Risk assessment of roadway roof fall based on combined weight matter-element extension model
-
摘要:
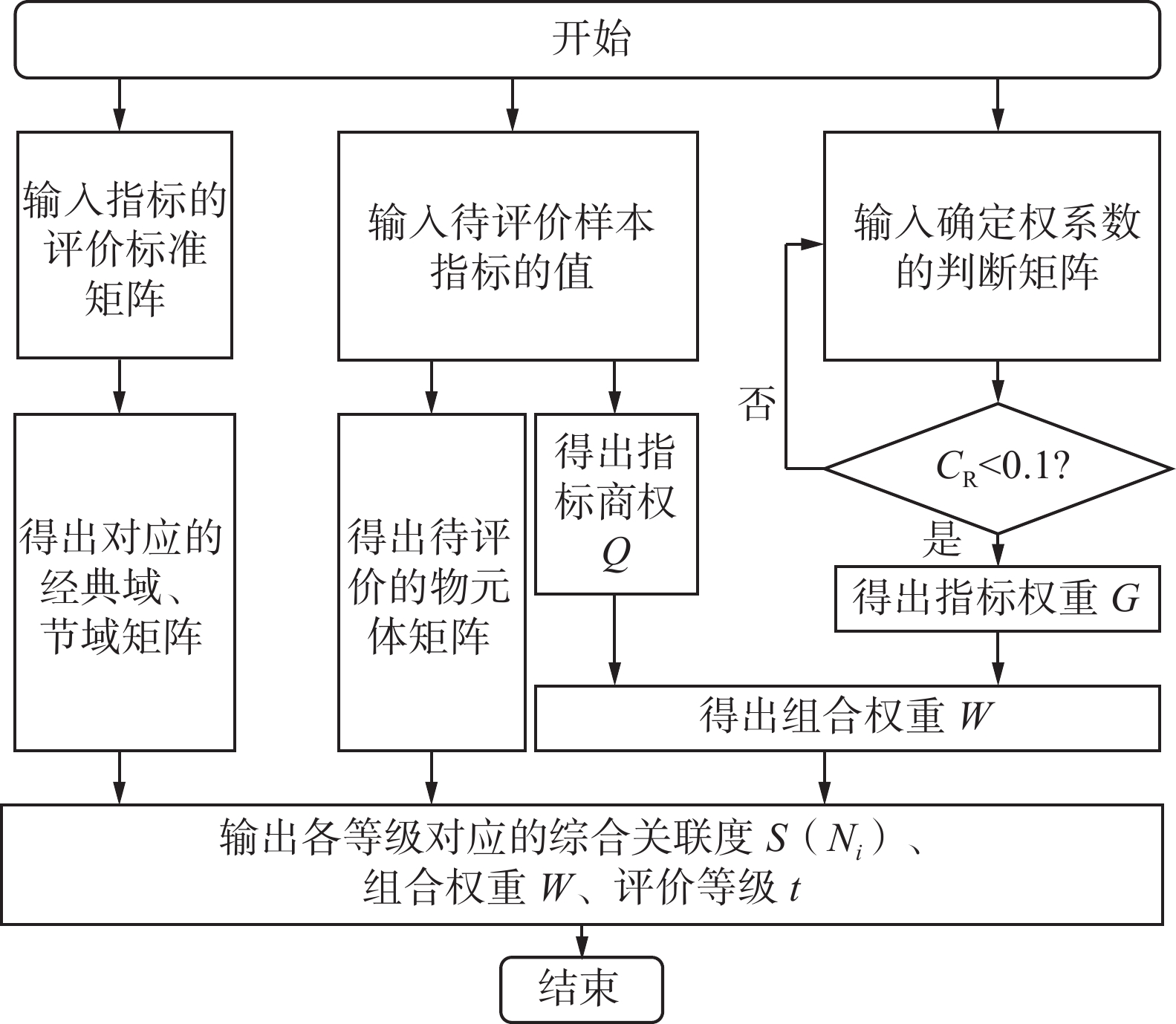
为了降低煤矿生产风险、及时预测和控制巷道冒顶风险,选取巷道稳定岩层厚度、地质条件、巷道断面形状等12项评价指标,构建巷道冒顶风险评价指标体系,提出了巷道冒顶的风险程度标准;采用层次分析(AHP)法和熵权(EW)法组合权重物元可拓理论建立了巷道冒顶风险评价模型,根据最大隶属度原则确定了巷道冒顶的风险程度;并基于JavaWeb开发了巷道冒顶风险评价系统(MW-MEW),应用该评价方法和MW-MEW系统对兴路煤矿C9回风联络巷冒顶的风险程度进行了评价,与AHP-物元可拓模型评价结果作对比。结果表明:该评价方法的评价结果符合实际工况,并优于AHP-物元可拓模型。
Abstract:In order to reduce the risk of coal mine production, timely predict and control the risk of roadway roof fall, twelve evaluation indexes such as the thickness of stable rock strata, geological conditions and cross-section shape of roadway were selected. The risk evaluation index system of roadway roof fall was constructed, and the risk degree standard of roadway roof fall was proposed. The risk evaluation model of roadway roof fall was established by using the combination weight matter-element extension theory of analytic hierarchy process (AHP) and entropy weight (EW). The risk degree of roadway roof fall was determined according to the principle of maximum membership degree, and the risk assessment system of roadway roof fall (MW-MEW) was developed based on JavaWeb. The evaluation method and MW-MEW system were applied to evaluate the risk degree of roof fall in C9 return air connecting roadway of Xinglu Coal Mine, and the evaluation results were compared with those of AHP-matter element extension model. The results showed that the evaluation results of the evaluation method were in line with the actual engineering situation and were better than the AHP-matter element extension model.
-
在全球能源需求不断攀升、温室气体排放问题被日益关注的背景下,开发利用煤层气成为能源研究的热点[1-4]。CO2增强煤层气回收(CO2-ECBM)技术,作为一种能提升煤层瓦斯产量并实现CO2封存的创新手段,已经得到广泛的研究和应用[5-7]。然而,在CO2驱替煤层瓦斯的过程中,研究仍然面临许多挑战,包括注入技术、煤层特性和地质条件等方面的复杂性。其中,作为影响CO2-ECBM项目的最主要的因素,多物理场作用下煤层地质特性的不确定性及其非线性演化一直是研究的重点。同时,作为煤层气/CO2运移的通道,煤层裂隙数目、复杂程度及表面粗糙度的改变、气体解吸附、基质变形、气体压力演化及裂隙-基质相互作用受到了相关从业者和研究人员的广泛关注[8-10]。近年来,流体在煤岩粗糙裂隙网络中的渗流受到地质、采矿等领域的广泛关注。
1. 瓦斯开采过程中多因素耦合效应的研究现状
CO2驱替煤层瓦斯(CO2-ECBM)技术得到了越来越多学者及相关从业者的关注[11-13]。实验研究包括:①CO2注入的机理、不同条件下的驱替效果,以及CO2与煤层反应的详细分析;②CO2-ECBM过程中多物理场耦合作用下的机理分析[14-16],不同压力、温度、地应力等多因素作用下CO2的驱替效率,以及CO2对煤层微观结构的影响;③CO2的特性驱替煤层瓦斯的研究[17-19]。尽管这些研究从工程条件、煤层地质因素、多场耦合效应等诸多因素对CO2-ECBM项目开展了充分且详尽的研究,然而,作为CO2及煤层瓦斯运移的主要通道,CO2-ECBM项目过程中煤层裂隙网络的行为,特别是裂隙粗糙性对气体运移的阻力及对产气量影响仍然缺乏定量且综合(不同开采条件及不同煤层的多物理场耦合效应下)的探究。尽管这些研究从实验、机制以及工程实地等角度极大地推动了CO2驱替效率的研究,然而这些研究(包括主流的热-流-固耦合模型)大多忽略了多场耦合效应下煤层裂隙网络的粗糙特性演化,以及这种非线性演化对CO2驱替项目的影响。而作为CO2及煤层气运移的主要通道,粗糙裂隙表面的非线性演化对气体渗流的影响至关重要。
2020年后,有关煤层裂隙的研究,通常集中于实验室煤样实验、CT/SEM扫描的研究[20]、基于数字岩心重构技术的研究[21-23]、采用离散裂隙网络(DFN)的研究[24-25]及采用分形理论、复杂网络理论的研究[26-28]等。尽管这些研究极大推动了煤层裂隙网络形态、行为、特性的精确表征,并实现了裂隙网络的演化对煤层气开采项目的探究,然而,这些研究受研究设备及计算量限制,很难实现工程尺度裂隙结构的定量研究。此外,有关裂隙粗糙程度的研究主要为实验测算表面粗糙度[29]、测算不同温度压力下裂隙粗糙度变化[30]、结合Wenzel理论解释了表面粗糙度对接触角的影响[31]等。然而,这些有关裂隙粗糙程度的研究难以实现在CO2驱替项目中煤层多物理场耦合效应下,裂隙粗糙程度的定量演化分析。这在瓦斯抽采率的评估以及CO2驱替的效果上有着重要的影响。
综上,为了突破CO2-ECBM项目中,煤层裂隙粗糙程度在多因素共同作用下的定量演化难以准确分析的行业瓶颈,并准确且定量的衡量裂隙粗糙程度在多物理场效应下对CO2的储存及煤层气的采收的影响;研究建立了一种创新的、跨学科的数学模型。模型提出了一类创新的、能够定量表征CO2-ECBM项目中煤层裂隙粗糙程度的参数,并将其与煤层的多物理场效应高度的耦合。此外,研究充分且全面地考虑了CO2驱替过程中CO2及瓦斯的吸附/解吸、2种气体的压力演化、吸附及气压诱导的煤层应力、地应力、煤层温度、煤层形变及裂隙粗糙度的共同作用。研究成果将为煤层气开采工程中,裂隙行为的定量分析提供全新的思路和帮助。
2. 考虑热-流-固耦合效应及裂隙粗糙的耦合方程
对于实地的CO2驱替工程,煤层瓦斯的产出涉及包括涉及瓦斯和CO2的竞争吸附、吸附及气压诱导的煤层应力、2种气体的压力演化、地应力、煤层温度、煤层形变及裂隙粗糙度的综合作用。因而,研究提出的考虑热-流-固耦合效应及裂隙粗糙的跨学科全耦合模型包括:①煤层瓦斯开采过程中的固体力学特性及孔隙率演化;②瓦斯开采过程中考虑裂隙粗糙程度的气体渗流模型;③瓦斯开采过程中的热传导方程。
2.1 瓦斯开采中的固体力学特性及孔隙率演化模型
根据煤层及瓦斯开采过程中的力学特性,煤层位移及应变存在如下关系:
$$ {\varepsilon _{ij}} = \dfrac{1}{2}({u_{i,j}} + {u_{j,i}}) $$ (1) 式中:$ {\varepsilon _{ij}} $为总应变不同方向上的分量;$ {u_{i,j}} $、$ {u_{j,i}} $为不同方向上的位移分量。
此外,外力作用下的煤层力学变形平衡方程可表示为:
$$ {\sigma _{ij}} + {f_i} = 0 $$ (2) 式中:$ {\sigma _{ij}} $为应力张量的分量;$ {f_i} $为力的分量。
在煤层瓦斯开采过程中,CO2的密度和黏度与甲烷(煤层气的主要成分)有所不同,CO2的注入会导致煤层这导致在煤层内部产生压力和流体流动的变化。CO2在注入煤层后,由于其较强的亲和力,会优先于甲烷被煤基质吸附。这种吸附过程主要发生在煤基质中的孔隙中。随着CO2的吸附,原本被煤基质吸附的甲烷分子会被置换出来,从而加强了瓦斯的开采效率。在这过程中,吸附从而诱导变形的关系可表示为[32]:
$$ \begin{gathered}\varepsilon_{ij}=\dfrac{1}{2G}\sigma_{ij}-\left(\dfrac{1}{6G}-\dfrac{1}{9K}\right)\sigma_{\mathrm{kk}}\delta_{ij}+\dfrac{\alpha}{3K}p\delta_{ij}+\dfrac{\varepsilon_{\mathrm{s}}}{3}\delta_{ij} \\ \end{gathered} $$ (3) 式中:$ G $为剪切弹性模量,MPa;$K$为煤体的体积模量,MPa;$ \sigma_{\mathrm{kk}} $为正应力分量;$ \alpha $为Biot系数;$ {\delta _{ij}} $为Kronecker delta符号;$ p $为瓦斯压力,MPa;$ \varepsilon\mathrm{_s} $为气体吸附应变。
联立式(1)~式(3),可得煤层瓦斯开采过程中的力学控制方程为:
$$ \begin{gathered} G{u_{i,jj}} + \dfrac{G}{{1 - 2v}}{u_{k,kj}} - \alpha {p_{,i}} - K{\varepsilon _{{\mathrm{s}},i}} - {\alpha _{\rm{T}}}{T_{,i}}K + {f_i} = 0 \end{gathered} $$ (4) 式中,$ \nu $为煤体的泊松比;$ {\alpha _{\mathrm{T}}} $为多因素共同作用下煤层热膨胀系数,K−1;T为煤层温度;下标i为变量分量。
煤层形变会导致煤层孔隙结构发生不同程度的非线性演化,且煤层开采过程中的多场耦合效应也会导致孔隙率的改变。KONG等[32]提出了综合考虑瓦斯压力、温度以及基质吸附、解吸变化引起的煤体变形效应下的孔隙度$\phi= $模型[32]:
$$ \phi=\dfrac{V_{\mathrm{f}}}{V}=1-\dfrac{1-\phi_0}{1+\varepsilon_{\mathrm{v}}}\left(1+\dfrac{\Delta V_{\mathrm{S}}}{V_{\mathrm{si}}}\right) $$ (5) 式中:$ {V_{\mathrm{f}}} $为煤层裂隙体积,m3;$ V $为总体积,m3;$ {V_{\mathrm{S}}} $为煤固体体积,m3;下标i为初始状态;$ {\phi _0} $为抽采前煤的孔隙度;$ {\varepsilon _{\mathrm{v}}} $为体积应变。
气体吸附总体积可由如下方程计算得出[33]:
$$ V = \dfrac{{{V_{{\mathrm{Lm}}}}{b_{\mathrm{m}}}{p_{\mathrm{m}}} + {V_{{\mathrm{Lc}}}}{b_{\mathrm{c}}}{p_{\mathrm{c}}}}}{{1 + {b_{\mathrm{m}}}{p_{\mathrm{m}}} + {b_{\mathrm{c}}}{p_{\mathrm{c}}}}} $$ (6) 式中:$ {V_{{\mathrm{Lm}}}} $、$ {V_{{\mathrm{Lc}}}} $为瓦斯和CO2的Langmuir体积常数,$ {{\mathrm{m}}^3}/{\mathrm{kg}} $;$ {b_{\mathrm{m}}} $、$ {b_{\mathrm{c}}} $为瓦斯和CO2的Langmuir压力常数,MPa;$ {p_{\mathrm{m}}} $、$ {p_{\mathrm{c}}} $为煤层中瓦斯和CO2的分压,MPa。
在开采过程中,因CO2驱替导致的气体的吸附和解吸引起基体的膨胀和收缩,总体积应变$ {\varepsilon _{\mathrm{S}}} $为CO2及瓦斯引起的应变之和:
$$ {\varepsilon _{\mathrm{S}}} = \dfrac{{{\varepsilon _{{\mathrm{Lm}}}}{b_{\mathrm{m}}}{p_{\mathrm{m}}} + {\varepsilon _{{\mathrm{Lc}}}}{b_{\mathrm{c}}}{p_{\mathrm{c}}}}}{{1 + {b_{\mathrm{m}}}{p_{\mathrm{m}}} + {b_{\mathrm{c}}}{p_{\mathrm{c}}}}} $$ (7) 式中:$ {\varepsilon _{{\mathrm{Lm}}}} $、$ {\varepsilon _{{\mathrm{Lc}}}} $为瓦斯和CO2的Langmuir吸附常数。
此外,因CO2驱替工程中的抽采效应导致的煤层固体体积应变为:
$$ \begin{gathered}\dfrac{\Delta V_{\mathrm{S}}}{V_{\mathrm{si}}}=\Delta\varepsilon_{\mathrm{S}}+\alpha_{\mathrm{T}}\Delta T-\dfrac{\alpha}{K_{\mathrm{S}}}\left(\Delta p_{\mathrm{m}}+\Delta p_{\mathrm{c}}\right)\end{gathered} $$ (8) 式中:KS为煤体颗粒固体的体积模量,MPa。
因此,多因素共同作用下煤层孔隙率的演化特性可通过联立式(5)~式(8)得出:
$$ \begin{split} &\begin{gathered} \phi = 1 - \dfrac{{1 - {\phi _i}}}{{1 + {\varepsilon _{\mathrm{v}}}}} \left[ {1 + \Delta \dfrac{{{\varepsilon _{{\mathrm{Lm}}}}{b_{\mathrm{m}}}{p_{\mathrm{m}}} + {\varepsilon _{{\mathrm{Lc}}}}{b_{\mathrm{c}}}{p_{\mathrm{c}}}}}{{1 + {b_{\mathrm{m}}}{p_{\mathrm{m}}} + {b_{\mathrm{c}}}{p_{\mathrm{c}}}}}} + \right. \\ \left. { {\alpha _{\mathrm{T}}}\Delta T - \dfrac{\alpha }{{{K_{\mathrm{S}}}}} \left( {\Delta {p_{\mathrm{m}}} + \Delta {p_{\mathrm{c}}}} \right)} \right] \end{gathered}\\[-16pt]& \end{split} $$ (9) 瓦斯开采过程中,多因素共同作用下的力学特性演化控制模型为:
$$ \left\{ \begin{gathered} G{u_{i,jj}} + \dfrac{G}{{1 - 2v}}{u_{k,kj}} - \alpha {p_{,i}} - K{\varepsilon _{s,i}} - {\alpha _{\mathrm{T}}}{T_{,i}}K + {f_i} = 0 \\ \phi = 1 - \dfrac{{1 - {\phi _i}}}{{1 + {\varepsilon _{\mathrm{v}}}}} \left[ {1 + \Delta \dfrac{{{\varepsilon _{{\mathrm{Lm}}}}{b_{\mathrm{m}}}{p_{\mathrm{m}}} + {\varepsilon _{{\mathrm{Lc}}}}{b_{\mathrm{c}}}{p_{\mathrm{c}}}}}{{1 + {b_{\mathrm{m}}}{p_{\mathrm{m}}} + {b_{\mathrm{c}}}{p_{\mathrm{c}}}}}}+ \right. \\ \qquad\qquad \left. { {\alpha _{\mathrm{T}}}\Delta T - \dfrac{\alpha }{{{K_{\mathrm{S}}}}} \left( {\Delta {p_{\mathrm{m}}} + \Delta {p_{\mathrm{c}}}} \right)} \right] \end{gathered} \right. $$ (10) 2.2 瓦斯开采中考虑裂隙粗糙的气体渗流模型
FAN等[34]根据质量守恒定律,并采用流体连续性方程,给出了在CO2增强的甲烷开采项目中,流体总流量Q的控制方程:
$$ \begin{gathered} Q = \dfrac{{\partial m}}{{\partial t}} - \dfrac{\phi }{{RT}} \nabla \left( {{D_{\mathrm{k}}} \nabla p} \right) - \nabla \left( {\dfrac{k}{\mu }\nabla p {\rho _{\mathrm{g}}}} \right) \\ \end{gathered} $$ (11) 式中:$ m $为气体质量,kg;t为时间,s;R为特定气体常数,取287.14 m2/(s2·K);μ为瓦斯动力黏度;ρg为气体密度,kg/m3;$ {D_{\mathrm{k}}} $为气体扩散系数,m2/s;$ k $为甲烷在煤层粗糙裂隙中运移时的渗透率,m2。
其中,根据流体质量守恒方程及理想气体状态方程,可得式(11)中的裂隙内气体的质量为[34]:
$$ \begin{split} &\begin{gathered} m = \dfrac{\phi }{{RT}} \left( {{p_{\mathrm{m}}}{M_{\mathrm{m}}} + {p_{\mathrm{c}}}{M_{\mathrm{c}}}} \right) + \left( {{\rho _{\mathrm{m}}}{M_{\mathrm{m}}} + {\rho _{\mathrm{c}}}{M_{\mathrm{c}}}} \right) \cdot \\ \dfrac{{{\varepsilon _{{\mathrm{Lm}}}}{b_{\mathrm{m}}}{p_{\mathrm{m}}} + {\varepsilon _{{\mathrm{Lc}}}}{b_{\mathrm{c}}}{p_{\mathrm{c}}}}}{{1 + {b_{\mathrm{m}}}{p_{\mathrm{m}}} + {b_{\mathrm{c}}}{p_{\mathrm{c}}}}} \end{gathered}\\[-16pt]& \end{split} $$ (12) 式中:ρm、ρc为瓦斯和 CO2的密度,kg/m3;$ {M_{\mathrm{m}}} $、$ {M_{\rm{c}}} $为气体摩尔质量。
如前文所述,在煤层瓦斯开采过程中的气体流动时,其渗流强度与煤层裂隙的粗糙程度直接相关,并在多场耦合特性下,将直接影响瓦斯的产量。因此,开展煤层裂隙网络粗糙特性的定量研究对探究实地煤层瓦斯开采过程中的多场耦合效应强度,揭示CO2与瓦斯的吸附特性,并评估、指导、制定优化的抽采方案是至关重要的。
考虑到煤层裂隙网络的粗糙特性,结合三次立方定律,煤层渗透率受粗糙裂缝表面的影响可由如下模型给出:
$$ \begin{gathered} k = {k_0} {\left[ {1 - \dfrac{{\sqrt 2 \gamma }}{{{a_i}}}\ln \left( {\dfrac{p}{{{p_0}}}} \right)} \right]^3} \cdot \dfrac{{\left[ {1 - b\left( {p - {p_0}} \right)} \right]}}{{1 + b\left( {p - {p_0}} \right)}} \end{gathered} $$ (13) 式中:$ {k_0} $为瓦斯开采前煤层的原位渗透率,m2;$ \gamma $为裂缝高度,m;$ {a_i} $为接触面积与裂缝面积之比;$ b $为裂隙粗糙特性参量,当$ b = 0 $时,断裂粗糙度对气体压力没有影响;p0为开采前瓦斯压力,MPa。
当$ b = 0 $时,有:
$$ k = {k_0} {\left[ {1 - \dfrac{{\sqrt 2 \gamma }}{{{a_i}}}\ln \left( {\dfrac{p}{{{p_0}}}} \right)} \right]^3} $$ (14) 由式(13)和式(14),可将裂隙粗糙度定量表示为参数$ \chi $的函数,即:
$$ \chi = \sqrt 2 \dfrac{\gamma }{{{a_i}}} $$ (15) 由式(15)可知,$ \chi $与裂隙粗糙的程度直接相关且成正比。将裂隙粗糙度函数$ \chi $代入式(13)、式(14),可得考虑裂隙粗糙程度的渗透率方程为:
考虑裂隙粗糙特性的影响:
$$ k=k_0\left[1-\chi\mathrm{ln}\left(\dfrac{p}{p_0}\right)\right]^3\dfrac{\left[1-b\left(p-p_0\right)\right]}{1+b\left(p-p_0\right)} $$ (16) 忽略裂隙粗糙度对瓦斯开采的影响:
$$ k={k}_{0} {\left[1-\chi \mathrm{ln}\left(\dfrac{p}{{p}_{0}}\right)\right]}^{3} $$ (17) 将式(12)、式(16)、式(17)代入式(11),可得定量分析裂隙粗糙特性及吸附/解吸2种气体的动力学演化、气体传热及孔隙率非线性演化的气体渗流控制方程。粗糙裂隙、光滑裂隙方程分别见式(18)、式(19):
$$ \begin{split} &\begin{gathered} {Q}_{\text{rc}}=\dfrac{\partial }{\partial t}\left[\dfrac{\phi }{RT} \left({p}_{\rm{m}}{M}_{\rm{m}}+{p}_{\rm{c}}{M}_{\rm{c}}\right)+\left({\rho }_{\rm{m}}{M}_{\rm{m}}+{\rho }_{\rm{c}}{M}_{\rm{c}}\right)\cdot\right. \\ \left.\dfrac{{\varepsilon }_{\rm{Lm}}{b}_{\rm{m}}{p}_{\rm{m}}+{\varepsilon }_{\rm{Lc}}{b}_{\rm{c}}{p}_{\rm{c}}}{1+{b}_{\rm{m}}{p}_{\rm{m}}+{b}_{\rm{c}}{p}_{\rm{c}}}\right]-\dfrac{\phi }{RT} \nabla \left({D}_{{\mathrm{k}}} \nabla p\right)- \\ \nabla \left(\dfrac{{k}_{0}}{\mu } {\left[1-\chi \mathrm{ln}\left(\dfrac{p}{{p}_{0}}\right)\right]}^{3} \dfrac{\left[1-b\left(p-{p}_{0}\right)\right]}{1+b\left(p-{p}_{0}\right)} \nabla p {\rho }_{\rm{g}}\right) \end{gathered}\\[-16pt]& \end{split}$$ (18) $$\begin{split} &\begin{gathered} {Q}_{\text{sc}}=\dfrac{\partial }{\partial t}\left[\dfrac{\phi }{RT} \left({p}_{\rm{m}}{M}_{\rm{m}}+{p}_{\rm{c}}{M}_{\rm{c}}\right)+\left({\rho }_{\rm{m}}{M}_{\rm{m}}+{\rho }_{\rm{c}}{M}_{\rm{c}}\right)\cdot\right.\\ \left.\dfrac{{\varepsilon }_{\rm{Lm}}{b}_{\rm{m}}{p}_{\rm{m}}+{\varepsilon }_{\rm{Lc}}{b}_{\rm{c}}{p}_{\rm{c}}}{1+{b}_{\rm{m}}{p}_{\rm{m}}+{b}_{\rm{c}}{p}_{\rm{c}}}\right]- \dfrac{\phi }{RT} \nabla \left({D}_{{\mathrm{k}}} \nabla p\right)-\\ \nabla \left({k}_{0} {\left[1-\chi \mathrm{ln}\left(\dfrac{p}{{p}_{0}}\right)\right]}^{3} \nabla p {\rho }_{\rm{g}}\right) \end{gathered}\\[-16pt]& \end{split}$$ (19) 式中:Qrc、Qsc分别为粗糙裂隙、光滑裂隙的流体总流量。
2.3 CO2驱替煤层瓦斯开采工程中的热传导模型
根据能量守恒定律、傅里叶定律,FANG H H等提出CO2驱替过程中CO2、煤层瓦斯及煤层的能量守恒方程为[35]:
$$\begin{split} &\begin{gathered} \dfrac{\partial }{{\partial t}}\left[ {{{\left( {\rho {C_{\mathrm{p}}}} \right)}_{\rm{c}}}T} \right] = \nabla \left( {\lambda \nabla T} \right) - {\alpha _{\mathrm{T}}}TK \dfrac{{\partial {\varepsilon _{\mathrm{S}}}}}{{\partial t}} - \\ {q_{{\mathrm{ad}}}} \dfrac{{\partial {\varepsilon _{\mathrm{V}}}}}{{\partial t}} \left( {\dfrac{{{\rho _{\mathrm{S}}}{\rho _{\rm{c}}}}}{{{M_{\rm{c}}}}} + \dfrac{{{\rho _{\mathrm{S}}}{\rho _{\rm{g}}}}}{{{M_{\rm{g}}}}}} \right) - \eta \nabla T \end{gathered}\\[-14pt]& \end{split} $$ (20) $$ \eta = - \left( {\dfrac{k}{{{\mu _{\mathrm{c}}}}}\nabla {p_{\mathrm{c}}} {\rho _{\mathrm{c}}}{C_{\mathrm{c}}} + \dfrac{k}{{{\mu _{\mathrm{g}}}}}\nabla {p_{\mathrm{g}}} {\rho _{\mathrm{g}}}{C_{\mathrm{g}}}} \right) $$ (21) 式中:$ {\left( {\rho {C_{\mathrm{p}}}} \right)_{\mathrm{c}}} $为煤层热容,J/(m3K);$ \lambda $为导热系数,W/(mK);ρS为煤岩颗粒的密度,kg/m3。
$$ \begin{gathered} {\left( {\rho {C_{\mathrm{p}}}} \right)_{\mathrm{c}}} = \left( {1 - {\phi _{\mathrm{c}}}} \right) {\rho _{\mathrm{S}}}{C_{\mathrm{S}}} + {\phi _{\mathrm{c}}} \left( {\dfrac{{{C_{\mathrm{c}}}{M_{\mathrm{c}}}{p_{\mathrm{c}}}}}{{RT}} + \dfrac{{{C_{\mathrm{g}}}{M_{\mathrm{g}}}{p_{\mathrm{g}}}}}{{RT}}} \right) \end{gathered} $$ (22) $$ \lambda = {\phi _{\mathrm{c}}} \left( {{\lambda _{\mathrm{g}}} + {\lambda _{\mathrm{c}}}} \right) + \left( {1 - {\phi _{\mathrm{c}}}} \right){\lambda _{\mathrm{S}}} $$ (23) 式中:$ {C_{\mathrm{S}}} $、$ {C_{\mathrm{c}}} $、$ {C_{\mathrm{g}}} $为煤、CO2、甲烷的比热容;$ \lambda _{\mathrm{S}} $为煤固体导热系数。
因此,联立式(16)、式(17)、式(20)和式(21),可得综合考虑内能、热对流、热传导、热变形能、吸附-解吸效应产生的热量及受煤层裂隙粗糙特性导致的流体非线性热流,共同作用下的能量传导控制方程为:
$$\begin{split} &\begin{gathered} \dfrac{\partial }{{\partial t}}\left[ {{{\left( {\rho {C_{\rm{p}}}} \right)}_{\rm{c}}}T} \right] = \nabla \left( {\lambda \nabla T} \right) - {\alpha _{\rm{T}}}TK \dfrac{{\partial {\varepsilon _{\rm{S}}}}}{{\partial t}} - \dfrac{{\partial {\varepsilon _{\mathrm{V}}}}}{{\partial t}} \cdot\\ \left( {\dfrac{{{\rho _{\mathrm{S}}}{\rho _{\rm{c}}}}}{{{M_{\rm{c}}}}} + \dfrac{{{\rho _{\mathrm{S}}}{\rho _{\rm{g}}}}}{{{M_{\rm{g}}}}}} \right) {\text{ }} + \nabla T \left[ {{k_0} {{\left[ {1 - \chi \ln \left( {\dfrac{p}{{{p_0}}}} \right)} \right]}^3} \cdot} \right.\\ \left.{ \dfrac{{\left[ {1 - b\left( {p - {p_0}} \right)} \right]}}{{1 + b\left( {p - {p_0}} \right)}} \dfrac{{{\mu _{\rm{c}}} + {\mu _{\rm{g}}}}}{{{\mu _{\rm{c}}} {\mu _{\rm{g}}}}} \left( {\nabla {p_{\rm{c}}}{\rho _{\rm{c}}}{C_{\rm{c}}} + \nabla {p_{\rm{g}}}{\rho _{\rm{g}}}{C_{\rm{g}}}} \right)} \right] \end{gathered}\\ \end{split} $$ (24) $$ \begin{split} &\begin{gathered} \dfrac{\partial }{{\partial t}}\left[ {{{\left( {\rho {C_{\rm{p}}}} \right)}_{\rm{c}}}T} \right] = \nabla \left( {\lambda \nabla T} \right) - {\alpha _{\rm{T}}}TK \dfrac{{\partial {\varepsilon _{\rm{S}}}}}{{\partial t}} - \dfrac{{\partial {\varepsilon _{\mathrm{V}}}}}{{\partial t}}\cdot \\ \left( {\dfrac{{{\rho _{\mathrm{S}}}{\rho _{\rm{c}}}}}{{{M_{\rm{c}}}}} + \dfrac{{{\rho _{\mathrm{S}}}{\rho _{\rm{g}}}}}{{{M_{\rm{g}}}}}} \right) {\text{ }} + \nabla T \left[ {{k_0} {{\left[ {1 - \chi \ln \left( {\dfrac{p}{{{p_0}}}} \right)} \right]}^3} \cdot }\right.\\ \left. {\dfrac{{{\mu _{\rm{c}}} + {\mu _{\rm{g}}}}}{{{\mu _{\rm{c}}} {\mu _{\rm{g}}}}} \left( {\nabla {p_{\rm{c}}}{\rho _{\rm{c}}}{C_{\rm{c}}} + \nabla {p_{\rm{g}}}{\rho _{\rm{g}}}{C_{\rm{g}}}} \right)} \right] \end{gathered}\\ \end{split} $$ (25) 其中,式(24)为考虑裂隙粗糙特性的瓦斯-CO2-煤层热传导控制方程,式(25)为忽略煤层裂隙粗糙度的控制方程。由式(24)可知,瓦斯开采过程中的热传导受到裂隙粗糙程度的影响。此外,吸附-解吸效应及2种气体渗流导致的热传导也受到裂隙粗糙程度的直接作用。这样就实现了本研究提出的创新的裂隙粗糙程度参数与CO2驱替工程中的多物理场效应高度的耦合。这是已发表的文献无法定量表征的。
值得一提的是,有限元模拟基于小变形假设,难以分析裂隙扩展、层间滑动错动等大变形行为。而在研究中,煤层渗透率被定义为裂隙粗糙程度的参数。进而采用偏微分方程组与开采过程中的热-流-固多场效应耦合。这样就绕过了有限元模拟无法实现既有几何的演化计算的瓶颈,从而实现了多场耦合效应下裂隙网络粗糙程度的全面分析。当然,这种做法与如近场动力学等能够将裂隙几何形状绘制出来的方法相比,无法实现在模型中绘制出裂隙几何,并做到绘制出裂隙的拓展方向;而是通过提出的裂隙粗糙度参数及其演化来表征裂隙粗糙程度的演化。即通过计算裂隙粗糙度参数的演化及其对开采效果的影响,来分析粗糙裂隙网络行为对煤层气开采的影响。
至此,研究提出的适用于CO2驱替煤层瓦斯的裂隙动力学模型已构建完成,跨学科的模型由式(4)、式(9)、式(12)、式(18)、式(24)构成。显而易见,与已发表的CO2驱替模型及热-流-固耦合模型相比,研究提出的跨学科模型能够定量且全面的探究裂隙表面粗糙程度对煤层气开采的影响,这是以往已发表的模型无法定量表征的。
3. 模拟流程及模型正确性验证
开展热-流-固耦合跨学科分析模型的正确性验证分析,选用NI等[36]的煤层气实地开采数据。实地煤层气开采为100 m×100 m×2 m的煤层,煤层中瓦斯的初始压力为2.02 MPa,煤层初始温度为313.15 K。左边界和下边界为固定约束,右边界及上边界存在压力。
由于模型的复杂性,使用常规的解析解方法直接求解变得极为困难。因此,研究考虑到裂隙粗糙参数、热-流-固的耦合效应及时间空间演化,选择了基于有限元法的COMSOL Multiphysics软件来进行求解和分析。在仿真过程中,首先从现有的CO2驱替现场数据或文献中提取煤层、甲烷和CO2的物理和力学参数,并将这些参数输入到COMSOL Multiphysics;再将第2章中开发的模型,特别是考虑裂隙粗糙程度的部分,整合到COMSOL Multiphysics中;然后,基于收集到的CO2驱替项目数据,构建模拟煤层的几何结构,设定适当的边界条件,并对指定的几何形状进行多物理场的设置;最后,依据工程实际条件,进行网格划分,并配置求解器以完成计算过程。煤层数值模拟主要参数见表1[35-37]。
表 1 煤层数值模拟主要参数Table 1. Numerical simulation of main parameters of coal seam参数 取值 煤层初始孔隙度 0.0423 煤层初始渗透率/m2 5.14×10−16 煤的杨氏模量/MPa 2710 煤固体杨氏模量/MPa 8134 泊松比 0.345 煤热膨胀系数/K−1 2.4×10−5 煤密度/(kg·m−3) 1.25×103 煤固体密度/(kg·m−3) 1.47×103 标准状态下的瓦斯密度/(kg·m−3) 0.717×103 标准条件下的CO2密度/(kg·m−3) 1.977×103 煤的比热容/(J·(K·kg)−1) 1255 CO2比热容/ (J·(K·kg)−1) 1250 煤层气比热容/ (J·(K·kg)−1) 2227 CO2动态黏度/(Pa·s) 1.38×10−5 煤层气动态黏度/(Pa·s) 1.03×10−5 为了验证模型的有效性,进行了一系列模拟计算,以预测不同开采天数下的产气量。这些模拟得到的产气量随后与实际现场收集的数据进行了比较,研究模型验证如图1所示。结果显示,使用本研究开发的模型进行仿真计算,得出的煤层气开采量与实地观测数据之间有很好的一致性。这一发现证明了考虑裂隙粗糙程度和多场耦合效应的模型在精确性和可靠性方面的有效性。
4. 实地项目模拟结果
研究提出的跨学科模型的正确性得到了充分的验证后,进而开展瓦斯开采项目的实地裂隙粗糙程度与煤层复杂热流固耦合特性相互作用的分析。主要从以下3个方面开展分析:①粗糙裂隙作用下,不同瓦斯开采时间下的煤层瓦斯压力及封存的CO2的压力演化;②研究提出的跨学科的裂隙粗糙特性表征参数对瓦斯开采量及CO2封存量的影响;③不同裂隙粗糙特性表征参数下影响瓦斯开采主要因素的全面评估。
4.1 不同开采时间下煤层瓦斯及CO2压力演化
粗糙裂隙行为演化下煤层中瓦斯压力、CO2压力的演化如图2、图3所示。
由图2可知:随着开采进程的进行,瓦斯压力由高瓦斯压力区域的煤层向瓦斯开采井逐渐降低。在开采2 000 d后,煤层中的瓦斯压力有着显著的变化。尽管上述结论是工程经验性的、众所周知的,但需要指出的是,图2中煤层瓦斯压力的时空演化均是考虑了煤层粗糙裂隙行为的。在开采进行时,CO2的注入会导致煤层原有应力平衡被破坏,并导致煤层产生不同程度的形变。而这种形变会导致原有裂隙扩展、新的裂隙网络生成。而这些改变会导致2种气体渗流压力的增大,并导致粗糙裂缝中,气体对粗糙壁面的压力更大。故随着瓦斯开采的进行,裂隙粗糙程度在更大压力的作用下向着更有利于气体渗流的趋势演化,即会使裂隙网络粗糙程度降低。进而在这种降低作用下,气体渗流会更加容易,进而再次加剧这一降低。
由图3可以看出:随着CO2的不断注入,煤层内CO2的压力逐渐升高,且高CO2压力区域集中于注入井附近。尽管上述研究结论是工程经验性的、众所周知的,但图3中显示的封存CO2压力的时空演化同样也是考虑了煤层粗糙裂隙行为的。而CO2的渗流趋势会受到裂隙粗糙程度的显著影响,并进而显著改变煤层中CO2的压力。这种改变是受煤层瓦斯开采过程中热-流-固耦合效应的影响的。
4.2 裂隙粗糙对瓦斯开采量及CO2封存量的影响
将煤层CO2注入井与瓦斯产出井对角线中点位置设置为监测点,2点连线位置设置为监测线,并探究2种气体压力演化。煤层瓦斯及CO2含量分析的监测位置如图4所示。不同裂隙粗糙参数$\chi $下,不同监测位置的煤层瓦斯压力、CO2压力演化如图5、图6所示。
由图5可知:随着开采的进行,煤层中原有的瓦斯被不断采出,因此不同开采时间下的煤层瓦斯呈现一致性的降低趋势。在相同开采时间下,更小的裂隙粗糙参数会导致更低的煤层瓦斯含量,也会导致煤层瓦斯下降得更快,即更高的开采效率。对于监测线上不同位置的瓦斯压力,更远的位置意味着离开采井更近,更多的瓦斯被采出,因而瓦斯压力更低。而不同裂隙粗糙参数下瓦斯含量与前文所述一致。裂隙粗糙参数与煤层瓦斯开采过程中的裂隙粗糙性成正比,即更大的裂隙粗糙参数意味着更加粗糙的裂隙内壁。在这种情况下,瓦斯渗流会更加困难,即更少的瓦斯会被产出。故随着裂隙粗糙参数的增大,更多的煤层瓦斯被更快的产出,因而煤层瓦斯含量呈现较快速度的降低。当裂隙粗糙参数由0.24降低至0.18时,瓦斯含量最大降低了32.5%。
由图6可知:随着CO2的不断注入,不同裂隙粗糙参数下煤层CO2压力不断升高。CO2的注入会导致煤层原有的应力平衡被破坏,煤层基质产生形变并导致裂隙网络受到不同程度的挤压变形。而作为气体渗流的主要通道,CO2的不断注入会导致粗糙裂隙内壁产生较大的压力,进而在长时间作用下,裂隙粗糙程度会不断降低。而更加光滑的裂隙会导致气体渗流更加容易。当$\chi $由0.24降低至0.18时,CO2压力最大增加了26.7%。
4.3 不同裂隙粗糙参数下瓦斯开采主要因素评估
在瓦斯开采过程中,CO2与瓦斯的吸附竞争机制发挥着关键作用。因CO2对煤的吸附能力强于瓦斯,当CO2被注入煤层时,它会优先吸附到煤的表面,并替换掉原本吸附在那里的瓦斯分子。这个过程不仅导致煤层中的瓦斯分子解吸并释放,而且还引起煤层物理和化学性质的变化,例如孔隙度和渗透性的增加,从而进一步促进瓦斯的释放。此外,这种竞争吸附过程受到煤的性质、温度和压力等多种因素的影响。随着CO2的持续注入,更多的瓦斯被排出,从而提高了煤层气的开采效率。因而,探究瓦斯开采过程中的2种气体吸附量对揭示瓦斯开采及运移机制是至关重要的。不同裂隙粗糙参数下煤层瓦斯、CO2的吸附量如图7、图8所示。
由图7、图8可知:随着开采的进行,CO2对煤层吸附量要优于瓦斯,因而随着开采时间的持续(CO2注入时间的增加),更多的瓦斯分子被置换出来,即不同裂隙粗糙参数下瓦斯的吸附量逐渐降低。此外,在相同的开采条件下,更大的裂隙粗糙参数意味着更加粗糙的裂隙表面,因而,CO2在更加粗糙的裂隙中运移的会更慢,即在其他参数一致的情况下,更大的裂隙粗糙参数导致更少的瓦斯渗流扩散。在这种情况下,与原生瓦斯分子竞争的CO2分子含量更少,故更大的裂隙粗糙参数下瓦斯吸附量更高,而CO2吸附量则更低。当$\chi $由0.24降低至0.18时,煤层瓦斯吸附量最大降低了31.7%,CO2吸附量最大升高了12.1%。
不同裂隙粗糙参数下煤层的渗透率如图9所示。作为评估开采效率的重要指标,煤层渗透率的大小将直接决定瓦斯开采效率。
由图9可知:随着开采的持续,不同裂隙粗糙参数下煤层渗透率逐渐升高。而在相同开采时间下,更大的裂隙粗糙参数会导致更低的煤层渗透率。此外,更大的裂隙粗糙参数情况下,煤层渗透率上升的速度更慢。因此,更大的裂隙粗糙参数意味着煤层内更加粗糙的裂隙网络,这种情况不利于煤层瓦斯的渗流,煤层的渗透率更低。因为开采扰动及CO2的不断注入,煤层中诸多新裂隙生成,原有的裂隙因气体注入而扩展,但更加粗糙的裂隙网络会导致裂隙内气体压力更小。故这种情况下,在热-流-固耦合作用下,热交换强度更低,煤层热膨胀效应更弱,且气体压力诱导的煤层形变更小。故裂隙网络行为扩展行为更弱,进而渗透率增加得更慢。当$ \chi $由0.24降低至0.18时,煤层渗透率由初始的2.47×10−16 m2增加至4.93×10−16 m2。这种程度的增加对于煤层瓦斯的开采是十分有利的。
研究实现了热-流-固耦合状态下,CO2注入及煤层气抽采项目过程中的裂隙粗糙程度对瓦斯含量、CO2含量、瓦斯及CO2竞争吸附的机制、煤层渗透性的影响的全面、综合、定量的分析。这些因素对于揭示CO2驱替的机制、提升CO2封存效率以及提高煤层气的产气量至关重要。
5. 结 语
1)研究提出的数学模型与实地瓦斯开采工程数据吻合较好,且主要模拟结果与工程经验十分吻合;提出的裂隙粗糙程度参数能够很好地表征煤层瓦斯开采过程中裂隙粗糙特性对开采效率的贡献。
2)CO2的注入会导致煤层原有应力平衡被破坏,并导致煤层产生不同程度的形变。而这种形变会导致原有裂隙扩展、新的裂隙网络生成。进而导致粗糙裂缝中,气体对粗糙壁面的压力更大,进而降低裂隙粗糙程度。
3)在热-流-固耦合效应作用下,裂隙粗糙程度对瓦斯开采效率及煤层物理-力学特性有着显著的影响。当$\chi $由0.24降低至0.18时,瓦斯含量最大降低了32.5%,CO2压力最大增加了26.7%;煤层瓦斯吸附量最大降低了31.7%,CO2吸附量最大升高了12.1%;煤层渗透率由初始的2.47×10−16 m2增加至4.93×10−16 m2。
-
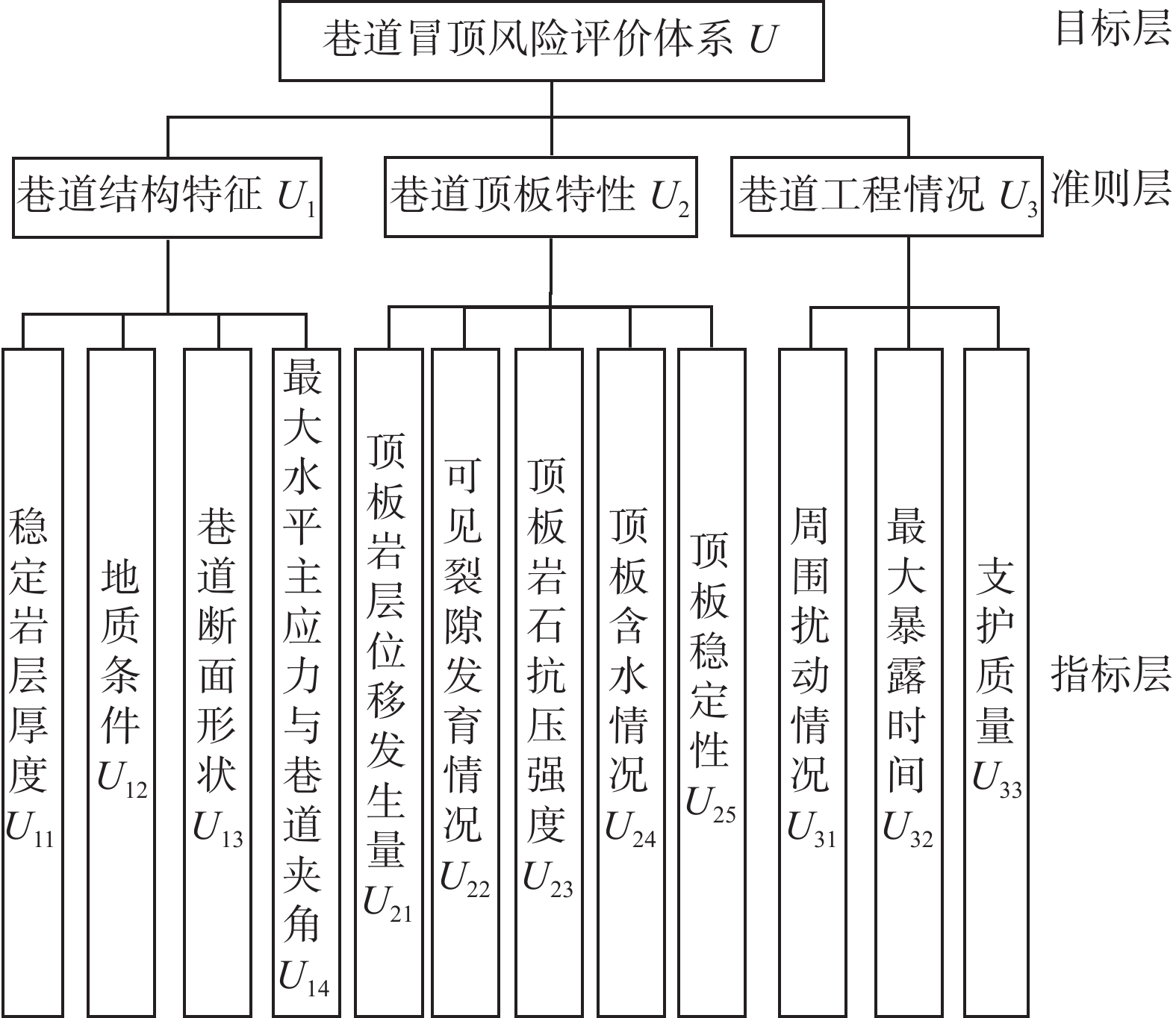
表 1 巷道冒顶风险评价指标概述
Table 1 Overview of roadway roof fall risk evaluation indexes
评价指标 指标概述 指标性质 稳定岩层厚度U11/m 巷道锚杆(索)支护时需要锚固在具有一定厚度的稳定岩层中,为保证锚固效果,稳定岩层厚度是直接的影响因素之一。 定量 地质条件U12 巷道岩层的地质条件包括巷道的埋深、巷道的构造应力、巷道围岩的断层以及地下水情况等,地质条件越复杂,巷道越容易变形。 定性 巷道断面形状U13 巷道断面形状是影响围岩稳定性的关键因素之一,断面形状将影响巷道围岩的应力分布,从而产生不同的围岩状态,一般情况下圆形断面形状巷道围岩稳定性最好。 定性 最大水平主应力与
巷道夹角U14/(°)随着最大水平主应力与巷道夹角的增大, 顶底板破坏深度先减小后增大,巷道顶底板破坏程度也随之增大,当夹角为90°时,巷道围岩破坏最为严重。 定量 顶板岩层移发生量U21/m 顶板岩层位移发生量是《煤矿安全规程》明确规定的观测指标,其超出临界支护值后,发生顶板冒落等物理现象,通过现场观测获取。 定量 可见裂隙发育情况U22/条 可见裂隙发育情况反映顶板稳定性,采用顶板窥视仪准确观察。 定量 顶板岩石抗压强度U23/MPa 顶板岩石抗压强度表征顶板的承载能力,由于受地心引力作用,岩体内应力积聚到某一区域,并产生拉应力,若拉应力超过了岩石的抗拉强度,则顶板岩会出现裂缝。 定量 顶板岩石含水情况U24 地表水流、渗入地下,与地下水共同对岩体浸润作用,导致顶板的力学性能发生了物理和化学变化,使顶板的作用力降低。 定性 顶板稳定性U25 煤矿巷道顶板稳定性直接影响冒顶风险,顶板的稳定性越好冒顶风险越低。 定性 周围扰动情况U31 在巷道周围发生扰动越大,影响顶板稳定性,更容易导致巷道冒顶。 定性 最大暴露时间U32/d 随着巷道顶板暴露在空气中的时间越长,其裸露的岩石与空气发生化学反应导致岩性降低,并受自重影响发生脱落。 定量 支护质量U33 支护的质量直接反应巷道顶板稳定性,支护质量越好顶板稳定性越好。 定性 表 2 巷道冒顶风险评价指标等级
Table 2 Roadway roof fall risk evaluation index grades
评价指标 评价等级 Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅳ V 极低风险 低风险 中风险 高风险 极高风险 稳定岩层厚度U11/m 6.0~7.5 4.5~6.0 3.0~4.5 1.5~3.0 0~1.5 地质条件U12 简单
0~2较简单
2~4较复杂
4~6复杂
6~8极复杂
8~10巷道断面形状U13 圆形
8~10拱形
6~8矩形
4~6梯形
2~4其他
0~2最大水平主应力与巷道夹角U14/(°) 0~18 18~36 36~54 54~72 72~90 顶板岩层位移发生量U21/m 0~0.07 0.07~0.14 0.14~0.21 0.21~0.28 0.28~0.5 可见裂隙发育情况U22/条 0~2 2~4 4~6 6~8 8~10 顶板岩石抗压强度U23/MPa 200~250 150~200 100~150 100~50 0~50 顶板岩石含水情况U24 无渗水
0~2微渗水
2~4微出水
4~6少量涌水
6~8大量涌水
8~10顶板稳定性U25 稳定
8~10较稳定
6~8较不稳定
4~6不稳定
2~4极不稳定
0~2周围扰动情况U31 无影响
0~2极小影响
2~4小影响
4~6大影响
6~8极大影响
8~10最大暴露时间U32/d 0~5 5~15 10~30 30~60 50~100 支护质量U33 好
8~10较好
6~8一般
4~6差
2~4极差
0~2表 3 无量纲化处理的巷道冒顶风险评价指标等级
Table 3 Dimensionless treatment of roadway roof fall risk evaluation index grades
评价指标 评价等级 Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅳ V 极低风险 低风险 中风险 高风险 极高风险 稳定岩层厚度U11 0.8~1.0 0.6~0.8 0.4~0.6 0.2~0.4 0.0~0.2 地质条件U12 0.0~0.2 0.2~0.4 0.4~0.6 0.6~0.8 0.8~1.0 巷道断面形状U13 0.8~1.0 0.6~0.8 0.4~0.6 0.2~0.4 0.0~0.2 最大水平主应力与巷道夹角U14 0.0~0.2 0.2~0.4 0.4~0.6 0.6~0.8 0.8~1.0 顶板岩层位移发生量U21 0.0~0.14 0.14~0.28 0.28~0.42 0.42~0.56 0.56~1.0 可见裂隙发育情况U22 0.0~0.2 0.2~0.4 0.4~0.6 0.6~0.8 0.8~1.0 顶板岩石抗压强度U23 0.8~1.0 0.6~0.8 0.4~0.6 0.2~0.4 0.0~0.2 顶板岩石含水情况U24 0.0~0.2 0.2~0.4 0.4~0.6 0.6~0.8 0.8~1.0 顶板稳定性U25 0.8~1.0 0.6~0.8 0.4~0.6 0.2~0.4 0.0~0.2 周围扰动情况U31 0.0~0.2 0.2~0.4 0.4~0.6 0.6~0.8 0.8~1.0 最大暴露时间U32 0.0~0.05 0.05~0.15 0.15~0.3 0.3~0.6 0.6~1.0 支护质量U33 0.8~1.0 0.6~0.8 0.4~0.6 0.2~0.4 0.0~0.2 表 4 巷道冒顶指标
Table 4 Roof fall indexes of roadway
巷道
编号评价指标 U11/m U12 U13 U14 U21/m U22/条 U23/MPa U24 U25 U31 U32/d U33 1 3.840 3.660 8.820 19.500 0.082 3.000 210.000 3.560 9.450 2.560 3.000 8.650 2 3.615 4.558 7.890 22.150 0.063 1.000 220.000 4.450 8.920 2.780 6.000 7.430 3 4.395 3.286 7.880 18.920 0.067 2.000 215.000 3.410 7.820 3.150 4.000 6.840 4 5.085 4.890 8.450 20.500 0.075 2.000 202.000 4.260 8.670 3.480 7.000 8.120 5 4.290 3.189 7.090 23.320 0.068 3.000 198.000 4.560 8.090 3.070 6.000 7.680 6 4.388 3.886 8.380 19.850 0.072 1.000 214.000 5.560 9.750 3.560 3.000 7.560 7 3.292 4.568 7.650 24.150 0.080 2.000 222.000 4.850 7.930 4.870 5.000 8.230 8 4.500 5.189 8.580 17.980 0.059 2.000 218.000 3.440 7.050 2.950 6.000 7.880 表 5 巷道冒顶指标标准化
Table 5 Roadway roof fall indexes standardization
巷道
编号评价指标 U11 U12 U13 U14 U21 U22 U23 U24 U25 U31 U32 U33 1 0.512 0.366 0.882 0.217 0.164 0.300 0.840 0.356 0.945 0.256 0.030 0.865 2 0.482 0.456 0.789 0.246 0.126 0.100 0.880 0.445 0.892 0.278 0.060 0.743 3 0.586 0.329 0.788 0.210 0.134 0.200 0.860 0.341 0.782 0.315 0.040 0.684 4 0.678 0.489 0.845 0.228 0.150 0.200 0.808 0.426 0.867 0.348 0.070 0.812 5 0.572 0.319 0.709 0.259 0.136 0.300 0.792 0.456 0.809 0.307 0.060 0.768 6 0.585 0.389 0.838 0.221 0.144 0.100 0.856 0.556 0.975 0.356 0.030 0.756 7 0.479 0.457 0.765 0.268 0.160 0.200 0.888 0.485 0.793 0.487 0.050 0.823 8 0.600 0.519 0.858 0.200 0.118 0.200 0.872 0.344 0.705 0.295 0.060 0.788 表 6 指标权重
Table 6 Indexes weight
目标层 准则层 准则层权重 指标层 指标层
权重AHP计算权重$ {G} $ EW计算权重$ {Q} $ 组合权重$ {W} $ 巷
道
冒
顶
风
险
评
价
体
系
U巷道结构特征U1 0.260 稳定岩层厚度U11 0.463 0.120 0.086 0.106 地质条件U12 0.275 0.072 0.097 0.087 巷道断面形状U13 0.085 0.022 0.068 0.040 最大水平主应力与巷道夹角U14 0.176 0.046 0.088 0.066 巷道顶板特性U2 0.413 顶板岩层位移发生量U21 0.221 0.091 0.081 0.089 可见裂隙发育情况U22 0.193 0.080 0.097 0.091 顶板岩石抗压强度U23 0.193 0.080 0.079 0.082 顶板岩石含水情况U24 0.117 0.048 0.095 0.071 顶板稳定性U25 0.276 0.114 0.073 0.095 巷道工程情况U3 0.327 周围扰动情况U31 0.297 0.097 0.076 0.089 最大暴露时间U32 0.163 0.054 0.099 0.075 支护质量U33 0.540 0.177 0.062 0.108 表 7 编号8巷道冒顶指标关联度
Table 7 Roof fall index correlation degree of No.8 roadway
巷道冒顶风险等级 U11 U12 U13 U14 U21 U22 U23 U24 U25 U31 U32 U33 I(极低风险) −0.333 −0.399 0.068 0.000 0.229 0.000 0.083 −0.295 −0.244 −0.244 −0.167 −0.054 II(低风险) 0.000 −0.198 −0.068 0.000 −0.157 0.000 −0.360 0.194 0.475 0.322 0.167 0.015 III(中风险) 0.000 0.156 −0.645 −0.500 −0.579 −0.500 −0.680 −0.140 −0.263 −0.263 −0.600 −0.470 IV(高风险) −0.333 −0.144 −0.763 −0.667 −0.719 −0.667 −0.787 −0.427 −0.508 −0.508 −0.800 −0.647 V(极高风险) −0.500 −0.369 −0.823 −0.750 −0.789 −0.750 −0.840 −0.570 −0.631 −0.631 −0.900 −0.735 表 8 评价巷道冒顶风险综合关联度计算及评价结果
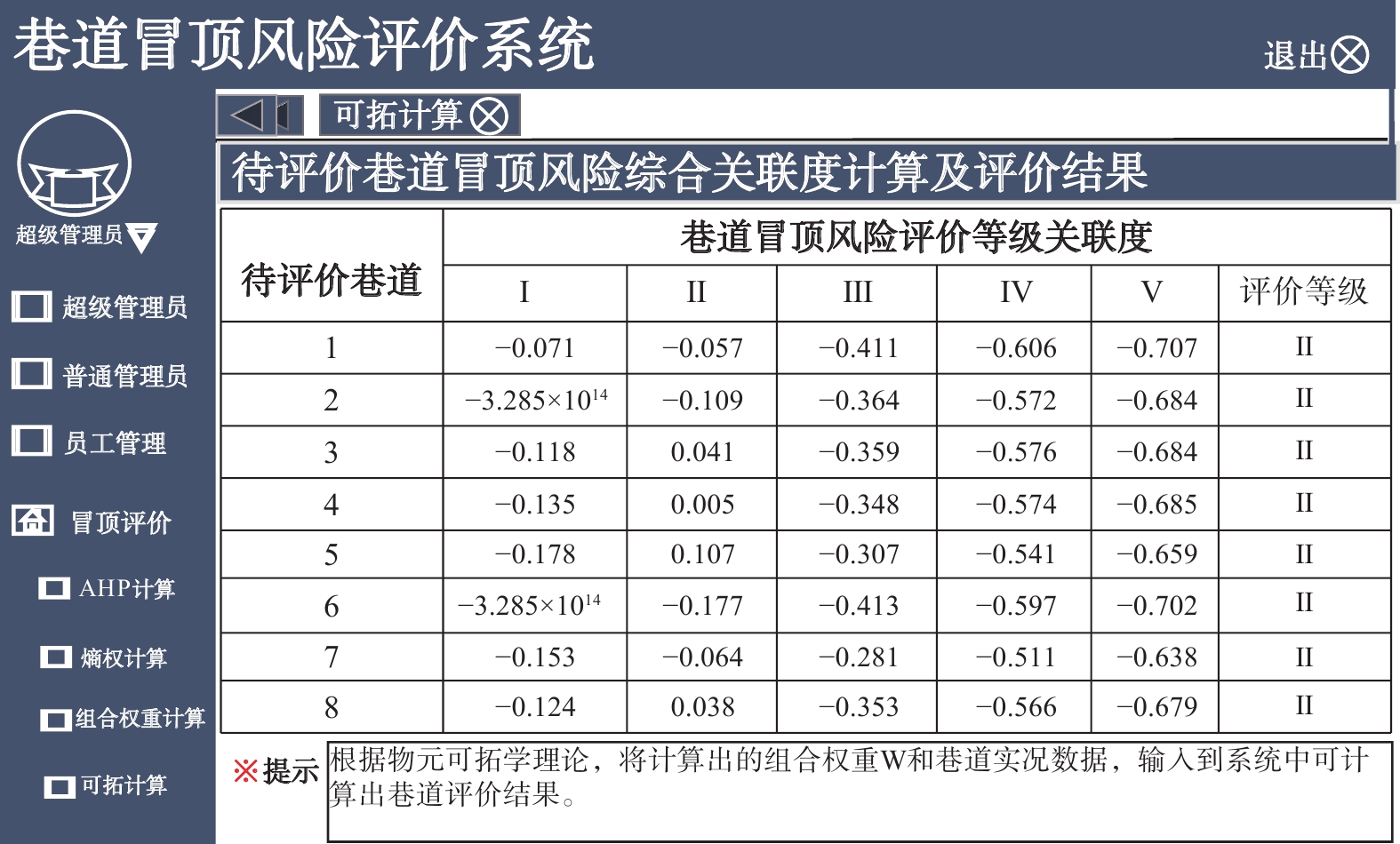
Table 8 Comprehensive correlation degree calculation and evaluation results of roadway roof fall risk evaluation
待评巷道编号 C9回风联络巷冒顶风险评价等级关联度 I(极低风险) II(低风险) III(中风险) IV(高风险) V(极高风险) 评价等级 1 −0.071 −0.057 −0.411 −0.606 −0.707 II 2 −3.285×1014 −0.109 −0.364 −0.572 −0.684 II 3 −0.118 0.041 −0.359 −0.576 −0.684 II 4 −0.135 0.005 −0.348 −0.574 −0.685 II 5 −0.178 0.107 −0.307 −0.541 −0.659 II 6 −3.285×1014 −0.177 −0.413 −0.597 −0.702 II 7 −0.153 −0.064 −0.281 −0.511 −0.638 II 8 −0.124 0.038 −0.353 −0.566 −0.679 II 平均值 −8.212×1013 −0.027 −0.355 −0.568 −0.680 II 表 9 AHP-可拓模型与组合权重-可拓模型评价结果对比
Table 9 Comparison of the evaluation results of AHP-extension model and combined weight-extension model
编号 实际等级 AHP-可拓模型 组合权重-可拓模型 评价等级 评价等级 1 II I II 2 III II II 3 II II II 4 III II II 5 II II II 6 II II II 7 II II II 8 II II II -
[1] 赵开功,李彦平. 我国煤炭资源安全现状分析及发展研究[J]. 煤炭工程,2018,50(10):185−189. ZHAO Kaigong, LI Yanping. Analysis and development suggestion for coal resources safety in China[J]. Coal Engineering, 2018, 50(10): 185−189.
[2] 侯芳芳. 煤炭资源安全现状分析及发展研究[J]. 资源信息与工程,2020,35(2):45−47. HOU Fangfang. Analysis of current situation and development of coal resource security[J]. Resource Information and Engineering, 2020, 35(2): 45−47.
[3] 马念杰,赵希栋,赵志强,等. 深部采动巷道顶板稳定性分析与控制[J]. 煤炭学报,2015,40(10):2287−2295. MA Nianjie, ZHAO Xidong, ZHAO Zhiqiang, et al. Stability analysis and control technology of mine roadway roof in deep mining[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2015, 40(10): 2287−2295.
[4] 何满潮. 深部建井力学研究进展[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(3):726−746. HE Manchao. Research progress of deep shaft construction mechanics[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(3): 726−746.
[5] 王卫军,范磊,马谕杰,等. 基于蝶形破坏理论的深部巷道围岩控制技术研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(1):157−167. WANG Weijun, FAN Lei, MA Yujie, et al. Research on surrounding rock control technology of deep roadway based on butterfly failure theory[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2023, 51(1): 157−167.
[6] 吕贵春,马云东,杨志勇. 模糊综合评价法在冒顶危险性评价中的应用[J]. 煤矿安全,2005(1):8−10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-496X.2005.01.003 LYU Guichun, MA Yundong, YANG Zhiyong. Applica-tion of fuzzy comprehensive evaluation methods in the roof fall dangerous evaluation[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2005(1): 8−10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-496X.2005.01.003
[7] 王琦,王洪涛,李术才,等. 大断面厚顶煤巷道顶板冒落破坏的上限分析[J]. 岩土力学,2014,35(3):795−800. WANG Qi, WANG Hongtao, LI Shucai, et al. Upper bound limit analysis of roof collapse mechanism of large section roadway with thick top coal[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2014, 35(3): 795−800.
[8] 杜志强. 煤矿巷道稳定性评价体系及其分析[J]. 陕西煤炭,2018,37(1):28−31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-749X.2018.01.007 DU Zhiqiang. Analysis of mine roadway stability assessment system[J]. Shaanxi Meitan, 2018, 37(1): 28−31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-749X.2018.01.007
[9] 崔铁军,马云东. 基于AHP-云模型的巷道冒顶风险评价[J]. 计算机应用研究,2016,33(10):2973−2976. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2016.10.023 CUI Tiejun, MA Yundong. Risk evaluation of roadway roof fall based on AHP-cloud model[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2016, 33(10): 2973−2976. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2016.10.023
[10] 史德俊,徐恒,王春来,等. 基于综合指数法的不良岩体巷道冒落危险性评价[J]. 现代矿业,2015,31(12):112−116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2015.12.042 SHI Dejun, XU Heng, WANG Chunlai, et al. Risk evaluation of roadway caving of weak rock mass based on comprehensive index method[J]. Modern Mining, 2015, 31(12): 112−116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2015.12.042
[11] 李季,彭博,马旺,等. 巷道冒顶隐患风险可拓评价模型研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2014,45(5):35−38. LI Ji, PENG Bo, MA Wang, et al. The research on extension evaluation model of roadway roof fall hidden risks[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2014, 45(5): 35−38.
[12] 范彦阳,季卫斌,郭平. 顶板冒顶隐患分区预测模型及应用实践[J]. 煤矿安全,2019,50(1):214−218. FAN Yanyang, JI Weibin, GUO Ping. Partition prediction model for hidden danger of roof fall and its application practice[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2019, 50(1): 214−218.
[13] 王志强,武超,石磊,等. 基于复变理论的双向不等压圆形巷道围岩应力及塑性区分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(S2):419−429. WANG Zhiqiang, WU Chao, SHI Lei, et al. Analysis of surrounding rock stress and plastic zone of two-way unequal pressure circular roadway based on complex variable theory[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2019, 44(S2): 419−429.
[14] 党伟. 深部采动巷道顶板稳定性的分析和控制[J]. 能源与节能,2020(10):11−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0802.2020.10.004 DANG Wei. Analysis and control of roof stability of deep mining roadway[J]. Energy and Energy Conservation, 2020(10): 11−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0802.2020.10.004
[15] 曾佑富,伍永平,来兴平,等. 复杂条件下大断面巷道顶板冒落失稳分析[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2009,26(4):423−427. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3363.2009.04.006 ZENG Youfu, WU Yongping, LAI Xingping, et al. Analysis of roof caving instability mechanism of large-section roadway under complex conditions[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2009, 26(4): 423−427. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3363.2009.04.006
[16] 杨光荣. 李家壕矿切眼顶板冒顶危险区预测原理与方法研究[D]. 北京:中国矿业大学(北京),2013:1-122. [17] 薛彦平,许广,唐又驰. 基于AHP的深部巷道围岩稳定性影响因素评价分析[J]. 数学的实践与认识,2013,43(6):157−164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0984.2013.06.019 XU Yanping, XU Guang, TANG Youchi. Evaluation analysis of stability influence factors of surrounding rock of deep tunnels based on AHP[J]. Mathematics in Practice and Theory, 2013, 43(6): 157−164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0984.2013.06.019
[18] 葛杨,刘松涛. 基于指数标度层次分析法和Vague集的雷达导引头干扰效能评估[J]. 探测与控制学报,2020,42(3):69−74. GE Yang, LIU Songtao. Radar seeker jamming effect evaluation based on exponential scale AHP and Vague set[J]. Journal of Detection & Control, 2020, 42(3): 69−74.
[19] 吴波,黄惟,陈辉浩,等. 基于熵权-可拓理论的瓦斯隧道施工安全风险评估[J]. 中国科技论文,2022,17(1):99−104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2022.01.014 WU Bo, HUANG Wei, CHEN Huihao, et al. Risk assessment of gas tunnel construction based on entropy method and extension theory[J]. China Science Paper, 2022, 17(1): 99−104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2022.01.014
[20] 马纪,刘希喆. 基于G2-熵权法的低压配网台区状态特性评估[J]. 电力自动化设备,2017,37(1):41−46. MA Ji, LIU Xizhe. Conditional characteristic evaluation based on G2-entropy weight method for low-voltage distribution network[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2017, 37(1): 41−46.
[21] 王卫军,袁超,余伟健,等. 深部大变形巷道围岩稳定性控制方法研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2016,41(12):2921−2931. WANG Weijun, YUAN Chao, YU Weijian, et al. Stability control method of surrounding rock in deep roadway with large deformation[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2016, 41(12): 2921−2931.
[22] 陈尚波. 复杂条件下空区诱发的岩移及顶板冒落效应研究[D]. 江西:江西理工大学,2014. [23] 刘洪涛,马念杰. 煤矿巷道冒顶高风险区域识别技术[J]. 煤炭学报,2011,36(12):2043−2047. LIU Hongtao, MA Nianjie. Coal mine roadway roof caving high risk areas recognition technology[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2011, 36(12): 2043−2047.
[24] 蒋力帅,马念杰,白浪,等. 巷道复合顶板变形坏特征与冒顶隐患分级[J]. 煤炭学报,2014,39(7):1205−1211. JIANG Lishuai, MA Nianjie, Bailang, et al. Deformation and failure characteristics and roof caving hidden danger classification of roadways compound roof[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2014, 39(7): 1205−1211.
[25] 蔡文. 可拓论及其应用[J]. 科学通报,1999(7):673−682. [26] 刘业娇,陈颖,任玉辉,等. 基于B/S模式的安全评价数据库管理系统研发[J]. 工业安全与环保,2020,46(8):56−59. LIU Yejiao, CHEN Ying, REN Yuhui, et al. Research and development of database management system for safety evaluation based on B/S mode[J]. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection, 2020, 46(8): 56−59.
[27] 伍玲. 基于J2EE的通信营业厅视频质量评价系统设计[J]. 无线互联科技,2017(3):15−16. WU Ling. Design of video quality evaluation system based on J2EE[J]. Wireless Internet Technology, 2017(3): 15−16.
[28] LI J H, MENG F X, WEN X M. The design and realization of Library MIS based on MVC[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2013, 756/759: 1114−1118.
[29] 王春丽. 基于SSM架构考核评价系统设计与实现[J]. 电脑编程技巧与维护,2020(12):8−11. [30] 肖宇. 复合顶板采动巷道围岩蝶形破坏机理研究[D]. 湘潭:湖南科技大学,2020.



 下载:
下载: