Macromolecular structure characterization and its model construction of high-sulfur coal in Jincheng
-
摘要:
从分子水平上认识、表征高硫煤的结构特征对于清洁高效利用高硫煤具有关键意义。利用工业元素分析、高分辨率透射电镜、激光解吸飞行时间质谱、13C核磁共振波谱和X射线光电子能谱技术对晋城高硫煤的分子结构进行表征。结果表明:晋城高硫煤中的芳香层片长度分布范围较宽,且以2×2和3×3形式居多;杂原子结构中氮原子以吡啶氮和吡咯氮为主,硫原子的存在形式包含硫醇、硫醚、噻吩、亚砜和砜等多种结构,氧原子主要存在于羟基、羰基、和醚氧中,同时,结构中脂肪侧链长度较短,且支链化程度较低。根据高分辨图像提供的芳香碳骨架信息,从中选取327个芳香层片作为结构模型的基本骨架,在依次实现脂肪结构和杂原子官能团的添加后对其进行优化,得到了与上述实验数据吻合的高硫煤分子结构模型,模型由95个单体分子组成,原子数量为18882个,分子式为C12119H6279O214N118S152,分子量为161 647Da。通过构建的分子结构模型可应用于进一步研究高硫煤的物理化学性质及反应性等。
Abstract:To understand and characterize the structure characteristics of high-sulfur coal at molecular level is of key significance for clean and efficient utilization of high-sulfur coal. The molecular structure of Jincheng high-sulfur coal was characterized by proximate analysis, ultimate analysis, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, laser desorption time of flight mass spectrometry, 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The results show that the aromatic lamellar length of Jincheng high-sulfur coal has a wide distribution range, and the form of 2×2 and 3×3 is the majority; in the heteroatomic structure, the nitrogen atoms are mainly pyridine nitrogen and pyrrole nitrogen, the sulfur atoms exist in the form of mercaptan, thioether, thiophene, sulfoxide and sulfone structures, and the oxygen atoms mainly exist in the hydroxyl group, carbonyl group, and ether oxygen, and the length of the adipose side chain in the structure is short, the degree of branched chain is low. According to the aromatic carbon skeleton information provided by the high-resolution image, 327 aromatic layers were selected as the basic skeleton of the structural model, which was optimized after the addition of aliphatic structure and heteroatomic functional groups in turn. The molecular structure model of high-sulfur coal was obtained in accordance with the above experimental data. The model consists of 95 individual molecules, 18 882 atoms in total. The molecular formula is C12119H6279O214N118S152 and the molecular weight is 161 647 Da. The molecular structure model can be applied to further study the physical and chemical properties and reactivity of high-sulfur coal.
-
煤矸石是煤炭采掘及洗选加工过程产生的干基灰分>50%的煤岩混合体,其主要组成成分为黏土矿、石英和硫铁矿以及残留碎煤等,属于一种热值利用价值低、具有可燃性的固体废弃物,其排放累积量巨大、资源利用率低,危害十分严重[1-2]。煤矸石的自燃主要为氧化反应及热解反应,随着温度升高产生CH4、CO、CO2等气体,会对周边环境产生一定影响[3-4]。为从微观水平上确定煤与煤矸石自燃的反应机理,邓军等[5]建立了羟基处于侧链活性结构邻位的小分子结构模型,发现侧链基团与氧气复合反应主要受最低未占据分子轨道成键能力决定,羟基影响活性基团前线轨道特征从而影响煤氧复合反应;郝长胜等[6]通过分峰拟合3种变质程度不同的煤样品红外光谱,发现随变质程度加深煤分子脂肪侧链变短,支链化程度提高,煤的芳碳率、芳氢率、芳香度和缩合度更高,结构更加稳定;肖旸等[7]也通过红外光谱分析煤样升温发现羟基活性高,脂肪烃含量多但氧化过程中变化不明显,芳香烃中C=C变化小,羟基与烷基发生氧化反应生成羧基,含氧官能团增多;赵婧昱等[8-9]采用程序升温氧化实验和原位傅里叶红外光谱实验发现,在临界温度阶段,羰基影响CH4、CO、C2H6、CO2气体,在干裂−活性−增速温度阶段,脂肪烃和羧基影响气体浓度,在增速−燃点温度阶段,羧基、羰基与气体浓度呈负相关的关系;王思栋等[10]利用自由基测定系统对煤矸石进行实验测定,发现含硫量提升会降低矸石快速氧化临界点并提高CO释放量,促进矸石自燃;刘向群等[11]利用程序升温−气相色谱联用实验将煤自燃氧化划分成4个阶段并确定了各阶段CO、CO2等标志气体的参数特征。众学者对煤分子中官能团及煤矸石自燃气体释放有较为深刻的研究,为研究提供了重要的指导与参考,但其多是对煤的官能团定性分析或矸石的自燃特征参数分析,而对于煤矸石自燃过程中活性官能团的转化规律分析尚有欠缺,且对于气体释放与活性官能团之间的关联缺乏系统性的分析研究。
内蒙古乌海市棋盘井镇是典型的煤炭工业城市,其煤炭生产规模庞大、开采历史悠久,长期以来该地区产生了约5.4亿t煤矸石,现堆存4.6 t,形成上百座煤矸石山,自燃情况时常发生,释放有毒有害气体污染环境,且还会造成气体中毒、坍塌、爆炸等一系列事故[12-14],对当地安全生产形成了一定的隐患。为此,采用原位漫反射傅里叶红外光谱法(in-situ DRIFTS)对内蒙古棋盘井镇煤矸石样品氧化燃烧过程中微观活性官能团演化进行分析,动态测试煤矸石在氧化燃烧过程中主要官能团随温度实时变化情况,并利用Spearman相关性分析法进行关联性验证;通过研究煤矸石自燃中官能团变化与气体释放规律,为煤矸石自燃机理研究与标志气体分析提供一定的参考。
1. 样品及实验
1.1 煤矸石样品制备
实验样品采选以内蒙古棋盘井镇某洗煤厂煤矸石山北面为采样面,采用梅花采样法采取样品后立刻密封保存、标记,运回实验室后将煤矸石样进行均化处理,将5个采样点取得的样品摇匀各取100 g充分混合,每份500 g样品,共3份。并通过JY200g多功能粉碎机粉碎及充分研磨,根据原位傅立叶红外光谱实验要求,并充分考虑试验的便利性,选得粒径150 μm煤矸石样品密封保存,以备后续试验。
依据现行GB/T 212—2008《煤的工业分析方法》,取煤矸石样进行3组平行测定,取平均值得到煤矸石样品的工业分析数据(表1),可知该煤矸石属于低灰中高碳型的洗矸。
表 1 煤矸石工业分析参数Table 1. Industrial analysis parameters of coal gangue %煤矸石样 水分 灰分 挥发分 固定碳 1 0.80 68.34 15.69 15.17 2 0.84 68.35 15.18 15.63 3 0.84 68.43 15.44 15.28 平均值 0.83 68.37 15.44 15.36 1.2 实验仪器与条件
采用原位漫反射红外光谱实验,结合漫反射、傅里叶红外光谱和原位技术对样品进行分析,使用德国布鲁克公司生产的INVENIO R的傅立叶变换红外光谱仪,在空气氛围下煤矸石样品红外表征采用原位漫反射红外。装置外侧接程序升温控制装置,实现动态升温过程中样品的红外光谱记录,以分析不同温度下各活性官能团的种类及变化情况。此次实验测试过程设置红外光谱仪器的扫描次数为17次,波谱扫描范围为4 000~600 cm−1,反应过程升温速率为2 ℃/min,控制程序升温温度范围为30~350 ℃,每10 min进行1次数据监测。
2. 煤矸石自燃过程活性官能团演化分析
2.1 红外谱图
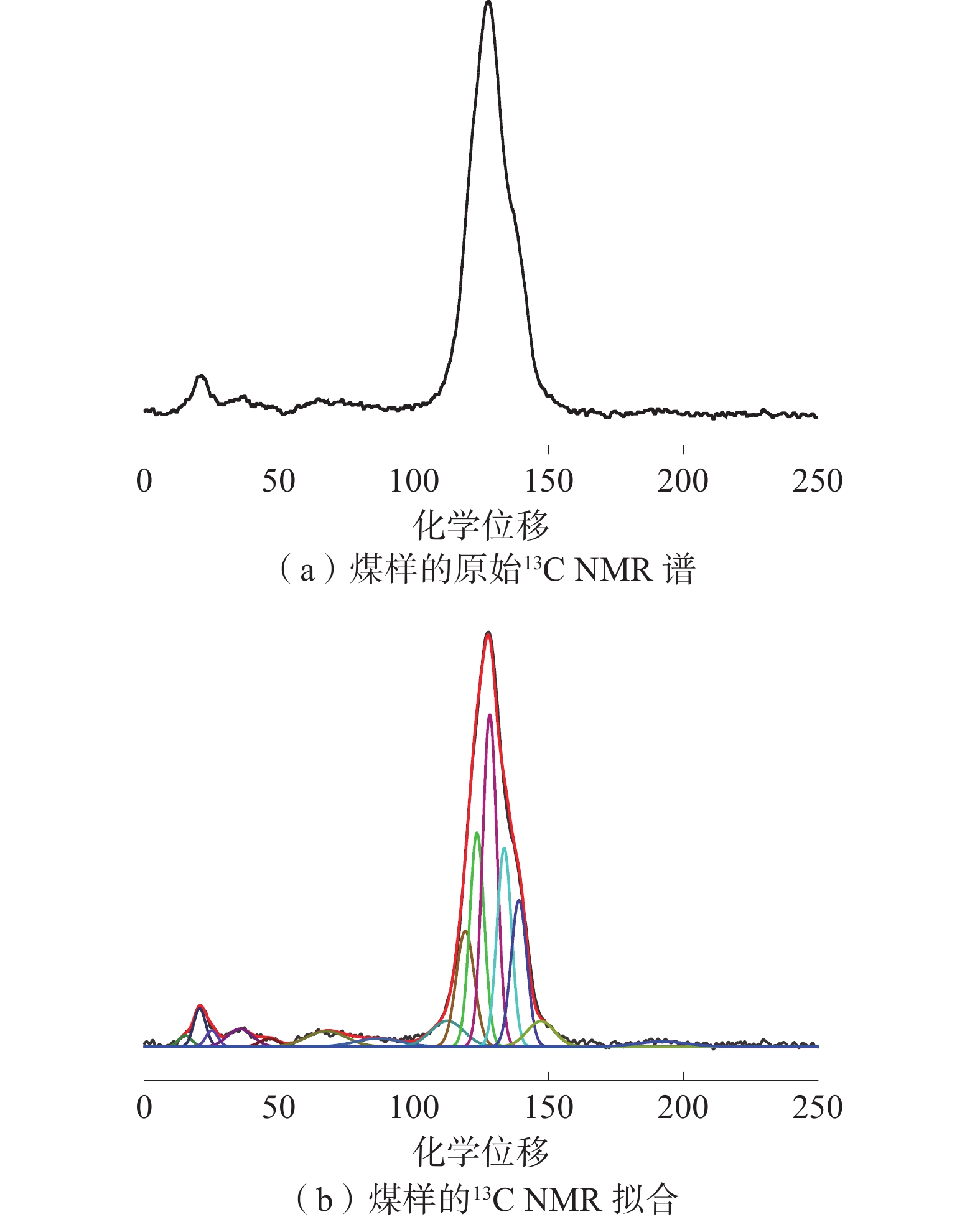
研究发现煤矸石30~350 ℃升温过程中有69.1、320.6 ℃特征温度点[15-18],可以将低温氧化划分为黄铁矿氧化及气体脱附阶段(30~69.1 ℃)、脱氧吸附阶段(69.1~320.6 ℃)及挥发分析出阶段(320.6 ℃以上)以便于分析。通过实验获得煤矸石样品氧化燃烧过程对应特征温度点下的原位红外光谱数据,利用Peakfit进行分峰拟合发现:各官能团峰位出现了一定的基团频率位移现象,峰形变化不大、峰面积变化明显;氧化过程中峰位3 045.8 cm−1处的−CH3、2 921.4 cm−1处的−CH2−在特征温度320.6 ℃左右含量微弱可忽略不计。
煤矸石低温氧化过程红外3D谱图如图1所示,煤矸石氧化特征温度点红外分峰拟合3D谱图如图2所示。根据图1与图2中在30 ℃空气氛围下红外分峰拟合结果以及特征官能团对应红外光谱吸收峰归属对照[19]可以得到煤矸石官能团特征峰参数,统计出的煤矸石在空气氛围下主要官能团的种类和数量分布状况如图3所示。
由图3可以看出,空气氛围下的官能团百分比含量呈现出:含氧官能团>芳香烃>脂肪烃,其中羟基含量最大为35.00%,C=C、C−H次之分别为18.88%、16.21%,苯中变形振动的H及苯环上孤立面外变形振动的H占比10.43%。结合对峰面积的分析发现煤矸石初始官能团含量较高、种类较多,芳香烃相对含量占比高于脂肪烃,含氧官能团相对含量高、占比大,尤其是羟基相对含量达到了35.00%。
由此可以明确煤矸石自燃过程中反应的主要官能团有羟基、脂肪烃、芳香烃和含氧官能团中的多种及−H、C≡C、C=N+−H。将氧化过程中各温度点的红外光谱进行分峰拟合得到各峰位官能团的峰面积以具体量化分析各官能团含量变化及转化规律。
2.2 羟基的转化规律
依据分峰拟合结果,以3 700~3 625 cm−1谱峰内游离的羟基、3 624~3 300 cm−1谱峰内分子间氢键为基础,选取3 691.3、3 651.3、3 623.1 cm−1左右峰位(发生位移的峰位按初始峰位处理)的官能团峰面积进行分析。羟基含量随温度的变化规律如图4所示。
由图4可知:氧化过程中羟基含量整体上随温度升高而增多。在黄铁矿氧化及气体脱附阶段,黄铁矿及分子量较小的化合物发生氧化分解,游离态羟基增多,但是在水分蒸发中又有消耗,故3 691.3、3 651.3 cm−1峰位游离羟基呈现出先增后降、先增后平稳的趋势;3 623.1 cm−1峰位分子内氢键相对较弱会优先断裂,但又在氧化中生成,也呈现出先增加后平稳的趋势;在吸氧增重阶段由于矸石吸附空气中氧气反应生成羟基,活性较高的羟基又与亚甲基(−CH2−)发生反应被消耗,故3 691.3、3651.3 cm−1峰位游离的羟基与3 623.1 cm−1峰位分子内氢键含量呈现为曲线波动上升;在320.6 ℃以后,随着氧化的深化羟基含量继续上升,而矸石彻底燃烧后游离羟基和分子间氢键会急剧减少参与到反应中。羟基(−OH)含量在煤矸石氧化燃烧过程中350 ℃之前为增长趋势且含量较高,主要是游离羟基及分子内氢键容易在其他官能团氧化过程中产生。
2.3 脂肪烃的转化规律
选取氧化过程3 045.8 cm−1 R−X−CH3结构中甲基−CH3的不对称伸缩振动、2 921.4 cm−1含氧环烷中−CH2−基团上H的不对称伸缩振动及1 448 cm−1−CH2−中H的面内变形振动进行分析。脂肪烃含量随温度的变化规律如图5所示。
由图5可以看出:氧化过程中脂肪烃中仅1 448 cm−1 −CH2−含量随温度变化明显,在黄铁矿氧化及气体脱附阶段中1 448 cm−1−CH2−含量先增后减,其余峰位基团无较大波动,这是因为脂肪烃反应可产生碳氢类气体,初期反应强度小;吸氧增重阶段由于矸石吸附氧气,脂肪烃发生相应的断裂与氧化反应不断生成CH4,在170 ℃达到活性温度点,所以2 921.4 cm−1含氧环烷中−CH2−含量在170 ℃开始大幅上升,至210 ℃之后迅速减少直到趋近消失;而相较于环烷结构2 921.4 cm−1−CH2−随温度升高在反应中不断被消耗,1 448 cm−1−CH2−的H面内变形振动比伸缩振动所需能量更高,其活性温度点也相对更高,且随着升温长链脂肪烃等结构与氧反应分解产生大量亚甲基,到230 ℃左右大量的不饱和键断裂,样品氧化速度大大加快,使得1 448 cm−1−CH2−的峰面积在此时开始急剧上升;320.6 ℃以后1 448 cm−1−CH2−含量持续增加,在达到活性温度点释放CH4后−CH2−含量将减少直至消失。可见脂肪烃官能团氧化过程中参与反应多,整体偏高且呈上升趋势。
2.4 芳香烃的转化规律
选取氧化过程中的1 652.7、1 616.8、756.1、700.3 cm−1处芳香烃结构的峰面积变化来描述芳香烃含量变化规律。芳香烃含量随温度的变化规律如图6所示。
由图6可知:氧化过程中芳香烃含量整体上随温度升高而上升。黄铁矿氧化及气体脱附阶段,1 616.8 cm−1峰位的苯环及与苯环相连的C=C骨架伸缩振动产生的峰面积恒定不变,1 652.7 cm−1峰位的C=C骨架伸缩峰面积先微弱减少后增加,756.1、700.3 cm−1峰位处的取代芳烃仅微弱增长,可见该阶段芳香烃官能团结构稳定,未发生较大反应;吸氧增重阶段C=C骨架含量在230 ℃之前较稳定,随后明显上升,1 616.8 cm−1C=C的增速是1 652.7 cm−1处的2倍,1 652.7 cm−1C=C骨架在310 ℃达到活性温度开始减少,而取代芳烃含量波动上升,其原因为苯环属较稳定结构并未反应,而煤矸石分子中链状或桥键结构发生断裂产生一部分取代芳烃基团导致其含量波动上升;320.6 ℃以后4个峰位的芳香烃结构含量均处于下降状态,表明在挥发分阶段及燃烧阶段,芳香烃随着反应加深不断被消耗。
氧化反应过程中芳香烃官能团的含量相对比较高,芳香烃中苯环及与苯环相连的C=C双键作为煤矸石中煤分子的结构骨架具有一定稳定性,在氧化反应的初期相对稳定,而取代芳烃也呈增长趋势。
2.5 含氧官能团的转化规律
对氧化过程中1 723.97、1 685.17 cm−1峰位羧酸酯类等中羰基、1 109 cm−1醚键中C−O−C的伸缩振动进行分析,总结含氧官能团的转化规律。含氧官能团含量随温度的变化规律如图7所示。
由图7可知:由于次生基团的产量于醚键的消耗量形成近乎平衡状态,1 109 cm−1峰位醚键中C−O−C的含量在氧化过程中波动不大;在黄铁矿氧化及气体脱附阶段,1 723.9、1 685.17 cm−1峰位羧酸酯类等中羰基C=O含量几乎为0,这是由于脂肪烃是产生羰基的主要官能团,此阶段脂肪烃未发生消耗;吸氧增重阶段1 685.17 cm−1峰位羰基含量在190 ℃后大幅增长,达到峰值后开始减少;1 723.9 cm−1峰位羰基230 ℃之前含量微弱,此后含量急剧增大并在320 ℃达到最大值,可以看出使得其变化趋势与2 921.4 cm−1含氧环烷中−CH2−基团相反,说明脂肪烃消耗生成羰基;320 ℃之后,1 685.17 cm−1峰位羰基含量增大直至脂肪烃消耗完毕,而1 723.9 cm−1峰位羰基被大量消耗,直至反应完毕,过程中产生CO、CO2等气体。煤矸石氧化燃烧过程中含氧官能团含量呈现出前期较为稳定,190 ℃后大幅提升的特点。
2.6 其他官能团的转化规律
由于煤矸石氧化过程中芳香醚、环氧化合物以及苯中H的变形振动与苯环上孤立的氢面外变形振动具有较高的活性,因此选择1 246.8、1 183.9 cm−1峰位的−H作为对象进行分析。其他官能团含量随温度的变化规律如图8所示。
由图8可知:在黄铁矿氧化及气体脱附阶段,1 246.8 cm−1芳香醚、环氧化合物以及苯中变形振动的H含量先少量增加后减少,而1 183.9 cm−1苯环上孤立的氢面外变形振动峰面积无明显变化;吸氧增重阶段中190 ℃后两峰面积上升,1 246.8 cm−1处基团含量于310 ℃增长到最大值后开始下降,而1 183.9 cm−1苯环上孤立的氢面外变形振动峰面积在增长至270 ℃后开始下降,290 ℃之后又开始持续升高;320 ℃之后,两者都出现下降趋势直至反应消耗完毕。
3. 气体产物与官能团相关性分析
相关性分析用来判断变量之间的统计学关联,并进行关联强度和方向的判断。选择Spearman相关性系数分析法,其适用于不明分布定距数据,2个数据序列的数据一一对应,等间距等比例,数据序列通常来自对同一组样本的多次测量或不同视角的测量。分析可知,棋盘井镇煤矸石氧化过程中气体析出量(H)与官能团含量(S)数据属于不明分布定距数据,可用Spearman相关进行分析,其系数计算公式为:
$$ R = 1 - 6S \frac{{{{\left( {{A_i} - {B_i}} \right)}^2}}}{{{n^2} - n}} = \frac{{1 - 6S {{\left( {{A_i} - {B_i}} \right)}^2}}}{{{n^2} - n}}(i=1\text{,}2,3\text{,}\cdots \text{,}n) $$ (1) 式中:n为样本量;Ai、Bi分别为被衡量的2个变量;R为相关系数,判定惯例为:|R|≥0.6表示高度相关,0.4≤|R|<0.6表示相关,|R|<0.4表示不相关,R>0为正相关,R<0为负相关,|R|越接近1相关性越强[20-22]。
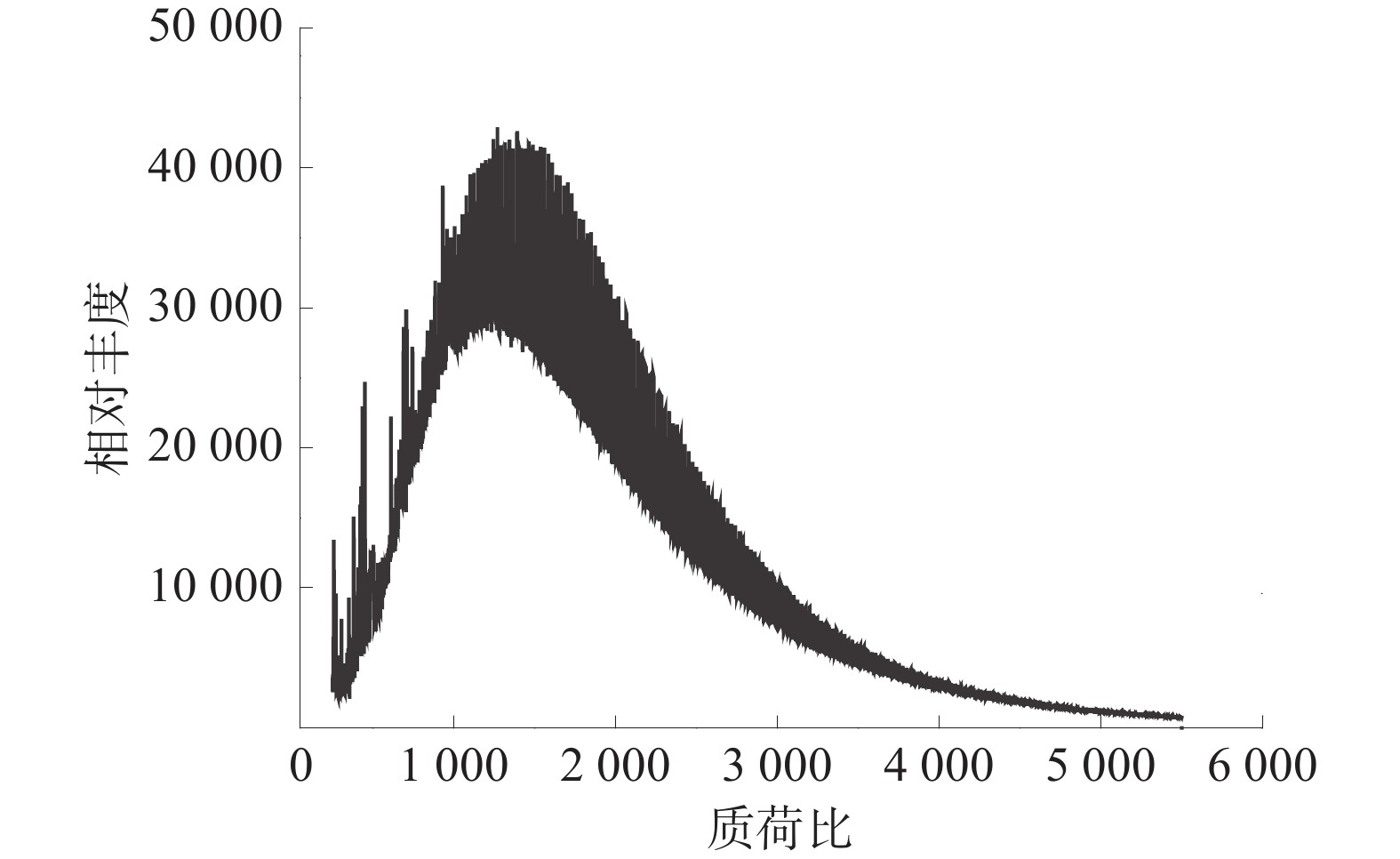
为获取气体产物数据来进行相关性分析,利用MS质谱法对矸石自燃中逸出的气体产物进行分离分析。利用四极质谱仪QMS403测试自燃中气相挥发物的逸出特性,选取煤矸石样品为(10±0.5) mg,利用氧化铝坩埚在干燥空气氛围下进行30~350 ℃升温测试,升温速率为5 K/min,流量为100 mL/min。燃烧气体产物通过恒温毛细管同步进入质谱分析仪,通过电场和磁场将运动的气体分子按质荷比分离后,监测得到的煤矸石低温氧化过程中3种主要气体离子流曲线如图9所示。
在原位红外光谱实验中未检测到含硫、氮官能团,故选择研究CH4、CO、CO2气体析出量在氧化燃烧过程中与各官能团之间的相关性。选择所研究的15个氧化过程中不同峰位活性官能团含量对气体析出量的影响,以不同温度时各气体析出量参考值H(H')作为Ai;不同温度时各活性官能团的含量S(S')作为Bi,得到煤矸石燃烧过程中气体析出量与官能团含量的Spearman相关性系数。氧化燃烧气体析出量与活性官能团Spearman相关系数矩阵图如图10所示。
由图10可知:煤矸石氧化燃烧过程中,CH4气体析出量与1 448 cm−1脂肪烃−CH2−中H的面内变形振动正相关性较大,说明很大程度上,氧化燃烧过程中所产生的CH4是脂肪烃官能团生成时产生或裂解产生。
CO析出量与3 651.3 cm−1游离的羟基、1 616.8 cm−1苯环及与苯环相连的C=C骨架伸缩振动、756.1、700.3 cm−1处的取代芳烃C−H、1 723.97、1 685.17 cm−1羧酸酯类等中羰基C=O伸缩振动高度正相关,相关系数均大于0.9,且有RC=O>RC=C>RC−H=R−OH,即CO主要是由羰基氧化生成,说明羰基在氧化燃烧中活性较大,而羟基、C=C骨架、取代芳烃C−H相关反应也会生成CO。
CO2析出量与3651.3 cm−1游离的羟基、3 623.1 cm−1分子内氢键、1 616.8 cm−1苯环及与苯环相连的C=C骨架伸缩振动、756.1、700.3 cm−1取代芳烃C−H、1 723.97、1 685.17 cm−1羧酸酯类等中羰基C=O伸缩振动及1 183.9 cm−1苯环上孤立的氢面外变形振动高度正相关,相关系数均大于0.9,且有R−OH=RC=O>RC−H>R−H>RC=C。理论上−COOH是CO2产生的主要官能团[23],而羟基(−OH)与羰基(C=O)反应生成−COOH,且通过原位红外光谱实验未检测到−COOH官能团存在,故而相关性分析得出羟基、羰基与CO2析出量之间有强相关性。由此可知脂肪烃中2 921.4 cm−1−CH2−基团与其他官能团之间无相关性,3 045.8 cm−1 R−X−CH3结构中甲基−CH3与其他官能团之间相关性弱。1 685.17 cm−1羰基C=O与除这2种官能团外其他官能团高度正相关,相关系数在0.81~0.97之间,可见该基团在氧化燃烧中活性大。
4. 结 论
1)煤矸石样品在空气氛围中初始状态官能团主要包含脂肪烃(−CH2−、−CH3)、芳香烃(C=C、C−H)、含氧官能团(−OH、O=C=O、C=O、C−O−C)3种类型及少数其他官能团(C=N+−H、−H、C≡C等),相对含量含氧官能团>芳香烃>脂肪烃,含氧官能团含量高,尤其是羟基相对含量达到了35.00%。
2)煤矸石氧化过程中羟基因水分蒸发、弱键断裂、与亚甲基反应被消耗以及生成羧基、碳氧化物气体而呈现波动上升;脂肪烃含量高、反应活跃,生成CH4;芳香烃中C=C官能团作为煤分子结构骨架较为稳定,取代芳烃含量波动上升;含氧官能团中C=O受脂肪烃影响,190 ℃后大幅提升,而C−O−C含量波动小。
3)CH4析出量主要随脂肪烃1 448 cm−1−CH2−含量升高而升高;CO有RC=O>RC=C>RC−H=R−OH,与羰基有很强的相关性,其主要由羰基氧化生成;而CO2有R−OH=RC=O>RC−H>R−H>RC=C,羟基与羰基反应生成羧基后与氧气生成CO2,反应中羰基的活性最大。
-
表 1 煤样的工业元素分析、硫形态分析及镜质体反射率
Table 1 Proximate and ultimate analysis, sulfur form analysis and vitrinite reflectance of coal sample
样品 Romax/% Mad/% Aad/% Vdaf/% C含量/% H含量/% O含量/% N含量/% S含量/% Sp含量/% Ss含量/% So含量/% JC-15 2.22 0.62 17.42 12.85 88.73 3.82 2.09 1.01 4.36 1.12 0.02 2.43 注:Romax为镜质体反射率;Mad 为水分;Aad为灰分;Vdaf为挥发分;Sp为硫化铁硫,Ss为硫酸盐硫;So为有机硫。 表 2 高硫煤的13C NMR结构参数计算结果
Table 2 Calculation results of 13C NMR structure parameters of high-sulfur coal
% fa faC fa' faH faN faP faS faB fal fal* falH falO 89.17 1.34 87.83 32.05 55.78 3.63 12.12 40.03 10.83 3.03 3.56 4.24 注[23]:fa为总sp2杂化碳;faC为羰基或羧基碳(δ>165);fa'为芳香碳;faH为质子化芳碳;faN为非质子化芳碳;faP为与羟基或醚氧结合的芳香碳(δ=148~165);faS为烷基化芳碳(δ=137~148);faB为芳香桥碳(δ=129~137);fal为总sp3杂化碳;fal*为CH3或季碳(δ=36~50);falH为CH或CH2;falO为与氧原子相连的脂肪碳(δ=50~90)。 表 3 高硫煤的XPS C(1s), N(1s)和S(2p)数据
Table 3 XPS C(1s), N(1s) and S(2p) data of high-sulfur coal
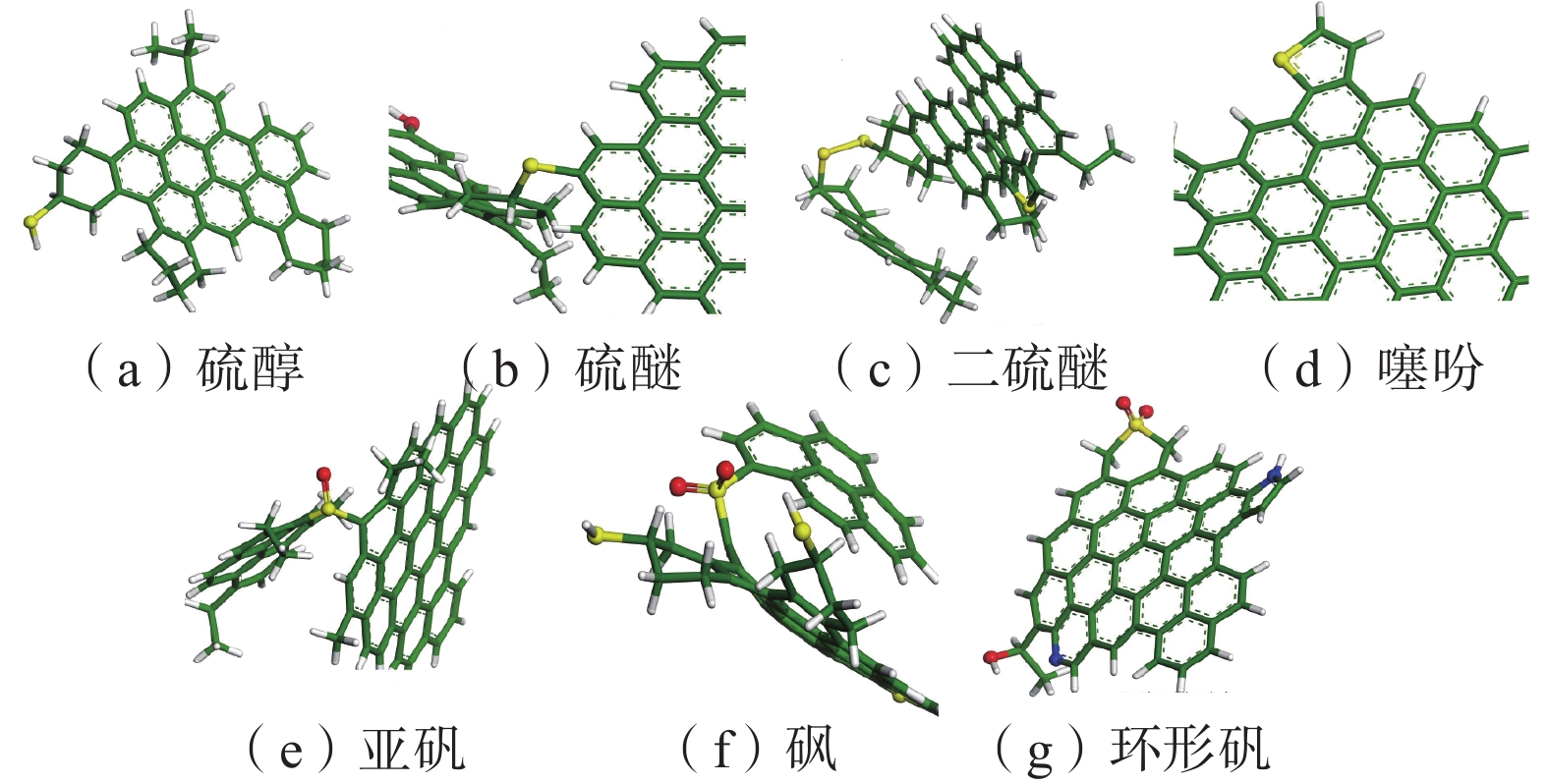
元素 峰位/eV 归属 相对面积/% C1s 284.4 C=C、C-H 51.8 285.6 C-O 33.9 287.1 C=O 8.2 289.2 COO- 6.1 N1s 398.3 吡啶氮 32.2 400.2 吡咯氮 47.1 401.3 质子化吡啶 14.3 402.8 氮氧化物 6.4 S2p 161.7 硫铁矿 0.7 162.7 硫醇(醚) 3.4 163.4 硫醇(醚) 13.2 164.0 噻吩 28.4 164.7 噻吩 28.8 165.6 亚砜 19.6 166.8 砜 5.9 表 4 芳香层片的结构参数
Table 4 Structural parameters of aromatic lamellae
芳香层片
Naphthalene长度范围/Å 占比/% 分子质量/Da 3.0~5.4 11.9 68~158 2×2 5.5~7.4 25.5 163~269 3×3 7.5~11.4 30.1 275~568 4×4 11.5~14.4 13.1 577~855 5×5 14.5~17.4 7.9 865~1192 6×6 17.5~20.4 5.2 1 204~1 577 7×7 20.5~24.4 3.9 1 591~2 163 8×8 24.5~28.4 2.4 2 178~2 828 表 5 模型中含氧/氮/硫官能团的种类及含量
Table 5 Types and contents of O/ N/S functional groups in the model
官能团类型 数量 含氧官能团 羟基 69 芳(脂)-氧-脂(芳) 65 羰基 32 含氮官能团 吡啶/质子化吡啶 55 吡咯/氮氧化物 63 含硫官能团 硫醇(醚) 25 噻吩 88 亚砜 30 砜 9 -
[1] 国家统计局. 中华人民共和国2020年国民经济和社会 发展统计公报[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2021. [2] CAI Shuangshuang, ZHANG Shengfu, WEI Yuyang, et al. A novel method for removing organic sulfur from high-sulfur coal: Migration of organic sulfur during microwave treatment with NaOH-H2O2[J]. Fuel, 2020, 289: 119800.
[3] SHEN Yanfeng, HU Yongfeng, WANG Meijun, et al. Speciation and thermal transformation of sulfur forms in high-sulfurcoal and its utilization in coal-blending coking process: A review[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2021, 35(7): 70−82.
[4] TANG Longfei, CHEN Songjiang, GUI Dongjiao, et al. Effect of removal organic sulfur from coal macromolecular on the properties of high organic sulfur coal[J]. Fuel, 2020, 259: 116264. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.116264
[5] 申岩峰,王美君,HU Yongfeng,等. 高硫炼焦煤化学 结构及硫赋存形态对硫热变迁的影响[J]. 燃料化学学 报,2020,48(2):144−153. SHEN Yanfeng, WANG Meijun, HU Yongfeng, et al. Effect of chemical structure and sulfur speciation of high-sulfur coking coals on sulfur transformation during pyrolysis[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2020, 48(2): 144−153.
[6] 兰安畅,郭春生,李耀谦,等. CO2抑制高硫煤自燃的 实验研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2022,53(1):44−48. LAN Anchang, GUO Chunsheng, LI Yaoqian, et al. Experimental research on CO2 inhibiting the spontaneous combustion of high sulfur coal[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(1): 44−48.
[7] 聂忠华. 高硫煤资源利用研究进展[J]. 价值工程,2020,39(16):227−228. NIE Zhonghua. Research progress in utilization of high sulfur coal resources[J]. Value Engineering, 2020, 39(16): 227−228.
[8] 唐跃刚,贺鑫,程爱国,等. 中国煤中硫含量分布特征 及其沉积控制[J]. 煤炭学报,2015,40(9):1977−1988. TANG Yuegang, HE Xin, CHENG Aiguo, et al. Occurrence and sedimentary control of sulfur in coals of China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2015, 40(9): 1977−1988.
[9] 刘贝,黄文辉,敖卫华,等. 沁水盆地晚古生代煤中硫 的地球化学特征及其对有害微量元素富集的影响[J]. 地学前缘,2016,23(3):59−67. LIU Bei, HUANG Wenhui, AO Weihua, et al. Geochemistry characteristics of sulfur and its effect on hazardous elements in the Late Paleozoic coal from the Qinshui Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23(3): 59−67.
[10] CHEN Cong, TANG Yuegang, GUO Xin. Comparison of structural characteristics of high-organic-sulfur and low-organic-sulfur coal of various ranks based on FTIR and Raman spectroscopy[J]. Fuel, 2022, 310: 122362.
[11] 何选明. 煤化学[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2010. [12] FUCHS W, SANDHOFF A G. Theory of Coal Pyrolysis[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry, 1942, 34(5): 567−571.
[13] CARLSON G A. Computer simulation of the molecular structure of bituminous coal[J]. Energy & Fuels, 1992, 6(6): 771−778.
[14] 赵正福,唐跃刚,魏强,等. 中低煤阶高有机硫煤含硫 结构演化特征[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2015,43(4):17−22. ZHAO Zhengfu, TANG Yuegang, WEI Qiang, et al. Evolution characteristics of sulfur-bearing structures of low and medium rank coal with high organic sulfur content[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2015, 43(4): 17−22.
[15] ZHANG Lanjun, LI Zhenghua, YANG Yonglaing, et al. Research on the Composition and Distribution of Organic Sulfur in Coal[J]. Molecules, 2016, 21(5): 630. doi: 10.3390/molecules21050630
[16] WEI Qiang, TANG Yuegang. 13C-NMR Study on structure evolution characteristics of high-organic-sulfur coals from typical chinese areas[J]. Minerals, 2018, 8(2): 49. doi: 10.3390/min8020049
[17] 葛涛,李洋,WANG MENG,等. 山西高硫气肥煤结 构表征与分子模型构建[J]. 光谱学与光析,2020,40(11):3373−3378. GE Tao, LI Yang, WANG MENG, et al. Structural characterization and molecular model construction of gas-fat coal with high sulfur in Shanxi[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2020, 40(11): 3373−3378.
[18] XIAO Jin, ZHONG Qifan, LI Fachuang, et al. Modeling the change of green coke to calcined coke using Qingdao high-sulfur petroleum coke[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2015, 29(5): 3345−3352.
[19] 陈国芳. 沁水煤田晋城矿区成煤环境分析[J]. 华北国 土资源,2016(3):18−19. [20] 张志军,王露,李浩. 煤分子结构模型构建及优化研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(2):245−253. ZHANG Zhijun, WANG Lu, LI Hao. Study on model construction and optimization of molecular structure[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49(2): 245−253.
[21] SONG Yu, JIANG Bao, MATHEWS J P, et al. Structural transformations and hydrocarbon generation of low-rank coal (vitrinite) during slow heating pyrolysis[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2017, 167: 535−544. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2017.08.003
[22] SHI Kaiyi, GUI Xiahui, TAO Xiuxiang, et al. Macromolecular structural unit construction of Fushun nitric-acid-oxidized coal[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2015, 29(6): 3566−3572.
[23] 冯炜,高红凤,王贵,等. 枣泉煤分子模型构建及热解 的分子模拟[J]. 化工学报,2019,70(4):1522−1531. FENG Wei, GAO Hongfeng, WANG Gui, et al. Molecular model and pyrolysis simulation of Zaoquan coal[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(4): 1522−1531.
[24] ZHANG Zhiqiang, KANG Qiannan, WEI Shuai, et al. Large scale molecular model construction of Xishan bituminous coal[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2017, 31(2): 1310−1317.
[25] 李霞,曾凡桂,司加康,等. 不同变质程度煤的高分辨 率透射电镜分析[J]. 燃料化学学报,2016,44(3):279−286. LI Xia, ZENG Fangui, SI Jiakang, et al. High resolution TEM image analysis of coals with different metamorphic degrees[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2016, 44(3): 279−286.
[26] ZHONG Qifan, MAO Qiuyun, ZHANG Lanyun, et al. Structural features of Qingdao petroleum coke from HRTEM lattice fringes: Distributions of length, orientation, stacking, curvature, and a large-scale image-guided 3D atomistic representation[J]. Carbon, 2018, 129: 790−802. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2017.12.106
[27] NIEKERK D V, MATHEWS J P. Molecular representations of permian-aged vitrinite-rich and inertinite-rich South African coals[J]. Fuel, 2010, 89(1): 73−82. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2009.07.020
[28] JAISWAL Y, PAL S L. Structural Characterization of Indian Vitrinite-Rich Bituminous Karharbari Coal[J]. ACS Omega, 2020, 5(12): 6336−6347. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.9b03674
[29] LEI Zhao, YANG Ding, ZHANG Yunhe, et al. Constructions of coal and char molecular models based on the molecular simulation technology[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2017, 45(7): 769−779. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(17)30038-5
[30] 张秀霞,吕晓雪,肖美华,等. 典型烟煤热解机理的反 应动力学模拟[J]. 燃料化学学报,2020,48(9):1035−1046. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(20)30071-2 ZHANG Xiuxia, LÜ Xiaoxue, XIAO Meihua, et al. Molecular reaction dynamics simulation of pyrolysis mechanism of typical bituminous coal via ReaxFF[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2020, 48(9): 1035−1046. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(20)30071-2



 下载:
下载: