Research on temperature effect of consolidation and bearing capacity of multi-source coal-based solid waste backfill
-
摘要:
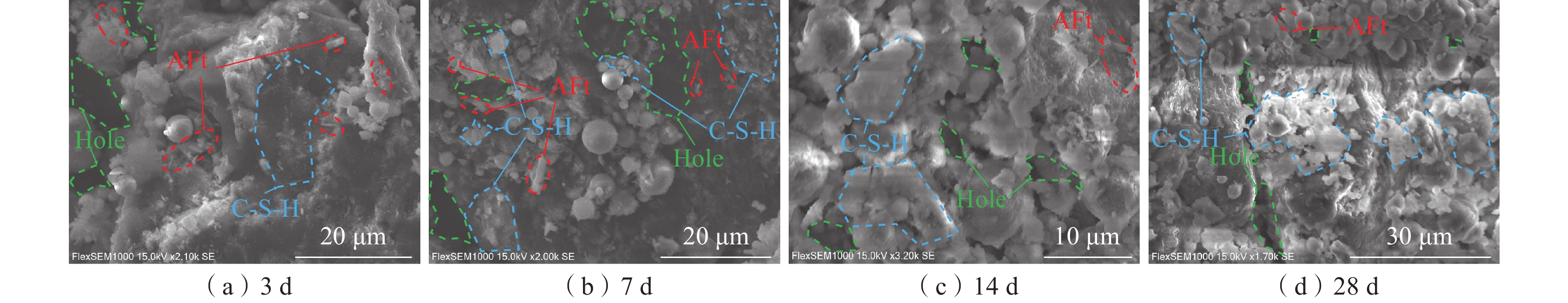
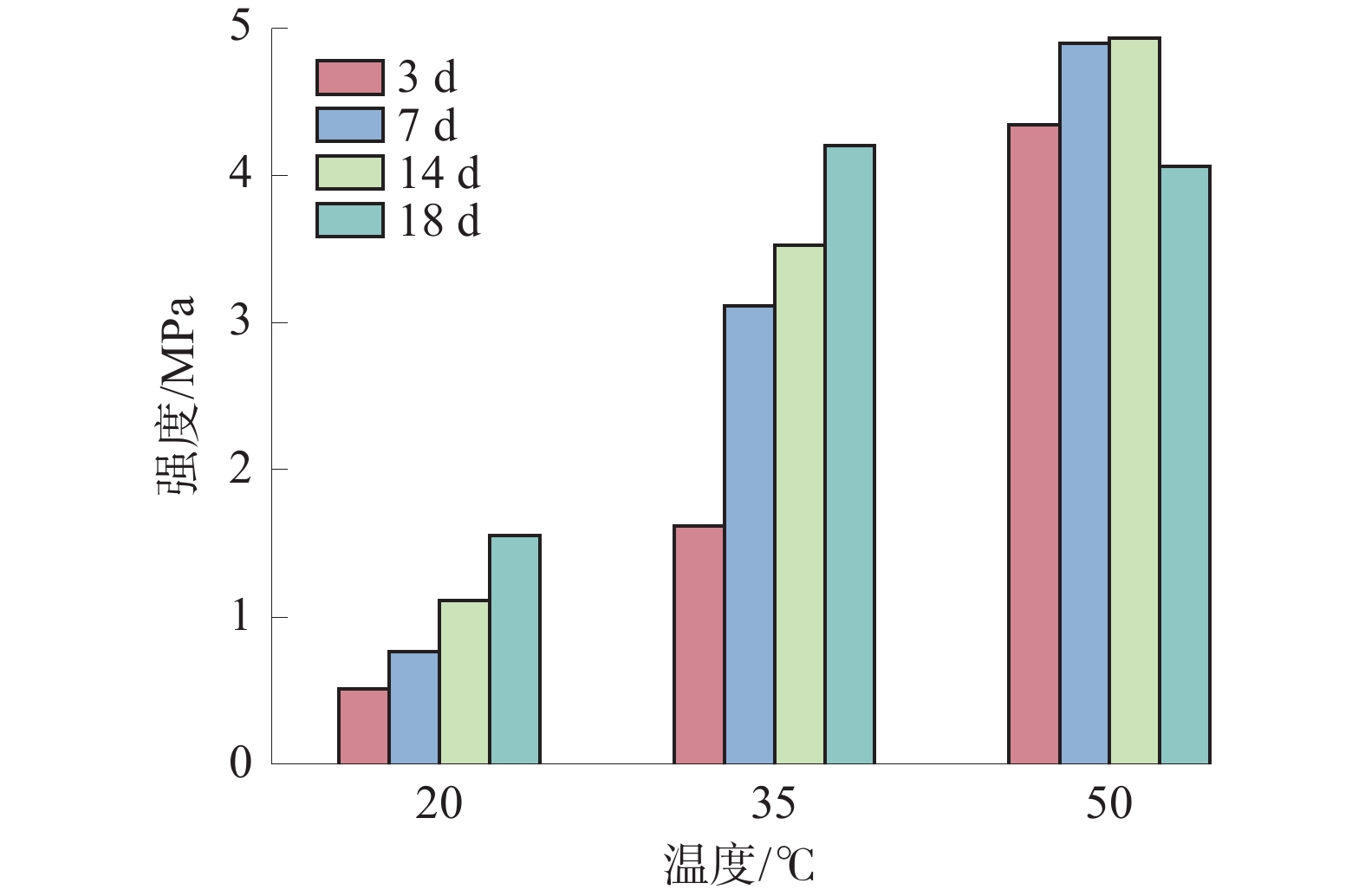
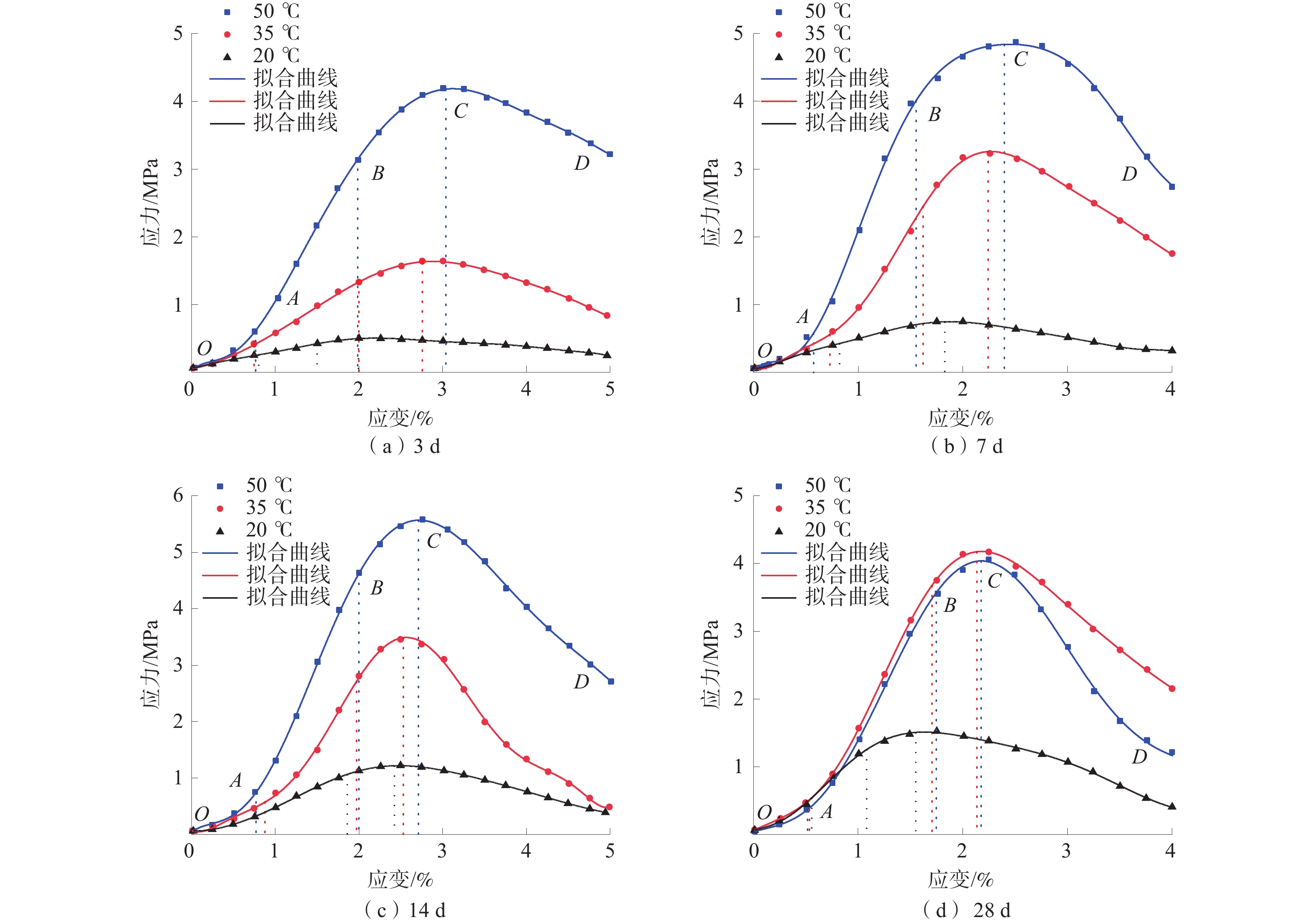
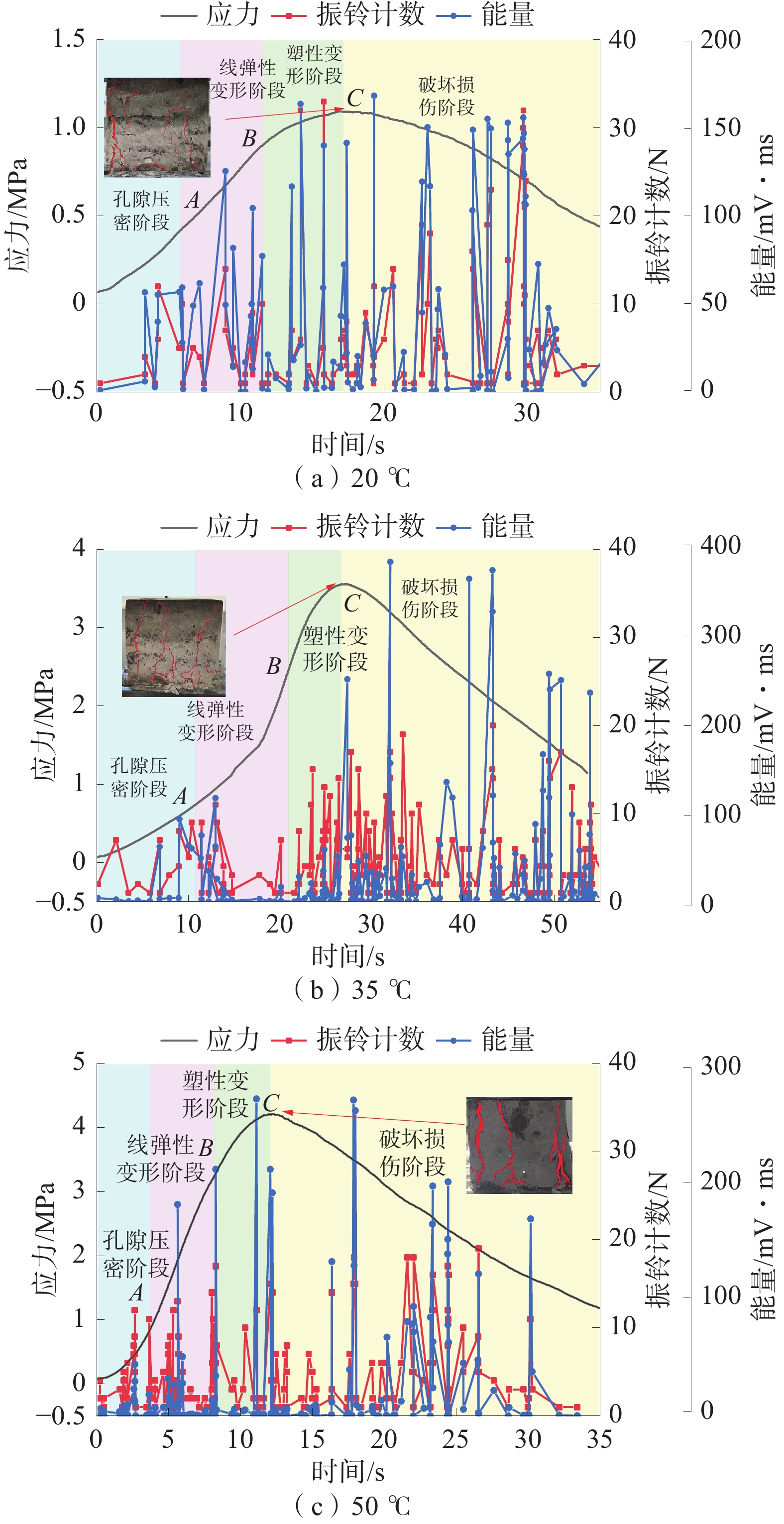
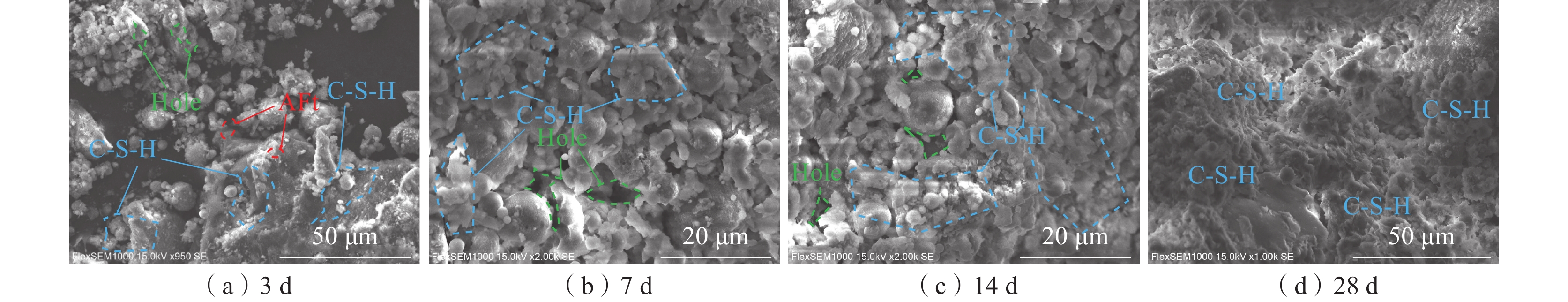
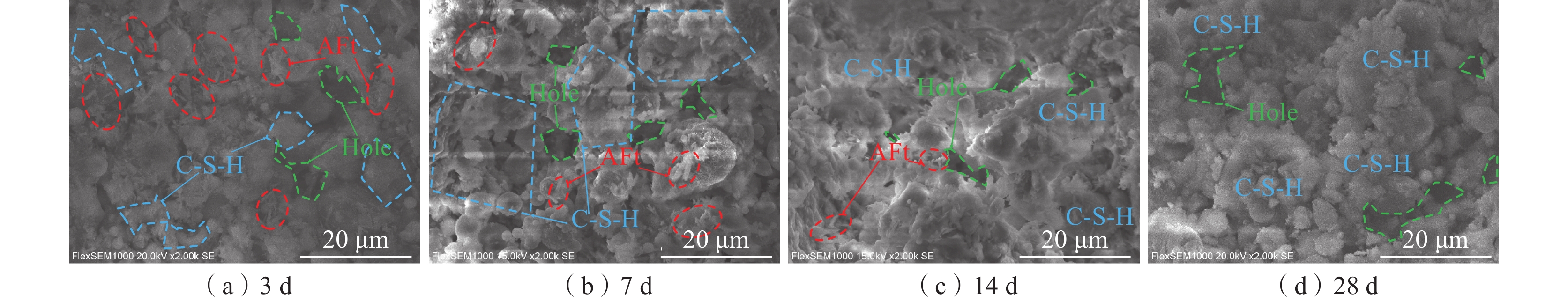
为研究煤基固废膏体充填体在煤矿深部高地温环境下的固结承载性能,采用单轴压缩和声发射试验,测试不同养护温度(20、35、50 ℃)和龄期(3、7、14、28 d)影响下膏体充填体强度与破坏特征;通过SEM测定充填胶结体微观形貌和矿物组成,从微观角度揭示养护温度对水化反应的影响规律。研究结果表明:伴随养护温度的升高,其对水化反应的影响逐渐从促进转变为抑制,28 d抗压强度在养护温度为35 ℃时达到最大值;声发射事件主要发生在压密和破坏阶段,养护温度提高促使声发射活动提前活跃,充填体破坏形态逐渐由延性破坏转变为脆性破坏;由于热损伤作用,高温养护加快了充填体早期水化反应速率,而对养护后期充填体内C-S-H和孔隙结构造成破坏,对其长期强度的增加产生不利影响。
Abstract:In order to study the consolidation bearing capacity of coal-based solid waste paste backfill in deep high ground temperature environment of coal mine, uniaxial compression and acoustic emission tests were used to test the strength and failure characteristics of paste backfill under different curing temperature conditions (20 ℃, 35 ℃ and 50 ℃) and ages (3 d, 7 d, 14 d and 28 d). The microstructure and mineral composition of the filling cement were measured by SEM, and the influence of curing temperature on the hydration reaction was revealed from the microscopic point of view. The results show that: with the increase of curing temperature, its influence on hydration reaction gradually changes from promotion to inhibition, and the 28 d compressive strength reaches the maximum at 35 ℃; acoustic emission events mainly occur in the compaction and failure stages. The increase of curing temperature promotes the activity of acoustic emission in advance, and the failure mode of filling body gradually changes from ductile failure to brittle failure; due to the thermal damage, high temperature curing accelerates the early hydration reaction rate of the filling body, and causes damage to the C-S-H and pore structure of the filling body in the later stage of curing, which has an adverse effect on the increase of its long-term strength.
-
Keywords:
- coal-based solid waste /
- filling mining /
- geothermal gradient /
- temperature effect /
- thermal damage
-
声波传输是实现矿用声波随钻测量的关键,钻柱作为信息传输通道,由不同尺寸的钻杆相连接而成,以钻杆中传播的声波为信息载体进行数据传输[1]。为了改善目前煤矿井下瓦斯抽采的钻孔施工中大部分处于“盲钻”的问题,有必要研究煤矿井下钻杆中声波的传输机制和特性。
国内外学者针对石油随钻信息传输技术领域的钻杆柱中声波传播特性开展了大量研究。针对钻杆中声波的传播特性和频谱特性的研究表明,物性参数和钻杆结构对声波的传输过程有显著影响,印证了钻杆用作煤矿井下无线数据传输信道的可行性[2]。为进一步深入了解钻杆内声波的传播规律,通过有限元法分析影响电磁随钻测量信号强度的因素,针对钻杆等周期性管柱中的信息传输,设计井下声波发生器以有效地产生声波和高效地传输声能,建立频谱特性的判断标准,通过评价函数对通带和频谱特性进行定量表征[3-5],有助于选取最优载波频率,减少井下因素对钻柱信号的不良效应。在实际工况中,钻柱振动会引起钻柱故障、井眼轨迹恶化、钻头过度磨损等问题,学者们通过建立振动模型和实验钻柱系统,从轴向力、钻柱水平位移和摩擦扭矩等角度分析钻柱在不同振动形式下的特性,确定导致钻井过程不稳定的主要因素[6-9],更好地降低水平井钻井时的钻柱振动。此外,考虑到钻柱波与井孔环境的相互作用,学者们通过建立物理模型和理论计算模型,研究了弯曲钻柱声波传播特性,得出了不同声源频率下声波信号的处理方法、衰减规律和有效传输距离[10-11];为进一步深入了解钻杆内声波的传播规律和井下信息传输的载体信号频率选择提供了参考。
考虑到煤矿井下实际工况条件的差异、不同信号加载方式等因素影响,钻杆柱中声波信号衰减和色散等问题也不可避免地有所差别,因此,有必要研究煤矿井下钻杆柱中声波传输特性。为此,基于声波在周期性结构中的波动方程分析声波在钻杆柱中的传播特性;通过有限元分析软件对声波在钻杆中的传播过程进行仿真,分析输出波形幅值衰减特性以及频散特性;搭建试验平台得到了声波幅值衰减特性和波形变化规律,验证了理论分析和建模仿真结果;研究结果将为声波传输系统的设计和通信的模式选择、编码与波形识别提供理论依据。
1. 钻杆柱中声波传播特性
对实际结构进行调研发现,钻具之间通过接头连接,因此钻柱并不具有本质上的连续性。针对钻杆中的声波传播特性研究,通常将钻杆看作周期性管串结构,仅考虑由等长度的钻杆组成的钻柱[1-2,5],周期性理想钻杆模型如图1所示。钻杆主要由管体和接头连接而成,管体部分为等截面的圆管,接头处截面积发生改变。结合周期性理想钻杆模型,建立等效周期性系统,周期性钻杆系统结构示意图如图2所示。图中:Li、Si、ρi分别为第i段的长度、横截面积、材料密度;uti为第i个单元内透射波的位移;uri为第i个单元内反射波的位移。
由图2可得:i为奇数时为钻杆段时,Li= L1,Si= S1,ρi=ρ1;i为偶数时为接头段时,Li= L2,Si= S2,ρi=ρ2。
1.1 声波在周期性结构中的波动方程
纵波常作为井下声波传输的载波形式,利用纵波在圆截面的直杆中的传播特性来近似表示声波在周期性结构钻柱中的传播特性。假设钻柱的阻抗为密度ρ和横截面积S的综合函数为F,针对纵波在钻柱结构中的传播,仅考虑质点的轴向位移$ u(x,t) $,钻杆中纵波波动方程为[12]:
$$ \rho s\frac{{\partial v}}{{\partial x}} = - \frac{{\partial F}}{{\partial x}} $$ (1) 式中:v为质点速度,$ v = \dfrac{{\partial u}}{{\partial t}} $;t为时间。
用x代替位置坐标,将油管柱的单位质量表示为:
$$ m = \int_0^{{x}} \rho (\xi )S(\xi ){\text{d}}\xi $$ (2) 式中:m为油管柱的质量坐标。
对式(2)求偏导可得:
$$ \frac{\partial F}{{\partial {{x}}}} = \frac{{\partial m}}{{\partial {{x}}}} \cdot \frac{\partial F}{{\partial m}} = \rho S\frac{\partial F}{{\partial m}} $$ (3) 式(1)在质量坐标下转换为:
$$ \frac{{\partial v}}{{\partial t}} = - \frac{{\partial F}}{{\partial m}} $$ (4) 式中:$ F = - {{\textit{z}}^2}\dfrac{{\partial u}}{{\partial m}} $,z为阻抗,$ {\textit{z}} = S\rho c $;c为声波波速。
由式(4)可得:
$$ \frac{{{\partial ^2}u}}{{\partial {t^2}}} = \frac{\partial }{{\partial m}}\left( {{{\textit{z}}^2}\frac{{\partial u}}{{\partial m}}} \right) $$ (5) $$ \frac{{{\partial ^2}F}}{{\partial {t^2}}} = {{\textit{z}}^2}\frac{{{\partial ^2}F}}{{\partial {m^2}}} $$ (6) 由上述公式可知,声波在钻杆中的衰减特征与其频率、阻带、带宽等因素密切相关。式(6)即为质量坐标系下的经典波动方程,是理论分析纵波周期性钻柱结构中的传播特性的基础。
1.2 钻柱中声波信道的频率传输
在零初始条件下,用Fourier变换求解质量坐标系下的经典波动方程可得[13]:
$$ \frac{{{{\mathrm{d}}^2}f}}{{{\mathrm{d}}{m^2}}} + {k^2}f = 0 $$ (7) 式中:$ f(m,\omega ) $为$ F(m,t) $的傅立叶变换;$ \omega $为角频率。
令$ K = \omega /z $,$ K(m,\omega ) $是$ \omega $的周期函数K,用$ {K_\xi } $表示为:
$$ {K_\xi } = \frac{\omega }{{{{\textit{z}}_\xi }}} = \frac{\omega }{{{\rho _\xi }{S_\xi }{c_\xi }}} $$ (8) 利用傅里叶定理,将式(7)的通解表示为:
$$ f = f(m,\omega ){{\mathrm{e}}^{ - {\mathrm{j}}Km}} $$ (9) 周期性钻杆系统由2个部分单元组成,将每一部分的基本特性视为是1组常数,用下标$ \xi $标记。将各部分长度记为$ {L_\xi } $,质量记为$ {m_\xi } $,则:
$$ {m_\xi } = {\rho _\xi }{S_\xi }{L_\xi } $$ (10) 在给定的长度L上,方程式(7)的解也可表示为:
$$ {f_L} = {A_L}{{\mathrm{e}}^{ - {\mathrm{j}}KSm}} + {B_L}{{\mathrm{e}}^{{\mathrm{j}}KSm}} $$ (11) 将式(11)代入到式(9),可得:
$$ {f_L} = {f_L}(m,\omega ){{\mathrm{e}}^{( - {\mathrm{j}}knL/m)}} $$ (12) 式中:$ {f_L}(m,\omega ) = {A_L}{{\mathrm{e}}^{{\mathrm{j}}( {kL/{m{ { - {K_\xi }} }}} )m}} + {B_L}{{\mathrm{e}}^{{\mathrm{j}}( {kL/{m{{ + K{K_\xi }} )m}}}}} $。
由式(12)计算可得s段质点的振速为:
$$ {v_L} = \left( {1/{z_\xi }} \right){g_L}(m,\omega ){{\mathrm{e}}^{( - {\mathrm{j}}kmL/m)}} $$ (13) 式中:$ {g_L}(m,\omega ) = {A_L}{{\mathrm{e}}^{{\mathrm{j}}\left( {kL//{K_s}} \right)m}} - {B_L}{{\mathrm{e}}^{{\mathrm{j}}\left( {kL//m + {K_\xi }} \right)m}} $。
在周期性钻杆系统x=0和x=Li 2个接头处,作用力和质点振速满足均是连续的边界条件[14],结合式(9)和式(13),应用Floquet理论,可得以下方程组:
$$ {f_{i - 1}}(0,\omega ) = {f_i}(0,\omega ) $$ (14-a) $$ \left( {1/{{\textit{z}}_2}} \right){g_{i - 1}}(0,\omega ) = \left( {1/{{\textit{z}}_1}} \right){g_i}(0,\omega ) $$ (14-b) $$ {f_{i - 1}}\left( { - {m_2},\omega } \right) = {f_i}\left( {{m_1},\omega } \right) $$ (14-c) $$ \left( {1/{{\textit{z}}_2}} \right){g_{i - 1}}\left( { - {m_2},\omega } \right) = \left( {1/{{\textit{z}}_1}} \right){g_i}\left( {{m_1},\omega } \right) $$ (14-d) 再将上面的方程组写成矩阵形式,即:
$$ \left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{{\textit{z}}_1}}&{{{\textit{z}}_1}}&{{{\textit{z}}_2}}&{{{\textit{z}}_2}} \\ 1&{ - 1}&1&{ - 1} \\ {{{\textit{z}}_1}{{\mathrm{e}}^{{\alpha _1}{y_1}}}}&{{{\textit{z}}_1}{{\mathrm{e}}^{\beta {\gamma _1}}}}&{{{\textit{z}}_2}{{\mathrm{e}}^{ - {\alpha _2}{\gamma _2}}}}&{{{\textit{z}}_2}{{\mathrm{e}}^{ - {\beta _2}{y_2}}}} \\ {{{\mathrm{e}}^{{\alpha _1}{\gamma _1}}}}&{ - {{\mathrm{e}}^{{\beta _1}{\gamma _1}}}}&{{{\mathrm{e}}^{ - {\alpha _2}{y_2}}}}&{ - {{\mathrm{e}}^{ - {\beta _y}{y_2}}}} \end{array}} \right)\left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{A_i}/{{\textit{z}}_1}} \\ {{B_i}/{{\textit{z}}_1}} \\ { - {A_{i - 1}}/{{\textit{z}}_2}} \\ { - {B_{i - 1}}/{{\textit{z}}_2}} \end{array}} \right) = \left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{l}} 0 \\ 0 \\ 0 \\ 0 \end{array}} \right) $$ (15) 式中:$ {\alpha _\xi } = {\mathrm{j}}\left( {kL/m - {K_\xi }} \right) $,$ {\beta _\xi } = {\mathrm{j}}\left( {kL/m - {K_\xi }} \right) $。
令式(15)=0,可得:
$$ \begin{split} & \begin{aligned} \cos\; kL = \cos \left( {\frac{{\omega {L_1}}}{{{c_1}}}} \right)\cos \left( {\frac{{\omega {L_2}}}{{{c_2}}}} \right) -\\ \frac{1}{2}\left( {\frac{{{{\textit{z}}_1}}}{{{{\textit{z}}_2}}} + \frac{{{{\textit{z}}_2}}}{{{{\textit{z}}_1}}}} \right)\sin \left( {\frac{{\omega {L_1}}}{{{c_1}}}} \right)\sin \left( {\frac{{\omega {L_2}}}{{{c_2}}}} \right) \end{aligned}\\[-14pt]& \end{split} $$ (16) 式中:c1、c2为阻抗z1、z2对应的声波波速。
当${\textit{z}}_1 \neq {\textit{z}}_2 $时,式(16)的解为非常数,即纵波声速与频率有关,发生了色散,此时方程称为色散方程。当$ |\cos\; kL| \lt 1 $时,方程有解,波数k为实数;反之,方程无解,波数k为复数。在波动方程中,当波数k为实数时,则其相应的频率信号相对无衰减通过,形成1条通带;当波数k为复数时,相应的频率由于衰减较大,形成了阻带,证实了声波在钻杆柱中的传播过程中,频率呈现出通带与阻带相间隔交替的梳状滤波器特征。
1.3 声波传播的衰减特性
声波沿钻杆传播的过程中,其信号强度随时间而衰减,主要受到接箍、声波频率及环境介质的阻尼等因素的影响[15]。声波在钻杆中传播时,其信号幅值随距离增加呈指数衰减。声波传输相对应的波动方程为:
$$ A = {A_0}{{\mathrm{e}}^{ - \alpha x}}{{\mathrm{e}}^{{\mathrm{j}}(\omega t - kx)}} $$ (17) 式中:A为声波在传播距离x处的波振幅;$ {A_0}{{\mathrm{e}}^{ - \alpha x}} $为波动方程中的包络线函数;A0为声波初始波振幅;α为声波的衰减系数。
声波的衰减系数可表示为:
$$ \alpha = \frac{1}{x}\ln \frac{{{A_0}}}{A} = \frac{{2.302\;6}}{x}\lg \frac{{{A_0}}}{A} $$ (18) 设声波信号的传播距离为xi,不同距离处的波振幅设为Ai,则衰减系数的一般表达式为:
$$ \alpha = \frac{1}{{\left( {{x_{i + 1}} - {x_i}} \right)}}\ln \frac{{{A_i}}}{{{A_{i + 1}}}}\quad i = 1,2,3, \cdots n$$ (19) 2. 钻杆声波传输有限元分析
钻杆连接示意如图3所示,钻杆两端通过螺纹与信号源(敲击端)以及公接头堵头(接收端)紧密扣接,振动传感器作为声波信号接收器安装于公接头堵头的外侧端面中心位置。
2.1 求解条件设定
采用通用隐式静力学求解钻杆重力载荷加载和接触状态,基于模态叠加法的模态动力学求解声波传递过程。计算时假设所有连接螺纹配合足够紧密的,不存在松动的可能,主要考虑钻杆自然搁置在水平地面/试验台上的情况。提取频率前定义钻杆与地面在重力载荷下的接触关系并计算其接触状态,获得真实的接触刚度。
钻杆材质为钢材,密度为7 850 kg/m3,弹性模量为210 GPa,泊松比为0.3。由于钻杆属于小质量构件,选用对高频信号较为敏感的beta材料刚度阻尼,阻尼系数由各个钻杆装配体的最低阶频率值和临界阻尼系数得出,临界阻尼系数取0.05。
为避免沙漏现象对声波传递能量的影响,单元类型选择全积分单元进行求解。将地面简化为解析刚体,对其参考点施加完全约束,并约束钻杆顶部中间节点的侧向自由度,避免钻杆在侧向产生不必要的滚动。实际计算时,将实测的加速度信号作为基础激励加载到敲击点,计算钻杆结构的实际响应过程。
2.2 不同因素的影响
为研究声波在钻杆中传播的影响因素,以钻杆有限元模型为基础,研究不同钻杆直径、不同敲击位置、不同放置形式以及埋沙注水2种工况下对声波传播特性和衰减规律的影响。选用最大幅值(对接收信号的正负最大值取绝对值后再平均)和时均幅值(接收信号围绕时间轴的面积除以信号接收时间0.05 s)2个指标来评估信号接收效果,以便对比不同因素作用下接收到的信号强度变化规律。
1)不同敲击位置的影响。以原始有限元模型为基础,改变敲击位置(竖直方向的最高点(a点)、敲击端面几何中心、竖直方向的最低点,得到的接收信号情况如图4所示。由图4可知,敲击位置从上到下,钻杆在重力的作用下,截面刚度沿着竖直方向逐渐增加,即越靠近接地侧截面刚度越大,越有利于信号传输,接收信号的最大幅值和时均幅值均逐渐增大,信号衰减变小。
2)钻杆直径的影响。增大钻杆直径分别进行计算,钻杆直径每次增加10 mm,即73.5 mm和83.5 mm。得到的不同钻杆直径下接收信号强度数据见表1。由表1可以看出,钻杆直径越大,钻杆的接收信号的时均幅值明显增大,信号衰减变小,当直径为83.5 mm时,接收信号的时均幅值为0.080。当钻杆直径越大时,在竖向重力作用下,钻杆的接地面积和接地刚度均增大,且直径增大的同时保持钻杆厚度不变,必然造成钻杆整体材料体积增加,材料的材料阻尼耗能增加,当阻尼耗能的影响幅度小于接地刚度的贡献幅度时,信号的整体衰减降低,表现出钻杆直径增大有利于信号传输的特性。
表 1 不同钻杆直径的信号强度数据Table 1. Signal strength data for different drill pipe diameters钻杆直径/mm 最大幅值 时均幅值 63.5 0.89 0.071 73.5 0.94 0.076 83.5 0.94 0.080 3)钻杆不同放置形式的影响。将钻杆竖直放置,钻杆上部为悬挂端,下部为敲击端,重力方向竖向向下。对比钻杆水平放置和竖直放置条件下的声波接收信号可得,竖直放置条件下声波信号强度低于水平放置,信号时均幅值降低了32%。在重力作用下,钻杆属于大柔度结构且轴向主要承受预拉力,钻杆整体刚度降低,由于声波在刚度较大的介质中传播距离更远,因此竖直放置条件下不利于声波信号的传输。
4)外部埋沙对声波传输的影响。将埋沙环境简化为一定大小的竖向载荷,并以体力的方式叠加在钻杆重力载荷上,总体力载荷大小为10倍钻杆重力。计算得到的接收信号强度数据表明,在外部埋沙条件下,受外部埋沙竖向压力载荷的影响,钻杆与地面接触压力增大,接触刚度有所增加,信号的最大幅值略有增加,但幅度较小,时均幅值大小与无埋沙情况基本一致,接收信号整体与无埋沙情况一致,故外部埋沙条件对钻杆信号接收影响很小,其影响基本可以忽略。
5)内部注水条件对声波传输的影响。针对钻杆内部注水的工作条件,计算时将内部水域简化为仅抗压的材料,模拟水的流体特性,计算得到的钻杆内部有无注水条件下的声波接收信号对比情况如图5所示。由图5可以看出,在内部注水条件下,接收端信号明显有所衰减,说明钻杆内部注水条件不利于信号传输。内部注水首先会增大钻杆的整体质量,使得钻杆和地面的接触压力增大,接触刚度增大,有利于信号的传输,但是内部注水同时也会增大水的黏性耗能,部分信号进入水域后必然造成信号能量的衰减。刚度增加的贡献小于水黏性耗能的贡献时,黏性耗能占主导因素,最终造成信号的整体衰减。
2.3 多根钻杆连接分析
简化钻柱有限元模型,侧重声波在钻柱远距离传输中的衰减特性研究。针对不同钻杆根数计算得到钻柱整体频率变化规律,随着连接钻杆数量的增加,整体钻柱的质量增大,钻杆与地面在连接头位置的接触点数增多,钻杆侧向刚度相对变小,故整体频率值降低,自振周期变长。接收信号强度随传输距离的衰减曲线如图6所示。
由图6可以看出,在较短距离(30 m以内)传输时,接收信号的最大幅值衰减较快,在较远距离(60 m以外)传输时,接收信号的最大幅值衰减幅度变缓,信号强度保持较好。在最大计算距离(300 m)时,接收信号的强度仍不低于60%,衰减倍数约为1.6倍。
考虑到接收信号幅值存在正负,且存在一定的波动,将接收信号的正负最大值取绝对值并平均作为信号强度指标SI($0 \leqslant {\mathrm{SI}} \leqslant 1$)[16]。对计算传输距离内的最大接收信号强度进行拟合,得到信号强度SI随传输距离d的衰减关系式为:
$$ {\text{SI}} = 0.988{{{d}}^{0.094}} $$ 由上式可以看出,衰减服从典型的幂函数衰减规律。与试验结果相比,仿真分析得到信号的衰减幅度略小,这是由于试验中可能存在接头扣紧力矩施加不足引起的局部松动,试验信号在这些位置的传输时衰减增大,而仿真模型中各钻杆的连接较试验连接更为理想,信号衰减较小。另外,试验条件下,信号总能量的一部分会以声波等形式传递到试验环境中,造成接收信号强度的进一步损失。
3. 钻杆声波传播试验
为研究声波在钻杆中的传播和衰减规律,搭建试验平台进行测试,试验平台结构示意图如图7所示。平台由声波信号发生设备、简易钻杆系统(不同数量的ϕ73 mm×1.5 m常规外平钻杆通过螺纹相连接)和信号接收模块3个部分组成。
声信号发生设备由驱动电源、信号发生器和换能器组成:驱动电源发出高压脉冲驱动信号;信号发生器按照固定频率发出控制信号;换能器将高压脉冲驱动信号转化为脉冲振动信号纵向敲击钻杆公接头端面。在较大的量程宽度内,选取了具有良好低频响应性能的压电式加速度传感器用于信号接收模块,利用示波器采集声波传感器信号进行输出显示和保存。
通过所搭建的测试平台,在不改变信号源敲击强度的条件下,以5 Hz的频率进行连续敲击,并逐渐增加钻杆柱的长度,记录接收到的原始波形。结果表明,4.5 m和289.5 m处所接收到的原始波形都较为清晰,信噪比相近,而信号的背景噪声稍大,毛刺较多。随后,为了降低信噪比、滤除背景噪声,截取峰值段波形进行傅里叶变换得到频域波形,频域波形如图8所示。
由图8可以看出,峰值段信号频域成分主要分布在1~3 kHz之间,因此对原始信号1~3 kHz以外的信号进行滤波,原始波形和滤波后波形叠加图如图9所示。
从滤波后得到的信号波形可以看出,背景噪声得到大幅消除,信号峰值基本没有衰减,信噪比得到提高,289.5 m处接收信号滤波效果更加明显。随后试验过程中,增加钻杆柱连接长度测试接收波形,每增加4根钻杆,即6 m钻杆柱,测试1组接收波形,统计所得的钻杆柱接收信号幅值变化与仿真分析结果一致,呈指数衰减趋势。
4. 结 语
1)以质量坐标系下的经典波动方程作为理论分析纵波周期性钻柱结构中的传播特性的基础。声波的频率传输过程中,其频带呈现出通、阻带交替的梳状滤波器结构特性,声波信号幅值近似按照指数规律衰减。
2)通过有限元分析钻杆声波传输过程得到:钻杆外直径越大、信号敲击端的敲击点位置距离地面越近,越有利于信号的传输,信号衰减少;钻杆内部注水条件下,接收信号明显衰减;而外部埋沙环境对信号强度的影响可以忽略;当多根钻杆连接时,接头部位钻杆与地面的接触点增多,钻杆侧向刚度相对变小,导致整体频率下降,自振周期变长。
3)钻杆柱中纵向传播的声波波形比较稳定,适合进行声波传输。在基本没有外部噪声的环境中传播时,短距离(4.5 m)和长距离(289.5 m)接收到的波形轮廓非常相似;接收信号峰值部分的频域成分集中在1个较窄的频域范围内,对此频域范围以外的频域进行滤波,能有效提高信噪比,获得良好的通频滤波效果。
-
-
[1] 张吉雄,张强,周楠,等. 煤基固废充填开采技术研究进展与展望[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(12):4167−4181. ZHANG Jixiong, ZHANG Qiang, ZHOU Nan, et al. Research progress and prospect of coal-based solid waste backfilling mining technology[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(12): 4167−4181.
[2] 杨科,魏祯,赵新元,等. 黄河流域煤电基地固废井下绿色充填开采理论与技术[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(S2):925−935. YANG Ke, WEI Zhen, ZHAO Xinyuan, et al. Theory and technology of green filling mining of solid waste underground in coal power base of Yellow River Basin[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(S2): 925−935.
[3] 孟卿. 宁夏灵武矿区地温状况及热害分布规律研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2019. [4] 王勇,吴爱祥,王洪江,等. 初始温度条件下全尾胶结膏体损伤本构模型[J]. 工程科学学报,2017,39(1):31−38. WANG Yong, WU Aixiang, WANG Hongjiang, et al. Damage constitutive model of cemented tailing paste under initial temperature effect[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2017, 39(1): 31−38.
[5] 戴元志,李平,白银,等. 低温下胶结充填体温度场和强度时变规律研究[J]. 河北工程大学学报(自然科学版),2020,37(2):80−87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9469.2020.02.013 DAI Yuanzhi, LI Ping, BAI Yin, et al. Study on the time-varying law of temperature field and strength of cemented paste backfill at low temperature[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Engineering (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 37(2): 80−87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9469.2020.02.013
[6] 刘炜震,郭忠平,黄万朋,等. 不同温度养护后胶结充填体三轴卸围压力学特性试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2022,41(11):2268−2282. LIU Weizhen, GUO Zhongping, HUANG Wanpeng , et al. Experimental study on mechanical characteristics under triaxial unloading confining pressure of cemented backfill after curing at different temperature[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2022, 41(11): 2268−2282.
[7] 白丽伟,赵润康,屈春来,等. 养护温度对胶结充填体力学特性的影响试验研究[J]. 黄金,2021,42(11):33−38. doi: 10.11792/hj20211106 BAI Liwei, ZHAO Runkang, QU Chunlai, et al. Experimental research on the influence of curing temperature on the mechanical properties of cemented filling body[J]. Gold, 2021, 42(11): 33−38. doi: 10.11792/hj20211106
[8] FALL M, CELESTIN J C, POKHAREL M. A contribution to understanding the effects of curing temperature on the properties of mine cemented tailings backfill[J]. Engineering Geology, 2010, 114: 397−400. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2010.05.016
[9] FALL M, POKHAREL M. Coupled effect of sulphate and temperature on the strength development of cemented tailings backfill: Portland cement-paste backfill[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2010, 32: 819−822. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2010.08.002
[10] 江飞飞,周辉,盛佳,等. 温度和龄期对砾石砂胶结充填体物理力学性能的影响[J].中南大学学报(英文版),2020,27(10):2999−3012. doi: 10.1007/s11771-020-4524-6 JIANG Feifei, ZHOU Hui, SHENG Jia, et al. Effects of temperature and age on physico-mechanical properties of cemented gravel sand backfills[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(10): 2999−3012. doi: 10.1007/s11771-020-4524-6
[11] 徐文彬,万昌兵,田喜春. 温度裂隙对充填体强度耦合效应及裂纹扩展模式[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2018,35(3):612−619. XU Wenbin, WANG Changbing, TIAN Xichun. Coupling effect of temperature and fracture on the strength and crack propagation mode of backfill mass[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2018, 35(3): 612−619.
[12] WU D, CAI S. Coupled effect of cement hydration and temperature on hydraulic behavior of cemented tailings backfill[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2015, 22(5): 1956−1964. doi: 10.1007/s11771-015-2715-3
[13] 陈秋松,张琦,齐冲冲,等. 磷石膏充填体强度和浸出毒性的温变规律[J]. 中国有色金属学报,2021,31(4):1084−1095. doi: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-39736 CHEN Qiusong, ZHANG Qi, QI Chongchong, et al. Temperature-depending characteristics of strength and leaching toxicity of phosphogympsum-based cemented paste backfill[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2021, 31(4): 1084−1095. doi: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-39736
[14] 张鹏,张文生,韦江雄,等. 养护温度对赤泥-矿渣碱激发胶凝材料强度和水化产物的影响[J]. 新型建筑材料,2017,44(10):1−3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-702X.2017.10.001 ZHANG Peng, ZHANG Wensheng, WEI Jiangxiong, et al. Influence of curing conditions on the strength, hydration properties of geopolymer synthesized from red mud and slag[J]. New Building Materials, 2017, 44(10): 1−3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-702X.2017.10.001
[15] LIU W, CHEN J, GUO Z, et al. Mechanical properties and damage evolution of cemented coal gangue-fly ash backfill under uniaxial compression: Effects of different curing temperatures[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 305: 124820. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.124820
[16] LIU W, GUO Z, WANG C, et al. Physico-mechanical and microstructure properties of cemented coal gangue-fly ash backfill: Effects of curing temperature[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 299: 124011. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.124011
[17] 华心祝,常贯峰,刘啸,等. 多源煤基固废充填体强度演化规律及声发射特征[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2022(8):1536−1551. HUA Xinzhu, CHANG Guanfeng, LIU Xiao, et al. Strength evolution law and acoustic-emission characteristics of multi-source, coal-based filling body of solid wastes[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2022(8): 1536−1551.
[18] 黄正栋,张东峰,张小强. 沿空留巷巷旁充填材料性能优化研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2021,52(8):59-65. HUANG Zhengdong, ZHANG Dongfeng, ZHANG Xiaoqiang. Optimization study on filling material beside gob-side entry retaining[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021, 52(08): 59-65+74.
[19] 赵志研. 大采高倾斜长壁工作面沿空留巷围岩控制技术[J]. 煤矿安全,2022,53(04):103−112. ZHAO Zhiyan. Surrounding rock control technology of gob-side entry retaining in inclined longwall face with large mining height[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(04): 103−112.
[20] 段运,王起才,杨子江,等. 蒸养对高强机制砂混凝土的热损伤效应研究[J]. 兰州交通大学学报,2022,41(5):6−12. DUAN Yun, WANG Qicai, YANG Zijiang, et al. Research on the thermal damage effect of steam curing on high strength manufactured sand concrete[J]. Journal of Lanzhou Jiaotong University, 2022, 41(5): 6−12.
[21] 冯国瑞,任亚峰,张绪言,等. 塔山矿充填开采的粉煤灰活性激发实验研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2011,36(5):732−737. FENG Guorui, REN Yafeng, ZHANG Xuyan, et al. The activating experimental research of fly ash for mining filling material in Tashan Mine[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2011, 36(5): 732−737.




 下载:
下载: