Molecular dynamics study on wettability difference between lignite dust and silica dust
-
摘要:
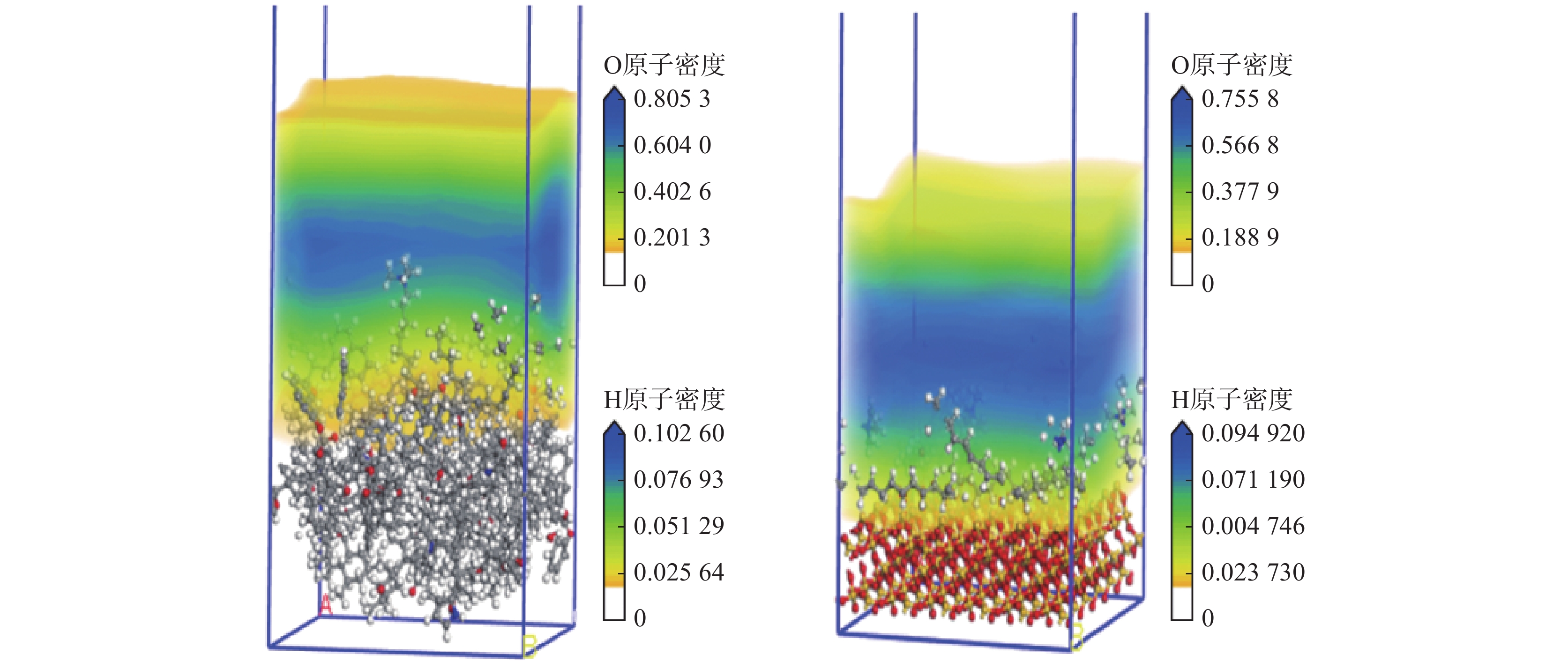
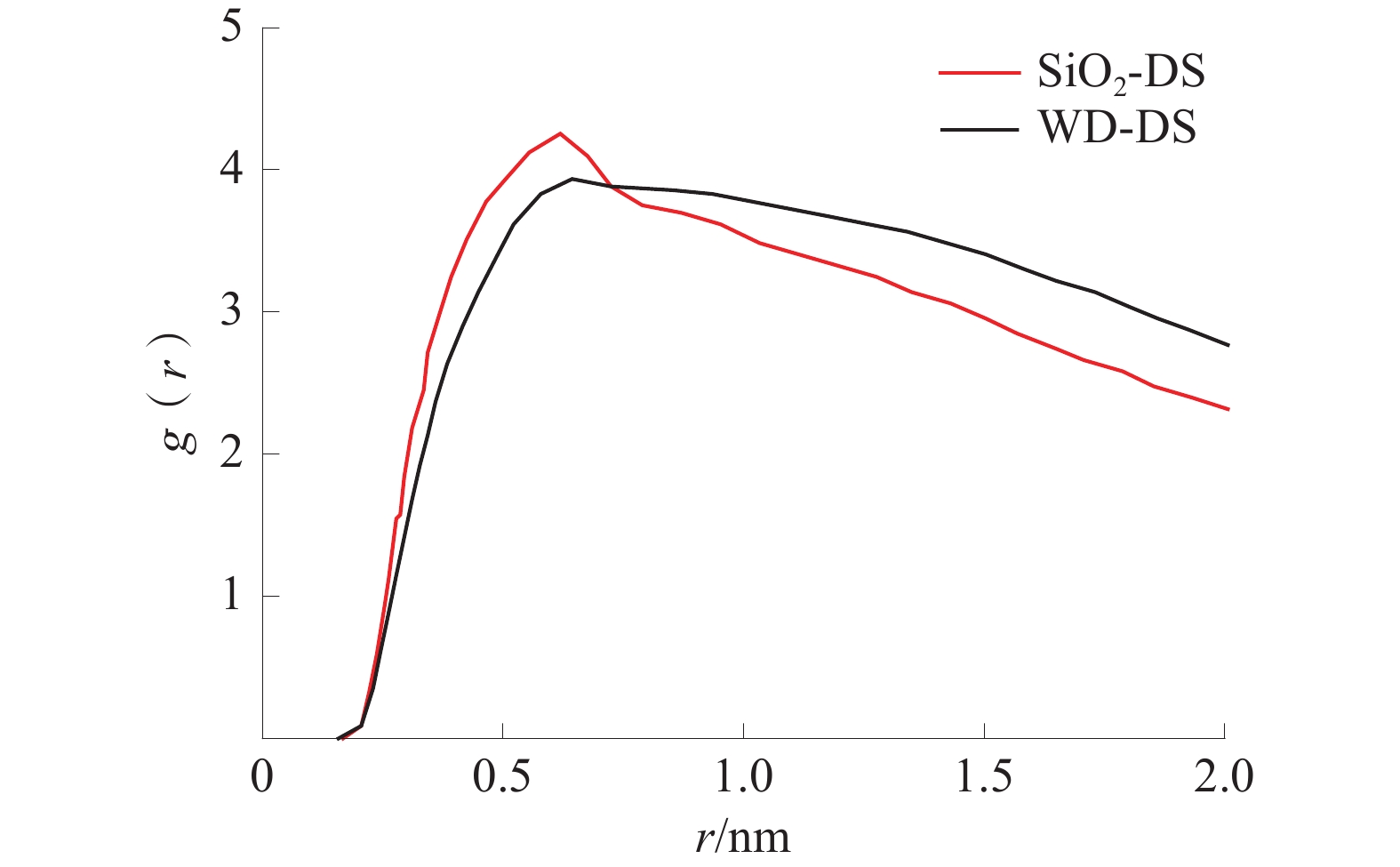
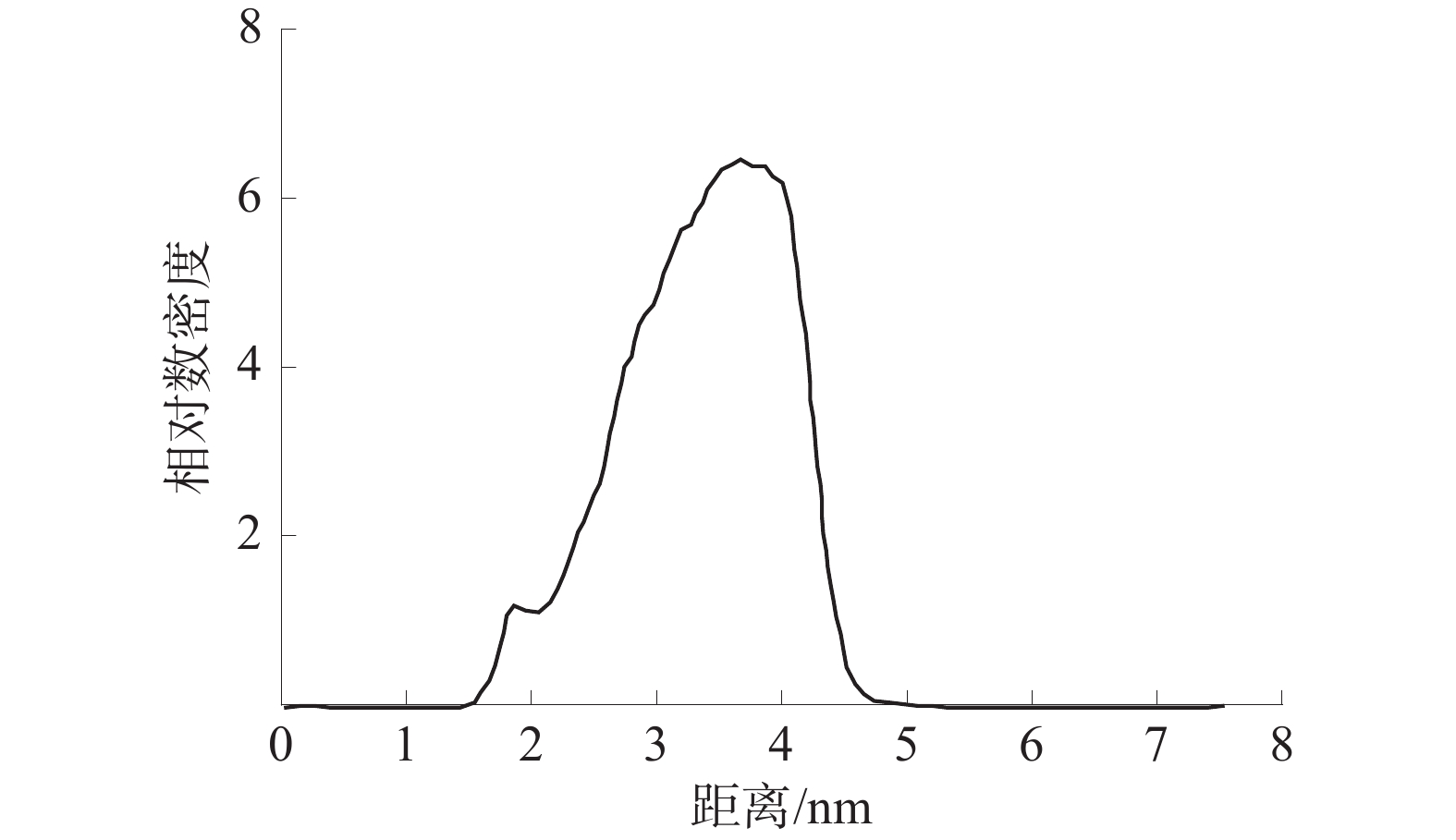
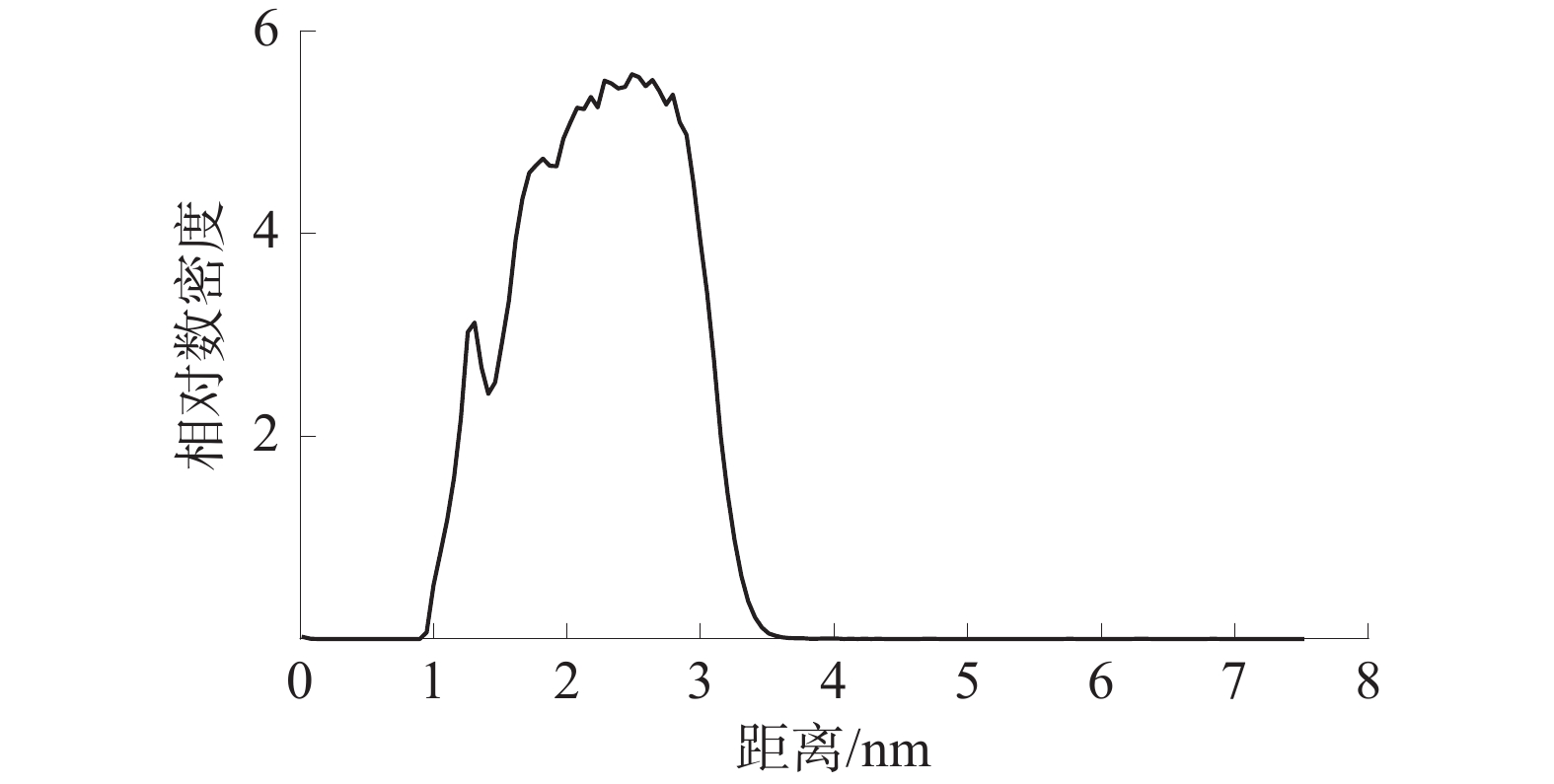
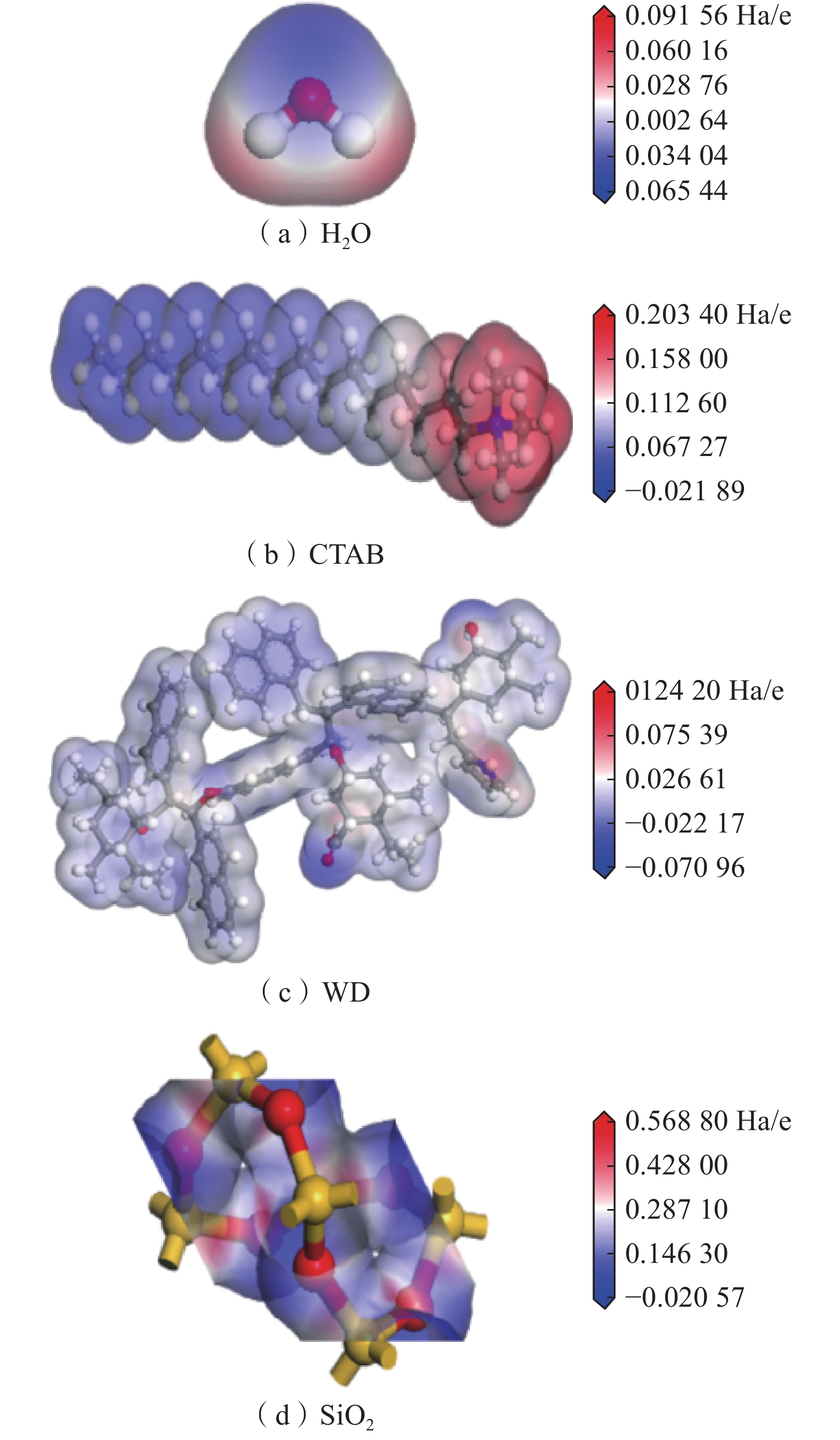
利用分子动力学模拟和量子化学方法,研究了褐煤煤尘与矽尘润湿机理的差异性;构建了水−表面活性剂−褐煤煤尘/矽尘模型,通过分子动力学模拟研究平衡后100 ps内各组分间相互作用能、径向分布函数(RDF)、均方位移(MSD)、自扩散系数(D)和相对数密度。结果表明:相对于矽尘,十六氨基三甲基溴化铵(CTAB)溶液与褐煤分子的相互作用能和自扩散系数较大、相对数密度峰值较高;基于褐煤煤尘与矽尘的静电势,SiO2的电势差变化幅度较大,可知活性剂吸附导致煤尘表面与水分子的电势差大小是影响表面润湿性差异的因素之一,但褐煤中官能团增加了分子间的相互作用,并在润湿过程中发挥着巨大作用。
Abstract:In this paper, the differences in the wetting mechanisms of lignite dust and silica dust were investigated using molecular dynamics simulations and quantum chemical methods. A water-surfactant-lignite coal dust/silica dust model was constructed and the interaction energy, radial distribution function (RDF), mean square displacement (MSD), self-diffusion coefficient (D) and relative number density among the components within 100 ps after equilibrium were investigated by molecular dynamics simulations. The results show that the interaction energy and self-diffusion coefficient between cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide(CTAB) solution and lignite molecules are larger and the peak value of relative number density is higher compared to silica dust; by comparing the electrostatic potential of lignite dust with that of silica dust, the magnitude of the potential difference of SiO2 varies widely, which shows that the size of the potential difference between the dust surface and water molecules due to active agent adsorption is one of the factors affecting the difference in surface wettability, but the functional groups in lignite increase the intermolecular interactions and play a significant role in the wetting process.
-
Keywords:
- silica dust /
- coal dust /
- wettability /
- molecular dynamics /
- quantum chemistry /
- dust control
-
煤矿粉尘是煤矿开采、运输及储存过程中伴随煤和岩石破碎而产生的混合性粉尘,主要含有煤尘、岩尘以及少量其他物质[1]。煤矿粉尘可分为呼吸性粉尘和非呼吸性粉尘。一般说来,小于5 μm的尘粒能到达并沉积于肺泡中,故称为呼吸性粉尘,是引起尘肺的主要尘粒[2-3]。在《国家职业病防治规划(2016—2020年)》《安全生产“十三五”规划》及《“健康中国2030”规划纲要》中,粉尘职业危害防治已被列入国家战略与重大需求[4]。口罩等防护用具作为煤矿环境劳动者个体防护的最后一道防线,其滤料的研发具有重要的研究意义。
防护用器具对气溶胶的过滤理论以纤维层空气过滤理论为基础,经过十几年的发展,纤维过滤理论已逐渐趋于成熟[5]。纤维过滤过程中,捕集颗粒物的过滤作用有:扩散效应、拦截效应、惯性效应、重力效应、和静电吸附[6]。与传统过滤介质相比,静电纺丝制备的纳米纤维膜具有优异的过滤性能、纤维直径小、孔隙率高、体积比显著的表面积压降[7-8]。目前,许多种高分子量聚合物,包括聚丙烯腈(PAN)、聚苯乙烯(PS)、聚乙烯醇(PVA)和聚丙烯(PP)等[9],已通过静电纺丝加工成纳米纤维,用于空气过滤器。聚对苯二甲酸乙二酯(PET)是世界上规模最大、应用最广泛的合成纤维,是由对苯二甲酸(TA)和乙二醇(EG)脱水酯化得到的半结晶热塑性饱和聚酯[10-12]。虽然静电纺丝技术已有多年历史,但其在聚酯方面的应用还比较少。李静等[13]运用PET与含氟基团改性的SiO2共混进行静电纺丝,构建具有微纳复合结构的低表面能表面,具有优良的超疏水性;ZANDER等[14]使用塑料瓶回收并重新聚合PET,但所制备电纺过滤膜对500 nm以下的颗粒去除效果微乎其微。因此,亟须制备一种对粉尘同时具备高过滤效率和低阻力的滤料。此外,作为一种个体防护材料,呼吸过程中细菌的繁殖对人类健康有很大的影响,当前很少将抗菌性静电纺丝纳米纤维膜作为煤矿井下个体防护材料。为此,以静电纺丝技术为基础,将聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯和银纳米颗粒共混,以制备煤矿粉尘个体防护滤料(PET/Ag);利用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)对纤维形貌、分布以及表面孔隙进行表征,利用X射线光电子能谱(XPS)对纤维表面的化学性质及组成进行分析;实验研究了PET/Ag纳米纤维膜作为个体防护材料的可行性,测试了其纤维膜的防水透湿性能、过滤性能以及抗菌性能。
1. 制备方法及实验测试
1)试剂。选用的试剂为:聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯(PET,99%)、二氯甲烷(DCM,99.5%,化学纯)、三氟乙酸(TFA,分析纯)、AgNO3溶液(0.1 mol/L)、N,N-二甲基甲酰胺(DMF,99.5%,分析纯)、聚乙烯吡咯烷酮(PVP,分析纯)。
2)纳米纤维膜的制备。将PET颗粒溶解于三氟乙酸和二氯甲烷的混合溶剂中(V(TFA)∶V(DCM)=4∶1),在室温下搅拌溶解成均一的PET纺丝溶液。通过液相还原法[15]制备银纳米粒子(AgNPs)。在pH=8的条件下,DMF作为还原剂,聚乙烯吡咯烷酮(PVP)作为保护剂,在DMF中煮沸AgNO3制备银纳米颗粒。将纳米银在去离子水中超声溶解1 h,与PET颗粒共混制备纺丝液,纳米银的含量为0.4%,然后在室温下磁力搅拌10 h,获得质量分数分别为8%、10%、12%的均一纺丝溶液。使用HZ-12静电纺丝机进行纳米纤维膜的制备。将制备的纺丝溶液置于5 mL注射器中,并使用注射泵以1 mL/h的速率推出。针头与20 kV高压电源相连。在静电纺丝过程中,针头与收集器之间的距离保持在15 cm,滚筒转速为100 r/min,温度保持在(25±2)℃,相对湿度为(35±5)%。控制纺丝时间为1、2、3 h,得到不同厚度的PET/Ag纳米纤维膜。
3)性能表征。通过扫描电子显微镜(SEM)(JSM-6360LV)观察纳米纤维膜的形态。将待测样品用导电胶带粘贴在样品台上,经喷金处理后,放入扫描电镜样品室,在10 kV加速电压下,观察纤维膜的微观形貌。在SEM图像中选择100根纳米纤维,使用图像处理软件(Image-Pro Plus)绘制纤维直径分布直方图,并计算纳米纤维平均直径;通过射线光电子能谱(XPS)(ESCALAB 250)测定电子的结合能,对纤维膜样品表面的化学性质及组成进行分析,了解其元素组成。通过水接触角测试仪(Dataphysics DCAT21)在室温和45%湿度条件下进行测试,水滴在纤维膜表面稳定后测定其接触角大小。
4)透湿性能测试。使用WPT-301水蒸气透过率测试仪测量材料的润湿性。在38 ℃、20% RH的条件下对每个样品进行3次重复测量。水蒸气透过率(WVP)由式(1)计算:
$$ {\mathrm{WVP}} = \frac{{\Delta w}}{t} \cdot \frac{x}{{A \cdot \Delta p}} $$ (1) 式中:Δw为质量变化,g;t为时间;x为膜的厚度,m;A为膜样品面积,m2;Δp 为38 ℃下通过膜的蒸汽压差,kPa。
5)过滤性能测试。使用LZC-K1型滤料综合测试仪对纳米纤维膜进行过滤性能测试,该仪器在计算纤维膜的过滤效率的同时还可通过传感器得出气流时的压阻值。过滤效率和品质因子由式(2)和式(3)计算。所得数据为3次测量的平均值和标准偏差。
$$ \eta = \frac{{N_1 - N_2}}{{N_1}} \times 100\% $$ (2) $$ {\mathrm{QF}} = \frac{{ - \ln (1 - \eta )}}{{\Delta p_1}} $$ (3) 式中:η为过滤效率;N1、N2分别为在通过纳米纤维膜之前和之后的气溶胶颗粒的数量;QF为品质因子;Δp1为相应压阻值。
6)抑菌性能测试。选择大肠杆菌(ATCC 25922)和金黄色葡萄球菌(ATCC 25923)作为实验微生物。首先,将制备的营养肉汁琼脂倒在无菌培养皿上,待其凝固,将大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌培养液(各0.5 mL)均匀涂在琼脂平板上;然后将纤维膜均匀切割成直径为1 cm的圆形,将掺杂AgNPs的样品和对照样品(PET膜)轻轻地放置在固化琼脂板上;最后将培养板在37 ℃下培养18 h,通过1个清晰的细菌抑菌圈直径来鉴定和评估抗菌活性,所得抑菌圈直径由图像处理软件进行量化。实验重复进行3次。
2. 实验结果讨论
2.1 纳米纤维膜的形态与结构
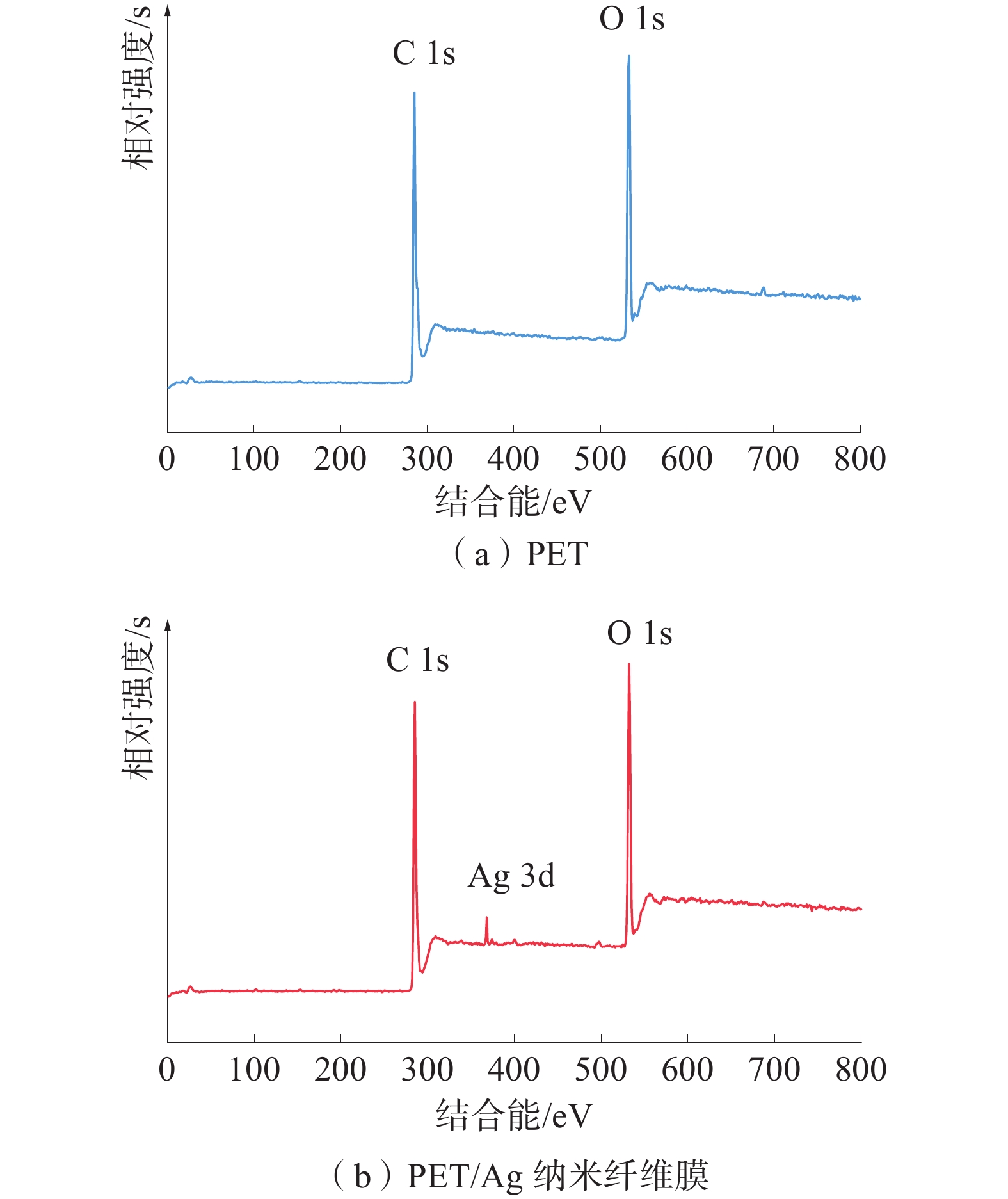
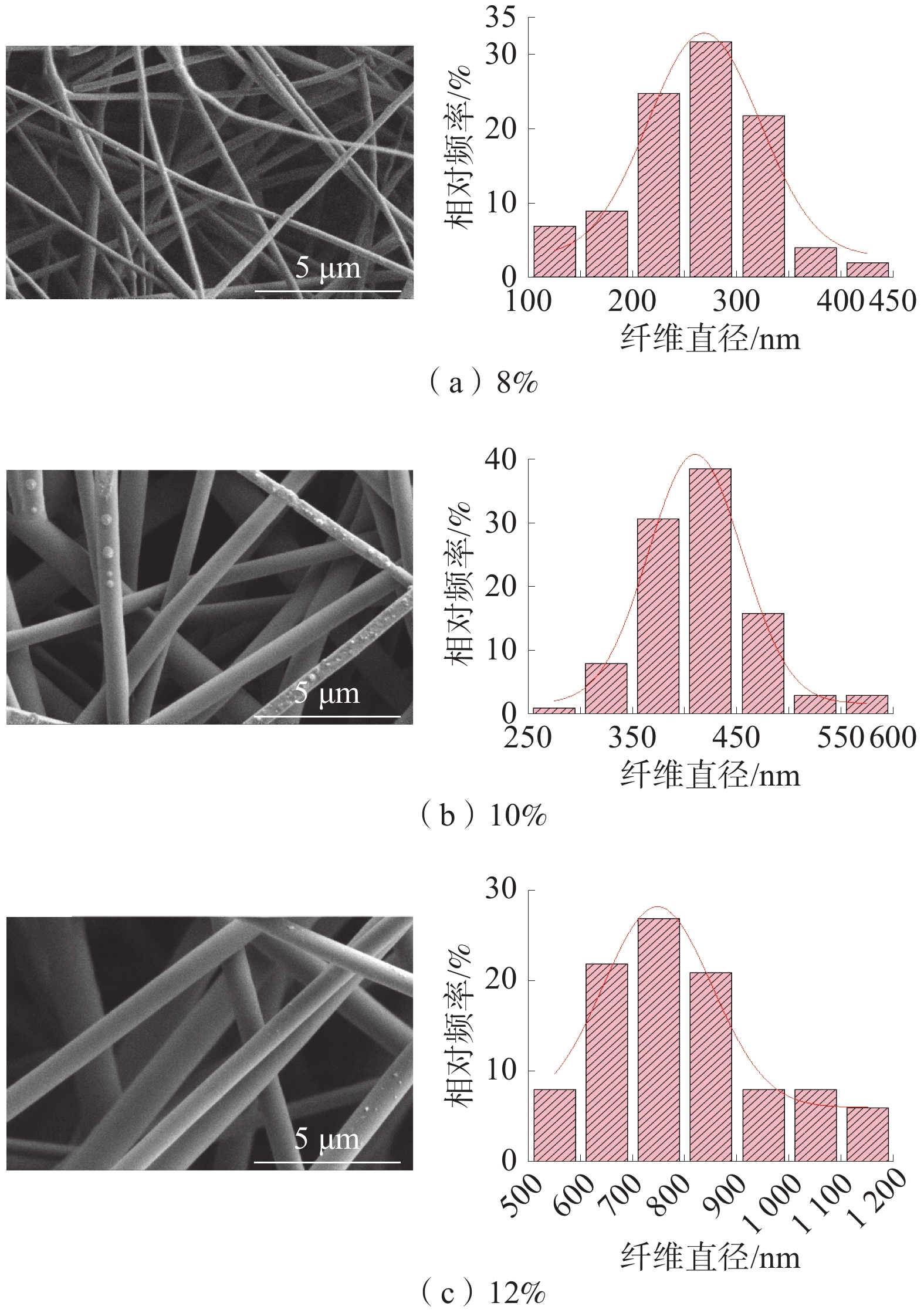
不同质量分数纺丝液所纺PET/Ag纳米纤维膜的SEM电镜图片如图1所示;通过射线光电子能谱(XPS)测定电子的结合能对PET和PET/Ag纳米纤维膜表面的元素组成进行分析得出的结果如图2所示。
由图1可知:通过调节纺丝液的质量分数,可以精确地控制纳米纤维膜的纤维径,而纤维直径的形态几乎不受影响,纤维间自由搭接,没有出现粘连现象,纤维间空隙较小,孔隙数目多,结构明显,单个纤维粗细均匀,没有出现串珠结构,纤维间无规则交织排列在一起,形成错综排列的网状结构[16-17]。纤维直径分布图显示了随机选取的100根纤维的直径大小分布,在1 mL/h的纺丝速率下,纳米纤维平均直径从质量分数8%时的298 nm增加到质量分数10%时的424 nm,到12%时的836 nm。纺丝液质量分数为8%的纤维膜的直径较小,主要集中在250~300 nm,纤维间空隙较小;纺丝液质量分数为10%的纤维膜的直径主要集中在400~450 nm;纺丝液质量分数为12%纤维膜的直径较大,主要集中在700~800 nm,纤维间空隙也相对较大。
由图2可以看出:PET纳米纤维膜表面的主要由C、O元素的峰非常明显,峰值分别对应284.6、531.5 eV;而PET/Ag的测试结果在284.6、367.8、531.5 eV处观察到3个峰,分别对应于C、Ag和O元素的峰, 367.8 eV处峰的出现说明Ag+还原成AgNPs并成功负载到PET膜上。相比之下,没有AgNPs负载的PET膜中没有出现Ag 3d峰。
2.2 纳米纤维膜的疏水性表征
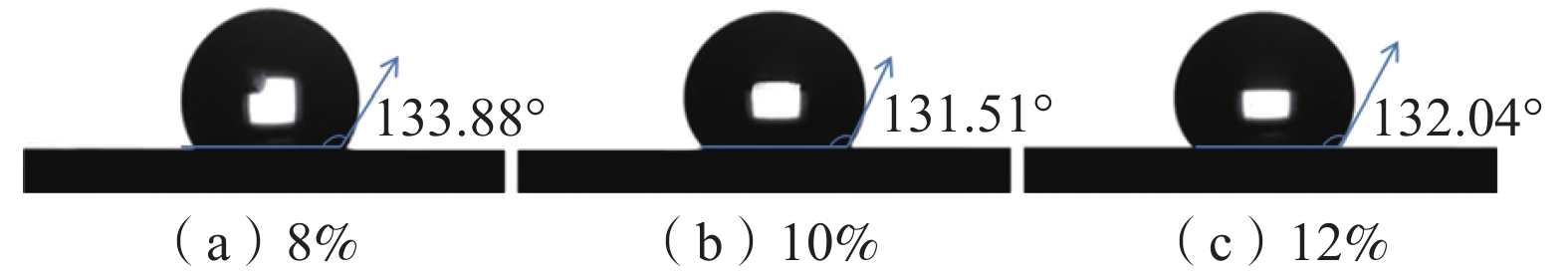
质量分数为8%、10%、12%的PET/Ag纺丝液纺丝2 h后纤维膜表面水接触角变化情况如图3所示。
由图3可知:对不同质量分数的PET/Ag膜,水接触角可以在较长时间内保持不变,表现为较好的疏水性;质量分数为8%、10%、12%PET/Ag纤维膜表面水接触角分别为133.88°、131.51°、132.04°。水接触角测试结果表明PET/Ag 膜具有较强的疏水性。
2.3 透湿性分析
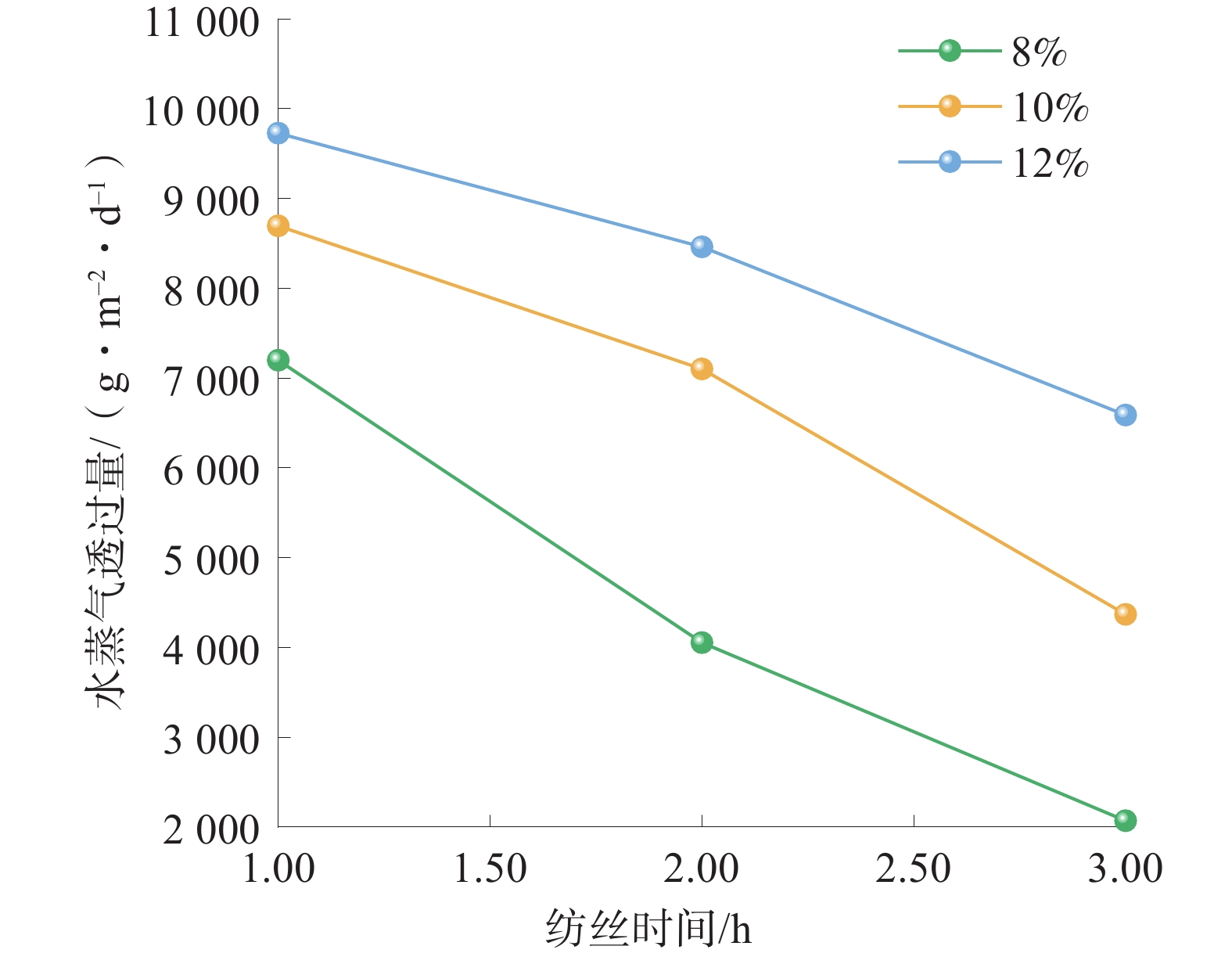
随着电纺时间的增加,PET/Ag纤维无规则交织排布,纤维的密集度不断增加,纤维间的空气流通通道愈加曲折,孔隙则不断减小[18]。不同质量分数的纺丝液在不同纺丝时间下纳米纤维膜的水蒸气透过量如图4所示。
纺丝液质量分数影响纤维直径大小,纺丝时间影响纳米纤维膜的厚度,而纤维直径和厚度都影响了纳米纤维膜的水蒸气流通路径。随着纺丝液质量分数的增加,PET/Ag纳米纤维膜的水蒸气透过量呈增加趋势,这可能是由于纺丝液质量分数影响了纤维直径的大小,较大的纤维直径有利于形成较大的孔隙,使水蒸气流通更加通畅;随着纺丝时间的增加,PET/Ag纳米纤维膜的水蒸气透过量呈减小趋势,这可能是由于纺丝时间影响了纳米纤维膜的厚度,较大的厚度会使纤维间孔隙通路变长,水蒸气流通路径更加曲折,阻力更大[19]。从PET/Ag纳米纤维膜的透湿性能来看,纺丝液质量分数为12%、纺丝1 h的纳米纤维膜透湿性最好,高达
9727.55 g/(m2·d),纺丝液浓度为8%、纺丝3 h的纳米纤维膜透湿性最差,为2069.82 g/(m2·d)。2.4 过滤性能测试分析
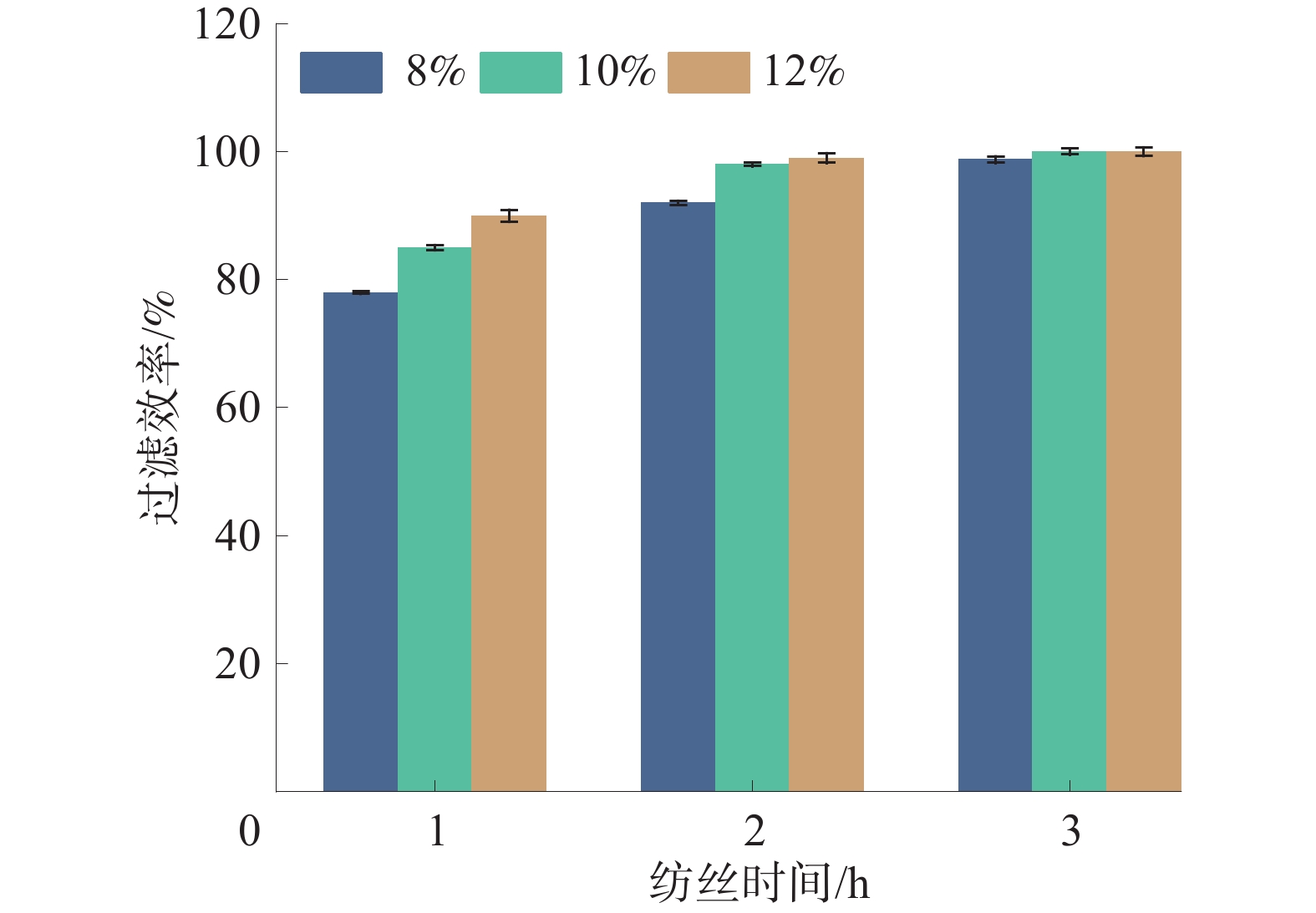
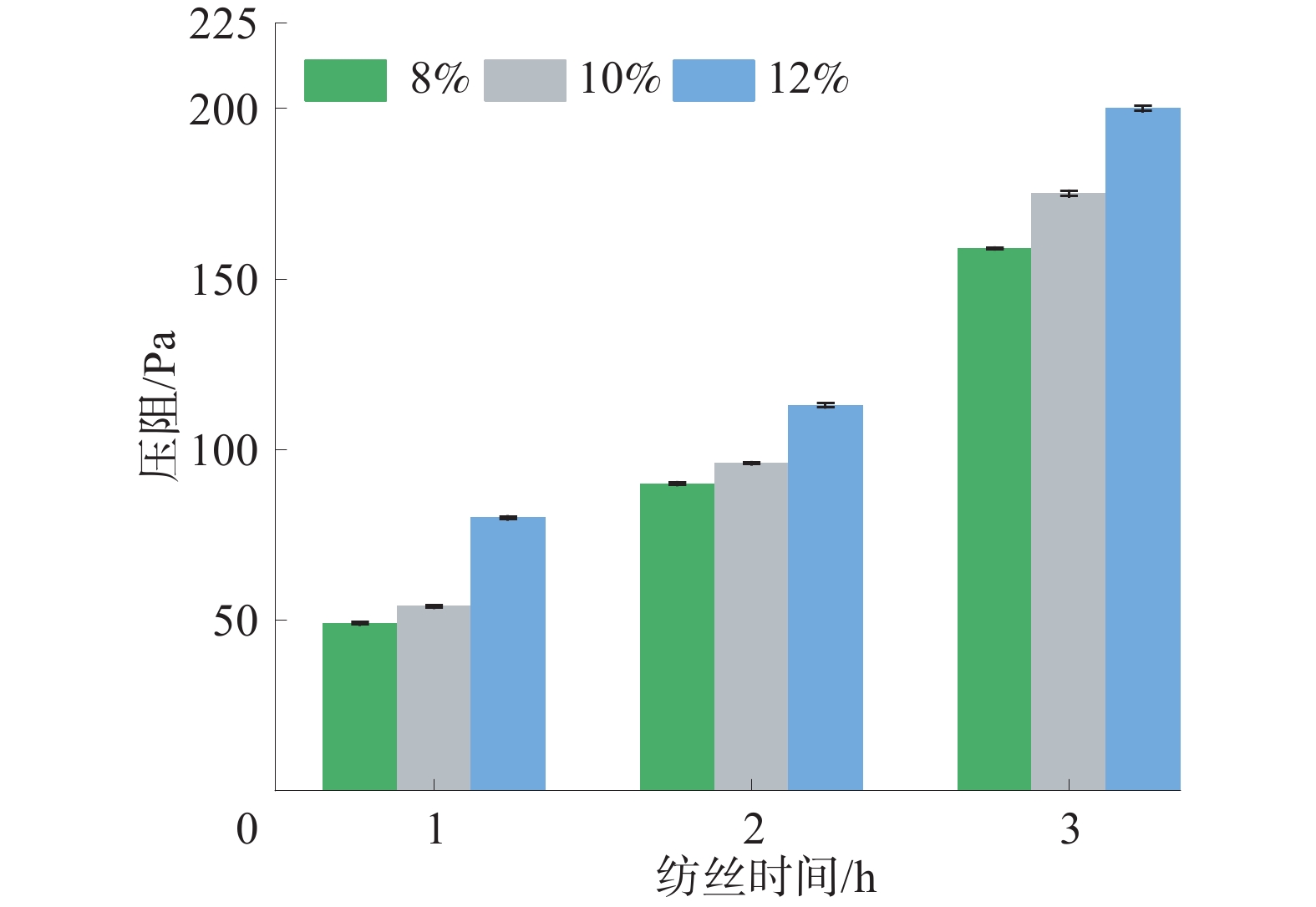
煤矿中大多数煤尘颗粒的直径在1~10 μm之间,LZC-K1型滤料综合测试仪能够产生粒径范围为0.3~10 μm的NaCl气溶胶颗粒,具有更强的穿透性[20-21]。因此,以NaCl颗粒作为测试介质,在85 L/min空气流量下更严苛地反映滤料的过滤效率。实验分别测试的不同纺丝时间下的PET/Ag纳米纤维膜对空气中颗粒物的过滤效果如图5所示;不同纺丝时间下的PET/Ag纳米纤维膜在过滤过程中的压阻值如图6所示。
由图5可以看出:纺丝液质量分数越高,PET/Ag纳米纤维膜的过滤效率越好,且随着纺丝时间的延长,不同质量分数的纺丝液所纺纳米纤维膜的颗粒物过滤效率呈增加趋势;其中,纺丝液质量分数为10%和12%的PET/Ag纳米纤维膜在纺丝3 h后的过滤效率都可达99.99%,纺丝液质量分数为8%的PET/Ag纳米纤维膜过滤效率为98.75%。结果表明:在一定时间内,增加纺丝时间,纳米纤维膜不断堆积,厚度随之增加,纤维之间气流通道更加曲折,纤维膜对颗粒物的过滤效果有所提升。因此,通过控制静电纺丝时间可以得到不同厚度,对颗粒物有不同过滤效果的材料。
由图6可以看出:纺丝液质量分数越高,PET/Ag纳米纤维膜的压阻值越高,且随着纺丝时间的延长,不同纺丝液浓度所纺纳米纤维膜的压阻值呈增加趋势;当纺丝时间为1 h时,8%、10%、12% PET纤维膜的压阻分别为78.2、85.1、90.2 Pa;当纺丝时间增加到3 h时,3种PET/Ag纳米纤维膜的压阻值分别为159.3、175.6、200.1 Pa。
结合不同PET/Ag纳米纤维膜的过滤效率,通过公式计算相对应的品质因子。通过计算可知:纺丝液质量分数为12%,纺丝时间为3 h时,PET/Ag纳米纤维膜的品质因子最低,为0.013 Pa−1;纺丝液质量分数为10%,纺丝时间为2 h时,PET/Ag纳米纤维膜的品质因子最高,为0.041 Pa−1,该条件下纳米纤维膜的水蒸气透过量为同时7 101.37 g/(m2·d),透湿性较好。
纺丝液质量分数为10%,纺丝时间为2 h时PET/Ag纳米纤维膜在15~85 L/min不同空气流量下的过滤效率、压阻和品质因子见表1。
表 1 不同空气流量下PET/Ag纳米纤维膜的过滤效率、压阻和品质因子Table 1. Filtration efficiency, pressure drop and quality factor of PET/Ag nanofiber membrane under different air flow conditions空气流量/(L·min−1) 过滤效率/% 压阻/Pa 品质因数/Pa−1 15 99.99 32.5 0.084 30 99.42 49.8 0.075 45 98.19 60.6 0.069 60 96.78 89.4 0.056 85 95.14 90.7 0.041 由表1可以看出:随着空气流量增加,流速增大,纳米纤维对颗粒物的拦截、扩散作用减弱,纳米纤维膜的过滤效率逐渐降低;并且流速增强时压力差随之增大,压阻随之升高,品质因子也呈降低趋势,综合性能随流量的增加表现得越来越差,即流量越大,口罩的防护性能和舒适性均随流量增加而变差。
2.5 抑菌性能分析
利用琼脂扩散法评价所制备滤料对微生物的作用效果如图7所示。
由图7(a)可以看出,在37 ℃下培养18 h后,PET纳米纤维膜对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌没有显示出任何抗菌活性,说明PET膜不具备抗菌性能。由图7(b)可以看出共混静电纺丝法制备的PET/Ag纳米纤维膜对2种细菌都显示出明显的抗菌活性,其中,对大肠杆菌的抑菌区直径最大,为18.12 mm,对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑菌区为13.25 mm;这可能是由于金黄色葡萄球菌的细胞壁较厚,蛋白质含量较少,因此其抑菌区直径要比大肠杆菌小。结果表明:PET/Ag纳米纤维膜对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌细菌都具备明显的抗菌活性,作为空气过滤材料能够有效抑制细菌繁殖,在个人防护领域具有广阔的应用前景。
3. 结 语
1)SEM图显示,PET/Ag电纺纤维较细,纤维形貌良好,纤维之间无规则排列在一起,没有出现粘连现象,纤维膜孔隙结构明显,单个纤维粗细均匀,没有出现串珠结构。通过调节纺丝液的质量分数,可以精确地控制纳米纤维膜的纤维直径,而纤维直径的形态几乎不受影响,纤维间自由搭接无规则交织排列在一起,形成错综排列的网状结构。XPS表明Ag+还原成AgNPs并成功负载到PET膜上。
2)水接触角测量表明PET/Ag纳米纤维膜表现为较好的疏水性。从PET/Ag纳米纤维膜的透湿性能来看,纺丝液质量分数和纺丝时间都影响了纳米纤维膜的水蒸气流通路径。纺丝液质量分数为12%、纺丝1 h的纳米纤维膜透湿性最好,高达9 727.55 g/(m2·d)。
3)增加纺丝时间,纳米纤维膜不断堆积,厚度随之增加,纤维之间气流通道更加曲折,纤维膜对颗粒物的过滤效果有所提升。因此,通过控制静电纺丝时间可以得到不同厚度,对颗粒物有不同过滤效果的材料。
4)随空气流量从15 L/min增加到85 L/min, PET/Ag纳米纤维对颗粒物的拦截、扩散作用减弱,纳米纤维膜的过滤效率逐渐降低。并且流速增强时压力差增大,压阻随之升高,综合性能随流量的增加表现得越来越差。
5)PET/Ag纳米纤维膜对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌细菌都具备明显的抗菌活性,作为空气过滤材料能够有效抑制细菌繁殖,在个人防护领域具有广阔的应用前景。
-
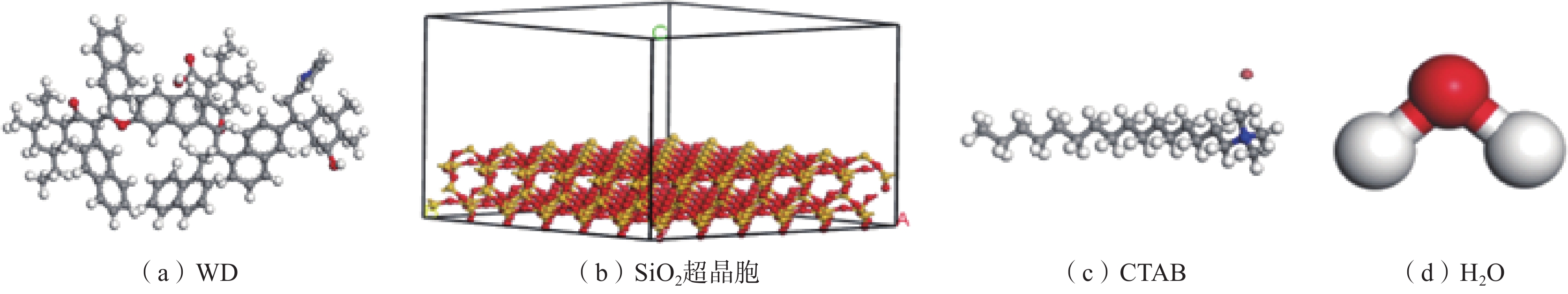
表 1 盒子或超晶胞参数
Table 1 Box or supercell parameters
名称 长/nm 宽/nm 高/nm 分子数量 α、β、γ/(°) 密度/ (g·cm−3) 水盒子 2.946 0 3.241 2 1.566 4 500 90 1.000 CTAB盒子 2.946 0 3.241 2 0.239 7 5 90 1.322 煤分子盒子 2.946 0 3.241 2 1.342 6 8 90 1.350 SiO2超晶胞 2.946 0 3.241 2 2.288 3 — 90 2.200 注:α、β、γ为三维空间中与x、y、z轴的夹角。 表 2 水−CTAB−煤尘/矽尘的相互作用能
Table 2 Interaction energies of water-CTAB-coal dust/silicon dust
体系 能量/(kcal·mol−1) 总能量 水和CTAB 粉尘 相互作用能 水−CTAB−煤尘 −2 739.640 2 −4 053.856 8 2 107.936 5 −793.720 4 水−CTAB−矽尘 −24 706.914 0 −4 065.075 7 −20 451.980 0 −135.598 0 注:1 kcal=4.184 kJ。 表 3 各个分子或晶胞的静电势对比表
Table 3 Comparison of the electrostatic potential of individual molecules or crystals
分子或晶胞种类 静电势/(Ha·e−1) 正 负 尾链 H2O 0.091 56 −0.065 44 — CTAB 0.203 40 — 0.021 89 WD 0.124 20 −0.070 96 — SiO2 0.568 80 −0.020 57 — -
[1] CHEN Z R, QIU H X, HONG Z X, et al. Molecular dynamics simulation of a lignite structure simplified model absorbing water[J]. Molecular Simulation, 2020, 46(1): 71−81. doi: 10.1080/08927022.2019.1674851
[2] QIU H X, CHEN Z R, WANG G H. Effect of dodecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide on the migration of water molecules in the pores of lignite: an experimental and molecular simulation study[J]. ACS Omega, 2020, 5(39): 25456−25466. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c04012
[3] 高正阳,杨维结. 不同煤阶煤分子表面吸附水分子的机理[J]. 煤炭学报,2017,42(3):753−759. GAO Zhengyang, YANG Weijie. Adsorption mechanism of water molecule on different rank coals molecular surface[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2017, 42(3): 753−759.
[4] XU L, PEI Z H. Preparation and optimization of a novel dust suppressant for construction sites[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2017, 29(8).
[5] HUANG Z A, ZHANG L H, YANG Z J, et al. Preparation and properties of a rock dust suppressant for a copper mine[J]. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 2019, 10(6): 2010−2017. doi: 10.1016/j.apr.2019.09.008
[6] CRAWFORD R J, MAINWARING D E. The influence of surfactant adsorption on the surface characterisation of Australian coals[J]. Fuel, 2001, 80(3): 313−320. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(00)00110-1
[7] ZHANG L, LI B, XIA Y C, et al. Wettability modification of Wender lignite by adsorption of dodecyl poly ethoxylated surfactants with different degree of ethoxylation: A molecular dynamics simulation study[J]. Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling, 2017, 76: 106−117. doi: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2017.06.028
[8] 陈璐瑶. 表面活性剂对二氧化硅粉尘润湿性影响的分子动力学研究[D]. 兰州:兰州大学,2021. [9] 孟筠青,王丽娟,王顾儒,等. 表面活性剂对硅尘润湿性影响的分子模拟[J]. 安全与环境学报,2023,23(7):2360−2365. MENG Junqing, WANG Lijuan, WANG Guru, et al. Molecular simulation of the influence of surfactants on the wettability of silica dust[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2023, 23(7): 2360−2365.
[10] 邱玄,钱玉鹏,陈彬,等. Pluronic F-68在萤石和石英表面的吸附特性及分散作用研究[J]. 金属矿山,2021(12):56−61. QIU Xuan, QIAN Yupeng, CHEN Bin, et al. Study on adsorption characteristics and dispersion of pluronic F-68 on the surface of fluorite and quartz[J]. Metal Mine, 2021(12): 56−61.
[11] WANG Z Q, WANG P Y, SONG H, et al. Dynamic wetting behavior of nanofluid droplet on a vertically vibrating surface: A molecular dynamics study[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2022, 347: 118360. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2021.118360
[12] ZHOU G, XING M Y, WANG K L, et al. Study on wetting behavior between CTAC and BS-12 with gas coal based on molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2022, 357: 118996. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2022.118996
[13] DELLEY B. From molecules to solids with the DMol3 approach[J]. 2000, 113(18): 7756-7764.
[14] GRIMME S. Accurate description of van der Waals complexes by density functional theory including empirical corrections[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2004, 25(12): 1463−1473. doi: 10.1002/jcc.20078
[15] LIU L, JIN J, LIN Y Y, et al. The effect of calcium on nitric oxide heterogeneous adsorption on carbon: A first-principles study[J]. Energy, 2016, 106: 212−220. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2016.02.148
[16] GRIMME S. Semiempirical GGA-type density functional constructed with a long-range dispersion correction[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2006, 27(15): 1787−1799. doi: 10.1002/jcc.20495
[17] LI W F, WANG H N, LI X, et al. Effect of mixed cationic/anionic surfactants on the low-rank coal wettability by an experimental and molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Fuel, 2021, 289: 119886. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119886
[18] XU J F, ZHANG Y, CHEN H X, et al. Effect of surfactant headgroups on the oil/water interface: an interfacial tension measurement and simulation study[J]. Journal of Molecular Structure, 2013, 1052: 50−56. doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2013.07.049
[19] 朱蓓蓓. 溴化锂水溶液微观特性的分子动力学研究[D]. 大连:大连海事大学,2010. [20] 韩方伟,胡福宏,奚志林,等. AEO3润湿褐煤性能及机理[J]. 煤炭学报,2023,48(10):3766−3775. HAN Fangwei, HU Fuhong, XI Zhilin, et al. Study on wettability and mechanism of AEO3 to lignite[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2023, 48(10): 3766−3775.



 下载:
下载: