Study on the influence of different surfactants on the wettability of coal
-
摘要:
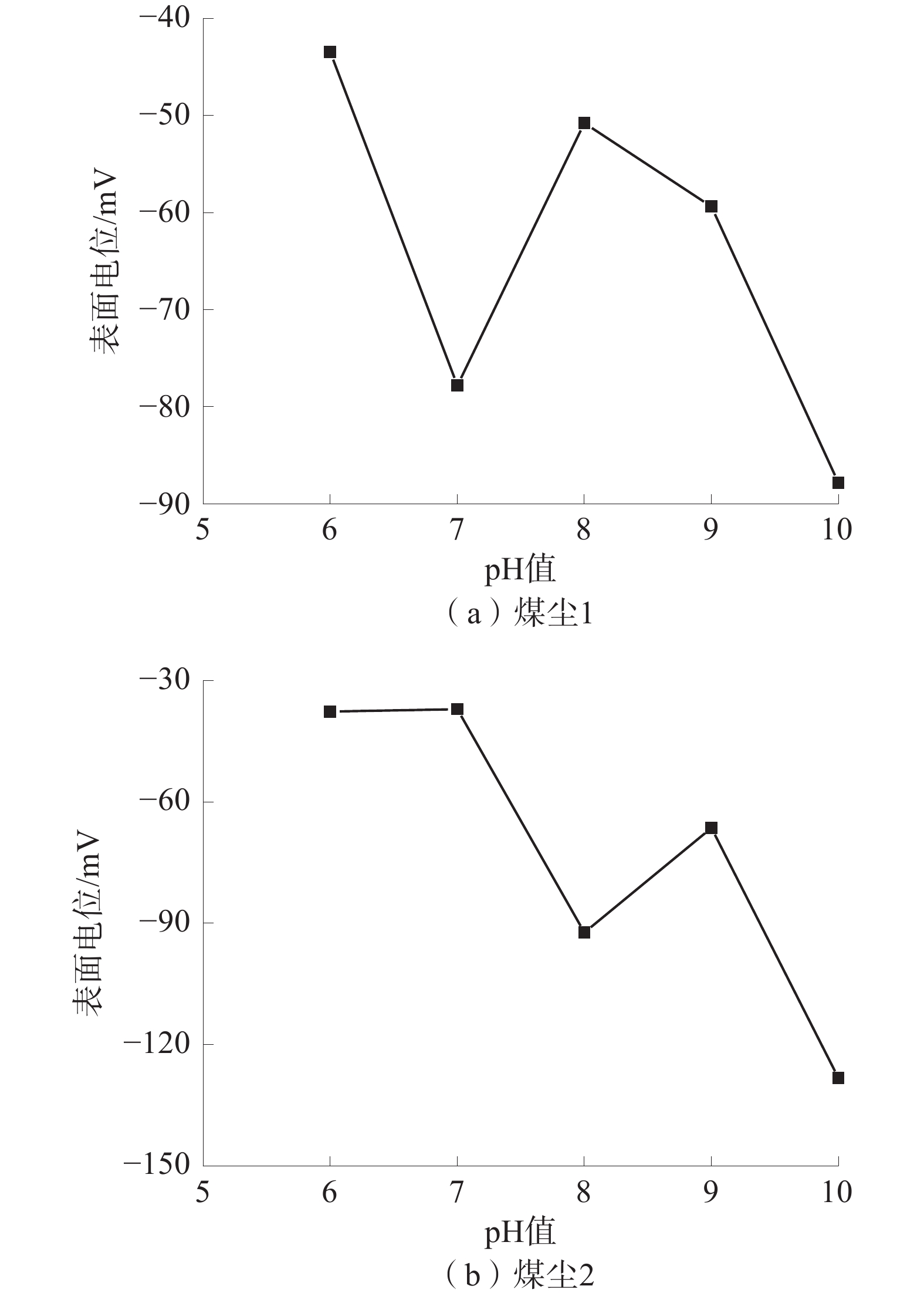
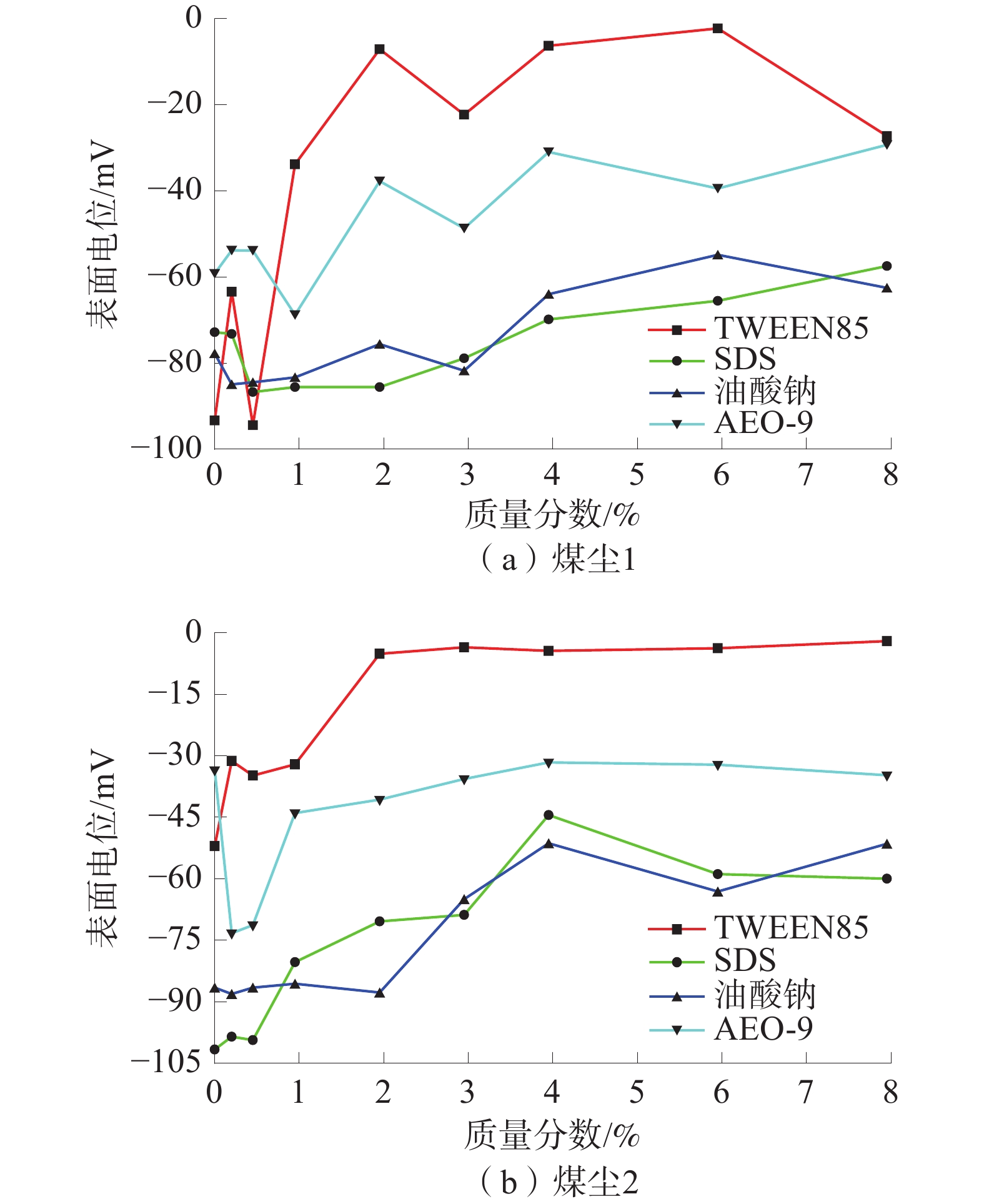
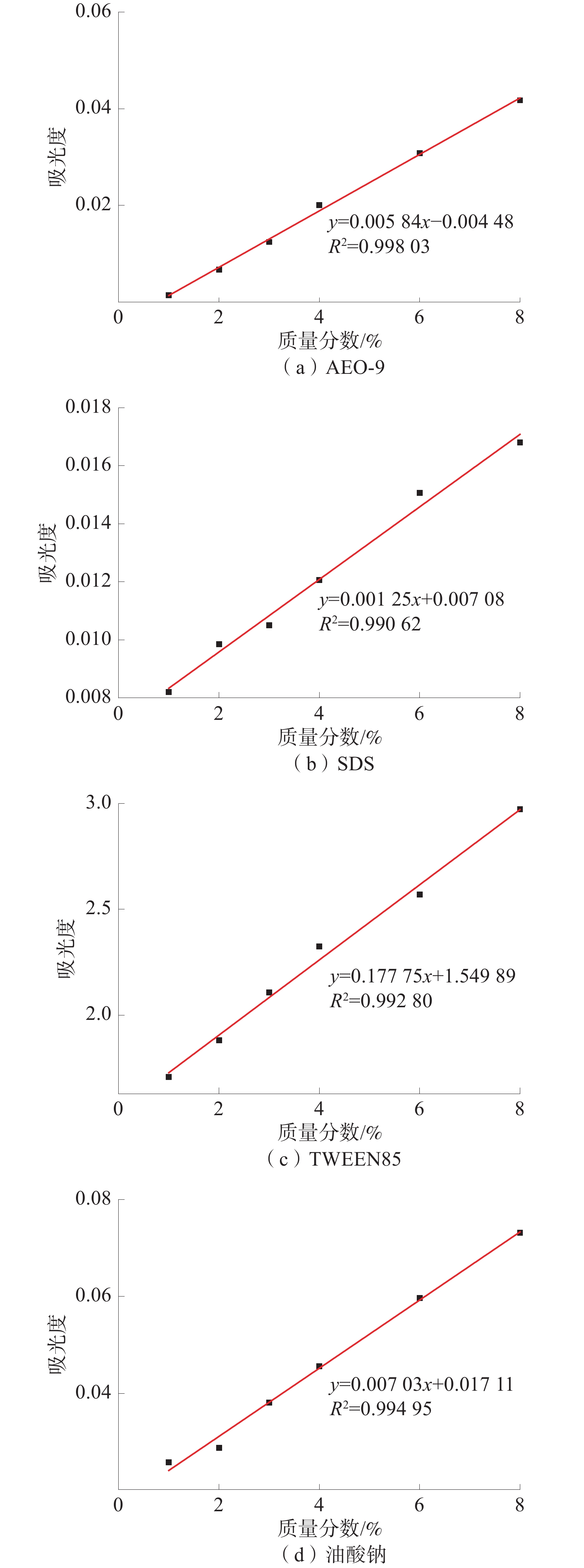
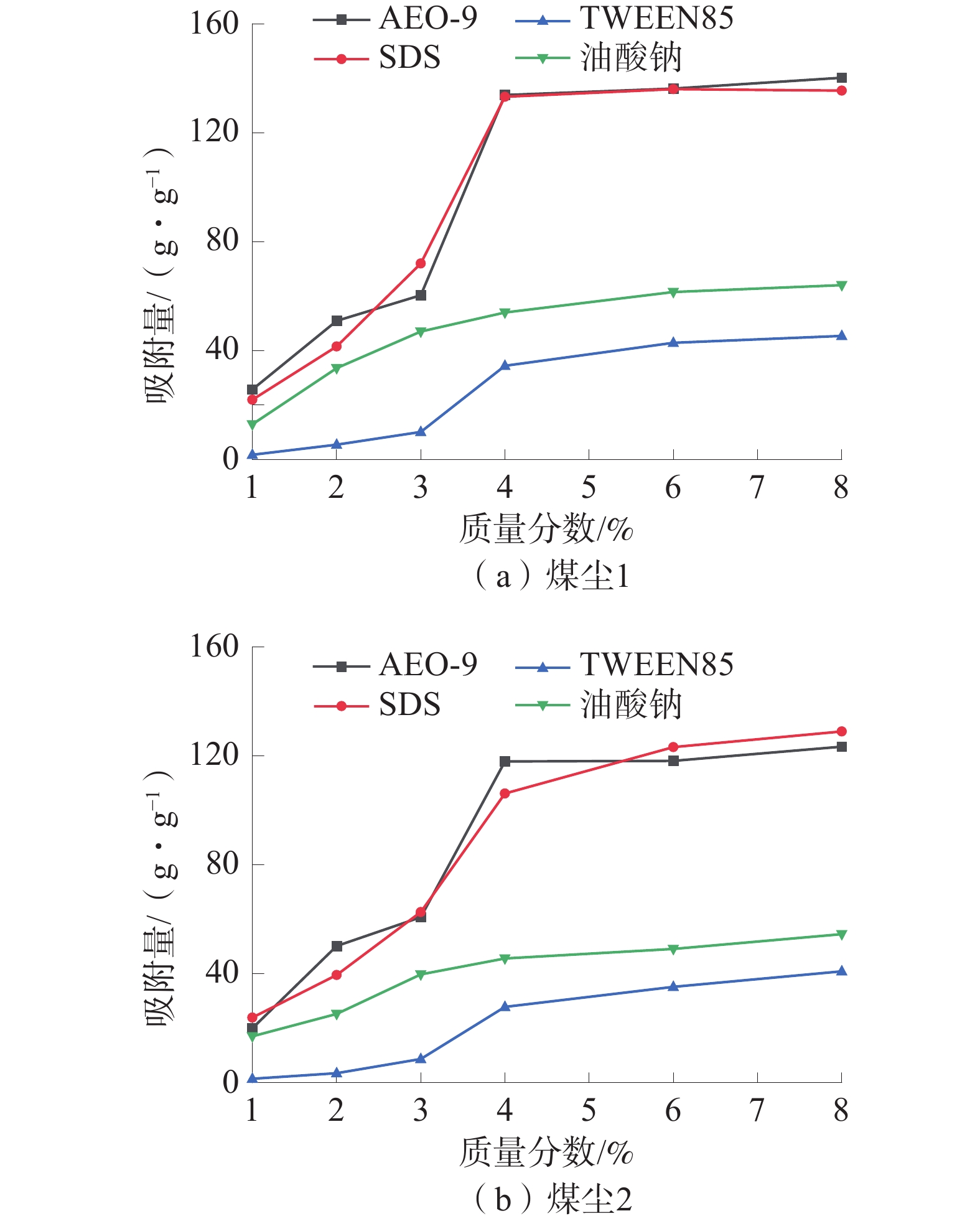
润湿性是煤尘抑尘剂的重要属性,直接影响抑尘剂对煤尘的降尘效果。选取了脂肪醇聚氧乙烯醚(AEO-9)、十二烷基硫酸钠(SDS)、TWEEN85、油酸钠(SODIUM OLEATE)4种表面活性剂和宁夏本地2种不同的煤尘作为研究对象,采用红外光谱、XPS分析、zeta电位、沉降实验、动态接触角测试等经典测试方法,研究了煤表面官能团以及表面电荷变化对润湿性的影响;并采用紫外分光光度法和低温氮气吸附法探索了煤的孔隙结构和吸附量对润湿性的影响。结果显示:非离子表面活性剂AEO-9和阴离子表面活性剂SDS对2种煤尘的润湿煤效果最佳,主要由于2种表面活性剂与煤尘表面的不同官能团均吸附稳定,且在同一质量分数下吸附速率快、吸附量大。
Abstract:Wettability is an important attribute of coal dust suppressant, which directly affects the effect of dust suppressant on coal dust. Four surfactants, AEO-9, SDS, Tween 85, and sodium oleate, and two kinds of local coal dust in Ningxia were selected as the research objects, infrared spectroscopy, XPS analysis, zeta potential, sedimentation experiment, dynamic contact angle test and other classic testing methods were used to study the influence of coal surface functional groups and surface charge changes on wettability. In addition, the effect of coal pore structure and adsorption amount on wettability was explored by UV spectrophotometry and low-temperature nitrogen adsorption method. The results showed that the nonionic surfactant fatty AEO-9 and the anionic surfactant SDS had the best wetting effect on the two kinds of coal dust, the main reason is that the two surfactants are adsorbed stably with different functional groups on the surface of coal dust, and the adsorption rate is fast and the adsorption capacity is large at the same concentration.
-
采动诱发覆岩裂隙贯穿覆岩隔水层,极易造成生态水资源破坏和矿井水害,对生态环境的破坏尤为明显。钱鸣高[1]提出了煤矿绿色开采的理念,认为保水开采是绿色开采中的一项重要内容。目前相关学者对导水裂隙带发育规律进行了大量的研究,提出了隔水层隔水性不受破坏是保水开采的关键[2-5],揭示了煤层赋存条件、开采方法、开采参数及关键层位置对导水裂隙带发育高度的影响[6-18],通过理论分析、数学软件模拟及对大量实测数据的分析,总结了多种导水裂隙带发育高度理论预计方法,构建了导水裂隙带发育高度预测模型[15-21]。覆岩导水裂隙带发育高度与覆岩移动变形息息相关,虽然前人已对导水裂隙带发育高度进行了大量研究,但将覆岩移动变形与覆岩导水裂隙带发育高度有机结合方面研究相对较少。为此,基于前人研究成果,以小保当矿区2−2号煤层为研究对象,通过理论分析、相似模拟实验和实例验证的方法研究导水裂隙带动态发育高度,借助概率积分法预计导水裂隙带上部岩层的曲率变形,给出1种导水裂隙带动态发育高度的理论预计方法,为进一步分析采动过程中导水裂隙带发育高度动态演化规律和预计导水裂隙带发育高度提供理论依据。
1. 导水裂隙带发育高度动态演化理论
1.1 导水裂隙带发育高度与曲率变形的关系
采动诱发的覆岩移动破坏具有明显分带性,根据移动破坏特征将覆岩分为“三带”,其中垮落带和裂隙带共同组成导水裂隙带,导水裂隙带上部至地表范围内的岩层为弯曲下沉带。导水裂隙带上部岩层作为导水裂隙带与弯曲下沉带分界岩层,其是否破断对导水裂隙带发育高度有重要影响,因此对导水裂隙带发育高度的研究以分析导水裂隙带上部岩层变形破坏为主。
采动后覆岩发生弯曲,其弯曲程度随工作面推进长度增大逐渐加剧,当导水裂隙带上部岩层弯曲程度超过自身极限时,裂缝沿其法线方向向上发育,发育高度取决于导水裂隙带上部岩层曲率变形Ki大小[22]。地表与导水裂隙带上部岩层分别为弯曲下沉带上部与下部边界,其移动变形属于同一问题的2方面,移动变形规律相似,采用概率积分法可对导水裂隙带上部岩层移动变形进行分析[23]。导水裂隙带发育高度形态如图1。
图1中:hs为导水裂隙带发育高度,m;δ为移动角,(°);φ为采动角,(°);Ki为导水裂隙带上部岩层曲率变形,10−3/m;H为开采煤层埋藏深度,m;z为导水裂隙带上部岩层埋深,m;ri为导水裂隙带上部岩层主要影响半径,m;li为导水裂隙带上部岩层平底点距开采边界距离,m。
导水裂隙带上部岩层各点曲率变形值Ki表达式为:
$$ {K_i} = - 2{\text{π }}\frac{{{\eta _i}m\;\cos\; \alpha }}{{r_i^3}}x{{\mathrm{e}}^{ - {\text{π }}\frac{{{x^2}}}{{r_i^2}}}} $$ (1) 式中:ηi为导水裂隙带上部岩层下沉系数;m为煤层开采高度,m;α为煤层倾角,(°);x为导水裂隙带上部岩层任一点位置。
煤层开采后覆岩发生破断,破断岩层在采空区发生堆积,由于岩石具有碎胀性,导水裂隙带上部岩层下沉值一般小于煤层开采高度m,其下沉系数ηi表达式为:
$$ {\eta _i} = \frac{{{w_i}}}{{m\;\cos \;\alpha }} $$ (2) 式中:wi为导水裂隙带上部岩层下沉值,m。
导水裂隙带上部岩层最大曲率变形值相应点位置x的表达式为:
$$ x = \frac{{{r_i}}}{{\sqrt {2{\text{π }}} }} = 0.4{r_i} $$ (3) 将式(3)代入式(1)中,可得导水裂隙带上部岩层最大曲率变形值Kimax表达式为:
$$ {K_{i\max }} = \pm 1.52\frac{{{\eta _i}m\;\cos\; \alpha }}{{r_i^2}} $$ (4) 采动诱发覆岩移动破坏是1个随工作面推进长度改变动态变化的过程,工作面推进长度增大,覆岩破坏发育高度、导水裂隙带上部岩层层位及曲率变形均发生变化,分析采动过程中覆岩动态破断规律,确定导水裂隙带上部岩层层位及曲率变形大小是预计导水裂隙带动态发育高度的关键。
1.2 采动覆岩动态破断规律
煤层采出后采空区上覆岩层失去支撑出现悬露,悬露长度lxi随工作面推进长度L增大而增大,工作面推进长度L与岩层悬露长度lxi的关系如图2。
图2中:lxi为岩层悬露长度,m;θ1、θ2分别为开切眼与工作面侧覆岩破断角,(°);L为工作面推进长度,m。由图2可知,工作面推进长度L与岩层悬露长度lxi存在如下关系:
$$ {l_{xi}} = L - \left( {H - z} \right)\left( {\cot \;{\theta _1} + \cot \;{\theta _2}} \right) $$ (5) 由式(5)可知:当岩层埋深一定时,工作面推进长度L越长,第i层岩层悬露长度lxi越大;当第i层岩层破断时悬露长度为其破断距lpi,此时工作面推进长度为第i层岩层破断时的推进长度Lpi。
由于破断岩层具有碎胀性,第i层岩层下部自由空间高度∆i随破断岩体垮落堆积逐渐减小,当下部自由空间高度∆i小于第i层岩层挠度fimax时,下部自由空间高度∆i不足以诱发第i层岩层破断,覆岩破断到一定高度后停止,此后即使工作面推进长度进一步增大至L≥Lpi时,第i层岩层及其上覆岩层不再发生破断[24]。第i层岩层下部自由空间高度∆i关系式为:
$$ {\Delta _i} = m - \left( {H - z} \right)\left( {{k_{\mathrm{c}}} - 1} \right)\;\cos\; \alpha $$ (6) 式中:∆i为下部自由空间高度,m;kc为岩石残余碎胀系数。
综上所述,结合工作面推进长度L、挠度fimax以及下部自由空间高度∆i给出1种采动中覆岩破断的判据,覆岩动态破断判据见表1。
表 1 覆岩动态破断判据Table 1. Dynamic fracture criterion of overburden rock推进长度/m 第i层岩层挠度/m 是否破断 L<Lpi fimax≥∆i 否 fimax<∆i 否 L≥Lpi fimax≥∆i 否 fimax<∆i 是 根据表1判断覆岩各岩层破断情况,可对采动中导水裂隙带上部岩层层位进行确定。若第i层岩层不破断,导水裂隙带于第i层岩层下部停止发育,第i层岩层为导水裂隙带上部岩层;反之则转入对第i+1层岩层破断情况进行判断。
1.3 导水裂隙带上部岩层下沉系数
同一煤层上覆不同层位岩层物理力学性质不同,各岩层性质及厚度存在明显差异,因此采动中相邻岩层会出现不均匀下沉现象。覆岩不均匀下沉示意图如图3。
由图3可知,当覆岩出现不均匀下沉时,若导水裂隙带上部岩层挠度小于下部自由空间高度即fimax<∆i,其下沉值为挠度fimax;若导水裂隙带上部岩层挠度不小于下部自由空间高度即fimax≥∆i,导水裂隙带上部岩层与下方岩层接触,其下沉值为下部自由空间高度∆i。综上所述,采动中导水裂隙带上部岩层下沉系数ηi是1个与其下部自由空间∆i及挠度fimax有关的分段函数,表达式为:
$$ \left\{ \begin{gathered} {\eta _i} = \frac{{{\Delta _i}}}{m}\left( {{f_{i\max }} \geqslant {\Delta _i}} \right) \\ {\eta _i} = \frac{{{f_{i\max }}}}{m}\left( {{f_{i\max }} < {\Delta _i}} \right) \\ \end{gathered} \right. $$ (7) 导水裂隙带上部岩层下沉系数与其曲率变形值直接相关,基于概率积分法,结合导水裂隙带上部岩层下沉系数分段函数分析,可得导水裂隙带上部岩层曲率变形值。
1.4 导水裂隙带动态发育高度
苏联学者Б·я·гвельцман[22]通过实测数据得出全部垮落法开采导水裂隙带发育高度hs与导水裂隙带上部岩层极限曲率Kt存在如下关系表达式:
$$ h_{\mathrm{s}}^2 = \frac{{7.25{\eta _i}m}}{{{K_{\mathrm{t}}}{{\left( {\cot \;\delta + \cot\; \varphi } \right)}^2}}} $$ (8) 式中:Kt为导水裂隙带上部岩层极限曲率,10−3/m。
由图1可知,覆岩采动角φ与移动角δ反切值表达式为:
$$ \cot \;\delta = \frac{{{r_i}}}{{\left( {H - z} \right)}} $$ (9) $$ \cot \;\varphi = \frac{{{l_i}}}{{\left( {H - z} \right)}} $$ (10) 采动后裂缝沿弯曲岩层法线方向向上发育,发育高度取决于导水裂隙带上部岩层曲率变形的大小,将式(4)、式(9)、式(10)代入式(8)中即可得到基于导水裂隙带上部岩层曲率变形的导水裂隙带发育高度预计公式:
$$ h_{\mathrm{s}}^2 = \frac{{4.77{{\left( {H - z} \right)}^2}r_i^2{K_{i\;\max }}}}{{{K_{\mathrm{t}}}{{\left( {{r_i} + {l_i}} \right)}^2}\;\cos\; \alpha }} $$ (11) 导水裂隙带动态发育高度预计流程如图4。
结合煤层赋存条件,判断采动中覆岩各岩层破断情况,确定不同工作面推进长度下导水裂隙带上部岩层层位、下沉系数和曲率变形,分析计算导水裂隙带动态发育高度。
2. 导水裂隙带发育高度相似模拟
2.1 工程概况
小保当矿区2−2号煤层倾角为0°~1°,属于近水平煤层,平均埋深为369.41 m,上覆基岩厚度为294.54 m,松散层厚度为68.87 m,平均采高6 m。各岩层相似模拟配比见表2。
表 2 相似模拟实验配比表Table 2. Similar simulation experiment ratio table序号 岩性 厚度/m 相似材料配比 河砂 石膏 大白粉 32 粉沙 2.70 9 1 9 31 细沙 53.80 9 1 9 30 红土 12.37 — — — 29 细粒砂岩 17.64 8 2 8 28 细粒砂岩 17.00 8 2 8 27 泥岩 7.00 9 2 8 26 细粒砂岩 2.20 8 2 8 25 砂质泥岩 7.77 9 4 6 24 细粒砂岩 18.96 8 3 7 23 砂质泥岩 8.68 9 4 6 22 细粒砂岩 3.09 8 2 8 21 砂质泥岩 12.10 9 4 6 20 砂质泥岩 12.00 9 4 6 19 细粒砂岩 5.00 8 2 8 18 砂质泥岩 6.48 9 4 6 17 细粒砂岩 13.64 8 2 8 16 粉砂岩 16.70 7 2 8 15 细粒砂岩 10.10 8 3 7 14 粉砂岩 6.01 7 2 8 13 细粒砂岩 13.01 8 3 7 12 粉砂岩 15.13 7 2 8 11 细粒砂岩 8.66 8 3 7 10 粉砂岩 19.40 7 2 8 9 细粒砂岩 9.88 8 3 7 8 粉砂岩 8.20 7 2 8 7 细粒砂岩 14.90 8 3 7 6 煤(1−1) 2.00 粉煤灰∶河砂∶石膏∶大白粉= 21∶1∶2∶21 5 细粒砂岩 18.75 8 3 7 4 粉砂岩 4.20 7 2 8 3 细粒砂岩 5.10 8 3 7 2 中粒砂岩 8.34 8 2 8 1 细粒砂岩 3.50 8 3 7 煤(2−2) 6.00 粉煤灰∶河砂∶石膏∶大白粉= 21∶1∶2∶21 根据2−2号煤层赋存条件选取几何相似常数αi=200、密度相似常数αρ=1.56、应力相似常数ασ=αiαρ=312,搭建尺寸为3 000 mm×1 700 mm×200 mm的相似模型。
2.2 相似模拟结果
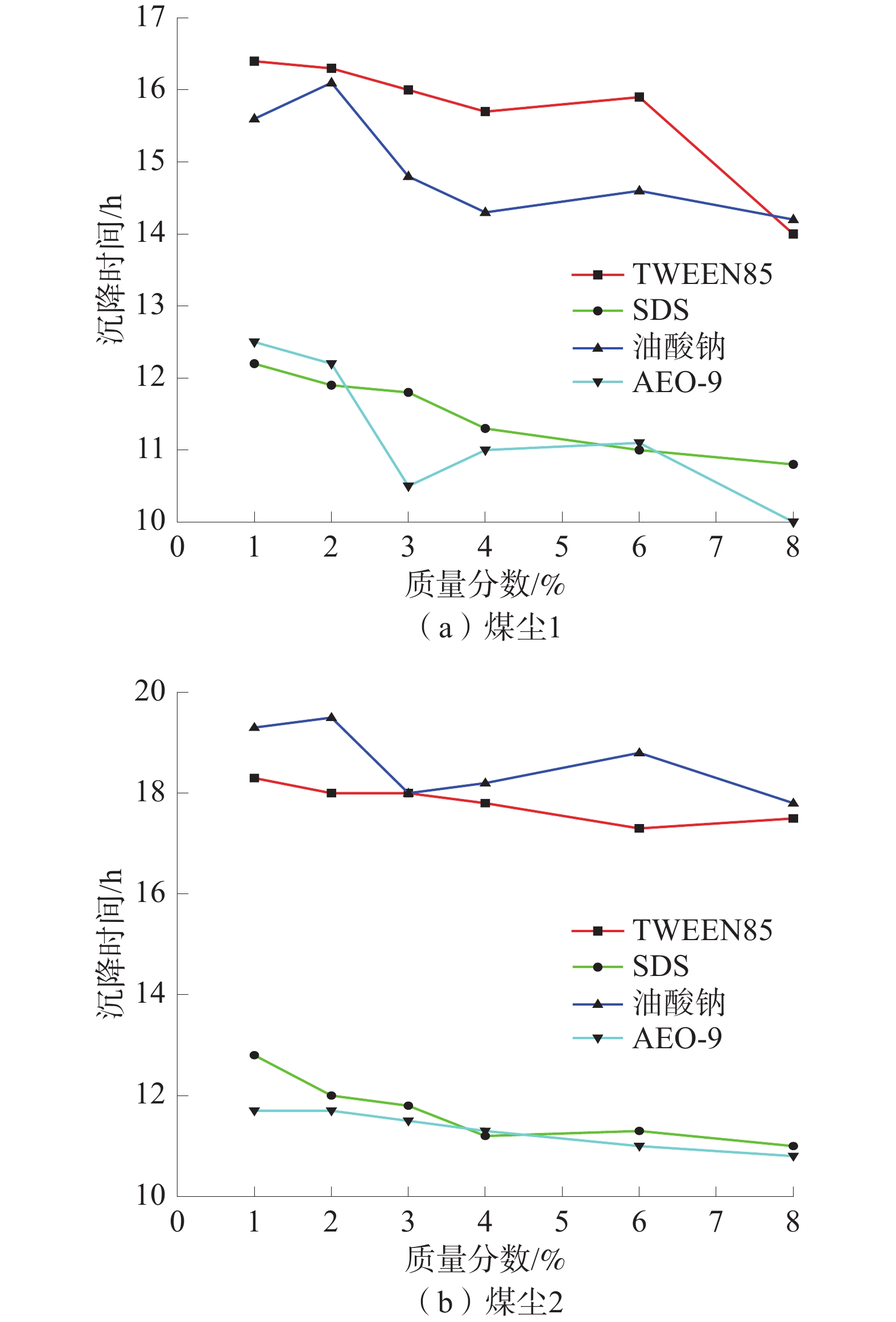
为减小边界效应,开切眼开掘位置距模型左边界40 cm(80 m),由开切眼处开始向右侧模拟开挖煤层,在距模型边界40 cm(80 m)处停止开采,煤层开采过程中采用PENTAXR-322NX型光学全站仪对模型测线进行观测。工作面推进不同距离时导水裂隙带发育高度如图5~图7。
由图5可知:当工作面推进至119 m时,覆岩10号岩层未发生破断,为工作面推进至119 m时导水裂隙带上部岩层,导水裂隙带发育至10号岩层下部,发育高度为63.6 m,为2−2号煤层采高(6 m)的10.6倍。
由图6可知:当工作面推进至278 m时,覆岩破坏发育高度随工作面推进而增大,导水裂隙带发育至16号岩层中部,16号岩层未破断,为工作面推进至278 m时导水裂隙带上部岩层,导水裂隙带发育高度155 m,为采高的25.8倍。
由图7可知:当工作面推进至428 m时开采完毕,覆岩垮落稳定后煤层开采达到充分采动,受下部自由空间高度限制,覆岩破坏发育高度不再随工作面推进而增大,导水裂隙带在16号岩层中部停止发育,发育高度不再随工作面推进而发生明显变化,覆岩16号岩层为导水裂隙带上部岩层,导水裂隙带最大发育高度155 m,为采高的25.8倍。
3. 导水裂隙带发育高度动态演化验证
3.1 导水裂隙带动态发育高度理论预计
根据覆岩破断判据,结合相似模拟实验现象及观测数据对采动过程中各岩层破断情况进行判定,覆岩破断情况判别表见表3。
表 3 覆岩破断情况判别表Table 3. Overburden rock fracture discrimination table岩层序号 岩层厚度/m Lpi/m ∆i/m 是否破断 16 16.70 212.0 4.52 否 15 10.10 212.0 4.63 是 14 6.01 168.0 4.69 是 13 13.01 168.0 4.82 是 12 15.13 155.0 4.97 是 11 8.66 126.0 5.06 是 10 19.40 126.0 5.25 是 9 9.88 119.0 5.35 是 8 8.20 99.0 5.43 是 7 14.90 99.0 5.58 是 6 2.00 99.0 5.60 是 5 18.75 90.0 5.79 是 4 4.20 76.0 5.83 是 3 5.10 76.0 5.88 是 2 8.34 53.0 5.97 是 1 3.50 41.6 6.00 是 由表3可知:当工作面推进至41.6 m时,煤层顶板发生破断,覆岩破坏开始向上发育;当推进长度达到53.0 m覆岩2号岩层发生破断,随着工作面推进长度增大,导水裂隙带逐步向上发育;在推进长度达到76.0 m时上覆3、4号岩层均发生破断,导水裂隙带发育至5号岩层下部;当推进至90.0 m时5号岩层发生破断,导水裂隙带进一步发育,其上覆6号~8号岩层在推进长度达到99.0 m时均发生破断;推进长度达到119 m时9号岩层破断,导水裂隙带发育至10号岩层下部;当推进至126.0 m时10号岩层与11号岩层发生同步破断,推进至155.0 m时12号岩层破断,导水裂隙带随覆岩破断向上发育;当推进长度达到168.0 m时13号、14号岩层同步破断,推进至212.0 m时覆岩15号岩层发生破断,由于f16max=6.61 m>∆16,16号岩层不破断,导水裂隙带于16号岩层下部停止发育,此后随着工作面推进长度增大,导水裂隙带发育高度不再发生明显变化。
为了进一步分析采动过程中的导水裂隙带动态发育高度,结合相似模拟实验现象及观测数据,以工作面推进长度119、278、428 m(在该推进长度下导水裂隙带上部岩层下沉系数分别对应其下沉系数的2个分段函数)为例预计2−2煤层开采过程中导水裂隙带发育高度,理论预计结果如下:
1)当工作面推进至119 m时10号岩层未破断,为导水裂隙带上部岩层。相似模拟实验观测得10号岩层l10=37.8 m,r10=38.2 m,下沉值w10=0.72 m,下沉系数η10=0.12,极限曲率Kt=1.30×10−3/m,推进至119 m时导水裂隙带上部岩层最大曲率变形值K10max=0.75×10−3/m,将上述数据代入式(11)中计算可得。工作面推进至119 m时导水裂隙带发育高度hs为62.4 m。
2)当工作面推进至278 m时,16号岩层未破断,为导水裂隙带上部岩层,相似模拟实验观测可得16号岩层l16=72.3 m,r16=72.9 m,下沉值w16=4.52 m,下沉系数η16=0.75,推进至278 m时导水裂隙带上部岩层最大曲率变形值K16max=1.29×10−3/m,将上述参数代入式(11)中计算可得工作面推进至278 m时导水裂隙带发育高度hs为160.8 m。
3)当工作面推进至428 m时,16号岩层仍未破断,下沉系数η16=0.75,曲率变形值K16 max=1.29×10−3/m,计算得当工作面推进至428 m时导水裂隙带发育高度仍为160.8 m,导水裂隙带发育高度不再随工作面推进长度增大发生明显变化,导水裂隙带最大发育高度hs为160.8 m。
3.2 相似模拟实验验证
当工作面推进至119 m时,相似模拟实验中导水裂隙带发育高度为63.6 m,理论预计结果为62.4 m,误差为1.9%;推进至278 m时,实验中导水裂隙带发育高度为155 m,理论预计结果为160.8 m,误差为3.6%;当2−2号煤层开采完成后,实验中导水裂隙带最大发育高度为155 m,理论预计导水裂隙带最大发育高度为160.8 m,误差为3.6%。
基于相似模拟实验及理论预计结果绘制的2−2煤层开采过程中导水裂隙带动态发育高度曲线图如图8。
由图8可知,导水裂隙带发育高度理论预计曲线与相似模拟实验曲线基本一致,误差为1.9 %~3.6%,两段曲线均表明采动中导水裂隙带发育高度随工作面推进长度增大发生变化,其发育形态大致可分为以下4个阶段。
1)缓慢发育阶段。煤层开采初期,采空区尺寸相对较小,受采空区大小限制导水裂隙带发育相对缓慢。
2)迅速发育阶段。工作面进一步推进,覆岩受采动影响程度增大,导水裂隙带随工作面推进长度增大快速发育。
3)发育变缓阶段。导水裂隙带发育至一定高度后,采动对导水裂隙带上部岩层影响程度逐渐降低,此时导水裂隙带发育高度随工作面推进增速逐渐减缓。
4)发育平稳阶段。当工作面推进至一定长度后,由于岩石具有碎胀性,破断岩层将覆岩下部自由空间填满,导水裂隙带上部岩层不再发生破断,导水裂隙带达到最大发育高度,不再随工作面推进长度增大发生明显变化。
3.3 实例验证
小保当一号井2−2号煤层平均埋深356.5 m,上覆基岩厚度为202.65~288.89 m,平均254.14 m,松散层厚度为70.26 m,煤层平均厚度为5.8 m。为验证覆岩导水裂隙带发育高度预计理论的可靠性,以小保当一号井2−2号煤层为研究对象,对覆岩导水裂隙带发育高度进行了现场实测。
现场对6个钻孔进行探查,探查结果表明覆岩导水裂隙带发育高度为152.01~175.57 m,为采高的26.21~30.27倍,切眼附近导水裂隙带发育高度最大,工作面内部发育高度较小。理论预计小保当矿区2−2号煤层覆岩导水裂隙带最大发育高度为160.8 m,与现场实测覆岩导水裂隙带发育高度基本一致。
4. 结 语
1)基于工作面推进长度、挠度及下部自由空间高度给出了覆岩动态破断判据和导水裂隙带上部岩层下沉系数分段函数,在此基础上给出了1种基于导水裂隙带上部岩层曲率变形的导水裂隙带动态发育高度预计方法。
2)通过相似模拟实验和理论预计方法,揭示了采动中导水裂隙带发育高度动态演化的4个阶段:缓慢发育阶段、迅速发育阶段、发育变缓阶段、发育平稳阶段。
3)以小保当矿区2−2号煤层为研究对象对导水裂隙带发育高度进行理论预计、相似模拟实验及现场实测,理论预计结果与相似模拟实验结果误差为1.9 %~3.6%,理论预计发育高度为160.8 m,与现场实测2−2号煤层开采导水裂隙带发育高度152.01~175.57 m基本吻合。
-
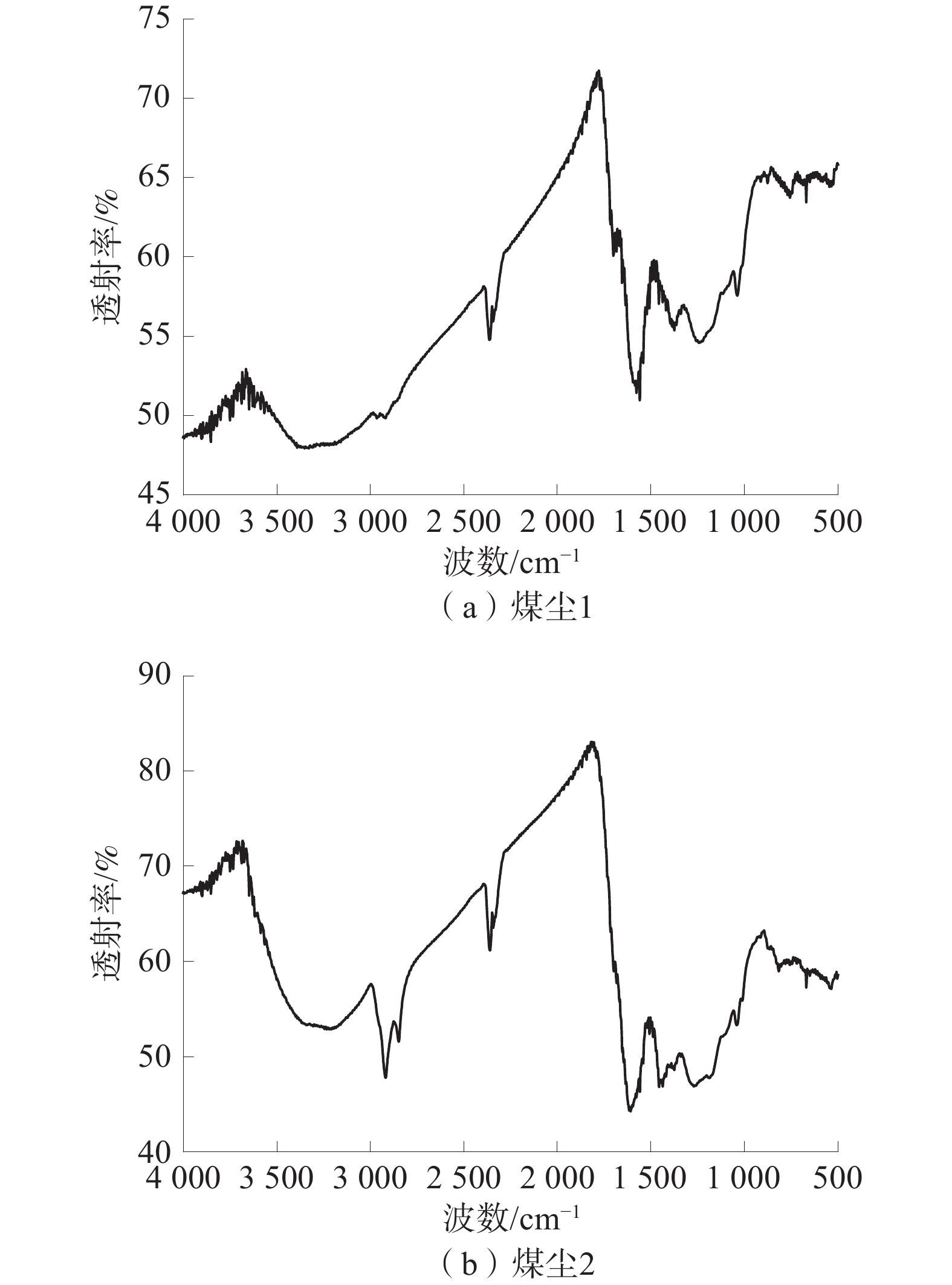
表 1 元素分析和工业分析
Table 1 Proximate and ultimate analysis of coal
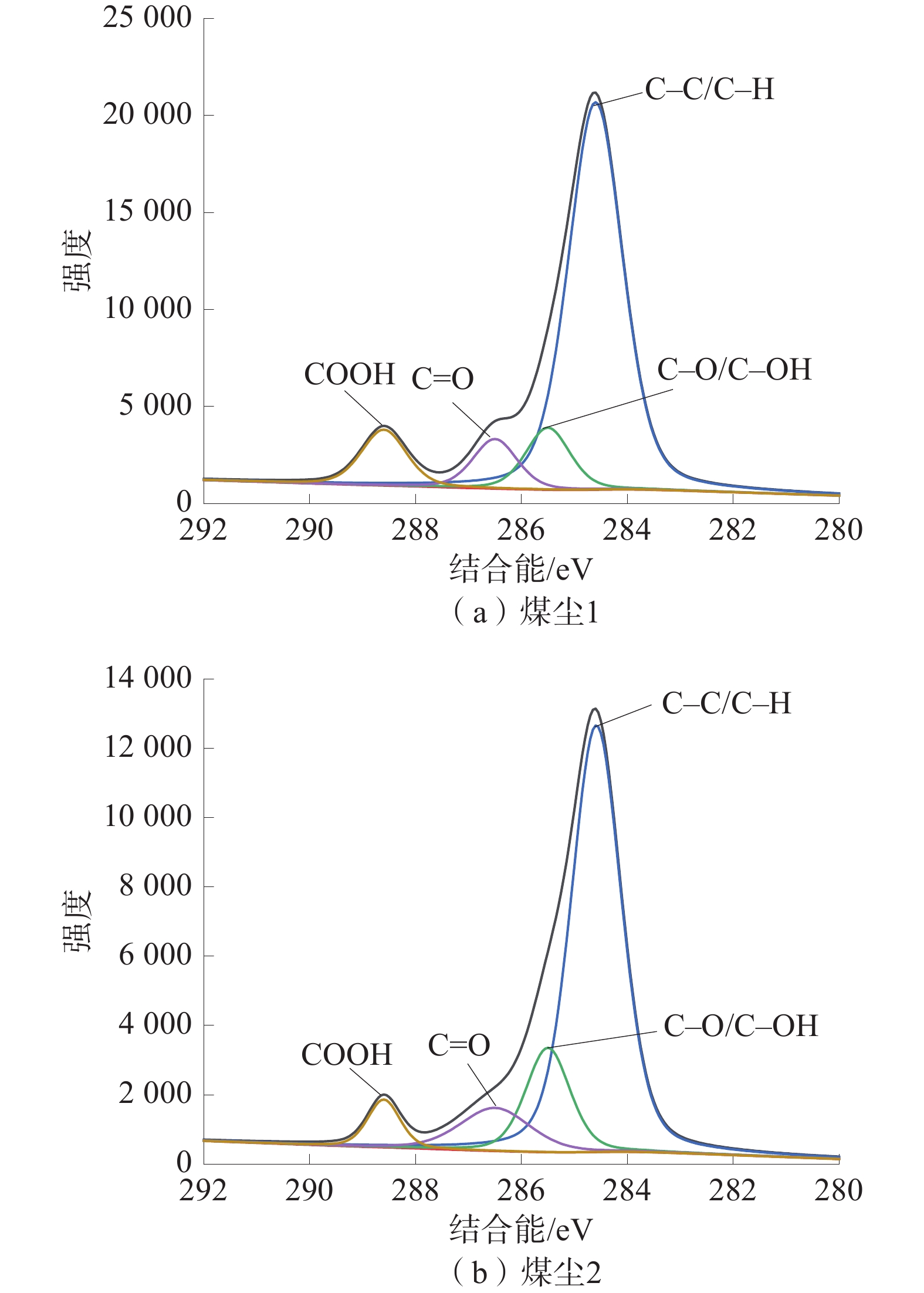
% 煤样 H质量分数 C质量分数 S质量分数 N质量分数 水分 灰分 挥发分 固定碳 1 3.56 62.75 0.51 2.55 8.33 8.82 33.65 55.19 2 5.56 68.37 0.60 2.74 9.99 4.17 43.24 43.24 表 2 煤尘各官能团含量
Table 2 Content of each functional group in coal dust
煤尘 官能团含量/% C−C/C−H C−O/C−OH C=O COOH 1 33.60 38.22 18.16 10.00 2 44.18 33.03 14.54 8.25 -
[1] XIE L, MU X Z, LU K, et al. The time-varying relationship between CO2 emissions, heterogeneous energy consumption, and economic growth in China[J]. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 2023, 25(8): 7769−7793. doi: 10.1007/s10668-022-02371-x
[2] LIU N, CHEN K, DENG E, et al. Study on dust suppression performance of a new spray device during drilling and blasting construction in the metro tunnel[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2023, 133: 104975. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2022.104975
[3] ZHOU Q, QIN B T, LI H Z, et al. Changes of physical properties of coal dust with crush degrees and their effects on dust control ability of the surfactant solution spray[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2022, 29(22): 33785−33795. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-17832-5
[4] CHENG J W, ZHENG X R, LEI Y D, et al. A compound binder of coal dust wetting and suppression for coal pile[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2021, 147: 92−102. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2020.08.031
[5] WANG H, ZHANG Q, WANG D, et al. Basic characteristics of mine dust suppression foam and the quantitative evaluation method of its performance[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2023, 48(4): 1584−95.
[6] XU G, HUANG J, HU G, et al. Experimental study on effective microwave heating/fracturing of coal with various dielectric property and water saturation[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2020, 6(1): 202:106−378. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2020.11.045
[7] CHANG P, ZHAO Z D, XU G, et al. Evaluation of the coal dust suppression efficiency of different surfactants: A factorial experiment[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2020, 595: 124686. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.124686
[8] ZHU S C, ZHAO Y Y, HU X M, et al. Study on preparation and properties of mineral surfactant–microbial dust suppressant[J]. Powder Technology, 2021, 383: 233−243. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2021.01.053
[9] CHANG P, CHEN Y, XU G, et al. Numerical study of coal dust behaviors and experimental investigation on coal dust suppression efficiency of surfactant solution by using wind tunnel tests[J]. Energy Sources, 2020, 43(17): 2173−88. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-18623-2
[10] WANG P F, HAN H, TIAN C, et al. Experimental study on dust reduction via spraying using surfactant solution[J]. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 2020, 11(6): 32−42. doi: 10.1016/j.apr.2020.02.010
[11] JIN H, ZHANG Y S, WU G G, et al. Optimization via response surface methodology of the synthesis of a dust suppressant and its performance characterization for use in open cut coal mines[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2022, 121: 211−223. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2021.12.006
[12] 沈军平,颜志丰,杨玲,等. 原生煤与构造煤孔隙结构的压力响应特征[J]. 煤炭技术,2022,41(9):103−107. SHEN Junping, YAN Zhifeng, YANG Ling, et al. Pressure response characteristics of pore structure primary coal and structural coal[J]. Coal Technology, 2022, 41(9): 103−107.
[13] 常明,董宪姝,李宏亮,等. 煤表面含氧官能团对矿井气体吸附特性的模拟研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2020,51(1):176−180. CHANG Ming, DONG Xianshu, LI Hongliang, et al. Simulation study on adsorption characteristics of mine gases by oxygen functional groups on coal surface[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2020, 51(1): 176−180.
[14] 陈煜朋,姜文忠,秦玉金,等. 煤的孔隙分布特征研究理论与方法综述[J]. 煤矿安全,2021,52(3):190−196. CHEN Yupeng, JIANG Wenzhong, QIN Yujin, et al. Review on research theory and methods of pore distribution characteristics of coal[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021, 52(3): 190−196.
[15] 汪李龙,康健婷,康天合,等. SDS溶液改变无烟煤润湿性与冲击产尘粒径分布的实验研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2020,51(1):30−37. WANG Lilong, KANG Jianting, KANG Tianhe, et al. Experimental study on influence of SDS solution on wettability and grain size distribution of impact crushing dust production in anthracite[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2020, 51(1): 30−37.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 朱翠,罗宇豪,王占刚,戴娟. 新型蚁群算法规划核电厂巡检机器人路径. 核电子学与探测技术. 2025(01): 107-115 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: