Experimental and simulation study on the effect of sulfur content on spontaneous combustion charcateristics of coal
-
摘要:
为了探究硫含量对煤炭自燃特性的影响,寻找防治高硫煤自燃灾害的高效途径;使用程序升温实验系统、综合热分析仪(TG/DSC)对典型高硫煤和典型低硫煤的氧化过程进行分析;使用量子化学模拟软件对高硫煤常用阻化剂Ca(OH)2、Na2CO3、MgCl2和2种煤中典型有机硫结构二苯硫醚 (C12H10S)、苯硫醇(C6H5SH)的络合作用进行计算。结果表明:高硫煤氧化过程中质量下降更快,放热量更大;热解失重和燃烧阶段中高硫煤的活化能相比低硫煤分别小9.16%和15.07%,高硫煤发生煤自燃的倾向更高;煤矿常用阻化剂中的Ca2+、Na+、Mg2+可以与二苯硫醚和苯硫醇络合形成络合物,形成络合物后2种有机硫结构的化学反应活性降低,能够对煤自燃起到抑制作用。
Abstract:To explore the influence of sulfur content on the spontaneous combustion characteristics of coal and find efficient ways to prevent and control the spontaneous combustion disaster of high sulfur coal, the oxidation processes of typical high sulfur coal and typical low sulfur coal were analyzed using a comprehensive thermal analyzer (TG/DSC) and a programmed heating experimental system. The complexation of commonly used inhibitors, Ca(OH)2, Na2CO3, MgCl2 and two typical organic sulfur structures, diphenyl sulfide (C12H10S) and benzenethiol (C6H5SH), in high sulfur coal and coal were calculated using quantum chemistry simulation software. The results showed that the mass loss rate during the oxidation process of high sulfur coal was faster, and the heat release was greater. The activation energies of high sulfur coal in the pyrolysis and combustion stages were 9.16% and 15.07% lower than those of low sulfur coal, respectively, indicating a higher tendency to spontaneous combustion. Na+, Mg2+, Ca2+ in the commonly used inhibitors in coal mines can form complexes with diphenyl sulfide and benzenethiol, and the chemical reactivity of the two organic sulfur structures decreases after forming complexes, which can inhibit the spontaneous combustion of coal.
-
煤炭是我国重要的能源支柱[1],在能源结构中占主体地位[2-3]。煤炭的开采通常伴随着安全事故的发生,包括瓦斯爆炸、透水、塌陷、顶板、火灾等[4],其中煤矿火灾是常见事故之一,多发于采空区。2001—2022年的数据表明[5-9],煤矿火灾事故总量虽然有着减少的趋势,但煤矿火灾伤亡数和事故数的比例在不断上升。煤矿火灾发生的主要原因是采空区遗煤自燃。煤自燃是煤炭自身产热大于煤炭向外界散发的热量从而导致热量积聚、温度上升,进而自发燃烧的现象。
煤自燃有着众多影响因素,如孔隙、结构、含水量、元素成分等。硫元素的含量是煤炭自燃的影响因素之一。煤中硫的主要存在形式分为无机硫和有机硫。学者们对于无机硫的研究主要围绕煤中黄铁矿的成分开展。DENG等[10]考察了不同黄铁矿含量的煤样对标志气体、温度和放热等自燃参数的影响,发现黄铁矿可以非线性地加速自燃过程,且黄铁矿含量为5%的煤样CO释放率和氧吸附量最大,黄铁矿含量为7%的煤样具有最大的热流率,黄铁矿含量为5%~7%对自燃的影响最为显著;YANG等[11]通过热分析表征了不同黄铁矿含量的煤在4种升温速率下的反应过程,计算了不同黄铁矿含量煤的活化能,发现煤样的表观活化能随着黄铁矿含量的增加而降低,即煤中黄铁矿可以促进煤的自燃;DING等[12]选取褐煤、烟煤、无烟煤3种不同变质程度的低硫煤煤样来研究黄铁矿对煤自燃的影响,结果发现Fe3+、Fe2+和H+对煤的低温氧化都有催化作用,其中Fe3+的催化能力最强,黄铁矿在干湿条件下对煤自燃都有催化作用,且潮湿环境下催化作用更显著;常绪华等[13]通过对10余种阻化剂的研究和筛选,得出水玻璃,Ca(OH)2、Na2CO3、NaHCO3、CaCl2、MgCl2等阻化剂对新峪矿高硫煤的氧化有明显的抑制作用。上述研究表明煤中无机硫对煤炭自燃有着促进作用。然而除了无机硫,煤中有机硫也是影响煤炭自燃特性的重要因素。煤中有机硫结构主要有硫醇、硫醚、噻吩等。国内外学者围绕有机硫对煤自燃的影响进行了深入研究。胡军等[14]研究了26个地区煤样中的有机硫,发现煤中有机硫含量多在1%范围内,高硫煤中主要以无机硫为主,低硫煤中主要以有机硫为主;王雪峰等[15]围绕金属离子对煤中含硫活性基团的影响进行研究,发现Ca2+能与煤中含硫结构形成配合物,形成配合物后分子的稳定性增强,化学活性减弱,起到抑制煤自燃的作用;叶正亮等[16]结合宏观与微观分析发现过硫酸钠可以作为一种防止高硫煤自燃的化学阻化剂;张兰君[17]、ZJANG等[18]通过程序升温、气相色谱、TG/DSC对有机硫模型化合物的自燃特性进行了实验分析,发现有机硫官能团中氧化活性最高的3个官能团为硫醇、硫醚、噻吩;ZHENG等[19]利用模型化合物,选择含有不同有机硫官能团的代表性有机硫模型化合物进行低温氧化实验和热分析,揭示了它们的氧化和热力学特性,获得了低温氧化过程中有机硫与煤中其他活性基团相互作用的机理;GAO等[20]通过低温氧化实验,研究了变质程度相近、有机硫含量不同的煤的自燃倾向,发现煤中有机硫的形态主要有硫醇类、硫醚类、噻吩类、砜类,经低温氧化后,煤中硫醇、硫醚、噻吩、甲基、亚甲基、吡啶含量下降,而砜、亚砜、硫酸根、羧基、氮氧化物等含氧基团含量增加,模型化合物低温氧化反应后,部分有机硫以芳香族硫或硫氧化物的形式存在,小部分硫以SO2和H2S气体的形式在固体氧化产物中逸出。上述研究表明,煤中有机硫的氧化会促进煤自燃的过程,通过抑制有机硫活性可以对煤自燃起到抑制作用。
现阶段高硫煤阻化剂的选取依据主要考虑阻化剂与煤中无机硫(FeS2)的相互作用,而阻化剂对高硫煤中有机硫的抑制作用却鲜有研究。为此,使用程序升温实验系统、综合热分析仪对典型高硫煤和典型低硫煤的氧化过程进行实验分析;使用量子化学模拟对高硫煤常用阻化剂中Na+、Mg2+、Ca2+和2种煤中典型有机硫结构(苯硫醇、二苯硫醚)的络合作用进行计算分析。
1. 研究方法
1)煤样选取。从若干煤样中筛选出硫元素占比差异较大且其余元素占比相近的2种煤样,分别代表典型低硫煤和典型高硫煤,煤样的元素分析见表1。
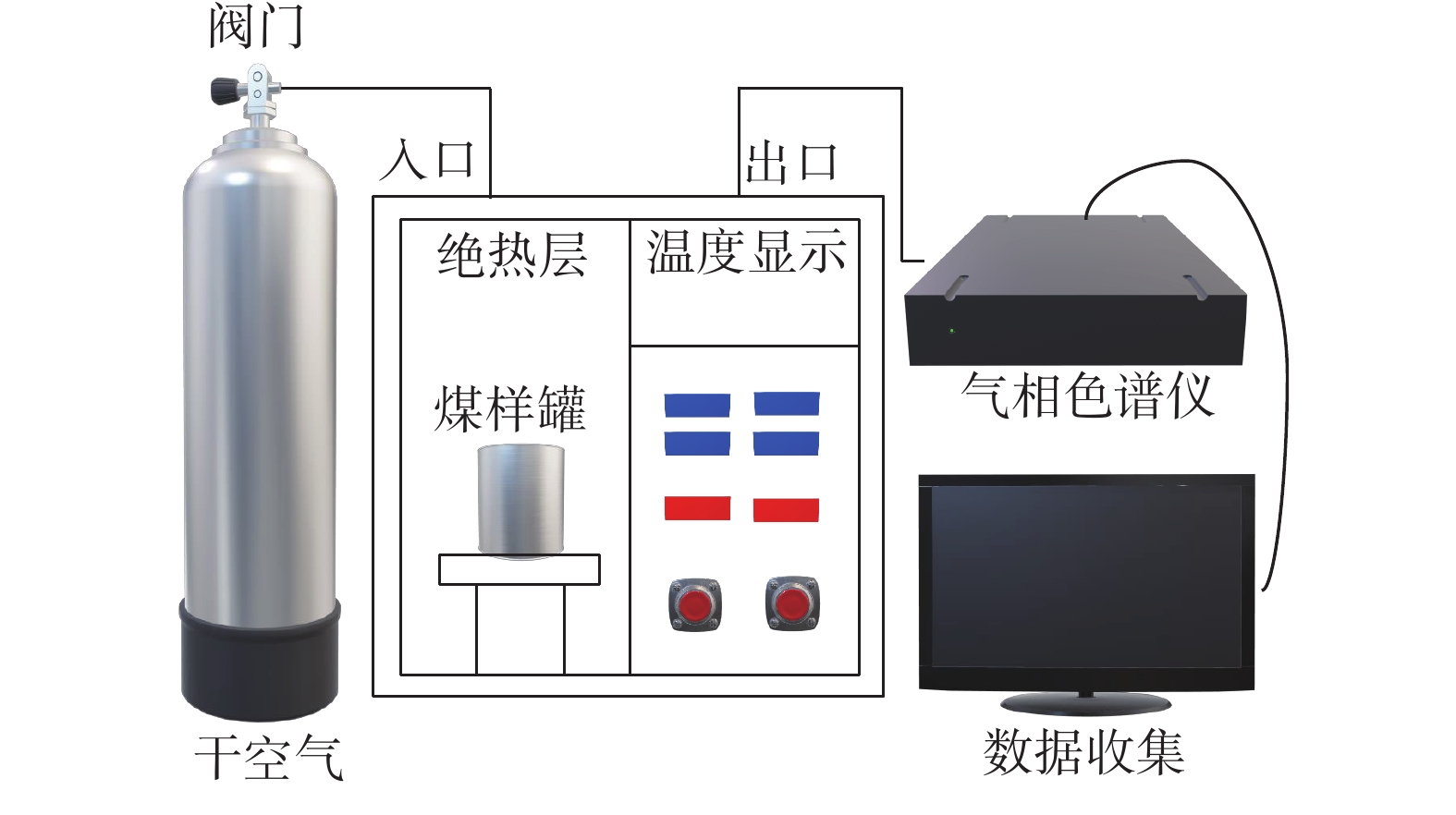
表 1 典型低硫煤的元素参数Table 1. Elemental parameters of typical low-sulfur coal% 种类 Cdaf含量 Hdaf含量 Odaf含量 Ndaf含量 Sdaf含量 低硫煤 90.41 3.92 3.29 1.26 1.12 高硫煤 86.8 4.35 3.15 0.95 4.75 2)程序升温实验系统。程序升温实验系统如图1。测试温度为20~200 ℃,升温速率为1 ℃/min,干空气通入速率为10 L/min,利用气相色谱仪检测各温度下CO与CO2体积分数。
3)热重/差示扫描量热测试(TG/DSC)。使用耐驰STA449F5同步热分析仪,获得样品的热重(TG)和差示扫描量热(DSC)曲线。升温区间为20~800 ℃,升温速率为10 K/min,保护气(N2/O2)和吹扫气(N2/O2)通入速率分别为30 mL/min和20 mL/min。
4)分子动力学模拟。使用Gaussian09软件,使用密度泛函理论(DFT)在B3LYP/6-31G(d)水平上对煤中含硫活性基团(苯硫醇、二苯硫醚)和Na+、Mg2+、Ca2+形成的络合物结构进行计算。对络合物的静电势图和HOMO/LUMO(最高占据轨道/最低非占据轨道)进行计算分析。
2. 实验结果
2.1 程序升温实验结果
通过2种煤样的程序升温实验系统测试结果可知,随着温度不断升高,陆续检测出CO2、CO、CH4等气体,其中CO2和CO在初期就可测得,二者的生成量可以用来进行煤自燃预测。煤样CO2体积分数变化曲线如图2,煤样CO体积分数变化曲线如图3。
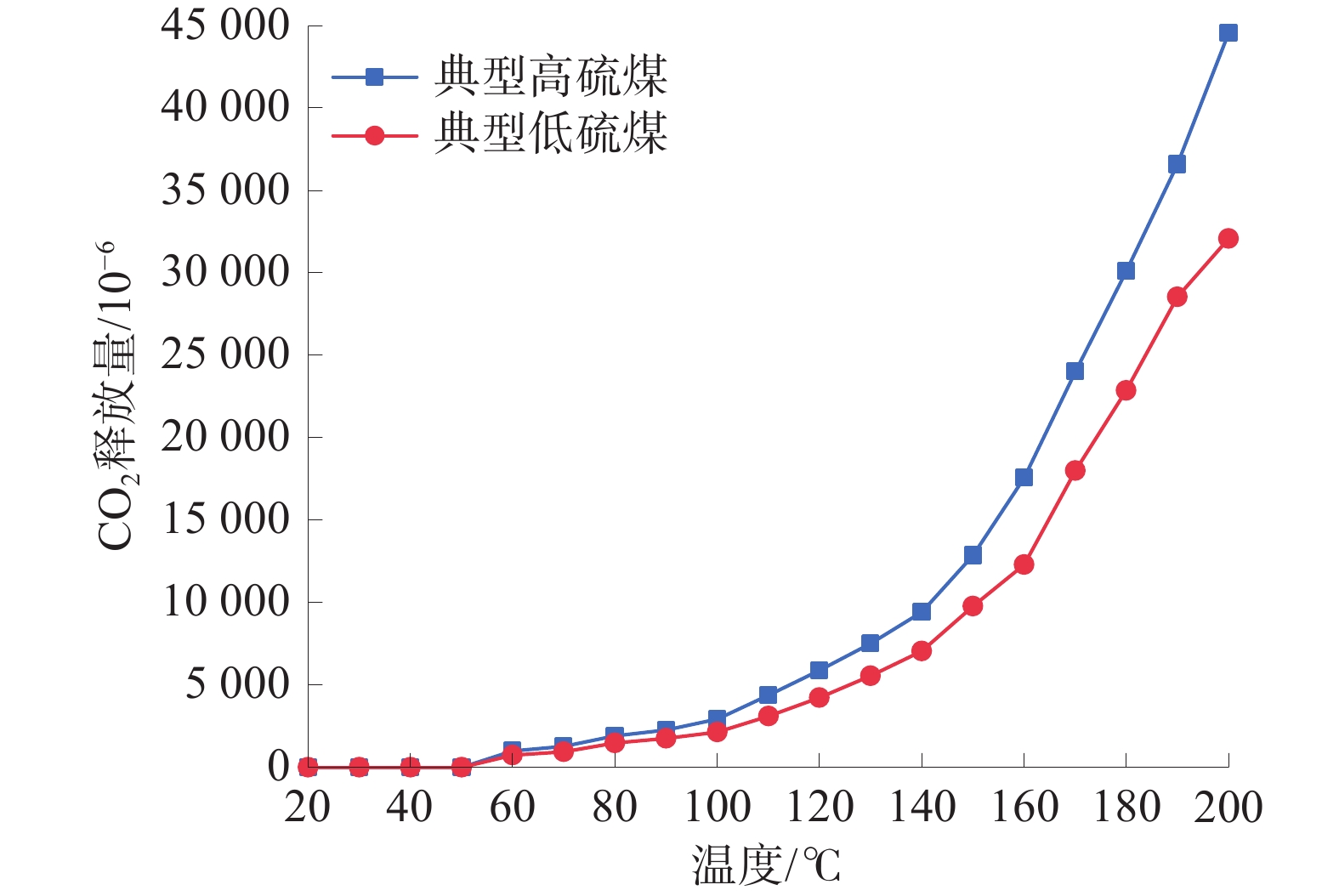
从图2可以看出:高硫煤和低硫煤的CO2体积分数曲线趋势基本一致。高硫煤在20~50 ℃时,CO2释放量随温度升高的变化较小,煤与氧气反应较为轻微;50 ℃后CO2体积分数随着温度升高显著增大;当煤样温度达到140 ℃后,CO2体积分数达到爆发式增加,总体符合指数关系。低硫煤相比高硫煤,煤样的特征温度向后推迟,160 ℃后,CO2体积分数才开始爆发式增加。
由图3可以看出:高硫煤和低硫煤的CO浓度曲线趋势也基本一致。高硫煤在20~110 ℃时,CO释放量随温度的升高变化较小,煤与氧气反应较为轻微;110 ℃后CO体积分数随着温度升高显著增加;当煤样温度达到160 ℃后,CO2体积分数达到爆发式增加,总体符合指数关系。低硫煤相比高硫煤,煤样的特征温度向后推迟,170 ℃后,CO2体积分数才开始爆发式增加。
综上,典型高硫煤在低温氧化过程中各温度阶段的CO2、CO标志气体释放量大于典型低硫煤,说明高硫煤相比低硫煤具有更高的自燃倾向。
2.2 热分析(TG/DSC)结果
对2种煤样进行热分析(TG/DSC),得到煤样的TG和DSC曲线,根据煤样氧化过程的特点定义5个特征温度点 (T1~T5)。典型高硫煤和典型低硫煤氧化过程的特征温度点见表2。
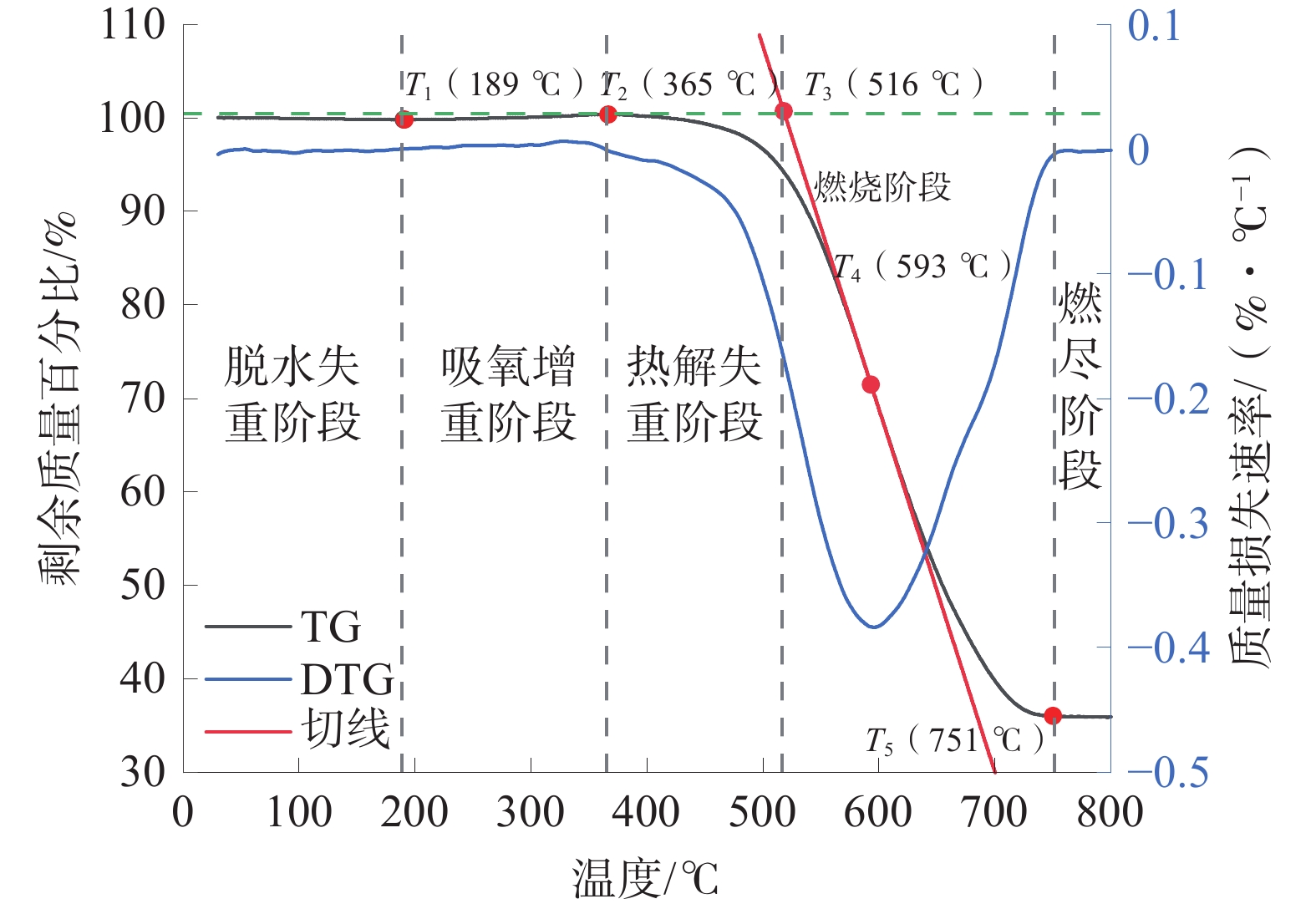
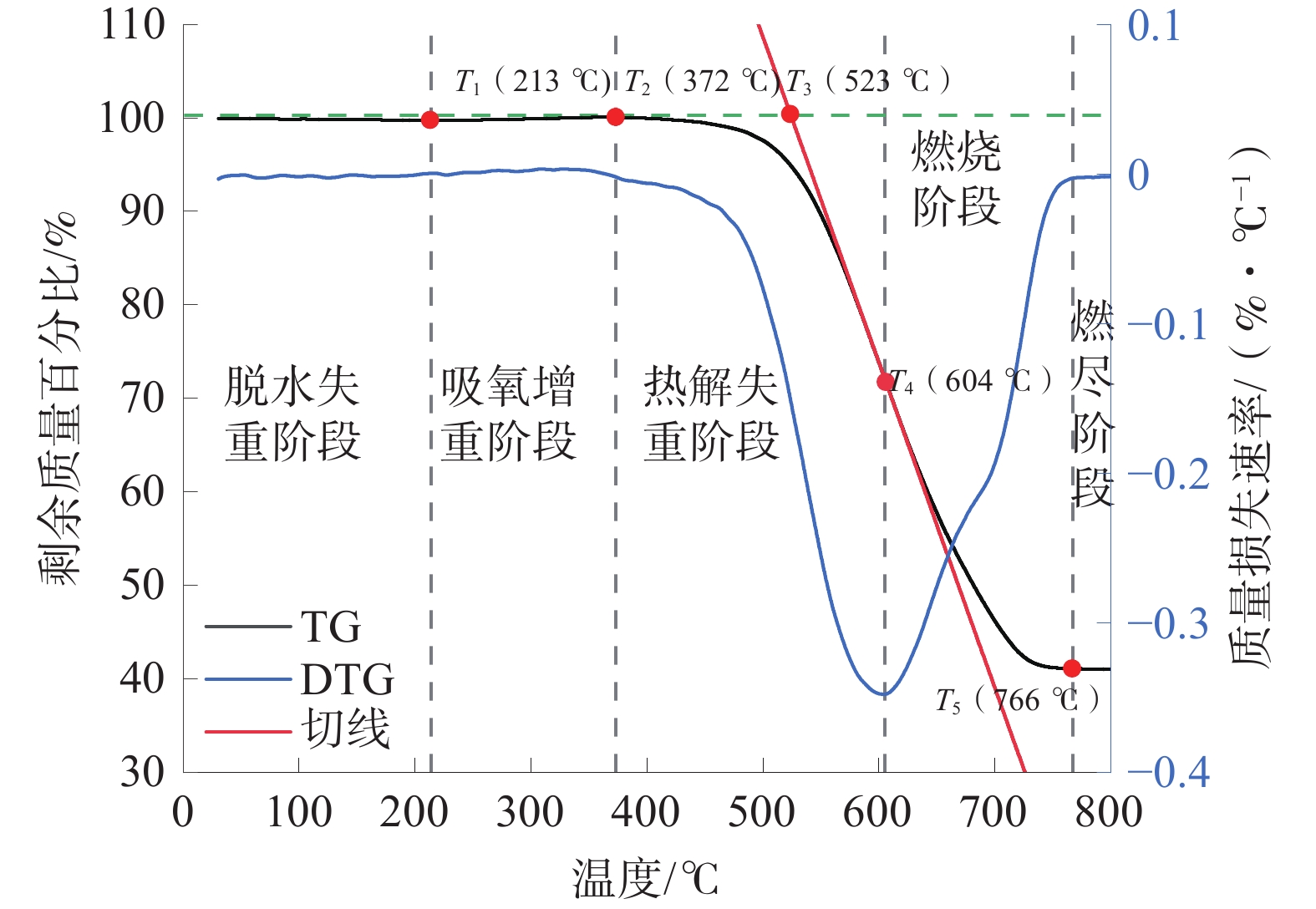
表 2 典型高硫煤和典型低硫煤氧化过程的特征温度点Table 2. Characteristic temperature points of typical high-sulfur coal and typical low-sulfur coal℃ 名称 T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 高硫煤 189 365 516 593 751 低硫煤 213 372 523 604 766 1)T1干裂温度。煤样由于脱水导致质量达到极小值时对应的温度,此时DTG数值上为0。
2)T2失重温度。煤样吸氧增重,质量达到极大值时即将受热分解质量下降时对应的温度,此时DTG数值上为0。
3)T3着火温度。煤样的着火温度点,过T4做TG曲线的切线,该切线与过T2的水平线交于一点,该点则为T3着火温度。
4)T4最大失重温度。煤样燃烧最剧烈时对应的温度,对应于DTG曲线的峰值。
5)T5燃尽温度。煤样停止燃烧且质量保持不变时的温度。
典型高硫煤的TG曲线图如图4,典型低硫煤的TG曲线图如图5。
从图4可以看出,煤样从室温到800 ℃的氧化过程被划分成脱水失重阶段、吸氧增重阶段、热解失重阶段、燃烧阶段、燃尽阶段5个阶段;随着温度上升,煤样中的水分蒸发,质量下降,当温度达到189 ℃时,煤样温度达到极小值;随着温度继续上升,煤样吸收空气中氧气进入吸氧增重阶段,质量略微上升;温度达到365 ℃时,煤样进入热解失重阶段,煤中的芳香环等有机结构受热分解,释放出CO2、CO等气体并放出大量热量;温度达到516 ℃时,煤样达到着火点,标志着煤样进入到氧化最剧烈的燃烧阶段;温度达到593 ℃时,煤样的燃烧最为剧烈;温度达到751 ℃时,煤样质量不再随温度的升高而变化,煤样进入燃尽阶段。
由图5可以看出:煤样从室温到800 ℃的氧化过程被划分成脱水失重阶段、吸氧增重阶段、热解失重阶段、燃烧阶段、燃尽阶段5个阶段;随着温度上升,煤样中的水分蒸发,质量下降,当温度达到213 ℃时,煤样温度达到极小值;随着温度继续上升,煤样吸收空气中氧气,进入吸氧增重阶段,质量略微上升;温度达到372 ℃时,煤样进入热解失重阶段,煤中的芳香环等有机结构受热分解,释放出CO2、CO等气体并放出大量热量;温度达到523 ℃时,煤样达到着火点,标志着煤样进入到氧化最剧烈的燃烧阶段;温度达到604 ℃时,煤样的燃烧最剧烈;当温度达到766 ℃时,煤样质量不再随温度的升高而变化,煤样进入燃尽阶段。
相比高硫煤,低硫煤的特征温度点均有不同程度提高,煤样的干裂温度升高了24 ℃、煤样的失重温度升高了7 ℃、煤样的着火温度升高了7℃、煤样的最大失重温度升高了11 ℃、煤样的燃尽温度升高了15 ℃。说明高硫煤相比低硫煤有更高的煤自燃倾向。
典型高硫煤和典型低硫煤的DSC曲线图如图6。
由图6可以看出:随着温度升高,2种煤样的放热量逐渐增大;温度在500 ℃附近,煤样达到着火点,放热量增幅较大;温度达到600 ℃附近,煤样放热量最大,分别为6.914、5.992 mW/mg。
通过以上分析可以得出:高硫煤在脱水失重、吸氧增重、热解失重和燃烧4个阶段的放热量相比低硫煤更高,发生煤自燃的风险更高。
煤炭氧化反应的活化能是影响煤炭火灾发生和发展的关键因素之一,活化能是指在化学反应过程中必须克服的能量障碍,也是能使反应发生的最小能量。活化能越小,代表氧化过程越容易发生。煤样热解失重和燃烧阶段的活化能可以通过Coats-Redfern积分(式(1))求得。由于煤炭氧化反应属于初级化学反应,故下式中g(a)取-ln(1-a)。
$$ {{\mathrm{ln}}}\left[\frac{g\left({{a}}\right)}{{T}^{2}}\right]={{\mathrm{ln}}}\left[\frac{AR}{\beta E}\right]\left(1-\frac{2RT}{E}\right)-\frac{E}{RT} $$ (1) 式中:g(a)为煤氧反应的模型函数;a为煤样的转化率,%;T为热力学温度,K;A为指前因子,min−1;R为通用气体常数,7.314 J/(mol·K);β为升温速率,K/min;E为活化能,kJ/mol。
使用ln[-ln(1-a)/T2]对1/T作图并进行曲线拟合,根据拟合直线的斜率为-E/R即可求出活化能。根据上述方法,得到的煤样热解失重和燃烧阶段的活化能大小见表3。
表 3 高硫煤和低硫煤在热解阶段和燃烧阶段的活化能Table 3. Activation energy of high-sulfur coal and low-sulfur coal in pyrolysis stage and combustion stage名称 温度区间/℃ 活化能/(kJ·mol−1) R2 高硫煤 365~516 75.112 0.98 516~751 32.767 0.99 低硫煤 372~523 82.689 0.99 523~766 38.582 0.98 通过表3可以得出:热解阶段中高硫煤的活化能大小为75.112 kJ/mol,低硫煤的活化能大小为82.689 kJ/mol;燃烧阶段中高硫煤的活化能大小为32.767 kJ/mol,低硫煤的活化能大小为38.582 kJ/mol;在热解阶段和燃烧阶段,高硫煤的活化能相比低硫煤分别小9.16%和15.07%。说明高硫煤的氧化过程更容易发生,需要更加注重高硫煤自燃灾害的防治。
2.3 阻化剂对煤中有机硫结构的影响
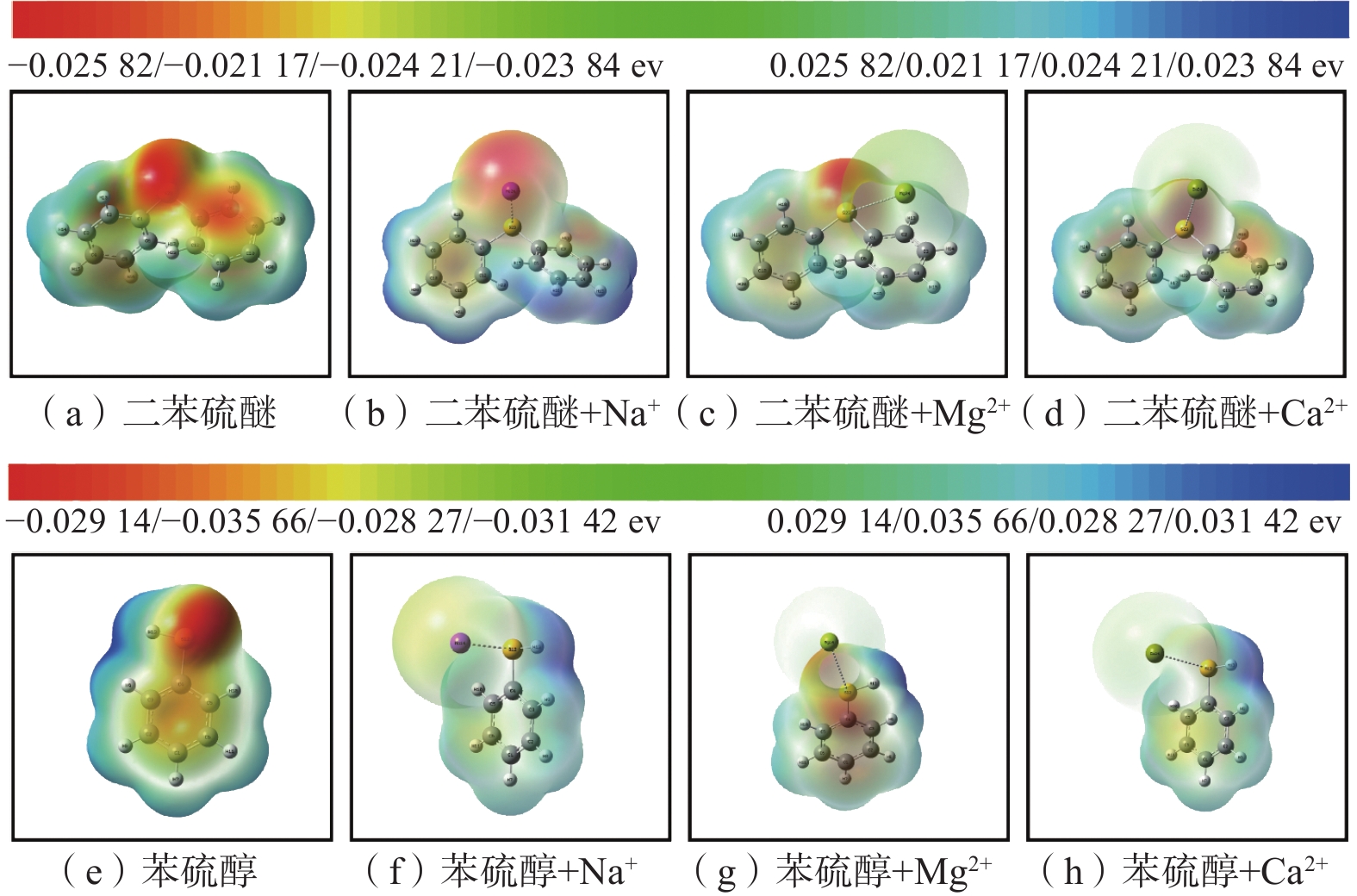
利用量子化学模拟软件对Ca2+、Na+、Mg2+与二苯硫醚和苯硫醇的络合作用进行计算。结果表明, Ca2+、Na+、Mg2+可以与二苯硫醚和苯硫醇形成络合物,计算得到络合物的分子结构如图7。络合物的键长、键角见表4、表5。
表 4 络合物键长表Table 4. Bond length of complexes配体与中心原子 原子 键长/nm C12H10S与Na S(23)-Na(24) 0.327 09 C12H10S与Mg S(23)-Mg(24) 0.528 43 C12H10S与Ca S(23)-Ca(24) 0.498 28 C6H5SH与Na S(12)-Na(14) 0.325 52 C6H5SH与Mg S(12)-Mg(14) 0.521 07 C6H5SH与Ca S(12)-Ca(14) 0.445 66 表 5 络合物键角表Table 5. Bond angles of complexes配体与中心原子 原子 键角/(°) C12H10S与Na C(1)-S(23)-Na(24) 93.236 9 C(7)-S(23)-Na(24) 105.486 0 C12H10S与Mg C(1)-S(23)-Mg(24) 52.447 9 C(7)-S(23)-Mg(24) 129.679 7 C12H10S与Ca C(1)-S(23)- Ca (24) 114.758 2 C(7)-S(23)- Ca (24) 82.508 9 C6H5SH与Na C(4)-S(12)- Na (14) 98.769 0 H(13)-S(12)- Na (14) 96.121 7 C6H5SH与Mg C(4)-S(12)- Mg (14) 158.753 9 H(13)-S(12)- Mg (14) 99.109 2 C6H5SH与Ca C(4)-S(12)-Ca(14) 98.016 6 H(13)-S(12)- Ca (14) 95.055 7 从表4可以看出:3种离子与2种有机硫结构形成的配位键键长中,Na+与二苯硫醚和苯硫醇形成的配位键键长最小,分别为0.327 09、0.325 52 nm。说明Na+与2种有机硫结构形成的络合物结构稳定性更强。
有机硫结构与络合物的静电势投影图如图8,图8中:红色代表负电性,亲电相关;蓝色代表正电性,亲核相关。
从图8(a)可以看出:二苯硫醚中H原子区域为蓝色,亲核相关;苯环上的C原子和S原子区域为红色,亲电相关。从图8(b)~图8(d)中可以看出,二苯硫醚与3种离子形成络合物后,红色区域与蓝色区域的颜色变淡,说明络合物的形成减弱了二苯硫醚的亲电反应能力和亲核反应能力。从图8(e)可以看出:苯硫醇中H原子区域为蓝色,亲核相关;苯环上的C原子和S原子区域为红色,亲电相关。从图8(f)~图8(h)中可以看出:形成络合物后,S原子区域的红色明显变淡;H原子区域的蓝色也一定程度变淡;说明络合物的形成降低了苯硫醇的亲电反应能力,减弱了苯硫醇的亲核反应能力。综上,Na+、Mg2+、Ca2+与2种有机硫形成络合物后降低了有机硫的化学活性。
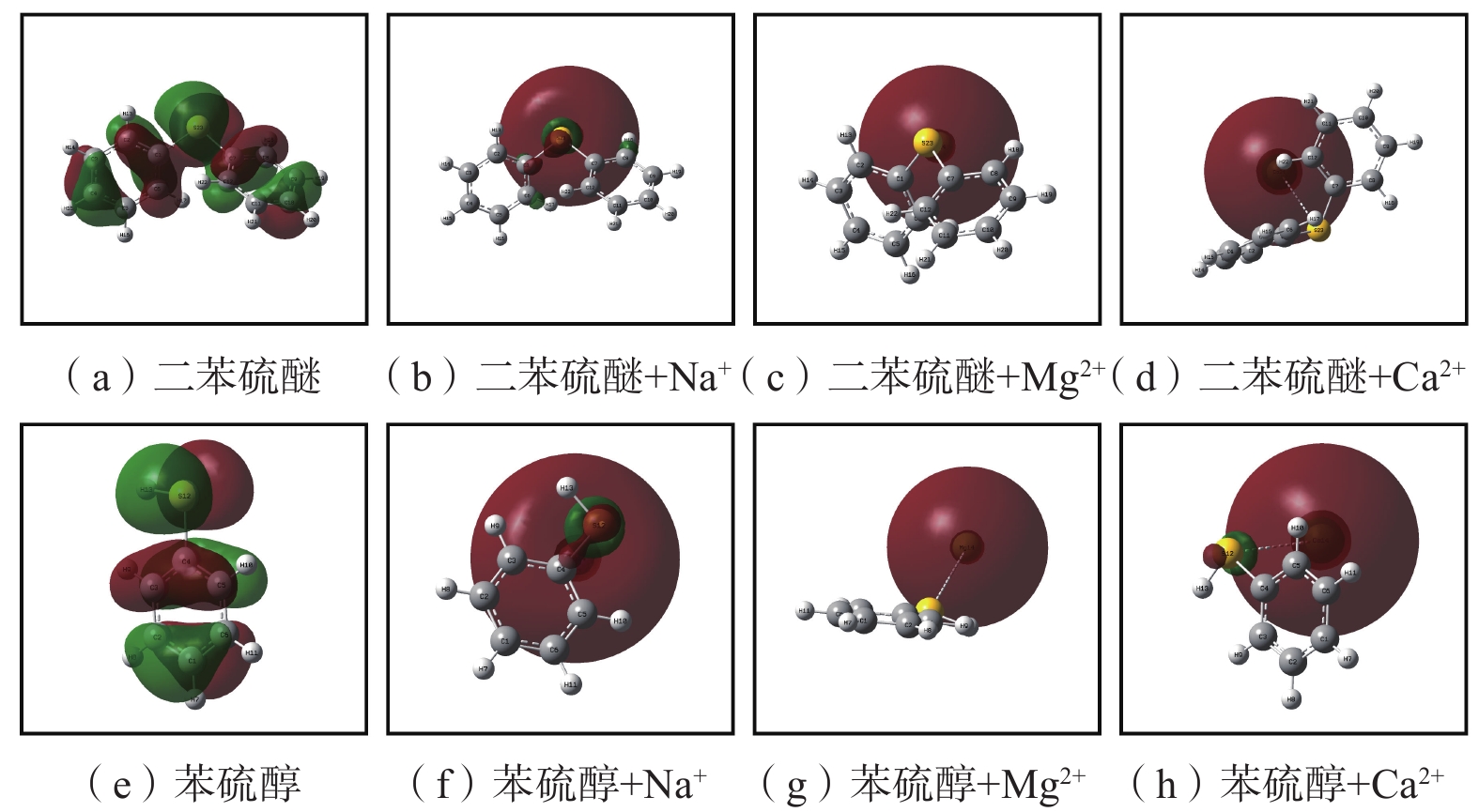
在1个分子中,HOMO/LUMO轨道决定了分子的主要性质。有机硫结构与络合物的HOMO图如图9,有机硫结构与络合物的LUMO图如图10。
从图9(a)可以看出:二苯硫醚的HOMO轨道主要由苯环上的C原子和S原子提供;从图9(b)~图9(d)可以看出:形成络合物后,络合物的HOMO轨道由金属原子提供,苯环上的C原子和S原子对HOMO轨道不做贡献;从图9(e)可以看出:苯硫醇的HOMO轨道主要由苯环上的C原子和S原子提供;从图9(f)~图9(h)可以看出:形成络合物后,络合物的HOMO轨道主要由金属原子提供,小部分由S原子提供。
从图10(a) 可以看出:二苯硫醚的LUMO轨道主要由2个苯环上的C原子和S原子提供;从图10(b)可以看出:二苯硫醚与Na+形成络合物后,提供LUMO轨道的原子相同,但红色和绿色部分体积减小;从图10(c)可以看出:二苯硫醚与Mg2+形成络合物后,2个苯环上的C原子和S原子对LUMO轨道的贡献减少,LUMO轨道主要由Mg原子提供;从图10(d)可以看出:二苯硫醚与Ca2+形成络合物后,LUMO轨道主要由Ca2+提供;从图10(e)可以看出:苯硫醇的LUMO轨道主要由苯环上的C原子提供;从图10(f)可以看出:苯硫醇与Na+形成络合物后,C原子的贡献降低,Ca原子的贡献较多;从图10(g)~图10(h)可以看出:苯硫醇与Mg2+、Ca2+形成络合物后,LUMO轨道由Mg原子和Ca原子提供,苯环无贡献。
综上所述,二苯硫醚和苯硫醇的轨道主要由S原子和苯环上的C原子提供,具有较高的化学活性,容易被氧气氧化;与金属离子形成络合物后,S原子和苯环上的C原子对分子轨道的贡献下降,降低了2种有机硫结构的化学活性。
3. 结 语
1)低硫煤相比高硫煤,CO2、CO煤自燃标志气体释放量较少,煤样氧化过程中特征温度点向高温方向推移,说明高硫煤相比低硫煤发生煤自燃的倾向更高。
2)热解阶段和燃烧阶段,高硫煤的活化能相比低硫煤分别小9.16%和15.07%。说明高硫煤的氧化过程更容易发生,需要更加重视高硫煤自燃灾害的防治。
3)Na+、Mg2+、Ca2+与2种有机硫形成络合物后降低了有机硫结构的化学活性,对煤自燃起到抑制作用。
4)Na+与二苯硫醚和苯硫醇形成的配位键键长较短,形成的络合物结构稳定性更强。从络合作用的角度, Na2CO3相比Ca(OH)2和MgCl2对预防高有机硫煤自燃的效果更好。
-
表 1 典型低硫煤的元素参数
Table 1 Elemental parameters of typical low-sulfur coal
% 种类 Cdaf含量 Hdaf含量 Odaf含量 Ndaf含量 Sdaf含量 低硫煤 90.41 3.92 3.29 1.26 1.12 高硫煤 86.8 4.35 3.15 0.95 4.75 表 2 典型高硫煤和典型低硫煤氧化过程的特征温度点
Table 2 Characteristic temperature points of typical high-sulfur coal and typical low-sulfur coal
℃ 名称 T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 高硫煤 189 365 516 593 751 低硫煤 213 372 523 604 766 表 3 高硫煤和低硫煤在热解阶段和燃烧阶段的活化能
Table 3 Activation energy of high-sulfur coal and low-sulfur coal in pyrolysis stage and combustion stage
名称 温度区间/℃ 活化能/(kJ·mol−1) R2 高硫煤 365~516 75.112 0.98 516~751 32.767 0.99 低硫煤 372~523 82.689 0.99 523~766 38.582 0.98 表 4 络合物键长表
Table 4 Bond length of complexes
配体与中心原子 原子 键长/nm C12H10S与Na S(23)-Na(24) 0.327 09 C12H10S与Mg S(23)-Mg(24) 0.528 43 C12H10S与Ca S(23)-Ca(24) 0.498 28 C6H5SH与Na S(12)-Na(14) 0.325 52 C6H5SH与Mg S(12)-Mg(14) 0.521 07 C6H5SH与Ca S(12)-Ca(14) 0.445 66 表 5 络合物键角表
Table 5 Bond angles of complexes
配体与中心原子 原子 键角/(°) C12H10S与Na C(1)-S(23)-Na(24) 93.236 9 C(7)-S(23)-Na(24) 105.486 0 C12H10S与Mg C(1)-S(23)-Mg(24) 52.447 9 C(7)-S(23)-Mg(24) 129.679 7 C12H10S与Ca C(1)-S(23)- Ca (24) 114.758 2 C(7)-S(23)- Ca (24) 82.508 9 C6H5SH与Na C(4)-S(12)- Na (14) 98.769 0 H(13)-S(12)- Na (14) 96.121 7 C6H5SH与Mg C(4)-S(12)- Mg (14) 158.753 9 H(13)-S(12)- Mg (14) 99.109 2 C6H5SH与Ca C(4)-S(12)-Ca(14) 98.016 6 H(13)-S(12)- Ca (14) 95.055 7 -
[1] 吴式瑜,王美丽. 煤炭在中国能源的地位[J]. 煤炭加工与综合利用,2006(5):2−8. WU Shiyu, WANG Meili. The position of coal in Chinese energy supply[J]. Coal Processing & Comprehensive Utilization, 2006(5): 2−8
[2] 谢和平,吴立新,郑德志. 2025年中国能源消费及煤炭需求预测[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(7):1949−1960. XIE Heping, WU Lixin, ZHENG Dezhi. Prediction on the energy consumption and coal demand of China in 2025[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2019, 44(7): 1949−1960
[3] 程子曌. 我国煤炭洗选加工和煤质现状及“十三五”展望[J]. 煤炭加工与综合利用,2017(5):17−20. CHENG Zizhao. The current situation of coal washing and processing, coal quality, and prospects for the 13th Five Year Plan in China[J]. Coal Processing & Comprehensive Utilization, 2017(5): 17−20
[4] 雷振兴. 煤矿安全事故的分类和预测研究[D]. 西安:西安理工大学,2010. [5] 诸利一,吕文生,杨鹏,等. 2007—2016年全国煤矿事故统计及发生规律研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2018,49(7):237−240. ZHU Liyi, LYU Wensheng, YANG Peng, et al. Statistical analysis and occurrence laws of coal mine accidents of China from 2007 to 2016[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2018, 49(7): 237−240
[6] 张俊文,杨虹霞. 2005—2019年我国煤矿重大及以上事故统计分析及安全生产对策研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2021,52(12):261−264. ZHANG Junwen, YANG Hongxia. Statistical analysis of major and above accidents in coal mines in China from 2005 to 2019 and study on countermeasures for safe production[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021, 52(12): 261−264.
[7] 刘艳亮. 2002~2016年我国煤矿事故统计分析及预防措施[J]. 陕西煤炭,2018,37(3):64−67. LIU Yanliang. Statistical analysis and preventive measures of coal mine accidents in China from 2002 to 2016[J]. Shaanxi Coal, 2018, 37(3): 64−67.
[8] 冯宇峰,王茜颖,倪坤,等. 20世纪以来我国煤矿安全发展历程及事故总体规律研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2023,54(3):251-256. FENG Yufeng, WANG Xiying, NI Kun, et al. Research on development history of coal mine safety and overall law of accidents in China since the 20th century[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(3): 251-256.
[9] 袁晓芳,朱明杰. 煤矿人因事故影响因素与组态路径分析[J]. 煤矿安全,2023,54(3):245-250. YUAN Xiaofang, ZHU Mingjie. Analysis on influencing factors and configuration paths of human-caused accidents in coal mines[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(3): 245-250.
[10] DENG J, MA X F, ZHANG Y T, et al. Effects of pyrite on the spontaneous combustion of coal[J]. International Journal of Coal Science & Technology, 2015, 2(4): 306−311.
[11] YANG F Q, LAI Y, SONG Y Z. Determination of the influence of pyrite on coal spontaneous combustion by thermodynamics analysis[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2019, 129: 163−167. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2019.06.023
[12] DING C, LI Z X, WANG J R, et al. Experimental research on the spontaneous combustion of coal with different metamorphic degrees induced by pyrite and its oxidation products[J]. Fuel, 2022, 318: 123642. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.123642
[13] 常绪华,王德明,时国庆. 采空区高硫煤自燃阻化技术试验分析[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2013,44(5):2118−2123. CHANG Xuhua, WANG Deming, SHI Guoqing. Experimental analysis of high sulfur coal spontaneous combustion inhibition technology in goaf[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2013, 44(5): 2118−2123.
[14] 胡军,郑宝山,王滨滨,等. 中国煤中有机硫的分布及其成因[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2005,33(5):15−18. HU Jun, ZHENG Baoshan, WANG Binbin, et al. Distribution and forming cause of organic sulfur in coals of China[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2005, 33(5): 15−18
[15] 王雪峰,邓汉忠,孙俊,等. 金属钙离子对煤中含硫活性基团的阻化效果研究[J]. 计算机与应用化学,2015,32(5):534−538. WANG Xuefeng, DENG Hanzhong, SUN Jun, et al. Study of inhibition effect of Ca2+ on sulfur contained active groups in coal[J]. Computers and Applied Chemistry, 2015, 32(5): 534−538.
[16] 叶正亮,李金亮,陆伟,等. 化学阻化剂对高硫煤的阻化实验研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2011,42(11):12−14. YE Zhengliang, LI Jinliang, LU Wei, et al. Study on chemical inhibitors prevent spontaneous combustion of the sulfur coal[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2011, 42(11): 12−14
[17] 张兰君. 有机硫对煤自燃特性影响研究[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2016. [18] ZHANG L J, LI Z H, HE W J, et al. Study on the change of organic sulfur forms in coal during low-temperature oxidation process[J]. Fuel, 2018, 222: 350−361. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.02.157
[19] ZHENG H Y, LI Y T, ZHANG L J, et al. Study on the effect of organic sulfur on coal spontaneous combustion based on model compounds[J]. Fuel, 2021, 289: 119846. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119846
[20] GAO F, JIA Z, SHAN Y F, et al. Influence of organic sulfur on low-temperature oxidation of coal and its transition characteristics[J]. ACS Omega, 2022, 7(44): 39830−39839. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c03824
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 薛恩思. CaCl_2溶液对煤自燃的阻化效果的影响实验研究. 煤矿安全. 2024(10): 64-71 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: