Prediction of development height of water-conducting fracture zone based on rotational subsidence
-
摘要:
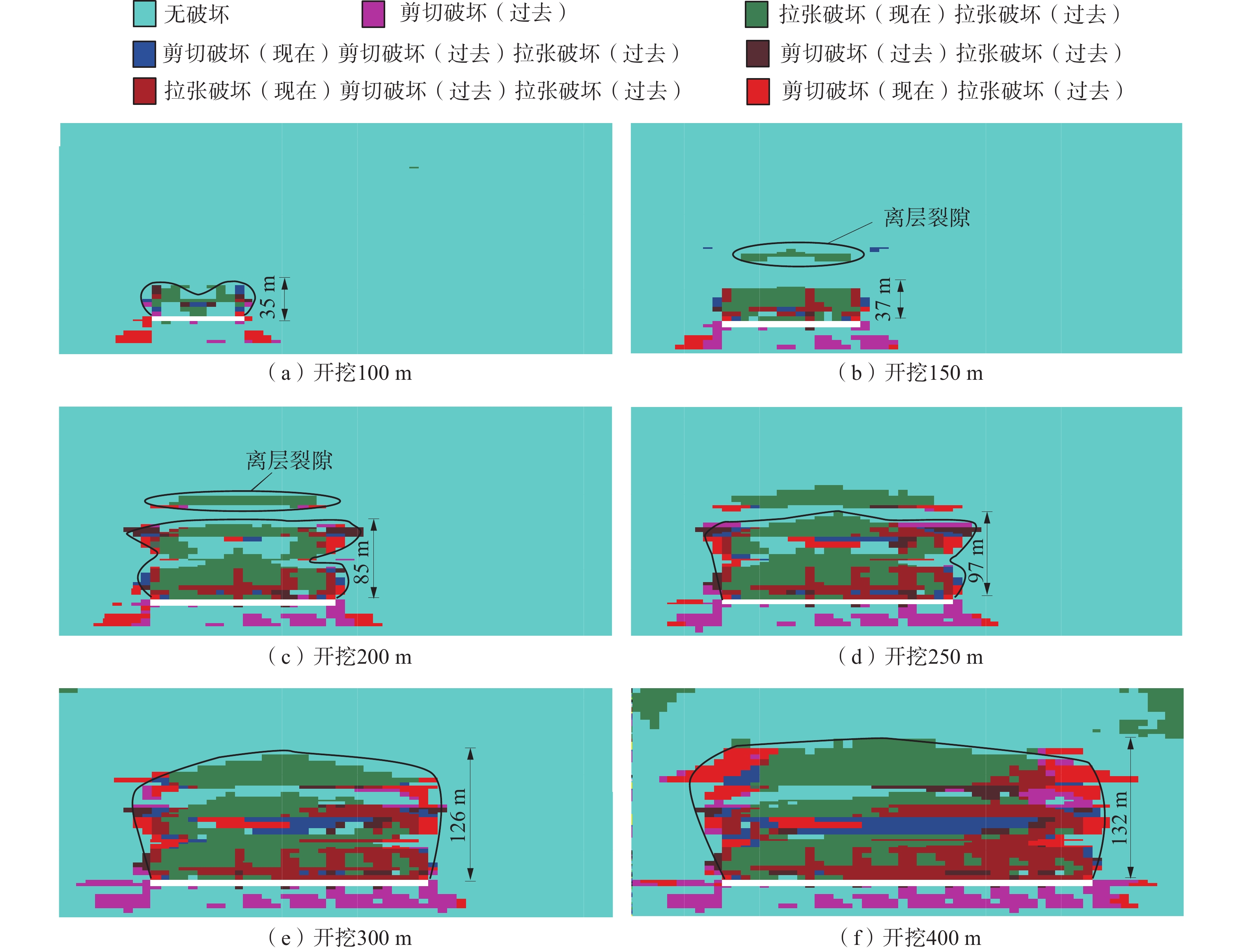
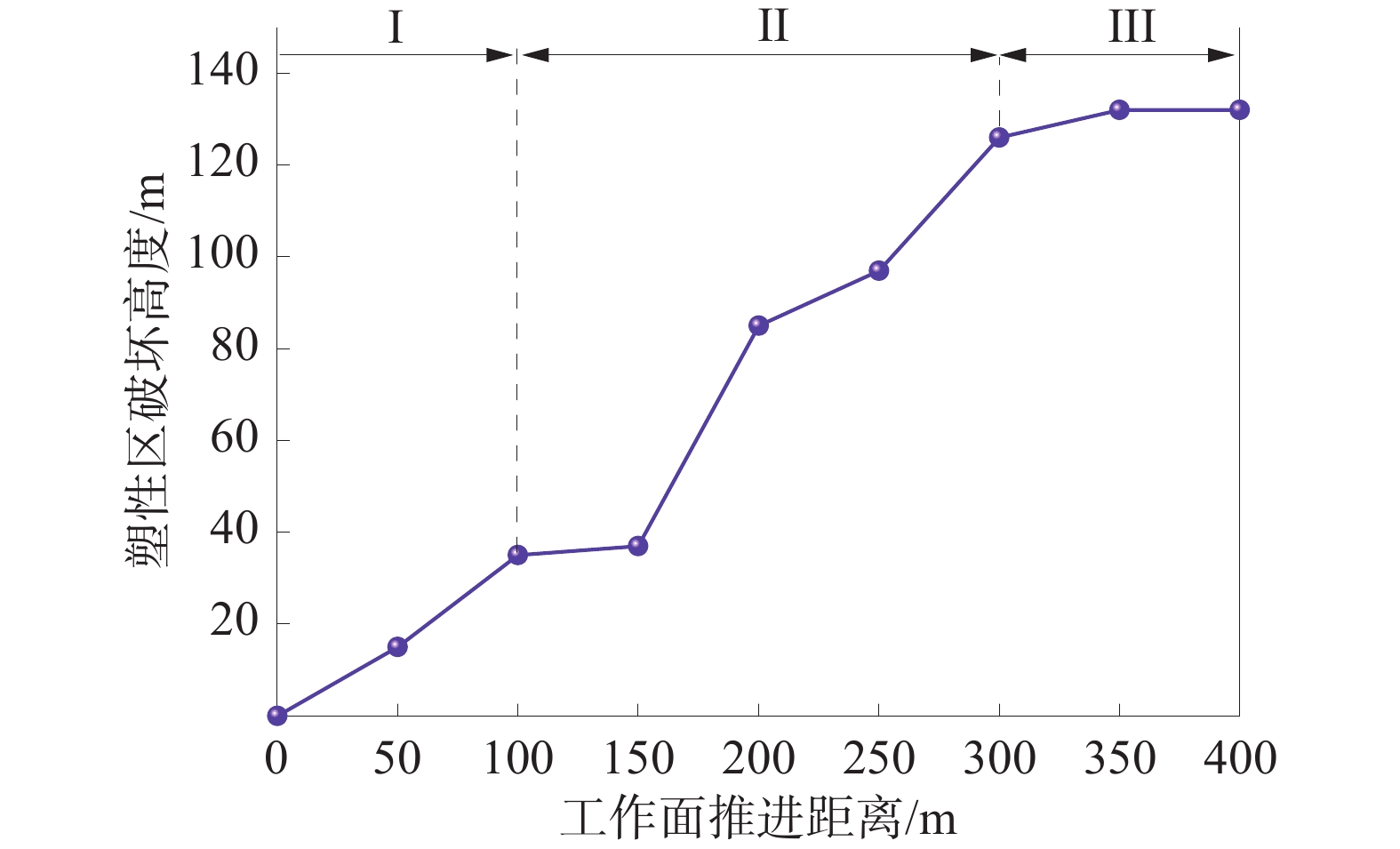
导水裂隙带发育高度是煤矿顶板防治水的重要参数。通过分析采动覆岩破坏过程,将裂隙带内岩层失稳破坏划分为产生垂向裂隙、形成砌体结构和回转失稳3个阶段;建立了岩层产生垂向裂隙及回转下沉的力学模型,在此基础上,提出了分析岩石产生垂向裂隙与回转失稳的最大下沉量来判断岩层破坏情况,回转下沉量值处于这2个阶段之间的岩层形成稳定的砌体结构,得出了计算导水裂隙带高度的新方法。以营盘壕2201工作面为例,采用理论方法和数值模拟对导水裂隙带高度进行预测,通过与现场实测数据的对比,理论计算(123.3 m)和数值模拟结果(132 m)与实测数据(115.5 m)接近,验证了所提方法的合理性。
Abstract:The development height of water-conducting fracture zone(WCFZ) is an important parameter for water disaster treatment in coal mine roof. In this paper, the failure process of mining overlying rock is analyzed, and the rock instability failure in the fracture zone is divided into three stages: vertical fracture formation, masonry structure formation and gyratory instability; a mechanical model of vertical cracks and gyration subsidence is established. On this basis, the maximum subsidence of vertical cracks and gyration instability is analyzed to judge the rock failure. The rock stratum with gyration subsidence value between these two stages forms a stable masonry beam structure, and a new method for calculating the height of WCFZ is obtained. Taking the 2201 working face of Yingpanhao as an example, the height of the WCFZ is predicted by theoretical method and numerical simulation. By comparing with the field measured data, the theoretical calculation (123.3 m) and numerical simulation results (132 m) are close to the measured data (115.5 m), which verifies the rationality of the proposed method.
-
煤炭是我国能源的压舱石和稳定器,对保障我国能源供给和能源安全具有重要意义。瓦斯爆炸是煤矿灾害事故中最具破坏力的事故之一[1-3]。随着大采高工作面一次采全高和综采放顶煤开采技术的广泛应用,采空区顶板垮落过程中岩体相互撞击摩擦产生火花已成为诱发采空区瓦斯爆炸事故的主要隐患。众多学者在岩石撞击升温[4-5]、摩擦闪温[6-7]、砂岩放电[8]、瓦斯引燃温度阈值[9-10]、瓦斯爆炸温度分布[11]、顶板失稳摩擦区域[12]等方面进行了研究。周应江等[13]以某工作面瓦斯事故为研究对象,开展了采空区瓦斯燃烧原因调查,发现该次瓦斯事故是因顶板垮落掉落的石英砂岩撞击摩擦产生火花引燃瓦斯;许家林等[14]、屈庆栋等[15]研究了顶板垮落撞击产生摩擦火花的诸多因素,认为开采厚度、岩块石英含量、干燥程度、接触压力与产生摩擦火花概率成正比;秦广鹏等[16-18]研究了坚硬顶板冒落过程中砂岩摩擦引燃采空区瓦斯机制,初步探讨了摩擦速度、石英含量与摩擦面热量密度之间的联系;陈琛等[19]建立了考虑高温热痕、岩壁、风流导热和风流对流的微分方程,确定了岩石摩擦引燃瓦斯的温度阈值;李冬等[20]研究表明岩石石英含量、摩擦面粗糙程度、撞击高度、摩擦时间等因素与岩石表面温度呈正相关;周锦龙等[21]开展了岩辊渐进摩擦试验,定量表征了岩石摩擦速度与最大闪温的关系。专家学者在岩石摩擦升温引发瓦斯燃烧爆炸取得的成果对防控采空区瓦斯爆炸起到了显著作用。针对现有研究中对定量化指标考虑不系统、指标研究不深入的问题,采用岩石摩擦效应引燃瓦斯试验系统,设计试验从砂岩摩擦速度、摩擦力、瓦斯浓度、SiO2含量等角度探究砂岩摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸机制,为防控采空区顶板垮落过程中岩体相互撞击摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸提供依据。
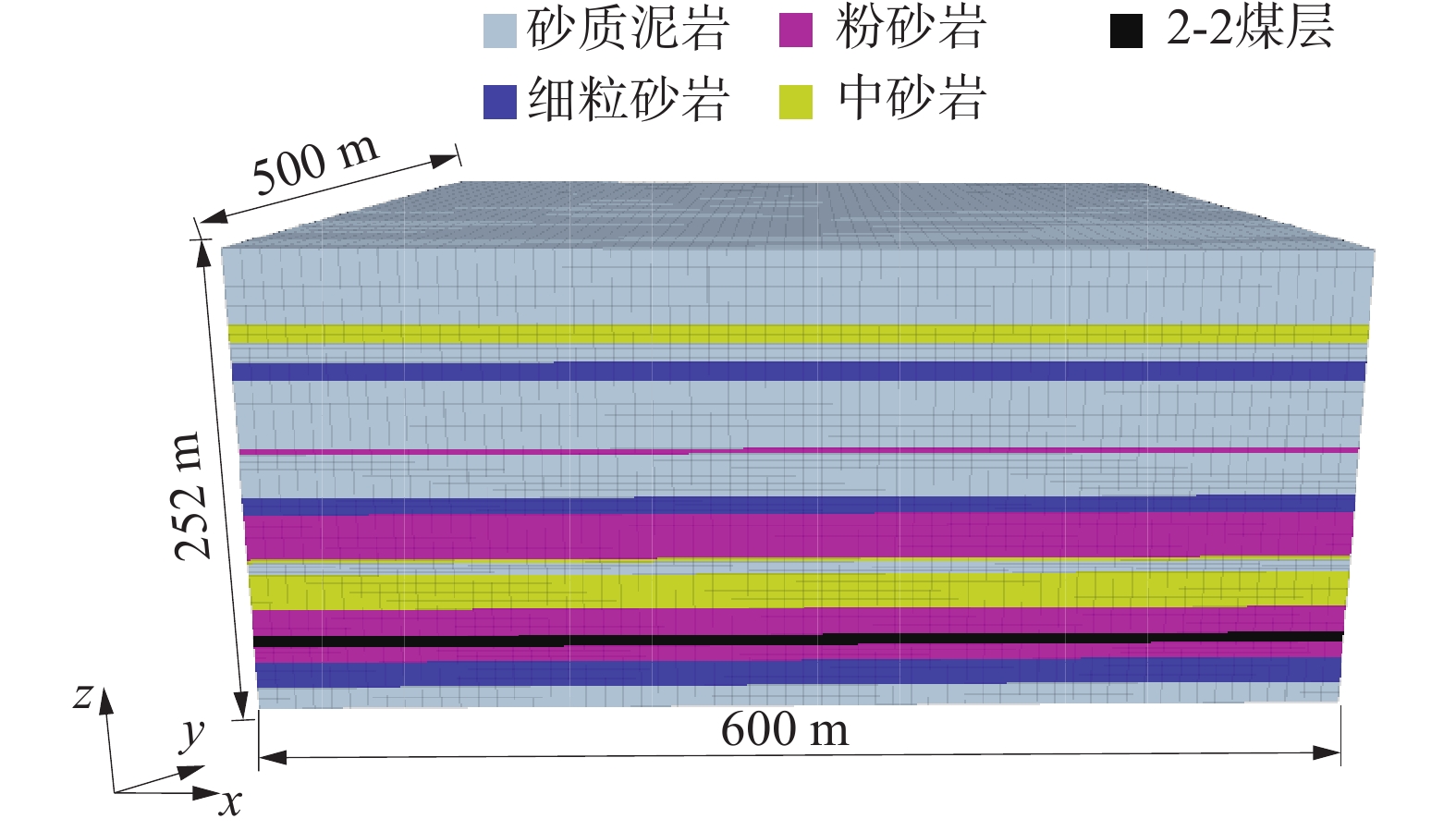
1. 工程背景
新疆某矿井田总体处于复式背斜的南翼,为单斜构造,伴有较多断层,局部褶皱发育,倾角6°~12°,区域断层特点基本沿北东向、近南北向发育,东部断层发育,西部深部相对简单。该矿N4107工作面走向方向长为2 128 m、倾斜方向长为240 m,工作面地面标高为+1 040~+1 100 m、井下标高为+530~+650 m、埋深472~573 m,工作面北部、西部为实体煤,南部为集中回风巷,东邻N4106采空区。N4107工作面回采4-1煤层,煤层由北向南逐渐变薄,煤岩类型以半暗型煤变半亮型煤为主,煤层厚度为8.25~9.17 m、平均为8.70 m,倾角5°~14°,平均为9°。4-1煤层瓦斯含量较高,N4107工作面经过预抽,瓦斯相对涌出量0.36 m3/t,绝对涌出量为4.36 m3/min。4-1煤层顶底板情况见表1。
表 1 4-1煤层顶底板基本力学参数Table 1. Basic mechanical parameters of 4-1 coal roof and floor岩样 岩性 破坏载荷/kN 抗压强度/MPa 弹性模量/GPa 基本顶 粉砂岩 66.38 35.74 11.42 直接顶 细砂岩 94.04 50.73 15.31 直接底 细砂岩 94.29 51.20 17.29 2. 试验设计
2.1 试 样
本次试验试样材料取自新疆某矿N4107工作面基本顶、直接顶与直接底中的砂岩,3组摩擦试件与旋转试件分别取自同一块岩块。使用岩石切磨一体机将煤、岩块进行切割、打磨,加工成内径为40 mm,外径为120 mm,高25 mm的环形旋转试件,共制备了3组试样。
利用X射线衍射仪对3组摩擦试件样本物相进行测定分析,得到基本顶、直接顶、直接底3组试样中SiO2含量分别为57.53%、67.85%、61.44%。
2.2 试验系统
岩石摩擦效应引燃瓦斯试验系统主要包括摩擦试验箱、动力控制系统、试件摩擦系统以及瓦斯监测系统4个部分。
1)摩擦试验箱。箱体由厚度为10 mm的钢板制成,箱体的长、宽、高分别为660、660、690 mm。试验箱前部开有30 mm×30 mm的泄爆口,试验时用塑料纸密封,瓦斯爆炸后产生气流能够及时从泄爆口排出,从而避免爆炸对设备造成损坏。泄爆口下部开有直径为10 mm的瓦斯注入口,瓦斯注入后用螺丝密封。试验箱右端为1块12 mm厚的可拆卸钢化玻璃,四周用密封封条密封,以便观察、记录试验现象。
2)动力控制系统。动力控制系统采用额定电压380 V、额定功率5.5 kW、转速2 800 r/min的三相异步电机为试验提供动力。电机转速通过变频器控制,变频器额定功率为7.5 kW,额定输出电流为17 A,输入电压为380 V。三相异步电机通过连接箱内工业联轴器与摩擦试验箱连接,将电机动力传导给试验箱内试件,其外部加装保护壳,提高试验的安全性。
3)试件摩擦系统。试件摩擦系统由试件加压装置、摩擦试件固定装置、旋转试件固定装置组成。试件加压装置为1块厚度为30 mm的“T”形钢板,钢板质量15 kg。其一端与箱体通过旋转轴连接,另一端用于悬挂重物增加配重。试件加压装置放下时“T”形钢板下方正好与旋转试件接触。摩擦试件固定装置的主要功能是固定摩擦试件,保证试验进行过程中摩擦试件与旋转试件稳定接触。摩擦试件固定装置由底部托板和上部的平口钳组成。底部托板固定在试件加压装置上,与试件加压装置形成1个平面,用于固定平口钳,保证摩擦试件水平。摩擦试件固定装置与试件加压装置通过螺栓连为一体,确保整体牢固。
4)瓦斯监测系统。瓦斯监测系统由瓦斯监测仪、监测探头和气体报警控制主机组成。瓦斯监测仪量程为0~100%,用于实时监测试验中瓦斯体积分数。
2.3 试验方案
依据工程现场采空区难以监测的位置局部瓦斯体积分数可能升高至瓦斯爆炸体积分数范围(5.0%~16.0%),确定试验中瓦斯体积分数范围。因工程现场中顶板垮落过程中岩块大小、形状及速度均不相同,根据岩石摩擦效应引燃瓦斯试验系统配重范围,将摩擦力参数设置为摩擦载质量15.0~19.0 kg。根据N4107工作面煤层最厚位置确定顶板最大垮落高度为9.17 m,按照自由落体理想状态,直接顶垮落至顶板最大速度为13.43 m/s,因此将摩擦速度参数设置为4.0~14.0 m/s。SiO2含量参数由采用X射线衍射仪对顶底板摩擦试件样本物相进行测定分析得到。
共设计19组试验,每组试验重复3次,命名为试验1、试验2、试验3,取3次试验平均值以避免试验误差。其中5组为不同瓦斯体积分数(6.0%、7.0%、8.5%、10.0%、11.5%)砂岩摩擦引燃瓦斯试验,5组为不同摩擦力(载质量15.0、16.0、17.0、18.0、19.0 kg)砂岩摩擦引燃瓦斯试验,3组为不同SiO2含量(57.53%、67.85%、61.44%)砂岩摩擦引燃瓦斯试验,6组为不同摩擦速度(4.0、6.0、8.0、10.0、12.0、14.0 m/s)砂岩摩擦引燃瓦斯试验。设计试验方案见表2。
表 2 摩擦引燃瓦斯试验方案Table 2. Friction ignition gas test schemes瓦斯体积
分数/%摩擦速度/
(m·s−1)摩擦载
质量/kg摩擦试件
SiO2含量/%重复试
验次数6.0 8.0 15 67.85 3 7.0 8.0 15 67.85 3 8.5 8.0 15 67.85 3 10.0 8.0 15 67.85 3 11.5 8.0 15 67.85 3 10.0 4.0 15 67.85 3 10.0 6.0 15 67.85 3 10.0 8.0 15 67.85 3 10.0 10.0 15 67.85 3 10.0 12.0 15 67.85 3 10.0 14.0 15 67.85 3 10.0 8.0 15 67.85 3 10.0 8.0 16 67.85 3 10.0 8.0 17 67.85 3 10.0 8.0 18 67.85 3 10.0 8.0 19 67.85 3 10.0 8.0 15 57.53 3 10.0 8.0 15 61.44 3 10.0 8.0 15 67.85 3 3. 试验结果
3.1 摩擦引燃瓦斯爆炸范围计算
采用高速摄像机记录摩擦引燃瓦斯直至瓦斯完全爆炸的全过程。导出该过程中瓦斯爆炸图像后,通过MATLAB编写程序获得瓦斯燃烧过程中的每帧图像的明度信息,确定瓦斯燃烧区域明度值范围,计算得出瓦斯燃烧比例。具体明度获取过程为:
1)通过MATLAB中imread函数获取瓦斯燃烧过程中的每帧图像。
2)遍历像素数组索引获取每帧图像像素坐标。
3)使用size函数来获取图片的尺寸以及rgb2xyz函数来获取像素的RGB值。
4)通过式(1)计算明度。
$$ L{\text{ = }}\sqrt[\leftroot{-1}\uproot{12}{{2.2}}]{{\frac{{{{\left( {R/{\text{255}}} \right)}^{{\text{2}}{\text{.2}}}} + {{\left( {{\text{1}}{\text{.5}}G/{\text{255}}} \right)}^{{\text{2}}{\text{.2}}}} + {{\left( {{\text{0}}{\text{.6}}B/{\text{255}}} \right)}^{{\text{2}}{\text{.2}}}}}}{{{\text{1 + 1}}{\text{.}}{{\text{5}}^{{\text{2}}{\text{.2}}}}{\text{ + 0}}{\text{.}}{{\text{6}}^{{\text{2}}{\text{.2}}}}}}}} $$ (1) 式中:L为明度值,范围为0~1;R为红色光功率,范围为0~255;G 为绿色光功率,范围为0~255;B为蓝色光功率,范围为0~255。
3.2 瓦斯体积分数对摩擦引燃瓦斯的影响
设置5组不同瓦斯体积分数(6.0%、7.0%、8.5%、10.0%、11.5%)砂岩摩擦引燃瓦斯试验,试验摩擦速度为8 m/s,摩擦载质量15 kg,摩擦试件SiO2含量为67.85%,每组试验重复3次,命名为试验1、试验2、试验3。当瓦斯体积分数为6.0%时,3次试验瓦斯均未爆炸,当瓦斯体积分数为7.0%、8.5%、10.0%、11.5%时,试验发生瓦斯爆炸,爆炸时摩擦速度均已达到8 m/s。不同瓦斯体积分数下砂岩摩擦引发瓦斯爆炸时间如图1所示。
为排除试验误差对试验结果的影响,取每组试验的3次瓦斯爆炸时间均值进行分析。试验中,当瓦斯体积分数为6.0%时,摩擦未引发瓦斯爆炸。由图1可知:摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸的最低体积分数为7.0%;随瓦斯体积分数增加,试验瓦斯发生爆炸时摩擦速度均已达到8 m/s;当瓦斯体积分数为7.0%时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间为32.33 s;瓦斯体积分数增加至8.5%时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间缩短至21.78 s,缩短幅度为32.63%;瓦斯体积分数增加为10.0%时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间缩短至19.63 s,缩短幅度为10.95%;随着瓦斯体积分数继续增加至11.5%时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间延长至23.16 s,延长幅度为17.98%。由此可得随瓦斯体积分数自6.0%开始增加,摩擦由未诱发瓦斯爆炸到诱发瓦斯爆炸,瓦斯体积分数继续增加后,摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸时间逐渐缩短,缩短幅度下降,瓦斯体积分数为10.0%时,摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸时间最短,随后瓦斯体积分数增加使摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸时间延长。
不同体积分数瓦斯在摩擦试验箱内爆炸过程如图2所示,不同体积分数瓦斯在摩擦试验箱内爆炸过程中瓦斯燃烧比例变化如图3所示。
由图2可知:摩擦试验箱内瓦斯爆炸过程分为砂岩摩擦面燃烧瓦斯与瓦斯爆炸扩散2个阶段。在砂岩摩擦面燃烧瓦斯阶段,摩擦试验箱内瓦斯被转动试件摩擦表面燃烧,在0~40 ms瓦斯燃烧路径为自摩擦试件与转动试件接触点沿环形转动试件表面顺时针方向蔓延,因此砂岩摩擦产生的高温热表面是砂岩摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸的主要原因。
由图3可知:瓦斯体积分数为7.0%、8.5%时,摩擦试验箱内全部瓦斯燃烧耗时140 ms;瓦斯体积分数为10.0%时,摩擦试验箱内全部瓦斯燃烧耗时100 ms;瓦斯体积分数为11.5%时,摩擦试验箱内全部瓦斯燃烧耗时80 ms;相同时刻摩擦试验箱内瓦斯燃烧比例随瓦斯体积分数的增加而增大。由此可知:瓦斯体积分数在7.0%~11.5%范围内,其体积分数的增加对瓦斯爆炸传播具有促进作用;瓦斯体积分数为7.0%、8.5%时,其燃烧比例变化趋势为缓慢增大-快速增大-缓慢增大;瓦斯体积分数为10.0%、11.5%时,其燃烧比例变化趋势为缓慢增大-快速增大-缓慢增大-快速增大,这是因为较高的瓦斯含量在燃烧后期已将氧气含量消耗至较低水平,因此对剩余瓦斯快速燃烧产生抑制作用。
3.3 摩擦力对摩擦引燃瓦斯的影响
设置5组不同摩擦力(载质量15.0、16.0、17.0、18.0、19.0 kg)砂岩摩擦引燃瓦斯试验,试验摩擦速度为8 m/s,瓦斯体积分数10.0%,摩擦试件SiO2含量为67.85%,每组试验重复3次。当瓦斯体积分数为6.0%时,3次试验瓦斯均未爆炸,当瓦斯体积分数为7.0%、8.5%、10.0%、11.5%时,试验发生瓦斯爆炸。不同载质量下砂岩摩擦引发瓦斯爆炸时间如图4所示。
为排除试验误差对试验结果的影响,取每组试验的3次瓦斯爆炸时间均值进行分析。5组不同砂岩摩擦力试验均引发瓦斯爆炸,爆炸时摩擦速度均已达到8 m/s。由图4可知:当摩擦试件载质量为15 kg时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间为19.63 s;当摩擦试件载质量增加至16 kg时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间缩短至18.95 s,缩短幅度为3.46%;当摩擦试件载质量增加至17 kg时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间缩短至18.17 s,缩短幅度为4.12%;当摩擦试件载质量增加至18 kg时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间缩短至17.14 s,缩短幅度为5.67%;当摩擦试件载质量增加至19 kg时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间缩短至16.13 s,缩短幅度为5.89%;随着摩擦试件载质量增加,摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸时间逐渐缩短,摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸时间缩短幅度逐渐增加。
3.4 石英成分对摩擦引燃瓦斯的影响
自N4107工作面基本顶、直接顶、直接底中取3组砂岩摩擦试件,利用X射线衍射仪对3组摩擦试件样本物相进行测定分析,得到基本顶、直接顶、直接底3组试样中SiO2含量分别为57.53%、67.85%、61.44%。每组试验重复3次。不同SiO2含量砂岩摩擦引发瓦斯爆炸时间如图5所示。
为排除试验误差对试验结果的影响,取每组试验的3次瓦斯爆炸时间均值进行分析。由图5可知:3组不同SiO2含量砂岩摩擦试验均引发瓦斯爆炸,爆炸时摩擦速度均已达到8 m/s;当砂岩摩擦试件SiO2含量为57.53%时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间为15.82 s;砂岩摩擦试件SiO2含量为61.44%时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间为17.44 s;当砂岩摩擦试件SiO2含量为67.85%时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间为19.63 s。因此认为砂岩摩擦试件SiO2含量影响着摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸的难易程度,更高SiO2含量的砂岩摩擦将增大诱发瓦斯爆炸的风险。
3.5 摩擦速度对摩擦引燃瓦斯的影响
设置6组不同摩擦速度(4.0、6.0、8.0、10.0、12.0、14.0 m/s)砂岩摩擦引燃瓦斯试验,试验载重15.0 kg,瓦斯体积分数10.0%,摩擦试件SiO2含量为67.85%,每组试验重复3次。当摩擦速度为4.0、6.0 m/s时,3次试验瓦斯均未爆炸,不同摩擦速度下砂岩摩擦引发瓦斯爆炸时间如图6所示。
为排除试验误差对试验结果的影响,取每组试验的3次瓦斯爆炸时间均值进行分析。由图6可知:当砂岩最大摩擦速度为8.0、10.0、12.0 m/s时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间分别为19.63、17.20、15.50 s,3组试验中瓦斯爆炸前转动试件已达到最大摩擦速度;当砂岩最大摩擦速度为14.0 m/s时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间为15.21 s,瓦斯爆炸前转动试件摩擦速度加速至12.9 m/s;当砂岩最大摩擦速度为6.0 m/s及以下时,长时间的摩擦并不会使转动试件表面升温至瓦斯着火点;当砂岩摩擦速度为8.0 m/s及以上时,长时间的摩擦使转动试件表面逐渐升温至瓦斯着火点,速度的增大有利于更快的升温;当摩擦速度达到12.9 m/s时,摩擦速度的加速过程已使转动试件表面升温至着火点。因此认为对于恒定加速度下摩擦试件有最低临界速度与最高临界速度:低于最低临界速度则转动试件表面不会升温至瓦斯着火点诱发瓦斯爆炸;高于最低临界速度且低于最高临界速度时,需在达到该速度后持续摩擦一定时间转动试件表面方可达到瓦斯着火点,在此速度区间内最大摩擦速度与摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸时间呈负相关。当摩擦速度达到最高临界速度时转动试件表面将升温至瓦斯着火点。
4. 结 语
1)瓦斯体积分数低于6.0%时,砂岩摩擦不能诱发瓦斯爆炸到诱发瓦斯爆炸,瓦斯体积分数为7.0%~11.5%时,摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸时间随瓦斯体积分数增加而先缩短后延长,瓦斯体积分数为10.0%时,摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸时间最短。
2)摩擦试验箱内瓦斯爆炸过程分为砂岩摩擦面燃烧瓦斯与瓦斯爆炸扩散2个阶段。在砂岩摩擦面燃烧瓦斯阶段,摩擦试验箱内瓦斯被转动试件摩擦表面燃烧,因此砂岩摩擦产生的高温热表面是砂岩摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸的主要原因。在瓦斯爆炸扩散阶段,瓦斯体积分数为7.0%、8.5%时,其燃烧比例变化趋势为缓慢增大-快速增大-缓慢增大;瓦斯体积分数为10.0%、11.5%时,其燃烧比例变化趋势为缓慢增大-快速增大-缓慢增大-快速增大。
3)随着摩擦试件载重增加使摩擦试件与转动试件之间摩擦力增大,加快了转动试件表面升温至瓦斯着火点,摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸时间逐渐缩短,且摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸时间缩短幅度逐渐增加。
4)砂岩摩擦试件SiO2含量影响着摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸的难易程度,更高SiO2含量的砂岩摩擦将增大诱发瓦斯爆炸的风险。
5)恒定加速度下摩擦试件有最低临界速度与最高临界速度。低于最低临界速度则转动试件表面不会升温至瓦斯着火点诱发瓦斯爆炸。高于最低临界速度且低于最高临界速度时,需在达到该速度后持续摩擦一定时间转动试件表面方可达到瓦斯着火点,在此速度区间内最大摩擦速度与摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸时间呈负相关。当摩擦速度达到最高临界速度时转动试件表面将升温至瓦斯着火点。
-
[1] 马军前,仝昕,李成银. 弱胶结地层采动覆岩活动规律及渗透性演化特征研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2020,48(S2):11−16. MA Junqian, TONG Xin, LI Chengyin. Study on movement laws and permeability evolution features of mining-induced overburden in weakly cemented strata[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48(S2): 11−16.
[2] 国家安全监管局,国家煤矿安监局,国家能源局. 建筑物-水体-铁路及主要井巷煤柱留设与压煤开采规范[M]. 北京:煤炭工业出版社,2017. [3] 王家臣,许家林,杨胜利,等. 煤矿采场岩层运动与控制研究进展−纪念钱鸣高院士“砌体梁”理论40年[J]. 煤炭科学术,2023,51(1):80−94. WANG Jiachen, XU Jialin, YANG Shengli, et al. Development of strata movement and its control in underground mining: In memory of 40 years of voussoir beam theory proposed by academician Minggao Qian[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2023, 51(1): 80−94.
[4] 刘卓然,赵高博. 综放开采覆岩破坏特征与导水断裂带高度模拟研究[J]. 矿业安全与环保,2021,48(6):12−18. LIU Zhuoran, ZHAO Gaobo. Investigation on overburden failure characteristic and height of water-conducted fracture zone due to fully mechanized caving mining[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection, 2021, 48(6): 12−18.
[5] XU J, YAN H, ZHANG Y, et al. The morphology of fully-aromatic polyamide separation layer and its relationship with separation performance of TFC membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2017, 541: 174−188.
[6] 张村,任赵鹏,韩鹏华,等. 西部矿区厚基岩特大采高工作面导水裂隙带发育特征[J]. 矿业科学学报,2022,7(3):333−343. ZHANG Cun, REN Zhaopeng, HAN Penghua, et al. Characteristic of the water-conducting fracture zone development in thick overburden working face with extra-large mining height in western mining area[J]. Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2022, 7(3): 333−343.
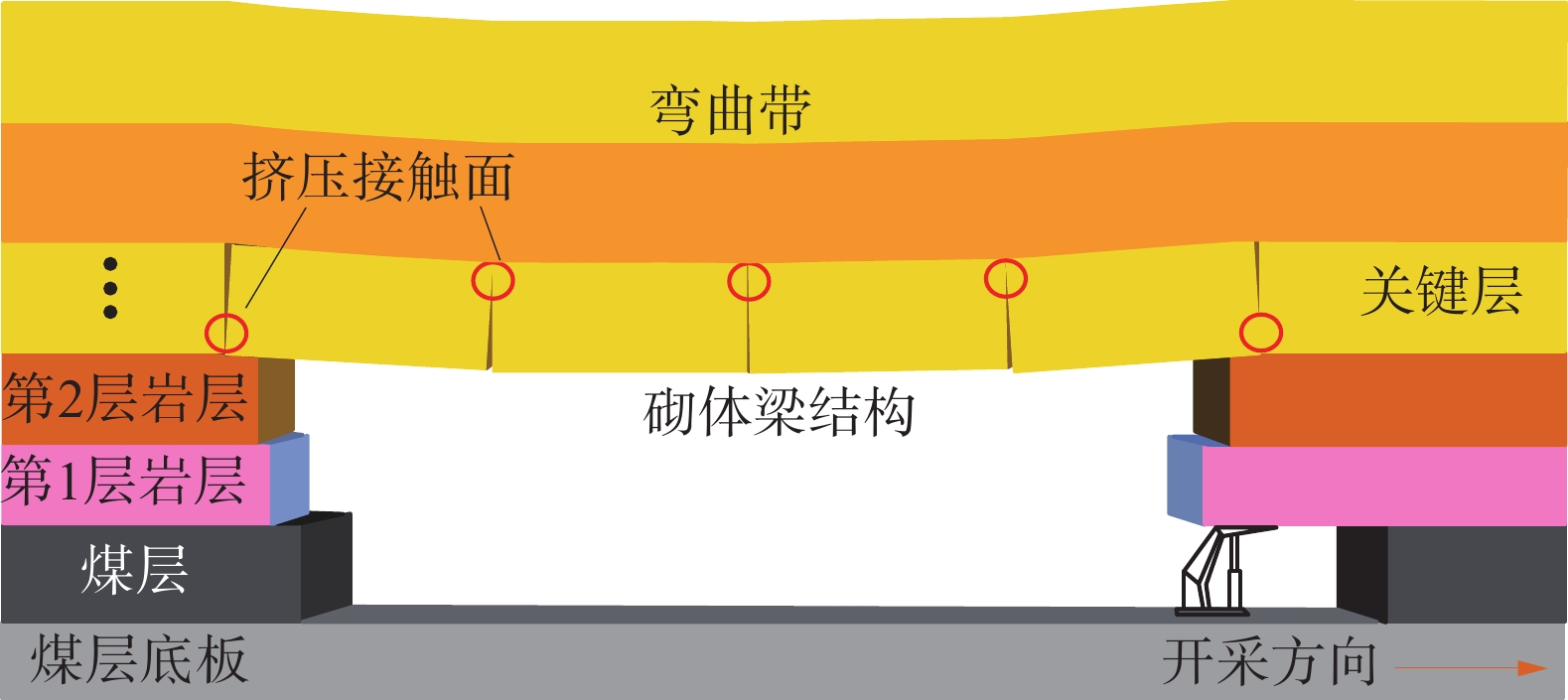
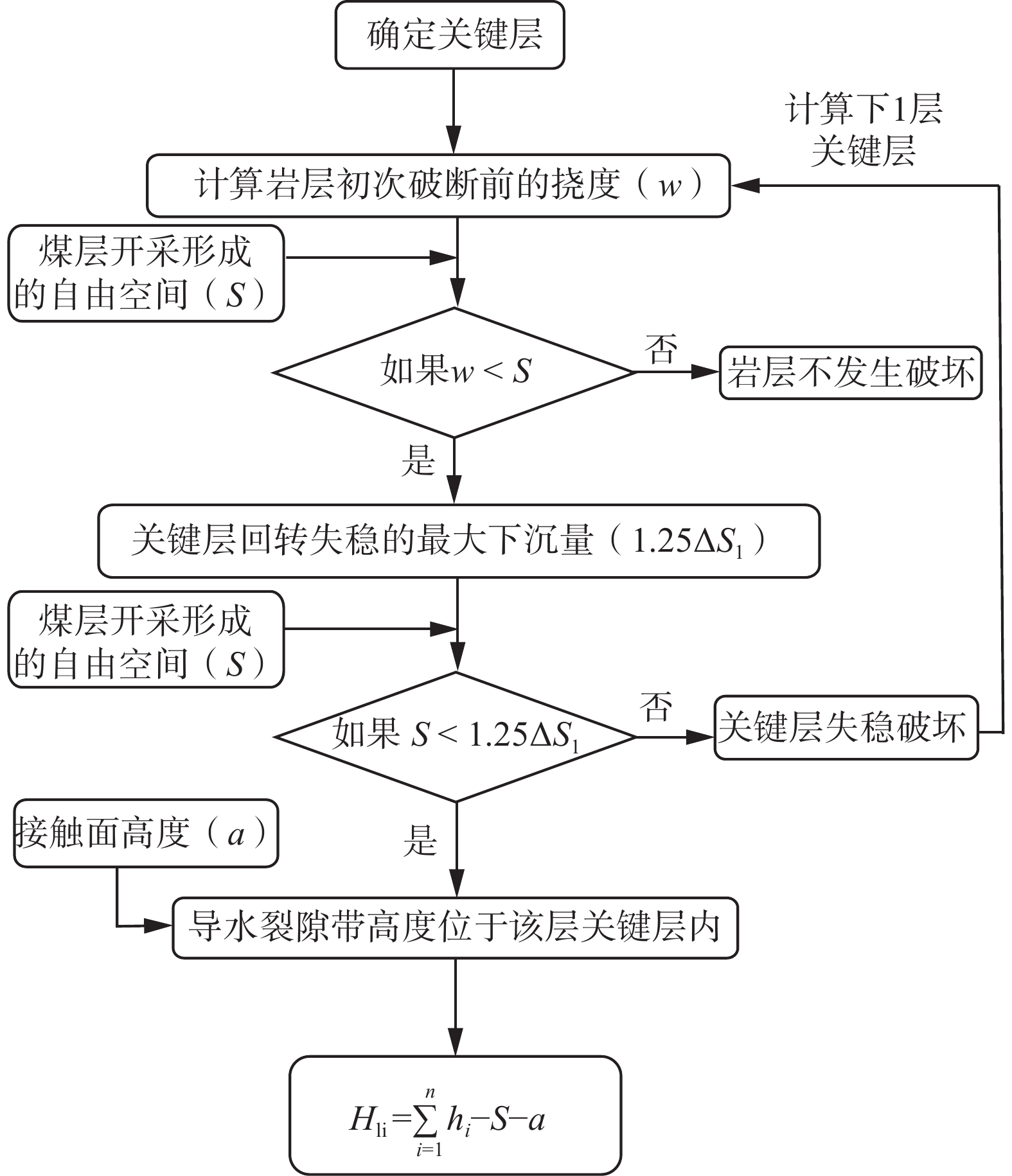
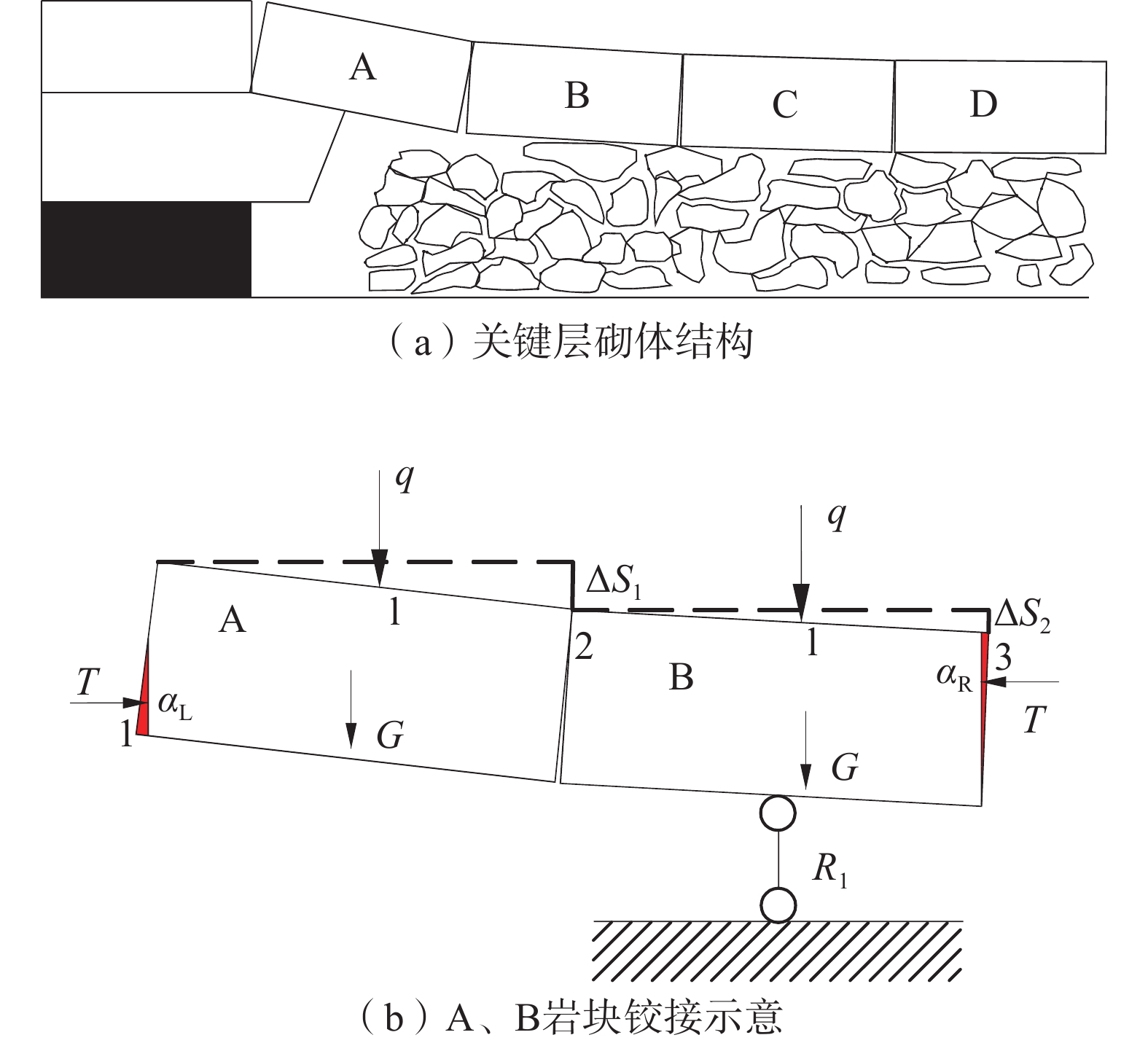
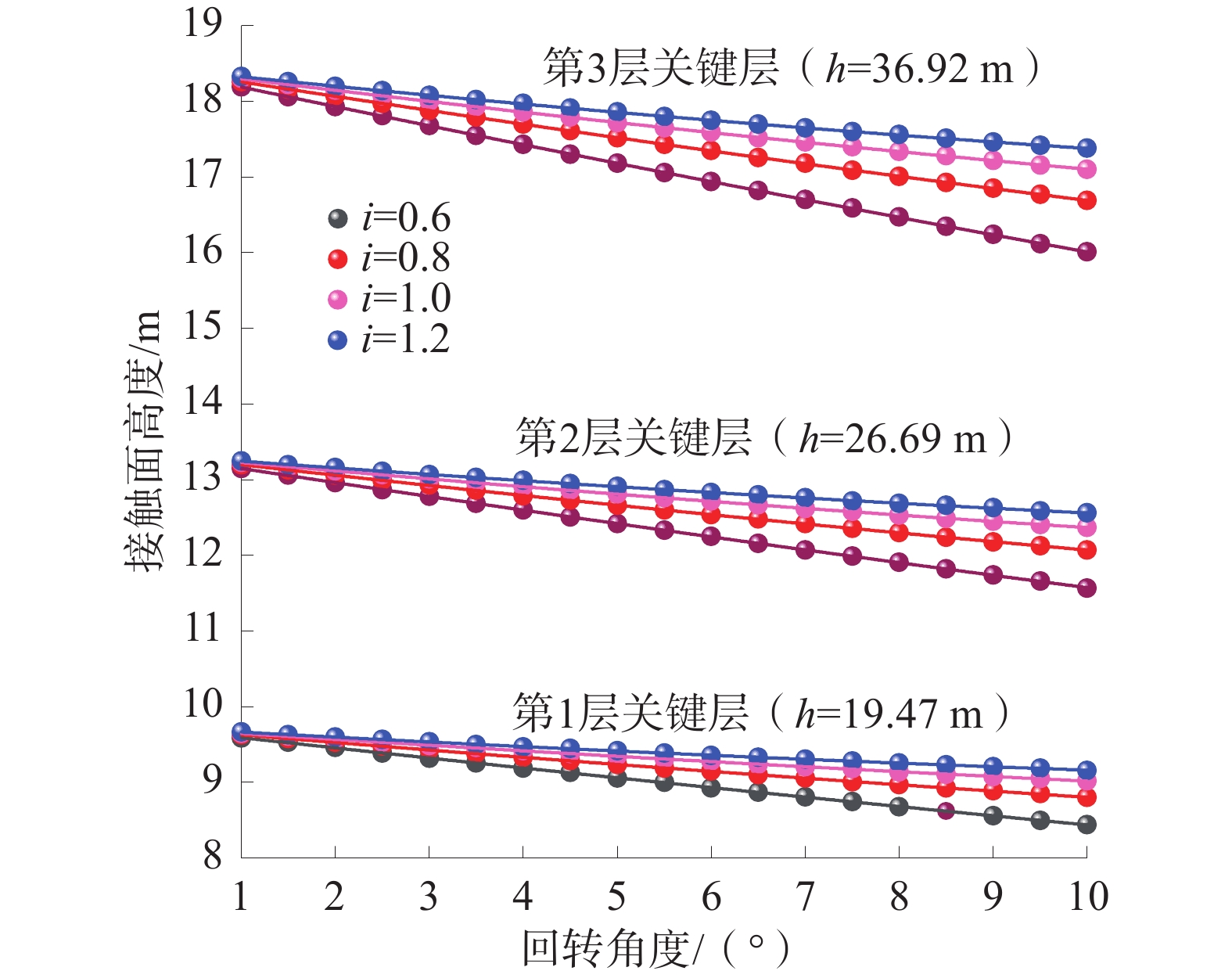
[7] 许家林,朱卫兵,王晓振. 基于关键层位置的导水裂隙带高度预计方法[J]. 煤炭学报,2012,37(5):762−769. XU Jialin, ZHU Weibing, WANG Xiaozhen. New method to predict the height of fractured water-conducting zone by location of key strata[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2012, 37(5): 762−769.
[8] 王创业,薛瑞雄,朱振龙. 不同采高和关键层对导水裂隙带发育的影响[J]. 煤矿安全,2016,47(3):169−171. WANG Chuangye, XUE Ruixiong, ZHU Zhenlong. Influence of different mining height and key stratum on development of water flowing fracture zone[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2016, 47(3): 169−171.
[9] 钱鸣高,缪协兴,许家林. 岩层控制中的关键层理论研究[J]. 煤炭学报,1996,21(3):225−230. QIAN Minggao, MIAO Xiexing, XU Jialin. Theoretical study of key stratum in ground control[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 1996, 21(3): 225−230.
[10] 贾栋,姜德义,陈结,等. 综放工作面覆岩破坏特征及裂隙演化相似模拟试验研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术,2022,18(3):19−25. JIA Dong, JIANG Deyi, CHEN Jie, et al. Similar simulation study on failure characteristics and fracture evolution of overlying strata in fully-mechanized caving face[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2022, 18(3): 19−25.
[11] 刘一扬,宋选民,朱德福,等. 大块度关键块动态结构力学行为及响应特征研究[J]. 岩土力学,2020,41(3):1019−1028. LIU Yiyang, SONG Xuanmin, ZHU Defu, et al. Dynamic structural mechanical behavior and response characteristicsof large key blocks[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020, 41(3): 1019−1028.
[12] GUO Wenbing, ZHAO Gaobo, LOU Gaozhong, et al. A new method of predicting the height of the fractured water-conducting zone due to high-intensity longwall coal mining in China[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2019, 52(8): 2789−2802.
[13] 郝钢,于鼎豪,徐营,等. 和善煤矿“两带”高度数值模拟及实测研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2023,54(9):174−179. HAO Gang, YU Dinghao, XU Ying, et al. Numerical simulation and field test of height of caving zone and fracture zone in Heshan Coal Mine[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2023, 54(9): 174−179.
[14] 孙利辉,纪洪广,蒋华,等. 弱胶结地层条件下垮落带岩层破碎冒落特征与压实变形规律试验研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2017,42(10):2565−2572. SUN Lihui, JI Hongguang, JIANG Hua, et al. Experimental study on characteristics of broken caving and regularity of compaction deformation of rocks in caving zone in the weakly cemented strata[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2017, 42(10): 2565−2572.



 下载:
下载: