Research on contributing factors of steeply inclined coal seam rock burst based on microseismic spatio-temporal information
-
摘要:
为掌握近直立煤层冲击地压致灾因素,基于矿井开采布局及现场微震监测数据,从时间和空间多维度对矿井微震事件的分布及历次冲击地压事件进行了深入分析,研究了不同开采深度下的致灾因素的演变规律。结果表明:近直立煤层的冲击地压主要由悬空顶板和中间岩柱对工作面产生的应力集中以及煤岩体破裂产生的动载扰动诱发,日推进度、开采深度及遗留煤柱与冲击地压事件的发生也具有强相关关系,是矿井冲击主要致灾因素;矿井浅部开采时中间岩柱受水平构造应力和自重应力对煤岩体产生的“撬动”作用是导致煤岩体失稳破坏的主控因素,进入深部开采后叠加了悬空顶板的“挤压”作用,冲击致灾因素转变为顶板和岩柱的“压+撬”共同作用,而遗留煤柱等因素影响程度减弱。
Abstract:In order to understand the factors leading to rock burst in steeply-inclined coal seams, based on the mining layout and on-site microseismic monitoring data, the distribution of mine microseismic events and previous rock burst events are deeply analyzed from time and space, and the evolution law of disaster factors under different mining depths is studied. The study shows that the rock burst in steeply-inclined coal seams is mainly caused by stress concentration on the working face due to the hanging roof and intermediate rock pillars, as well as the dynamic disturbance induced by the fracture of the coal and rock mass. The daily advance rate, mining depth, and remaining coal pillars are strongly correlated with the occurrence of rock burst events, and are the main factors leading to rock burst in the mine. During shallow mining, the “prying force” effect of the intermediate rock pillars caused by the horizontal tectonic stress and the self-weight stress on the coal-rock mass is the main factor causing instability and failure of the coal-rock mass. After entering deep mining, the “extrusion” effect of the hanging roof is superimposed on the “prying force” effect of the intermediate rock pillars, and the factors leading to rock burst change to the combined “extrusion + prying force” effect of the roof and pillars.
-
煤炭资源是我国主体能源,而超过20%煤炭资源储存于位于西部急倾斜煤层[1-2],其地质、应力和开采条件等与缓倾斜/倾斜煤层差异巨大,向深部开采过程中冲击地压等煤岩动力灾害的防治形势日趋严峻。冲击地压致灾因素辨识是采取针对性防治措施的前提,能大大提高防冲措施的施加效能并降低成本。曹民远等[2-3]基于数据统计的方法分析发现上覆遗留煤柱是近直立煤层冲击地压显现的主要致灾因素,采掘扰动等是冲击地压显现的影响因素;杜涛涛等[4]利用微震监测系统对近直立煤层的“高阶段”区域和围岩进行探测,发现煤体高应力集中和诱冲关键层是冲击地压的主要致灾因素;李兵[5]通过开展不同区域冲击倾向性鉴定、不同尺度冲击危险性评价以及利用微震系统,从微震能量分布与历史矿压显现规律,分析得到了矿井冲击隐蔽致灾因素;李振武等[6]采用理论分析和数值模拟方法,研究了工作面推进过程中覆岩运动及矿压显现规律,辨识工作面冲击地压的诱发因素;荣海等[7]利用地质动力区划方法发现急倾斜特厚煤层的冲击地压事件主要发生于断裂带以及应力梯度区和高应力区的煤岩体中;张冬阳[8]采用层次分析法确定了大屯矿区冲击致灾因素并定量化确定了断层构造等因素的影响权重;陈凡等[9]分析了煤层厚度、倾角、开采深度及采掘干扰等与矿震事件分布的相关性,利用层次分析法(AHP)确定冲击主控因素及对应权重;乔中栋等[10]根据某工作面回采期间全部冲击事件,辨识对冲击事件影响较大的4个致灾因素,并利用层次分析法,计算不同条件下各因素的影响权重,总结其演化规律,为矿井冲击地压防治提供可靠的统计分析结果。此外,还有大量学者[11-15]从地质条件、开采技术和环境因素等方面对井下冲击地压的主控因素进行了辨识。
然而,冲击地压本身是多因素共同作用的结果,不同致灾因素之间存在复杂的非线性关系,目前已有的致灾因素辨识多基于专家经验分析和复杂力学计算,难以及时适应井下多变的地质环境,导致冲击地压的防治缺乏针对性[16]。微震监测系统具有数据连续性、自动监测等优点,主要通过采集顶板破碎或煤岩体断裂产生的震动波信号以判断顶板的运移和煤岩体的破裂从而实现矿井大范围内震动场、应力场等监测[17-18]。利用现场微震监测数据可以辅助相关人员进行动态、实时的主控因素辨识。为此,以乌东煤矿作为工程背景,从时间和空间角度研究其历次冲击地压事件前后微震监测数据的分布信息,辨识冲击地压的主要致灾因素,并分析其随采深增加的演化规律,为冲击地压的高效、精准防治提供理论依据。
1. 工程概况
1.1 工作面背景
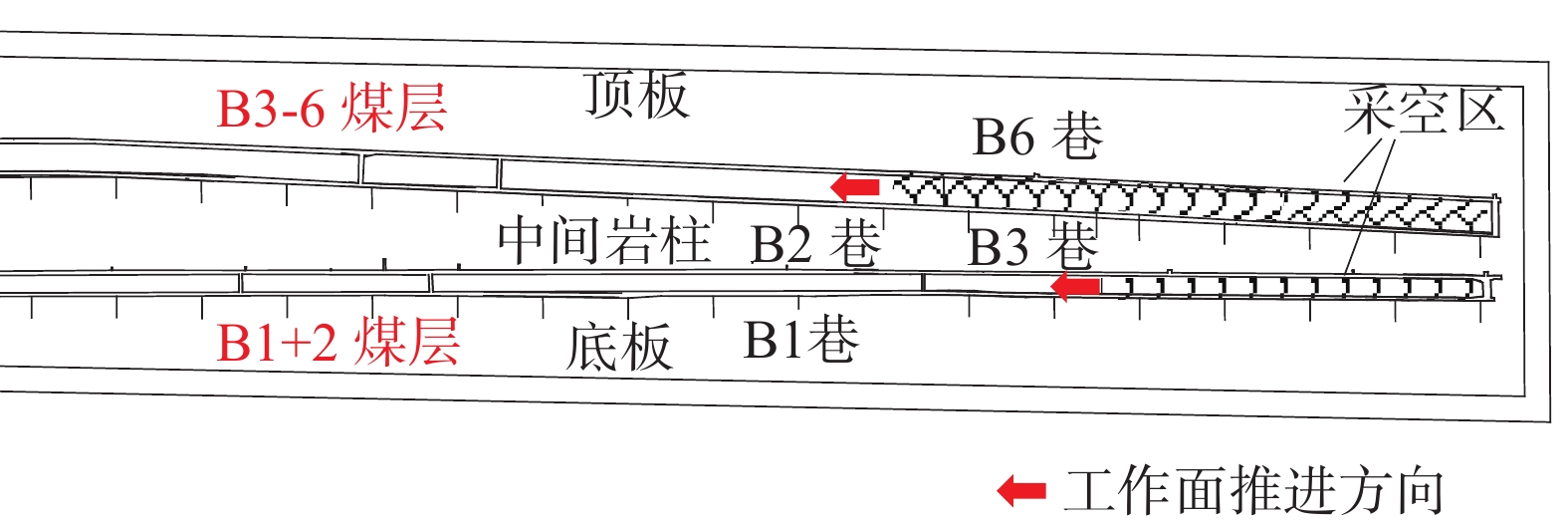
乌东煤矿受早期地质构造运动影响形成典型近直立特厚煤层,目前该矿主要开采南采区B3-6和B1+2煤层,工作面示意图如图1所示。
乌东煤矿南采区煤层平均倾角达87°,两煤层之间由厚度为70~101 m的近直立悬空岩柱分隔。经实验室测定,B3-6、B1+2煤层具有弱冲击倾向性,单轴抗压强度分别为19.801、18.317 MPa,顶底板则以砂岩、粉砂岩和砂质泥岩为主,质地坚硬[1]。该矿采用水平分段综放开采技术开采,阶段开采高度达25 m,各工作面采深跨度较大,随着浅部煤炭资源的枯竭,开采深度的增加导致冲击地压发生频率迅速增高[19]。
1.2 工作面冲击地压事件概述
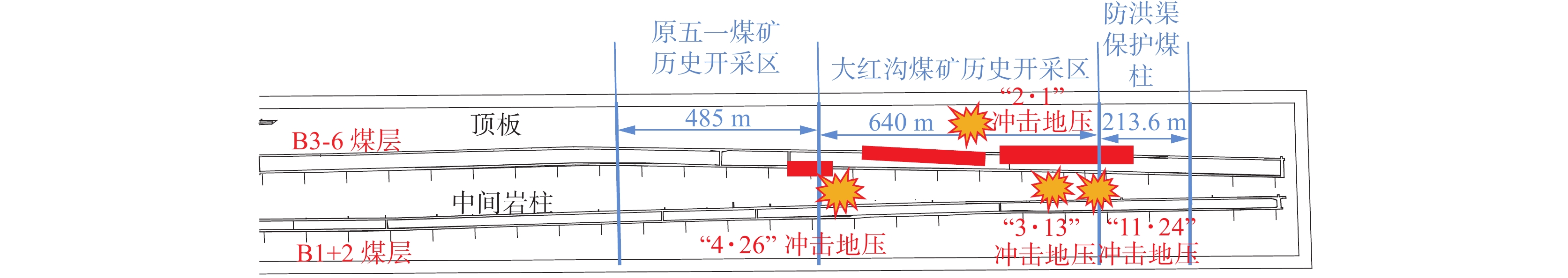
乌东煤矿南采区历史上共发生6次严重冲击地压事件,全部集中于先开采的B3-6煤层,分别为[19]:发生在+500 m B3-6工作面的“2·27”和“7·2”冲击事件(2013年),+475 m B3-6工作面的“3·13”冲击事件(2015年)和+450 m B3-6工作面的“11·24”(2016年)、“2·1”和“4·26”冲击事件(2017年)。由于+500 m B3-6工作面微震监测数据不全,故本文主要研究其它冲击事件,各事件的冲击破坏区域及震源位置如图2所示。
由图2可知:历次冲击地压事件的破坏区域主要位于上覆原五一煤矿历史开采区、大红沟煤矿历史开采区及防洪渠煤柱区,显现位置主要以回采巷道为主且集中于超前工作面;冲击事件破坏程度不一,破坏形式以底鼓、帮鼓、顶板下沉、肩窝下沉为主,且在+500 m开采水平呈现由北(N)帮向南(S)帮、从上到下的方向性,在+475 m和+450 m开采水平呈现由南(S)帮向北(N)帮的方向性。说明乌东煤矿不同开采水平的冲击地压事件主控因素不同,而冲击地压的主控因素辨识是对其进行有效防治的关键,因此有必要研究各冲击事件主控因素并分析其随采深增加的演化规律。
2. 近直立煤层冲击地压致灾因素分析
微震事件的时空分布与矿井应力场、震动场等具有强相关关系,因此从时间和空间多维度对不同开采水平的微震监测数据进行深入分析,可有效辅助冲击地压的致灾因素辨识。
2.1 微震空间维度分析
2.1.1 震动场空间分布规律
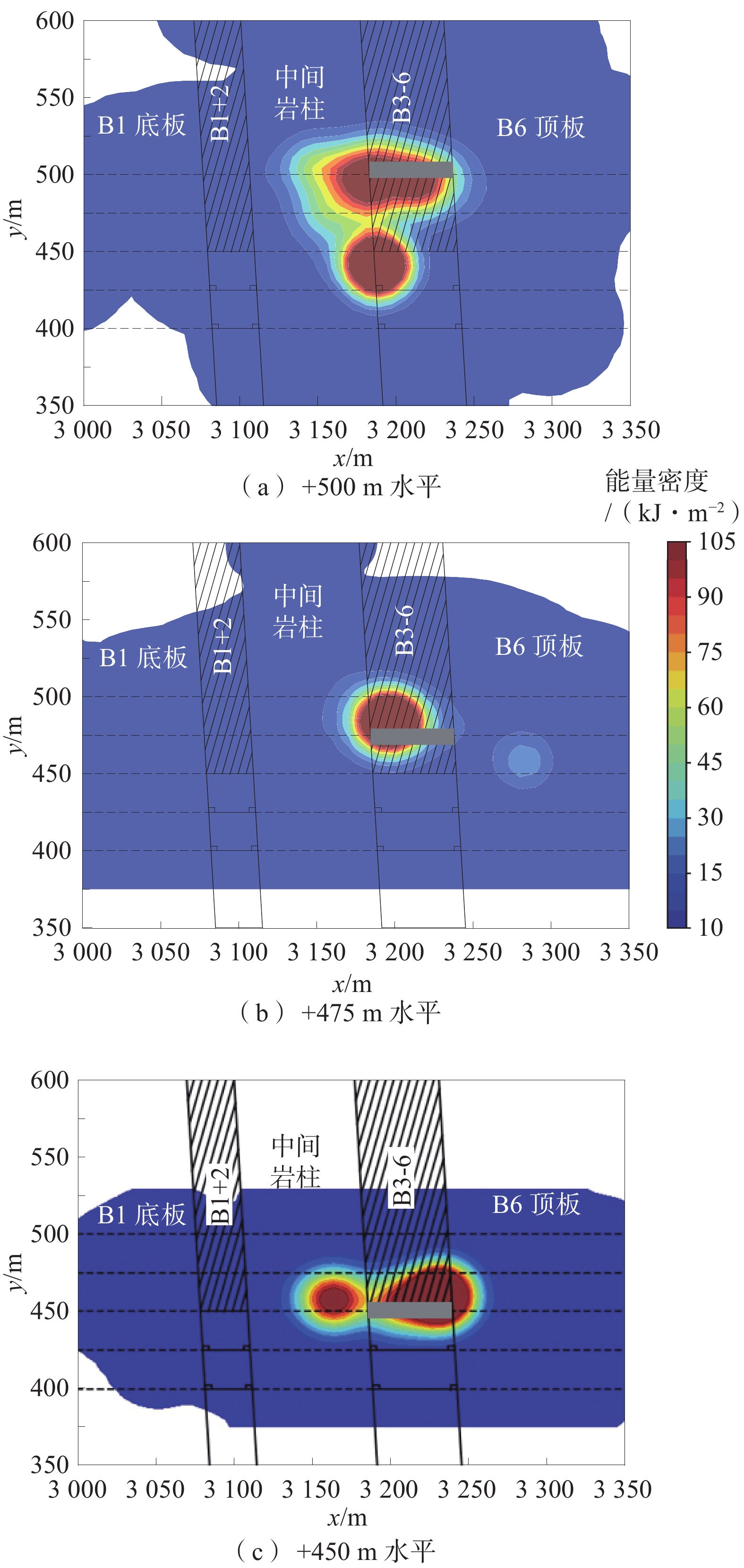
利用Python中matplotlib第三方库绘制B3-6煤层不同采深工作面回采全过程微震的能量密度云图(图3),分析不同位置煤岩体单位面积的能量释放大小。
由图3可知:红色矿震高能区随采深增加由纵向分布且集中于岩柱侧转变为横向分布于顶板和岩柱侧,即在浅部开采时中间岩柱受水平构造应力和自重应力对煤岩体产生的“撬动”作用是导致煤岩体失稳破坏的主要因素,而进入深部开采后由于采空区黄土的变形与下沉,B6顶板悬空面积逐渐增大并发生弯曲变形,对工作面产生“挤压”作用,其内部储存的弹性能瞬间释放从而诱发大能量矿震事件,也就是说悬空顶板与中间岩柱对煤岩体的“压+撬”共同作用是B3-6煤层冲击地压的主要致灾因素之一[20]。
2.1.2 应力场空间分布规律
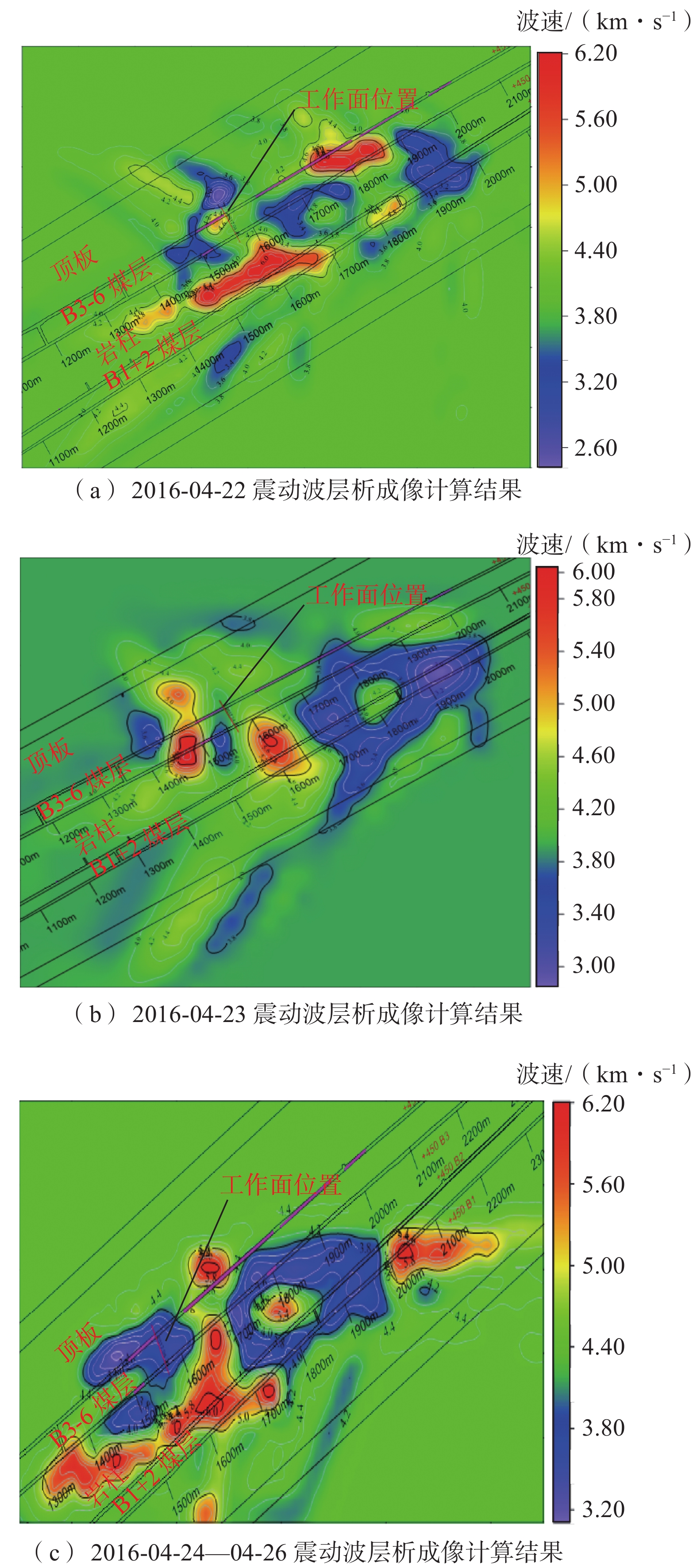
研究表明煤岩体内部纵波波速随承载应力的增加而增加,因此,利用震动波层析成像技术绘制冲击地压发生前波速异常云图,以“4·26”冲击地压事件为例,绘制的结果如图4所示。
由图4(a)可知:高波速区域主要集中在B3-6煤层和中间岩柱,表明上述区域应力集中,同时在工作面走向位置的高波速区有向B3-6煤体延伸的趋势,这意味着随着采空区的不断增加,中间岩柱可能发生大规模断裂,从而对工作面施加动态载荷。由图4(b)可知:高波速区集中于中间岩柱和悬空顶板,相比前1 d该区域聚集程度更高且最大波速上升至6.0 m/s,应力集中程度加剧,这表明该区域一旦受到强动载扰动则极易诱发冲击地压,现场实测结果也显示此次冲击地压的震源位于工作面前方的中间岩柱中。由图4(c)可知:冲击发生后工作面周围的波速异常程度减小的则显示在冲击地压发生后,工作面附近小范围内的波速异常程度减小,应力集中区远离中间岩柱破裂带向深部转移,这是由于中间岩柱破裂产生的能量突然释放导致的,表明此次冲击地压的主要致灾因素为中间岩柱。
通过微震能量场和震动场的空间演化规律,揭示出近直立层间岩柱和悬空顶板对煤体撬动和挤压产生的高应力集中以及岩柱破裂产生的动载荷为乌东煤矿的主要诱冲因素之一。
2.2 微震时序维度分析
通过对乌东煤矿南采区B3-6煤层发生的冲击地压事故前后微震监测数据进行统计分析,重点研究日推进度、开采深度等冲击地压致灾因素与冲击事故之间的关联以确定主要致冲因素。
2.2.1 日推进度关联分析
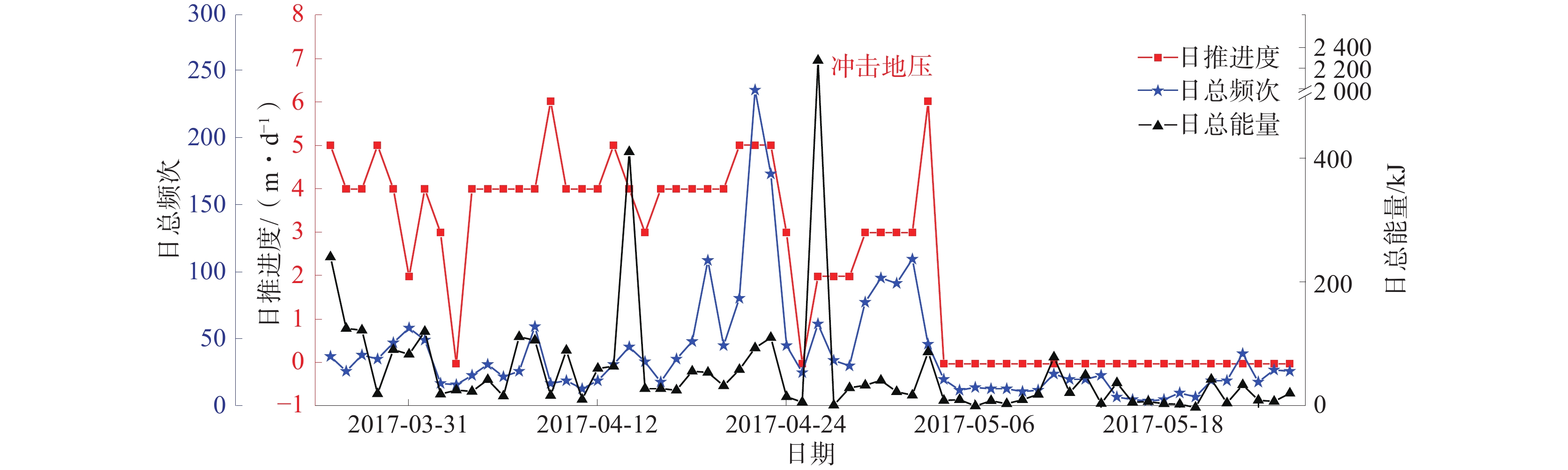
井下开采活动不仅对煤岩体施加连续不断地动载扰动,并破坏了其内部的应力平衡,开采活动的强度对于围岩活动性程度具有重要影响。以“4·26”事件前后2个月的微震监测数据为例,绘制的日推进度与微震日总能量、频次的时序演化曲线如图5所示。
由图5可以看出:自4月1日至10日,乌东煤矿日推进度由0 m/d迅速上升至6 m/d,产生了较大的波动,在4月14日该矿出现了1次能量大于105 J的大能量矿震事件但并未造成明显破坏;之后继续以4 m/d左右的推进度开采,但在4月23日后日推进度迅速由5 m/d降为0 m/d,紧接着发生了“4·26”冲击地压事件。表明开采强度与冲击地压的发生具有明显正相关关系,开采活动的剧烈变化会使煤岩体内部积聚的弹性能以较大的速率释放出来,从而增加冲击地压的发生概率[21],因此,开采强度的波动程度为冲击地压的致灾因素之一。
2.2.2 上覆遗留煤柱关联分析
遗留煤柱的存在会造成附近区域的应力分布不均衡,煤岩体内部积聚弹性能至储能极限后会导致冲击地压的发生。乌东煤矿南采区上覆有防洪渠保护煤柱、大红沟煤矿和原五一煤矿历史开采区遗留煤柱,工作面开采至下方时受其影响冲击危险程度增大。+450 m B3-6工作面为例,绘制的全工作面微震日总能量、频次的时序演化曲线如图6所示,其中①、②、③分别表示开采防洪渠煤柱区、大红沟煤矿历史开采区和原五一煤矿历史开采区期间,④表示停产。
由图6可知:当工作面位置由正常开采区进入遗留煤柱影响区时,日总能量和频次出现剧烈上升,同时微震整体能级也出现明显升高,特别在+450 m B3-6工作面过②、③区域时该现象最为显著;而在工作面出遗留煤柱影响区后,微震能量和频次较之前出现明显下降。同时,图2中也可以看出+450 m B3-6工作面历次冲击地压事件震源位置都集中于②、③遗留煤柱影响区,这表明遗留煤柱是乌东煤矿冲击地压的致灾因素之一,并且受特殊地质条件及开采方式影响,该矿上覆遗留煤柱在经过多分层开采后仍对冲击地压存在明显影响。
2.2.3 开采深度关联分析
乌东煤矿采用水平分段综放开采技术开采,阶段开采高度达25 m,各工作面采深跨度较大,且不同采深工作面几乎都发生过严重冲击地压事件,因此需研究不同采深对冲击地压事件的影响。以B3-6煤层各开采水平工作面微震监测数据为研究对象,绘制各能级微震事件的能量、频次占比分布图的B3~6煤层各水平如图7所示。
由图7可知:随着开采深度的增加,1×104 J及以上能级的微震事件占开采全过程释放总能量的比例越来越高,而其发生频次的占比却降低了,其形式逐渐由“低能高频”转化为“高能低频”,说明进入深部开采阶段后,煤岩体内部微裂隙扩展至宏观断裂面的过程缩短,其内部积聚的高弹性应变能由阶段性耗散逐渐转变为瞬间释放,更容易造成煤岩体突然、剧烈的破坏,围岩冲击危险程度增加、工作面发生冲击危险的概率及破坏程度也随之增加,因此,开采深度也是影响冲击地压事故的一项重要影响因素。
综上,通过微震的时空演化信息,得到了乌东煤矿应力场、震动场等分布特征,得出近直立煤层冲击地压主要致灾因素包括悬空顶板和层间岩柱的“压+撬”作用、各历史开采区的遗留煤柱导致的应力集中和动静载扰动以及矿井开采强度和采深,对以上因素进行针对性防治是降低近直立煤层开采过程冲击地压危险的关键。
3. 近直立煤层致冲因素定量辨识
根据历次冲击地压事件的发生情况,对不同开采水平下各致灾因素进行定量辨识。目前,很多学者采用层次分析法对冲击地压的主控因素进行权重量化,但是,在对各指标因素的重要程度进行对比的时候,常规的 AHP 方法往往使用1~9标记法来构建判断矩阵,但是这样会使得矩阵比较主观盲目,不能体现出人们评估思路的模糊特性。用三角模糊数来代表专家对指标重要程度的判断,从而建立了1个模糊判断矩阵,进而来确定评估指标的权重。可以有效避免这一情况的发生。
3.1 基于三角模糊数改进AHP的权重分析方法
1)根据得到的影响近直立煤层冲击危险的因素,使用一种单层次的模型结构,该模型结构包含1个决策目标C和1层准则层,该准则层是隶属于目标C的n个因素(A1,A2,A3,$\cdots $,An)。
2)对准则层各影响因素两两对比进行重要性判断,得到结果为$ a_{i j}=\left(l_{ij}, m_{i j}, p_{ij}\right) $,$ a_{i j} $为因素 i 比j的相对重要程度,$ l_{ij} $为重要程度的下限,$ p_{ij} $为重要程度的上限,$ m_{{ij}} $为重要程度的最大可能值,$ a_{ji}=\left(1 / l_{i j}, 1 / m_{ij}, 1 / p_{ij}\right) $。
3)构建模糊中值矩阵$ {\boldsymbol{M}}=\left(m_{ij}\right)_{n \times n} $,并进行一致性检验。
$$ \boldsymbol{M}=\left[\begin{array}{cccc} m_{11} & m_{12} & \cdots & m_{1 n} \\ m_{21} & m_{22} & \cdots & m_{2 n} \\ \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots \\ m_{n 1} & m_{n 2} & \cdots & m_{n n} \end{array}\right] $$ 4)生成模糊判断因子矩阵E:
$$ {\boldsymbol{E}}=\left[\begin{array}{cccc} 1 & 1+s_{12} & \cdots & 1+s_{1 n} \\ 1+s_{21} & 1 & \cdots & 1+s_{2 n} \\ \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots \\ 1+s_{n 1} & 1+s_{n 2} & \cdots & 1 \end{array}\right] $$ 式中:$ s_{i j}=\left(p_{i j}-l_{i j}\right) /\left(2 m_{i j}\right) $,$ s_{ij} $为专家评价的标准偏差,数值较大,表示该评价具有较强的模糊性和较低的可信度;数值较低,说明了该方法的可靠性较高,且具有较低的模糊性。所以,它所组成的模糊判定因素矩阵 E本质上就是1个专家判定的可信度矩阵。
5)构造1个调整判断矩阵Q,其中Q = M × E,同时,把Q转化成对角线为1的矩阵Q’。
$$ Q^{\prime}=\left[\begin{array}{cccc} 1 & \delta_{12} & \cdots & \delta_{1 n} \\ \delta_{21} & 1 & \cdots & \delta_{2 n} \\ \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots \\ \delta_{n 1} & \delta_{n 2} & \cdots & 1 \end{array}\right] $$ 6)权重计算。用特征值法对上述矩阵Q’ 进行计算,得到因素 i 的权重,同时归一化处理得到各个因素的权重ω。
3.2 冲击地压事件影响因素权重量化
根据近直立煤层冲击地压主要致灾因素:顶板和岩柱(A1)、历史遗留煤柱(A2)、开采强度(A3)、开采深度(A4),建立单层次模型。进行乌东煤矿B3-6煤层发生的各冲击地压事件的主控因素进行权重量化分析。
以B3-6煤层+500 m开水水平发生的“2·27”冲击事故为例进行详细的权重计算。此事件的影响因素重要程度判断结果见表1。对模糊中值矩阵$ {\boldsymbol{M}}=\left(m_{ij}\right)_{n \times n} $进行一致性检验。计算得其随机一致性比率CR=0.072<0.1,满足要求。
表 1 “2·27”冲击事故影响因素重要程度判断结果Table 1. Determination results of the importance of factors affecting the “2-27” rock burst accident顶板和岩柱 遗留煤柱 开采强度 开采深度 顶板和岩柱 (1,1,1) (1.74,3.92,8.12) (1.54,2.15,7.56) (0.89,1.76,4.09) 遗留煤柱 (0.09,0.84,0.57) (1,1,1) (0.87,1.65,4.45) (0.19,0.47,3.37) 开采强度 (0.13,0.46,0.69) (0.23,0.65,1.12) (1,1,1) (0.19,0.35,0.88) 开采深度 (0.15,0.34,1.1 ) (0.20,2.34,4.13) (1.23,2.23,4.76) (1,1,1) 生成模糊判断因子矩阵:
$$ {\boldsymbol{E}}=\left[\begin{array}{cccc} 1.00 & 3.92 & 2.15 & 1.76 \\ 0.84 & 1.00 & 1.65 & 0.47 \\ 0.46 & 0.65 & 1.00 & 0.35 \\ 0.34 & 2.34 & 2.23 & 1.00 \end{array}\right] $$ 计算调节矩阵:
$$ {\boldsymbol{Q}}={\boldsymbol{M}} \times {\boldsymbol{E}}=\left[\begin{array}{rrrr} 13.74 & 11.53 & 15.86 & 25.05 \\ 5.91 & 5.34 & 6.60 & 9.69 \\ 3.74 & 3.31 & 4.09 & 6.04 \\ 9.35 & 7.45 & 9.71 & 16.27 \end{array}\right] $$ 转化为对角线为1的矩阵:
$$ {\boldsymbol{Q}}^{\prime}=\left[\begin{array}{cccc} 1.00 & 2.15 & 3.88 & 1.54 \\ 0.43 & 1.00 & 1.61 & 0.60 \\ 0.27 & 0.62 & 1.00 & 0.37 \\ 0.68 & 1.39 & 2.37 & 1.00 \end{array}\right] $$ 利用特征值法求得的顶板和岩柱、遗留煤柱、开采强度、开采深度的权重矩阵为:W=[0.428 4,0.181 3,0.113 2,0.277 1]。
可知造成该事故的最大权重因素为顶板和岩柱,即主控因素为顶板和岩柱,其次是开采深度,可见开采深度对冲击的影响相当大。除此之外,在对不同开采水平历次冲击地压事件的致灾因素进行权重量化后可知,在矿井由浅部到深部开采过程中,顶板和岩柱、开采深度的影响逐渐增大,其产生的动静载和“压撬”作用导致的应力集中成为诱发冲击地压的主控因素;遗留煤柱、开采强度的影响逐渐减小。
4. 结 语
1)基于微震空间震动场及应力场分布信息,得出:乌东矿近直立煤层冲击地压主要由悬空顶板和中间岩柱对工作面产生的应力集中以及岩体破裂产生的动载扰动诱发的。
2)通过分析日推进度、开采深度及遗留煤柱等冲击地压致灾因素与冲击事故之间的关联性,得出上述因素与冲击事件具有强相关关系,是近直立煤层的主要致灾因素。
3)乌东煤矿历次冲击地压事件的破坏程度、破坏形式不一,冲击地压主控因素随采深增加发生较大变化,在浅部受遗留煤柱应力集中影响大于深部,并且在经过多分层开采后遗留煤柱应力作用仍存在。
4)近直立煤层不同开采深度下冲击地压的致灾因素的演变规律为:浅部开采时中间岩柱受水平构造应力和自重应力对煤岩体产生的“撬动”作用是导致煤岩体失稳破坏的主要因素,而深部开采则叠加了顶板的“挤压”作用,冲击致灾因素转变为顶板和岩柱的“压+撬”共同作用。
-
表 1 “2·27”冲击事故影响因素重要程度判断结果
Table 1 Determination results of the importance of factors affecting the “2-27” rock burst accident
顶板和岩柱 遗留煤柱 开采强度 开采深度 顶板和岩柱 (1,1,1) (1.74,3.92,8.12) (1.54,2.15,7.56) (0.89,1.76,4.09) 遗留煤柱 (0.09,0.84,0.57) (1,1,1) (0.87,1.65,4.45) (0.19,0.47,3.37) 开采强度 (0.13,0.46,0.69) (0.23,0.65,1.12) (1,1,1) (0.19,0.35,0.88) 开采深度 (0.15,0.34,1.1 ) (0.20,2.34,4.13) (1.23,2.23,4.76) (1,1,1) -
[1] 陈建强,宋大钊,常博,等. 近直立煤层冲击危险静动态评价方法研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2023,51(9):24−34. doi: 10.12438/cst.2022-1256 CHEN Jianqiang, SONG Dazhao, CHANG Bo, et al. Static-dynamic coupling rockburst risk assessment method in near-vertical coal seams[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2023, 51(9): 24−34. doi: 10.12438/cst.2022-1256
[2] 曹民远,陈建强,闫瑞兵,等. 基于数据分析的近直立煤层冲击地压致灾因素研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2019,47(12):32−37. CAO Minyuan, CHEN Jianqiang, YAN Ruibing, et al. Study on factors affecting rock burst of sub-erectcoal seam based on data analysis[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2019, 47(12): 32−37.
[3] 曹民远,孙雪亮,杨磊,等. 急倾斜煤层综放工作面冲击危险性评价研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2019,47(2):47−52. CAO Minyuan, SUN Xueliang, YANG Lei, et al. Study on rock burst risk assessment of fully-mechanized top coal caving mining face in steep coal seam[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2019, 47(2): 47−52.
[4] 杜涛涛,李康,蓝航,等. 近直立特厚煤层冲击地压致灾过程分析[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2018,35(1):140−145. DU Taotao, LI Kang, LAN Hang, et al. Rockburst process analysis in steeply-inclined extremely-thick coal seam[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2018, 35(1): 140−145.
[5] 李兵. 张双楼煤矿冲击地压隐蔽致灾因素分析及治理技术研究[J]. 中国煤炭,2022,48(S2):76−85. LI Bing. Analysis of the rock burst hidden disaster-causing factors and study on the control technology in Zhangshuanglou Coal Mine[J]. China Coal, 2022, 48(S2): 76−85.
[6] 李振武,何建新,沈建波. C2316工作面冲击地压诱发因素及矿压显现特征分析[J]. 煤炭与化工,2023,46(1):1−3. LI Zhenwu, HE Jianxin, SHEN Jianbo. Analysis on inducing factors of rockburst and characteristics of ground pressure behavior in No. C2316 Face[J]. Coal and Chemical Industry, 2023, 46(1): 1−3.
[7] 荣海,张宏伟,陈建强,等. 基于多因素模式识别的急倾斜特厚煤层冲击地压危险性预测[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2018,35(1):125−132. RONG Hai, ZHANG Hongwei, CHEN Jianqiang, et al. Rockburst-risk prediction in steep-inclined and extremely thick coal seams based on the multi-factor pattern recognition method[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2018, 35(1): 125−132.
[8] 张冬阳. 大屯矿区冲击矿压主控因素与危险性矿震判识研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2021. [9] 陈凡,曹安业,窦林名,等. 基于区域划分与主控因素辨识的冲击危险性评价方法[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(3):607−615. CHEN Fan, CAO Anye, DOU Linming, et al. Method of coal burst hazard assessment based on region division and identification of main impact factors[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2018, 43(3): 607−615.
[10] 乔中栋,屈英,苏仁元,等. 冲击地压致灾因素相关性分析及权重判断[J]. 煤炭技术,2019,38(3):121−123. QIAO Zhongdong, QU Ying, SU Renyuan, et al. Correlation analysis and weight judgement of disaster factors caused by rock burst[J]. Coal Technology, 2019, 38(3): 121−123.
[11] 张科学,亢磊,何满潮,等. 矿井煤层冲击危险性多层次综合评价研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2020,48(8):82−89. ZHANG Kexue, KANG Lei, HE Manchao, et al. Research on multi-level comprehensive evaluation of coal seam rockburst risk in underground mine[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48(8): 82−89.
[12] 曹安业,刘耀琪,蒋思齐,等. 临地堑开采冲击地压发生机制及主控因素研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2022,39(1):36−44. CAO Anye, LIU Yaoqi, JIANG Siqi, et al. Occurrence mechanism and main control factors of coal burst near graben mining[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2022, 39(1): 36−44.
[13] 李康,陈建强,赵志鹏,等. 临空巷道冲击地压耦合致灾因素及时空演化过程研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2019,47(12):76−82. LI Kang, CHEN Jianqiang, ZHAO Zhipeng, et al. Study on disaster-causing factors and evolution process of rock burst in roadway near gob[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2019, 47(12): 76−82.
[14] 王明强,王永建,张强,等. 唐山矿冲击地压影响因素的主控性指标[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版),2021,40(5):415−419. WANG Mingqiang, WANG Yongjian, ZHANG Qiang, et al. Main control index of influencing factors of rock burst in Tangshan Mine[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University(Natural Science), 2021, 40(5): 415−419.
[15] 刘中柱. 褶皱构造区特厚煤层开采冲击地压孕育致灾因素及诱冲机理研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2021. [16] 齐庆新,赵善坤,李海涛,等. 我国煤矿冲击地压防治的几个关键问题[J]. 煤矿安全,2020,51(10):135−143. QI Qingxin, ZHAO Shankun, LI Haitao, et al. Several key problems of coal bump prevention and control in China’s Coal Mines[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2020, 51(10): 135−143.
[17] 蔡武,窦林名,李振雷,等. 微震多维信息识别与冲击矿压时空预测−以河南义马跃进煤矿为例[J]. 地球物理学报,2014,57(8):2687−2700. CAI Wu, DOU Linming, LI Zhenlei, et al. Microseismic multidimensional information identification and spatio-temporal forecasting of rock burst: A case study of Yima Yuejin coal mine, Henan, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2014, 57(8): 2687−2700.
[18] 孙庆国,王存文,姜福兴. 微地震监测系统在冲击地压预测预报中的应用[J]. 煤矿安全,2007,38(12):55−57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-496X.2007.12.019 SUN Qingguo, WANG Cunwen, JIANG Fuxing. Application of microseismic monitoring system on rock burst forecasting and prediction[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2007, 38(12): 55−57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-496X.2007.12.019
[19] LI Zhenlei, HE Shengquan, SONG Dazhao, et al. Microseismic temporal-spatial precursory characteristics and early warning method of rockburst in steeply inclined and extremely thick coal seam[J]. Energies, 2021, 14(4): 1186. doi: 10.3390/en14041186
[20] 何学秋,陈建强,宋大钊,等. 典型近直立煤层群冲击地压机理及监测预警研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(6):13−22. HE Xueqiu, CHEN Jianqiang, SONG Dazhao, et al. Study on mechanism of rock burst and early warning of typical steeply inclined coal seams[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49(6): 13−22.
[21] 何生全. 近直立煤层群综放开采冲击地压机理及预警技术研究[D]. 北京:北京科技大学,2021. -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 董志伟,杨世瑜,白帆,程晓强. 综采工作面瓦斯分源抽采技术研究与应用. 当代化工研究. 2025(03): 121-123 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: