Experimental study on the effect of CaCl2 solution on the inhibition effect of coal spontaneous combustion
-
摘要:
将质量分数为20%的CaCl2溶液作为阻化剂,将原煤分别置于不同温度(30、50、70、90 ℃)的CaCl2溶液中浸泡不同时长,以制备不同预阻化程度的煤样,借助程序升温实验和红外光谱实验,研究CaCl2溶液对煤自燃的阻化效果。结果表明:随着预阻化温度的升高和预阻化时长的增加,煤表面活性基团(−CH3、−CH2和−COOH、−C=O)的含量以及煤耗氧速率显著降低,预阻化率和交叉点温度明显提高;提高预阻化温度和增加预阻化时长均能够明显提高阻化剂对煤自燃特性的抑制率。
Abstract:In this paper, CaCl2 solution was used as an inhibitor. Raw coal was soaked in CaCl2 solution with a mass concentration of 20%, and inhibited coal samples were prepared at different temperature conditions (30 ℃, 50 ℃, 70 ℃ and 90 ℃) for different periods of time. The inhibition effect of CaCl2 solution on coal spontaneous combustion was studied through temperature programmed tests and infrared spectrum experiments. It was found that the content of surface active groups (−CH3, −CH2, −COOH, −C=O) and coal oxygen consumption rate decreased significantly with the increase of pre-inhibition temperature and pre-inhibition time. The inhibition rate and cross point temperature also increase significantly. The results show that increasing the pre-inhibition temperature and the pre-inhibition time can obviously improve the inhibitory effects on the spontaneous combustion characteristics of coal.
-
煤的分子结构中含有烷基侧链、羟基、碳氧基等多种官能团[1],在煤炭开采、储存和运输的过程中容易通过吸附作用跟氧发生复合反应,产生热量并引发自燃,从而威胁矿工身心健康、破坏煤矿安全并造成经济损失和环境污染[2]。因此,煤炭自燃灾害的高效防治技术就成为目前世界主要产煤国的重要研究课题之一[3]。
喷洒阻化剂或压注阻化剂是煤矿现场常用的一种防灭火技术,阻化剂可以通过与煤表面的烷基、羟基和羧基等发生化学反应,破坏煤表面反应活化能较低的化学结构,同时降低表面活性基团浓度,削弱煤表面吸附氧的能力,从而降低煤自然发火的风险[4-5]。研究人员一直致力于寻找、选择合适的阻化剂并不断探讨、优化阻化剂的使用条件。DOU等[6]发现邻苯二酚与聚乙二醇可以促进煤表面形成醚键,对于防治煤自燃有很好的抑制作用;ZHANG等[7]发现在含磷离子液体浸泡后的煤表面,脂肪烃类官能团会大大减少,从而达到抑制煤自燃的目的;SLOVAK等[8]还发现尿素(CO(NH2)2)和卤素无机盐可以提高煤在低温氧化过程中的活化能。然而上述研究都是将阻化剂溶液喷洒在开采后的煤表面,阻化剂的有效覆盖率较低,不能长时间发挥抑制作用,属于后阻化过程。预阻化过程与后阻化过程恰恰相反,可以在开采前向煤层注入阻化剂溶液,使阻化剂完全渗透到煤体的裂纹孔隙中,不仅能够有效延长阻化剂的作用时间,提高抑制煤自燃的效果,还可以有针对性地对不同开采区域实现定位抑制,提升阻化效率。
同时,考虑到阻化剂的经济成本、使用效果和安全环保性等其他因素,目前矿井广泛大量使用的是MgCl2、CaCl2等无机类卤盐阻化剂。然而以往的研究结果[9-11]表明卤盐类无机阻化剂的化学阻化作用非常微弱,难以显著地降低活性官能团的浓度,无法从本质上改变煤的自燃倾向性。因此,研究如何改善卤盐阻化剂的化学阻化效率,对提高阻化剂的现场使用效果具有重要意义。
另外,阻化剂抑制煤自燃的本质是一种化学反应,其阻化效果会受到阻化剂类型及浓度、预阻化压力以及温度等诸多因素的影响。牛国秀等[12]发现当向煤层钻孔内压注Na2CO3溶液预阻化煤层时,在预阻化压力为5.5~9 MPa、质量分数为5%的条件下,对煤自燃的抑制效果较好;张延松等[13]发现预阻化压力为8 MPa、阻化时间为8 h时,Na2CO3能够使煤的自然发火期分别增加12.6%、10.7%。但关于阻化剂抑制煤自燃的研究主要集中在阻化剂类型、阻化剂浓度、预阻化压力等方面,目前关于预阻化温度和预阻化时长的研究较少。为此,研究选择质量分数为20%的CaCl2溶液[14-17]作为卤盐阻化剂的典型代表,通过控制预阻化温度和预阻化时长2个变量制备不同预阻化程度的煤样;借助程序升温实验和傅里叶变换红外光谱实验评估预阻化温度和预阻化时长对抑制煤自燃的阻化程度,从而确定是否可以通过调节预阻化温度和与预阻化时长提高CaCl2溶液的阻化效果。
1. 实验过程与方法
按照“煤样采集→原煤煤样制备→阻化剂水溶液制备→阻化煤样制备”的顺序开展煤样制备工作。实验使用的煤样来自宁夏灵武市磁窑堡镇羊场湾煤矿。煤样采集后使用保鲜膜紧紧包裹并置于密封袋中迅速运送到实验室。煤样的元素分析和工业分析结果见表1。
表 1 煤样的元素分析和工业分析Table 1. Ultimate analysis and proximate analysis results of raw coal% C元素
质量分数H元素
质量分数N元素
质量分数O元素
质量分数S元素
质量分数水分 灰分 挥发分 82.13 4.42 0.80 11.45 1.19 4.52 3.69 33.13 将采集到的新鲜煤样5 kg粉碎后使用0.35~0.56 mm的标准筛进行筛分,然后放入恒温干燥箱的惰性气体环境中,在45 ℃的条件下干燥,每隔1 h称重1次,待煤样恒重后,取出放入广口玻璃瓶密封备用。
称取CaCl2阻化剂试样20 g,放入100 mL烧杯中,用少量蒸馏水进行溶解,待全部溶解后,移入100 mL容量瓶中用蒸馏水稀释至标线,充分摇匀后制得质量分数为20%的CaCl2溶液。
分别称取原煤煤样30 g,放入装有100 mL质量分数为20%的CaCl2溶液的烧杯中,将烧杯置于不同温度(30、50、70、90 ℃;质量分数20%的CaCl2溶液沸点为105 ℃)的恒温水浴,不断搅拌,经过一定时间(0.5、1.0、3.0、5.0、7.0 h)后,取出过滤,放入恒温干燥箱的惰性气体环境中并在45 ℃恒温条件下进行干燥,24 h后,每隔1 h称重1次,压碎脱水干燥过程中产生的结块,待煤样恒重后,取出放入广口玻璃瓶密封备用。水浸煤样的制备过程,除了用去离子水代替质量分数20%的CaCl2溶液外,其他操作与阻化煤样的制备过程完全相同。
1)程序升温实验。采用KSS-5690A型程序升温-气相色谱联用实验装置,模拟煤低温氧化过程。首先将25 g待测煤样装入样品罐,通入流量为100 mL/min的N2对煤样罐进行管路气密性检查。之后将N2流量调整为50 mL/min,30 ℃恒温下加热20 min后,将N2切换为干燥空气,流量为50 mL/min,同时以1.5 ℃/min的升温速率对煤样进行程序升温至200 ℃,每隔20 ℃采集气样并分析检测。
2)傅里叶变换红外光谱实验。取1.0 mg煤样加入150 mg溴化钾粉末中研磨,20 MPa下压片制得厚度为0.1 mm的薄片。采用傅里叶变换红外谱测定仪(VERTEX80/80v)在500~
4000 cm−1范围对原煤和阻化煤样表面官能团进行表征。2. 结果与讨论
2.1 CO的生成特性
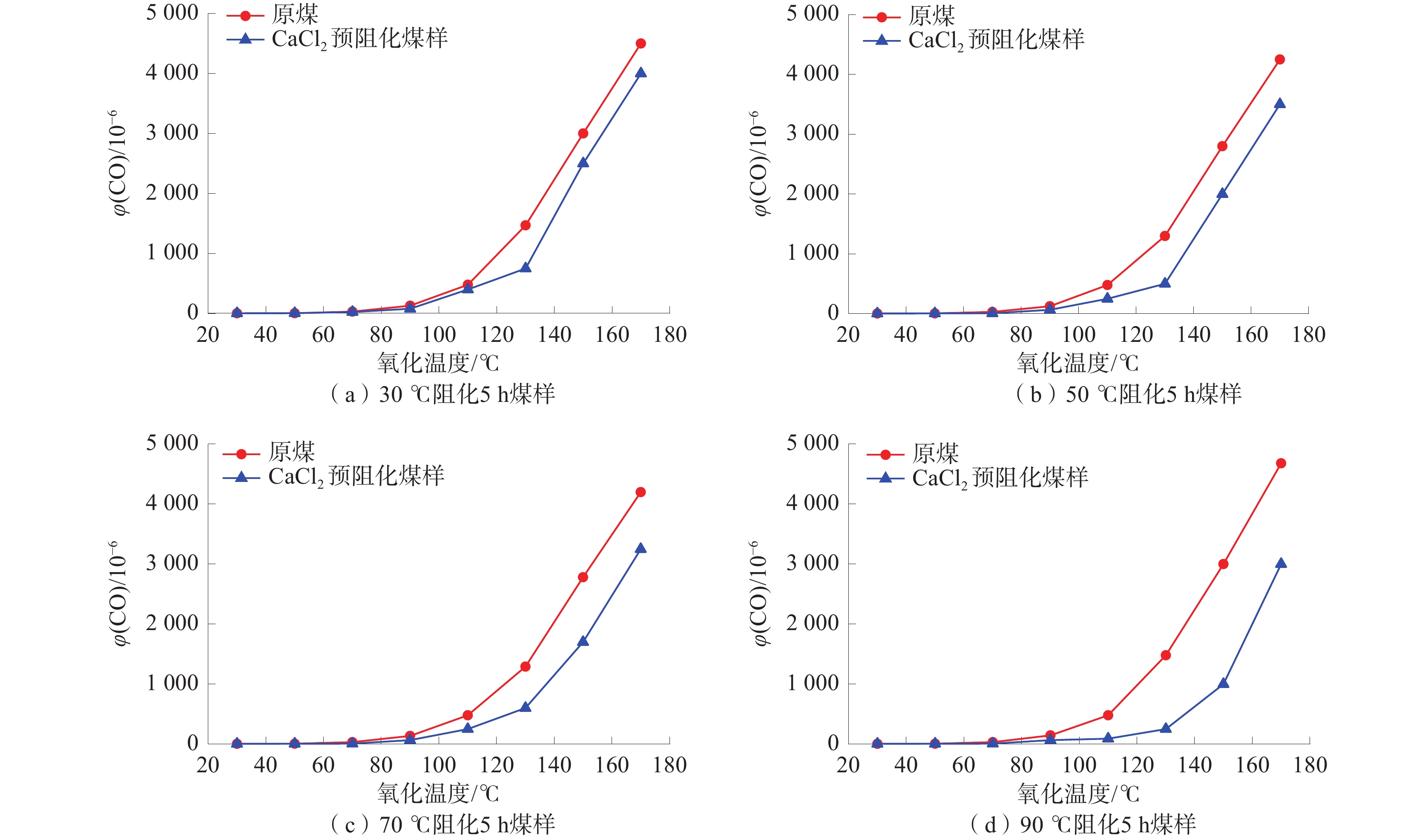
煤与氧一旦发生氧化反应,就会生成CO气体。生成的CO体积分数和煤温、煤的氧化程度之间均具有良好的相关性[18-19]。故通过对煤样开展程序升温实验并测定氧化生成的CO体积分数来评价CaCl2溶液的预阻化效果。原煤和预阻化煤样低温氧化作用下CO生成曲线如图1所示。
由图1可知:随着氧化温度的升高,70 ℃以下原煤煤样和预阻化煤样生成的CO量都较少,且CO量增加较为缓慢,属于缓慢氧化阶段;70 ℃之上CO产量随着温度的升高呈指数型快速增长,属于快速氧化阶段。无论在缓慢氧化阶段还是在快速氧化阶段,原煤煤样和预阻化煤样对应的CO生成量不同。不同温度下被CaCl2预阻化过的煤样,其CO产量始终明显低于原煤煤样。说明CaCl2溶液对于煤样的预阻化效果明显。
实验研究了不同预阻化温度下制备的煤样在氧化过程中生成CO与预阻化温度之间的关系。不同预阻化程度煤样的CO生成曲线对比图如图2所示。实验发现当预阻化温度恒定时,CO的生成量随着预阻化温度的升高而逐渐减少,表明提高预阻化温度可显著抑制煤的自燃。
由图2可知:预阻化时长分别为0.5、1.0、3.0、5.0、7.0 h,预阻化温度为50 ℃时,预阻化煤样的CO生成量分别为原煤煤样CO生成量的0.91、0.85、0.80、0.73、0.70,表明提高预阻化温度可显著增强抑制煤自燃的效果,即提高预阻化温度,能够有效促进阻化剂与煤表面活性基团的反应,减少煤表面活性基团的浓度,这一点同样可以通过预阻化煤样的红外光谱吸收曲线图得到进一步的证实。
实验还发现,在相同的预阻化温度下,预阻化时间越长,氧化过程中CO生成量越低。将煤样在70 ℃预阻化1 h,煤温达到130 ℃时,氧化产生CO量为
1049.65 ×10−6;而70 ℃预阻化7 h的煤样,当氧化温度达到130 ℃时,生成的CO只有498.86×10−6。这与煤块中阻化剂溶液穿透半径的大小有关。预阻化时间越长,阻化剂溶液的渗透半径越大,使得煤孔表面有较多的活性基团失去活度,从而增加氧化反应能垒,降低了煤与氧之间的氧化能力。2.2 预阻化率
预阻化率是对预阻化效果进行定量评价的指标,通过煤样被预阻化前后释放CO气体的相对变化量来进行描述[20]。据文献[21],在煤低温氧化过程中,预阻化率可以通过式(1)计算得到。
$$ R_t\left({\mathrm{CO}}\right)=\frac{\varphi_{t,1}\left({\mathrm{CO}}\right)-\varphi_{t,2}\left({\mathrm{CO}}\right)}{{w}_{1}\left(t\right)}\times 100\text{%} $$ (1) 式中:$R_t$(CO)为温度t时的预阻化率,%;$\varphi_{t,1} $(CO)为原煤低温氧化过程中温度为t时CO体积分数,10−6;$\varphi_{t,2} $(CO)为预阻化煤低温氧化过程中温度为t时CO体积分数,10−6。
低温氧化过程中,经不同预阻化温度、预阻化时长作用后煤样的预阻化率实验结果如图3所示。
由图3(a)可以看出,预阻化温度70 ℃时,以预阻化时长为7 h的煤样为例,其预阻化率约为预阻化时长为0.5 h煤样的2.2~2.8倍。故预阻化温度恒定时,随着预阻化时长的增加,预阻化率呈上升趋势,即预阻化时间越长,预阻化率越高。从图3(b)可以看出,90 ℃处理5 h煤样的预阻化率约为30 ℃处理5 h煤样的1.81倍,由此可得预阻化时长相同条件下,随着预阻化温度的增加,预阻化率呈上升趋势,即预阻化温度越高,预阻化率越高。
为了进一步阐明低温氧化过程中,不同预阻化程度的煤样在不同温度阶段的预阻化效果随温度变化的,以预阻化时长7 h为例,研究了不同预阻化温度下,预阻化率随氧化温度的变化规律;以预阻化温度为90 ℃为例,研究了不同预阻化时长下,预阻化率随氧化温度的变化规律。结果发现预阻化率随氧化温度的变化可以分为30~70、70~130、130~170 ℃ 3个阶段:在30~70 ℃和130~170 ℃温度范围下,预阻化率随着氧化温度的升高呈下降趋势;而在70~130 ℃范围内预阻化率基本保持不变。
2.3 煤样的交叉点温度
在煤样低温氧化实验开始时,煤样的温度低于温控箱的温度,随着煤样的自反应放热和传热的作用,煤样温度会逐渐升高,最终超过温控箱温度。在这个过程中,煤温和箱温的交叉点对应的温度,称之为交叉点温度(CPT)[22]。煤在氧化过程产热能力越强,升温速率越快,CPT越低。因此,CPT也可以用来评估的煤自燃倾向性。不同预阻化程度煤样的CPT试验结果如图4所示。
由图4可以看出:CPT随着预阻化温度的升高而升高预阻化时间越长,CPT越高;随着预阻化温度的升高和预阻化时长的增加,预阻化作用明显增强。
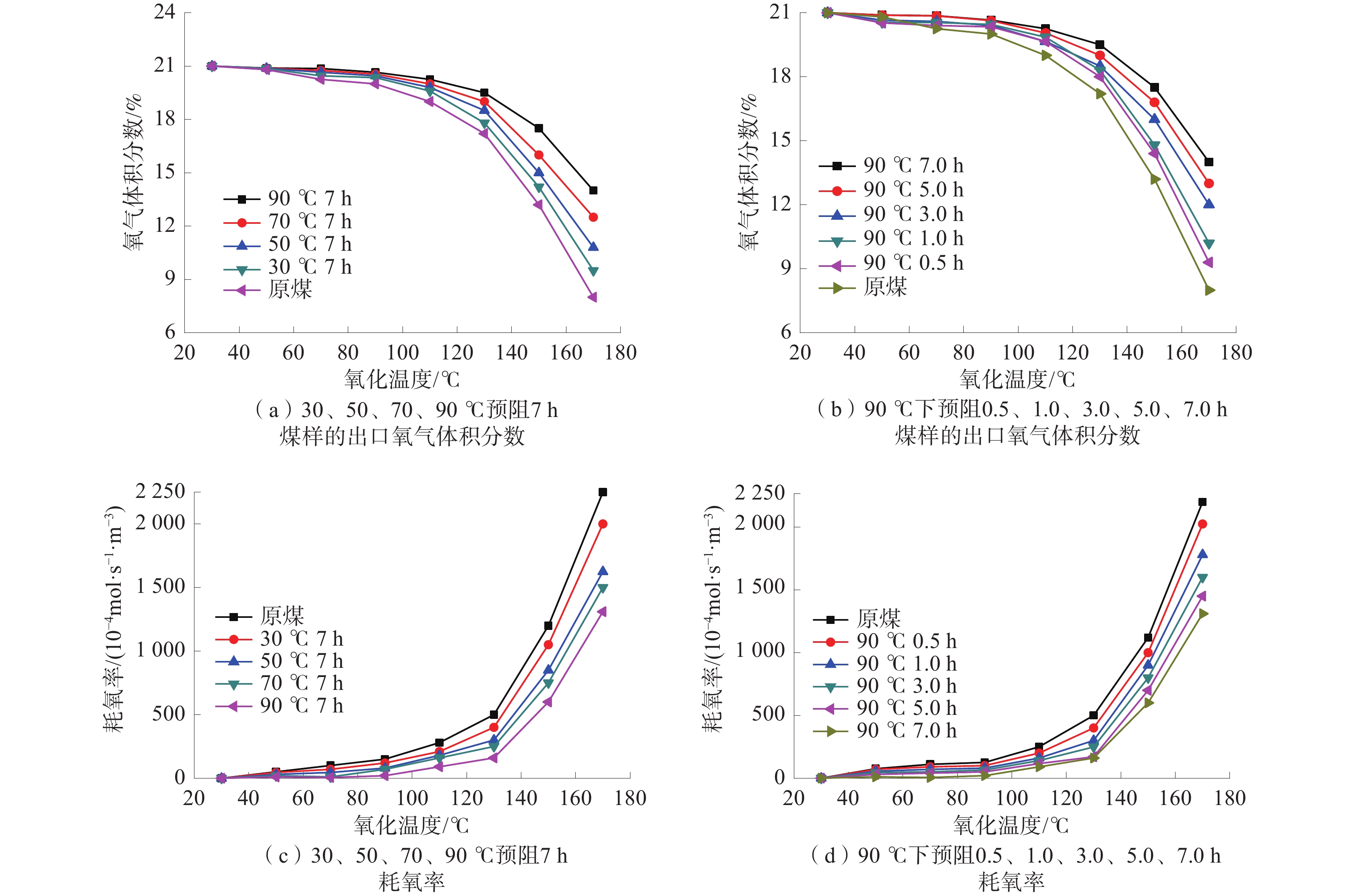
2.4 O2的消耗特性
煤和氧反应的产热速率越高,越利于积聚热量以使煤温升高,且产热速率与耗氧率成正比。耗氧率也可以用来反映煤的自燃倾向性大小。耗氧率可根据式(2)来计算[22]。
$$ R_{t}\left({\mathrm{O}}_2\right)=\frac{Q{c}_{\mathrm{in}}({\mathrm{O}}_2)}{SH}{\mathrm{ln}}\frac{Q{c}_{\mathrm{in}}({\mathrm{O}}_2)}{{{c}_{ {\mathrm{out}}}}({\mathrm{O}}_2)} $$ (2) 式中:$R_{t}\left({\mathrm{O}}_2\right) $为煤样温度为t时的耗氧率,mol/(m3·s);Q为实验中的空气流量,m3/s;S为煤样截面积,m2;${{c}_{ {\mathrm{out}}}}({\mathrm{O}}_2) $为出口氧气浓度,mol/m3;H为煤样高度,m;$ c_{\mathrm{in}}(\mathrm{O}_2) $为进口氧气浓度,mol/m3。
不同预阻化程度煤样的耗氧特性图如图5所示。
由图5可见:耗氧率随着预阻化温度的升高和预阻化时间的延长而逐渐降低;当煤样温度达到为170 ℃时,原煤的耗氧率为0.28 mol/(m3·s);而煤样在90 ℃条件下预阻化7 h后,当煤样温度达到170 ℃耗氧率可降至0.12 mol/(m3·s),产热率和自燃风险明显降低,说明CaCl2溶液对于煤样预阻化效果明显。
2.5 煤表面官能团的变化
为了探讨预阻化温度对煤表面官能团的影响,对不同预阻化温度下的煤样进行了红外光谱分析。红外光谱特征峰的位置可以表征煤表面官能团种类,特征峰的面积可以反映官能团含量。
煤波数范围主要可分为
3200 ~3600 cm−1(羟基官能团)、2800 ~3000 cm−1(脂肪族碳氢侧链)和1500 ~1800 cm−1(含氧官能团)。其中3428 cm−1对应于−OH的振动峰;2955 cm−1对应于甲基−CH3的不对称振动峰;2920 、2850 cm−1主要对应于−CH2的不对称振动峰;1600 cm−1主要对应于羰基C=O的特征峰、1700 cm−1主要对应于羧基COOH的特征峰。此外,处于1375 cm−1位置为−CH3的对称弯曲振动峰;1250 cm−1位置为C=O的伸缩振动峰。不同预阻化温度下的煤样红外光谱图如图6所示。由图6可以看出,不同预阻化温度处理的煤样,具有相似的特征吸收峰,且吸收峰位置基本不变;但随着预阻化温度的升高,吸收峰的面积明显变小,尤其是煤中脂肪族碳氢侧链和含氧官能团的吸收峰面积减少。这说明随着预阻化温度的升高,煤中的主要活性基团种类并未改变,仅含量减少,意味着煤样自燃风险降低,阻化效果增强,说明质量分数为20%的CaCl2溶液对煤的预阻化作用显著。
3. 结 论
1)在使用CaCl2溶液预阻化煤体时,提高预阻化温度和增加预阻化时长均能够明显提高阻化剂对煤自燃特性的抑制率,有效降低煤自燃风险。
2)提高预阻化温度,能够有效促进阻化剂与煤表面活性基团的反应,减少煤表面活性基团的含量,降低煤与氧发生氧化反应的能力,降低煤自燃倾向性,抑制煤自燃的发生。延长预阻化时长,能够增加阻化剂溶液在煤孔内的渗透、润湿范围,使得有更多的活性基团失去活性,从而增加氧化反应能垒,降低了煤发生自燃的风险。
-
表 1 煤样的元素分析和工业分析
Table 1 Ultimate analysis and proximate analysis results of raw coal
% C元素
质量分数H元素
质量分数N元素
质量分数O元素
质量分数S元素
质量分数水分 灰分 挥发分 82.13 4.42 0.80 11.45 1.19 4.52 3.69 33.13 -
[1] 车利明. 未来中长期我国煤炭供应能力预测[J]. 中国煤炭,2016,42(3):5−8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-530X.2016.03.001 CHE Liming. Prediction of Chinese coal supply ability in mid-long term in the future[J]. China Coal, 2016, 42(3): 5−8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-530X.2016.03.001
[2] 袁晓芳,朱明杰. 煤矿人因事故影响因素与组态路径分析[J]. 煤矿安全,2023,54(3):245−250. YUAN Xiaofang, ZHU Mingjie. Analysis on influencing factors and configuration paths of human-caused accidents in coal mines[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2023, 54(3): 245−250.
[3] 冯宇峰,王茜颖,倪坤,等. 20世纪以来我国煤矿安全发展历程及事故总体规律研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2023,54(3):251−256. FENG Yufeng, WANG Xiying, NI Kun, et al. Research on development history of coal mine safety and overall law of accidents in China since the 20th century[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2023, 54(3): 251−256.
[4] 邓军,白祖锦,肖旸,等. 煤自燃灾害防治技术现状与挑战[J]. 煤矿安全,2020,51(10):118−125. DENG Jun, BAI Zujin, XIAO Yang, et al. Present situation and challenge of coal spontaneous combustion disasters prevention and control technology[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2020, 51(10): 118−125.
[5] 刘军见,唐一博,刘洪刚. 硫含量对煤自燃特性的影响实验与模拟研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2024,55(2):99−106. LIU Junjian, TANG Yibo, LIU Honggang. Experimental and simulation study on the effect of sulfur content on spontaneous combustion charcateristics of coal[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2024, 55(2): 99−106.
[6] DOU G L, WANGD M, ZHONGX X, et al. Effectiveness of catechin and poly(ethylene glycol) at inhibiting the spontaneous combustion of coal[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2014, 120: 123−127. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2013.12.016
[7] ZHANG W Q, JIANGS G, HARDACREC, et al. Inhibitory effect of phosphonium-based ionic liquids on coal oxidation[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2014, 28(7): 4333−4341.
[8] SLOVÁK V, TARABA B. Urea and CaCl2 as inhibitors of coal low-temperature oxidation[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2012, 110(1): 363−367. doi: 10.1007/s10973-012-2482-4
[9] 程子朦,李绍英,白丽梅,等. 镁盐阻化剂抑制煤自燃特性的实验研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2024,55(1):126−131. CHENG Zimeng, LI Shaoying, BAI Limei, et al. Experimental study on the inhibition of spontaneous combustion characteristics of coal by magnesium salt inhibitor[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2024, 55(1): 126−131.
[10] 石必明. 易自燃煤低温氧化和阻化的微观结构分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2000,25(3):294−298. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2000.03.017 SHI Biming. The micro structure analysis of the spontaneous combustion coal in oxidization and inhibition at low temperature[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2000, 25(3): 294−298. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2000.03.017
[11] 庞叶青,张奇. 阻化剂氯化镁抑制煤自燃的实验研究[J]. 同煤科技,2020(3):51−54. PANG Yeqing, ZHANG Qi. Research of inhibitor suppression on coal spontaneous combustion by magnesium chloride[J]. Datong Coal Science & Technology, 2020(3): 51−54.
[12] 牛国秀,姚建,康怀宇,等. 煤层预注阻化剂防治采空区煤自然发火试验研究[J]. 煤矿开采,2009,14(1):25−28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6225.2009.01.008 NIU Guoxiu, YAO Jian, KANG Huaiyu, et al. Test research on preventing spontaneous combustion in gob with pre-injecting inhibitor into coal[J]. Coal Mining Technology, 2009, 14(1): 25−28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6225.2009.01.008
[13] 张延松,解庆鑫,孟祥豹,等. 煤层预注阻化液防治煤自然发火的实验研究[J]. 煤炭工程,2018,50(11):87−90. ZHANG Yansong, XIE Qingxin, MENG Xiangbao, et al. Experimental study on the prevention and control of coal spontaneous combustion by inhibitor solution pre-injection[J]. Coal Engineering, 2018, 50(11): 87−90.
[14] TANG Y B, LI Z H, YANG Y, et al. Effect of inorganic chloride on spontaneous combustion of coal[J]. Journal of the Southern African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 2015, 115(2): 87−92. doi: 10.17159/2411-9717/2015/v115n2a1
[15] DARIUSZ Obracaj, TUNG Vu Tien, MAREK Korzec, et al. Effect of calcium chloride solution on the spontaneous combustion of coal using Olpiński method[J]. Fuel, 2020, 339(1): 126903−126908.
[16] 王德明. 矿井火灾学[M]. 徐州:中国矿业大学出版社,2008. [17] 蔡永乐. 矿井内因火灾防治理论与实践[M]. 北京:煤炭工业出版社,2001. [18] 仲晓星,候飞,曹威虎,等. 基于等转化率法的煤氧化自热动力学参数测试方法[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(6):1727−1737. ZHONG Xiaoxing, HOU Fei, CAO Weihu, et al. Testing approach of self-heating kinetic parameters of coal oxidation based on iso-conversional method[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(6): 1727−1737.
[19] 王要令. 煤自燃新型协效阻化剂的研究[J]. 消防科学与技术,2015,34(4):520−522. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2015.04.030 WANG Yaoling. Study on new synergistic inhibitors of coal spontaneous combustion[J]. Fire Science and Technology, 2015, 34(4): 520−522. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2015.04.030
[20] WANGD M, XINH H, QIX Y, et al. Reaction pathway of coal oxidation at low temperatures: A model of cyclic chain reactions and kinetic characteristics[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2016, 163: 447−460. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2015.10.019
[21] QIAO Ling, DENG Chunbao, DAI Fengwei, et al. Experimental study on a metal-chelating agent inhibiting spontaneous combustion of coal[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2019, 33(9): 9232−9240.
[22] LIJ H, LIZ H, YANGY L, et al. Study on the generation of active sites during low-temperature pyrolysis of coal and its influence on coal spontaneous combustion[J]. Fuel, 2019, 241: 283−296. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.12.034



 下载:
下载: