Study on the significant effects of ignition energy and gas volume fraction on gas explosion pressure and flame propagation speed
-
摘要:
在长35 m、截面积为200 mm×200 mm的封闭管道中,选取点火能量和瓦斯体积分数2个影响因素,采用正交试验法对瓦斯爆炸最大火焰传播速度、瓦斯爆炸压力峰值、压力上升速率进行研究,得出了在不同点火能量和不同瓦斯体积分数条件下的瓦斯−空气混合气体爆炸显著性影响规律。结果表明:在相同瓦斯体积分数情况下,火焰传播速度从点火位置开始,随着传播距离的增加而逐渐增大,在泄爆舱入口处达到最大值,点火能量越大,火焰传播速度越快;在相同点火能量情况下,最大火焰传播速度随瓦斯体积分数升高先上升后下降,瓦斯体积分数为9.5%时最大;从极差和显著性影响分析可知,瓦斯体积分数、点火能量和两者交互作用对最大火焰传播速度均有显著性影响,显著性影响由大到小为瓦斯体积分数>点火能量>两者交互作用;在相同瓦斯体积分数情况下,瓦斯爆炸压力峰值和压力上升速率均随点火能量的增加而升高,点火能量越大,压力峰值和压力上升速率越高;在相同点火能量情况下,压力峰值和压力上升速率随瓦斯体积分数的升高先升高后降低,瓦斯体积分数为9.5%时最大;在极差和显著性影响方面,瓦斯体积分数、点火能量均对压力峰值和压力上升速率有显著性影响,且点火能量>瓦斯体积分数,两者交互作用则对压力峰值和压力上升速率没有显著性影响。
Abstract:The maximum flame propagation speed, the peak pressure and the pressure rise rate of gas explosion were studied under the influence of two factors of ignition energy and gas volume fraction, by using the orthogonal experimental method in a closed pipeline with a length of 35 m and a cross-sectional area of 200 mm×200 mm. The significant impact law of gas-air mixture explosion under different ignition energy and gas volume fraction conditions was obtained. The experimental results show that under the same gas volume fraction, the flame propagation speed of gas explosion gradually increases with the extension of propagation distance from the ignition position, reaching the maximum value near the outlet, and the larger the ignition energy is, the greater the flame propagation speed is; under the same ignition energy, the maximum flame propagation speed first increases and then decreases with the increase of gas volume fraction, reaching its maximum at a gas volume fraction of 9.5%; from the analysis of range and significance effects, gas volume fraction and ignition energy and their interaction have significant effects on the maximum flame propagation speed, and the significant effects are as follows: the gas volume fraction > the ignition energy > their interaction; under the same gas volume fraction, the peak pressure and the pressure rise rate of gas explosion both increase with the increase of ignition energy, the larger the ignition energy, the higher the peak pressure and the pressure rise rate; under the same ignition energy, the peak pressure and the pressure rise rate first increase and then decrease with the increase of gas volume fraction, with the maximum value at a gas volume fraction of 9.5%; in the aspects of range and significance effects, the gas volume fraction and the ignition energy have a significant impact on the peak pressure and the pressure rise rate, the significance effects are as follows: the ignition energy > the gas volume fraction, and the interaction between the two has no significant effect on the peak pressure and the pressure rise rate.
-
煤炭是我国能源的压舱石和稳定器,对保障我国能源供给和能源安全具有重要意义。瓦斯爆炸是煤矿灾害事故中最具破坏力的事故之一[1-3]。随着大采高工作面一次采全高和综采放顶煤开采技术的广泛应用,采空区顶板垮落过程中岩体相互撞击摩擦产生火花已成为诱发采空区瓦斯爆炸事故的主要隐患。众多学者在岩石撞击升温[4-5]、摩擦闪温[6-7]、砂岩放电[8]、瓦斯引燃温度阈值[9-10]、瓦斯爆炸温度分布[11]、顶板失稳摩擦区域[12]等方面进行了研究。周应江等[13]以某工作面瓦斯事故为研究对象,开展了采空区瓦斯燃烧原因调查,发现该次瓦斯事故是因顶板垮落掉落的石英砂岩撞击摩擦产生火花引燃瓦斯;许家林等[14]、屈庆栋等[15]研究了顶板垮落撞击产生摩擦火花的诸多因素,认为开采厚度、岩块石英含量、干燥程度、接触压力与产生摩擦火花概率成正比;秦广鹏等[16-18]研究了坚硬顶板冒落过程中砂岩摩擦引燃采空区瓦斯机制,初步探讨了摩擦速度、石英含量与摩擦面热量密度之间的联系;陈琛等[19]建立了考虑高温热痕、岩壁、风流导热和风流对流的微分方程,确定了岩石摩擦引燃瓦斯的温度阈值;李冬等[20]研究表明岩石石英含量、摩擦面粗糙程度、撞击高度、摩擦时间等因素与岩石表面温度呈正相关;周锦龙等[21]开展了岩辊渐进摩擦试验,定量表征了岩石摩擦速度与最大闪温的关系。专家学者在岩石摩擦升温引发瓦斯燃烧爆炸取得的成果对防控采空区瓦斯爆炸起到了显著作用。针对现有研究中对定量化指标考虑不系统、指标研究不深入的问题,采用岩石摩擦效应引燃瓦斯试验系统,设计试验从砂岩摩擦速度、摩擦力、瓦斯浓度、SiO2含量等角度探究砂岩摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸机制,为防控采空区顶板垮落过程中岩体相互撞击摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸提供依据。
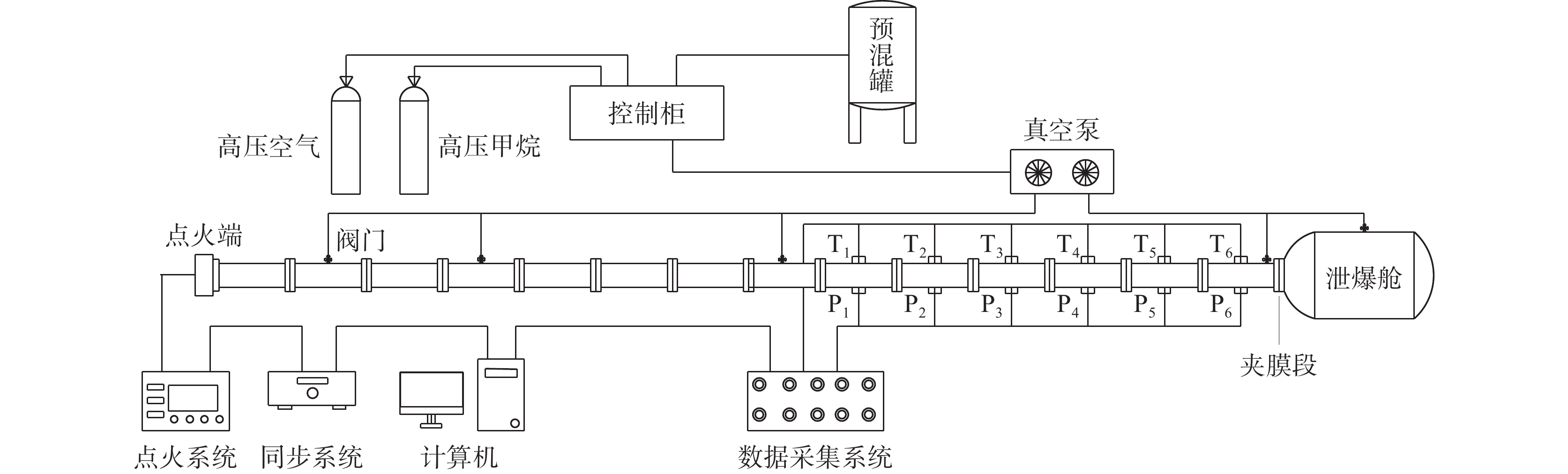
1. 工程背景
新疆某矿井田总体处于复式背斜的南翼,为单斜构造,伴有较多断层,局部褶皱发育,倾角6°~12°,区域断层特点基本沿北东向、近南北向发育,东部断层发育,西部深部相对简单。该矿N4107工作面走向方向长为2 128 m、倾斜方向长为240 m,工作面地面标高为+1 040~+1 100 m、井下标高为+530~+650 m、埋深472~573 m,工作面北部、西部为实体煤,南部为集中回风巷,东邻N4106采空区。N4107工作面回采4-1煤层,煤层由北向南逐渐变薄,煤岩类型以半暗型煤变半亮型煤为主,煤层厚度为8.25~9.17 m、平均为8.70 m,倾角5°~14°,平均为9°。4-1煤层瓦斯含量较高,N4107工作面经过预抽,瓦斯相对涌出量0.36 m3/t,绝对涌出量为4.36 m3/min。4-1煤层顶底板情况见表1。
表 1 4-1煤层顶底板基本力学参数Table 1. Basic mechanical parameters of 4-1 coal roof and floor岩样 岩性 破坏载荷/kN 抗压强度/MPa 弹性模量/GPa 基本顶 粉砂岩 66.38 35.74 11.42 直接顶 细砂岩 94.04 50.73 15.31 直接底 细砂岩 94.29 51.20 17.29 2. 试验设计
2.1 试 样
本次试验试样材料取自新疆某矿N4107工作面基本顶、直接顶与直接底中的砂岩,3组摩擦试件与旋转试件分别取自同一块岩块。使用岩石切磨一体机将煤、岩块进行切割、打磨,加工成内径为40 mm,外径为120 mm,高25 mm的环形旋转试件,共制备了3组试样。
利用X射线衍射仪对3组摩擦试件样本物相进行测定分析,得到基本顶、直接顶、直接底3组试样中SiO2含量分别为57.53%、67.85%、61.44%。
2.2 试验系统
岩石摩擦效应引燃瓦斯试验系统主要包括摩擦试验箱、动力控制系统、试件摩擦系统以及瓦斯监测系统4个部分。
1)摩擦试验箱。箱体由厚度为10 mm的钢板制成,箱体的长、宽、高分别为660、660、690 mm。试验箱前部开有30 mm×30 mm的泄爆口,试验时用塑料纸密封,瓦斯爆炸后产生气流能够及时从泄爆口排出,从而避免爆炸对设备造成损坏。泄爆口下部开有直径为10 mm的瓦斯注入口,瓦斯注入后用螺丝密封。试验箱右端为1块12 mm厚的可拆卸钢化玻璃,四周用密封封条密封,以便观察、记录试验现象。
2)动力控制系统。动力控制系统采用额定电压380 V、额定功率5.5 kW、转速2 800 r/min的三相异步电机为试验提供动力。电机转速通过变频器控制,变频器额定功率为7.5 kW,额定输出电流为17 A,输入电压为380 V。三相异步电机通过连接箱内工业联轴器与摩擦试验箱连接,将电机动力传导给试验箱内试件,其外部加装保护壳,提高试验的安全性。
3)试件摩擦系统。试件摩擦系统由试件加压装置、摩擦试件固定装置、旋转试件固定装置组成。试件加压装置为1块厚度为30 mm的“T”形钢板,钢板质量15 kg。其一端与箱体通过旋转轴连接,另一端用于悬挂重物增加配重。试件加压装置放下时“T”形钢板下方正好与旋转试件接触。摩擦试件固定装置的主要功能是固定摩擦试件,保证试验进行过程中摩擦试件与旋转试件稳定接触。摩擦试件固定装置由底部托板和上部的平口钳组成。底部托板固定在试件加压装置上,与试件加压装置形成1个平面,用于固定平口钳,保证摩擦试件水平。摩擦试件固定装置与试件加压装置通过螺栓连为一体,确保整体牢固。
4)瓦斯监测系统。瓦斯监测系统由瓦斯监测仪、监测探头和气体报警控制主机组成。瓦斯监测仪量程为0~100%,用于实时监测试验中瓦斯体积分数。
2.3 试验方案
依据工程现场采空区难以监测的位置局部瓦斯体积分数可能升高至瓦斯爆炸体积分数范围(5.0%~16.0%),确定试验中瓦斯体积分数范围。因工程现场中顶板垮落过程中岩块大小、形状及速度均不相同,根据岩石摩擦效应引燃瓦斯试验系统配重范围,将摩擦力参数设置为摩擦载质量15.0~19.0 kg。根据N4107工作面煤层最厚位置确定顶板最大垮落高度为9.17 m,按照自由落体理想状态,直接顶垮落至顶板最大速度为13.43 m/s,因此将摩擦速度参数设置为4.0~14.0 m/s。SiO2含量参数由采用X射线衍射仪对顶底板摩擦试件样本物相进行测定分析得到。
共设计19组试验,每组试验重复3次,命名为试验1、试验2、试验3,取3次试验平均值以避免试验误差。其中5组为不同瓦斯体积分数(6.0%、7.0%、8.5%、10.0%、11.5%)砂岩摩擦引燃瓦斯试验,5组为不同摩擦力(载质量15.0、16.0、17.0、18.0、19.0 kg)砂岩摩擦引燃瓦斯试验,3组为不同SiO2含量(57.53%、67.85%、61.44%)砂岩摩擦引燃瓦斯试验,6组为不同摩擦速度(4.0、6.0、8.0、10.0、12.0、14.0 m/s)砂岩摩擦引燃瓦斯试验。设计试验方案见表2。
表 2 摩擦引燃瓦斯试验方案Table 2. Friction ignition gas test schemes瓦斯体积
分数/%摩擦速度/
(m·s−1)摩擦载
质量/kg摩擦试件
SiO2含量/%重复试
验次数6.0 8.0 15 67.85 3 7.0 8.0 15 67.85 3 8.5 8.0 15 67.85 3 10.0 8.0 15 67.85 3 11.5 8.0 15 67.85 3 10.0 4.0 15 67.85 3 10.0 6.0 15 67.85 3 10.0 8.0 15 67.85 3 10.0 10.0 15 67.85 3 10.0 12.0 15 67.85 3 10.0 14.0 15 67.85 3 10.0 8.0 15 67.85 3 10.0 8.0 16 67.85 3 10.0 8.0 17 67.85 3 10.0 8.0 18 67.85 3 10.0 8.0 19 67.85 3 10.0 8.0 15 57.53 3 10.0 8.0 15 61.44 3 10.0 8.0 15 67.85 3 3. 试验结果
3.1 摩擦引燃瓦斯爆炸范围计算
采用高速摄像机记录摩擦引燃瓦斯直至瓦斯完全爆炸的全过程。导出该过程中瓦斯爆炸图像后,通过MATLAB编写程序获得瓦斯燃烧过程中的每帧图像的明度信息,确定瓦斯燃烧区域明度值范围,计算得出瓦斯燃烧比例。具体明度获取过程为:
1)通过MATLAB中imread函数获取瓦斯燃烧过程中的每帧图像。
2)遍历像素数组索引获取每帧图像像素坐标。
3)使用size函数来获取图片的尺寸以及rgb2xyz函数来获取像素的RGB值。
4)通过式(1)计算明度。
$$ L{\text{ = }}\sqrt[\leftroot{-1}\uproot{12}{{2.2}}]{{\frac{{{{\left( {R/{\text{255}}} \right)}^{{\text{2}}{\text{.2}}}} + {{\left( {{\text{1}}{\text{.5}}G/{\text{255}}} \right)}^{{\text{2}}{\text{.2}}}} + {{\left( {{\text{0}}{\text{.6}}B/{\text{255}}} \right)}^{{\text{2}}{\text{.2}}}}}}{{{\text{1 + 1}}{\text{.}}{{\text{5}}^{{\text{2}}{\text{.2}}}}{\text{ + 0}}{\text{.}}{{\text{6}}^{{\text{2}}{\text{.2}}}}}}}} $$ (1) 式中:L为明度值,范围为0~1;R为红色光功率,范围为0~255;G 为绿色光功率,范围为0~255;B为蓝色光功率,范围为0~255。
3.2 瓦斯体积分数对摩擦引燃瓦斯的影响
设置5组不同瓦斯体积分数(6.0%、7.0%、8.5%、10.0%、11.5%)砂岩摩擦引燃瓦斯试验,试验摩擦速度为8 m/s,摩擦载质量15 kg,摩擦试件SiO2含量为67.85%,每组试验重复3次,命名为试验1、试验2、试验3。当瓦斯体积分数为6.0%时,3次试验瓦斯均未爆炸,当瓦斯体积分数为7.0%、8.5%、10.0%、11.5%时,试验发生瓦斯爆炸,爆炸时摩擦速度均已达到8 m/s。不同瓦斯体积分数下砂岩摩擦引发瓦斯爆炸时间如图1所示。
为排除试验误差对试验结果的影响,取每组试验的3次瓦斯爆炸时间均值进行分析。试验中,当瓦斯体积分数为6.0%时,摩擦未引发瓦斯爆炸。由图1可知:摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸的最低体积分数为7.0%;随瓦斯体积分数增加,试验瓦斯发生爆炸时摩擦速度均已达到8 m/s;当瓦斯体积分数为7.0%时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间为32.33 s;瓦斯体积分数增加至8.5%时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间缩短至21.78 s,缩短幅度为32.63%;瓦斯体积分数增加为10.0%时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间缩短至19.63 s,缩短幅度为10.95%;随着瓦斯体积分数继续增加至11.5%时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间延长至23.16 s,延长幅度为17.98%。由此可得随瓦斯体积分数自6.0%开始增加,摩擦由未诱发瓦斯爆炸到诱发瓦斯爆炸,瓦斯体积分数继续增加后,摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸时间逐渐缩短,缩短幅度下降,瓦斯体积分数为10.0%时,摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸时间最短,随后瓦斯体积分数增加使摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸时间延长。
不同体积分数瓦斯在摩擦试验箱内爆炸过程如图2所示,不同体积分数瓦斯在摩擦试验箱内爆炸过程中瓦斯燃烧比例变化如图3所示。
由图2可知:摩擦试验箱内瓦斯爆炸过程分为砂岩摩擦面燃烧瓦斯与瓦斯爆炸扩散2个阶段。在砂岩摩擦面燃烧瓦斯阶段,摩擦试验箱内瓦斯被转动试件摩擦表面燃烧,在0~40 ms瓦斯燃烧路径为自摩擦试件与转动试件接触点沿环形转动试件表面顺时针方向蔓延,因此砂岩摩擦产生的高温热表面是砂岩摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸的主要原因。
由图3可知:瓦斯体积分数为7.0%、8.5%时,摩擦试验箱内全部瓦斯燃烧耗时140 ms;瓦斯体积分数为10.0%时,摩擦试验箱内全部瓦斯燃烧耗时100 ms;瓦斯体积分数为11.5%时,摩擦试验箱内全部瓦斯燃烧耗时80 ms;相同时刻摩擦试验箱内瓦斯燃烧比例随瓦斯体积分数的增加而增大。由此可知:瓦斯体积分数在7.0%~11.5%范围内,其体积分数的增加对瓦斯爆炸传播具有促进作用;瓦斯体积分数为7.0%、8.5%时,其燃烧比例变化趋势为缓慢增大-快速增大-缓慢增大;瓦斯体积分数为10.0%、11.5%时,其燃烧比例变化趋势为缓慢增大-快速增大-缓慢增大-快速增大,这是因为较高的瓦斯含量在燃烧后期已将氧气含量消耗至较低水平,因此对剩余瓦斯快速燃烧产生抑制作用。
3.3 摩擦力对摩擦引燃瓦斯的影响
设置5组不同摩擦力(载质量15.0、16.0、17.0、18.0、19.0 kg)砂岩摩擦引燃瓦斯试验,试验摩擦速度为8 m/s,瓦斯体积分数10.0%,摩擦试件SiO2含量为67.85%,每组试验重复3次。当瓦斯体积分数为6.0%时,3次试验瓦斯均未爆炸,当瓦斯体积分数为7.0%、8.5%、10.0%、11.5%时,试验发生瓦斯爆炸。不同载质量下砂岩摩擦引发瓦斯爆炸时间如图4所示。
为排除试验误差对试验结果的影响,取每组试验的3次瓦斯爆炸时间均值进行分析。5组不同砂岩摩擦力试验均引发瓦斯爆炸,爆炸时摩擦速度均已达到8 m/s。由图4可知:当摩擦试件载质量为15 kg时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间为19.63 s;当摩擦试件载质量增加至16 kg时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间缩短至18.95 s,缩短幅度为3.46%;当摩擦试件载质量增加至17 kg时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间缩短至18.17 s,缩短幅度为4.12%;当摩擦试件载质量增加至18 kg时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间缩短至17.14 s,缩短幅度为5.67%;当摩擦试件载质量增加至19 kg时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间缩短至16.13 s,缩短幅度为5.89%;随着摩擦试件载质量增加,摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸时间逐渐缩短,摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸时间缩短幅度逐渐增加。
3.4 石英成分对摩擦引燃瓦斯的影响
自N4107工作面基本顶、直接顶、直接底中取3组砂岩摩擦试件,利用X射线衍射仪对3组摩擦试件样本物相进行测定分析,得到基本顶、直接顶、直接底3组试样中SiO2含量分别为57.53%、67.85%、61.44%。每组试验重复3次。不同SiO2含量砂岩摩擦引发瓦斯爆炸时间如图5所示。
为排除试验误差对试验结果的影响,取每组试验的3次瓦斯爆炸时间均值进行分析。由图5可知:3组不同SiO2含量砂岩摩擦试验均引发瓦斯爆炸,爆炸时摩擦速度均已达到8 m/s;当砂岩摩擦试件SiO2含量为57.53%时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间为15.82 s;砂岩摩擦试件SiO2含量为61.44%时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间为17.44 s;当砂岩摩擦试件SiO2含量为67.85%时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间为19.63 s。因此认为砂岩摩擦试件SiO2含量影响着摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸的难易程度,更高SiO2含量的砂岩摩擦将增大诱发瓦斯爆炸的风险。
3.5 摩擦速度对摩擦引燃瓦斯的影响
设置6组不同摩擦速度(4.0、6.0、8.0、10.0、12.0、14.0 m/s)砂岩摩擦引燃瓦斯试验,试验载重15.0 kg,瓦斯体积分数10.0%,摩擦试件SiO2含量为67.85%,每组试验重复3次。当摩擦速度为4.0、6.0 m/s时,3次试验瓦斯均未爆炸,不同摩擦速度下砂岩摩擦引发瓦斯爆炸时间如图6所示。
为排除试验误差对试验结果的影响,取每组试验的3次瓦斯爆炸时间均值进行分析。由图6可知:当砂岩最大摩擦速度为8.0、10.0、12.0 m/s时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间分别为19.63、17.20、15.50 s,3组试验中瓦斯爆炸前转动试件已达到最大摩擦速度;当砂岩最大摩擦速度为14.0 m/s时,瓦斯平均爆炸时间为15.21 s,瓦斯爆炸前转动试件摩擦速度加速至12.9 m/s;当砂岩最大摩擦速度为6.0 m/s及以下时,长时间的摩擦并不会使转动试件表面升温至瓦斯着火点;当砂岩摩擦速度为8.0 m/s及以上时,长时间的摩擦使转动试件表面逐渐升温至瓦斯着火点,速度的增大有利于更快的升温;当摩擦速度达到12.9 m/s时,摩擦速度的加速过程已使转动试件表面升温至着火点。因此认为对于恒定加速度下摩擦试件有最低临界速度与最高临界速度:低于最低临界速度则转动试件表面不会升温至瓦斯着火点诱发瓦斯爆炸;高于最低临界速度且低于最高临界速度时,需在达到该速度后持续摩擦一定时间转动试件表面方可达到瓦斯着火点,在此速度区间内最大摩擦速度与摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸时间呈负相关。当摩擦速度达到最高临界速度时转动试件表面将升温至瓦斯着火点。
4. 结 语
1)瓦斯体积分数低于6.0%时,砂岩摩擦不能诱发瓦斯爆炸到诱发瓦斯爆炸,瓦斯体积分数为7.0%~11.5%时,摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸时间随瓦斯体积分数增加而先缩短后延长,瓦斯体积分数为10.0%时,摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸时间最短。
2)摩擦试验箱内瓦斯爆炸过程分为砂岩摩擦面燃烧瓦斯与瓦斯爆炸扩散2个阶段。在砂岩摩擦面燃烧瓦斯阶段,摩擦试验箱内瓦斯被转动试件摩擦表面燃烧,因此砂岩摩擦产生的高温热表面是砂岩摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸的主要原因。在瓦斯爆炸扩散阶段,瓦斯体积分数为7.0%、8.5%时,其燃烧比例变化趋势为缓慢增大-快速增大-缓慢增大;瓦斯体积分数为10.0%、11.5%时,其燃烧比例变化趋势为缓慢增大-快速增大-缓慢增大-快速增大。
3)随着摩擦试件载重增加使摩擦试件与转动试件之间摩擦力增大,加快了转动试件表面升温至瓦斯着火点,摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸时间逐渐缩短,且摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸时间缩短幅度逐渐增加。
4)砂岩摩擦试件SiO2含量影响着摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸的难易程度,更高SiO2含量的砂岩摩擦将增大诱发瓦斯爆炸的风险。
5)恒定加速度下摩擦试件有最低临界速度与最高临界速度。低于最低临界速度则转动试件表面不会升温至瓦斯着火点诱发瓦斯爆炸。高于最低临界速度且低于最高临界速度时,需在达到该速度后持续摩擦一定时间转动试件表面方可达到瓦斯着火点,在此速度区间内最大摩擦速度与摩擦诱发瓦斯爆炸时间呈负相关。当摩擦速度达到最高临界速度时转动试件表面将升温至瓦斯着火点。
-
表 1 试验工况表
Table 1 Experimental condition table
A 工况 B1 B2 B3 A1 A1B1 A1B2 A1B3 A2 A2B1 A2B2 A2B3 A3 A3B1 A3B2 A3B3 表 2 点火能量为10.56 mJ时的火焰传播速度
Table 2 Flame propagation speed at ignition energy of 10.56 mJ
瓦斯体积分数/% 火焰传播速度/(m·s−1) T1~T2 T2~T3 T3~T4 T4~T5 T5~T6 5.5 68.75 93.31 148.08 209.27 227.70 9.5 308.86 370.03 424.39 511.36 535.30 14.0 84.03 124.54 229.46 315.11 376.33 表 3 不同瓦斯体积分数条件下的各参数值
Table 3 Parameter values under different gas volume fraction conditions
瓦斯体积
分数/%斜率 截距 相关
系数火焰传播
速度的不
确定度斜率的
不确定度截距的
不确定度5.5 741.05 − 3461.8 0.983 14.82 80.27 391.22 9.5 1 016.1 − 4521.5 0.988 16.69 90.42 440.71 14.5 1 325.4 − 6232.8 0.991 19.61 106.24 517.80 表 4 不同点火能量条件下的各参数值
Table 4 Parameter values under different ignition energy conditions
点火能
量/mJ斜率 截距 相关
系数火焰传播
速度的不
确定度斜率的
不确定度截距的
不确定度4.76 1 207.4 −5 563.6 0.994 14.23 77.11 375.83 10.35 1 016.1 −4 521.5 0.988 16.69 90.42 440.71 25.35 1 176.8 −5 253.0 0.987 20.70 112.31 546.51 表 5 火焰传播速度特征参数表
Table 5 Characteristic parameters of flame propagation speed
传感器编号 传感器间距/mm 火焰传播速度/(m·s−1) 工况A1B1 工况A1B2 工况A1B3 工况A2B1 工况A2B2 工况A2B3 工况A3B1 工况A3B2 工况A3B3 T1~T2 1 666 45.24 182.35 70.54 68.75 308.86 84.03 80.81 356.59 107.93 T2~T3 1 667 74.68 241.38 101.97 93.31 370.03 124.64 110.05 406.98 141.43 T3~T4 1 667 126.35 316.44 168.31 148.08 424.39 229.46 173.28 456.96 262.60 T4~T5 1 666 156.77 407.04 252.16 209.27 511.36 315.11 262.53 565.90 376.33 T5~T6 2 267 174.44 452.49 315.11 227.70 535.30 376.33 297.08 621.44 402.52 表 6 最大火焰传播速度显著性影响结果
Table 6 Significant effect results of the maximum flame propagation speed
来源 自由度 均方 F值 分位数Fa 结果 A 2 23 956.22 143.22 5.71 显著性影响 B 2 138 829.35 829.67 5.71 显著性影响 AB 4 953.03 5.70 4.72 显著性影响 误差 9 167.33 总和 17 表 7 瓦斯爆炸压力峰值和压力上升速率特征参数表
Table 7 Gas explosion pressure peak and pressure rise rate characteristic parameters table
工况 爆炸压力峰值/kPa 爆炸压力上升速率/(kPa·s−1) A1B1 98 155 A1B2 144 251 A1B3 112 178 A2B1 124 217 A2B2 180 326 A2B3 146 248 A3B1 150 263 A3B2 217 425 A3B3 168 303 表 8 瓦斯爆炸压力峰值显著性影响结果
Table 8 Significant effect results of gas explosion pressure peak value
来源 自由度 均方 F值 分位数Fa 结果 A 2 5460.59 8.68 5.71 显著性影响 B 2 4960.59 7.89 5.71 显著性影响 AB 4 74.04 0.12 4.72 没有显著性影响 误差 9 628.89 总和 17 表 9 瓦斯爆炸压力上升速率显著性影响结果
Table 9 Significant effect results of gas explosion pressure rise rate
来源 自由度 均方 F值 分位数Fa 结果 A 2 2761061.91 61.67 5.71 显著性影响 B 2 2422795.24 54.12 5.71 显著性影响 AB 4 67402.38 1.51 4.72 没有显著性影响 误差 9 44769.00 总和 17 -
[1] 蓝航,陈东科,毛德兵. 我国煤矿深部开采现状及灾害防治分析[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2016,44(1):39−46. LAN Hang, CHEN Dongke, MAO Debing. Current status of deep mining and disaster prevention in China[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2016, 44(1): 39−46.
[2] CHEN X J, LI L Y, WANG L, et al. The current situation and prevention and control countermeasures for typical dynamic disasters in kilometer-deep mines in China[J]. Safety Science, 2019, 115: 229−236. doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2019.02.010
[3] 景国勋,穆璐璐. 煤矿瓦斯爆炸事故统计分析及应急管理研究[J]. 安全与环境学报,2023,23(10):3657−3665. JING Guoxun, MU Lulu. Study on statistical analysis and emergency management of coal mine gas explosion accident[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2023, 23(10): 3657−3665.
[4] 黄文祥,李树刚,李孝斌,等. 不同点火能量作用下管道内瓦斯爆炸火焰传播特征[J]. 煤矿安全,2011,42(8):7−10. HUANG Wenxiang, LI Shugang, LI Xiaobin, et al. Flame propagation characteristics of gas explosion that under different ignition energy in duct[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2011, 42(8): 7−10.
[5] 仇锐来. 点火能量对瓦斯爆炸火焰传播速度的影响[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2011,39(3):52−55. QIU Ruilai. Ignition energy influenced to travel speed of gas explosion flame[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2011, 39(3): 52−55.
[6] 仇锐来,张延松,司荣军,等. 点火能量对瓦斯爆炸传播影响的实验研究[J]. 矿业安全与环保,2011,38(1):6−9. QIU Ruilai, ZHANG Yansong, SI Rongjun, et al. Experimental study on influence of ignition energy upon gas explosion propagation[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection, 2011, 38(1): 6−9.
[7] 仇锐来. 点火能量对瓦斯爆炸传播的数值模拟研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2011,42(1):5−8. QIU Ruilai. Numerical simulation study of gas expl-osion dissemination in ingnition energy[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2011, 42(1): 5−8.
[8] 李润之,司荣军. 点火能量对瓦斯爆炸压力影响的实验研究[J]. 矿业安全与环保,2010,37(2):14−16. LI Runzhi, SI Rongjun. Experimental study on impact of ignition energy on gas explosion pressure[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection, 2010, 37(2): 14−16.
[9] 李润之,司荣军. 瓦斯浓度对爆炸压力及压力上升速率影响[J]. 西安科技大学学报,2010,30(1):29−33. LI Runzhi, SI Rongjun. Effect of gas concentration on the explosion pressure and pressure rise rate[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Science and Technology, 2010, 30(1): 29−33.
[10] 徐景德,赖芳芳,杨鑫,等. 强火源条件下瓦斯点火化学热力学特征[J]. 煤矿安全,2015,46(2):158−160. XU Jingde, LAI Fangfang, YANG Xin, et al. Chemical thermodynamics characteristics of gas ignition under strong fire source[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2015, 46(2): 158−160.
[11] 司荣军. 瓦斯浓度对爆炸传播影响的数值模拟研究[J]. 工业安全与环保,2011,37(4):29−30. SI Rongjun. Simulation research of gas concentration on explosion propagation[J]. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection, 2011, 37(4): 29−30.
[12] 赵军凯,王磊,滑帅,等. 瓦斯浓度对瓦斯爆炸影响的数值模拟研究[J]. 矿业安全与环保,2012,39(4):1−4. ZHAO Junkai, WANG Lei, HUA Shuai, et al. Numerical simulation study on the influence of gas concentration on gas explosion[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection, 2012, 39(4): 1−4.
[13] 蔺伟,回岩,王成,等. 瓦斯体积分数对火焰传播规律影响的实验研究[J]. 北京理工大学学报,2015,35(6):551−555. LIN Wei, HUI Yan, WANG Cheng, et al. Experimental investigation about the influence of gas concentration on flame propagation[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2015, 35(6): 551−555.
[14] 余明高,陈传东,王雪燕,等. 管道内瓦斯非均匀预混火焰传播特性实验研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(6):1781−1790. YU Minggao, CHEN Chuandong, WANG Xueyan, et al. Experimental study on combustion characteristics of non-uniform premixed gas within a pipeline[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(6): 1781−1790.
[15] 李祥春,聂百胜,杨春丽,等. 封闭空间内瓦斯浓度对瓦斯爆炸反应动力学特性的影响[J]. 高压物理学报,2017,31(2):135−147. LI Xiangchun, NIE Baisheng, YANG Chunli, et al. Effect of gas concentration on kinetic characteristics of gas explosion in confined space[J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2017, 31(2): 135−147.
[16] 贾泉升,司荣军,李润之,等. 定容条件下瓦斯爆炸超压及爆后气体成分试验研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2019,50(12):1−5. JIA Quansheng, SI Rongjun, LI Runzhi, et al. Experimental study on overpressure and gas composition after gases explosion under constant volume condition[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2019, 50(12): 1−5.
[17] 张莉聪,刘立萍,徐景德. 瓦斯煤尘爆炸火焰传播机理的实验测试系统研究[J]. 华北科技学院学报,2014,11(4):19−24. ZHANG Licong, LIU Liping, XU Jingde. Research on experiment test system of mechanism of fame propagation for gas and coal dust explosion[J]. Journal of North China Institute of Science and Technology, 2014, 11(4): 19−24.



 下载:
下载: