Study of intermediate principal stress effect on progressive damage and permeability characteristics of unloading sandstone
-
摘要:
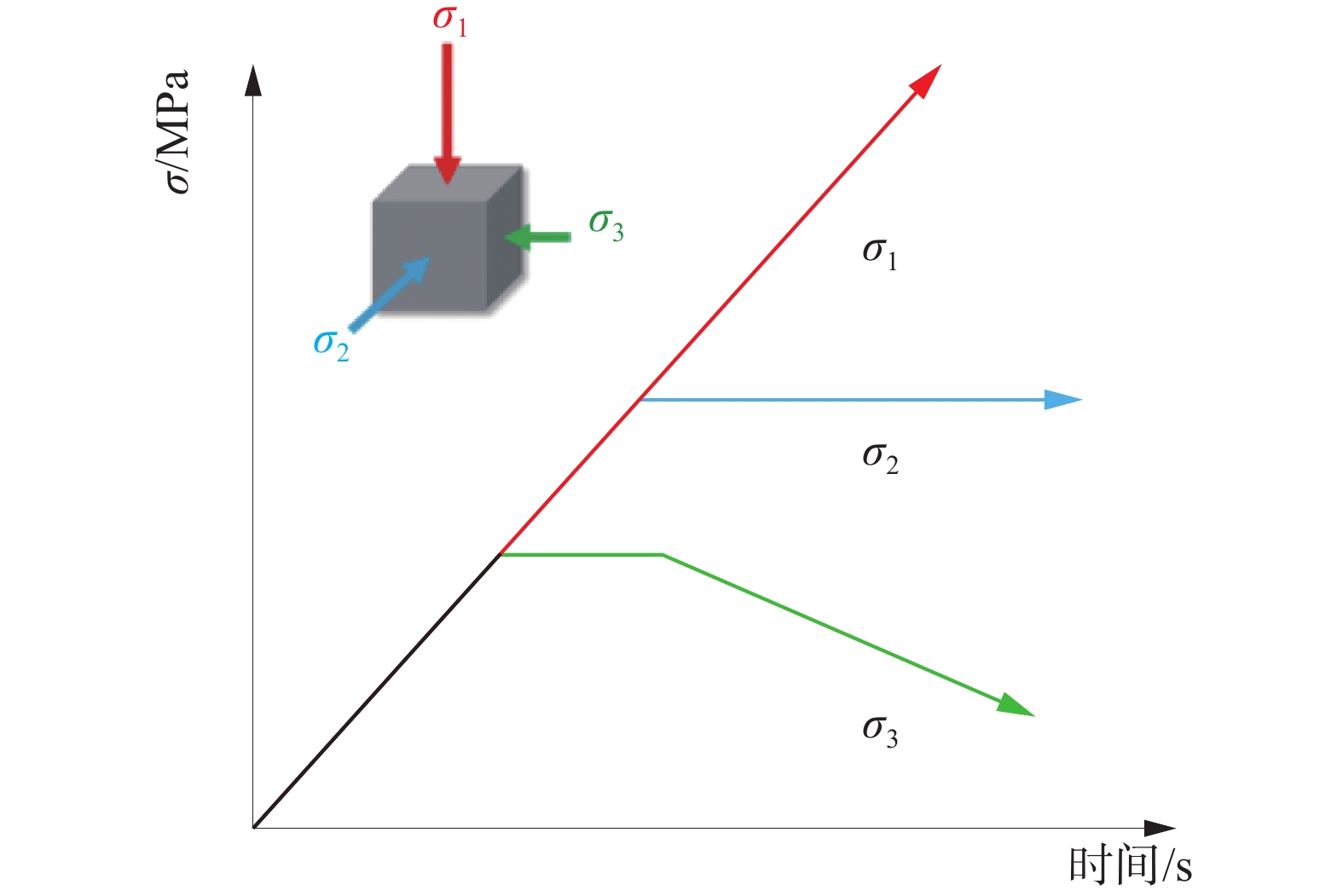
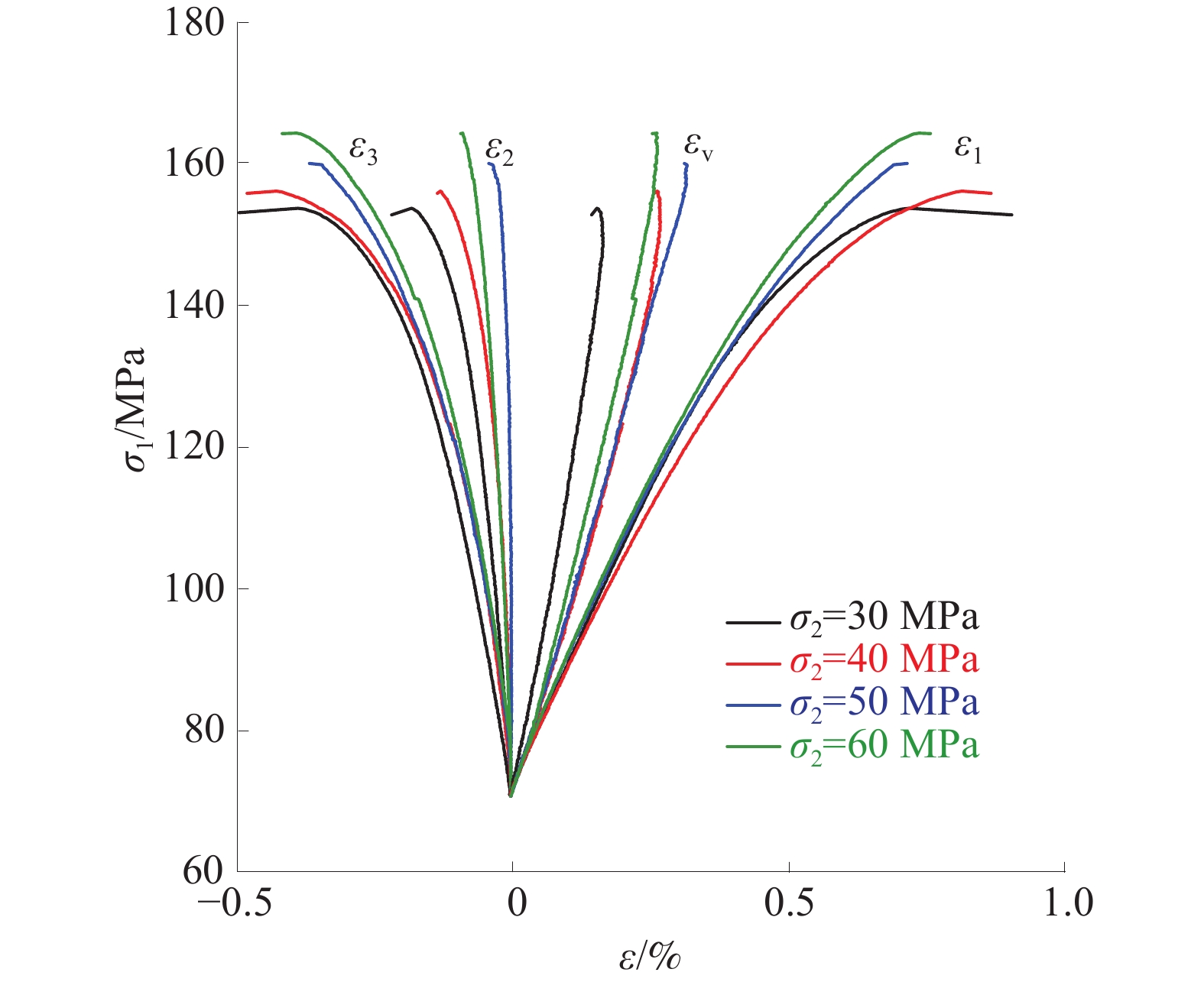
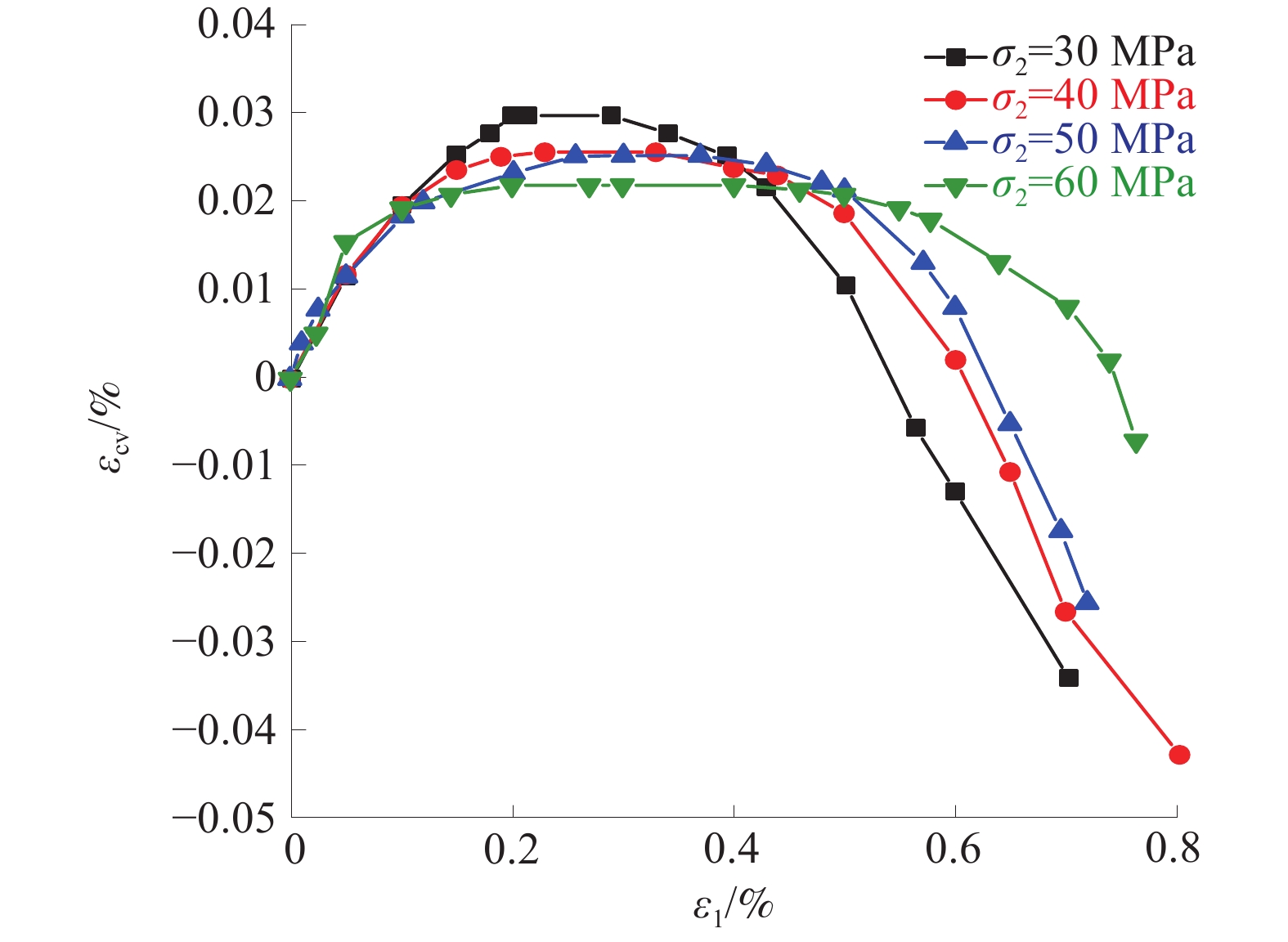
为了探究中间主应力对卸荷砂岩渐进破坏及渗流特性的影响,基于多功能真三轴流固耦合试验系统,以含气砂岩为研究对象,进行不同中间主应力条件下的卸荷试验;得到与裂纹体应变、损伤变量相关的指数型渗透率模型。结果表明:随着中间主应力的增加,裂纹闭合应力、起裂应力、损伤应力均呈现增加趋势,弹性段与微小裂纹扩展阶段在峰前应变中的占比增加;在微小裂纹扩展阶段,中间主应力方向上的变形受到约束,对最小主应力方向产生的压缩效应随着中间主应力的增大而增强;在宏观裂纹扩展阶段,损伤应力与峰值应力比较接近,试样破坏呈脆性特征;随着中间主应力的增加,初期渗透率减少量呈下降趋势,渗透率升高点发生后移。
Abstract:In order to investigate the effect of intermediate principal stress on the progressive damage and permeability characteristics of unloading sandstone, the unloading test was carried out under different intermediate principal stress conditions based on a multifunctional true triaxial fluid-solid coupling test system with gas-bearing sandstone as the research object; the exponential permeability model related to the cracked volume strain and damage variable were obtained. The results show that the crack closure stress, crack initiation stress and damage stress increase with the increase of intermediate principal stress, and the percentage of elastic section and microcrack extension stage in the pre-peak strain increases. The deformation in the direction of the intermediate principal stress is restrained in the microcrack extension stage, and the compression effect on the direction of the minimum principal stress is enhanced with the increase of the intermediate principal stress; in the macroscopic crack extension stage, the damage stress is closer to the peak stress, and the damage of the specimen is brittle in character. With the increase of the intermediate principal stress, the initial permeability reduction shows a decreasing trend and the point of elevated permeability shifts backward.
-
煤炭作为一种重要开采资源其产生的粉尘污染对从业者的身体健康、生产安全及设备的正常运转存在严重威胁[1-2]。作为主要治理手段之一的湿式降尘技术,存在煤尘捕集效率低、水雾润湿性能较差等弊端[3-5],寻找一种能够有效解决上述局限的煤尘治理技术成为迫切需求。水雾荷电作为一种新型气溶胶处理技术,具有改善雾滴分布、降低雾滴粒径等优势,该技术从物理层面上优化了雾滴的性能,利用荷电液滴与煤尘颗粒物间的静电引力作用促进粉尘团聚沉降。表面活性剂能从化学层面上显著降低溶液的表面张力,增强溶液的渗透与润湿性能,从而提高水雾对微细粉尘的捕集能力。2种技术基于不同层面和原理提升了水雾对煤尘的沉降效率。
诸多学者已经分别对雾滴荷电技术与表面活性剂增强溶液润湿性能开展了研究。FORBES 等[6]利用电流体动力学模拟及实验确定了不同条件下超声液滴的荷电机制,发现液滴的最佳荷电状态与外加电场强度存在线性函数关系;WANG等[7]研究发现,在电晕放电释放的电荷诱导下,微米级液滴接近瑞利极限发生破碎,亚微米级液滴的密度增加;孙伊伟等[8]采用网状目标法,探究了多参数对液滴感应荷电效果的影响,并确定了影响荷电效果的多因素次序;QI等[9]通过对脱硫废水进行预充电处理,利用荷电水雾蒸发促进烟气内颗粒物团聚沉降,结果表明,该手段可提高对细颗粒物的去除效率;张政等[10]探究了十二烷基硫酸钠(SDS)对烟煤的润湿机理,发现SDS可增强溶液对烟煤的润湿性,对煤尘的捕集效率显著提高;HAO等[11]发现,在外加电场作用下,活性液滴表面的O−H键电场排列较液滴内部的O−H键的电场排列更大,分子极化作用增强,有助于增强液滴的表面反应性;廖洋波等[12]探究了含十二烷基硫酸钠(SDS)的水溶液在微凹槽阵列聚二甲基硅氧烷(PDMS)表面的电润湿行为,发现在电场和SDS溶液协同作用下,液滴的润湿行为发生改变。
目前,对于上述2项技术的研究已经十分完善,现有结果表明,二者独立使用对于煤尘捕集效率的提升均呈现向好趋势。然而,二者联合使用下,液滴的荷电效应与活性分子效应对于煤尘的沉降是否存在协同或拮抗作用尚不清楚。此外,当捕尘液滴与煤尘粒径比约为1时,液滴润湿性能最佳[13-14],故治理粒径10 μm以下的呼吸性粉尘,捕尘液滴粒径应确定为微米级。而对于微米尺度的液滴在外加电场的荷电过程中,场致荷电效应主导整个荷电过程。在此限定背景下,开展的研究更是几乎完全空白。
微米活性水雾在场致荷电作用下可能表现出不同的荷电效果和对煤尘的润湿性能,对于了解这些差异并针对性地开发煤尘治理技术具有重要意义。因此,聚焦于微米活性液滴在场致荷电作用下的荷电效果,以及对难浸润无烟煤的润湿性能研究,探究了荷电与溶液活性处理对液滴荷电效果、粒径的影响,并对荷电活性水雾的润湿性能及动态降尘效果进行了分析。研究成果对于微细粉尘的治理提供新的技术手段;对提升粉尘治理效率、改善溶液润湿性能具有指导意义。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 样品制备
煤根据其变质程度的不同,可分为褐煤、烟煤、无烟煤。其中,无烟煤含碳量相对较高,含氧官能团较少,故其湿润性能最差。因此,研究选取山西运城无烟难浸润煤作为实验煤样。首先,利用行星球磨机对煤样进行12 h的充分研磨;之后将样品送入真空干燥箱中烘干12 h,温度设定为50 ℃;完成上述操作后,利用震动筛分器对煤尘颗粒进行筛选,收集粒径≤38 μm的煤尘并密封保存,作为后续实验样品。
根据表面活性剂的不同亲水基类型,可分为阴离子、阳离子、非离子和两性离子表面活性剂。当表面活性剂加入水中时,亲水基朝水一侧,而疏水基朝煤一侧。依据相似相溶原理,煤尘更容易与表面活性剂的疏水基相互作用,从而提高润湿性能。因此,首先对煤样表面电性进行确定,进而选用适宜的活性剂类型。采用Zeta电位测量仪对煤样表面电位进行测定,根据频谱漂移分析技术计算煤尘表面电势,重复进行3次。3次煤尘表面总电势测量结果分别为−35.24、−35.21、−35.26 mV,煤样表面电势为负值。由于阳离子和两性离子表面活性剂2种类型的表面活性剂亲水头均含有阳离子,具有正电性,与煤尘表面负电荷相互吸引,导致亲水基朝煤一侧,疏水基朝水一侧,进而使煤尘表面更加疏水,润湿性能降低,故阳离子和两性离子表面活性剂不适合用于改善煤尘的润湿性。而非离子表面活性剂对外显电性较小,在综合考量上述因素后,阴离子表面活性剂是改善煤尘润湿性能的最佳选择[15]。
十二烷基硫酸钠(SDS)是一种润湿性能良好的阴离子表面活性剂,SDS分子结构如图1所示。
SDS分子同时包含疏水性的烷基链和亲水性的硫酸盐基团,这种两性结构使得SDS能够有效改善液体在固体表面的润湿性能[16-17]。基于此,研究选取SDS单体表面活性剂来配制活性溶液。在配制活性溶液时,表面活性剂的添加浓度需考虑溶液黏度、发泡性能等因素。诸多学者在研究中发现,当SDS溶液质量分数为0.1%时,溶液多尺度性能最佳[10]。因此,按照质量分数为0.1%来配制SDS活性溶液。
1.2 喷雾方式
喷嘴的结构组成直接决定雾化效果的优劣。常见的压力喷嘴受制于其高压泵水的作用原理,必然存在喷射范围不易控制、雾滴不细腻且耗水量较大等劣势[18]。常规内混式气液两相喷嘴虽然相较高压水喷嘴雾化性能有所改善,但在高流速和高压力条件下,亦无法实现理想的气液混合效果,导致喷出雾滴粒径较大且分布不够均匀[19]。因此,研究选用跨音速气动喷嘴,该类型喷嘴对上述缺陷进行了补足并优化,喷雾雾化性能优异,在适宜工况下所产生的雾滴粒径低至微米级[20]。
跨音速气动喷嘴在进行造雾时,气端由空压机提供持续稳定的气流,通过调节气压阀门使进气压力保持稳定;喷嘴内部气体流动产生负压可实现虹吸汲水,液端由储水箱直接供水。团队针对跨音速气动喷嘴的雾化性能开展了大量实验,最终确定跨音速气动喷嘴可实现最佳雾化效果的工况为气压0.3 MPa[21]。因此,后续实验都在此工况下进行喷雾。
1.3 荷电方式
微米级液滴在外加电场中荷电时,场致荷电作用主导了整个荷电过程[22],故电场是影响雾滴荷电效果的最直接因素。因此,研究选用紫铜芒刺环形电极,采用电晕荷电的方式对雾滴进行荷电。此种电极与荷电方式的主要优势在于施加的高电势及电极形状能够显著增强电场强度,并且利用电晕放电电子崩现象的发生增强空间电荷密度,进而提高雾滴的荷电量与荷电概率。
在非均匀电场中,电势决定了带电粒子的受力与运动状态,电场强度与分布直接受电极荷载电压大小的影响。由于正、负电极几何中心连线位置上的空间电荷与电场线最为密集,利用仿真软件对此处不同电压下的电场强度进行分析,不同电压下电极间电场分布如图2所示。
由图2可知,电场强度随着电极荷载电压的增加呈增大趋势。但由于受到电晕击穿电压等条件限制,在此电极配置下荷载电压超过−20 kV,电晕放电现象不再稳定。因此,在后续实验中,将−20 kV作为最佳荷电效果的电极荷载电压,同时作为荷载电压的上限。
1.4 表征方法
1)雾滴荷电效果。为探究纯水和SDS活性溶液在不同电场强度下的荷电响应情况,电极荷载电压设定为−10~−20 kV。将荷电电流作为衡量雾滴荷电效果的指标,利用雾滴荷电效果测量系统,对质量分数为0.1%的SDS活性溶液与普通水雾的雾滴荷电效果进行测量。测量系统主要由金属矩形桶与金属网组成,金属网置于金属矩形桶内,微安电流表一端与其相连接。雾化后的离散液滴经电极荷电喷入荷电液滴收集装置,与接地端形成回路,由微安电流表测得荷电电流。
2)粒径分布。利用马尔文激光粒度仪,对质量分数为0.1%的SDS荷电活性溶液、质量分数为0.1%的SDS活性溶液、普通荷电水雾以及普通水雾的雾滴粒径及分布进行测定。雾滴信息监测区域设定为距喷嘴出口2 cm,在实验过程中位置保持不变。
3)接触角。接触角是评价降尘溶液表面润湿性能的关键参数。使用接触角分析仪(Theta Lite, UK)测量质量分数为0.1%的SDS荷电活性溶液、质量分数为0.1%的SDS活性溶液、普通荷电水雾、普通水雾样品对煤尘的接触角。在测量接触角前,将处理好的煤样利用压片机压成片,压片机压力设置为50 MPa,保压时间2 min。
4)动态降尘效果。利用搭建的模拟巷道平台来测定不同喷雾手段的降尘效果,水雾降尘系统如图3所示 。模拟巷道平台主要由巷道管路、粉尘气溶胶发生器、除雾器(防止含尘气流中的水雾对粉尘浓度测定的干扰)、风机、直读式粉尘浓度测定仪组成。巷道管路由3个1 500 mm×1 000 mm×800 mm的箱体组成,从左至右依次编号为1号~3号。粉尘发生器的发尘端与1号箱体左侧的孔隙相连接,喷嘴和电极环置于1号箱体上方,除雾器置于1号和2号箱体连接处。风机设置在3号箱体尾部,通过改变频率大小来调整巷道中含尘气流的风速。粉尘浓度测试仪置于2号箱体内,其始终处于巷道中间位置。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 微米活性液滴荷电效果
不同荷电电压下,纯水与活性溶液的荷电效果如图4所示。
从趋势上看,随着荷电电压由−10 kV增至−20 kV,水与质量分数为0.1%的SDS溶液的荷电效果均呈现增长趋势,这表明荷电电压与荷电效果存在明显的正相关关系;从比例关系上看,水的荷电效果从−5.44 μA增至−13.15 μA,增长率为141.7%,质量分数为0.1%的SDS溶液的荷电效果由−6.68 μA增至−19.26 μA,增长率为188.3%。结果表明:水和质量分数为0.1%的SDS溶液的荷电效果对于荷电电压变化的响应略有差异,这很大程度上是由物质本身特性决定的。水是一种极性分子,结构相对简单,对电场的响应相对较差;而SDS分子特殊的结构与离子特性使其对电场的响应更为敏感。首先,SDS在水溶液中会形成胶束结构,分子中疏水性的烷基链朝向内部,而亲水性的硫酸根则朝向外部,这种结构使得SDS分子在水中的排列更加有序,从而获得更佳的荷电效果;其次,SDS分子在水溶液中会解离成十二烷基硫酸根离子和钠离子,水溶液离子浓度的增加有助于增加溶液的电导率,进一步提升荷电效果。
2.2 微米荷电活性液滴粒径分布
不同处理手段得到的微米水雾雾滴特征粒径如图5所示,普通水雾与荷电活性水雾的粒径分布如图6所示。
由图5可以看出,荷电水雾、活性水雾与荷电活性水雾相较于普通水雾各项雾滴特征粒径均呈现减小趋势。从荷电的角度分析,由于荷电处理会改变液滴间的静电作用,因此,无论是普通水雾还是活性喷雾,在经过荷电处理后的雾滴各项特征粒径均有所减小。这主要由于荷电后的雾滴往往携带同种电荷,相互间表现出大小不等的电荷斥力,阻碍了颗粒的聚集和凝结,从而导致液滴更易发生破碎。并且,当液滴首次发生破碎后,其荷电状态及液滴之间的相互作用又会发生改变,进而再次影响到液滴的破碎及粒径大小。从溶液活性处理的角度来看,添加表面活性剂会降低溶液的表面张力与分散作用,从而使得雾滴更易破碎,雾滴粒径更小。值得注意的是,在荷电处理与表面活性剂的联合作用下,荷电活性水雾的各项特征粒径最小,以SMD(索特尔平均粒径)为例,粒径仅为5.54 μm,较普通水雾降低了47.93%。结果表明,当液滴处于微米级别时,荷电处理与添加活性剂对于增强液滴破碎以及减小雾滴粒径存在协同效应,二者联用可获得更小粒径的微米雾滴。
由图6可以看出:荷电活性水雾的雾滴粒径集中分布在5~10 μm,当雾滴粒径超过13.26 μm时,累积分布率达到100%,表明所有雾滴粒径均小于该值;普通水雾的雾滴粒径集中分布在10~20 μm,当雾滴粒径超过23.54 μm时,累积分布率达到100%。综合来看,荷电活性水雾整体的雾滴粒径相较于普通水雾更小,分布也更加集中,荷电与表面活性剂二者协同作用下更易获得小微米粒径雾滴。
2.3 液滴−煤尘表面润湿性
不同处理手段得到的溶液与运城无烟煤之间的固-液接触角如图7所示;将3次接触角实验的结果取平均值并计算其变化率,不同处理手段水雾接触角变化率结果如图8所示。
由图7可以看出,纯水由于其所具有的表面张力较大,与无烟煤接触形成的接触角也较大,表现出一定的疏水性。对溶液进行不同手段的处理,无论是荷电还是添加SDS活性剂均会增强溶液的润湿性能,从而使接触角减小。当二者联合使用时,将结合荷电效应与表面活性剂的优势,增强溶液的润湿性能,表现出更强的亲水性。
由图8可知,经过荷电处理的水−煤接触角较纯水降低29.46%,质量分数为0.1%的SDS溶液的接触角较纯水降低44.33%。对比2种处理手段可以发现,添加表面活性剂的方式对溶液润湿性能的改善效果更为明显,这种化学改性手段的作用效果强于物理手段。当2种方式耦合使用时,对于接触角的降低表现出协同作用,较纯水-煤接触角降低了62.31%。
2.4 微米活性荷电液滴动态降尘效果
普通水雾与荷电活性水雾在降尘前后的粉尘浓度及降尘效率见表1。
表 1 喷雾降尘前后粉尘质量浓度及降尘效率Table 1. Dust mass concentration and dust reduction efficiency before and after spraying降尘措施 降尘前粉尘质量浓度/
(mg∙m−3)降尘后粉尘质量浓度/
(mg∙m−3)除尘效率/
%全尘 呼吸性
粉尘全尘 呼吸性
粉尘全尘 呼吸性
粉尘荷电活性水雾 663.81 234.53 54.62 22.39 91.77 90.45 普通水雾 662.44 235.58 189.24 78.32 71.44 66.76 由表1可知:普通水雾对无烟煤煤尘的沉降效果较差,对全尘及呼吸性粉尘的沉降效率仅为71.44%与66.76%;而荷电活性水雾对全尘及呼吸性粉尘的沉降效率高达91.77%与90.45%,对煤尘的沉降效率显著提升。
3. 结 论
1)在外加电场作用下,纯水和SDS溶液微米水雾的荷电效果均随电极荷载电压的增大而提升,但SDS活性溶液对电场的响应更为敏感。
2)水雾荷电、溶液活性处理2种手段均会不同程度的降低雾滴粒径,后者效果更佳。二者联合作用下,对于增强微米雾滴破碎及减小雾滴粒径存在协同效应。
3)与水雾荷电相比,溶液活性处理对溶液湿润性能的改善更为明显。2种处理手段联合使用对于接触角的降低表现出协同作用。
4)微米荷电活性水雾对无烟煤煤尘的降尘效果显著提升,在电极荷载电压为-20 kV、SDS质量分数为0.1%条件下,荷电活性水雾对全尘及呼吸性粉尘的降尘效率高达91.77%、90.45%。
-
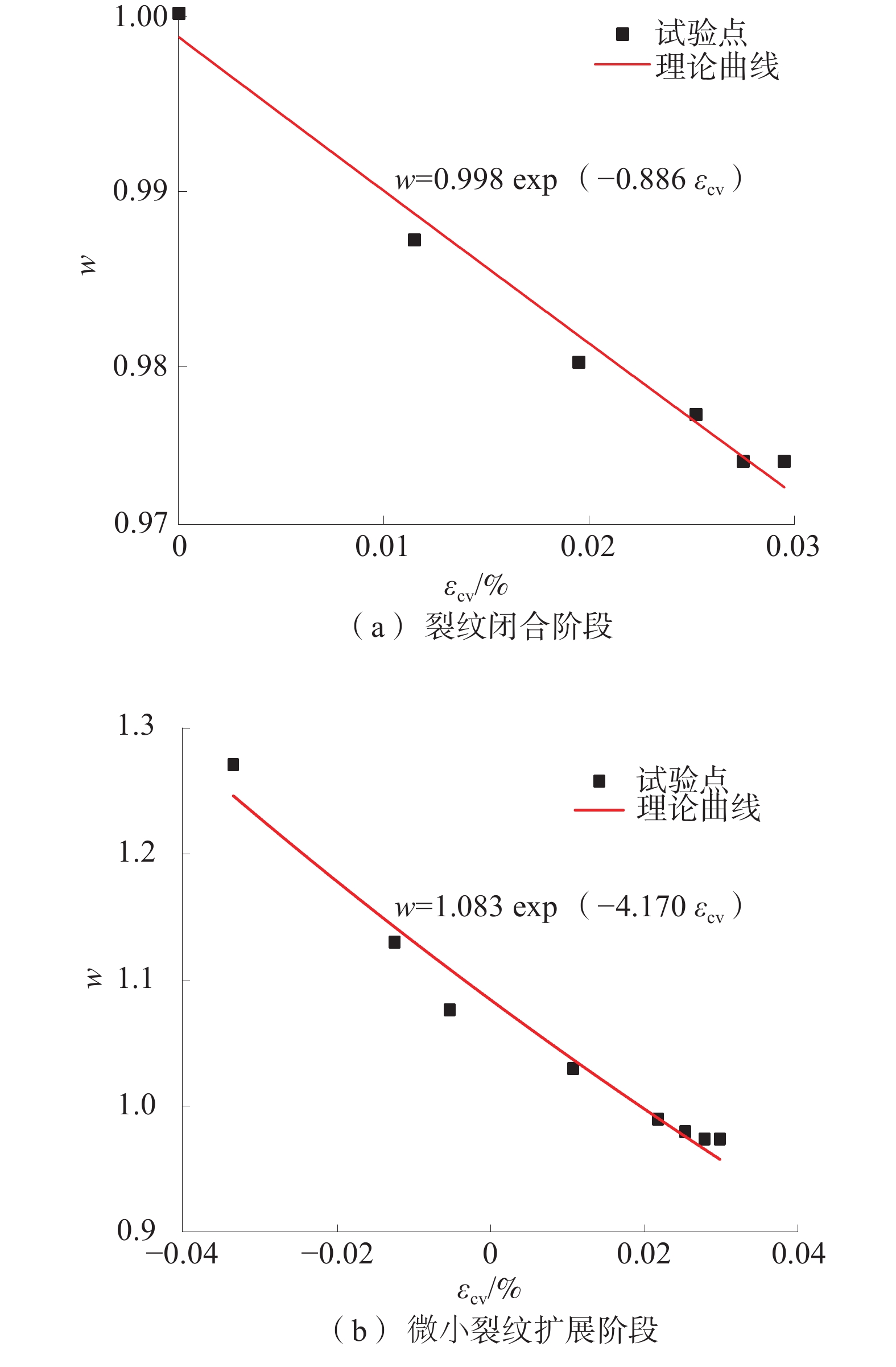
表 1 不同中间主应力条件下裂纹体应变-渗透率拟合曲线
Table 1 Crack volume strain-permeability fitting curves under different intermediate principal stress conditions
中间主应力/MPa 阶段 曲线 相关系数R2 30 裂纹闭合阶段 ${k \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {k {{k_0} = }}} \right. } {{k_0} = }}0.998{{\mathrm{e}}^{ - 0.888{\varepsilon _{{\text{cv}}}}}}$ 0.982 裂纹扩展阶段 ${k \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {k {{k_0} = }}} \right. } {{k_0} = }}1.080{{\mathrm{e}}^{ - 4.190{\varepsilon _{{\text{cv}}}}}}$ 0.972 40 裂纹闭合阶段 ${k \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {k {{k_0} = }}} \right. } {{k_0} = }}{{\mathrm{e}}^{ - 6.220{\varepsilon _{{\text{cv}}}}}}$ 0.973 裂纹扩展阶段 ${k \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {k {{k_0} = }}} \right. } {{k_0} = }}1.073{{\mathrm{e}}^{ - 3.980{\varepsilon _{{\text{cv}}}}}}$ 0.969 50 裂纹闭合阶段 ${k \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {k {{k_0} = }}} \right. } {{k_0} = }}0.997{{\mathrm{e}}^{ - 0.595{\varepsilon _{{\text{cv}}}}}}$ 0.906 裂纹扩展阶段 ${k \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {k {{k_0} = }}} \right. } {{k_0} = }}1.056{{\mathrm{e}}^{ - 3.312{\varepsilon _{{\text{cv}}}}}}$ 0.863 60 裂纹闭合阶段 ${k \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {k {{k_0} = }}} \right. } {{k_0} = }}{{\mathrm{e}}^{ - 0.967{\varepsilon _{{\text{cv}}}}}}$ 0.905 裂纹扩展阶段 ${k \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {k {{k_0} = }}} \right. }{{k_0} = }}1.112{{\mathrm{e}}^{ - 6.280{\varepsilon _{{\text{cv}}}}}}$ 0.935 表 2 不同中间主应力条件下损伤-渗透率拟合曲线
Table 2 Damage-permeability fitting curves under different intermediate principal stress conditions
中间主应力/MPa 阶段 曲线 相关系数R2 30 裂纹闭合 ${k \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {k {{k_0} = }}} \right. } {{k_0} = }}{{\mathrm{e}}^{ - 0.058D + 0.019{D^2}}}$ 0.994 裂纹扩展 ${k \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {k {{k_0} = }}} \right. } {{k_0} = }}{{\mathrm{e}}^{ - 0.003 + 0.325D + 0.016{D^2}}}$ 0.998 40 裂纹闭合 ${k \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {k {{k_0} = }}} \right. } {{k_0} = }}{{\mathrm{e}}^{0.002 - 0.029D + 0.010{D^2}}}$ 0.998 裂纹扩展 ${k \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {k {{k_0} = }}} \right. } {{k_0} = }}{{\mathrm{e}}^{ - 0.024 - 0.218D + 0.146{D^2}}}$ 0.985 50 裂纹闭合 ${k \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {k {{k_0} = }}} \right. } {{k_0} = }}{{\mathrm{e}}^{0.001 - 0.038D + 0.020{D^2}}}$ 0.998 裂纹扩展 ${k \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {k {{k_0} = }}} \right. } {{k_0} = }}{{\mathrm{e}}^{ - 0.030 - 0.149D + 0.260{D^2}}}$ 0.850 60 裂纹闭合 ${k \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {k {{k_0} = }}} \right. } {{k_0} = }}{{\mathrm{e}}^{0.006 - 0.048D + 0.024{D^2}}}$ 0.998 裂纹扩展 ${k \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {k {{k_0} = }}} \right. } {{k_0} = }}{{\mathrm{e}}^{0.002 - 0.204D + 0.370{D^2}}}$ 0.805 -
[1] 谢和平,张泽天,高峰,等. 不同开采方式下煤岩应力场-裂隙场-渗流场行为研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2016,41(10):2405−2417. XIE Heping, ZHANG Zetian, GAO Feng, et al. Stress- fracture-seepage field behavior of coal under different mining layouts[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2016, 41(10): 2405−2417.
[2] 尹光志,李文璞,李铭辉,等. 加卸载条件下原煤渗透率与有效应力的规律[J]. 煤炭学报,2014,39(8):1497−1503. YIN Guangzhi, LI Wenpu, LI Minghui, et al. Permeability properties and effective stress of raw coal under loading-unloading conditions[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2014, 39(8): 1497−1503.
[3] 李地元,孙志,李夕兵,等. 不同应力路径下花岗岩三轴加卸载力学响应及其破坏特征[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(S2):3449−3457. LI Diyuan, SUN Zhi, LI Xibing, et al. Mechanical response and failure characteristics of granite under different stress paths in triaxial loading and unloading conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(S2): 3449−3457.
[4] CHANG C, HAIMSON B. True triaxial strength and deformability of the german continental deep drilling program(KTB) deep hole amphibolite[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2000, 105(B8): 18999−19013. doi: 10.1029/2000JB900184
[5] MOGI K. Effect of the intermediate principal stress on rock failure[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 1967, 72(20): 5117−5131. doi: 10.1029/JZ072i020p05117
[6] MOGI K. Fracture and flow of rocks under high triaxial compression[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 1971, 76(5): 1255−1269. doi: 10.1029/JB076i005p01255
[7] 王凯,郭阳阳,王刚,等. 真三轴路径下含瓦斯复合煤岩体渗流及力学破坏特性研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2023,48(1):226−237. WANG Kai, GUO Yangyang, WANG Gang, et al. Seepage and mechanical failure characteristics of gas-bearing composite coal-rock under true triaxial path[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2023, 48(1): 226−237.
[8] 尹光志,鲁俊,李星,等. 中间主应力对砂岩扩容及强度特性影响[J]. 煤炭学报,2017,42(4):879−885. YIN Guangzhi, LU Jun, LI Xing, et al. Influence of intermediate principal stress on dilation and strength characteristics of sandstone[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2017, 42(4): 879−885.
[9] 李文璞,王泽,冯国瑞,等. 真三轴采动卸荷条件下砂岩扩容行为和非共轴性研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2023,48(S1):71−81. LI Wenpu, WANG Ze, FENG Guorui, et al. Research on sandstone dilation behavior and non-coaxiality under different stress Lode angle conditions[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2023, 48(S1): 71−81.
[10] 蒋长宝,陈昱霏,尹光志,等. 中间主应力与层理方向对页岩力学和渗透特性影响的试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2017,36(7):1570−1578. JIANG Changbao, CHEN Yufei, YIN Guangzhi, et al. Experimental study on the effect of intermediate principal stress and bedding direction on mechanical properties and permeability of shale[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 36(7): 1570−1578.
[11] 马德,赵育云,郭德龙,等. 孔周煤岩体渐进性破坏过程裂隙和应变能演化特征[J]. 煤矿安全,2022,53(3):16−23. MA De, ZHAO Yuyun, GUO Delong, et al. Evolution characteristics of cracks and strain energy during progressive failure of coal and rock masses around the hole[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(3): 16−23.
[12] 张俊文,宋治祥,范文兵,等. 真三轴条件下砂岩渐进破坏力学行为试验研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(9):2700−2709. ZHANG Junwen, SONG Zhixiang, FAN Wenbing, et al. Experimental investigation on progressive damage mechanical behavior of sandstone under true triaxial condition[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2019, 44(9): 2700−2709.
[13] 彭俊,蔡明,荣冠,等. 裂纹闭合应力及其岩石微裂纹损伤评价[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2015,34(6):1091−1100. PENG Jun, CAI Ming, RONG Guan, et al. Stresses for crack closure and its application to assessing stress-induced microcrack damage[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 34(6): 1091−1100.
[14] 陈岩,左建平,宋洪强,等. 煤岩组合体循环加卸载变形及裂纹演化规律研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2018,35(4):826−833. CHEN Yan, ZUO Jianping, SONG Hongqiang, et al. Deformation and crack evolution of coal-rock combinedb body under cyclic loading-unloading effects[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2018, 35(4): 826−833.
[15] 张杰,何义峰,罗南洪,等. 浅埋煤层群重复采动覆岩运移及裂隙演化规律研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2022,53(3):58−65. ZHANG Jie, HE Yifeng, LUO Nanhong, et al. Research on overburden movement and fracture evolution of repeated mining in shallow coal seams group[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(3): 58−65.
[16] 程远平,刘洪永,郭品坤,等. 深部含瓦斯煤体渗透率演化及卸荷增透理论模型[J]. 煤炭学报,2014,39(8):1650−1658. CHENG Yuanping, LIU Hongyong, GUO Pinkun, et al. A theoretical model and evolution characteristic of mining-enhanced permeability in deeper gassy coal seam[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2014, 39(8): 1650−1658.
[17] WEN Z, JING S, JIANG Y, et al. Study of the fracture law of overlying strata under water based on the flow-stress-damage model[J]. Geofluids, 2019: 3161852.
[18] 王伟,郑志,王如宾,等. 不同应力路径下花岗片麻岩渗透特性的试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(2):260−267. WANG Wei, ZHENG Zhi, WANG Rubin, et al. Experimental study of permeability properties of granitic gneiss under different stress paths[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(2): 260−267.
[19] CHEN Haipeng, CHEN Yuanping, ZHOU Hongbin, et al. Damage and permeability development in coal during unloading[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2013, 46(6): 1377-1390.
[20] 徐树媛,张永波,相兴华,等. 采空区裂隙岩体渗流特征及渗透性试验研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2022,53(4):36−44. XU Shuyuan, ZHANG Yongbo, XIANG Xinghua, et al. Experimental study on seepage characteristics and permeability of fractured rock mass in goaf[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(4): 36−44.
[21] 李春元,崔春阳,雷国荣,等. 深部开采岩体围压卸荷-渗流致拉破裂机制[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(8):3069−3082. LI Chunyuan, CUI Chunyang, LEI Guorong, et al. Tensile fracture mechanism of rock mass induced by the unloading-seeping of confining pressure in deep coal mining[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(8): 3069−3082.
[22] 刘先珊,王科,许明. 低渗储层砂岩渗流–应力–损伤渐裂过程的渗透特性演化研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2018,40(9):1584−1592. LIU Xianshan, WANG Ke, XU Ming. Permeability evolution of low-permeability reservoir sandstone considering hydraulic- mechanical-damage coupling effect during gradual fracturing process[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2018, 40(9): 1584−1592.
[23] 周银波,李晓丽,李晗晟,等. 煤体吸附变形对3种气体渗透率演化的影响[J]. 煤矿安全,2021,52(11):16−21. ZHOU Yinbo, LI Xiaoli, LI Hansheng, et al. Influence of coal adsorption deformation on permeability evolution of three kinds of gas[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021, 52(11): 16−21.
[24] 宋涛,李博涛,魏宗勇,等. 煤体孔隙结构对瓦斯吸附和放散性能的影响实验研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2022,53(6):12−18. SONG Tao, LI Botao, WEI Zongyong, et al. Experimental study on effect of pore structure of coal on gas adsorption and dispersion properties[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(6): 12−18.
[25] LI Minghui, YIN Guangzhi, XU Jiang, et al. A novel true triaxial apparatus to study the geomechanical and fluid flow aspects of energy exploitations in geological formations[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2016, 49(12): 4647−4659. doi: 10.1007/s00603-016-1060-7
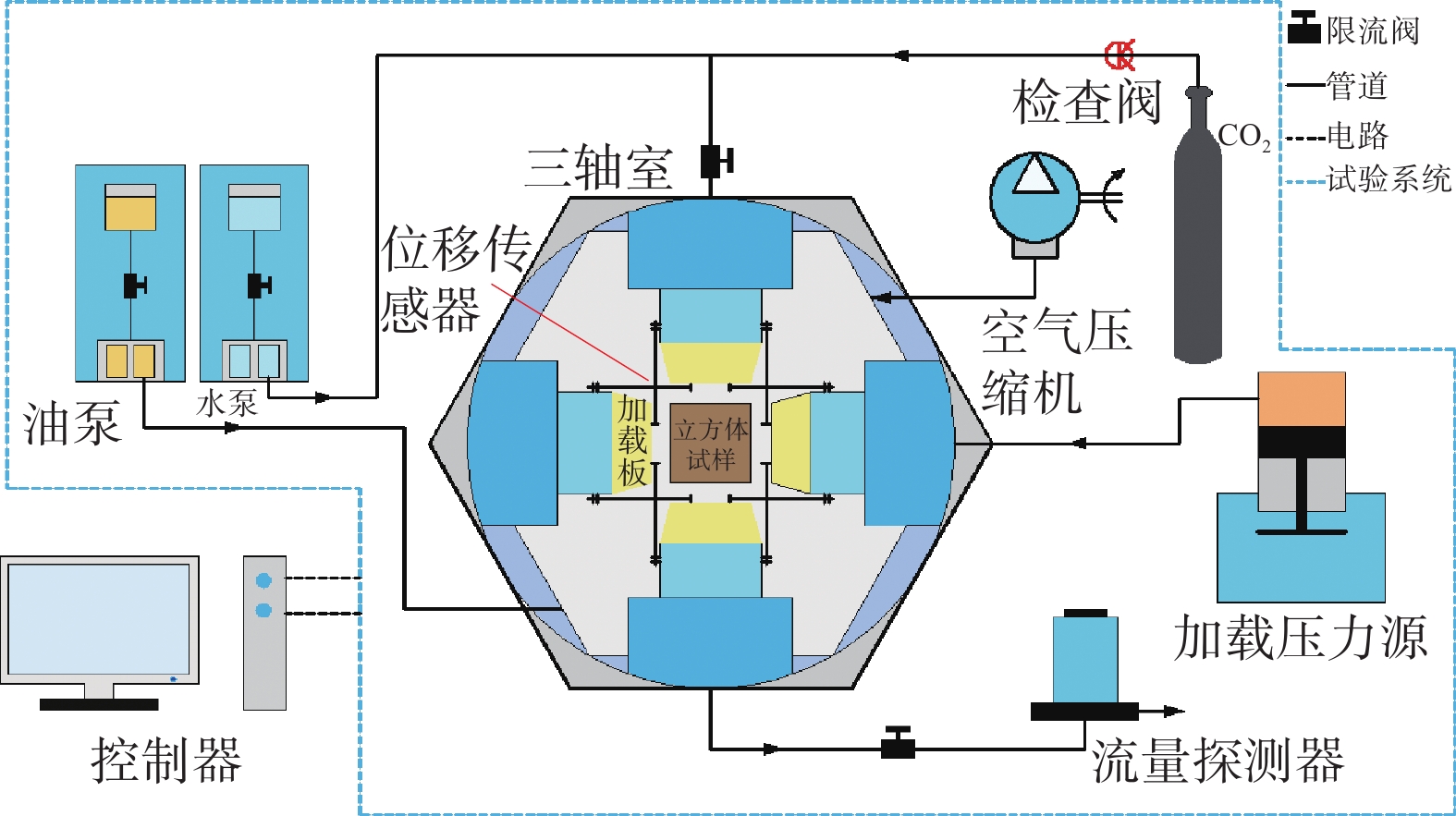
[26] 尹光志,李铭辉,许江,等. 多功能真三轴流固耦合试验系统的研制与应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2015,34(12):2436−2445. YIN Guangzhi, LI Minghui, XU Jiang, et al. A new multi-functional true triaxial fluid-solid coupling experiment system and its applications[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 34(12): 2436−2445.




 下载:
下载: