Research on the effect of managerial pro-social rule breaking on miner safety deviance behavior
-
摘要:
为探究领导者亲社会违规对矿工安全偏离行为的影响机制,在现有研究基础上,引入控制威胁感、制度敬畏心、预期同事安全偏离、预期同事对安全偏离的道德谴责为中介变量,建立了领导者亲社会违规影响矿工安全偏离行为的多中介模型;以3家煤矿的391名矿工为研究对象进行3个时间点追踪问卷调查来收集研究数据,并运用SPSS、Mplus进行数据分析以验证研究假设。结果表明:领导者亲社会违规会正向影响矿工安全偏离行为;控制威胁感、制度敬畏心、预期同事安全偏离、预期同事对安全偏离的道德谴责在其中起部分中介作用。
Abstract:In order to explore the influence mechanism of managerial pro-social rule breaking on miner safety deviance behavior, based on existing research, this study introduces the sense of self-control resource depletion threat, system awe, expected coworkers’ safety deviance and expected coworkers’ moral condemnation of safety deviance as mediating variables, and establishes a multiple mediation model of the influence of managerial pro-social rule breaking on miners safety deviance behavior. 391 miners from 3 coal mines were used as research objects to collect research data through three time-point follow-up questionnaires, and SPSS and Mplus were used for data analysis to verify the research hypothesis. The results show that the managerial pro-social rule breaking positively affects the miners’ safety deviance behavior, and the sense of self-control resource depletion threat, system awe, expected coworkers’ safety deviance and expected coworkers’ moral condemnation of safety deviance play some mediating roles.
-
煤炭开采机械化程度不断提高,粉尘量也明显增多,在煤炭掘进和开采过程中都会产生大量的煤尘、矽尘等混合性粉尘,会给作业人员的生命健康带来巨大的危害。因此对存在粉尘的长期作业场所,粉尘治理成了越来越重视的问题。
随着分子模拟技术的发展,经常使用分子动力学模拟研究分子之间的微观相互作用[1-2]。高正阳等[3]研究了4种不同煤阶煤分子表面水分子吸附的微观机理;XU等[4]和HUANG等[5]分别研制了针对建筑工地粉尘和岩石粉尘的新型环保抑尘剂,并通过试验得出新型抑尘剂具有突出的抑尘效果;CRAWFORD等[6]研究了表面活性剂对不同煤表面特性的影响,发现添加表面活性剂可以明显降低煤的接触角,提高煤的润湿效果;ZHANG等[7]通过分子动力学模拟研究了表面活性剂对褐煤吸附行为和润湿性的影响,发现表面活性剂可以改变水与褐煤之间的相互作用力;陈璐瑶[8]研究了表面活性剂结构对SiO2粉尘润湿性,通过分子动力学模拟,得出SiO2表面基团性质是影响SiO2润湿性的根本原因;孟筠青等[9]探究不同种类表面活性剂及其复配对SiO2润湿性的影响,同时结合沉降试验,找出SiO2粉尘润湿效果最好的单体表面活性剂及复配溶液;邱玄等[10]通过分子动力学模拟了 Pluronic F-68 在萤石和石英表面的吸附行为,结果显示 Pluronic F-68在石英上的吸附能力更强。
上述研究表明,分子模拟已成为研究润湿和吸附性能的重要方法[11-12]。但研究都是针对单一性粉尘研究润湿性。为此,借助于Materials studio分子模拟软件构建模型,采用分子动力学模拟和量子化学的方法,以表面活性剂CTAB为例,研究褐煤煤尘、矽尘的润湿机理的差异性。
1. 模拟方法
1.1 模拟体系构建
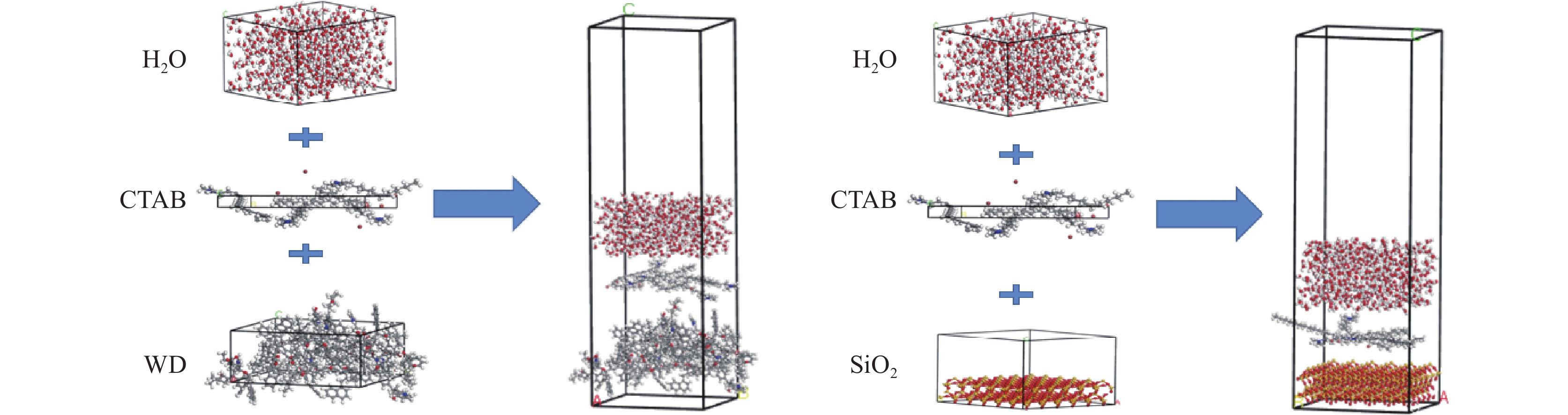
采用Materials Studio 分子模拟软件,构建了水−表面活性剂−褐煤煤尘/矽尘模型。初始模型如图1所示。
选用Wender经典褐煤模型,其煤分子结构如图1(a)所示;矽尘模型为SiO2超晶胞(图1(b)),添加1.5 nm的真空层以消除周期性的影响;表面活性剂选用十六烷基三甲基溴化铵(CTAB)(图1(c))。利用MS中Amorphous Cell 模块构建各个盒子,盒子详细参数见表1。
表 1 盒子或超晶胞参数Table 1. Box or supercell parameters名称 长/nm 宽/nm 高/nm 分子数量 α、β、γ/(°) 密度/ (g·cm−3) 水盒子 2.946 0 3.241 2 1.566 4 500 90 1.000 CTAB盒子 2.946 0 3.241 2 0.239 7 5 90 1.322 煤分子盒子 2.946 0 3.241 2 1.342 6 8 90 1.350 SiO2超晶胞 2.946 0 3.241 2 2.288 3 — 90 2.200 注:α、β、γ为三维空间中与x、y、z轴的夹角。 通过build layer构成水−表面活性剂−褐煤/矽尘(SiO2)2个模型,并在体系上方都添加了0.5 nm真空层。模拟体系的构建如图2所示,模拟平衡后水的密度场分布图如图3所示。
1.2 计算模拟方法
1)分子动力学模拟。运用Forcite模块对褐煤分子、水分子、CTAB分子和SiO2超晶胞进行结构优化。首先采用Geometry Optimization任务中通过Smart算法进行局部结构优化。然后,利用Amorphous Cell 模块构建500个水分子盒子、5个表面活性剂盒子、8个褐煤分子盒子,通过build layer构成模型,在模型上方添加0.5 nm真空层。然后,为了得到模型全局最小和稳定的能量,在Anneal任务中采用NVT系综(温度为298 K)进行退火动力学模拟。最后,在Dynamics任务中采用NVT系综进行1 ns的分子动力学模拟,其中力场采用COMPASSⅡ,电荷采用Forcefield assigned。
2)量子化学模拟。量子力学计算在DMol3模块中完成[13],在广义梯度近似(GGA)[14]下,利用BLYP泛函模拟电子交换和相关相互作用[15],模拟精度为Fine,其中SCF收敛精度为0.000 001。选择所有由D极化函数(DNP)增强的电子双数值原子轨道作为基础集,并将轨道截止质量定为良好。smearing的值选择为0.005,并且在计算过程中不考虑基集叠加误差(BSSE)[16],因为在DMol3中实现的数值基集可最小化甚至消除基集叠加误差。
2. 模拟结果
2.1 相互作用能
在模拟体系中,水分子的形态和流动的差异性主要是受表面活性剂水溶液和褐煤分子或者SiO2相互作用的结果。相互作用能可以数字化体现分子之间的相互作用的强度,如果相互作用能为负值,则表明吸附过程是自发进行的;若相互作用能为正值,则反之。相互作用能的绝对值越大时,分子之间的相互作用也越强。通过分子动力学模拟,计算体系相互作用能公式如下:
$$ {E_{{{\mathrm{inter}}} }} = {E_{{\mathrm{total}}}} - \left( {{E_{\mathrm{i}}} + {E_{{\mathrm{w + s}}}}} \right) $$ (1) 式中:$ {E_{{{\mathrm{inter}}} }} $为活性剂水溶液与煤或SiO2的相互作用能;$ {E_{{\mathrm{total}}}} $为体系内的总能量;$ {E_{\mathrm{i}}} $为体系中褐煤分子或者SiO2的能量;$ {E_{{\mathrm{w + s}}}} $为水和表面活性剂的能量。
根据式(1)计算出平衡后体系的相互作用能,结果见表2。由表2可以看出,褐煤煤尘体系(简称WD-DS)的相互作用能的绝对值比矽尘体系(简称SiO2-DS)的大,说明相同条件下,褐煤分子和活性剂水溶液的相互作用强度更强,褐煤煤尘表面吸附水的能力更强。
表 2 水−CTAB−煤尘/矽尘的相互作用能Table 2. Interaction energies of water-CTAB-coal dust/silicon dust体系 能量/(kcal·mol−1) 总能量 水和CTAB 粉尘 相互作用能 水−CTAB−煤尘 −2 739.640 2 −4 053.856 8 2 107.936 5 −793.720 4 水−CTAB−矽尘 −24 706.914 0 −4 065.075 7 −20 451.980 0 −135.598 0 注:1 kcal=4.184 kJ。 2.2 径向分布函数(RDF)
径向分布函数(RDF)被定义为特定原子在r距离内的密度与容重的比率。换句话说,特定原子的密度随与参考分子距离的变化随体积密度的变化表示RDF。所以,它可以用来演示给定分子周围的密度分布,数学表达式如下:
$$ g\left( r \right) = {{{\mathrm{d}}N} / {( {4\rho {\pi ^2}} )}} $$ (2) 式中:$ {\mathrm{d}}N $为与中心的距离为$ r $到$ r + {\mathrm{d}}r $之间的原子数目,个;$ \pi $为圆周率,取3.141 592 6;$ \rho $为该原子的平均数目密度。
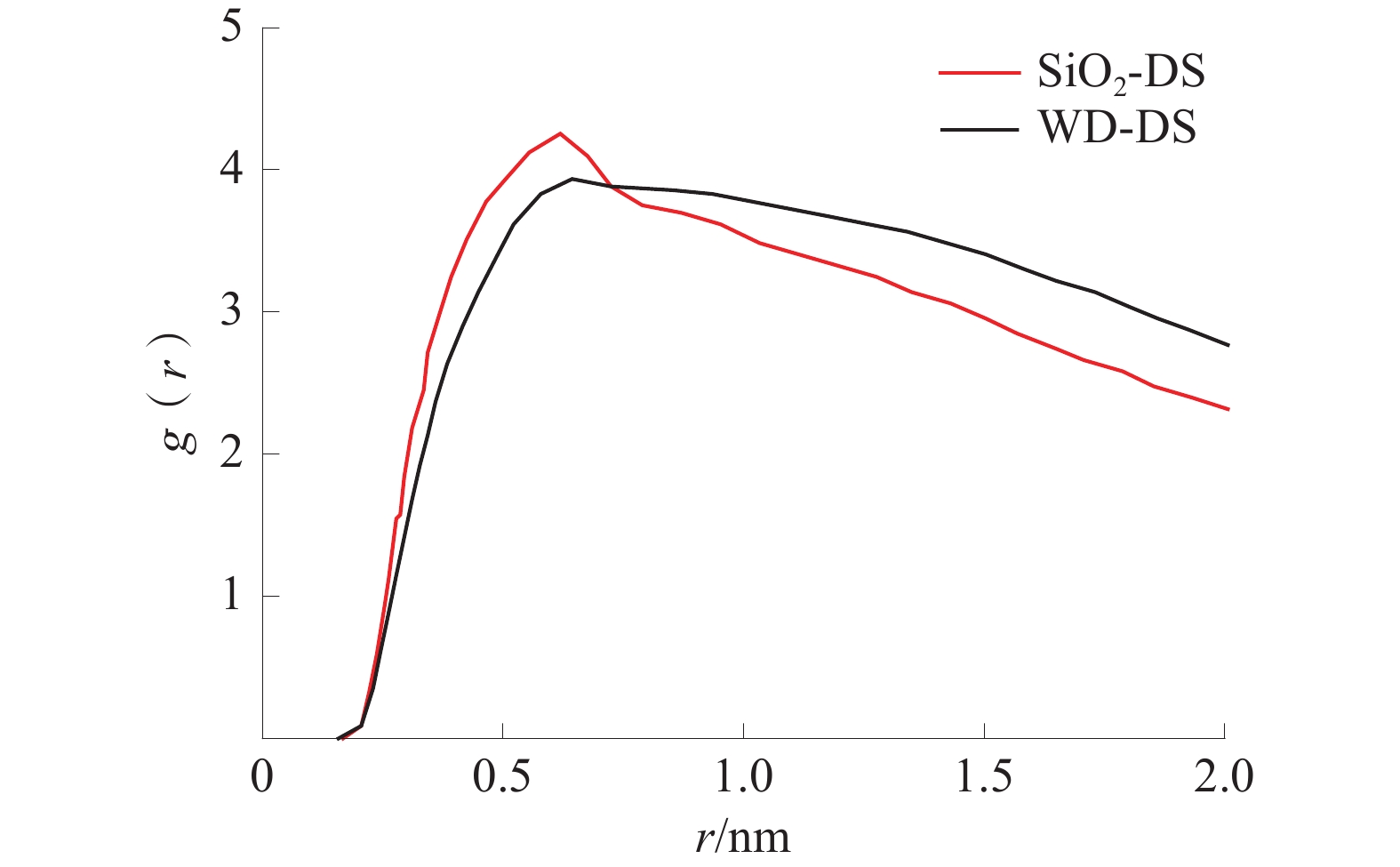
根据分子动力学模拟的结果,分析得到的CTAB头基和H2O的径向分布曲线如图4所示,CTAB尾基和H2O的径向分布曲线如图5所示。
由图4可以看出,模拟平衡后,CTAB头基和水分子在WD-DS和SiO2-DS中的0.619 nm和0.597 nm处出现峰值,且SiO2-DS的峰值要比WD-DS的高,0.7 nm两曲线出现交点;WD-DS在0.885 nm处又出现第二峰,交点之后WD-DS的径向分布曲线一直在SiO2-DS的上方,两者缓慢下降。根据峰的位置判断3处峰是因为CTAB头基和水之间的静电力作用而形成的,虽然SiO2-DS出现的峰值要高,但WD-DS总体有2个峰值,并且交点以后WD-DS的径向分布曲线高于SiO2-DS的,说明WD-DS中头基和水的相互作用更强。
由图5可以看出,0.7 nm之前SiO2-DS的径向分布曲线略微高于WD-DS的曲线,0.7 nm之后相反。两曲线在1.4、1.6 nm处出现强峰,显然WD-DS的CTAB尾基和水分子的相互作用强于SiO2-DS。
2.3 均方位移和自扩散系数
均方位移MSD用来描述时间变化下目标粒子空间位置与初始位置的偏差程度。通过计算水分子的MSD和扩散系数D,可以进一步阐明表面活性剂加入对水分子运动的影响[17]。可以将MSD对时间的曲线拟合成直线$ y = ax + b $,然后利用以下公式计算扩散系数。
$$ {\mathrm{MSD}} = \frac{1}{N}\sum\limits_{{{i}} = 1}^N {{{{{[}}{{{r}}_i}\left( t \right){{ - }}{{{r}}_i}\left( 0 \right){{]}}}^{{2}}}} $$ (3) $$ D = \frac{a }{6} $$ (4) 式中:$ N $为粒子数;$ {r_i}\left( t \right) $为$ i $粒子在$ t $时刻的位置;$ {r_i}\left( 0 \right) $为$ i $粒子的初始位置;$ a $为拟合之后直线的斜率。
水分子的MSD拟合直线如图6所示。根据图6均方位移MSD拟合直线的斜率计算可得自扩散系数DWD=0.004 5 nm2/ps和$D_{{\mathrm{SiO}}_2 }$=0.004 2 nm2/ps,从D的取值来看,CTAB增强了褐煤煤尘和矽尘的润湿性,使得表面和水的相互作用增强,加速了水分子的运动,进而提高了表面的润湿性,但对褐煤的效果更好。
2.4 数密度
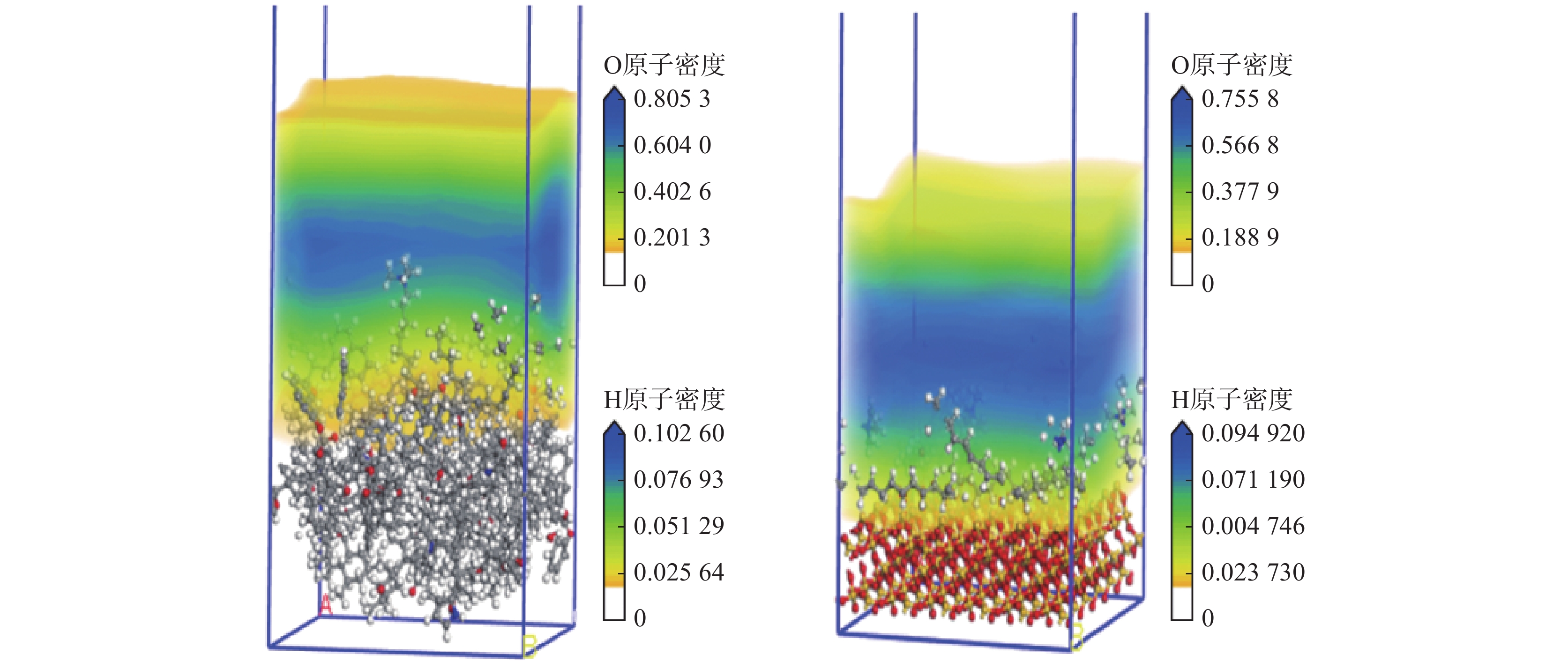
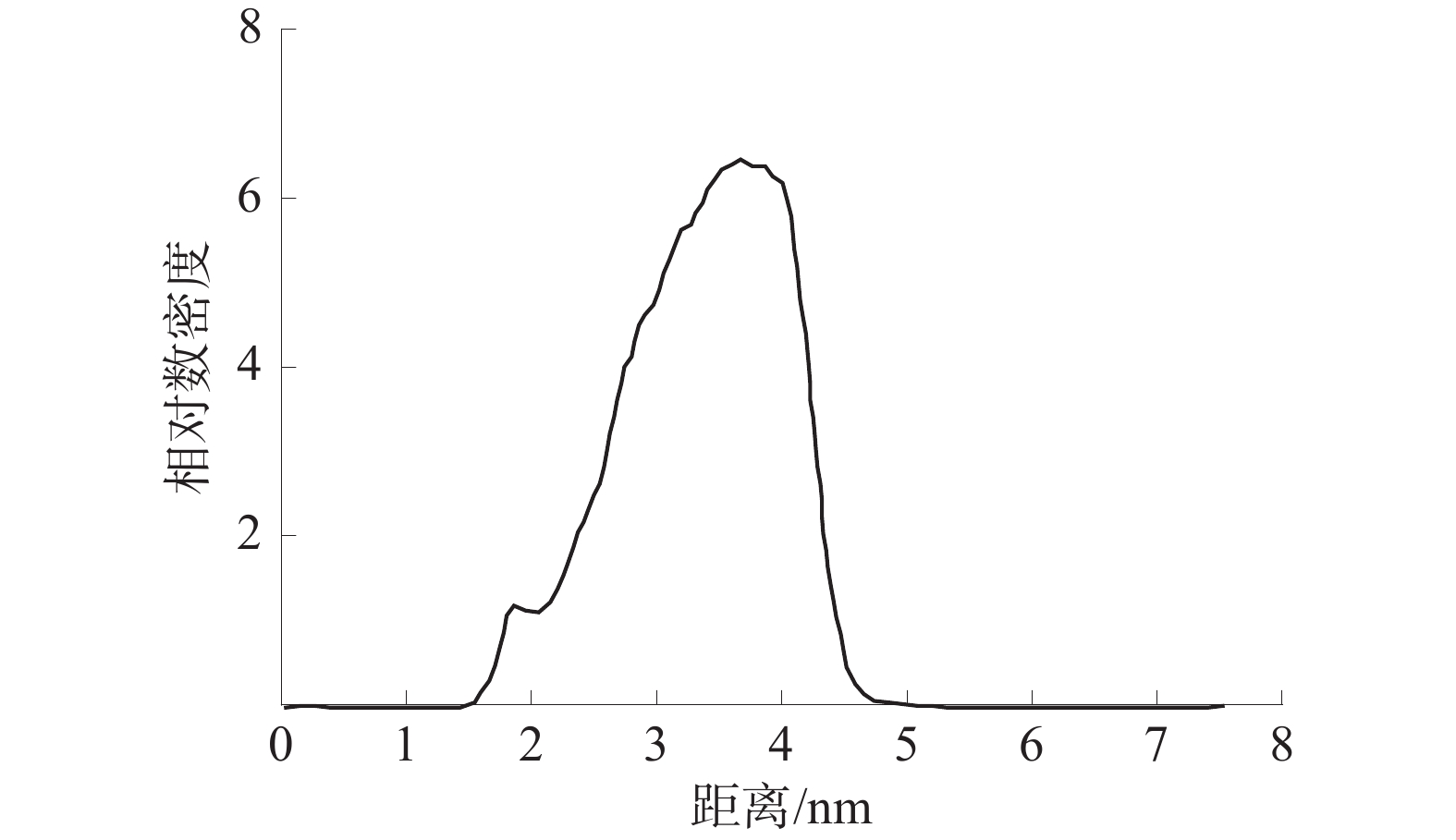
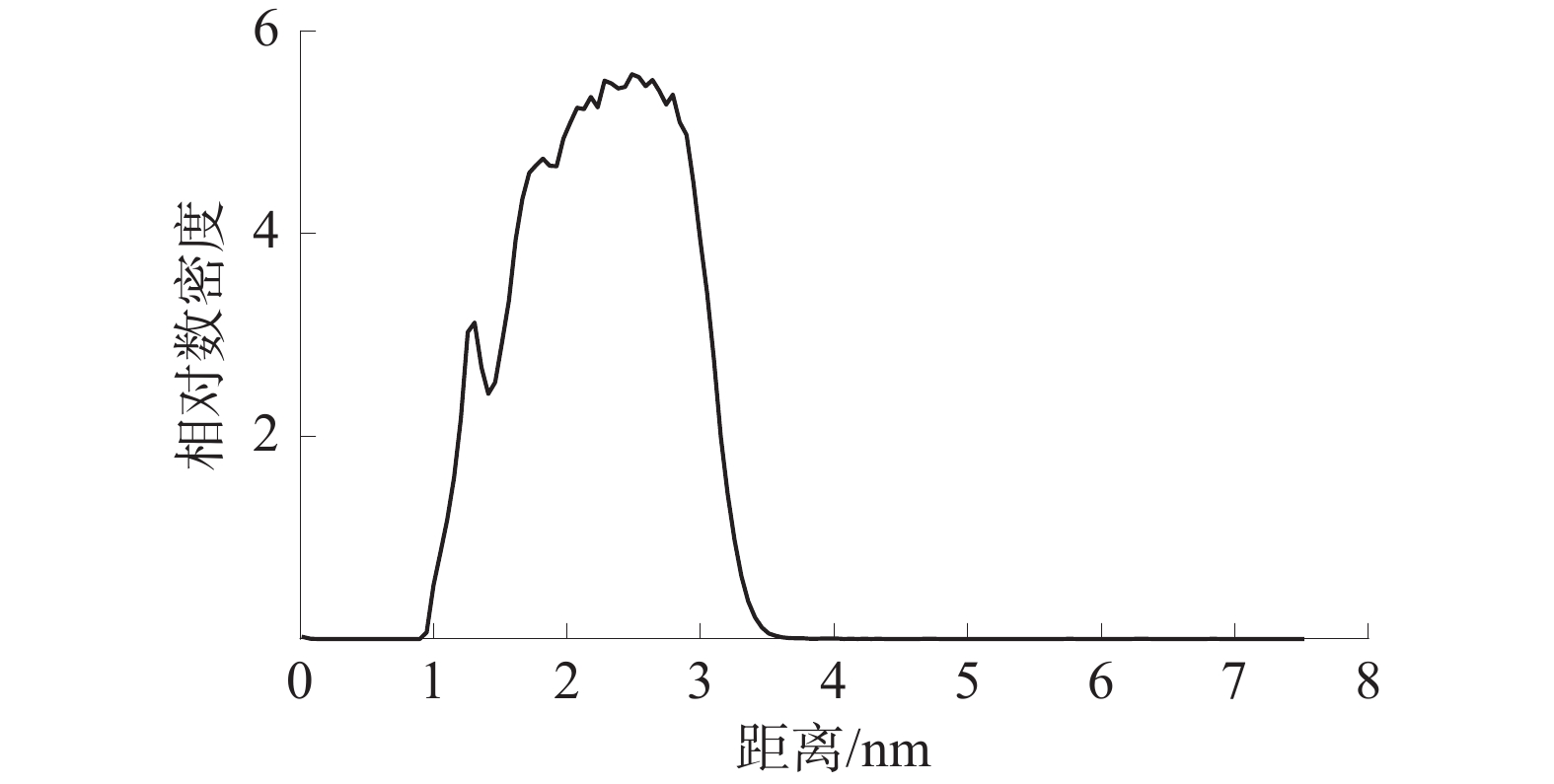
界面区域是相变现象发生的主要场所,是其本质就是从一种相态密度快速变化至另一种相态密度的区域。根据10−90准则[18-19],界面厚度被定义为密度为其体积相密度的10%~90%的2个位置之间的距离。仅对z轴方向水分子的相对数密度进行分析,WD-DS中的水分子相对数密度如图7所示,SiO2-DS中的水分子相对数密度如图8所示。
由图7和图8可知:WD-DS中水的最大相对数密度为6.49,并依据10−90准则得出最大相对数密度的10%和90%位点之间的距离约为1.71、3.30 nm,由此可以算出活性剂水溶液和煤的界面厚度约为1.59 nm;同理,算得活性剂水溶液和SiO2的界面厚度约为0.971 nm。由此可得WD-DS的固液界面层厚度大于SiO2-DS。
3. 静电势
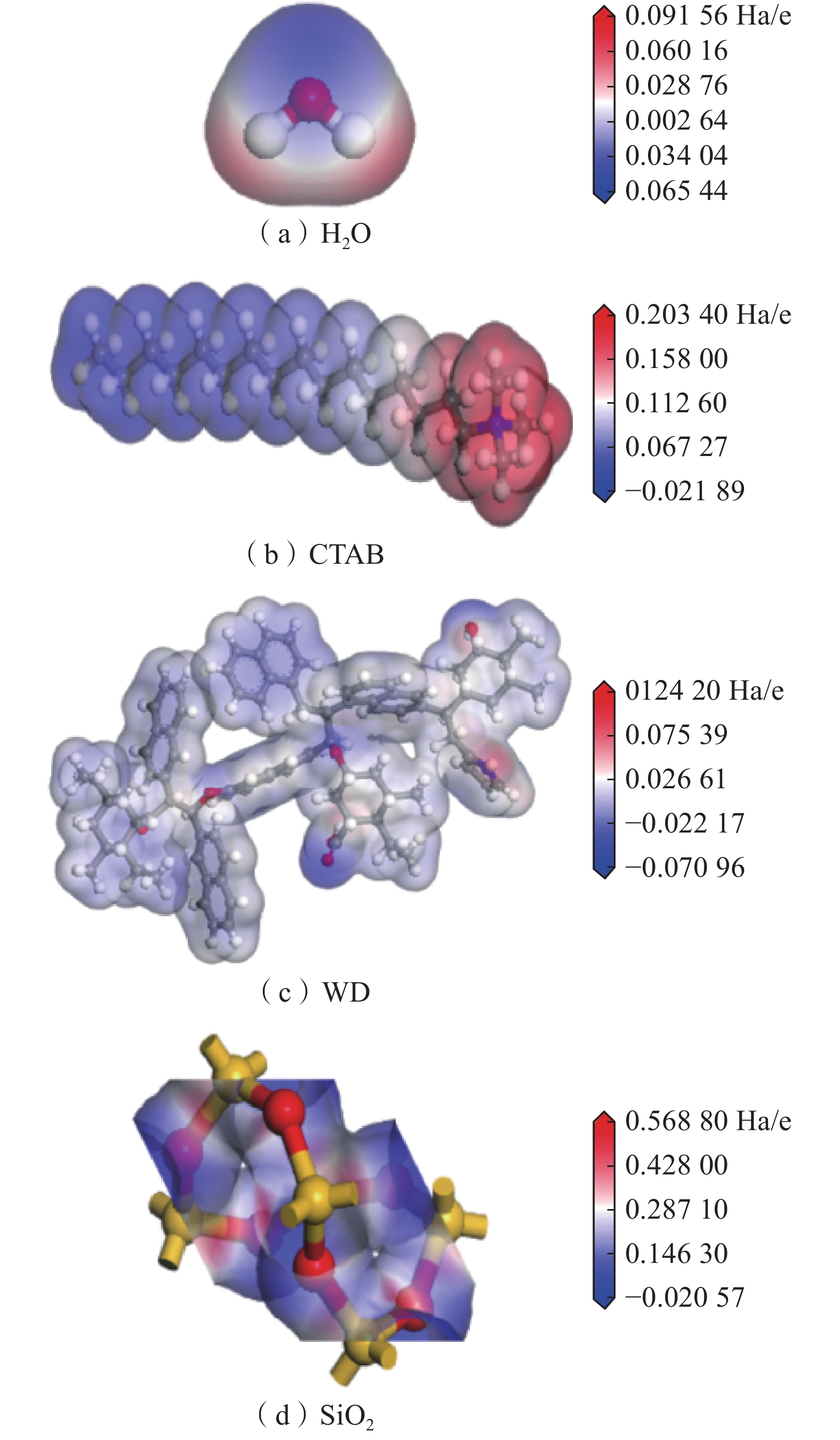
静电势ESP是指从无穷远处移动单位正电荷至该点时所需做的功。分析分子表面静电势可预测其容易发生吸附的位点。各个分子或晶胞静电势图如图9所示。图中:红色区域表示正电荷,该区域的电子收缩表明它很难失去电子,且可以相对容易地接受电子形成氢键;蓝色区域表示负电荷,该区域较容易提供电子形成氢键;白色区域表示电位接近于0的区域,具有相对稳定结构[20]。各个分子或晶胞的静电势对比表见表3。
表 3 各个分子或晶胞的静电势对比表Table 3. Comparison of the electrostatic potential of individual molecules or crystals分子或晶胞种类 静电势/(Ha·e−1) 正 负 尾链 H2O 0.091 56 −0.065 44 — CTAB 0.203 40 — 0.021 89 WD 0.124 20 −0.070 96 — SiO2 0.568 80 −0.020 57 — CTAB头基的最大正静电势0.203 40 Ha/e,大于水分子的最大正静电势0.091 56 Ha/e,可以得出 CTAB的头基是亲水的。尾链的正静电势为0.021 89 Ha/e,小于水分子的最大负静电势0.065 44 Ha/e,因此,CTAB尾链是疏水的。
平衡后,CTAB头基一部分吸附于WD表面的负静电势位置,另一部分与水进行吸附。当头基和WD表面负静电势吸附时,头基会占据原先水分子吸附的界面位置,尾基存在疏水性,朝向水中。吸附前该位置与水分子的电势差为0.162 52 Ha/e,当头基吸附后,该位置与水的电势差变为0.092 85 Ha/e,WD的亲水性减弱。CTAB尾基一部分吸附于WD表面的负静电势位置时,吸附后电势差变为0.274 36 Ha/e, WD的亲水性增强。CTAB头基尾基吸附电势差变化是增大的,对WD分子亲水性是增强的,润湿性有所提升。同理,CTAB对SiO2的润湿作用有所提升。相比之下SiO2加入活性剂之后的电势差增幅更大,润湿效果应该更好。
通过对分子间相互作用能对比可知,WD与水分子之间的作用能更大,润湿性更好,可能主要是因为WD分子中存在大量官能团,比如醚、醇、羧酸、酚、酮等,官能团的存在一定程度上会增加氢键的形成,进而增强分子间的相互作用力,这可能是SiO2和活性剂水溶液的相互作用较弱的原因,导致了SiO2润湿性差。
4. 结 语
1)基于分子动力学模拟的相互作用能和均方位移定量分析表明:在同等质量的WD和SiO2、相同表面活性剂CTAB水溶液条件下,WD和活性剂水溶液的相互作用能为−793.720 4 kcal/mol,SiO2的为−135.598 0 kcal/mol,即CTAB对WD的润湿性较好;结合水分子自扩散系数D验证了CTAB对WD的润湿性较好,其中DWD=0.004 5 nm2/ps 和$D_{{\mathrm{SiO}}_2 } $=0.004 2 nm2/ps,D值越大,水的扩散效果越好。
2)基于分子动力学模拟的径向分布函数和相对数密度的定性分析表明:相较于尾基,CTAB头基和水峰值高、作用强,矽尘和水作用相比于WD弱;由相对数密度所得的固液界面厚度可知,WD和水的界面厚度1.59 nm大于SiO2和水的0.971 nm,所以WD中沿z轴方向润湿性效果好。
3)静电势分析结果表明:表面活性剂CTAB头基是亲水头基,尾基是疏水的。活性剂吸附使得表面发生电势差的变化是影响表面润湿性的因素,CTAB对SiO2和WD 都有润湿效果,单单考虑电势差的变化程度,SiO2的电势差变化程度要大,但是考虑到WD官能团的作用,WD和CTAB水溶液的相互作用能大,CTAB对WD润湿性更好。
-
表 1 描述性统计分析
Table 1 Descriptive statistics analysis
变量 平均值 标准差 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 年龄 2.340 0.826 1 — — — — — — — 受教育程度 2.550 0.822 −0.018 1 — — — — — — 工作年限 2.370 0.787 0.0750 0.121* 1 — — — — — MPSRB 3.015 0.702 −0.072 −0.086 −0.008 1 — — — — SA 2.715 0.768 −0.054 0.081 −0.122* −0.232** 1 — — — SDMC 2.533 0.733 −0.029 −0.025 −0.058 −0.140** 0.204** 1 — — ACSD 2.663 0.743 0.093 0.123* 0.028 0.254** −0.193** −0.023 1 — SCD 2.727 0.712 0.021 0.147** 0.103* 0.143** −0.108* 0.205** 0.143** 1 MSD 2.892 0.750 0.035 0.133** 0.125* 0.329** −0.286** −0.275** 0.275** 0.261** 注:SA为制度敬畏心;SDMC为预期同事对安全偏离的道德谴责;ACSD为预期同事安全偏离;SCD为控制威胁感。***为P<0.001;**为P<0.01;*为P<0.05。 表 2 MPSRB和中介变量的回归分析结果
Table 2 Regression analysis of MPSRB and mediating variables
变量类型 类别 中介变量SA 中介变量SDMC 中介变量ACSD 中介变量SCD 模型1 模型2 模型3 模型4 模型5 模型6 模型7 模型8 控制变量 年龄 −0.039 −0.055 −0.023 −0.032 0.085 0.103* 0.015 0.025 受教育程度 0.090* 0.071 −0.017 −0.028 0.112* 0.134* 0.119* 0.131** 工作年限 −0.127* −0.125* −0.050 −0.049 0.006 0.004 0.077 0.076 自变量 MPSRB — −0.253** — −0.152** — 0.291** — 0.161** ΔR2 0.026 0.053 0.004 0.021 0.024 0.075 0.029 0.025 ΔF值 3.444* 21.983** 0.561 8.278** 3.186* 31.986** 3.893* 10.122** 表 3 MPSRB、中介变量以及MSD回归分析结果
Table 3 Regression analysis of MPSRB, mediating variables and MSD
变量类型 类别 因变量(Y)MSD 模型1 模型2 模型3 模型4 模型5 模型6 模型7 控制变量 年龄 0.026 0.049 0.015 0.020 0.003 0.022 0.012 受教育程度 0.110* 0.138** 0.135** 0.106* 0.081 0.080 0.089* 工作年限 0.104* 0.101* 0.068 0.090* 0.102* 0.084 0.053 自变量 MPSRB — 0.370*** — — — — 0.216** 中介变量 SA — — −0.281** — — — −0.131** SDMC — — — −0.272** — — −0.263** ACSD — — — — 0.263** — 0.146** SCD — — — — — 0.250** 0.241** ΔR2 0.031 0.119 0.081 0.101 0.097 0.086 0.296 ΔF值 4.078** 53.735*** 35.069** 10.865** 10.350** 9.021** 19.979** 表 4 中介效应检验
Table 4 Mediating effect test
效应类型 Effect SE t值 P 95%CI Sobel检验 LLCI(最低) ULCI(最高) Z值 P值 总效应 0.352 0.051 6.865 0.000 0.251 0.452 — — 直接效应 0.197 0.049 3.985 0.001 0.010 0.294 — — 间接效应 MPSRB→SA→MSD 0.032 0.014 — — 0.010 0.066 2.377 0.018 MPSRB→SDMC→MSD 0.041 0.018 — — 0.012 0.082 2.492 0.013 MPSRB→ACSD→MSD 0.044 0.016 — — 0.017 0.081 2.890 0.004 MPSRB→SCD→MSD 0.038 0.016 — — 0.012 0.077 2.502 0.012 -
[1] 李宣东,胡兵,石福泰,等. 煤矿瓦斯爆炸事故不安全动作多维属性统计及特征分析[J]. 煤矿安全,2024,55(1):233−240. LI Xuandong, HU Bing, SHI Futai, et al. Multidimensional attribute statistics and characteristic analysis of unsafe actions in coal mine gas explosion accidents[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2024, 55(1): 233−240.
[2] BRYANT P C, DAVIS C A, HANCOCK J I, et al. When rule makers become rule breakers: Employee level outcomes of managerial pro-social rule breaking[J]. Employee Responsibilities and Rights Journal, 2010, 22(2): 101−112. doi: 10.1007/s10672-009-9114-6
[3] 赵富强,陈耘,张光磊. 施工企业辱虐管理对安全偏离行为的影响研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报,2015,25(6):8−14. ZHAO Fuqiang, CHEN Yun, ZHANG Guanglei. Research on effects of abusive supervision on safe behavior deviance in engineering construction enterprises[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2015, 25(6): 8−14.
[4] 李磊,李浩,李睿涵,等. 非正式组织视角下煤矿工人不安全行为形成路径研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2024,55(1):241−249. LI Lei, LI Hao, LI Ruihan, et al. Study on causes of coal miners’ unsafe behavior based on informal organization[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2024, 55(1): 241−249.
[5] 吕威建,吕永卫. 角色压力对矿工不安全行为的影响研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2021,52(4):255−259. LYU Weijian, LYU Yongwei. Study on the influence of role stressors on miners’ unsafe behavior[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021, 52(4): 255−259.
[6] 禹敏,栗继祖. 基于心理健康中介作用的安全压力对矿工安全行为的影响[J]. 煤矿安全,2019,50(12):253−256. YU Min, LI Jizu. Effect of mediating role on safety behavior of miners based on mental health of safety stress[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2019, 50(12): 253−256.
[7] CHAE B, ZHU R. Environmental disorder leads to self-regulatory failure[J]. Journal of Consumer Research, 2014, 40(6): 1203−1218. doi: 10.1086/674547
[8] 张芷璐,卢国斌,姜福川. 基于自我控制和职业倦怠中介作用的矿工心理韧性对安全绩效的影响[J]. 煤矿安全,2023,54(2):246−251. ZHANG Zhilu, LU Guobin, JIANG Fuchuan. Influence of mental toughness of miners on safety performance based on mediating effect of self-control and job burnout[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2023, 54(2): 246−251.
[9] DEHART-DAVIS L, CHEN J, LITTLE T D. Written versus unwritten rules: The role of rule formalization in green tape[J]. International Public Management Journal, 2013, 16(3): 331−356. doi: 10.1080/10967494.2013.825193
[10] MENG L, WANG X. Awe in the workplace promotes pro-social behavior[J]. PsyCh Journal, 2023, 12(1): 44−53. doi: 10.1002/pchj.593
[11] 姜福川,安泽文. 矿工不安全行为的5M传播模型研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术,2023,19(11):86−92. JIANG Fuchuan, AN Zewen. Research on 5M propagation model for unsafe behavior of miners[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2023, 19(11): 86−92.
[12] FLEMING C J. Pro-social rule breaking at the street level: The roles of leaders, peers, and bureaucracy[J]. Public Management Review, 2020, 22(8): 1191−1216. doi: 10.1080/14719037.2019.1619817
[13] MIRANDA G A, WELBOURNE J L. Examining incivility through a moral lens: Coworker morality appraisals, other-condemning emotions, and instigated incivility[J]. Journal of Business Ethics, 2023, 182(2): 501−519. doi: 10.1007/s10551-021-04955-5
[14] 胡华,朱征,杨朦晰,等. 得失之间:领导底线心智对员工亲团队不道德行为的影响研究[J]. 外国经济与管理,2021,43(10):120−134. HU Hua, ZHU Zheng, YANG Mengxi, et al. Gain and loss: Influence of leader bottom-line mentality on employee unethical pro-group behavior[J]. Foreign Economics & Management, 2021, 43(10): 120−134.
[15] DAHLING J J, CHAU S L, MAYER D M, et al. Breaking rules for the right reasons? An investigation of pro-social rule breaking[J]. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 2012, 33(1): 21−42. doi: 10.1002/job.730
[16] SHIOTA M N, KELTNER D, JOHN O P. Positive emotion dispositions differentially associated with Big Five personality and attachment style[J]. The Journal of Positive Psychology, 2006, 1(2): 61−71. doi: 10.1080/17439760500510833
[17] LIN S H J, JOHNSON R E. A suggestion to improve a day keeps your depletion away: Examining promotive and prohibitive voice behaviors within a regulatory focus and ego depletion framework[J]. Journal of Applied Psychology, 2015, 100(5): 1381−1397. doi: 10.1037/apl0000018
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 刘啸. 吸附条件下含裂隙煤体渗透率演化规律数值模拟分析. 煤矿安全. 2025(03): 12-20 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: