Optimization simulation of fracturing parameters under different soft/hard coal + surrounding rocks in Yuwu Mine
-
摘要:
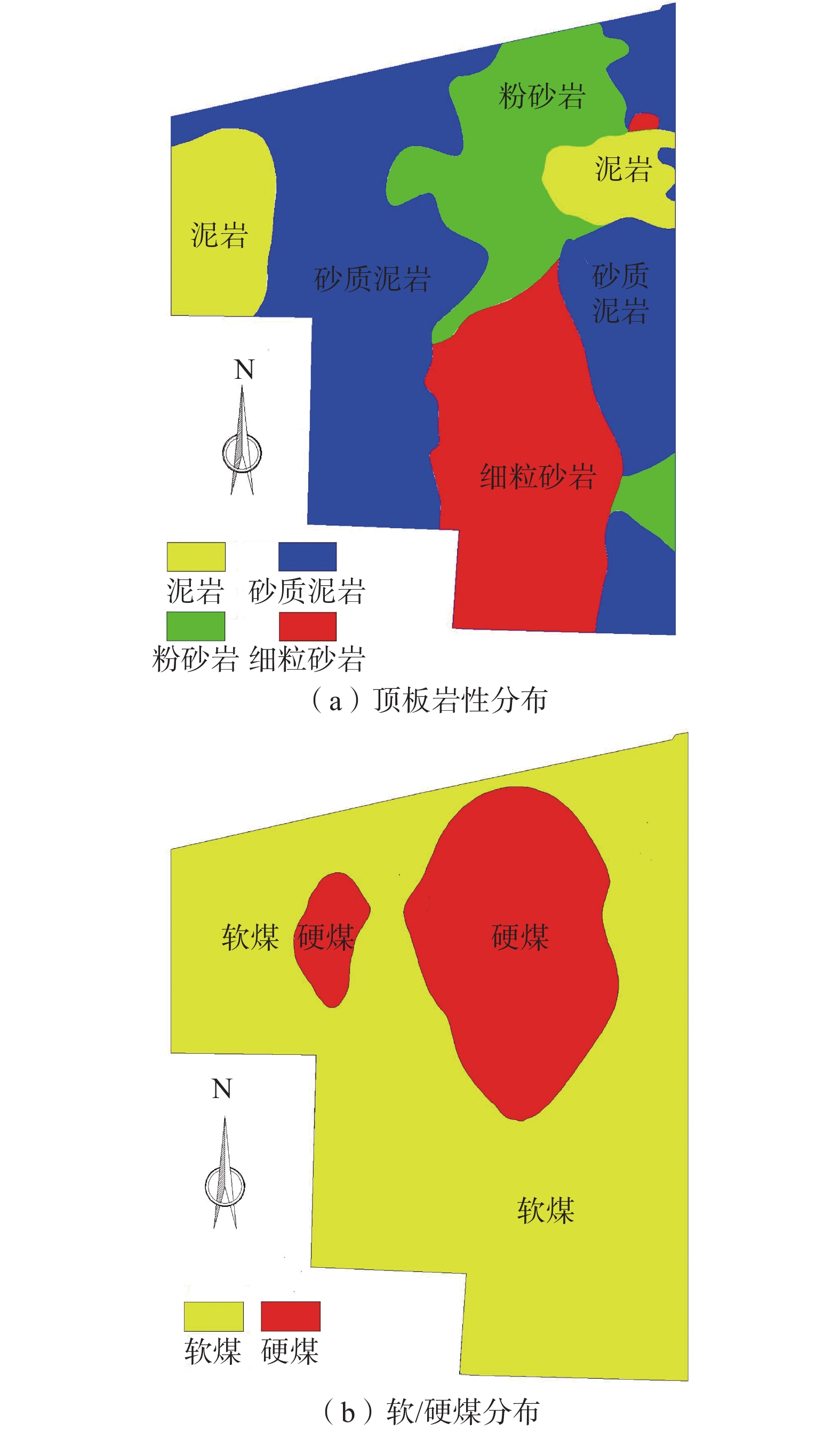
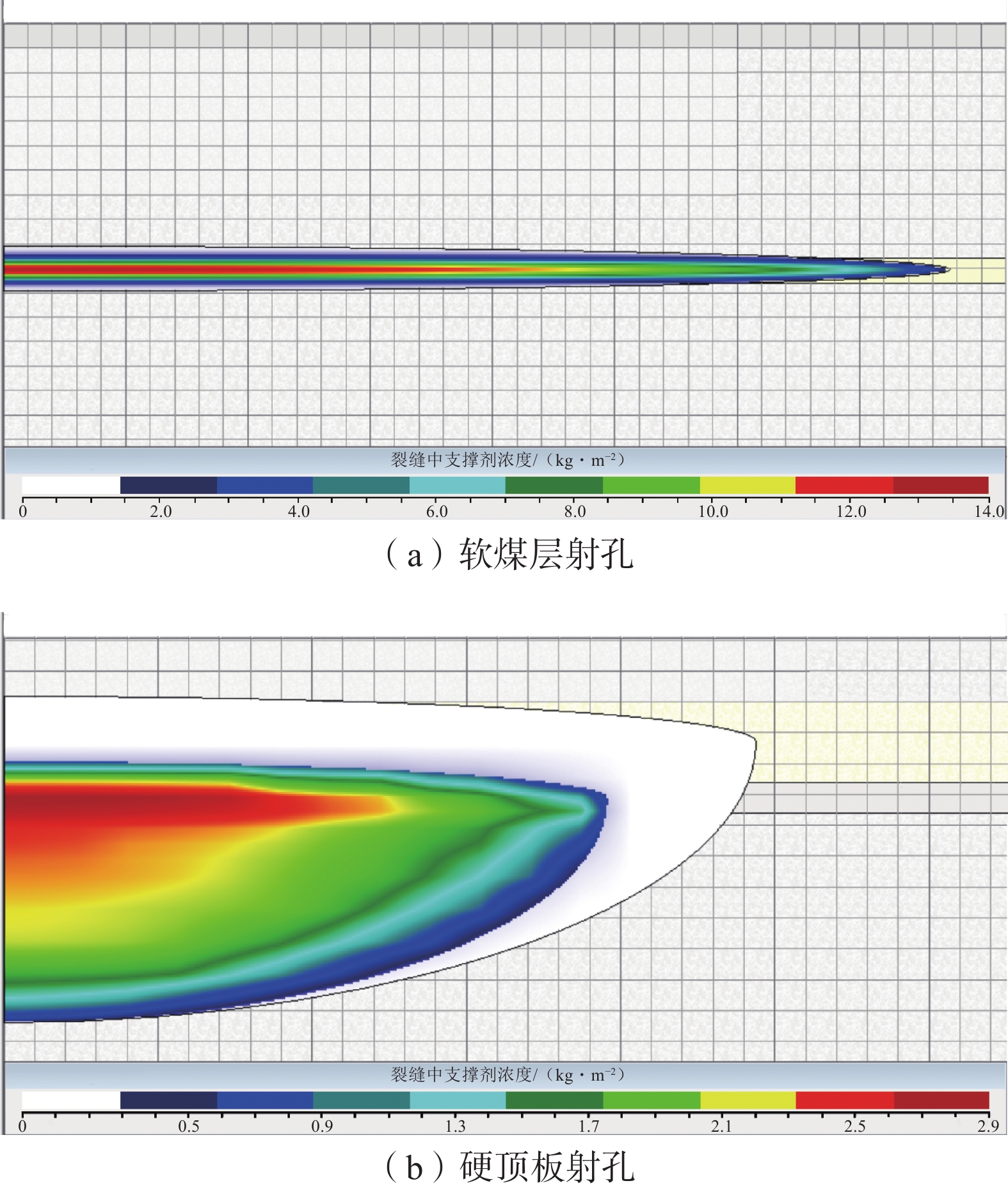
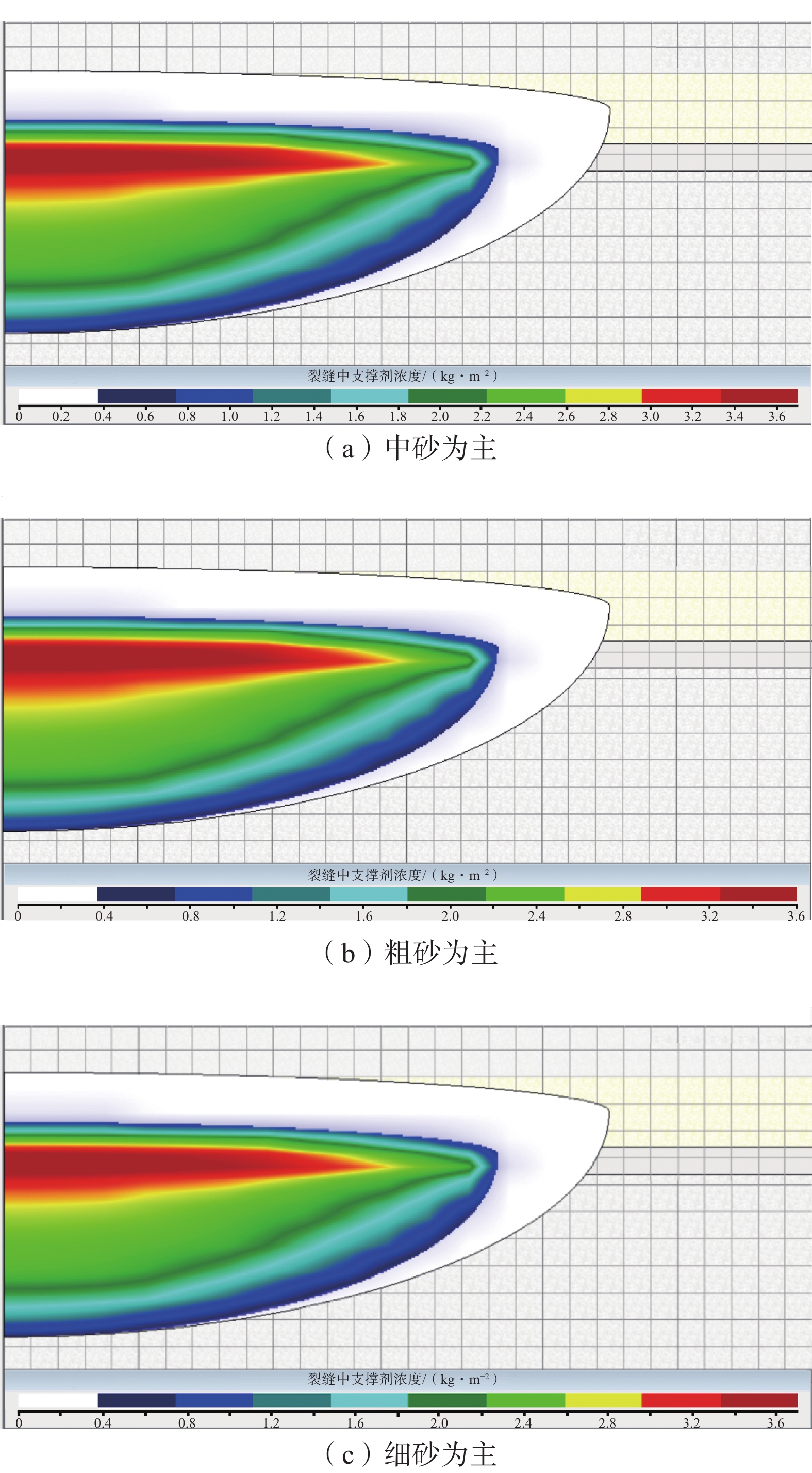
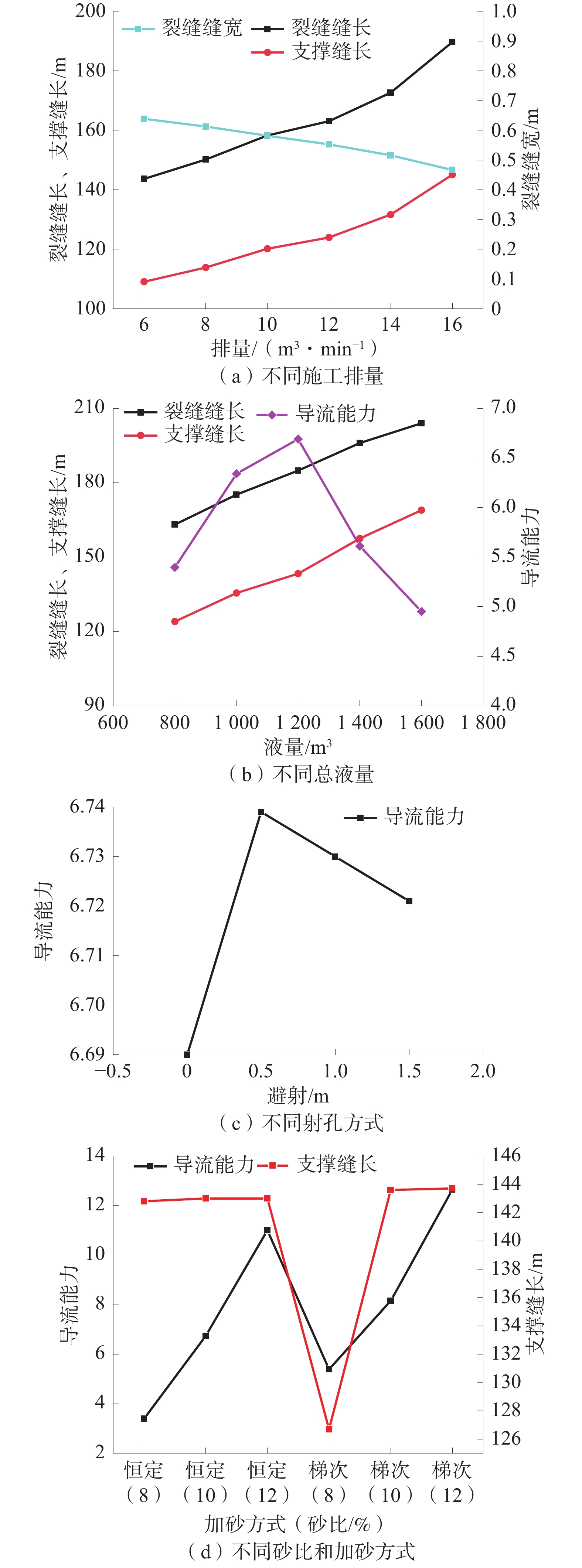
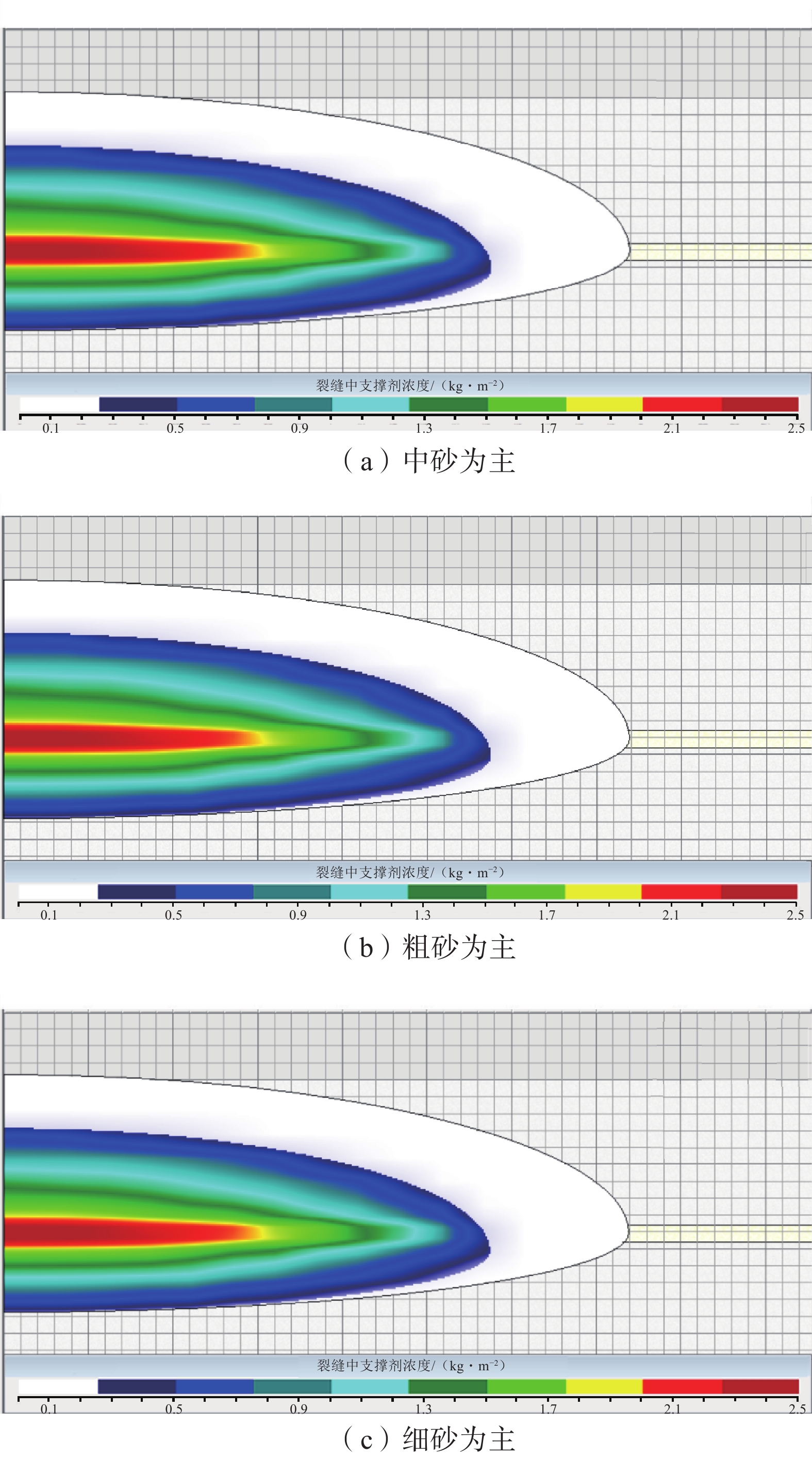
为了提高水力压裂效果,针对余吾矿3#煤层强度差异大,顶/底板岩性存在多种组合类型,水力压裂参数与其组合类型匹配性差的问题,借助水力压裂数值模拟软件,分别模拟了不同软/硬煤+围岩组合类型(软顶硬煤、硬顶软煤、硬顶硬煤),不同水力压裂参数(射孔方式、施工排量、总液量、加沙方式、砂比、支撑剂粒径)下的裂缝缝长、裂缝缝宽、导流能力等,并以此作为优化评价参数,优化水力压裂泵注参数。结果表明:硬顶软煤组合时,在顶板2~4 m范围内射孔压裂,施工排量为8~10 m3/min,平均砂比在12%左右最佳;硬顶硬煤组合时,施工排量应大于12 m3/min,采用“前置液−携砂液”的循环递进式加砂方式,可以提高造缝范围和撑缝长度;总液量大于1 400 m3,第1次和第2次的平均砂比分别为8%和12%左右;软顶硬煤组合时,煤层顶/底部分煤层段避射,施工排量10 m3/min左右为最佳;这3种情况下支撑剂以中砂为主。
Abstract:In order to improve the effectiveness of hydraulic fracturing, a numerical simulation software for hydraulic fracturing was used to address the issues of large differences in strength and poor compatibility between hydraulic fracturing parameters and different combinations of roof/ floor strata in 3# coal seam of Yuwu Mine. The fracture extension length, fracture width, flow conductivity of various combinations of coal and surrounding rock types (soft roof and hard coal, hard roof and soft coal, hard roof and hard coal) under different hydraulic fracturing parameters (perforating mode, construction displacement, total fluid volume, sand injection way, sand ratio, proppant particle size) were simulated, and based on this, the corresponding hydraulic fracturing pump injection parameters are optimized. The results indicate that when the combination is hard roof and soft coal, perforation and fracturing within a 2-4 m range of the roof is most effective, the pumping rate should be 8-10 m3/min, with an optimal average sand ratio of around 12%. For the combination of hard roof and hard coal, the pumping rate should be greater than 12 m3/min. A cyclic progressive sand-carrying fluid technique (using “pre-liquid - carrying sand liquid”) should be employed to increase the fracturing range and length of propped fractures; the total liquid volume is greater than 1 400 m3, and the average sand ratio of the first and second times is about 8% and 12%, respectively; for the combination of soft roof and hard coal, selective perforation and fracturing of certain coal layers in the roof and floor is recommended, with an optimal pumping rate of around 10 m3/min. In all three cases, the proppant is predominantly medium sand.
-
在煤矿井下,煤层瓦斯压力测定(比如胶囊-黏液封孔等)和钻孔瓦斯涌出初速度测定均需要向钻孔内送入封孔器。当封孔器在钻孔内移动时,封孔器端头与钻孔残留煤渣相互作用;一方面,钻孔残留煤渣会阻碍封孔器移动,另一方面,受封孔器端头力学作用,煤渣出现堆积现象;如果堆积严重,封孔器难以快速到达钻孔预定位置,参数测定可能失败(比如钻孔瓦斯涌出初速度测定,要求2 min内将封孔器送入预定位置并密封钻孔)。
为减轻钻孔残留煤渣对封孔器移动的影响,学者们从排渣和减阻2个方面进行了研究。在排渣方面:刘涛[1]提出了环缝式引射器输送钻孔煤渣技术;王永龙等[2-3]提出了双动力低螺旋钻杆排渣技术和刻槽钻杆排渣技术;杜长胜等[4]提出了脉动通风与钻杆分风联合作用排渣技术,李国强等[5]提出了旋风分离除渣技术;李栋等[6]提出了射流排水排渣技术;张辉等[7]提出了泵吸反循环钻进排渣技术;潘竞涛等[8]提出了下行定向钻孔氮气泡沫幂律多相流携渣解堵技术;汪义龙等[9]提出了煤层定向钻孔气举排渣技术;李成成[10]提出了“逐级升压切缝、低压旋转排渣”的排渣技术;张宏杰等[11]提出了“高螺旋机械排渣为主、液动排渣为辅”的复合排渣技术;童碧等[12]提出了基于整体式螺旋钻杆的复合排渣工艺技术;何将福等[13]提出了三通道反循环排渣技术;张宏钧等[14]提出了螺旋钻杆与压风复合排渣技术。在减阻方面:齐黎明等[15]提出了在封孔器前端安设锥面端头的减阻技术;周福宝等[16]提出了让高压气流从钻孔孔壁与抽采管之间流出,从而减轻煤渣阻碍抽采管移动的技术方案。
如果排渣技术过度使用,会扰动钻孔孔壁并产生新的煤渣甚至于塌孔;由此可见,排渣技术虽然可降低钻孔残留煤渣数量,但不能将残留煤渣清除;因此,仅采用排渣技术是不够的,需补充应用减阻技术。在封孔器前端安设锥面端头可以有效降低残留煤渣阻力[15],是一种简单、实用的减阻技术;封孔器锥面端头(简称锥面端头)与钻孔残留煤渣的力学作用及其减阻机理是该技术推广应用中亟待解决的基础理论问题,并且锥面端头设计也需要进一步优化,在公开的文献资料中,未见相关研究成果。为此,从理论上分析锥面端头与钻孔残留煤渣的力学作用,探索锥面端头减阻机理,并进行工程应用。
1. 锥面端头前方钻孔残留煤渣堆积状况分类
锥面端头前方残留煤渣堆积状况如图1所示。
由图1可以看出,随着锥面端头移动,锥面端头前方堆积的残留煤渣(简称堆积煤渣)越来越厚。根据堆积煤渣是否超过锥面端头锥顶,锥面端头前方钻孔残留煤渣堆积状况可分为2类:堆积煤渣未超过锥顶和堆积煤渣超过锥顶。
2. 锥面端头移动最小推力理论分析
2.1 堆积煤渣未超过锥顶时的最小推力
假定锥面端头在钻孔内呈水平状态,以锥面端头锥底最低点O为原点,锥面端头移动方向(锥面端头轴线方向)为x轴正方向,垂直向上为z轴正方向,y轴正方向垂直于平面xOz,并指向右侧,建立直角坐标系,锥面端头受力分析如图2所示。
在图2中,锥面CAOB为锥面端头与煤渣的接触面(简称接触面),O1点为锥底圆心,2θ为锥面角度;C点为锥面上接触面与非接触面分界线的顶点,位于x轴正上方;h为堆积煤渣厚度。
锥面端头受力如下:封孔器推力F1整体作用于x轴正方向;重力G整体作用于z轴负方向;煤渣压力F2(挤压应力σ的总称)垂直于接触面并指向锥面端头内部;煤渣摩擦阻力F3与接触面相切并垂直于z轴(锥面端头以近水平形式移动,并不断破坏堆积煤渣的稳定性,与滑块在固定斜面的移动有着本质区别)。
为便于受力分析,需对煤渣压力与煤渣摩擦阻力沿x轴、y轴、z轴3个方向进行分解,并求出各分力计算方法。
y轴、z轴方向分力微元挤压应力分析如图3所示。由于图2中锥面CAO和锥面CBO沿平面CDO对称分布,因此,取锥面CBO进行分析即可。先作2个平行于yOz平面的截面(间距为dx),再从圆锥的中心轴线作2个截面(夹角为dβ),在锥面CBO上取微元(面积为ds),并进行受力分析。
根据图3(a),微元面积可表示为:
$$ \mathrm{d}s=\frac{\mathrm{d}x}{\mathrm{c}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{s}\;\varphi }(H-x)\frac{r}{H}\mathrm{d}\beta $$ (1) 式中:s为锥面CBO的面积,m2;x为x轴坐标,m;φ为沿x轴方向的锥面角度,(°);H为圆锥高度,m;r为锥面端头锥底半径,m;β为夹角,(°)。
根据图3(b),微元承受的挤压应力可分解为平行于x轴的分应力dF2x和沿着截面指向圆心的分应力dF2yz,dF2yz可表示为:
$$ {\mathrm{d}}{F}_{2{yz}}=\sigma (H-x)\frac{r}{H}{\mathrm{d}}x{\mathrm{d}}\beta $$ (2) 式中:F2yz为锥面CBO的煤渣压力沿着截面指向圆心分力,N;σ为接触面挤压应力,Pa。
对F2yz进行分解,力分解示意图如图4所示。
根据图4,F2yz平行于y轴的分力F2y可表示为:
$$ F_{2{{{y}}}}=\int_0^{\frac{h}{\mathrm{t}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{n}\; \theta}}\; \sigma(H-x)\frac{r}{H}(1-\mathrm{cos}\; \alpha)\mathrm{d}x $$ (3) 式中:F2y为F2yz平行于y轴的分力(锥面CBO的煤渣压力沿y轴方向分力),N;h为堆积煤渣厚度,m;θ为锥面端头锥面角度的1/2值,(°);α为弧线对应夹角,(°)。
根据三角函数关系,有:
$$ (H-x)\frac{r}{H}(1-\mathrm{c}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{s}\;\alpha )=h-x\mathrm{t}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{n}\;\theta $$ (4) 将式(4)代入式(3)并积分,有:
$$ {F}_{2{y}}=\sigma \frac{{h}^{2}}{2\mathrm{t}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{n}\;\theta }=\sigma {S}_{\vartriangle CDO} $$ (5) 式中:${S}_{\vartriangle CDO} $为$\vartriangle $CDO的面积,m2。
$\vartriangle $CDO为锥面CBO沿y轴的投影,因此,因此,锥面CBO的煤渣压力沿y轴方向分力等于挤压应力σ与投影面积SCDO之积。
同理,F2yz平行于z轴的分力F2z可表示为:
$$ {F}_{2{z}}={\int }_{0}^{\frac{h}{\mathrm{t}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{n}\;\theta }}\sigma (H-x)\frac{r}{H}\mathrm{s}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\;\mathrm{\alpha }\mathrm{d}x $$ (6) 式中:F2z为F2yz平行于z轴的分力(锥面CBO的煤渣压力沿z轴方向分力),N。
根据三角函数关系,有:
$$ (H-x)\frac{r}{H}\mathrm{s}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\;\mathrm{\alpha }=\sqrt{2Rh-{h}^{2}}(1-\frac{\mathrm{t}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{n}\;\theta }{h}x) $$ (7) 将式(7)代入式(6)并积分,有:
$$ {F}_{2{z}}=\sigma \frac{h}{2\mathrm{t}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{n}\;\theta }\;\sqrt{2Rh-{h}^{2}}=\sigma {S}_{\vartriangle CBD} $$ (8) 式中:${S}_{\vartriangle CBD} $为三角形CBD的面积,m2。
$\vartriangle $CBD为锥面CBO沿z轴的投影,因此,锥面CBO的煤渣压力沿z轴方向分力等于挤压应力σ与投影面积SCBD之积。
x轴方向分力微元挤压应力分析图如图5所示。图3中平行于x轴的微元分应力dF2x是φ的函数,由于φ非固定值,不便求解;为此,先作2个平行于xOy平面的截面(间距为dz),再作2个平行于xOz平面的截面(间距为dy),在锥面CBO上取微元(面积为ds),并进行受力分析。

同理,图5中微元面积可表示为:
$$ \mathrm{d}s=\frac{\mathrm{d}y}{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\;\varphi }\mathrm{d}z $$ (9) 式中:y为y轴坐标,m;z为z轴坐标,m。
图5中微元承受的挤压应力平行于x轴的分应力dF2x可表示为:
$$ \mathrm{d}{F}_{2{x}}=\sigma \mathrm{d}y\mathrm{d}z $$ (10) 式中:F2x为锥面CBO的煤渣压力沿x轴方向分力,N。
对式(10)进行积分,有:
$$ {F}_{2{x}}=\frac{\sigma }{2}({r}^{2}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{c}\mathrm{c}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{s}\frac{r-h}{r}-\sqrt{2rh-{h}^{2}}(r-h))=\sigma {S }_{BDO} $$ (11) 式中:SBDO为割圆BDO的面积,m2。
割圆BDO为锥面CBO沿x轴的投影,因此,锥面CBO的煤渣压力沿x轴方向分力等于挤压应力σ与投影面积SBDO之积。
同理,锥面CBO的煤渣摩擦阻力在x轴、y轴2个方向的分力F3x、F3y等于挤压应力σ、摩擦阻力系数f和投影面积(投影平面与分力方向平行且包含z轴,投影面积分别为SCDO、SBDO)之积,可表示为:
$$ {F}_{3{x}}=\sigma f{S}_{CDO}=\mathrm{\sigma }f\frac{{h}^{2}}{2\mathrm{tan}\;\theta } $$ (12) $$ {F}_{3{y}}=\frac{\sigma }{2}f({r}^{2}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{c}\mathrm{c}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{s}\frac{r-h}{r}-\sqrt{2rh-{h}^{2}}(r-h)) $$ (13) 式中:F3x为锥面CBO的煤渣摩擦阻力沿x轴方向分力,N;F3y为锥面CBO的煤渣摩擦阻力沿y轴方向分力,N;f为锥面端头与煤渣的最大静摩擦系数。
当封孔器推力F1达到一定数值(最小推力F)时,锥面端头才能突破煤渣阻力向前移动,x轴、y轴、z轴3个方向的受力均处于平衡状态。y轴方向受力呈对称分布,自然平衡;x轴、z轴方向受力平衡方程可表示为:
$$ F=2{F}_{2{x}}+2{F}_{3{x}} $$ (14) $$ G=2{F}_{2\textit{z}} $$ (15) 式中:F为锥面端头移动最小推力,N;G为锥面端头重力,N。
将式(8)、式(11)、式(12)代入式(14)和式(15),并解方程,有:
$$\begin{split} &\begin{gathered} F = G\left(\mathrm{t}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{n}\; \theta\left(\frac{r^2\mathrm{a}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{c}\mathrm{c}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{s}\; \frac{r-h}{r}}{h\sqrt{2rh-h^2}} - \frac{r-h}{h}\right) + f\sqrt{\frac{h}{2r-h}}\right) \\ 0 < h \leqslant r \end{gathered}\\[-16pt]& \end{split} $$ (16) 根据式(16)可知,锥面端头移动最小推力F与端头重力G、端头锥面角度的一半值θ、端头锥面与煤渣的最大静摩擦系数f属于正相关,与堆积煤渣厚度h和端头锥底半径r的相关性,无法直接判定。
假设端头重力G为50 N,端头锥面角度的一半值θ为30°,最大静摩擦系数f为0.1,通过数值计算并绘制得到的锥面端头移动最小推力F随堆积煤渣厚度h和端头锥底半径r的变化曲线如图6所示。
根据图6可知:锥面端头移动最小推力F与堆积煤渣厚度h和端头锥底半径r也属于正相关。
2.2 堆积煤渣超过锥顶时的受力分析
当堆积煤渣超过锥顶时,根据是否超过锥面端头锥底最高点,可将残留煤渣堆积情况进一步划分,本研究仅分析未超过锥面端头锥底最高点的情形。
锥面端头与煤渣发生力学作用的面积相当于整个锥面与非接触面的面积之差,并忽略锥面端头锥面上方煤渣重力。在式(16)中,令h=r,求得的F值乘以2,即为整个锥面与煤渣接触条件下的锥面端头移动最小推力;再令h=2r−h,求得的F值,即为非接触面与煤渣接触条件下的锥面端头移动最小推力;上述两者之差即为堆积煤渣超过锥顶时的锥面端头移动最小推力F,如式(17):
$$\begin{split} &\begin{gathered} F=G\mathrm{t}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{n}\;\theta \left(\pi +\frac{f}{\mathrm{t}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{n}\;\theta}\left(1-\sqrt{\frac{2r}{h}-1}\right)-\right.\\ \left.\left. \frac{{r}^{2}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{c}\mathrm{c}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{s}\;\frac{h-r}{r}}{\left(2r-h\right)\sqrt{2rh-{h}^{2}}}+\frac{h-r}{2r-h}\right)\right. \qquad r < h \leqslant 2r \end{gathered}\\[-18pt]& \end{split} $$ (17) 3. 锥面端头移动最小推力试验研究
锥面端头移动最小推力F的影响因素较多,因篇幅受限,仅试验研究锥面端头移动最小推力随端头锥面角度的变化规律,并验证理论分析结果的可靠性。
试验方案如下:采用弹簧秤牵拉带有锥面端头的封孔器并让其在含煤渣的管道内匀速移动,弹簧秤显示读数即为锥面端头移动最小推力;锥面角度分别是60°、45°、30°、20°、18°、15°,共6组试验。试验装置设计图如图7所示,锥面端头移动最小推力与锥面角度的关系曲线如图8所示。
由图8可知:锥面角度增加,锥面端头移动最小推力升高,并且上升速率加快;移动距离越远,上升速率加快趋势越明显。根据式(16),锥面端头移动最小推力F与tan θ成正比,tan θ为正切函数,随θ增大而升高并且上升速度逐渐加快。由此可见,试验研究结果与理论分析结果基本一致。
4. 锥面端头减阻机理
与平面端头相比,锥面端头可以通过接触面对堆积煤渣施加平行于y轴的侧向力;因此,可通过分析侧向力来探索锥面端头减阻机理。因篇幅受限,以堆积煤渣未超过锥顶的情形为例,进行分析。
堆积煤渣承受的侧向力Fy是锥面端头y轴方向受力的反作用力,方向由接触面指向堆积煤渣,并平行于y轴,有:
$$ {F}_{{y}}={F}_{2{y}}-{F}_{3{y}} $$ (18) 将式(5)、式(13)、式(15)代入式(18),有式(19):
$$\begin{split} &\begin{gathered} {F}_{{y}}=G\frac{h}{2\sqrt{2rh-{h}^{2}}}-\frac{G\mathrm{t}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{n}\;\theta }{h\sqrt{2rh-{h}^{2}}}f({r}^{2}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{c}\mathrm{c}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{s}\;\frac{r-h}{r}-\\ \sqrt{2rh-{h}^{2}}(r-h)) \end{gathered}\\[-19pt]& \end{split} $$ (19) 式中:Fy为堆积煤渣承受的侧向力,N。
根据式(19)可知,θ越小,Fy越大,即锥面端头越尖,Fy越大。
与锥面端头相接触的煤渣,在侧向力Fy的推动下,向钻孔孔壁侧移动(或被压缩);导致锥面端头通过后,锥面端头后方残留煤渣增加,锥面端头前方堆积煤渣减少,堆积煤渣厚度h降低;锥面端头越尖,侧向力Fy越大,堆积煤渣厚度h越低。
锥面端头移动的突破点通常位于接触面顶端(堆积煤渣未超过锥顶时,在C点;堆积煤渣超过锥顶,在锥面端头锥顶),如果接触面顶端承受的应力超过该点的堆积煤渣剪切应力,则堆积煤渣遭到破坏、锥面端头可向前移动。
由于堆积煤渣相邻颗粒之间具有一定的咬合作用,图9(b)的某片煤渣薄板受侧向力挤压后,受压效应向前传递(距离越远,效应越弱),导致该煤渣薄板至钻孔孔壁一侧应力升高,而至钻孔中心一侧应力下降(相当于1根受压弹簧,从某个位置施加新力后,受压一侧弹簧绷紧程度加强,而另一侧弹簧绷紧程度减弱);虽然煤渣属于散体,单片煤渣薄板微观上的受压效应传递能力较低,但是,当众多煤渣薄板的微观受压效应传递累积起来时,宏观上可以在一定程度上影响应力分布。
在全体煤渣薄板受压效应传递综合作用下,从C点到钻孔孔壁(E1、E2)的堆积煤渣应力变化如下:靠近C点一侧应力下降,靠近钻孔孔壁(E1、E2)一侧应力上升,C点(位于钻孔中心,并且距侧向力最近)应力下降大。根据散体动力学理论[17],摩尔库伦破坏准则适用于散体,堆积煤渣剪切应力与正应力成正比。因此,受侧向力挤压效应传递的影响,堆积煤渣C点及其邻近区域的剪切应力降低,C点下降值最大。
综上所述,锥面端头减阻机理如下:锥面端头越尖(θ越小),侧向力Fy越大,堆积煤渣厚度h越低、接触面顶端及其临近区域堆积煤渣剪切应力越小,堆积煤渣对锥面端头移动的阻碍能力越弱。
注:C点及其邻近区域堆积煤渣受力破坏后,堆积煤渣整体失去稳定性,靠近钻孔孔壁(E1、E2)一侧堆积煤渣应力自然得到释放。
5. 封孔器端头优化改进与现场试验
根据锥面端头移动最小推力与影响因素的关系,可从以下几个方面对锥面端头开展优化设计:①采用低密度材料制作锥面端头,降低端头重力;②适当减小端头锥面角度;③采用喷漆等措施提高端头锥面的光滑性,降低端头锥面与煤渣的最大静摩擦系数;④采用更细的封孔器,从而减小端头锥底半径。
在文献[15]中,将1个空心外罩(锥面角度约20°)安设于钻孔瓦斯涌出初速度测定装置的封孔器端头,端头由台阶式转变为锥面式;在此基础上,根据锥面端头优化设计思路,对封孔器端头作进一步改进。
根据图8,当锥面角度较低时,降低锥面角度改变锥面端头移动最小推力的作用不大;由于端头锥底半径与封孔器主体部分一致,而主体部分需要考虑膨胀性能、耐压性能和膨胀液输送、内置管道气体流动阻力等因素,截面尺寸(目前为38 mm)很难进一步缩小。因此,从如下2个方面对封孔器端头进行改进:①将空心外罩的制作材料由不锈钢改合金,减轻端头质量;②对封孔器锥面端头打蜡,降低端头锥面与煤渣的最大静摩擦系数。
在开滦矿区钱家营矿1355工作面进行了钻孔瓦斯涌出初速度测定现场试验,现场试验数据见表1。
表 1 现场试验数据Table 1. Experimental data in field test封孔器型号 最高送入孔深/m 孔深/m 时间/min 原始型 16 8 1.2 10 1.3 12 1.5 14 1.7 16 2.0 改进型 >20 8 0.9 10 1.0 12 1.2 14 1.3 16 1.5 18 1.7 20 1.9 由表1可知:改进型封孔器送入阻力小、推进速度快、送入钻孔深度大。
6. 结 语
1)锥面端头与煤渣接触面所承受的煤渣压力沿x轴、y轴、z轴的分力均等于挤压应力与投影面积之积;锥面端头与煤渣接触面所承受的摩擦阻力沿x轴、y轴的分力也均等于挤压应力、摩擦阻力系数和投影面积之积。
2)从理论上推导了锥面端头移动最小推力计算公式,它与端头质量、端头锥面角度、端头锥面与煤渣的最大静摩擦系数、堆积煤渣厚度和端头锥底半径均具有正相关性,为锥面端头优化设计指明了方向。
3)锥面端头移动最小推力与锥面角度呈正切函数关系,随锥面角度增大而升高并且上升速度逐渐加快。
4)通过侧向力分析,揭示了锥面端头减阻机理;锥面端头越尖,侧向力越大,堆积煤渣厚度越低、接触面顶端及其临近区域堆积煤渣剪切应力越小,堆积煤渣对锥面端头移动的阻碍能力越弱。
5)根据锥面端头优化设计思路改进后的封孔器端头,可以降低送入阻力、提高送入速度与孔深。
-
表 1 水力压裂模拟所需基本参数
Table 1 Basic parameters required for hydraulic fracturing simulation
项目 取值 项目 取值 层位 3#煤层 硬煤层弹性模量/GPa 4.20 施工井段/m 593~598 硬煤层泊松比 0.26 地层温度/℃ 25 软煤层弹性模量/GPa 1.50 压裂液 活性水 软煤层泊松比 0.32 顶板岩性 砂岩/泥岩 底板岩性 泥岩 砂岩弹性模量/GPa 34.6 泥岩弹性模量/GPa 12.5 砂岩泊松比 0.22 泥岩泊松比 0.32 -
[1] 张群,降文萍,姜在炳,等. 我国煤矿区煤层气地面开发现状及技术研究进展[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2023,51(1):139−158. ZHANG Qun, JIANG Wenping, JIANG Zaibing, et al. Present situation and technical research progress of coalbed methane surface development in coal mining areas of China[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2023, 51(1): 139−158.
[2] 李宗源,倪小明,石延霞,等. 马必东区块水力喷射分段压裂工艺优化与应用[J]. 煤矿安全,2021,52(12):78−83. LI Zongyuan, NI Xiaoming, SHI Yanxia, et al. Optimization and application of hydraulic injection segmental fracturing process in Mabidong Block[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021, 52(12): 78−83.
[3] 周博成,熊炜,赖建林,等. 武隆区块常压页岩气藏低成本压裂技术[J]. 石油钻探技术,2022,50(3):80−85. ZHOU Bocheng, XIONG Wei, LAI Jianlin, et al. Low-cost fracturing technology in normal-pressure shale gas reservoirs in Wulong Block[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2022, 50(3): 80−85.
[4] 蒋廷学,周珺,廖璐璐. 国内外智能压裂技术现状及发展趋势[J]. 石油钻探技术,2022,50(3):1−9. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2022065 JIANG Tingxue, ZHOU Jun, LIAO Lulu. Development status and future trends of intelligent fracturing technologies[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2022, 50(3): 1−9. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2022065
[5] 王小华,罗浩然,张丰收. 水平井射孔压裂完井下控制近井筒裂缝复杂度的参数优化[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2022,41(6):1223−1234. WANG Xiaohua, LUO Haoran, ZHANG Fengshou. Parameter optimization for controlling the complexity of near-wellbore fractures for perforated fracturing of horizontal wells[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2022, 41(6): 1223−1234.
[6] 陈凯,张东明,任发科. 水力压裂试验中煤体扰动应力变化规律研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2023,54(3):79−84. CHEN Kai, ZHANG Dongming, REN Fake. Study on variation law of coal disturbance stress in hydraulic fracturing test[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2023, 54(3): 79−84.
[7] 张丰收,吴建发,黄浩勇,等. 提高深层页岩裂缝扩展复杂程度的工艺参数优化[J]. 天然气工业,2021,41(1):125−135. ZHANG Fengshou, WU Jianfa, HUANG Haoyong, et al. Technological parameter optimization for improving the complexity of hydraulic fractures in deep shale reservoirs[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(1): 125−135.
[8] 蒋宝云,周玉龙,陈莉,等. 滨425区块非均质油藏压裂裂缝参数优化[J]. 科学技术与工程,2021,21(22):9322−9329. JIANG Baoyun, ZHOU Yulong, CHEN Li, et al. Optimization of fracture parameters for heterogeneous reservoir in B425 block[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(22): 9322−9329.
[9] 周再乐,张广清,熊文学,等. 水平井限流压裂射孔参数优化[J]. 断块油气田,2015,22(3):374−378. ZHOU Zaile, ZHANG Guangqing, XIONG Wenxue, et al. Perforating parameter optimization of limit entry fracturing for horizontal wells[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2015, 22(3): 374−378.
[10] 刘尧文. 复杂构造区深层页岩气藏射孔参数优化及应用−以涪陵页岩气田白马区块为例[J]. 天然气工业,2021,41(1):136−145. LIU Yaowen. Optimization of application of perforation parameters of deep shale gas reservoirs in complex structural areas: A case study of the Baima Block of Fuling shale gas field[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(1): 136−145.
[11] 綦民辉,孙伟,王倩,等. 射孔参数对薄煤层群压裂起裂的影响研究[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2020,42(6):745−751. QI Minhui, SUN Wei, WANG Qian, et al. Influences of perforation parameters on the fracture initiation in thin coal bed groups[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2020, 42(6): 745−751.
[12] 朱海燕,徐鑫勤,钟安海,等. 深层页岩油水平井密切割裂缝均衡扩展数值模拟−以胜利油田YYP1井为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2022,43(1):229−240. ZHU Haiyan, XU Xinqin, ZHONG Anhai, et al. Numerical simulation of evenly propagating hydraulic fractures with smaller cluster spacing in the horizontal well YYP1 for deep shale oil in the Shengli Oilfield[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(1): 229−240.
[13] 娄毅,胡海洋,姜秉仁,等. 贵州复杂地层应力扰动压裂技术研究及应用[J]. 煤矿安全,2023,54(4):29−35. LOU Yi, HU Haiyang, JIANG Bingren, et al. Research and application of stress disturbance fracturing technology in complex formations in Guizhou Province[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2023, 54(4): 29−35.
[14] 李俊峰. 沁水盆地郑庄井田煤层气分段压裂水平井开发技术[J]. 煤矿安全,2023,54(6):34−40. LI Junfeng. Development technology of coalbed methane horizontal wells with staged fracturing in Zhengzhuang Field of Qinshui Basin[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2023, 54(6): 34−40.
[15] 从常奎. 王峰煤矿3#煤顶板水力压裂裂缝扩展模拟研究[J]. 煤炭技术,2022,41(1):137−141. CONG Changkui. Simulation research on hydraulic fracturing crack propagation of No.3 coal roof in Wangfeng coal mine[J]. Coal Technology, 2022, 41(1): 137−141.
[16] 王世斌,王刚,陈雪畅,等. 基于PFC2D-COMSOL的煤层水力压裂增透促抽瓦斯数值模拟研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2022,53(10):132−140. WANG Shibin, WANG Gang, CHEN Xuechang, et al. Study on permeability improvement and gas extraction by coal seam hydraulic fracturing based on PFC2D-COMSOL numerical simulation[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(10): 132−140.
[17] 张勇年,马新仿,王怡,等. 沁端区块煤层气水平井分段压裂裂缝参数优化研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2016,44(9):178−184. ZHANG Yongnian, MA Xinfang, WANG Yi, et al. Optimized study on fracture coefficient of sectional fracturing in coalbed methane horizontal well in Qinduan Block[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2016, 44(9): 178−184.
[18] 赵金洲,何弦桀,李勇明,等. FracproPT软件在二次加砂压裂模拟与施工参数优化中的应用[J]. 石油与天然气化工,2014,43(4):416−420. ZHAO Jinzhou, HE Xianjie, LI Yongming, et al. Application of FracproPT software in secondary sanding fracturing simulation and construction parameters optimization[J]. Chemical Engineering of Oil & Gas, 2014, 43(4): 416−420.
[19] 倪小明,王延斌,韩文龙,等. 煤层气开发地质单元划分与应用实践[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(7):2562−2574. NI Xiaoming, WANG Yanbin, HAN Wenlong, et al. Division and application of development geological units for coalbed methane[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(7): 2562−2574.
[20] 张苗,邹明俊,吕乐乐,等. 水力压裂过程中陶粒支撑剂运移规律及粒级配比优化[J]. 煤矿安全,2022,53(2):16−19,26. ZHANG Miao, ZOU Mingjun, LYU Lele, et al. Migration law of ceramsite proppant and its granularity matching during coalbed methane fracturing[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(2): 16−19,26.
[21] 王志荣,胡凯,杨杰,等. 软煤储层顶板水平井穿层工况下压裂缝扩展模型[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2019,47(6):20−25. WANG Zhirong, HU Kai, YANG Jie, et al. Extension model of fracturing cracks of translayer horizontal well in roof of soft coal reservoir[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2019, 47(6): 20−25.
[22] 边利恒,熊先钺,王炜彬. 低渗透软煤储层压裂改造研究[J]. 煤炭技术,2017,36(2):185−186. BIAN Liheng, XIONG Xianyue, WANG Weibin. Research on stimulation of low permeability soft coal formation[J]. Coal Technology, 2017, 36(2): 185−186.
[23] 倪小明,李哲远,王延斌. 煤储层水力压裂后渗透率预测模型建立及应用[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2014,42(6):92−95. NI Xiaoming, LI Zheyuan, WANG Yanbin. Establish and application on prediction model about permeability of coal reservoir after hydraulic fracture[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2014, 42(6): 92−95.




 下载:
下载: