Effect and optimization of anionic and cationic surfactants on the performance of self-diverting acids in coal
-
摘要:
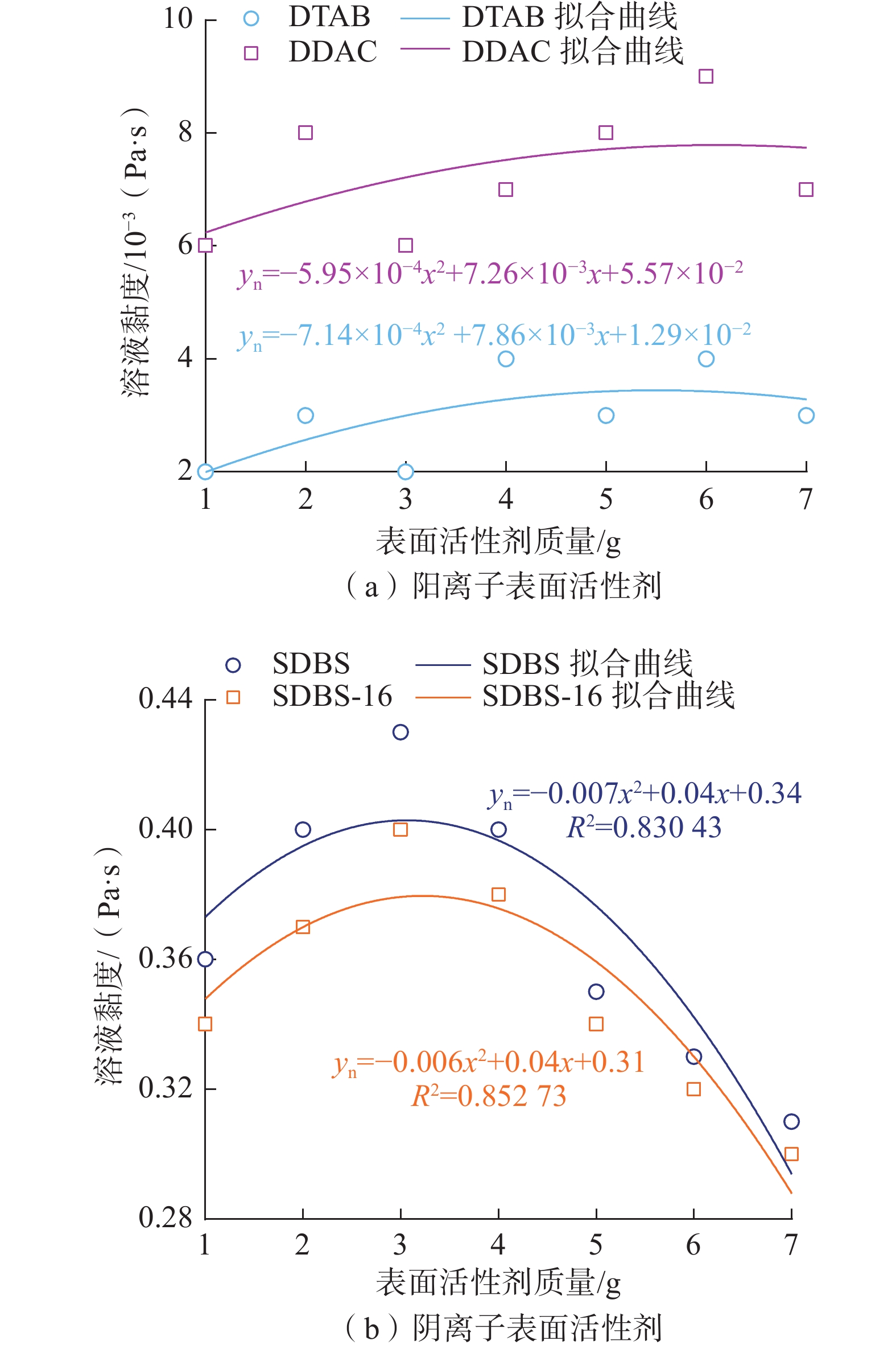
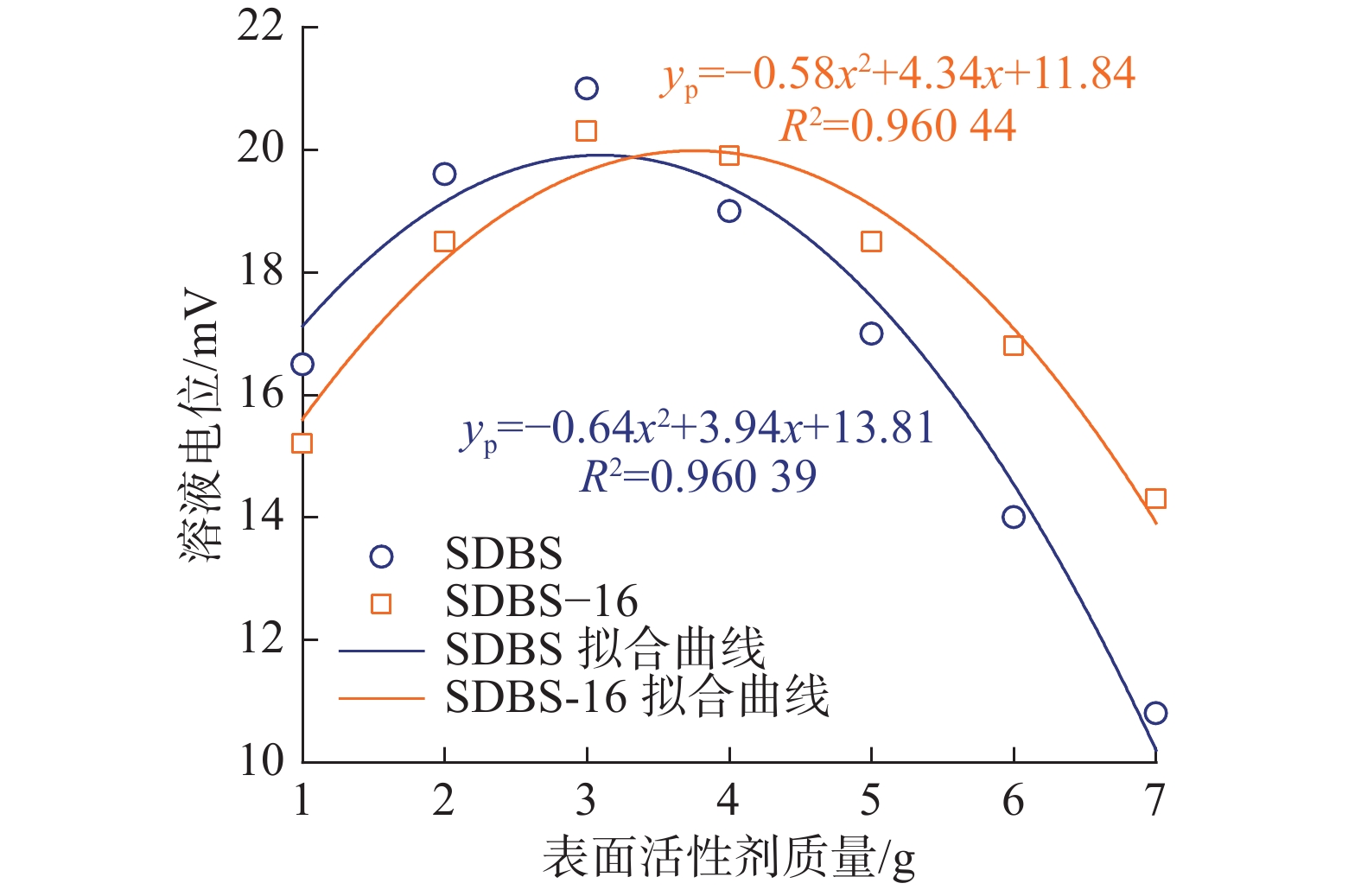
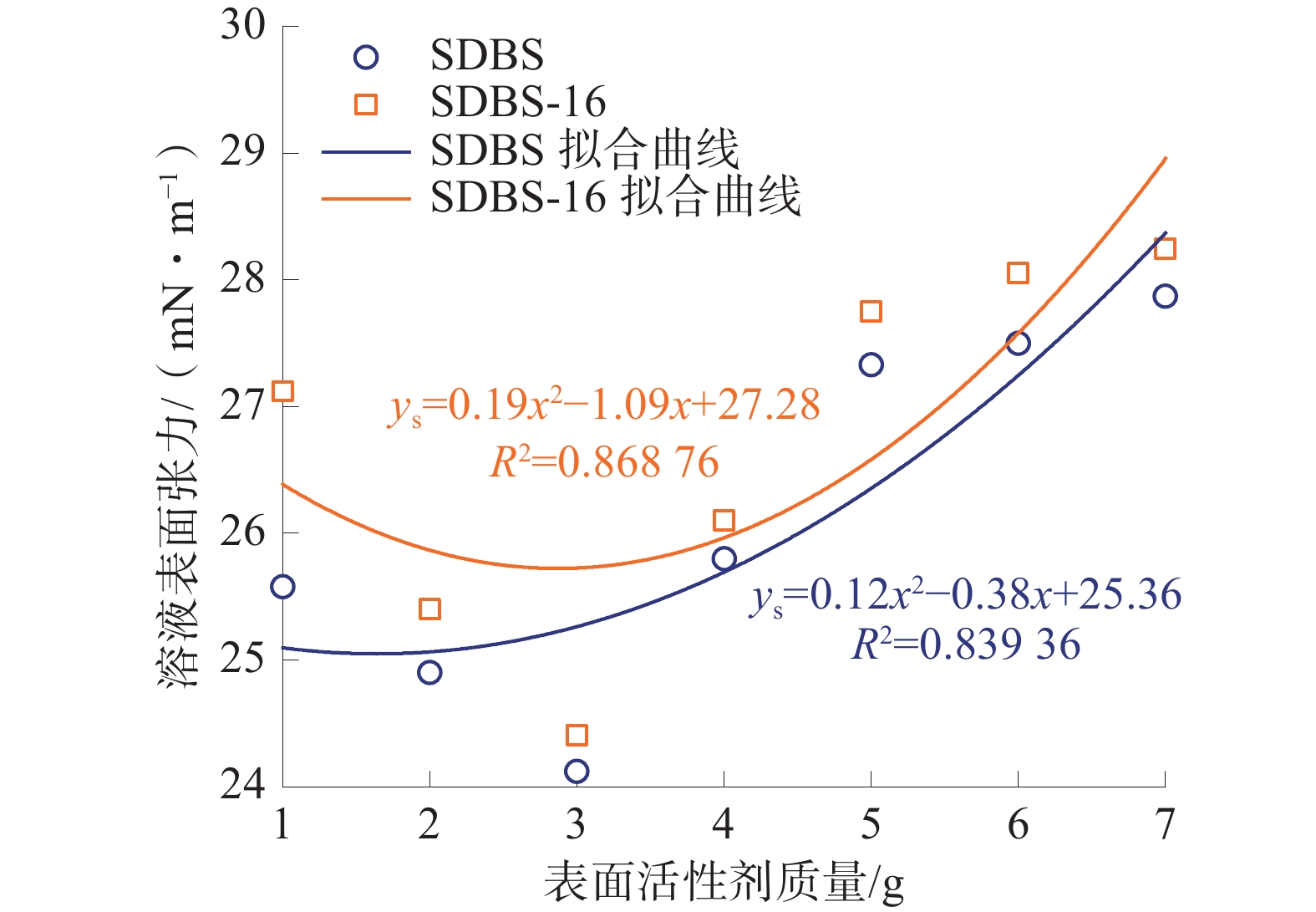
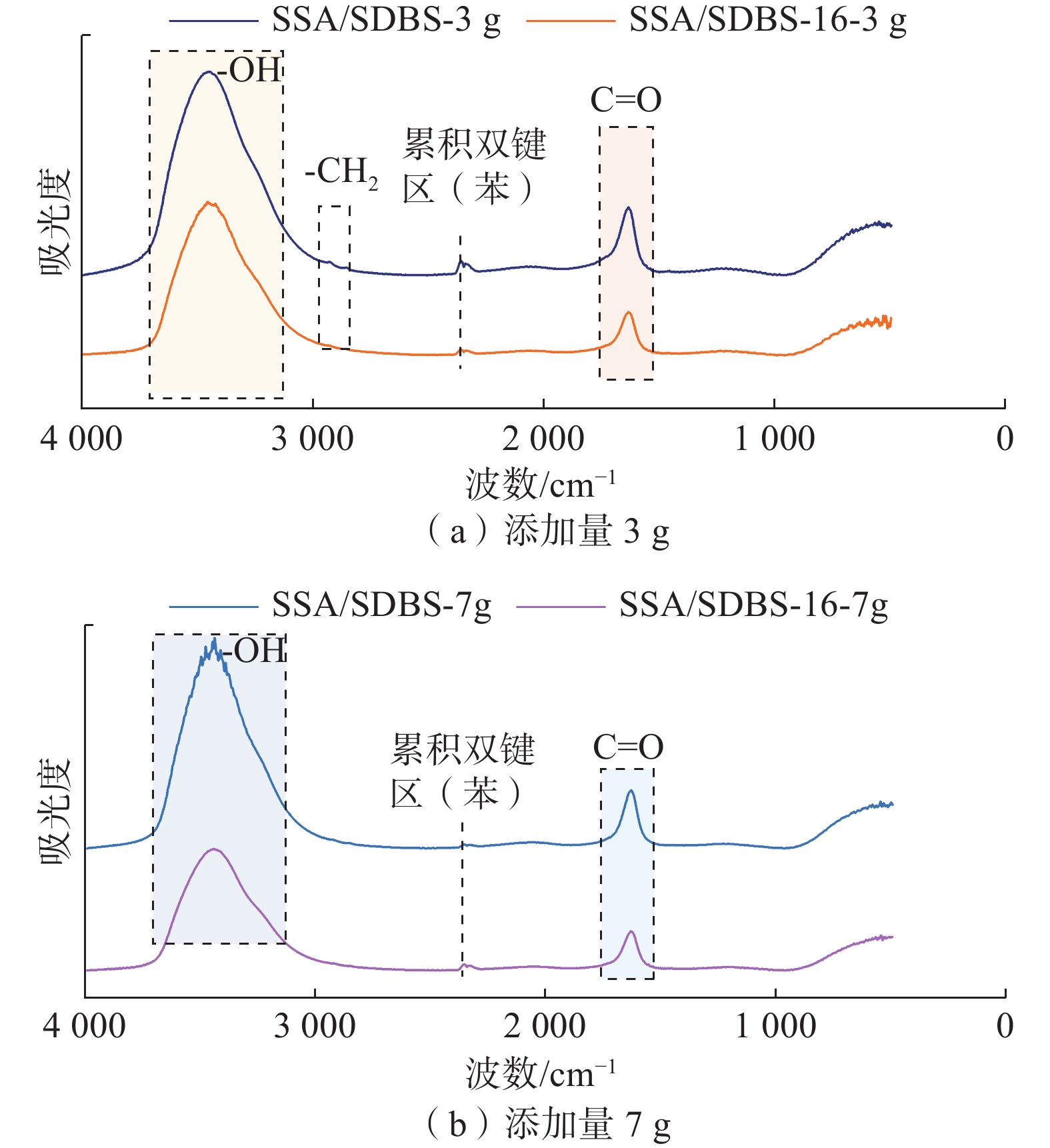
针对煤矿粉尘污染严重问题,研究了煤层OAPB自转向酸液均匀布酸,从而提高煤体含水率,借助黏度、荷电性、官能团等方法研究了不同阴阳离子表面活性剂对自转向酸液增黏、润湿性能的影响规律,探究了性能变化的内部原因,并根据测试结果进行了优选。结果表明:阳离子表面活性剂会直接导致自转向酸液破胶,阴离子表面活性剂的添加使自转向酸液黏度增加;SSA/SDBS润湿性能较好,表面张力最低为24.12 mN/m;SSA/SDBS-16表面张力值总体较高,自身润湿性能差,对煤体的吸附性能也较弱;通过红外实验发现在SSA/SDBS作用下OAPB分子更倾向于形成氢键,并通过三轴渗流实验验证了自转向酸液的渗流效果。
Abstract:Aiming at the serious problem of dust pollution in coal mines, the OAPB automatic diverting acid solution of coal seams was studied to uniformly distribute acid, so as to improve the water content of coal bodies. In order to achieve better results in coal mines, this paper studied the effects of different anionic and cationic surfactants on the viscosity and wettability of self-diverting acid using methods such as viscosity, chargeability, and functional groups, explored the internal causes of performance changes, and optimized based on the test results. The results show that cationic surfactants can directly cause gel breaking of self-diverting acid, and the addition of anionic surfactants can increase the viscosity of self-diverting acid. SSA/SDBS has good wettability, with a minimum surface tension of 24.12 mN/m; SSA/SDBS-16 has an overall higher surface tension value, poor self-wetting performance, and weaker adsorption performance on the coal bodies. Through infrared experiments, it was found that OAPB molecules tended to form hydrogen bonds under the action of SSA/SDBS, and the percolation effect of self-diverting acid solution was verified through triaxial percolation experiments.
-
排土场边坡的失稳每年都会造成大量人员伤亡和巨大的经济损失,以往对排土场边坡破坏的研究表明,大多数事故与地下水或暴雨天气密切相关[1-3]。因此,在边坡稳定性分析中应该考虑水的作用。近年来,关于水对边坡稳定性的影响,国内外学者开展了大量的研究工作。付天光[4]在分析含水率对边坡抗剪强度参数影响的基础上,利用强度折减法计算边坡安全系数,结果表明,含水率的增加降低了边坡安全系数,易导致边坡失稳破坏;海龙等[5]利用数值计算软件分析了降雨时间和强度对边坡稳定性的影响,系统分析了降雨时间和强度对边坡安全系数的影响规律;何忠明等[6]对不同降雨类型进行了物理相似模拟实验,探究了降雨时长、降雨强度、边坡角度对边坡安全系数的响应规律;李晓凤等[7]从水对边坡潜在滑面影响的角度论述了边坡失稳机理,提出了工程防治水措施和方法;杨志刚等[8]采用有限元强度折减法分析了正常工况和暴雨工况2种情况下边坡安全系数,认为暴雨条件弱化了边坡的物理力学参数,导致边坡易出现失稳破坏;董法等[9]考虑了降雨强度和时间对孔隙水压的影响,分析了降雨—坡体自重共同作用下的边坡失稳特征,结果表明,边坡位移随降雨量的增加而增大,降雨量越大,边坡岩体达到饱和状态历时越短。此外,学者们还针对水对黄土边坡[10]、软岩边坡[11]、人工填土边坡[12]的稳定性影响进行了大量的研究。
综上所述,以某露天煤矿水浸泥岩基底内排土场边坡为工程背景、不同含水率下泥岩弱层抗剪强度参数为依据、数值计算软件为手段,阐述了泥岩弱层含水率对内排土场边坡稳定性的影响,为类似工程提供参考。
1. 工程概况
某露天矿内排土场共有9个排土台阶,边坡单台阶高度为20 m,台阶坡面角为36°,边坡角为11°,排弃物料总垂高为180 m,平均平盘宽度为80 m。目前,内排土场受地下水影响严重,地下水的补给来源于大气降水和东帮地下水侧向补给2方面。受排土场结构影响,排土场地表为压实的细粒泥质成分含量较高的散料,垂向渗透系数较小,大气降水补给量较小;排土场内部及基底主要受东帮地下水侧向补给的影响。内排土场内部垂向基本是粗粒、中粒、细粒循环的富有规律性的分布,但这种状态只存在排土场形成初期,伴随时间推移,排土场不同深度发生不同程度的固结沉降(不均匀沉降),破坏了排土场垂向上结构特征,造成垂向渗透性增强,导致内排土场东侧中上部的地下水补给可以汇集到排土场底部,最终向内排坡脚汇集排泄,极易造成边坡坡脚出现滑坡,进而导致整个边坡失稳。目前,内排土场自上而下地层依次为排弃物料、泥岩弱层、砂质泥岩、粉砂岩、基岩层,地层垂直高度分别为180.0、5.0、32.0、43.5、279.5 m。
2. 不同含水率泥岩弱层直剪试验
现场采集不同含水状态的泥岩弱层样本,采用“烘干法”获得泥岩弱层的含水率(ωn)分别为24.7%、25.9%、28.9%、29.7%、32.1%、38.3%,按照GB/T 50123—1999《土工试验方法标准》制备泥岩弱层的直剪试样,采用四联无级变速应变控制式直接剪切仪开展泥岩固结快剪试验。剪切速率为0.8 mm/min,垂直压力分别为100、200、300、400 kPa,依据文献[13]所述方法计算不同含水率下泥岩弱层黏聚力和内摩擦角。
利用方程τ=c+σtanφ拟合不同垂直压力下抗剪强度。式中,τ为剪切应力,MPa;c为黏聚力,kPa;φ为内摩擦角,(°);R2为拟合系数,R2>0.93,表明拟合效果较好。不同含水率和垂直压力下抗剪强度如图1所示,含水率对泥岩弱层黏聚力和内摩擦角的影响规律分别如图2和图3所示。
由图1、图2、图3可知:泥岩弱层黏聚力和内摩擦角随含水率的增加呈非线性减小的二次函数分布规律,但其减小的幅度不同;当含水率由24.7%增至29.7%时,黏聚力由55.72 kPa降至24.96 kPa,内摩擦角由33.2°降至16.2°,含水率每增加1%,黏聚力减少6.15 kPa,内摩擦角减少3.4°;当含水率由29.7%增至38.3%时,黏聚力由24.96 kPa降至4.09 kPa,内摩擦角由16.2°降至8.1°,含水率每增加1%,黏聚力仅减少2.43 kPa,内摩擦角仅减少0.94°。
造成上述结果的主要原因包括2方面:①泥岩弱层内部含有较多的黏性亲水矿物,含水率增加,造成可溶性矿物颗粒及颗粒间胶结物的溶解[14],颗粒间结合水膜厚度增大,致使矿物颗粒之间的距离增加,摩擦力减小[15],导致试样产生初始损伤;②在剪切外载和垂直压力作用下孔隙及裂隙中自由水产生孔隙压力,孔隙及裂隙尖端出现拉应力集中区,加速试样破坏。
综上所述,结合水导致试样出现初始损伤,自由水导致试样在加载过程中出现叠加损伤,二者共同作用是泥岩弱层黏聚力和内摩擦角减小的根本原因。
3. 泥岩弱层含水率对边坡失稳模式的影响
3.1 数值计算模型
基于抗剪强度折减法利用PHASE2数值计算软件对某露天矿水浸泥岩基底边坡变形破坏机理和安全系数进行分析。在抗剪强度折减法(SSR)技术中假定边坡材料满足摩尔−库仑准则。这种线性破坏模型的1个特点是可以用主应力和剪应力进行明确地表达,且摩尔−库仑准则所需要的参数易于获取。
对于摩尔−库仑材料,剪切强度可由式(1)确定:
$$ \frac{\tau }{F} = c' + \sigma \tan \;\varphi ' $$ (1) 式中;F为强度折减系数或边坡安全系数;τ为剪切应力, MPa;c'、φ'为摩尔−库仑剪切强度参数。
$$ c' = \frac{c}{F} $$ (2) $$ \varphi ' = \arctan \left(\frac{{\tan \;\varphi }}{F}\right) $$ (3) 式中:c为黏聚力,MPa;φ为内摩擦角,(°)。
寻找使原稳定边坡(F≥1)处于破坏边缘的安全值F,主要步骤如下:①建立边坡的有限元模型,赋予初始材料参数,开始计算并记录边坡的最大变形;②增大F(或SRF)值,按式(2)和式(3)计算此时的摩尔−库仑材料参数,将新的强度参数输入到边坡模型中,重新计算,记录最大变形。③重复步骤②,继续增大F值,直到有限元模型不收敛于某个解,即边坡失效,刚刚超过发生破坏的临界F值即为边坡安全系数。
抗剪强度折减法的主要优点是它使用了折减的强度参数作为模型新的输入参数,这使得该技术可以与任何现有的有限元分析软件一起使用。
根据边坡工程地质模型,采用数值计算软件建立的边坡数值计算模型如图4所示。
为了消除边界效应的影响,采用八节点四边形网格建立边坡模型;单元尺寸比为0.03;从坡顶到左边界的距离应大于坡宽的2.5倍;从坡脚到右边界的距离应至少为坡宽的2倍;从坡脚到底边界的距离至少为坡高的2倍[16]。因此,边坡水平长度为888 m,边坡右侧边界至坡脚水平距离为1 776 m,边坡左侧边界至坡顶水平距离为2 220 m,边坡垂直高度为180 m,模型底部边界距离坡脚垂直高度为360 m。模型左右边界施加水平约束,底部边界施加垂直约束,从而构成位移边界条件,以保持整个系统的受力平衡。本次模型中各种材料均采用摩尔−库伦模型进行描述。坡顶、坡底及平盘中部各布置1个监测点,共计30个监测点,监测不同工况下边坡的水平位移和垂直位移。
3.2 边坡位移变化特征
不同泥岩弱层含水率下各监测点水平位移和垂直位移分布规律如图5和图6所示,边坡最大位移随泥岩弱层含水率变化规律如图7所示。
1)边坡垂直位移主要分布在边坡中部偏上,最大垂直位移位于边坡坡顶,随含水率的增大,边坡垂直位移逐渐增大,范围也逐渐增加。最大垂直位移呈现先缓慢增加后快速增加的变化趋势,含水率由24.7%增至29.7%,最大垂直位移由102 mm增至175 mm,增幅仅为71.6%;含水率由29.7%增至38.3%,最大垂直位移由175 mm增至564 mm,增幅达222.3%。
2)边坡水平位移几乎贯穿于整个排弃物料台阶,最大水平位移位于边坡中上部台阶。随着含水率增加,最大水平位移呈现先缓慢增加后快速增加的变化趋势,含水率由24.7%增至29.7%,最大水平位移由232 mm增至330 mm,增幅仅为42.2%;含水率由29.7%增至38.3%,最大水平位移由330 mm增至592 mm,增幅为79.4%。
3)导致边坡产生变形失稳的因素较多,大量工程实践表明,水是影响边坡稳定的重要因素之一,在边坡变形破坏过程中起着举足轻重的作用。泥岩弱层含水率的增加,大幅弱化了泥岩弱层黏聚力和内摩擦角,强化了泥岩弱层的润滑作用,剪应力效应增强,易导致边坡产生剪切滑动,最终引起边坡水平位移和垂直位移的增加。水平位移普遍大于垂直位移,说明该工况下,边坡主要以水平运动为主。
3.3 最大剪应变变化特征
不同含水率下边坡最大剪应变分布云图如图8所示。
由图8可知:最大剪应变随泥岩弱层含水率的增加逐渐增大。低含水率下(24.7%、25.9%),边坡最大剪应变集中在坡体后缘,边坡主要呈现圆弧形或类圆弧形滑移破坏,但最大剪应变和剪切破坏范围较小,未贯通至地表;当泥岩弱层含水率大于28.9%,边坡破坏模式基本一致,主要呈现沿排土场基底接触面的滑移破坏,且最大剪应变贯通至坡顶,随着含水率的增加,泥岩弱层的抗剪强度参数减小,坡体潜在滑动范围增大。低含水率下(24.7%、25.9%),排弃物料在自重作用下产生固结下沉,仅在坡体内部造成小范围剪切破裂带;随着含水率增加,泥岩弱层的润滑作用增强,致使边坡出现自坡顶至坡脚方向的剪切滑动,最终将导致边坡呈现坡顶至泥岩弱层的圆弧形滑动。
3.4 安全系数变化特征
不同泥岩弱层含水率ωn和厚度下边坡安全系数Fs变化曲线如图9所示。
根据《煤炭工业露天矿设计规范》相关规定,内排土场稳定的临界安全系数取1.2,因此,设置边坡安全系数警戒线为1.2。由图9可知:随着泥岩弱层含水率的增加,边坡安全系数呈线性减小的变化趋势;当泥岩弱层含水率由24.7%增加至38.3%,边坡安全系数由1.73降至0.92,降幅为46.82%;含水率的增加,弱化了泥岩弱层的抗剪强度参数,导致边坡位移增加,易出现剪切滑移破坏;在含水率为29.7%至32.1%之间,存在1个临界含水率,使得安全系数恰为边坡储备要求的1.20。因此,为了保证边坡安全,应密切关注基底含水量变化,及时疏干排水,控制泥岩弱层含水率不超过30%。
4. 结 语
1)泥岩弱层的黏聚力和内摩擦角随含水率的增加呈非线性减小的二次函数分布规律;结合水易使试样出现初始损伤、自由水易导致试样在加载过程中出现叠加损伤是造成泥岩弱层黏聚力和内摩擦角减小的根本原因。
2)边坡最大水平位移和最大垂直位移均位于边坡中上部台阶,随着含水率的增加呈现先缓慢增加后快速增加的变化趋势。
3)最大剪应变与含水率呈正相关关系,随着含水率的增加,边坡主要呈现沿排土场基底接触面的滑移破坏,边坡以水平运动为主。
4)边坡安全系数与含水率呈负相关关系,为保证边坡稳定,建议泥岩弱层含水率不超过30%。
-
-
[1] 秦波涛,周刚,周群,等. 煤矿综采工作面活性磁化水喷雾降尘技术体系与应用[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(12):3891−3901. QIN Botao, ZHOU Gang, ZHOU Qun, et al. Dust removal system and application of the surfactant-magnetized water spray in the fully mechanized mining face of coal mines[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(12): 3891−3901.
[2] YANG He, CHENG Weimin, LIU Zhen, et al. Study on the dynamic evolution law of the effective stress in the coal seam water infusion process based on fractal theory[J]. Fractals, 2020, 28(5): 2050086. doi: 10.1142/S0218348X20500863
[3] 许满贵,刘欣凯,文新强. 煤矿综掘工作面高效喷雾降尘系统[J]. 湖南科技大学学报(自然科学版),2015,30(2):1−7. XU Mangui, LIU Xinkai, WEN Xinqiang. Full-mechanized excavation face efficient sprinkler & dust fall system[J]. Journal of Hunan University of Science & Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 30(2): 1−7.
[4] YU Haiming, JIN Yeechung, CHENG Weimin, et al. Multiscale simulation of atomization process and droplet particles diffusion of pressure-swirl nozzle[J]. Powder Technology, 2020, 379: 127−143.
[5] 秦玉金,苏伟伟,田富超,等. 煤层注水微观效应研究现状及发展方向[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2020,49(3):428−444. QIN Yujin, SU Weiwei, TIAN Fuchao, et al. Research status and development direction of microcosmic effect under coal seam water injection[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2020, 49(3): 428−444.
[6] 刘五车,李贺,鲁义,等. 低透煤层化学改性增透技术研究现状及展望[J]. 能源与环保,2022,44(1):207−214. LIU Wuche, LI He, LU Yi, et al. Research status and prospect of chemical modification and permeability enhancement technology for low permeability coal seam[J]. China Energy and Environmental Protection, 2022, 44(1): 207−214.
[7] REYDICK D B, LUC G T, KAREN M S. X-ray μCT investigations of the effects of cleat demineralization by HCl acidizing on coal permeability[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2018, 55: 206−218. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2018.05.007
[8] 胡千庭,李晓旭,陈强,等. 酸性压裂液防治低渗煤层水锁损害实验研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(12):4466−4481. HU Qianting, LI Xiaoxu, CHEN Qiang, et al. Mitigating water blockage in low-permeability coal seam by acid-based fracturing fluid[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(12): 4466−4481.
[9] 齐宁,邓爽,李侠清,等. 碳酸盐岩自转向酸酸液流动模拟实验研究与评价[J]. 科学技术与工程,2016,16(30):11−16. QI Ning, DENG Shuang, LI Xiaqing, et al. Research and evaluation on flow simulation experiments of self-diverting acid in carbonate rocks[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2016, 16(30): 11−16.
[10] ZHAO Liqiang, CHEN Xiang, ZOU Honglan, et al. A review of diverting agents for reservoir stimulation[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019, 187: 106734.
[11] 徐中良,戴彩丽,赵明伟,等. 酸压用交联酸的研究进展[J]. 应用化工,2017,46(12):2424−2427. XU Zhongliang, DAI Caili, ZHAO Mingwei, et al. Research and application progress of crosslinked gelled acid[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2017, 46(12): 2424−2427.
[12] VERNÁEZ O, GARCÍA A, CASTILLO F, et al. Oil-based self-degradable gels as diverting agents for oil well operations[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science & Engineering, 2016, 146: 874−882.
[13] 刘友权,赵万伟,王小红,等. 粘弹体表面活性剂自转向酸特点及其在川渝气田的应用[J]. 石油与天然气化工,2008,37(S1):103−107. LIU Youquan, ZHAO Wanwei, WANG Xiaohong, et al. The performance evaluation and field application of viscoelstic surfactant based self-diverting acid in Sichuan-Chongqing gas field[J]. Chemical Engineering of Oil and Gas, 2008, 37(S1): 103−107.
[14] XIE Yao, CHENG Weimin, YU Haiming, et al. Effect of self-diverting acid viscosity and the chemical structure of coal under different acid environment[J]. Powder Technology, 2022, 398: 117125. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2022.117125
[15] 宋奇,王志明,杨蕾,等. 低伤害转向酸化技术室内研究[J]. 应用化工,2015(S1):96−99. SONG Qi, WANG Zhiming, YANG Lei, et al. Experimental study of low damage diversion of acidification[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2015(S1): 96−99.
[16] 何春明,陈红军,赵洪涛,等. VES自转向酸体系流变性能[J]. 油气地质与采收率,2010,17(4):104−107. HE Chunming, CHEN Hongjun, ZHAO Hongtao, et al. Study on rheological of VES self-diversion acid system[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2010, 17(4): 104−107.
[17] LIU Ming, ZHANG Shicheng, MOU Jianye, et al. Diverting mechanism of viscoelastic surfactant-based self-diverting acid and its simulation[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science & Engineering, 2013, 105: 91−99.
[18] ZHU Qi, LIU Pingli, ZHAO Liqiang, et al. Laboratory study on a novel self-diverting gel acid system thickener[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2012, 463–464: 868–876.
[19] YAN Zhihu, DAI Caili, ZHAO Mingwei, et al. Development, formation mechanism and performance evaluation of a reusable viscoelastic surfactant fracturing fluid[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2016: 115–122.
[20] XIE Hongchao, NI Guanhua, XIE Jingna, et al. The effect of SDS synergistic composite acidification on the chemical structure and wetting characteristics of coal[J]. Powder Technology, 2020, 367: 253−265. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2020.03.056
[21] 詹宁宁,张丽锋. 自转向酸液在海上油田的应用[J]. 当代化工,2022,51(3):603−606. ZHAN Ningning, ZHANG Lifeng. Application of self-steering acid in offshore oil field[J]. Contemporary Chemical Industry, 2022, 51(3): 603−606.
[22] CHOI F, CHEN R X, ACOSTA E J. Predicting the effect of additives on wormlike micelle and liquid crystal formation and rheology with phase inversion phenomena[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2020, 564: 216−229. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.12.105
[23] 侯磊,武培怡. 二维相关红外光谱分析技术在高分子表征中的应用[J]. 高分子学报,2022,53(5):522−538. HOU Lei, WU Peiyi. Applications of two-dimensional correlation infrared spectroscopy in the characterization of polymers[J]. Acta Polymerica Sinica, 2022, 53(5): 522−538.
[24] 闫文付,徐如人. 凝聚液态水溶液中的化学反应[J]. 化学进展,2022,34(7):1454−1491. YAN Wenfu, XU Ruren. Chemical reactions in aqueous solutions with condensed liquid state[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2022, 34(7): 1454−1491.
[25] XIE Yao, CHENG Weimin, YU Haiming. Study on viscosification law of OAPB self-diverting acid by acid concentration and inorganic salt in coal[J]. Fuel, 2022, 317: 123545. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.123545
[26] 孙勇. 预氧化对煤表面关键官能团影响的实验研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2021,52(8):51−58. SUN Yong. Experimental study for the effect of pre-oxidization on functional groups of coal surface[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021, 52(8): 51−58.




 下载:
下载: