Research on energy evolution characteristics and stability of coal pillar-roof structure
-
摘要:
煤矿事故的发生大多是由煤柱及其上覆顶板岩层失稳破坏引起的。为了研究不同煤-岩高度比对煤柱-顶板结构变形破坏及能量演化机制的影响,对煤-岩高度比分别为1∶3、1∶2、1∶1、2∶1及3∶1的煤-岩组合体进行了单轴加载及循环加卸载试验,研究了煤-岩结构体变形与能量演化之间的变化关系,利用加卸载响应比对煤-岩组合体的稳定性进行分析,对煤-岩组合体稳定性进行定量评价。结果表明:煤-岩组合体在单轴加载及循环加卸载作用下的峰值强度均随着煤-岩高度比的增加而逐渐降低,煤-岩组合体在循环加卸载作用下的峰值强度均低于单轴加载试验中的峰值强度,煤-岩高度比越大,循环载荷作用下组合体峰值强度降低率越小;组合体输入能、弹性能和耗散能随应力增加呈非线性增加,煤-岩高度比与组合体循环载荷过程中产生的平均弹性应变、平均弹性能、平均残余应变、平均耗散能、总残余应变和加卸载响应呈正比关系,与总弹性应变、总弹性能和总耗散能呈反比关系。
Abstract:The occurrence of coal mine accidents is mostly caused by the instability and failure of the coal pillar and its overlying roof rock layer. To study the influence of different coal-rock height ratios on the deformation failure and energy evolution mechanism of the coal pillar-roof system, uniaxial loading and cyclic loading and unloading tests are conducted on coal-rock structural body with coal-rock height ratios of 1∶3, 1∶2, 1∶1, 2∶1, and 3∶1, respectively. The relationship between deformation and energy evolution of coal-rock structural body are analyzed, and the stability of coal-rock structural body are quantitatively evaluated through the load-unload response ratio. The test results show that the peak strength of coal-rock structural body under uniaxial loading and cyclic loading gradually decreases with the increase of coal-rock height ratio. The peak strength of coal-rock structural body under cyclic loading test is lower than that in uniaxial loading test. The higher the coal-rock height ratio, the smaller the reduction rate of the peak strength of the structural body under cyclic loading; the input energy, elastic energy and dissipative energy of the composite increase nonlinearly with the increase of stress. The coal-rock height ratio is positively proportional to the average elastic strain, average elastic energy, average residual strain, average dissipative energy, total residual strain and loading and unloading response, and inversely proportional to the total elastic strain, total elastic energy and total dissipative energy of the composite during cyclic loading.
-
为了保障煤矿安全高效开采,煤矿井下留设了大量煤柱,这些煤柱及其顶板系统的稳定性决定了整个采场乃至地表的安全,一旦组合系统体发生失稳破坏,将导致灾难性后果[1-2]。大量研究证明,许多煤矿事故的发生不仅是煤柱或顶板岩层单独失稳引起的,而是煤层及其顶板岩层所构成的煤-岩系统失稳引发的[3-6]。同时,在煤矿开采过程中,煤-岩系统除受地应力作用外,还会受到硐室爆破、巷道掘进及工作面回采等工程活动的影响[7-9]。煤-岩系统在类似循环加卸载作用下必然会引起损伤,使煤柱-顶板结构的承载能力降低,导致巷道、煤柱发生失稳破坏[10-12]。因此,对循环加卸载作用下的煤柱-顶板结构变形破坏及能量演化特征进行研究,能够为煤矿开采过程中煤柱-顶板结构变形破坏、能量演化机制等研究提供参考,有效控制煤-岩系统变形失稳,预测防治灾害事故的发生,保证煤矿安全高效生产。
截至目前,许多学者将煤柱-顶板结构简化为煤-岩组合体,对其力学特性和能量演化特征进行研究。赵毅鑫等[13]对比分析了不同煤-岩组合体煤岩组合体失稳破坏过程中红外热像、声发射特征及应变的变化规律,得到了煤-岩组合体渐进失稳的前兆特征;左建平等[14-15]研究了煤-岩组合体在循环载荷作用下的力学特性、能量演化规律及破坏特征;陈光波等[16]研究了不同岩性和不同煤-岩高度比对煤-岩组合体力学特性和能量积聚规律的影响;李谭等[17]分析了煤-岩组合体在循环加卸载作用下的能量耗散规律;郭伟耀等[18]通过PFC数值模拟软件对比分析了岩石强度和煤-岩高度比对煤-岩组合体力学特性的影响;窦林名等[19-20]利用声发射和电磁辐射分析了岩石强度对煤-岩组合体冲击倾向性的影响规律;陈绍杰等[21]对比分析了不同煤-岩高度比砂岩顶板-煤柱组合体的力学特性和破坏规律;姜耀东等[22]研究分析了不同轴向载荷下煤-岩组合体失稳滑动的产生条件和位移演化特征;王晓南等[23]研究了煤-岩组合体发生冲击破坏时的声发射特征和微震信号的强度变化规律。
以上学者对煤-岩组合体的力学特性、声发射特征及能量演化规律等进行了大量研究,但是,不同加载条件下煤-岩高度比对煤-岩组合体变形特征、能量演化和渐进失稳特征研究较少。为此,以不同煤-岩高度比的煤-岩组合体为研究对象,分别进行单轴压缩试验和单轴循环加卸载试验,通过加卸载过程中的柔量变化对煤-岩组合体加载和卸载过程中的变形特征进行分析,研究煤-岩结构体变形与能量演化之间的变化关系;在此基础上利用加卸载响应比对煤-岩组合体的稳定性进行分析,对煤-岩组合体稳定性进行定量评价,通过加卸载响应比得到了煤-岩结构体稳定性与煤-岩高度比之间的变化关系。
1. 试验部分
试验所选用的砂岩、煤来自晋能集团马道头煤矿8208工作面顶板和巷旁煤柱。由于巷旁留设煤柱的高度是一致的,但是煤柱上方顶板岩层的厚度是变化的,所以将现场中煤柱和顶板的高度比进行简化,将实验室中煤-岩组合体的煤-岩高度比分别设置为1∶3、1∶2、1∶1、2∶1和3∶1,通过实验室中不同煤-岩高度比对煤-岩组合体的能量演化和稳定性的影响反应现场中不同顶板厚度对煤柱-顶板的影响。首先将砂岩和煤试块加工成直径50 mm,高度不同的圆柱体,要求圆柱体两端平行度不大于0.02 mm,然后按照1∶3、1∶2、1∶1、2∶1和3∶1的煤-岩高度比,将砂岩试件和煤试件组合成$\phi $50 mm×100 mm的标准试件,砂岩试件和煤试件之间用AB胶黏结。部分试件如图1。
试验采用TAW-2000KN微机控制电液伺服岩石力学试验系统,试验采用应力控制模式,加载速率1.5 kN/s。首先进行煤-岩组合体单轴加载试验,获得煤-岩组合体力学参数。然后进行煤-岩组合体循环加卸载试验,先以1.5 kN/s速度进行加载,当载荷达到12 kN(煤单轴抗压强度的35%~45%)时,以相同速率卸载至2 kN,再以1.5 kN/s的速度加载至14 kN,然后再以相同的速率卸载至2 kN,后1次循环的加载应力峰值比前1次循环的应力峰值增加2 kN,以此方式继续进行加载、卸载,直至煤-岩组合体发生破坏停止试验,每组试验选择3个试件进行试验。
2. 试验结果
2.1 峰值应力
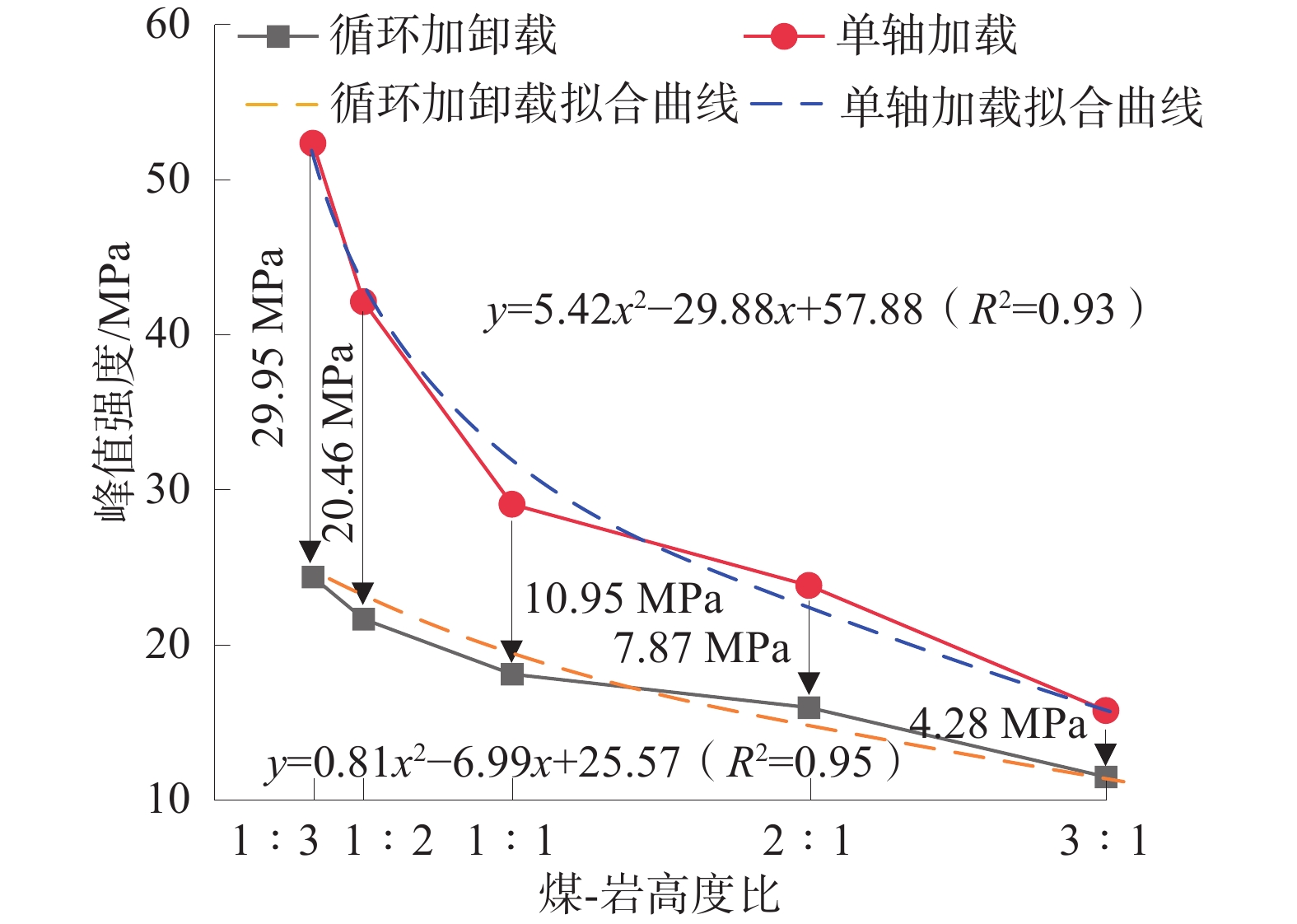
不同高度比的组合体在单轴加载试验和循环加卸载试验中的平均峰值强度如图2。
从图2中能够看出:煤-岩组合体在单轴加载及循环加卸载作用下的峰值强度均随煤-岩高度比的增加而逐渐降低;煤-岩高度比越小,岩石发生轴向压缩变形所消耗的能量相对越多,即煤-岩组合体内岩石高度越大,其发生轴向变形破坏时需要的轴向应力越大,进而提高了组合体整体的峰值强度。
相同高度比的煤-岩组合体在循环加卸载试验中的峰值强度均低于单轴加载试验中的峰值强度。当煤-岩高度比为1∶3、1∶2、1∶1、2∶1和3∶1时,煤-岩组合体在循环加卸载作用下的峰值强度比单轴加载作用下的峰值强度分别降低了27.95、20.46、10.95、7.87、4.28 MPa。煤-岩高度比越小,由循环加卸载引起的组合体峰值强度降低量越大。因为煤-岩高度比越小,煤-岩组合体的峰值强度越高,循环加卸载的次数越多,煤-岩组合体中裂隙发育、扩展的时间越多,裂隙发展的越充分,使得煤-岩组合体在循环加卸载作用下的峰值强度降低量越大。
2.2 变形特征
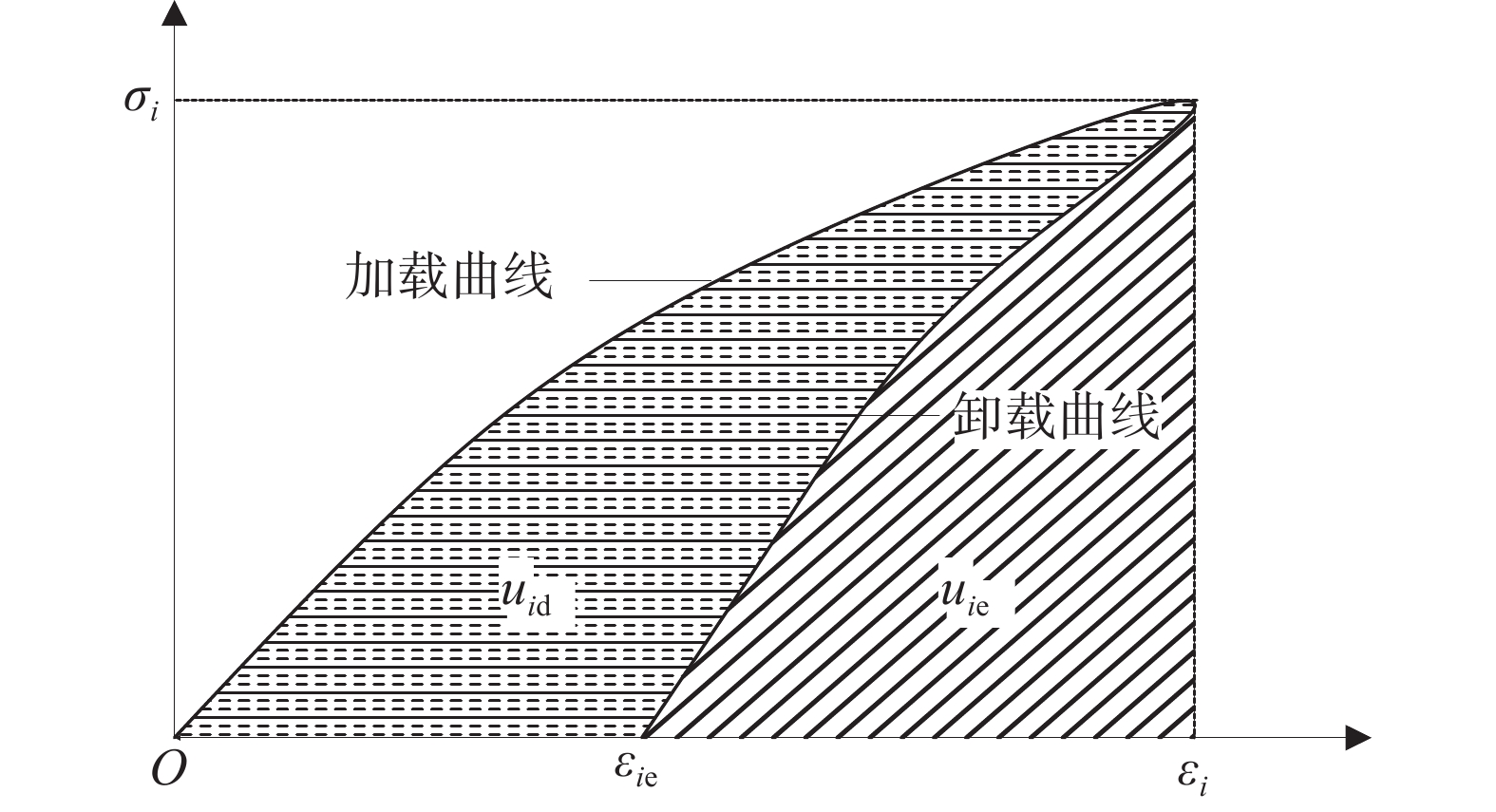
弹性应变和残余应变能够有效反映煤-岩组合体在外部载荷作用下的变形特征。循环加卸载过程中弹性应变与残余应变计算示意图如图3。
2.2.1 弹性应变演化特征
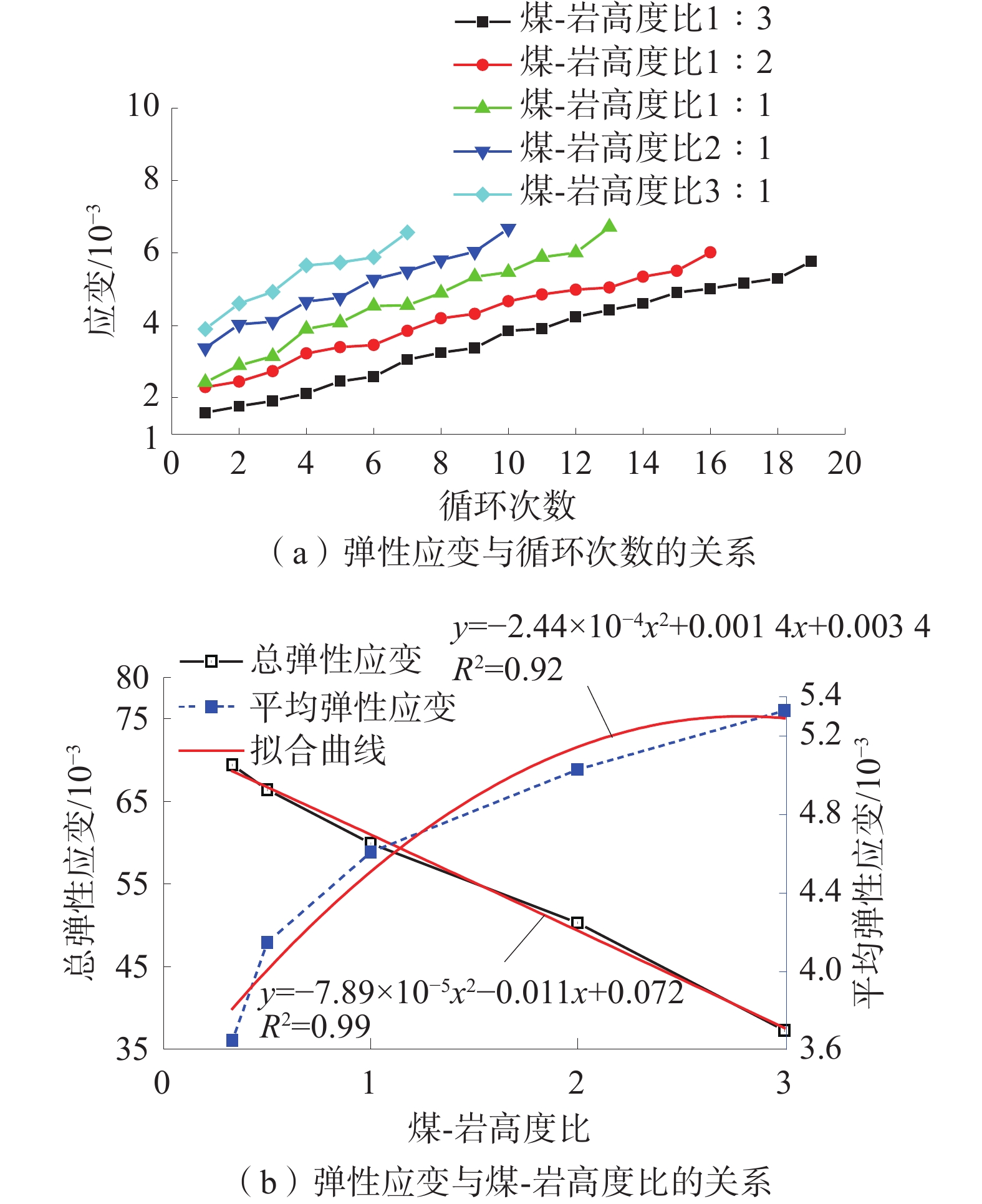
弹性应变变化规律如图4。
由图4(a)可知:弹性应变随循环次数的增加而增加。当循环次数相同时,煤-岩高度比越大,弹性应变也越大。
由图4(b)可知:随煤-岩高度比的增加,组合体平均弹性应变逐渐增加,总弹性应变逐渐降低;煤-岩高度比从1∶3增加至3∶1过程中,组合体平均弹性应变增加率为46.03%,总弹性应变降低率为46.25%。主要是因为煤-岩高度比大的组合体弹性模量较小,相同载荷作用下产生的弹性应变较大,平均每次循环产生的弹性应变较大。同时,煤-岩高度比大的组合体破坏时需要的应力较小,使得组合体的循环加卸载次数较少,发生破坏时累计的弹性应变较少。
2.2.2 残余应变演化特征
残余应变变化规律如图5。
从图5(a)可以看出:煤-岩组合体在第1次循环时产生的残余应变较大;当煤-岩高度比分别为1∶3、1∶2、1∶1、2∶1及3∶1时,组合体在第1次循环产生的残余应变分别占总残余应变的46.05%、48.85%、58.40%、63.21%及69.57%;随着循环次数的增加,残余应变急剧下降,这主要是由于煤-岩组合体中的孔洞、裂隙在第1次循环载荷作用下被压实,从而形成较大的残余应变;煤-岩高度比越大,组合体在第1次循环过程中产生的残余应变占总残余应变的百分比越大。分析认为:组合体中煤试件内部的孔洞、裂隙较多,煤-岩高度比越大,煤试件占煤-岩组合体的体积百分比越大,组合体内存在的孔洞、裂隙数量越多,载荷作用下产生的残余变形越大,组合体稳定性越差。根据放大的残余应变与循环次数的关系曲线发现:在组合体破坏前,残余应变与循环次数的关系曲线存在较大的波峰,主要是组合体产生了较大的裂隙或是断裂,发生了较大的残余应变,是引起试件最终失稳破坏的前兆。
由图5(b)可知:随着煤-岩高度比的增加,组合体平均残余应变和总残余应变逐渐增加;煤-岩高度比从1∶3增加至3∶1过程中,组合体的平均残余应变和总残余应变分别增加了123.26%、506.20%;煤-岩高度比越大,煤-岩组合体在循环加卸载作用下的平均残余应变和总残余应变也越大,主要是因为煤-岩高度比较大的煤-岩组合体的弹性模量较小,相同载荷作用下产生的残余应变较大,组合体稳定性较差。
2.3 柔量演化特征
岩石材料变形破坏过程中应变与应力的比值称为柔量。柔量$\Delta \dot \varepsilon _i^ + $是表征加载或卸载过程中岩石变形难易程度的物理量,即增加或减少单位应力的应变增量(MPa−1)[24-25]:
$$ \Delta \dot \varepsilon _i^ + = \frac{{\Delta \varepsilon _i^ + }}{{\Delta \sigma }} $$ (1) 式中:$ \Delta \sigma $为应力增量;$ \Delta \varepsilon _i^ + $为加载过程中应变增量,加载时的应变即为弹性应变和残余应变的和。
在对煤-岩结构体变形量进行计算时,是将煤-岩组合体看成一个整体进行计算的,所以此处柔量计算公式中的变形是煤-岩组合体的总变形量。
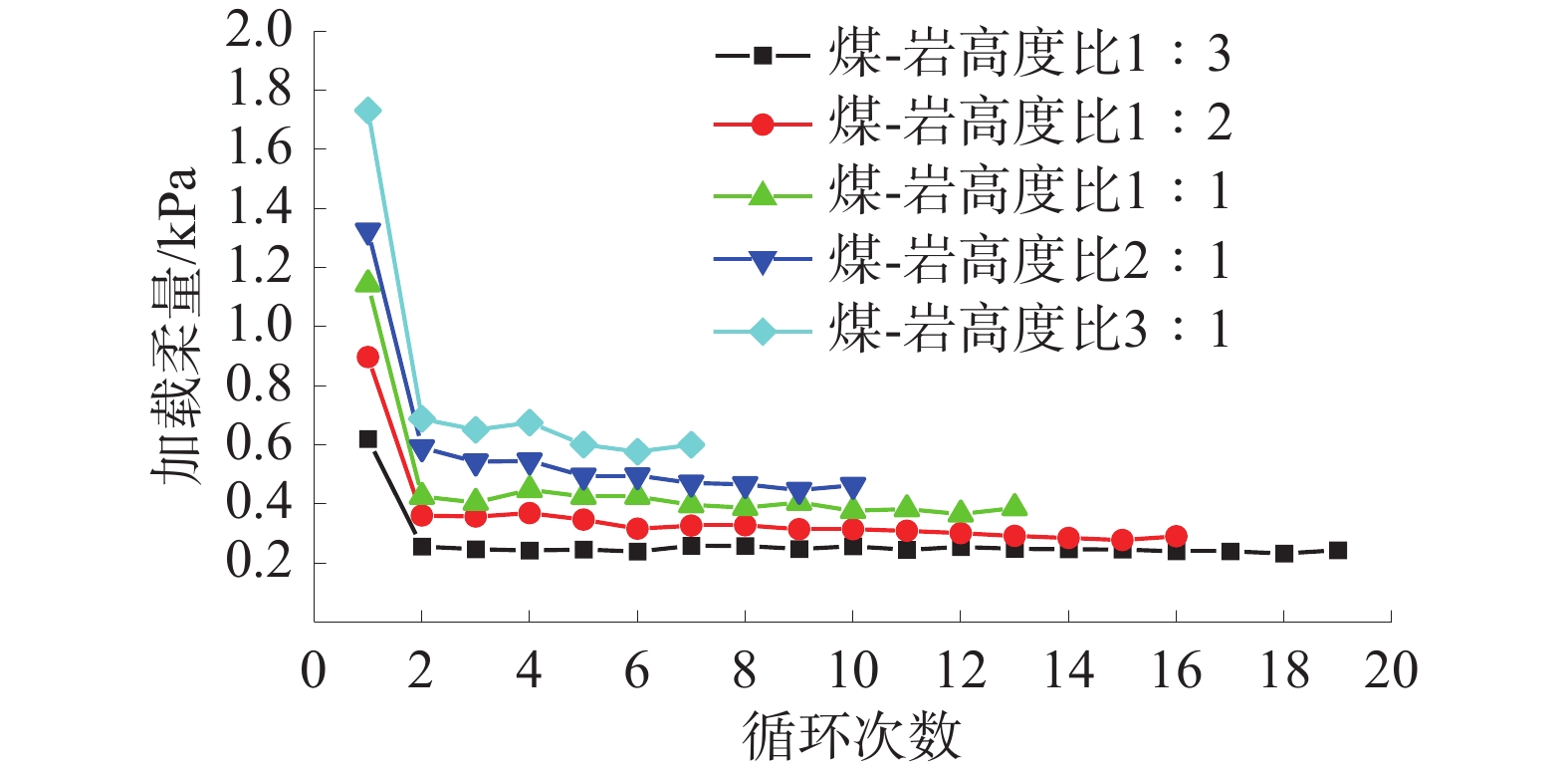
煤-岩组合体在加卸载作用下的柔量变化曲线如图6。
由图6可知:在第1次循环加卸载结束时,组合体产生的加载柔量较大,后随着循环次数的增加,加载柔量迅速降低;加载柔量变化曲线大致呈“L”形。主要是由于煤-岩组合体内存在大量孔隙和裂隙,循环加卸载初期,较小的载荷变化使得煤-岩组合体产生较大变形。后随着循环载荷增加,煤-岩组合体内孔隙裂隙逐渐被压实,载荷增加引起的组合体变形量减少,组合体柔量变化不大,大致呈直线发展。
循环次数相同时,煤-岩高度比越大,加载柔量越大,说明煤-岩高度比越大,单位应力变化引起的应变越大,组合体易发生形变,稳定性差。主要是因为煤试件的弹性模量小,相同载荷下产生变形量大,煤-岩高度比越大,煤试件在组合体中的体积比例越大,相同载荷下产生变形量大,组合体稳定性差。
3. 能量演化特征
岩石的变形破坏是能量驱动下的一种状态失稳现象[26-28]。通过应力-应变曲线能够表征循环加卸载过程中的能量变化。循环加卸载应力-应变曲线如图7。
加载曲线下的面积为第i次循环中试件的输入能量ui,卸载曲线下的面积为该次循环产生的弹性能uie,两者之差为该次循环产生的耗散能uid,计算公式如下:
$$ {u_i} = \int_O^{{\varepsilon _i}} \sigma {\rm{d}}\varepsilon $$ (2) $$ u_{i {\rm{e}}}=\int_{\varepsilon_{i {\rm{e}}}}^{\varepsilon_i} \sigma {\rm{d}} \varepsilon $$ (3) $$ {u_{i{\rm{d}}}} = {u_i} - {u_{i{\rm{e}}}} $$ (4) 式中:εi为第i次循环中试件的总应变;εie为第i次循环中试件的弹性应变;σ为应力。
3.1 能量演化特征
能量变化曲线如图8。
由图8能够看出,在整个循环加卸载过程中,组合体内部的弹性能密度始终比耗散能密度大,表明组合体内部弹性能密度占输入能密度的比例始终较大。
在循环加卸载初期,输入能、弹性能和耗散能的增长速率较低,能量-应力关系曲线相对较为平缓,输入能和弹性能曲线较为接近,说明此阶段输入能主要以弹性能的方式储存在组合体内部,仅有较小部分演化为耗散能。随着应力逐渐增加,组合体进入弹性变形阶段,输入能、弹性能和耗散能呈近似线性增长。随着应力继续增加,组合体输入能、弹性能和耗散能大幅度增加,组合体进入破裂发展阶段。
整个循环加卸载过程中能量演化趋势用函数关系式进行表达,能量演化拟合方程见表1。
表 1 循环载荷过程中能量演化拟合方程Table 1. Fitting equation of energy evolution during cyclic loading煤-岩高度比 输入能拟合方程 弹性能拟合方程 耗散能拟合方程 1∶3 ui1=6.03×10−5σ2+0.002 1σ−0.014
(R2=0.99)uie1=−1.05×10−5σ2+0.003 3σ−0.021
(R2=0.97)uid1=7.09×10−5σ2−0.001 1σ+0.006 5
(R2=0.98)1∶2 ui2=7.71×10−5σ2+0.002 2σ−0.007
(R2=0.98)uie2=2.92×10−5σ2+0.002 5σ−0.010
(R2=0.98)uid2=4.79×10−5σ2−2.81×10−4σ+0.002 9
(R2=0.97)1∶1 ui3=−5.19×10−7σ2+0.005 3σ−0.022
(R2=0.98)uie3=−3.71×10−5σ2+0.004 9σ−0.021
(R2=0.98)uid3=3.66×10−5σ2+4.47×10−4σ−5.98×10−4
(R2=0.98)2∶1 ui4=1.77×10−4σ2+0.003 6σ−0.014
(R2=0.99)uie4=9.87×10−5σ2+0.003 1σ−0.011
(R2=0.99)uid4=7.80×10−5σ2+5.07×10−4σ−0.002 0
(R2=0.98)3∶1 ui5=5.22×10−5σ2+0.009 0σ−0.038
(R2=0.99)uie5=−6.47×10−5σ2+0.008 4σ−0.036
(R2=0.98)uid5=1.17×10−4σ2+5.15×10−4σ−0.001 9
(R2=0.98)从表1能够看出:拟合效果显著,相关性系数R2均在0.97以上,煤-岩组合体在循环加卸载作用下的输入能、弹性能和耗散能随着轴向应力水平的增加而呈非线性增长。
当作用在煤-岩组合体上的载荷相同时,煤-岩高度比越大,作用在组合体上的输入能、弹性能和耗散能越多。当煤-岩高度比分别为1∶3、1∶2、1∶1、2∶1和3∶1时,组合体破坏时的弹性能较第1次循环结束时弹性能的增加率分别为2122.71%、798.25%、470.17%、447.00%及329.88%;组合体破坏时的耗散能较第1次循环结束时耗散能的增加率分别为1588.06%、757.87%、592.74%、500.24%及263.50%。煤-岩高度比越大,煤-岩组合体在循环载荷作用下的弹性能和耗散能的增加率越低。这主要是由于煤-岩高度比小的组合体在循环加卸载初期较小载荷作用下产生的弹性能较少,破坏时的弹性能较多,循环加卸载初期的弹性能与破坏时的弹性能差异较大,使得弹性能增加率较大。煤-岩高度比越大,组合体中岩石高度越小,循环加卸载初期的较小载荷使其产生较大残余应变,产生的耗散能较多,但其循环次数少,破坏前产生的耗散能较少,循环加卸载初期的耗散能与破坏前的耗散能的差值较小,所以耗散能增加率也较小。
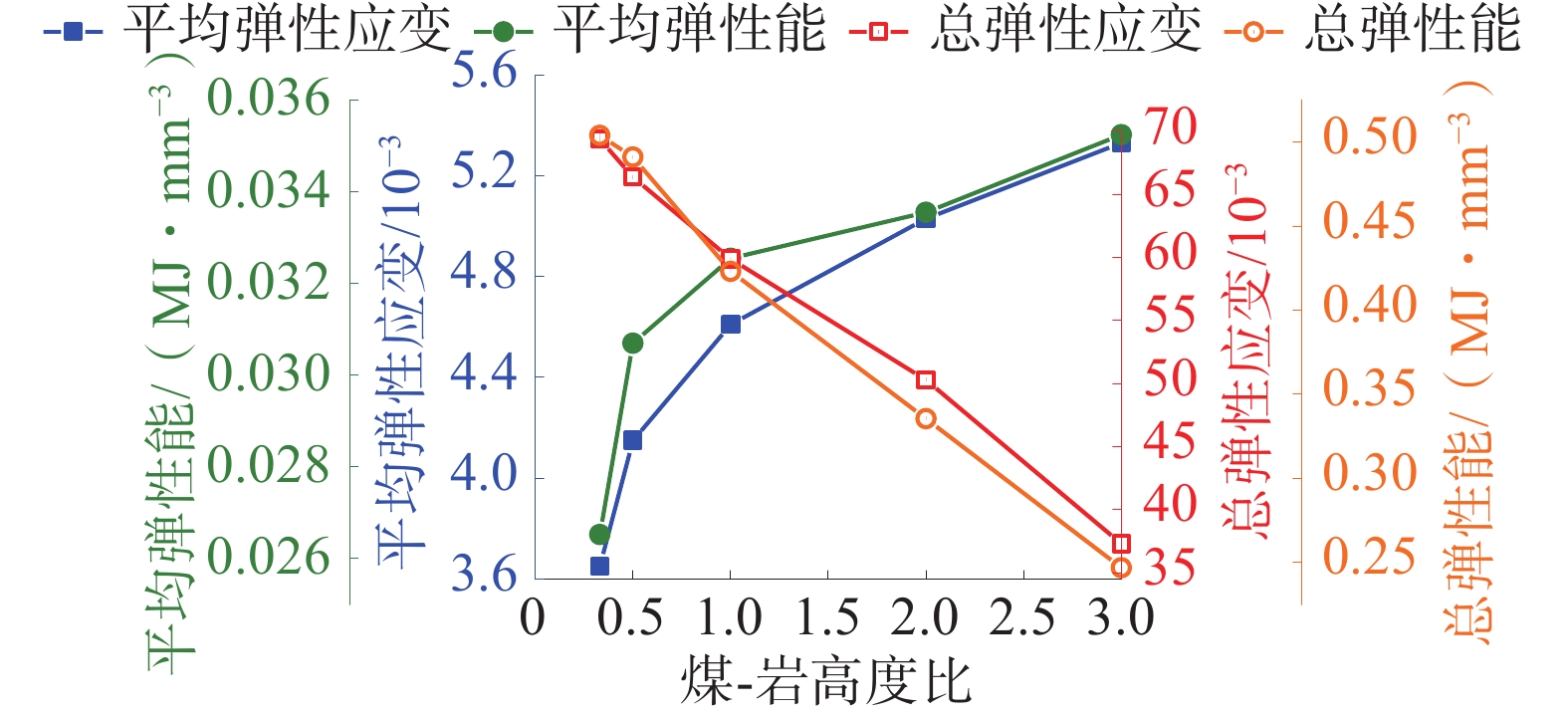
组合体在循环加卸载作用下平均弹性能、总弹性能与煤-岩高度比的变化曲线如图9。
由图9可知:随着煤-岩高度比的增加,组合体的平均弹性能逐渐增加,总弹性能逐渐降低;高度比为3∶1的组合体比高度比为1∶3的组合体平均弹性能增加了32.87%,总弹性能降低了51.05%;煤-岩高度比越大,煤-岩组合体平均每次循环产生的弹性能越大,但总弹性能越低,主要是由于煤-岩高度比大的组合体强度较小,在循环加卸载作用下平均每次循环产生的弹性能较多,但其循环次数较少,使得累计的总弹性能也较少。
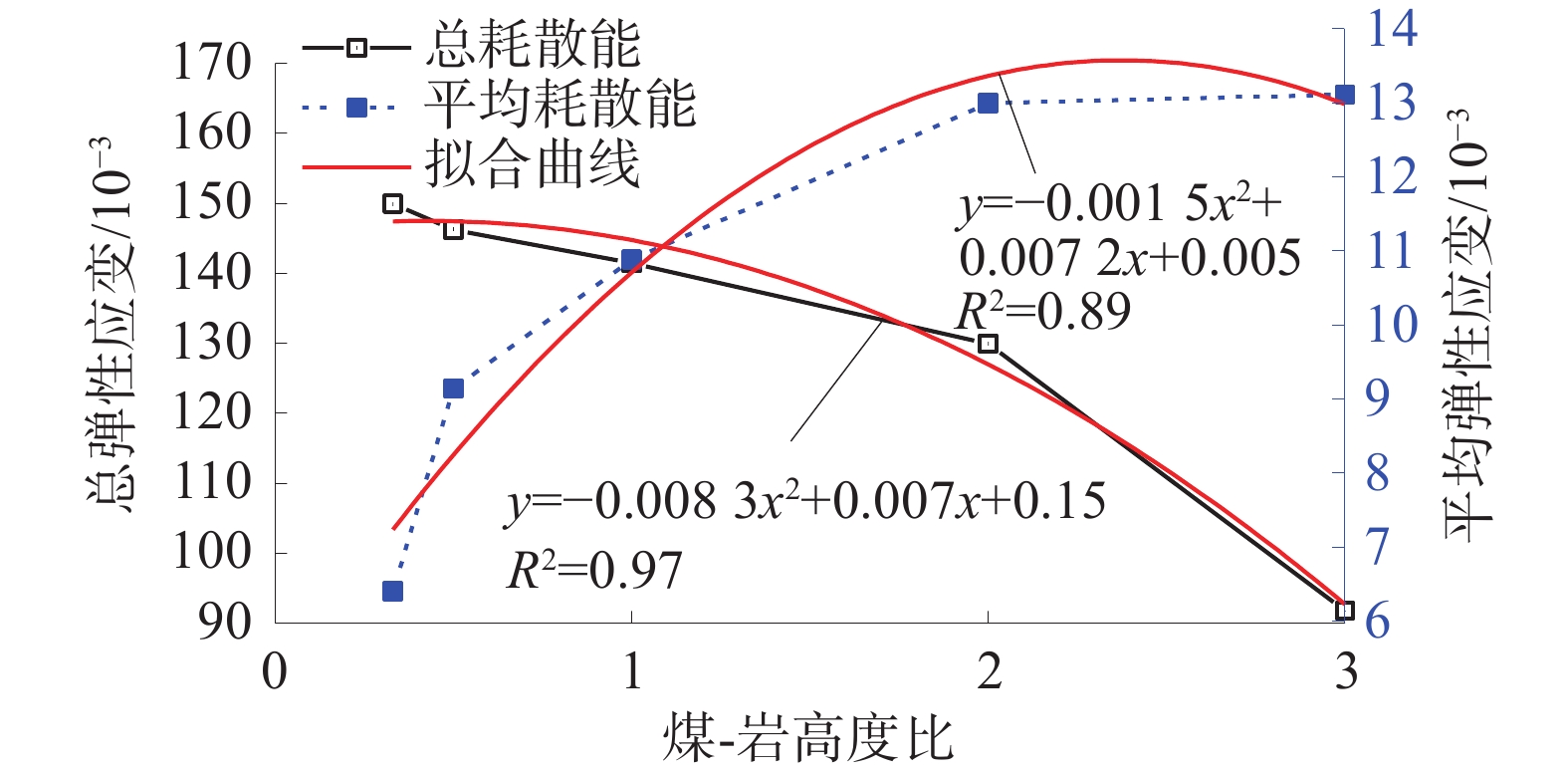
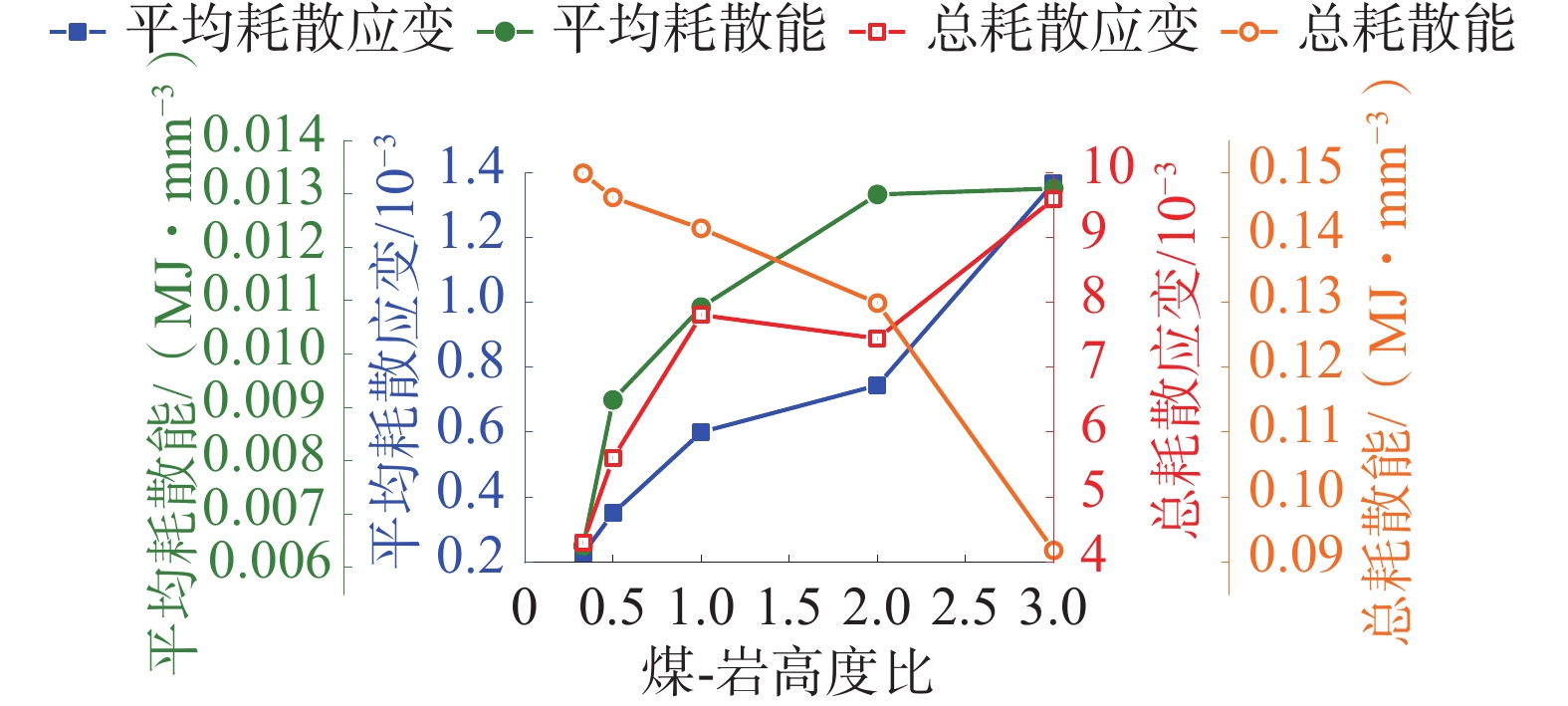
组合体在循环加卸载作用下平均耗散能、总耗散能与煤-岩高度比的变化曲线如图10。
由图10可知:随着煤-岩高度比的增加,组合体平均耗散能逐渐增加,总耗散能逐渐降低;高度比为3∶1的组合体比高度比为1∶3的组合体平均耗散能增加了104.84%,总耗散能降低了38.82%;煤-岩高度比越大,煤-岩组合体在循环加卸载作用下平均每次循环产生的耗散能越大,但总耗散能越低,主要是由于煤-岩高度比大的组合体峰值强度较小,相同载荷作用下岩石产生的残余应变较大,使得平均每次循环产生的耗散能较多。同时,煤-岩高度比大的组合体发生失稳破坏需要的载荷也相应较小,循环次数较少,累计的总耗散能较少。
3.2 变形与能量演化
根据煤-岩组合体在循环加卸载过程中变形特征及能量演化特征的,得到的弹性应变与弹性能、残余应变与耗散能的变化趋势分别如图11、图12。
从图11可以看出:弹性应变和弹性能的变化趋势相似;组合体的平均弹性应变与平均弹性能均随着煤-岩高度比的增加而逐渐升高,组合体的总弹性应变与总弹性能均随着煤-岩高度比的增加而逐渐降低。说明组合体在外力载荷作用下产生的弹性能主要用于组合体内部的弹性应变。
从图12可以看出:平均残余应变与平均耗散能的变化趋势相似,但组合体的总残余应变与总耗散能的变化趋势相反;组合体的平均残余应变与平均耗散能均随着煤-岩高度比的增加而逐渐升高;总残余应变随着煤-岩高度比的增加而增加,总耗散能随着煤-岩高度比的增加而逐渐降低。说明煤-岩高度比越大,较小的耗散能就会产生较大的残余应变,也间接说明了煤-岩高度比越大,煤-岩组合峰值强度越小,组合体越不稳定。
3.3 弹性能量指数
弹性能量指数WET能够反映煤样加载过程中能量的积聚与耗散。弹性能量指数越大,破坏时发生冲击的可能性也就大,煤柱-顶板结构越不稳定。岩石的弹性能量指数WET作为冲击地压的倾向性指标并给出了判别标准:
$$ \left\{\begin{array}{cc}{W}_{{\rm{ET}}}\geqslant 5.0& 强冲击倾向\\ 2.0\leqslant {W}_{{\rm{ET}}}\leqslant 5.0& 弱冲击倾向\\ {W}_{{\rm{ET}}} \lt 2.0& 无冲击倾向\end{array} \right.$$ (5) 煤-岩组合体在循环加卸载过程中的破坏均是开始于组合体中的煤试件,第1条宏观裂隙出现在煤试件中,试验最后的终止也是以煤试件的完全失稳而停止;在整个循环加卸载过程中,岩石试件起到的作用是储存加载过程对煤-岩组合体做功的能量施加在岩石试件上的部分能量,卸载过程又将这部分储存的能量向外释放,这部分向外释放的能量有一部分作用在煤试件上,进一步促进煤试件的渐进失稳[29-31]。在煤-岩组合体循环加卸载试验中,煤-岩组合体的稳定性主要取决于煤试件的稳定性,所以选择弹性能量指数作为煤-岩组合体稳定性的参考依据之一。
不同煤-岩高度比的组合体的弹性能量指数变化曲线如图13。
由图13可知:弹性能量指数随循环次数的增加而呈现出不同程度的波动,当煤-岩高度比为1∶3的组合体在循环到第8、第9和第13次时的弹性能量指数>5.0,此时的煤-岩组合体均具有强冲击倾向。组合体的弹性能指数随着循环次数的增加虽有一定的波动,在第13次循环前具有一定的上涨趋势。这说明煤-岩组合体强度越强,在循环加卸载作用下的弹性能指数具有上涨的趋势;煤-岩组合体强度越小,在循环加卸载作用下的弹性能指数具有缓慢下降的趋势。
4. 加卸载响应比
加卸载响应比(LURR)理论由中国学者尹祥础提出,最初用于地震预测[32]。在此基础上,许多学者应用LURR理论来分析煤柱的稳定性[33-34]。
加卸载响应比主要是定量描述非线性系统偏离稳态的程度,以应变作为响应。
$$ X = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{\Delta p \to 0} \frac{{\Delta R}}{{\Delta p}} = \frac{{\Delta \varepsilon }}{{\Delta \sigma }} = \frac{1}{E} $$ (6) 式中:X为响应;ΔR、Δp分别为荷载p和响应R对应的增量;Δε、Δσ分别为应变和应力的变化;E为弹性模量。
加卸载响应比Y可表示为,
$$ Y = \frac{{{X_ + }}}{{{X_ - }}} = \frac{{{1 \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {1 {{E_ + }}}} \right. } {{E_ + }}}}}{{{1 \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {1 {{E_ - }}}} \right. } {{E_ - }}}}} $$ (7) 式中:X+、X−分别为加载响应和卸载响应;E+、E−分别为加载弹性模量和卸载弹性模量。
对于线性系统,X+=X-=c(c为常数),加卸载响应比Y=1;对于非线性系统,Y值与系统状态有关;当系统稳定时,Y≈1;当系统偏离稳定状态时,Y>1;当系统不稳定时,Y→∞。因此,Y值可以定量地描述非线性系统的偏离度。
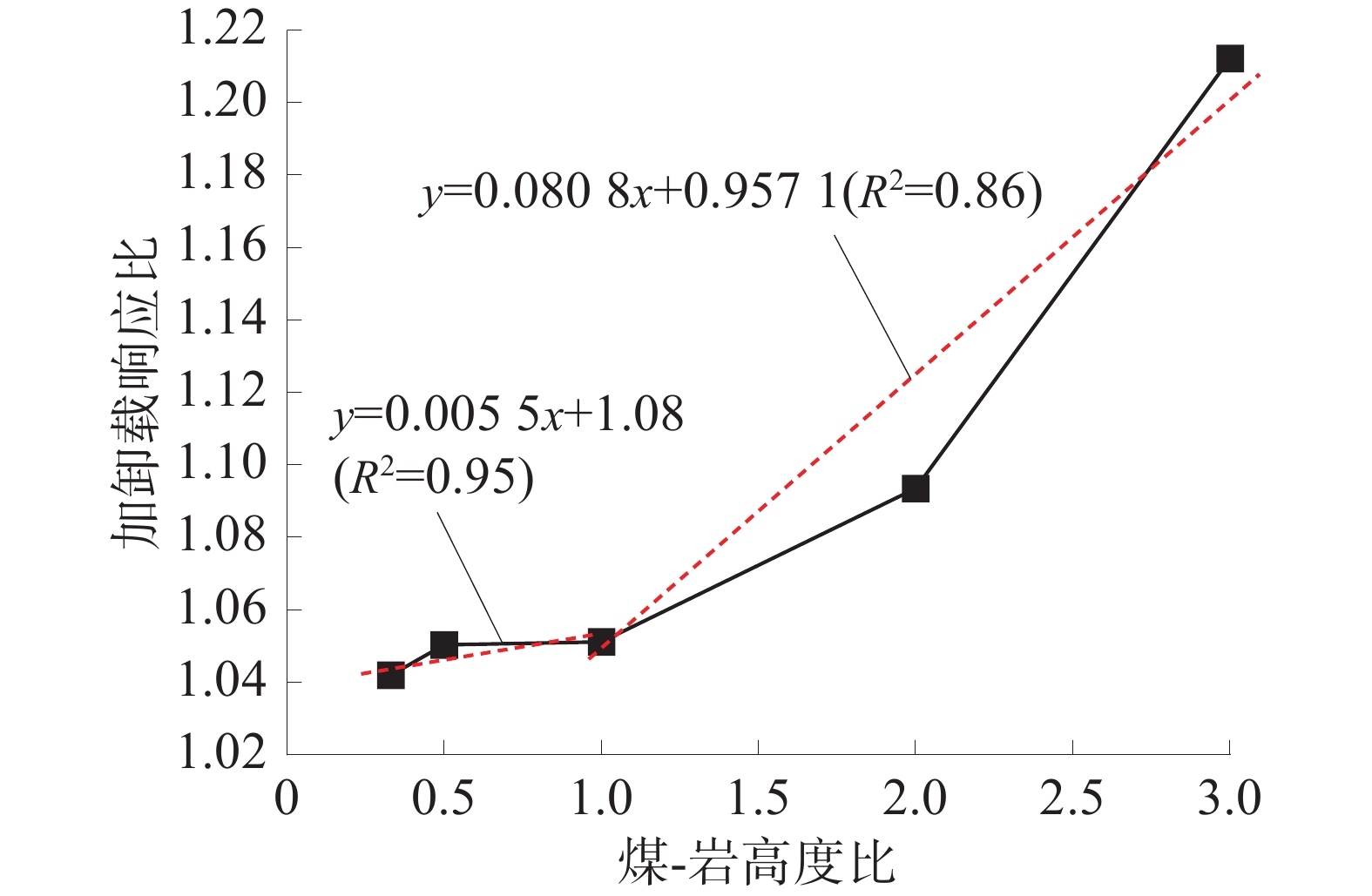
不同煤-岩高度比的煤-岩组合体的加卸载响应比变化曲线如图14,煤-岩组合体平均加卸载响应比随不同煤-岩高度比的变化曲线如图15。
由图14可知:在循环加卸载初期和后期,响应比较大,响应比在循环加卸载中期变化较为平稳,说明煤-岩组合体在循环加卸载初期和后期的稳定性较差,在循环加卸载中期稳定性较好,但组合体在循环加卸载初期和后期稳定性差的原因是不同的。由于煤-岩组合体内存在大量的原生孔洞、裂隙,以及组合体中煤试件和岩石试件交接处存在一定缝隙,使得组合体稳定性较差,随着循环加卸载载荷逐渐增加,组合体内部原生孔洞、裂隙逐渐被压缩,加卸载响应比逐渐降低,在1.0~1.1的范围内波动,组合稳定性逐渐增强。随着循环载荷继续增加,被压缩裂隙逐渐向外扩展延伸,相互贯通,形成较大宏观裂隙,并伴随有煤壁外鼓、片帮等现象,此时组合体响应比再次升高,组合体稳定性差。
由图15可知:随着煤-岩高度比的增大,平均加卸载响应比逐渐增大;煤-岩高度比越大,加卸载响应比越大,煤-岩组合体在循环加卸载作用下越不稳定。主要是因为煤试件中孔洞、裂隙较为发育,载荷作用下的稳定性差,煤试件在组合体中的体积比例越大,相同载荷下产生越容易产生变形,组合体稳定性越差。
在煤-岩高度比由1∶3提高到3∶1的过程中,加卸载响应比提高了14.05%。其中,当煤-岩高度比从1∶3增加到1∶1时,加卸载响应比增加0.88%;当煤-岩高度比从1∶1增加到3∶1时,加卸载响应比增加了13.29%。当煤-岩高度比<1时,加卸载响应比随煤-岩高度比的增大变化较小;当煤-岩高度比>1时,加卸载响应比随煤-岩高度比的增大而变化较大。将加卸载响应比与煤-岩高度比进行拟合,拟合结果如下:
当煤岩高度比从1∶3增加到1∶1时:
$$ y=0.005 \;5x+1.08 (R^{2}=0.95) $$ (8) 当煤岩高度比从1∶1增加到3∶1时:
$$ y=0.080 \;8x+0.957\;1 (R^{2}=0.86) $$ (9) 5. 变形破坏与能量演化机制
煤-岩组合体在循环载荷作用下发生疲劳损伤,在远低于其强度极限下发生破坏。煤-岩高度比越大,煤试件在组合体中所占的比例越大,组合体发生破坏时需要的能量也越少,越容易发生变形,稳定性越差。煤-岩高度比小的组合体失稳破坏时,储存在岩石内的能量向外释放,加剧了组合体中煤试件的破坏程度,进一步降低了组合体的稳定性。同时,煤-岩高度比越大,峰值强度越小,较小的载荷就会促使裂隙发育、扩展,组合体破坏经历的循环次数越少,稳定性越差。
此外,煤-岩组合体的变形破坏除受能量演化机制影响外,还受煤试件和岩石试件之间连接方式的影响。煤-岩组合体中岩石试件与煤试件之间的连接方式主要有2种:①岩石试件与煤试件通过黏结剂黏结为1个整体,岩-煤交界面处存在黏聚力;②岩石试件与煤试件自然叠放为1个整体,岩-煤交界面不存在黏聚力。
岩石试件与煤试件的连接方式影响着组合体的力学特性,不同连接方式下组合体的强度特性不完全相同,主要研究岩石试件和煤试件间采用黏结剂进行黏结的组合体的力学特性。文献[13]和文献[35]认为,当煤-岩界面的黏聚力和摩擦力大于煤岩界面岩石一侧的极限拉应力,岩石试件发生破裂破坏。对试验过程中煤-岩组合体裂隙发育、扩展情况进行观察,裂隙首先在组合体中煤试件内发育,且裂隙沿轴向应力方向扩展,裂隙扩展至煤-岩交界面处未向岩石试件延伸,岩石试件在循环加卸载过程中未形成较大裂隙扩展。说明煤-岩交界面的黏聚力和摩擦力小于煤岩交界面岩石一侧的极限拉应力,岩石试件未发生变形破裂破坏。
6. 结 论
1)煤-岩组合体在单轴加载及循环加卸载作用下的峰值强度均随煤-岩高度比的增加而逐渐降低。相同高度比的煤-岩组合体在循环加卸载试验中的峰值强度均低于单轴加载试验中的峰值强度。煤-岩高度比越大,由循环加卸载引起的组合体峰值强度降低量越小。
2)煤-岩高度比越大,煤-岩组合体在循环加卸载作用下平均弹性应变、平均残余应变和总残余应变越大。煤-岩高度比越大的组合体在第1次循环过程中产生的残余应变占总残余应变的百分比越大。加载柔量变化曲线大致呈倾斜的“L”形。煤-岩高度比越大,加载柔量越大,单位应力变化引起的应变越大。
3)当作用在煤-岩组合体上的载荷相同时,煤-岩高度比越大,作用在组合体上的输入能、弹性能和耗散能越多。煤-岩高度比与平均弹性应变、平均弹性能、平均残余应变、平均耗散能和总残余应变呈正比关系,与总弹性应变、总弹性能和总耗散能呈反比关系。
4)煤-岩高度比越大,加卸载响应比越大,煤-岩组合体在循环加卸载作用下越不稳定。当煤-岩高度比<1时,加卸载响应比随煤-岩高度比的增大变化较小;当煤-岩高度比>1时,加卸载响应比随煤-岩高度比的增大而变化较大。
-
表 1 循环载荷过程中能量演化拟合方程
Table 1 Fitting equation of energy evolution during cyclic loading
煤-岩高度比 输入能拟合方程 弹性能拟合方程 耗散能拟合方程 1∶3 ui1=6.03×10−5σ2+0.002 1σ−0.014
(R2=0.99)uie1=−1.05×10−5σ2+0.003 3σ−0.021
(R2=0.97)uid1=7.09×10−5σ2−0.001 1σ+0.006 5
(R2=0.98)1∶2 ui2=7.71×10−5σ2+0.002 2σ−0.007
(R2=0.98)uie2=2.92×10−5σ2+0.002 5σ−0.010
(R2=0.98)uid2=4.79×10−5σ2−2.81×10−4σ+0.002 9
(R2=0.97)1∶1 ui3=−5.19×10−7σ2+0.005 3σ−0.022
(R2=0.98)uie3=−3.71×10−5σ2+0.004 9σ−0.021
(R2=0.98)uid3=3.66×10−5σ2+4.47×10−4σ−5.98×10−4
(R2=0.98)2∶1 ui4=1.77×10−4σ2+0.003 6σ−0.014
(R2=0.99)uie4=9.87×10−5σ2+0.003 1σ−0.011
(R2=0.99)uid4=7.80×10−5σ2+5.07×10−4σ−0.002 0
(R2=0.98)3∶1 ui5=5.22×10−5σ2+0.009 0σ−0.038
(R2=0.99)uie5=−6.47×10−5σ2+0.008 4σ−0.036
(R2=0.98)uid5=1.17×10−4σ2+5.15×10−4σ−0.001 9
(R2=0.98) -
[1] 赵毅鑫,姜耀东,祝捷,等. 煤岩组合体变形破坏前兆信息的试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2008,27(2):339−346. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.02.016 ZHAO Yixin, JIANG Yaodong, ZHU Jie, et al. Experimental study on precursory information of deformations of coal-rock composite samples before failure[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(2): 339−346. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.02.016
[2] 陈绍杰,郭惟嘉,程国强,等. 深部条带煤柱蠕变支撑效应研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2012,29(1):48−53. CHEN Shaojie, GUO Weijia, CHENG Guoqiang, et al. Research on creep supporting effect of deep strip pillar[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2012, 29(1): 48−53.
[3] 肖晓春,樊玉峰,吴迪,等. 组合煤岩破坏过程能量耗散特征及冲击危险评价[J]. 岩土力学,2019,40(11):4203−4212. XIAO Xiaochun, FAN Yufeng, WU Di, et al. Energy dissipation feature and rock burst risk assessment in coal-rock combinations[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(11): 4203−4212.
[4] 付斌,周宗红,王友新,等. 不同煤岩组合体力学特性的数值模拟研究[J]. 南京理工大学学报,2016,40(4):485−492. FU Bin, ZHOU Zonghong, WANG Youxin, et al. Numerical simulation of different combination of coal and rock sample mechanics and acoustic emission characteristics[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2016, 40(4): 485−492.
[5] 窦林名,陆菜平,牟宗龙,等. 组合煤岩冲击倾向性特性试验研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2006,23(1):43−46. DOU Linming, LU Caiping, MOU Zonglong, et al. Rock burst tendency of coal-rock combinations sample[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2006, 23(1): 43−46.
[6] MA Qing, TAN Yunliang, LIU Xuesheng, et al. Effect of coal thicknesses on energy evolution characteristics of roof rock-coal-floor rock sandwich composite structure and its damage constitutive model[J]. Composites Part B Engineering, 2020, 198(1): 108086.
[7] YANG Ke, WEI Zhen, CHI Xiaolou, et al. Experimental research on the mechanical characteristics and the failure mechanism of coal-rock composite under uniaxial load[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2020, 2020(1): 1−11.
[8] YIN Dawei, MENG Xiangxi. Numerical simulation on uniaxial compression failure of a roof rock–coal–floor rock composite sample with coal persistent joint[J]. Geotechnical & Geological Engineering, 2018, 37: 13−23.
[9] MATHEY M. Modelling coal pillar stability from mine survey plans in a geographic information system[J]. Journal of the Southern African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 2018, 118(2): 157−164. doi: 10.17159/2411-9717/2018/v118n2a9
[10] SWIFT G W, REDDISH D J. Stability problems associated with an abandoned ironstone mine[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology & the Environment, 2002, 61(3): 227−239.
[11] 贺广零,黎都春,翟志文,等. 采空区煤柱-顶板系统失稳的力学分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2007,32(9):897−901. HE Guangling, LI Duchun, ZHAI Zhiwen, et al. Analysis of instability of coal pillar and stiff roof system[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2007, 32(9): 897−901.
[12] 解兴智. 浅埋煤层房柱式采空区顶板-煤柱稳定性研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2014,42(7):1−4. XIE Xingzhi. Study on stability of roof-coal pillar in room and pillar mining goaf in shallow depth seam[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2014, 42(7): 1−4.
[13] 赵毅鑫,姜耀东,祝捷,等. 煤岩组合体变形破坏前兆信息的试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2008,27(2):339−346. ZHAO Yixin, JIANG Yaodong, ZHU Jie, et al. Experimental study on precursory information of deformations of coal-rock composite samples before failure[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(2): 339−346.
[14] 左建平,陈岩,崔凡. 不同煤岩组合体力学特性差异及冲击倾向性分析[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2018,47(1):81−87. ZUO Jianping, CHEN Yan, CUI Fan. Investigation on mechanical properties and rock burst tendency of different coal-rock combined bodies[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2018, 47(1): 81−87.
[15] 左建平,谢和平,孟冰冰,等. 煤岩组合体分级加卸载特性的试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2011,32(5):1287−1296. ZUO Jianping, XIE Heping, MENG Bingbing, et al. Experimental research on loading-unloading behavior of coal-rock combination bodies at different stress levels[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2011, 32(5): 1287−1296.
[16] 陈光波,张帅,李谭,等. 煤岩组合体性质与比例影响力学特性规律[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版),2021,40(3):198−205. CHEN Guangbo, ZHANG Shuai, LI Tan, et al. Influence of properties and proportion of coal-rock combined body on the law of mechanical properties[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University(Natural Science), 2021, 40(3): 198−205.
[17] 李谭,张尚波,陈光波,等. 循环载荷下煤-岩组合体能量耗散与损伤特征研究[J]. 太原理工大学学报,2022,53(4):649−659. LI Tan, ZHANG Shangbo, CHEN Guangbo, et al. Study on energy dissipation and damage characteristics of coal-rock structural body under cyclic loading[J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology, 2022, 53(4): 649−659.
[18] 郭伟耀,周恒,徐宁辉,等. 煤岩组合体力学特性模拟研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2016,47(2):33−35. GUO Weiyao, ZHOU Heng, XU Ninghui, et al. Simulation study of mechanical properties of coal rock combination[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2016, 47(2): 33−35.
[19] 窦林名,陆菜平,牟宗龙,等. 组合煤岩冲击倾向性特性试验研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2006,23(1):43−46. DOU Lingming, LU Caiping, MU Zonglong, et al. Rock burst tendency of coal-rock combinations sample[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2006, 23(1): 43−46.
[20] 窦林名,田京城,陆菜平,等. 组合煤岩冲击破坏电磁辐射规律研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2005,24(19):143−146. DOU Linming, TIAN Jingcheng, LU Caiping, et al. Research on electromagnetic radiation rules of composed coal-rock burst failure[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(19): 143−146.
[21] 陈绍杰,尹大伟,张保良,等. 顶板–煤柱组合体力学特性及其渐进破坏机制研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2017,36(7):1588−1598. CHEN Shaojie, YIN Dawei, ZHANG Baoliang, et al. Mechanical characteristics and progressive failure mechanism of roof-coal pillar structure[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 36(7): 1588−1598.
[22] 姜耀东,王涛,宋义敏,等. 煤岩组合组合失稳滑动过程的实验研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2013,38(2):177−182. JIANG Yaodong, WANG Tao, SONG Yimin, et al. Experimental study on the stick-slip process of coal-rock composite samples[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2013, 38(2): 177−182.
[23] 王晓南,陆菜平,薛俊华,等. 煤岩组合体冲击破坏的声发射及微震效应规律试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2013,34(9):2569−2575. WANG Xiaonan, LU Caiping, XUE Junhua, et al. Experimental research on rules of acoustic emission and microseismic effects of burst failure of compound coal-rock samples[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(9): 2569−2575.
[24] 张海龙,汤杨,任汀,等. 岩石广义流变柔量、模量时间依存性[J]. 工程科学与技术,2021,53(5):62−69. ZHANG Hailong, TANG Yang, REN Ting, et al. Time-dependence of generalized rheological-compliance and rheological-modulus about rock[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 2021, 53(5): 62−69.
[25] 苗胜军,王辉,杨鹏锦,等. 近疲劳强度循环荷载对泥质石英粉砂岩力学特性影响研究[J]. 岩土力学,2021,42(8):2109−2119. MIAO Shengjun, WANG Hui, YANG Pengjin, et al. Effect of cyclic loading near fatigue strength on mechanical properties of argillaceous quartz siltstone[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(8): 2109−2119.
[26] 陈光波,秦忠诚,张国华,等. 受载煤岩组合体破坏前能量分布规律[J]. 岩土力学,2020,41(6):2021−2033. CHEN Guangbo, QIN Zhongcheng, ZHANG Guohua, et al. Law of energy distribution before failure of a loaded coal-rock combined body[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020, 41(6): 2021−2033.
[27] 尹大伟,陈绍杰,邢文彬,等. 不同加载速率下顶板-煤柱组合体力学行为试验研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(5):1249−1257. YIN Dawei, CHEN Shaojie, XING Wenbin, et al. Experimental study on mechanical behavior of roof-coal pillar structure body under different loading rates[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2018, 43(5): 1249−1257.
[28] GAO Fuqiang, KANG Hongpu, YANG Lei. Experimental and numerical investigations on the failure processes and mechanisms of composite coal-rock specimens[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 1−13. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56847-4
[29] 王延辉,党崇哲. 非均质结构对煤岩组合体强度及破坏特征影响的离散元研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2023,54(3):147−152. WANG Yanhui, DANG Chongzhe. Discrete element study on influence of heterogeneous structure on strength and failure characteristics of coal rock combination[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2023, 54(3): 147−152.
[30] 张杰,何义峰,罗南洪,等. 浅埋煤层群重复采动覆岩运移及裂隙演化规律研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2022,53(3):58−65. ZHANG Jie, HE Yifeng, LUO Nanhong, et al. Research on overburden movement and fracture evolution of repeated mining in shallow coal seams group[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(3): 58−65.
[31] 孟祥军. 沿空掘巷沿空侧向顶板变形与弯矩的基础梁分析[J]. 煤矿安全,2021,52(5):207−215. MENG Xiangjun. Analysis of foundation beam of lateral roof deformation and bending moment in gob-side driving roadway[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021, 52(5): 207−215.
[32] 尹祥础,刘月. 加卸载响应比—地震预测与力学的交叉[J]. 力学进展,2013,43(6):555−580. YIN Xiangchu, LIU Yue. Load-unload response ratio-an interplay between earthquake prediction and mechanics[J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2013, 43(6): 555−580.
[33] 杨宇江,李元辉. 基于加卸载响应比理论的矿柱动力稳定性分析[J]. 岩土力学,2013,34(S1):324−330. YANG Yujiang, LI Yuanhyui. Dynamic stability analysis of pillar based on loading-unloading response ratio theory[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(S1): 324−330.
[34] 杨宇江,李元辉, 尹国光,等. 露天转地下开采境界矿柱安全厚度稳定性分析[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版),2011,32(7):1032−1040. YANG Yujiang, LI Yuanhui, YIN Guoguang, et al. Stability analysis of boundary pillars safety thickness for transition from open pit to underground mining[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2011, 32(7): 1032−1040.
[35] LI Tan, CHEN Guangbo, LI Yanhui, et al. Study on progressive instability characteristics of coal-rock composite structure with the different height ratios[J]. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering, 2022, 40(3): 1−14.
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: