The Influence of low-temperature cold shock saturated water on the permeability characteristics of coal body and experimental study on permeability enhancement
-
摘要:
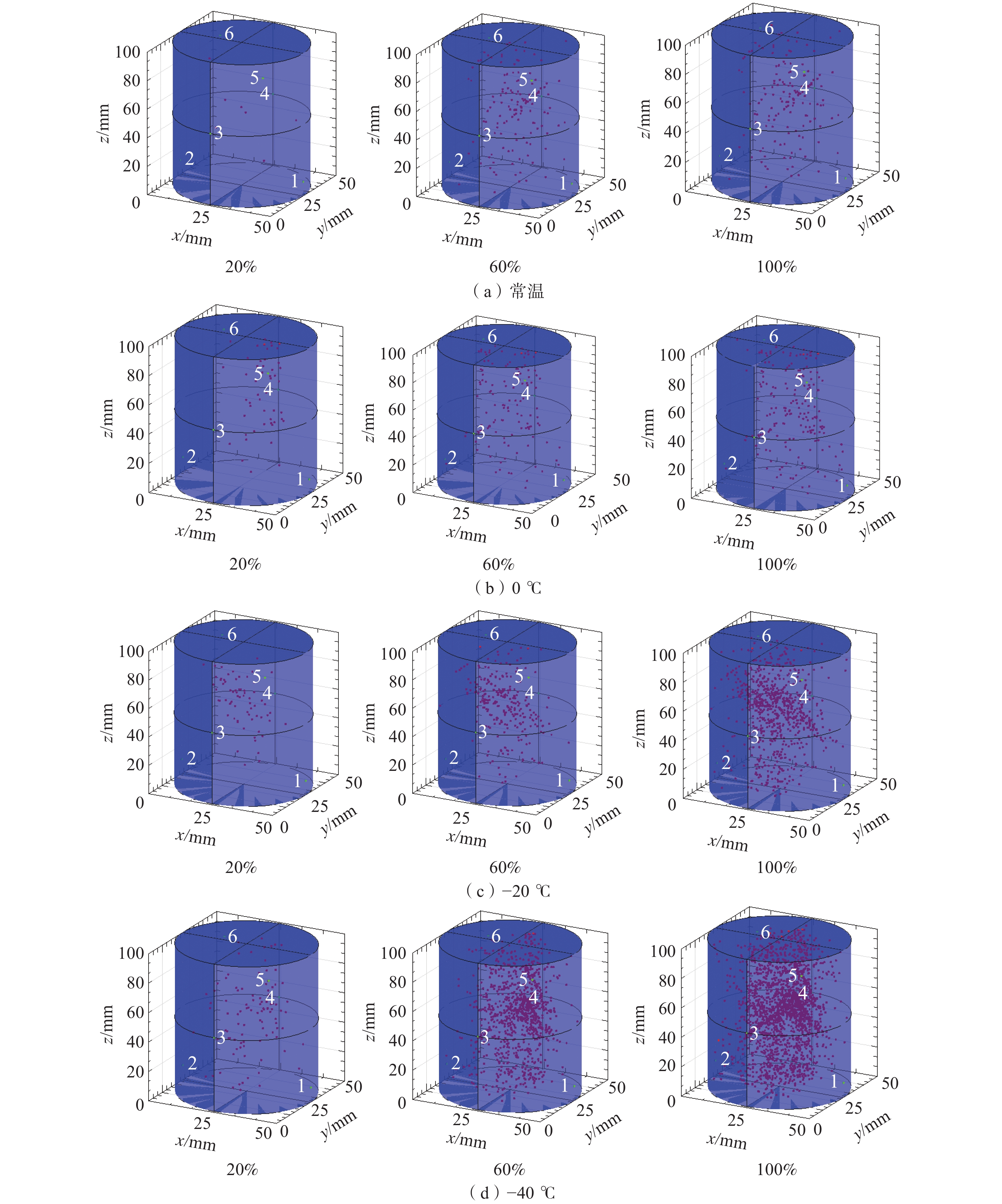
煤层气开发工作中,由于煤层的普遍渗透率较低,需采取有效的增透技术来提高煤层气抽采效率,低温致裂增透技术被广泛研究和应用。通过对煤体进行低温冷冲击饱水处理,模拟实际开采中的低温环境,以探究不同温度冷冲击饱水煤体的力学特性及渗流规律;采用负压饱水装置对试样进行饱水处理,试样完全饱水后,放入高低温试验箱,分别对不同试样进行常温、0、−20、−40 ℃的冲击;饱水试样冷冲击处理完成后,使用三轴渗流仪进行渗流试验和三轴压缩试验。试验结果表明:冷冲击处理饱水试样,会对试样造成损伤,煤体内部裂隙发育扩张,试样抗压强度减小,渗透率增大;随着冷冲击温度的降低,试样的渗透率逐渐增大;−40 ℃冲击的试样初始渗透率最大,较常温试样增长了202.9%。
Abstract:In the development of coalbed methane (CBM), due to the generally low permeability of coal beds, effective permeability enhancement technology is needed to improve the extraction efficiency of CBM. Among them, low-temperature fracturing and permeability enhancement technology has been widely studied and applied. In this paper, we simulate the low-temperature environment in actual mining by applying low-temperature cold impact water saturation treatment to the coal body, in order to investigate the mechanical properties and seepage law of the coal body saturated with cold impact water at different temperature conditions. Negative pressure water-saturated device is used to saturate the specimen, after the specimen is completely saturated with water, it is put into the high and low temperature test chamber, and different specimens are impacted at room temperature, 0 ℃, −20 ℃ and −40 ℃, respectively. After the cold shock treatment of water-saturated specimens was completed, a triaxial percolation meter was used to carry out percolation test and triaxial compression test. The test results show that: cold shock treatment of water-saturated specimens will cause damage to the specimen, the development and expansion of internal cracks in the coal body, the specimen compressive strength decreases, and the permeability increases. And with the decrease of cold impact temperature, the permeability of the specimen gradually increases. The initial permeability of the specimen impacted at −40 ℃ was the largest, which increased by 202.9% compared with the normal temperature specimen.
-
CO2-ECBM开采是一种相对高效的煤层气开采技术[1]。煤层中CO2和CH4竞争吸附的微观机制是制约CO2-ECBM的主要机制[2-3]。煤是一种复杂的大分子化合物,因此,从分子水平研究煤层中CO2和CH4的竞争吸附机制至关重要。
与其他大分子有机化合物不同,煤大分子具有分子组成多样化和化学结构复杂的特征[4-5]。因此,合理地构建煤的大分子模型是在分子水平上研究煤的结构和煤中气体的竞争吸附机理的前提条件。目前,常用X射线光电子能谱(XPS)、拉曼光谱(Raman spectroscopy)、高分辨率透射电子显微镜(HRTEM)、13C核磁共振(13C-NMR)和傅里叶变换红外光谱(FTIR)等技术对煤的分子结构进行研究和分析[6-9]。相建华等[10]基于成庄矿煤的工业分析、元素分析、13C-NMR、XPS等实验结果,构建了其大分子结构模型,并采用分子力学和分子动力学方法对所得煤结构模型进行结构优化,结果表明分子间芳香层片的定向排列是高煤级煤结构中短程有序的原因;王绍清等[11]基于HRTEM研究了煤的石墨化过程,指出石墨微晶形成过程还伴随着结构缺陷的演化;NIEKERK等[12]利用HRTEM测量了煤的芳香条纹的大小和分布,并根据13C-NMR在芳香骨架上加入硫、氮、氧、脂肪链侧链和交联键,从而建立了2种南非煤的分子模型;MOKONE等[13]利用岩相分析、元素分析、氦密度、13C-NMR、HRTEM等方法构建了含氧、氮、硫的多环芳烃分子结构,提供了更好、更准确的芳香烃测量方法。随着HRTEM等技术在煤结构分析中的应用,学者们对煤大分子碳骨架结构的认知有了更进一步的提高,这些技术的进步都有利于更全面的表征煤大分子的结构特征,从而为气体在煤中的竞争吸附模拟奠定基础。
学者们针对CO2和CH4在煤中的竞争吸附特性展开了一系列研究。ZHENG等[14]利用核磁共振手段研究了亚烟煤和无烟煤中CO2与CH4的竞争吸附特性,结果表明CO2的注入可使吸附CH4的解吸效率提高14%~26%;WEI等[15]对中煤级煤中CO2和CH4气体的竞争吸附进行了实验研究,结果表明CH4浓度的下降速率随着CO2注入压力的增加表现为先增大后趋于稳定的趋势;DANG等[16]利用分子模拟方法研究了褐煤中CO2和CH4的吸附行为,结果表明CO2对CH4的吸附选择性随着压力的增加表现为先迅速下降后趋于稳定的趋势,这说明气体压力是影响竞争吸附行为的重要因素。此外,也有学者认为气体的分子动力学直径也是CH4和CO2在煤中竞争吸附行为的主导因素[17]。虽然有部分学者采取一系列方法研究了CO2和CH4在煤中的竞争吸附行为,但对于CO2和CH4在分子水平的竞争吸附机制仍需要进一步探讨。
合理的大分子模型是模拟CO2对CH4在煤中竞争吸附性能的基础。为此,基于东曲矿8号煤的大分子结构模型开展了CO2和CH4的单组分与双组分竞争吸附研究,分析了不同吸附摩尔比条件下的吸附量和吸附选择性参数,并从相互作用能和势能分布角度揭示了竞争吸附机理,研究结果对于实现CO2置换CH4和提高煤层气采收率具有重要的意义。
1. 模型结构及模拟方法
东曲矿8号煤的工业分析与元素分析结果为:水分含量2.12%,灰分含量4.06%,挥发分含量13.24%,最大镜质组反射率1.82%,C元素含量91.52%,H元素含量4.04%,O元素含量2.46%,N元素含量1.43%;S元素含量0.56%。
通过HRTEM、13C-NMR、XPS和FTIR构建了东曲矿8号煤的大分子结构(C1258H644O24N16 S2),模型构建过程如图1。
图1中,HRTEM用于确定煤大分子的碳骨架结构,13C-NMR、XPS和FTIR用于确定脂肪结构和官能团结构的分布。通过Materials Studio软件对煤大分子结构进行分子力学与分子动力学优化,力场设置为COMPASS Ⅱ,最终得到东曲矿8号煤的最低能量构型(图1d)。由于煤中存在一些难以清除的小分子[17],其模型的密度(1.40 g/cm3)略低于实测密度(1.42 g/cm3)。在Atom Volume & Surfaces模块中运用半径为1.65 nm的圆球探针对孔隙空间进行探测(图1e),所得煤大分子中的孔隙体积为6493.21 Å3(1 Å=10−10 m)。
采用Materials Studio软件中的吸附模块进行了吸附模拟。模拟温度和最大吸附压力分别设置为298.15 K和30 MPa,根据吸附质气体压力确定气体摩尔比。为了研究CH4和CO2的竞争吸附特性,采用了单组分与不同摩尔比的双组分气体吸附方案。气体吸附模拟参数见表1。
表 1 气体吸附模拟参数Table 1. Gas adsorption simulation parameters编号 摩尔比/% 压力/MPa CH4 CO2 CH4 CO2 1 100 — 30 — 2 — 100 — 30 3 40 60 12 18 4 50 50 15 15 5 60 40 18 12 基于蒙特卡洛方法对煤大分子模型进行CH4和CO2等温吸附模拟,计算固定压力下的等温吸附量来表征气体在特定压力下的吸附性能。模拟过程采用COMPASS Ⅱ力场,平衡步数为100 000 步,生产步数为1 000 000 步,并计算平均吸附量。通过Langmuir公式获得了气体的吸附等温线[18]。朗格缪尔拟合公式为:
$$ V=a b p /(1+b p) $$ (1) 式中:V为气体吸附量,mmol/g;a为压力趋于无穷大时的最大吸附量,mmol/g;b为吸附常数,1/MPa;p为吸附压力,MPa。
2. 模拟结果
2.1 单组分气体吸附
东曲矿8号煤单组分气体的等温吸附曲线如图2,单组分等温吸附曲线的朗格缪尔拟合参数见表2。
表 2 单组分等温吸附曲线的朗格缪尔拟合参数Table 2. Langmuir fitting parameters of single component isothermal adsorption curves气体 a/(mmol·g−1) b/MPa−1 R2/% CH4 4.55 0.43 99.77 CO2 5.79 0.92 99.85 单组分气体吸附条件下CH4和CO2的气体吸附量均随着压力的增大而呈现先快速增加后稳定的趋势,符合I型等温吸附特征。单组分吸附条件下CO2的吸附量显著大于CH4的吸附量,为煤中CH4的置换提供了理论依据。CO2的吸附常数b的值也大于CH4的吸附常数,这说明CO2比CH4更容易达到最大吸附量。主要原因是CO2与煤大分子之间的作用力较强,且CO2分子之间具有较强的相互作用力[19]。
2.2 双组分竞争吸附
2.2.1 气体吸附量
双组分竞争吸附下的等温吸附曲线如图3,双组分竞争吸附等温吸附曲线的朗格缪尔拟合参数见表3。
表 3 双组分竞争吸附等温吸附曲线的朗格缪尔拟合参数Table 3. Langmuir fitting parameters of dual component competitive adsorption isothermal adsorption curves摩尔比(CO2 ∶CH4) a/(mmol·g−1) b/MPa−1 R2/% 60%∶40% 4.21 1.10 99.85 50%∶50% 4.14 1.08 99.91 40%∶60% 4.06 0.95 99.88 双组分竞争吸附下的等温吸附规律同样符合Ⅰ型等温线特征。在CO2/CH4竞争吸附体系中,总吸附量随着CO2的摩尔分数的增大而增大;当CO2的摩尔分数为60%时总吸附量达到最大值(4.21 mmol/g),当CO2的摩尔分数为40%时总吸附量最小(4.06 mmol/g)。对比3种不同摩尔比吸附条件下的吸附常数可以发现,CO2的摩尔分数越大,竞争吸附越容易达到最大吸附量。双组分气体的吸附特性与竞争吸附过程中的吸附选择性有关。
2.2.2 吸附选择性
在竞争吸附体系中,吸附选择性系数是评价气体间竞争吸附的重要指标之一。气体竞争吸附体系中CO2对CH4的吸附选择性系数$S_{{\mathrm{CO}}_2/{\mathrm{CH}}_4} $的定义如下[20]:
$$ S_{\mathrm{CO}_{2} / \mathrm{CH}_{4}}=\frac{x_{\mathrm{CO}_{2}} / x_{\mathrm{CH}_{4}}}{y_{\mathrm{CO}_{2}} / y_{\mathrm{CH}_{4}}} $$ (2) 式中:$ S_{\mathrm{CO}_{2} / \mathrm{CH}_{4}} $为CO2对CH4的吸附选择性系数;$x_{\mathrm{CO}_{2}} 、 x_{\mathrm{CH}_{4}} $为CO2和CH4在吸附相中的摩尔分数;$y_{\mathrm{CO}_{2}} 、 y_{\mathrm{CH}_{4}} $为体积相中CO2和CH4的摩尔分数。
当$ S_{\mathrm{CO}_{2} / \mathrm{CH}_{4}} $>1时,表明CO2容易吸附于煤大分子中,选择性系数越高,吸附效果就越好。CO2和CH4的在煤大分子中的双组分竞争吸附的选择性系数如图4。
对比不同摩尔分数条件下的吸附选择性系数随气体压力的变化规律可以发现:不同条件下CO2对CH4的选择性吸附系数始终大于1;当CO2的摩尔分数为60%和50%时,吸附选择性系数随着气体压力的增大而增大;当CO2的摩尔分数为40%时,吸附选择性系数随着气体压力的增大而呈减小趋势;不同摩尔比的CO2和CH4竞争吸附体系中,吸附选择性系数$S_{{\mathrm{CO}}_2/{\mathrm{CH}}_4} $随着CO2摩尔分数的减小而增大。因此,较低摩尔分数的CO2具有较强的竞争吸附性能,有利于采收率的提高。
2.3 相互作用能
相互作用能指的是吸附前后系统总能量的变化量,CH4和CO2在煤大分子中的吸附主要由范德华能和静电能引起[21]。因此,进一步分析了单组分与双组分竞争吸附条件下的相互作用能的变化。不同吸附体系的相互作用能如图5。
由图5(a)可知,单组分气体吸附条件下,相互作用能随着吸附量的增加而增加,其中,CH4吸附体系的范德华能介于−70.71 kcal/mol和−271.25 kcal/mol之间(1 kcal=4.186 kJ),CO2吸附体系的范德华能介于−68.87 kcal/mol和−254.98 kcal/mol之间,2种单组分气体吸附体系的范德华能并无明显差异;CH4吸附体系的静电能介于−0.44 kcal/mol和−2.01 kcal/mol之间,而CO2吸附体系的静电能介于−34.07 kcal/mol和−140.29 kcal/mol之间。静电能在CO2与煤大分子的吸附过程中发挥了重要的作用。气体在煤中的等量吸附热可用于判断物理吸附与化学吸附[22],与CH4吸附往较低的吸附热不同,CO2吸附往往具有较大的吸附热,这与静电作用引起的化学吸附具有密切的关系。
由图5(b)可知,双组分竞争吸附条件下,双组分竞争吸附体系的范德华能介于−15.34 kcal/mol和−295.03 kcal/mol之间,静电能介于−14.56 kcal/mol和−90.86 kcal/mol之间;不同摩尔比体系的范德华能与静电能均随着CO2摩尔分数的增加而显著增加;如总吸附量为1 mmol/g的条件下,当CO2的摩尔分数由40%增加至60%,吸附体系的范德华能由−15.63 kcal/mol增加至−72.66 kcal/mol,静电能则由−14.56 kcal/mol增加至30.23 kcal/mol;且吸附量越大,由CO2摩尔比增加导致的范德华能和静电能的增加幅度也越大。这是由于体系中总吸附量随着CO2的摩尔分数的增大而增大,从而导致相互作用能的增加。
2.4 势能分布
气体分子的势能分布有利于判别气体在煤大分子中的竞争吸附位点[23]。吸附势的绝对值越大,吸附作用就越强,吸附位点也更具优势。单组分与双组分竞争吸附条件的势能分布如图6。
由图6可知,势能分布形式基本表现为正态分布;单组分CO2的吸附势于−7.05 kcal/mol时达到优势吸附位点,高于CH4的吸附势(−3.95 kcal/mol)。煤中含有一定数量的羧基和羟基的等含氧官能团,而CO2比CH4优先吸附这些极性官能团[10],与煤大分子的相互作用更强,因此,CO2的吸附位点更具优势。
对比3种不同摩尔比条件下的势能分布可以发现:CO2的摩尔比可以改变CH4吸附势的分布,当CO2的摩尔比由60%降低至50%和40%,CH4的吸附势由−4.15 kcal/mol降低至−4.05 kcal/mol和−3.85 kcal/mol。CO2的摩尔比的降低抑制了CH4的吸附。CH4吸附势的降低有利于CO2对CH4的竞争吸附,因此,较低的CO2摩尔比有利于采收率的提高,这与吸附选择性分析中得到的结果是一致的。
3. 结 语
1)单组分吸附模拟中CO2的吸附量和吸附常数显著大于CH4的吸附量。双组分竞争吸附模拟中的总吸附量随着CO2的摩尔分数的增大而增大,吸附常数也表现出相同的规律。
2)不同摩尔比条件下的双组分吸附模拟中CO2对CH4的选择性吸附系数始终大于1。CO2摩尔分数越大,选择性吸附系数越小,较低摩尔分数的CO2具有较强的竞争吸附性能。
3)相互作用能随着吸附量的增大而显著增大,CO2吸附体系中较大的静电能促进了煤大分子对CO2的吸附,因此,不同摩尔比体系的相互作用能随着CO2摩尔分数的增加而显著增加。
4)单组分条件下CO2的吸附势大于CH4的吸附势。双组分竞争吸附条件下CH4的吸附势随着CO2摩尔比的降低而降低,这有利于CO2对CH4的竞争吸附,验证了吸附选择性分析的结果。
-
表 1 试样参数及冲击温度
Table 1 Specimen parameters and impact temperatures
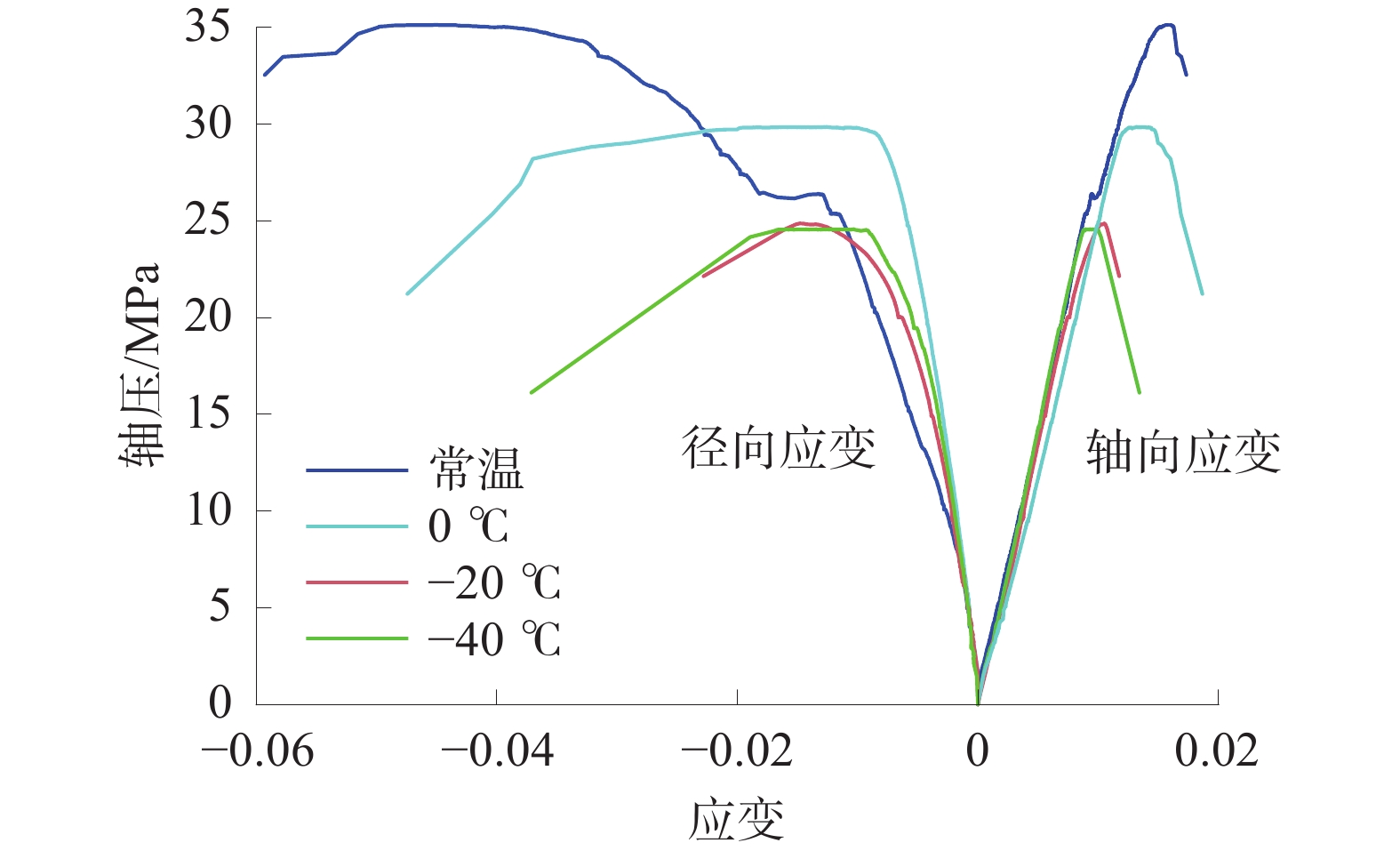
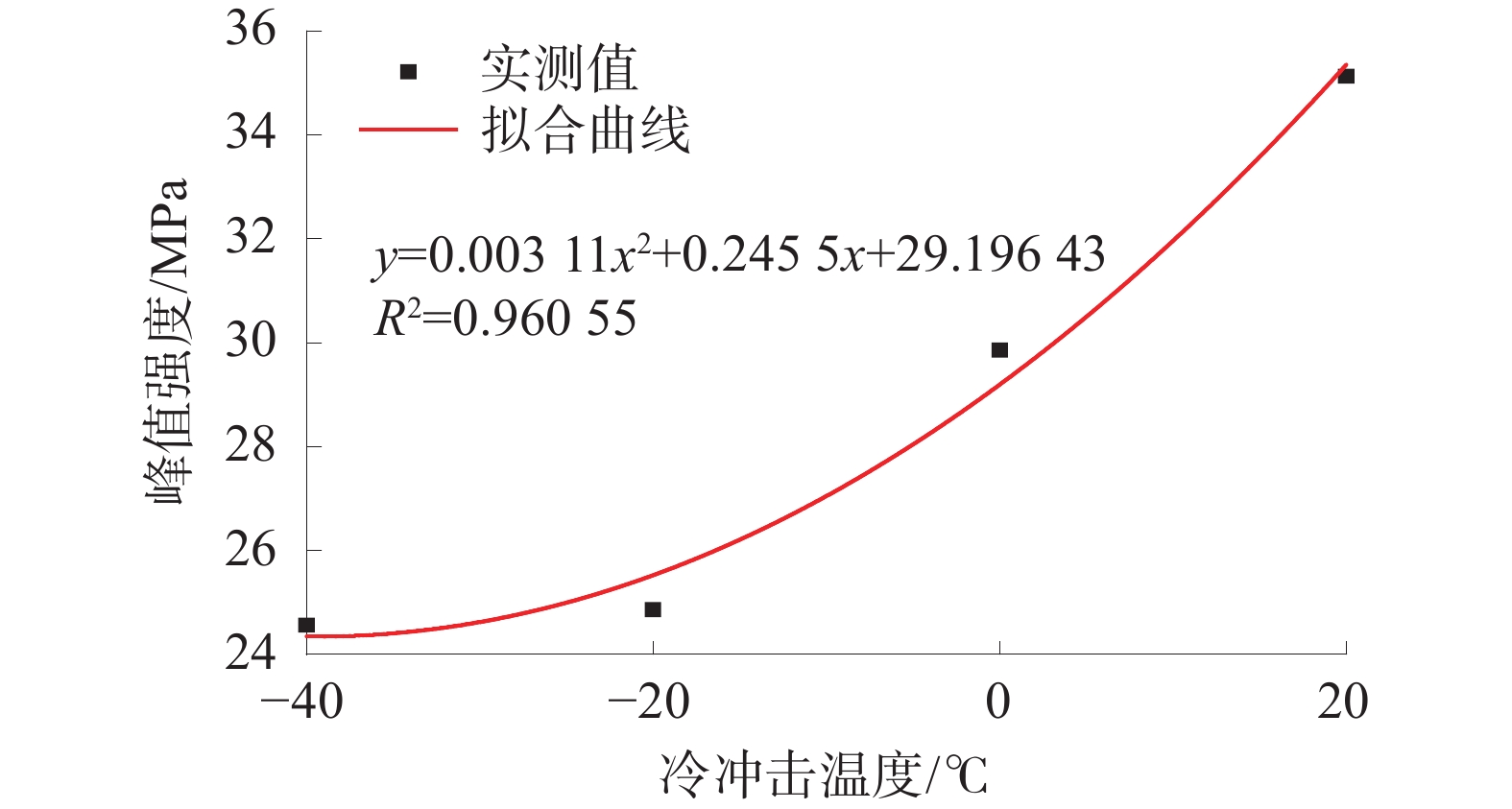
试样编号 尺寸/(mm×mm) 冲击温度/ ℃ 1# ϕ50.22×102.01 — 2# ϕ50.12×101.53 0 3# ϕ50.34×101.23 −20 4# ϕ50.24×101.06 −40 表 2 试样的峰值强度及应变
Table 2 Peak strength and strain of specimens
试样 峰值强度/MPa 峰值轴向应变 峰值径向应变 1# 35.128 66 0.017 34 −0.059 28 2# 29.859 87 0.018 67 −0.047 44 3# 24.866 24 0.011 76 −0.022 80 4# 24.570 70 0.013 43 −0.037 12 表 3 常温及不同温度冷冲击处理试样渗透率表
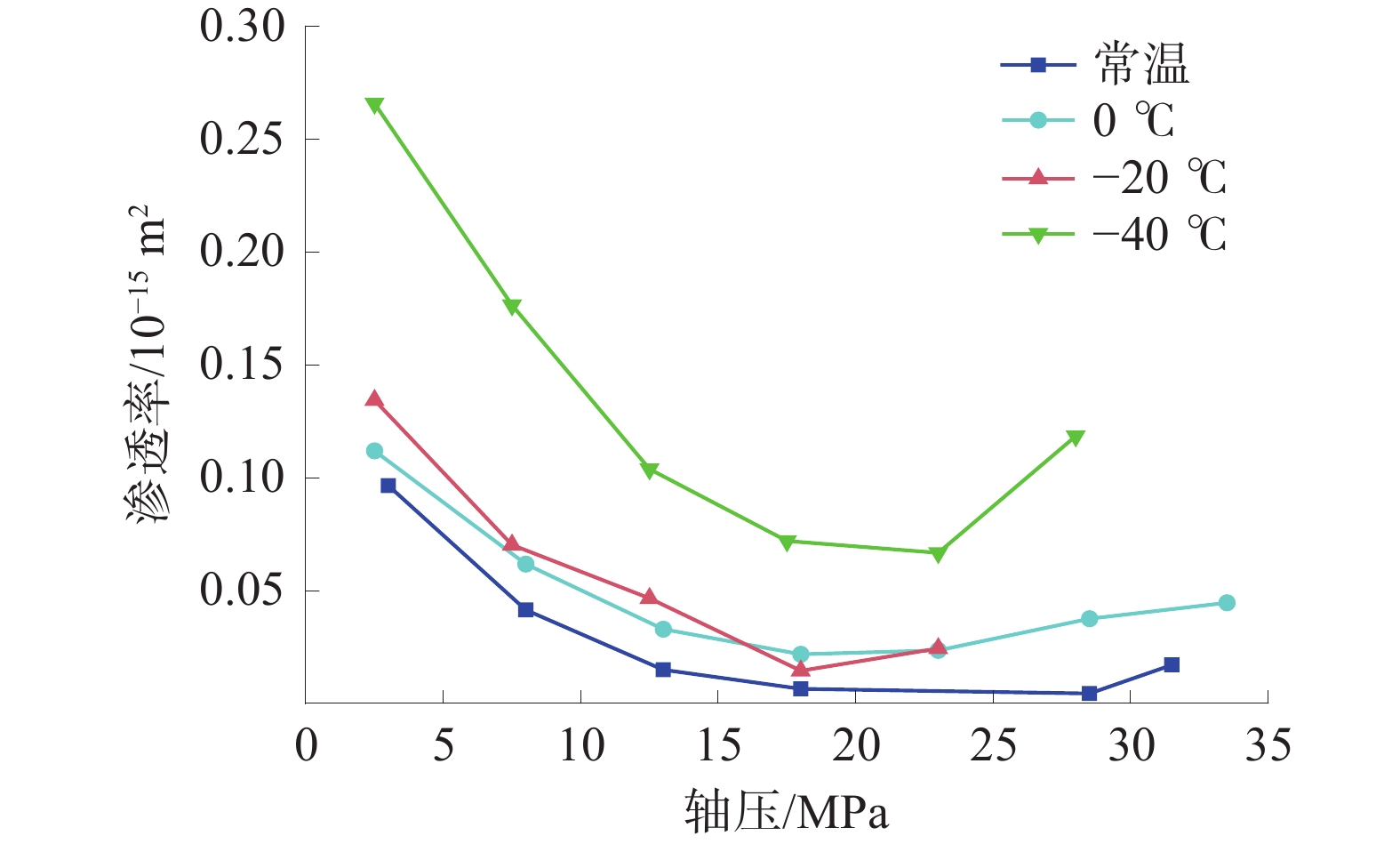
Table 3 Permeability table of samples treated with cold shock at normal temperature and different temperatures
试样 冷冲击
温度/ ℃初始渗透率/
10−15 m2较常温试样
渗透率增幅/%较上一档冷冲击
处理试样的
渗透率增幅/%1 常温 0.096 6 — — 2 0 0.111 9 15.89 15.89 3 −20 0.134 4 39.19 20.10 4 −40 0.292 5 202.90 117.62 -
[1] 张超林,王恩元,王奕博,等. 近20年我国煤与瓦斯突出事故时空分布及防控建议[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2021,49(4):134−141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.04.016 ZHANG Chaolin, WANG Enyuan, WANG Yibo, et al. Spatial-temporal distribution of outburst accidents from 2001 to 2020 in China and suggestions for prevention and control[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2021, 49(4): 134−141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.04.016
[2] 秦勇,袁亮,胡千庭,等. 我国煤层气勘探与开发技术现状及发展方向[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2012,40(10):1−6. QIN Yong, YUAN Liang, HU Qianting, et al. Status and development orientation of coal bed methane exploration and development technology in China[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2012, 40(10): 1−6.
[3] 荆俊杰,于丽雅,延婧. 高瓦斯低渗煤层水力造穴增透技术优化研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2022,53(1):8−14. JING Junjie, YU Liya, YAN Jing. Research on optimization of hydraulic flushing and permeability enhancement technology in high gas and low permeability coal seam[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(1): 8−14.
[4] 冯仁俊. 煤层群分层水力压裂与多层综合压裂增透效果对比研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2021,52(12):21−28. FENG Renjun. Comparative study on permeability enhancement effect of separate-layer fracturing and multi-layers comprehensive fracturing in coal seam group[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021, 52(12): 21−28.
[5] 田苗苗,张磊,薛俊华,等. 液氮致裂煤体技术研究现状及展望[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022,50(7):191−198. TIAN Miaomiao, ZHANG Lei, XUE Junhua, et al. Study and prospection of liquid nitrogen fracturing coal technology[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2022, 50(7): 191−198.
[6] 王登科,孙刘涛,魏建平. 温度冲击下煤的微观结构变化与断裂机制[J]. 岩土力学,2019,40(2):529−538. WANG Dengke, SUN Liutao, WEI Jianping. Microstructure evolution and fracturing mechanism of coal under thermal shock[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(2): 529−538.
[7] 张震,刘高峰,李宝林,等. CO2相变致裂煤的纳米孔隙尺度改造效应[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2023,42(3):672−684. ZHANG Zhen, LIU Gaofeng, LI Baolin, et al. Transformed effect of nano-pores in coal by CO2 phase transition fracturing[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2023, 42(3): 672−684.
[8] ALLEN J C, BAUER C L. Method of increasing the permeability of a subterranean hydrocarbon bearing formation: US338727 A [P]. 1968-09-27.
[9] MCDANIEL B W, GRUNDMANN S R, ENDRCK W D, et al. Field applications of cryogenic nitrogen as a hydraulic-fracturing fluid[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 1998, 50(3): 38−39. doi: 10.2118/0398-0038-JPT
[10] 李波,吕小权,黄来胜,等. 低温作用下煤体细观结构变化及相变致裂实验研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术,2020,16(7):25−29. LI Bo, LYU Xiaoquan, HUANG Laisheng, et al. Experimental study on meso-structure change and phase-transforming fracturing of coal under low temperature[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2020, 16(7): 25−29.
[11] 翟成,孙勇. 低温循环致裂煤体孔隙结构演化规律试验研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2017,45(6):24−29. ZHAI Cheng, SUN Yong. Experimental study on evolution of pore structure in coal after cyclic cryogenic fracturing[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2017, 45(6): 24−29.
[12] 张春会,张海霞,于永江,等. 饱水度和再溶浸对液氮冷冻煤致裂的影响[J]. 煤炭学报,2016,41(S2):400−406. ZHANG Chunhui, ZHANG Haixia, YU Yongjiang, et al. Effects of saturation and re-submersion on coal fracturing subjected to liquid nitrogen shock[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2016, 41(S2): 400−406.
[13] 张磊,卢硕,唐俊,等. 液氮溶浸时间对烟煤渗流特性的影响及传热过程模拟[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2021,38(6):1231−1239. ZHANG Lei, LU Shuo, TANG Jun, et al. Effect of liquid nitrogen immersion time on seepage characteristics of bituminous coal and simulation of heat transfer process[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2021, 38(6): 1231−1239.
[14] 戎彦龙,王毅,赵东,等. 冷冲击条件下饱水试样结构损伤规律研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术,2022,18(10):86−93. RONG Yanlong, WANG Yi, ZHAO Dong, et al. Research on structural damage law of water-saturated coal sample under cold shock conditions[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology in China, 2022, 18(10): 86−93.
[15] GB/T 23561.9—2009煤和岩石物理力学性质测定方法[S]. [16] WINKLER E M. Frost damage to stone and concrete: Geological considerations[J]. Engineering Geology, 1968, 2(5): 315−323. doi: 10.1016/0013-7952(68)90010-0
[17] YAMABE T, NEAUPANE K M. Determination of some thermo-mechanical properties of Sirahama sandstone under subzero temperature condition[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2001, 38(7): 1029−1034. doi: 10.1016/S1365-1609(01)00067-3




 下载:
下载: