$ (5) 由式(5)可知:当岩层埋深一定时,工作面推进长度L越长,第i层岩层悬露长度lxi越大;当第i层岩层破断时悬露长度为其破断距lpi,此时工作面推进长度为第i层岩层破断时的推进长度Lpi。
由于破断岩层具有碎胀性,第i层岩层下部自由空间高度∆i随破断岩体垮落堆积逐渐减小,当下部自由空间高度∆i小于第i层岩层挠度fimax时,下部自由空间高度∆i不足以诱发第i层岩层破断,覆岩破断到一定高度后停止,此后即使工作面推进长度进一步增大至L≥Lpi时,第i层岩层及其上覆岩层不再发生破断[24]。第i层岩层下部自由空间高度∆i关系式为:
$$ {\Delta _i} = m - \left( {H - z} \right)\left( {{k_{\mathrm{c}}} - 1} \right)\;\cos\; \alpha $$ (6) 式中:∆i为下部自由空间高度,m;kc为岩石残余碎胀系数。
综上所述,结合工作面推进长度L、挠度fimax以及下部自由空间高度∆i给出1种采动中覆岩破断的判据,覆岩动态破断判据见表1。
表 1 覆岩动态破断判据Table 1. Dynamic fracture criterion of overburden rock推进长度/m 第i层岩层挠度/m 是否破断 L<Lpi fimax≥∆i 否 fimax<∆i 否 L≥Lpi fimax≥∆i 否 fimax<∆i 是 根据表1判断覆岩各岩层破断情况,可对采动中导水裂隙带上部岩层层位进行确定。若第i层岩层不破断,导水裂隙带于第i层岩层下部停止发育,第i层岩层为导水裂隙带上部岩层;反之则转入对第i+1层岩层破断情况进行判断。
1.3 导水裂隙带上部岩层下沉系数
同一煤层上覆不同层位岩层物理力学性质不同,各岩层性质及厚度存在明显差异,因此采动中相邻岩层会出现不均匀下沉现象。覆岩不均匀下沉示意图如图3。
由图3可知,当覆岩出现不均匀下沉时,若导水裂隙带上部岩层挠度小于下部自由空间高度即fimax<∆i,其下沉值为挠度fimax;若导水裂隙带上部岩层挠度不小于下部自由空间高度即fimax≥∆i,导水裂隙带上部岩层与下方岩层接触,其下沉值为下部自由空间高度∆i。综上所述,采动中导水裂隙带上部岩层下沉系数ηi是1个与其下部自由空间∆i及挠度fimax有关的分段函数,表达式为:
$$ \left\{ \begin{gathered} {\eta _i} = \frac{{{\Delta _i}}}{m}\left( {{f_{i\max }} \geqslant {\Delta _i}} \right) \\ {\eta _i} = \frac{{{f_{i\max }}}}{m}\left( {{f_{i\max }} < {\Delta _i}} \right) \\ \end{gathered} \right. $$ (7) 导水裂隙带上部岩层下沉系数与其曲率变形值直接相关,基于概率积分法,结合导水裂隙带上部岩层下沉系数分段函数分析,可得导水裂隙带上部岩层曲率变形值。
1.4 导水裂隙带动态发育高度
苏联学者Б·я·гвельцман[22]通过实测数据得出全部垮落法开采导水裂隙带发育高度hs与导水裂隙带上部岩层极限曲率Kt存在如下关系表达式:
$$ h_{\mathrm{s}}^2 = \frac{{7.25{\eta _i}m}}{{{K_{\mathrm{t}}}{{\left( {\cot \;\delta + \cot\; \varphi } \right)}^2}}} $$ (8) 式中:Kt为导水裂隙带上部岩层极限曲率,10−3/m。
由图1可知,覆岩采动角φ与移动角δ反切值表达式为:
$$ \cot \;\delta = \frac{{{r_i}}}{{\left( {H - z} \right)}} $$ (9) $$ \cot \;\varphi = \frac{{{l_i}}}{{\left( {H - z} \right)}} $$ (10) 采动后裂缝沿弯曲岩层法线方向向上发育,发育高度取决于导水裂隙带上部岩层曲率变形的大小,将式(4)、式(9)、式(10)代入式(8)中即可得到基于导水裂隙带上部岩层曲率变形的导水裂隙带发育高度预计公式:
$$ h_{\mathrm{s}}^2 = \frac{{4.77{{\left( {H - z} \right)}^2}r_i^2{K_{i\;\max }}}}{{{K_{\mathrm{t}}}{{\left( {{r_i} + {l_i}} \right)}^2}\;\cos\; \alpha }} $$ (11) 导水裂隙带动态发育高度预计流程如图4。
结合煤层赋存条件,判断采动中覆岩各岩层破断情况,确定不同工作面推进长度下导水裂隙带上部岩层层位、下沉系数和曲率变形,分析计算导水裂隙带动态发育高度。
2. 导水裂隙带发育高度相似模拟
2.1 工程概况
小保当矿区2−2号煤层倾角为0°~1°,属于近水平煤层,平均埋深为369.41 m,上覆基岩厚度为294.54 m,松散层厚度为68.87 m,平均采高6 m。各岩层相似模拟配比见表2。
表 2 相似模拟实验配比表Table 2. Similar simulation experiment ratio table序号 岩性 厚度/m 相似材料配比 河砂 石膏 大白粉 32 粉沙 2.70 9 1 9 31 细沙 53.80 9 1 9 30 红土 12.37 — — — 29 细粒砂岩 17.64 8 2 8 28 细粒砂岩 17.00 8 2 8 27 泥岩 7.00 9 2 8 26 细粒砂岩 2.20 8 2 8 25 砂质泥岩 7.77 9 4 6 24 细粒砂岩 18.96 8 3 7 23 砂质泥岩 8.68 9 4 6 22 细粒砂岩 3.09 8 2 8 21 砂质泥岩 12.10 9 4 6 20 砂质泥岩 12.00 9 4 6 19 细粒砂岩 5.00 8 2 8 18 砂质泥岩 6.48 9 4 6 17 细粒砂岩 13.64 8 2 8 16 粉砂岩 16.70 7 2 8 15 细粒砂岩 10.10 8 3 7 14 粉砂岩 6.01 7 2 8 13 细粒砂岩 13.01 8 3 7 12 粉砂岩 15.13 7 2 8 11 细粒砂岩 8.66 8 3 7 10 粉砂岩 19.40 7 2 8 9 细粒砂岩 9.88 8 3 7 8 粉砂岩 8.20 7 2 8 7 细粒砂岩 14.90 8 3 7 6 煤(1−1) 2.00 粉煤灰∶河砂∶石膏∶大白粉= 21∶1∶2∶21 5 细粒砂岩 18.75 8 3 7 4 粉砂岩 4.20 7 2 8 3 细粒砂岩 5.10 8 3 7 2 中粒砂岩 8.34 8 2 8 1 细粒砂岩 3.50 8 3 7 煤(2−2) 6.00 粉煤灰∶河砂∶石膏∶大白粉= 21∶1∶2∶21 根据2−2号煤层赋存条件选取几何相似常数αi=200、密度相似常数αρ=1.56、应力相似常数ασ=αiαρ=312,搭建尺寸为3 000 mm×1 700 mm×200 mm的相似模型。
2.2 相似模拟结果
为减小边界效应,开切眼开掘位置距模型左边界40 cm(80 m),由开切眼处开始向右侧模拟开挖煤层,在距模型边界40 cm(80 m)处停止开采,煤层开采过程中采用PENTAXR-322NX型光学全站仪对模型测线进行观测。工作面推进不同距离时导水裂隙带发育高度如图5~图7。
由图5可知:当工作面推进至119 m时,覆岩10号岩层未发生破断,为工作面推进至119 m时导水裂隙带上部岩层,导水裂隙带发育至10号岩层下部,发育高度为63.6 m,为2−2号煤层采高(6 m)的10.6倍。
由图6可知:当工作面推进至278 m时,覆岩破坏发育高度随工作面推进而增大,导水裂隙带发育至16号岩层中部,16号岩层未破断,为工作面推进至278 m时导水裂隙带上部岩层,导水裂隙带发育高度155 m,为采高的25.8倍。
由图7可知:当工作面推进至428 m时开采完毕,覆岩垮落稳定后煤层开采达到充分采动,受下部自由空间高度限制,覆岩破坏发育高度不再随工作面推进而增大,导水裂隙带在16号岩层中部停止发育,发育高度不再随工作面推进而发生明显变化,覆岩16号岩层为导水裂隙带上部岩层,导水裂隙带最大发育高度155 m,为采高的25.8倍。
3. 导水裂隙带发育高度动态演化验证
3.1 导水裂隙带动态发育高度理论预计
根据覆岩破断判据,结合相似模拟实验现象及观测数据对采动过程中各岩层破断情况进行判定,覆岩破断情况判别表见表3。
表 3 覆岩破断情况判别表Table 3. Overburden rock fracture discrimination table岩层序号 岩层厚度/m Lpi/m ∆i/m 是否破断 16 16.70 212.0 4.52 否 15 10.10 212.0 4.63 是 14 6.01 168.0 4.69 是 13 13.01 168.0 4.82 是 12 15.13 155.0 4.97 是 11 8.66 126.0 5.06 是 10 19.40 126.0 5.25 是 9 9.88 119.0 5.35 是 8 8.20 99.0 5.43 是 7 14.90 99.0 5.58 是 6 2.00 99.0 5.60 是 5 18.75 90.0 5.79 是 4 4.20 76.0 5.83 是 3 5.10 76.0 5.88 是 2 8.34 53.0 5.97 是 1 3.50 41.6 6.00 是 由表3可知:当工作面推进至41.6 m时,煤层顶板发生破断,覆岩破坏开始向上发育;当推进长度达到53.0 m覆岩2号岩层发生破断,随着工作面推进长度增大,导水裂隙带逐步向上发育;在推进长度达到76.0 m时上覆3、4号岩层均发生破断,导水裂隙带发育至5号岩层下部;当推进至90.0 m时5号岩层发生破断,导水裂隙带进一步发育,其上覆6号~8号岩层在推进长度达到99.0 m时均发生破断;推进长度达到119 m时9号岩层破断,导水裂隙带发育至10号岩层下部;当推进至126.0 m时10号岩层与11号岩层发生同步破断,推进至155.0 m时12号岩层破断,导水裂隙带随覆岩破断向上发育;当推进长度达到168.0 m时13号、14号岩层同步破断,推进至212.0 m时覆岩15号岩层发生破断,由于f16max=6.61 m>∆16,16号岩层不破断,导水裂隙带于16号岩层下部停止发育,此后随着工作面推进长度增大,导水裂隙带发育高度不再发生明显变化。
为了进一步分析采动过程中的导水裂隙带动态发育高度,结合相似模拟实验现象及观测数据,以工作面推进长度119、278、428 m(在该推进长度下导水裂隙带上部岩层下沉系数分别对应其下沉系数的2个分段函数)为例预计2−2煤层开采过程中导水裂隙带发育高度,理论预计结果如下:
1)当工作面推进至119 m时10号岩层未破断,为导水裂隙带上部岩层。相似模拟实验观测得10号岩层l10=37.8 m,r10=38.2 m,下沉值w10=0.72 m,下沉系数η10=0.12,极限曲率Kt=1.30×10−3/m,推进至119 m时导水裂隙带上部岩层最大曲率变形值K10max=0.75×10−3/m,将上述数据代入式(11)中计算可得。工作面推进至119 m时导水裂隙带发育高度hs为62.4 m。
2)当工作面推进至278 m时,16号岩层未破断,为导水裂隙带上部岩层,相似模拟实验观测可得16号岩层l16=72.3 m,r16=72.9 m,下沉值w16=4.52 m,下沉系数η16=0.75,推进至278 m时导水裂隙带上部岩层最大曲率变形值K16max=1.29×10−3/m,将上述参数代入式(11)中计算可得工作面推进至278 m时导水裂隙带发育高度hs为160.8 m。
3)当工作面推进至428 m时,16号岩层仍未破断,下沉系数η16=0.75,曲率变形值K16 max=1.29×10−3/m,计算得当工作面推进至428 m时导水裂隙带发育高度仍为160.8 m,导水裂隙带发育高度不再随工作面推进长度增大发生明显变化,导水裂隙带最大发育高度hs为160.8 m。
3.2 相似模拟实验验证
当工作面推进至119 m时,相似模拟实验中导水裂隙带发育高度为63.6 m,理论预计结果为62.4 m,误差为1.9%;推进至278 m时,实验中导水裂隙带发育高度为155 m,理论预计结果为160.8 m,误差为3.6%;当2−2号煤层开采完成后,实验中导水裂隙带最大发育高度为155 m,理论预计导水裂隙带最大发育高度为160.8 m,误差为3.6%。
基于相似模拟实验及理论预计结果绘制的2−2煤层开采过程中导水裂隙带动态发育高度曲线图如图8。
由图8可知,导水裂隙带发育高度理论预计曲线与相似模拟实验曲线基本一致,误差为1.9 %~3.6%,两段曲线均表明采动中导水裂隙带发育高度随工作面推进长度增大发生变化,其发育形态大致可分为以下4个阶段。
1)缓慢发育阶段。煤层开采初期,采空区尺寸相对较小,受采空区大小限制导水裂隙带发育相对缓慢。
2)迅速发育阶段。工作面进一步推进,覆岩受采动影响程度增大,导水裂隙带随工作面推进长度增大快速发育。
3)发育变缓阶段。导水裂隙带发育至一定高度后,采动对导水裂隙带上部岩层影响程度逐渐降低,此时导水裂隙带发育高度随工作面推进增速逐渐减缓。
4)发育平稳阶段。当工作面推进至一定长度后,由于岩石具有碎胀性,破断岩层将覆岩下部自由空间填满,导水裂隙带上部岩层不再发生破断,导水裂隙带达到最大发育高度,不再随工作面推进长度增大发生明显变化。
3.3 实例验证
小保当一号井2−2号煤层平均埋深356.5 m,上覆基岩厚度为202.65~288.89 m,平均254.14 m,松散层厚度为70.26 m,煤层平均厚度为5.8 m。为验证覆岩导水裂隙带发育高度预计理论的可靠性,以小保当一号井2−2号煤层为研究对象,对覆岩导水裂隙带发育高度进行了现场实测。
现场对6个钻孔进行探查,探查结果表明覆岩导水裂隙带发育高度为152.01~175.57 m,为采高的26.21~30.27倍,切眼附近导水裂隙带发育高度最大,工作面内部发育高度较小。理论预计小保当矿区2−2号煤层覆岩导水裂隙带最大发育高度为160.8 m,与现场实测覆岩导水裂隙带发育高度基本一致。
4. 结 语
1)基于工作面推进长度、挠度及下部自由空间高度给出了覆岩动态破断判据和导水裂隙带上部岩层下沉系数分段函数,在此基础上给出了1种基于导水裂隙带上部岩层曲率变形的导水裂隙带动态发育高度预计方法。
2)通过相似模拟实验和理论预计方法,揭示了采动中导水裂隙带发育高度动态演化的4个阶段:缓慢发育阶段、迅速发育阶段、发育变缓阶段、发育平稳阶段。
3)以小保当矿区2−2号煤层为研究对象对导水裂隙带发育高度进行理论预计、相似模拟实验及现场实测,理论预计结果与相似模拟实验结果误差为1.9 %~3.6%,理论预计发育高度为160.8 m,与现场实测2−2号煤层开采导水裂隙带发育高度152.01~175.57 m基本吻合。
-
表 1 岩石物理力学参数
Table 1 Rock physical and mechanical parameters
岩石密度/
(g·cm−3)单轴抗压强度/
MPa剪切模量/
GPa泊松比 抗拉强度/
MPa2.59 110.9 23.09 0.266 5.39 表 2 HJC模型参数
Table 2 HJC model parameters
A B C N D1 D2 EFmin 0.203 6 2.26 0.002 04 0.94 0.04 1 0.01 pcrush/MPa μcrush plock/GPa μlock K1/GPa K2/GPa K3/GPa 37 1.41×10−5 1.2 0.020 5 28.85 37.67 21.12 注:D1、D2为损伤失效参数;EFmin为断裂前的最小塑性应变;plock为压实极限状态下的静水压力。 表 3 空气材料参数
Table 3 Air material parameters
空气密度/(kg·m−3) C0 C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 E/(MJ·m−3) 1.29 0 0 0 0 0.4 0.4 0 0.25 表 4 炸药材料参数
Table 4 Explosive material parameters
炸药密度/
(g·cm−3)爆速/
(m·s−1)AJ/GPa BJ/GPa R1 R2 ω E/(GJ·m−3) 1.18 5 122 276.2 8.44 5.2 2.1 0.5 3.87 表 5 切缝管、护壁套管材料参数
Table 5 Material parameters of Slotted tube and protective wall sleeve
密度/(g·cm−3) 弹性模量/GPa 泊松比 屈服强度/MPa 1.25 3.6 0.35 35 表 6 工程试验结果统计
Table 6 Statistics of engineering test results
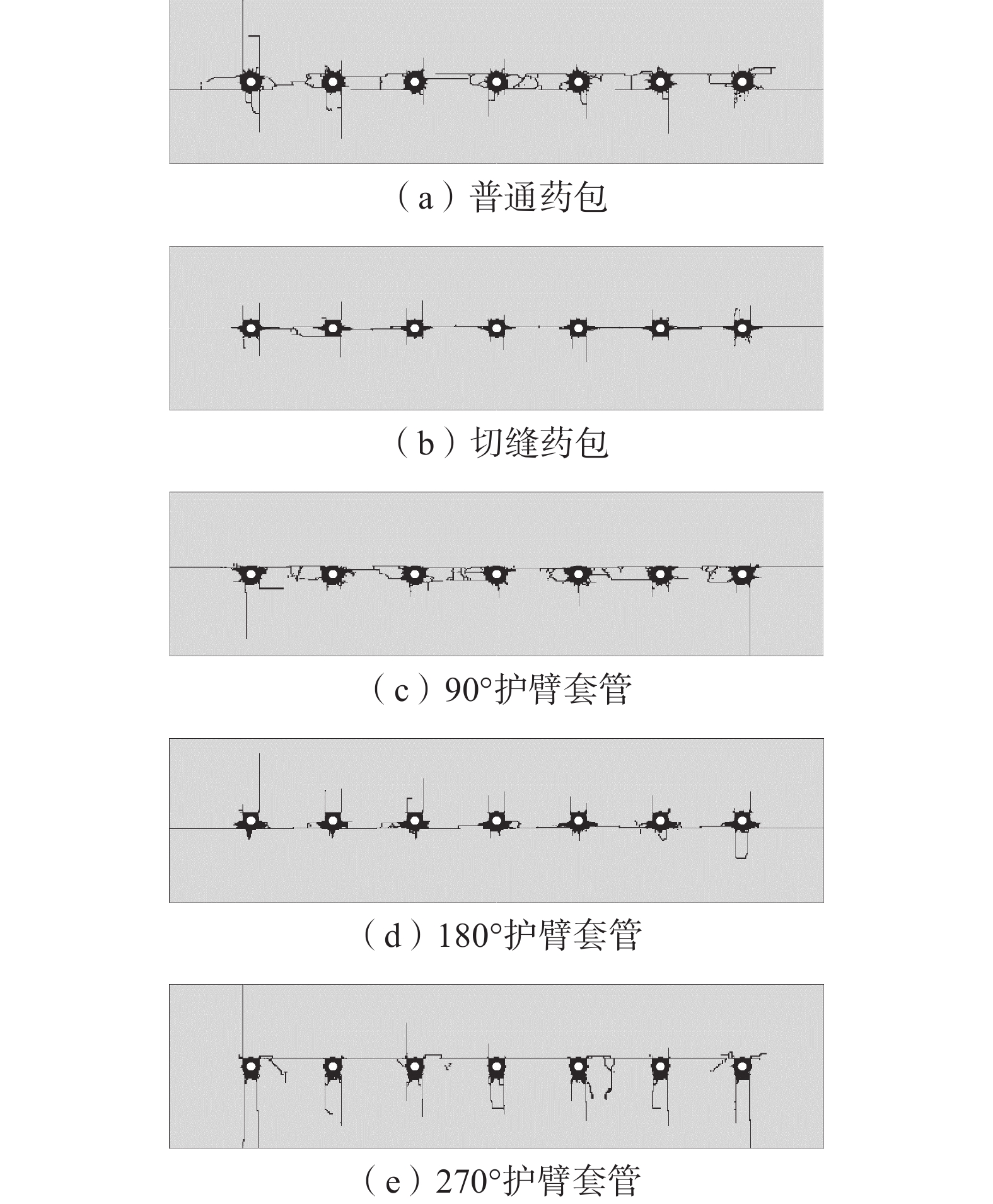
试验组号 帮部位置 爆破方案 超欠挖量/mm 半眼痕率/% 再生裂隙 炮眼利用率/% 周边成型质量 1 左 普通药包爆破 245 0 裂隙区 86 较差 1 右 切缝药包爆破 87 60 2~3条 91 相对平整光滑 2 左 90°套管护壁爆破 170 30 3~4条 82 较差 2 右 180°套管护壁爆破 116 50 1~2条 87 相对平整光滑 3 左 270°套管护壁爆破 28 70 1条 88 平整光滑 3 右 普通药包爆破 232 20 裂隙区 82 较差 4 左 切缝药包爆破 71 70 1~2条 89 平整光滑 4 右 90°套管护壁爆破 183 20 4~5条 87 较差 5 左 180°套管护壁爆破 109 40 1~2条 85 相对平整光滑 5 右 270°套管护壁爆破 −19 90 1条 92 平整光滑 6 左 普通药包爆破 238 10 裂隙区 87 较差 6 右 切缝药包爆破 75 70 1~2条 93 平整光滑 7 左 90°套管护壁爆破 166 30 3~4条 87 相对平整光滑 7 右 180°套管护壁爆破 106 50 1~2条 90 相对平整光滑 8 左 270°套管护壁爆破 25 70 1条 85 平整光滑 8 右 普通药包爆破 229 20 裂隙区 88 较差 -
[1] 谢华刚,吴玲丽. 切缝药包定向断裂控制爆破研究综述[J]. 工程爆破,2011,17(2):26−30. XIE Huagang, WU Lingli. Review on research of cutting seam charge directional fracture controlled blasting[J]. Engineering Blasting, 2011, 17(2): 26−30.
[2] 陈帅志,付晓强,陈正拜,等. 基于LS-DYNA的切缝药包爆破数值模拟分析[J]. 煤炭技术,2018,37(10):62−64. CHEN Shuaizhi, FU Xiaoqiang, CHEN Zhengbai, et al. Numerical simulation analysis of slotted cartridge blasting based on LS-DYNA[J]. Coal Technology, 2018, 37(10): 62−64.
[3] 申涛,罗宁,戚福州,等. 切缝药包岩石巷道光面爆破数值模拟与优化研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2020,37(4):674−680. SHEN Tao, LUO Ning, QI Fuzhou, et al. Numerical simulation and optimization of smooth blasting in rock roadway with split-tube charge holder[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2020, 37(4): 674−680.
[4] 时启鹏,郑洪运,王永宝,等. 沿空留巷双向聚能爆破炮孔间距参数研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2022,53(1):219−225. SHI Qipeng, ZHENG Hongyun, WANG Yongbao, et al. Study on parameters of blast hole spacing for gob side entry retaining by bidirectional shaped charge blasting[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(1): 219−225.
[5] 袁坤德,龚成. 光面护壁爆破的护壁效果及作用机理探讨[J]. 西南科技大学学报(自然科学版),2006,21(4):47−52. YUAN Kunde, GONG Cheng. Breast wall effect of double-pipe protecting borehole wall blasting and its functional mechanism[J]. Journal of Southwest University of Science and Technology, 2006, 21(4): 47−52.
[6] 蒲传金,郭学彬,肖正学,等. 岩土控制爆破的历史与发展现状[J]. 爆破,2008,25(3):42−46. PU Chuanjin, GUO Xuebin, XIAO Zhengxue, et al. History and development state of rock control blasting[J]. Blasting, 2008, 25(3): 42−46.
[7] 杨仁树,左进京,李永亮,等. 不同切缝管材质下切缝药包爆炸冲击波传播特性研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2019,48(2):229−235. YANG Renshu, ZUO Jinjing, LI Yongliang, et al. Experimental study of slotted cartridge explosion shock wave propagation characteristic with different cutting seam pipe material[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2019, 48(2): 229−235.
[8] 岳中文,田世颖,张士春,等. 单向围压作用下切缝药包爆破爆生裂纹扩展规律的研究[J]. 振动与冲击,2019,38(23):186−195. YUE Zhongwen, TIAN Shiying, ZHANG Shichun, et al. Expanding law of cracks formed by slotted cartridge blast under unidirectional confining pressure[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2019, 38(23): 186−195.
[9] 史国利,肖成龙,郑昌达,等. 切缝药包不耦合装药爆破损伤破坏的分形研究[J]. 中国矿业,2020,29(3):105−109. SHI Guoli, XIAO Chenglong, ZHENG Changda, et al. Fractal research on blasting damage of slotted cartridge decoupling charge blasting[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2020, 29(3): 105−109.
[10] 郭东明,朱若凡,张伟,等. 聚能管爆破参数对周边爆破效果的影响[J]. 爆破,2023,40(4):96−102. GUO Dongming, ZHU Ruofan, ZHANG Wei, et al. Influence of slotted pipe blasting parameters on surrounding blasting[J]. Blasting, 2023, 40(4): 96−102.
[11] 王雁冰,李书萱,耿延杰,等. 切缝药包爆破定向断裂机理及围岩损伤特性分析[J]. 工程科学学报,2023,45(4):521−532. WANG Yanbing, LI Shuxuan, GENG Yanjie, et al. Directional fracture mechanism and surrounding rock damage characteristics of slotted cartridge blasting[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2023, 45(4): 521−532.
[12] YANG Renshu, ZUO Jinjing. Experimental study on directional fracture blasting of cutting seam cartridge[J]. Shock and Vibration, 2019, 2019(5): 1085921.
[13] 赵志鹏,欧阳烽,何富连,等. 切顶沿空留巷双向聚能爆破关键参数研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2022,53(2):226−233. ZHAO Zhipeng, OUYANG Feng, HE Fulian, et al. Study on key parameters of bidirectional shaped charge blasting for gob side entry retaining with roof cutting and pressure relief[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(2): 226−233.
[14] 杨仁树,苏洪. 基于动态焦散线实验的护壁药包机理研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2019,48(3):467−473. YANG Renshu, SU Hong. The mechanism of wall-protecting explosion based on dynamic caustic test[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2019, 48(3): 467−473.
[15] 张志呈,肖正学,张志恆,等. 护壁爆破在煤矿巷道掘进中的应用[J]. 煤矿爆破,2009(4):31−33. ZHANG Zhicheng, XIAO Zhengxue, ZHANG Zhiheng, et al. Application of protecting borehole wall blasting technology in roadway excavation[J]. Coal Mine Blasting, 2009(4): 31−33.
[16] 康永全,孟海利,郭云龙,等. 隧道周边孔差异化爆破作用机理及试验研究[J]. 铁道建筑,2022,62(7):114−117. KANG Yongquan, MENG Haili, GUO Yunlong, et al. Mechanism and experiment research of tunnel peripheral hole differential blasting[J]. Railway Engineering, 2022, 62(7): 114−117.
[17] 杨东启,刘建庄,贺健宇,等. 轴向动荷载作用下煤系石灰岩损伤特性研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2023,54(2):107−112. YANG Dongqi, LIU Jianzhuang, HE Jianyu, et al. Research on damage characteristics of coal-measure limestone under axial dynamic load[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2023, 54(2): 107−112.
[18] 秦桂芳,曾灿,徐间锋,等. 基于HJC损伤本构模型的灰岩隧道光面爆破数值模拟及工程验证[J]. 爆破器材,2022,51(6):45−51. QIN Guifang, ZENG Can, XU Jianfeng, et al. Numerical simulation and engineering verification of smooth blasting in limestone tunnel based on HJC damage constitutive model[J]. Explosive Materials, 2022, 51(6): 45−51.
[19] 方书昊,霍雨佳,郭晋麟,等. 不同动载对煤岩块的破坏作用数值模拟[J]. 煤矿安全,2021,52(1):184−188. FANG Shuhao, HUO Yujia, GUO Jinlin, et al. Numerical simulation of failure of coal and rock blocks under different dynamic loads[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021, 52(1): 184−188.
[20] TIMOTHY J HOLMQUIST, GORDON R JOHNSON. A computational constitutive model for glass subjected to large strains, high strain rates and high pressures[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2011, 78(5): 051003. doi: 10.1115/1.4004326
[21] 毕程程. 华山花岗岩HJC本构参数标定及爆破损伤数值模拟[D]. 合肥:合肥工业大学,2018. [22] 段宝福,柴明星,魏玉冠,等. 切缝药包参数对切缝效果的影响研究[J]. 煤炭技术,2024,43(5):29−33. DUAN Baofu, CHAI Mingxing, WEI Yuguan, et al. Study on influence of slit charge parameters on slit effect[J]. Coal Technology, 2024, 43(5): 29−33.
[23] 钟靖涛. 花岗岩动力学特性及循环爆破下损伤累积效应研究[D]. 合肥:合肥工业大学,2019. -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 朱翠,罗宇豪,王占刚,戴娟. 新型蚁群算法规划核电厂巡检机器人路径. 核电子学与探测技术. 2025(01): 107-115 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: