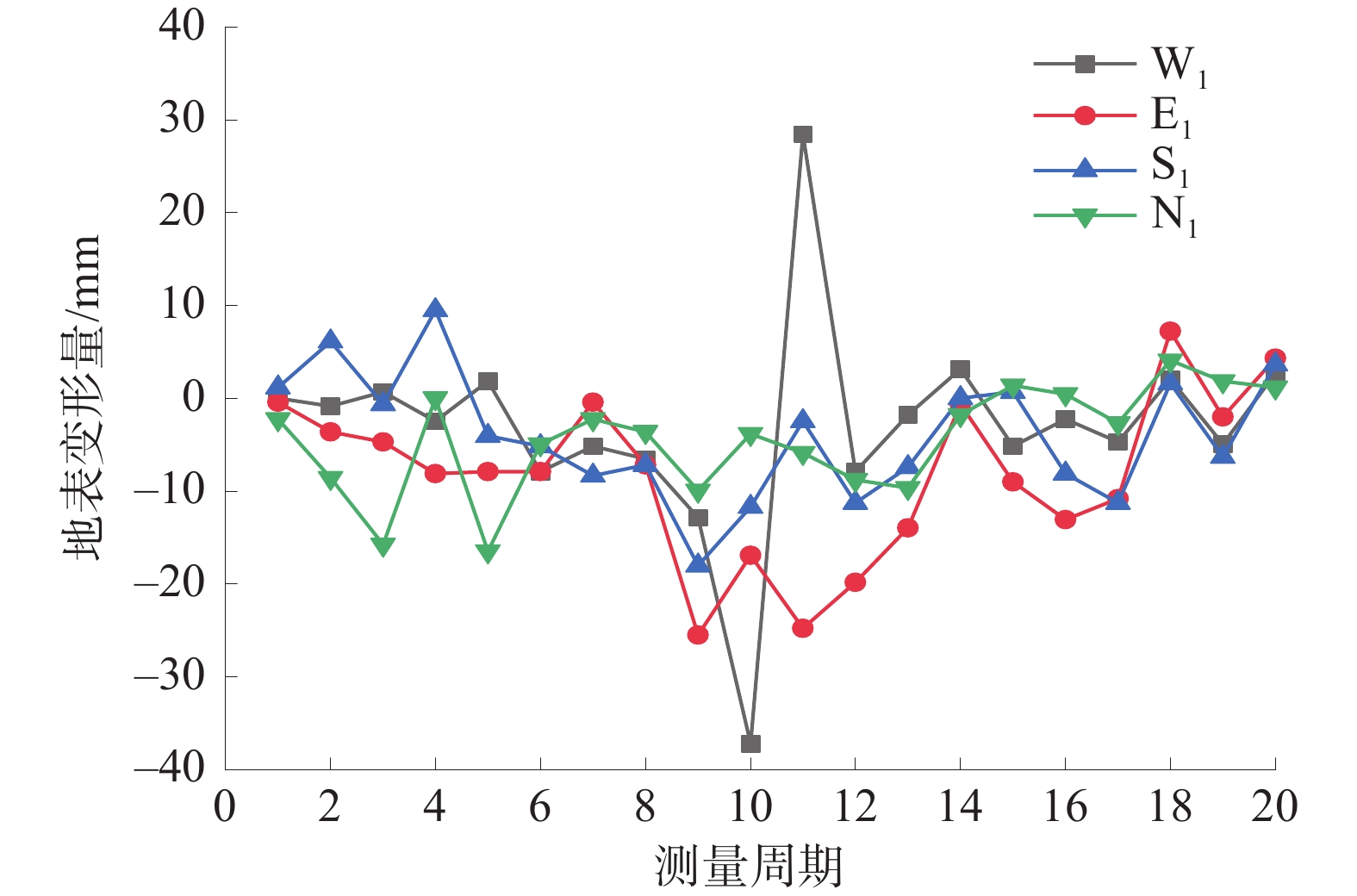
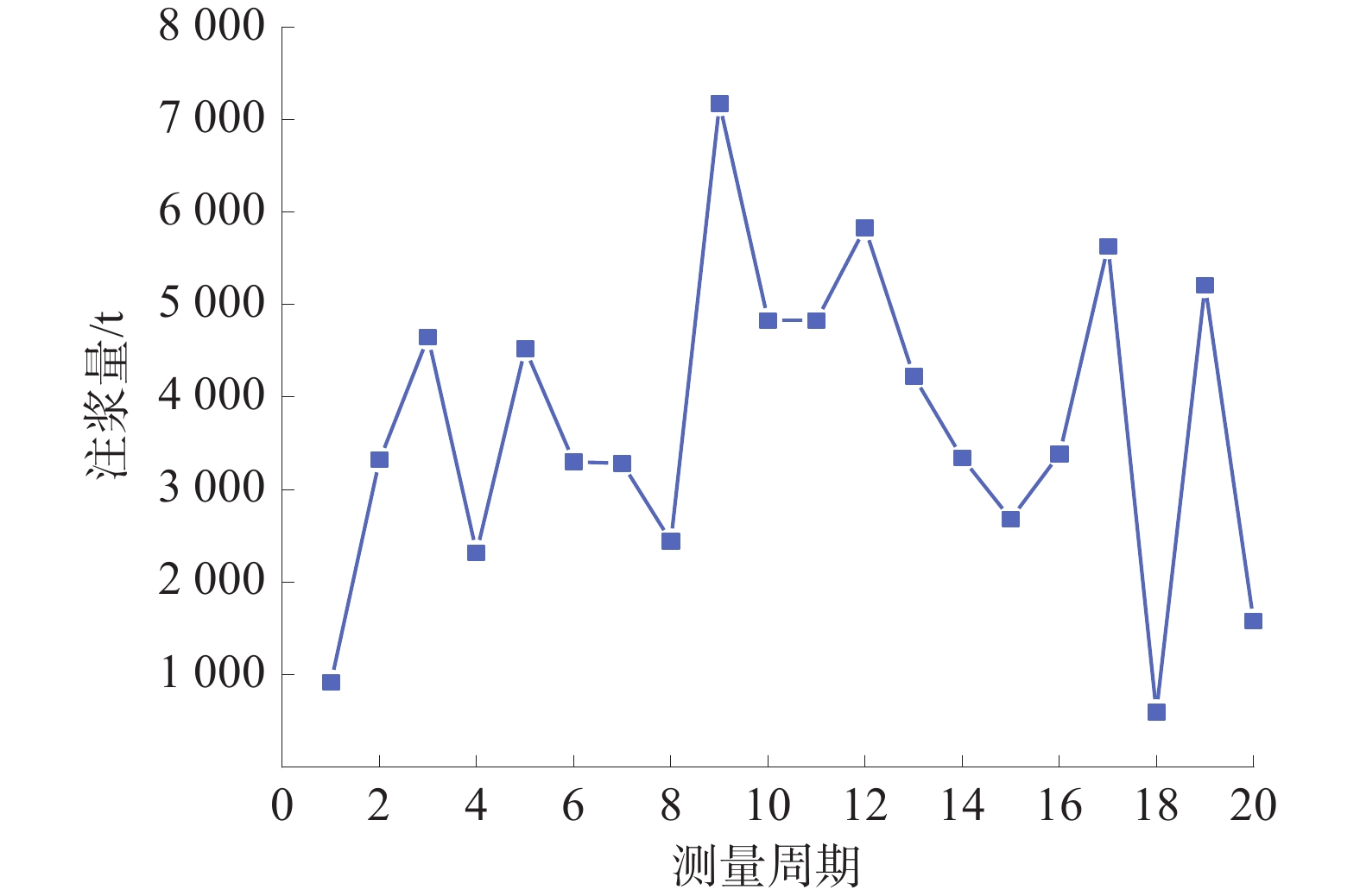
Grouting reconstruction of loose aquifer overlying work face and its effect test
-
摘要:
为解放浅部“四含”煤柱资源,以五沟煤矿一采区1010-1工作面为试验对象,采用劈裂注浆法,连续与间歇注浆相结合的注浆工艺对“四含”及其底部基岩风化带进行注浆加固试验。结果表明:“四含”治理区岩性复杂,富水性弱,主要接受侧向区域径流补给,注浆改造工程将采用地面直孔结合定向斜孔逐排施工驱水固沙方案;混合浆液强度受制于粉煤灰掺比比例,且混合浆液强度、结石率均高于水泥净浆,粉煤灰掺量为20%时,结石率最高;浆液在“四含”中扩散极不均一,注浆过程需通过控制注浆量控制浆液扩散范围,注浆对地表影响体现在浆液扩散和压力传导,并以压力传导为主;注后取心孔样品真密度略有增大,含水率略有减小,抗压强度、抗拉强度、抗剪强度略有增大;基岩风氧化带注浆后岩层抗压强度随采样深度增加呈现先增大后减小再增大的趋势,其抗压强度增强约2~5倍。
Abstract:In order to liberate the shallow quaternary loose aquifer coal pillar resources, taking the 1010-1 working face of the first mining area of Wugou Coal Mine as the test object, the grouting reinforcement test of quaternary loose aquifer and the weathering zone of the bedrock at the bottom was carried out by using the splitting grouting method and the grouting technology combining continuous and intermittent grouting. The results show that: the quaternary loose aquifer control area has complex lithology and weak water content, and mainly receives runoff recharge from the lateral area. The grouting reconstruction project adopts the water displacement and sand fixation scheme of the ground straight hole combined with the directional oblique hole row by row; the strength of the mixed slurry is subject to the ratio of fly ash, and the strength and stone rate of the mixed slurry are higher than those of the cement net slurry. When the fly ash content is 20%, the stone rate is the highest; the diffusion of grout in the quaternary loose aquifer is very uneven, the grouting process needs to control the grout diffusion range by controlling the grouting amount, the influence of grouting on the surface is reflected in the grout diffusion and pressure conduction, and the pressure conduction is the main one; after injection, the true density and water content of the core hole samples slightly increased, while the compressive strength, tensile strength and shear strength slightly increased; with the increase of sampling depth, the compressive strength of the rock layer in the wind-oxidized zone of bedrock increased first, then decreased and then increased, and the compressive strength increased about 2-5 times.
-
随着我国煤炭资源开采工艺、机械设备、智能化水平等方面的提升[1],埋藏于浅部且赋存条件良好的煤炭资源开采速率不断增大,使得煤炭资源开采逐步迈向地下深部。深部围岩地质环境与浅部相比具有新的突出特征,即高应力、高温度、高渗透压力以及采矿诱发的强开采扰动[2],在深埋环境采矿过程中极易诱发冲击地压灾害对人员及设备造成损害。冲击地压通常指由于地下深部空间掘进或矿体开采而诱发的强烈围岩动力学现象,主要表现为:围岩体突然崩落及硐室、巷道、采场等位置围岩发生大变形等,严重时会出现气浪或巨响[3],这将给深部地下煤炭资源开采带来巨大安全隐患。而井下煤体本身的冲击倾向性是发生冲击地压的前提要素[4],煤体的冲击倾向性是指煤体受到外力作用所积蓄的弹性能量,并达到某一条件时发生冲击破坏的能力和内在属性,是地下煤炭开采诱发冲击地压的必要条件。前人已给出多种评价煤体冲击倾向性指标,如:冲击能速度指数WST[5]、模量指数Kλ[6]、冲击能量指数KE[7]、动态破坏时间DT[8] 、剩余弹性能指数CEF[9]等。宫凤强等[10]通过对5种煤样进行了相关实验,比较了16种煤体冲击倾向性指标,结果表明剩余弹性能指数对于煤体的冲击倾向性评判最为准确。事实上,煤体多种形式破坏均始于其内部原生微裂隙;随着外界载荷的施加,微裂隙发生扩展演化为宏观裂纹;在深部高应力扰动条件下,煤体中裂纹扩展到某一阶段,其内部积累的弹性能突然释放,致使冲击地压显现。因此,研究冲击载荷作用下煤体动态断裂行为特征对于探明冲击地压形成机理具有重要意义。对于煤岩体材料,在外界应力条件下更易于发生张拉型(I型)断裂,张财贵等[11]采用边裂纹平台圆环试件成功测定了岩石Ⅰ型动态断裂韧度值;刘瑞峰等[12]、徐文涛等[13]测定了爆炸载荷下岩石Ⅰ型断裂韧度及裂纹动态扩展规律研究;李欣等[14]开展了卸荷条件下岩石Ⅰ型动态断裂行为规律研究;赵毅鑫等[15]对煤体开展了Ⅰ型动态断裂行为研究;龚爽等[16]研究了层理角度对煤体Ⅰ型动态断裂韧度值的影响;WANG等[17]通过单边缺口梁试件定量分析了冲击速度、层理角度、层理介质弹性模量、层理间距和层理宽度对煤体I型动态断裂韧度的影响;GONG等[18]测定了不同含水率煤体的动态I型断裂参数。而关于冲击倾向性对煤体动态断裂行为影响研究的相关报道较为少见。为此,对不同煤样进行了冲击倾向性试验,同时通过霍普金森杆(SHPB)试验系统对以上煤体单边缺口梁试件进行动态断裂试验研究,并对受冲击载荷后煤体破碎程度进行分析,旨在探明不同冲击倾向性对煤体动态断裂行为特性的影响。
1. 试验概况
1.1 煤体试样制备
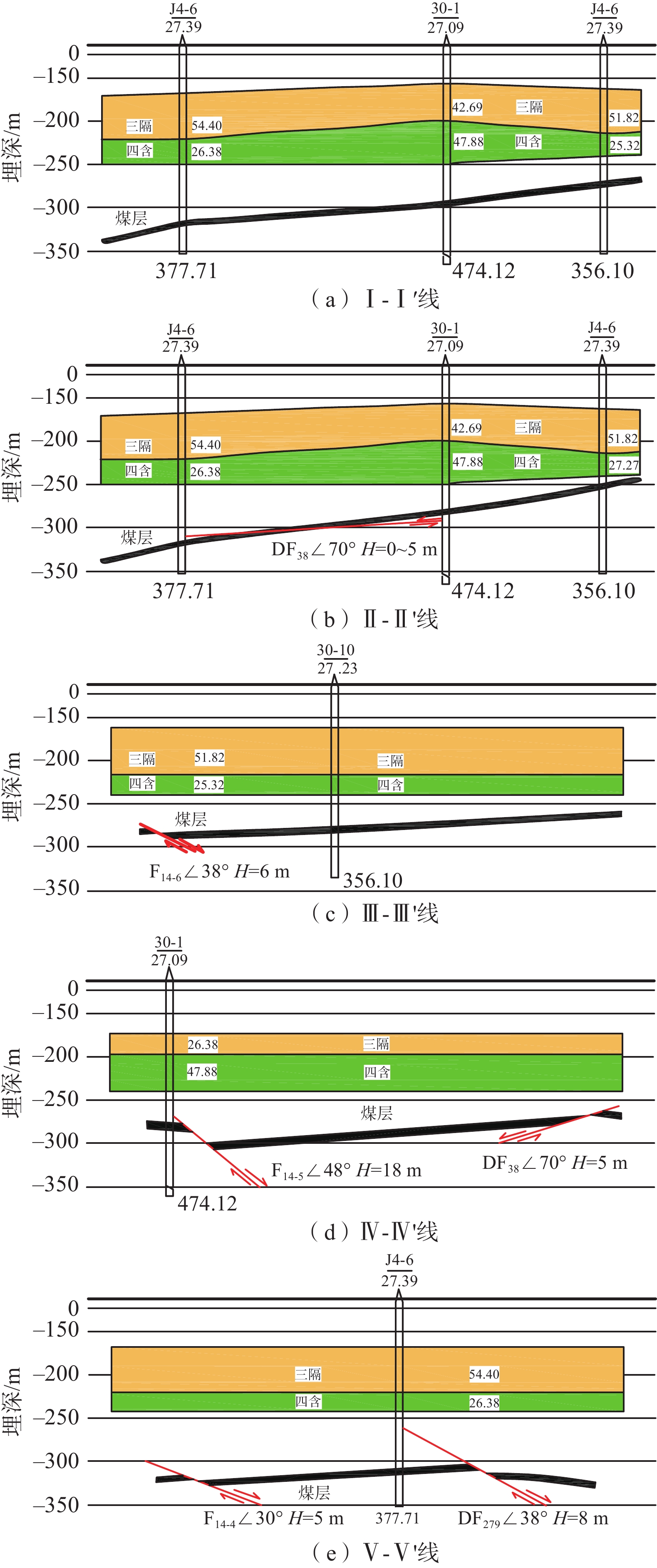
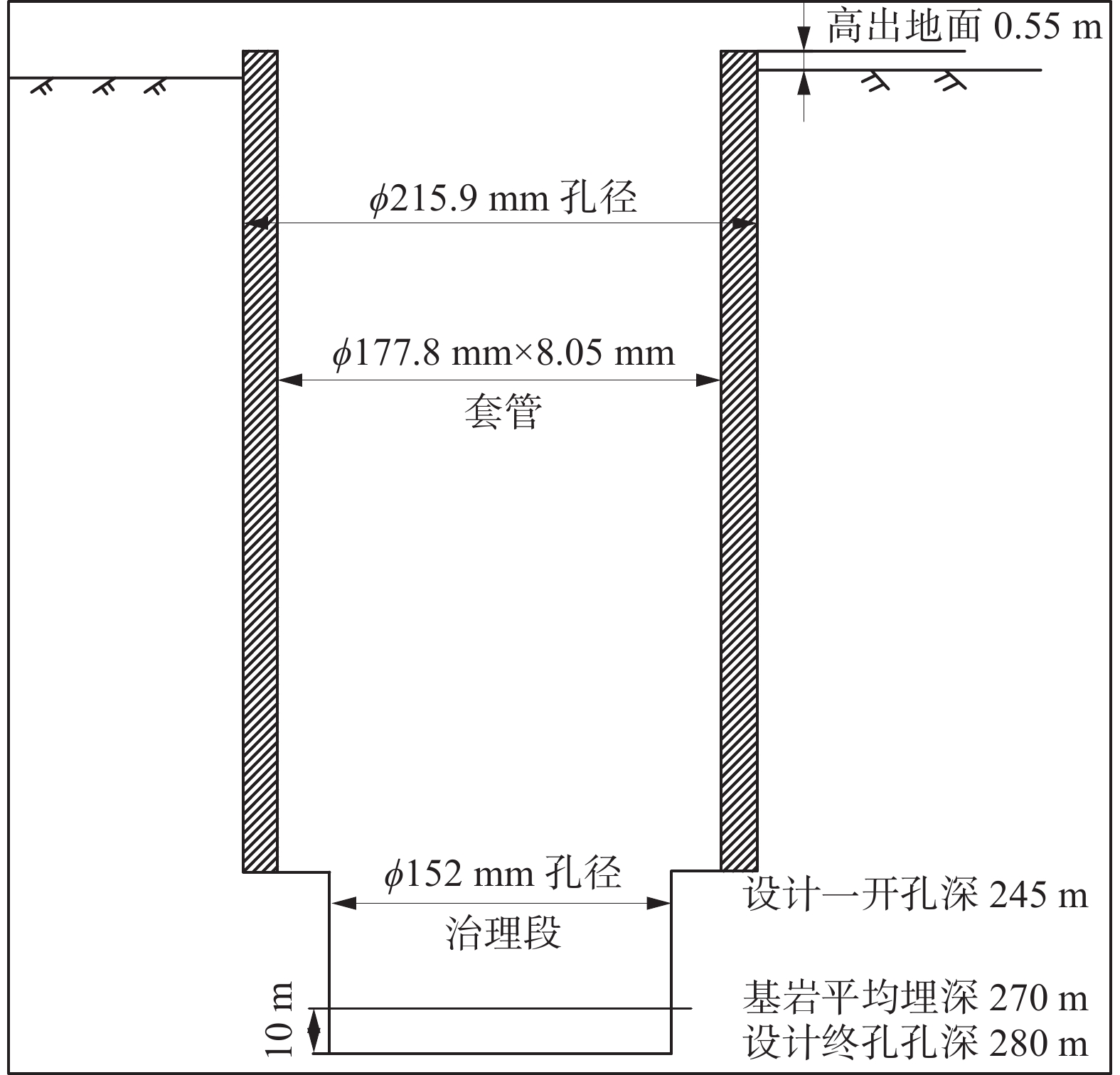
采用的3种煤样分别取自内蒙古自治区鄂尔多斯市布尔台煤矿、新疆吐鲁番托克逊县雨田煤矿及新疆昌吉市屯宝煤矿采煤工作面附近巷道内。以上原始煤样自井下获得后,即刻采用聚氯乙烯薄膜将煤体样本密封,以防止空气风化作用对后续试验结果造成影响。在实验室内,按照国际岩石力学学会(ISRM)标准将煤样制备成直径50 mm、高度100 mm的圆柱体试件以开展静力学试验,其加工长度误差<2 mm,试件上下两端面抛光后的不均匀度<0.05 mm,对称轴最大偏差≤0.25°。同时,制备长度L为100 mm、高度H为40 mm、厚度B为40 mm的I型单边缺口梁试件,以开展煤体的动态I型断裂韧度测定试验;其中通过厚度1 mm的金刚砂锯片在梁试件底边中心位置垂直预置1条贯穿裂缝,最后使得该条预置裂缝长度与梁试件高度之比R/H为0.35,下部2支撑辊轮分别距离试件边界1/5L处。I型单边缺口梁试件如图1。以上3种样品进行了工业分析,工业分析结果及煤体基本物理参数见表1。
表 1 3种煤的工业分析及基本物理参数Table 1. Proximate analysis and basic physical parameters of three kinds of coal specimens煤样出处 含水率/% 灰分/% 挥发分/% 固定碳/% 镜质体反射率/% 密度/(g·cm−3) 波速/(m·s−1) 布尔台
煤矿0.83 7.92~
9.8530.11~
30.6261.24~
61.580.82~
0.931.39 2231.6 雨田
煤矿0.67 7.05~
9.3329.89~
30.2461.98~
62.270.81~
0.911.43 2358.7 屯宝
煤矿0.51 7.14~
9.6129.57~
30.6162.12~
62.740.83~
0.921.48 2489.2 1.2 试验设备
采用SAS-2000型岩石力学多功能试验系统对3种煤试件开展冲击倾向性测定试验及准静态I型断裂韧度测定试验,该试验设备可实现施加最大载荷2000 kN,包含位移控制和载荷控制2种加载模式,加载速率可调控为0.0001~1.000 0 mm/s和0.005~1.000 kN/s。此外通过ALT1000型分离式霍普金森压杆(SHPB)试验系统对以上3类煤体I型单边缺口梁试件进行动力学试验。SHPB试验系统及煤体I型单边缺口梁试件如图2。
SHPB试验装置中入射杆、透射杆、吸收杆、压力冲头均采用高强度Cr合金钢制成,冲击载荷加载通过高压气体驱动合金冲击头实现。试验过程中,通过SG型动态应变片和超动态应变仪监测入射杆和透射杆中传播时产生应变信号、通过示波器进行应力波形采集;同时采用光纤光栅与SSI855型高频动态FBG对以上煤试件的动态应变进行实时监测。
1.3 试验步骤
对煤试件进行3种类型试验,包括煤体冲击倾向性静力学试验、准静态煤体I型断裂韧度测定试验、冲击载荷作用下煤体动态I型断裂试验。
1.3.1 煤体冲击倾向性测试试验
煤体冲击倾向性测试试验具体步骤如下:
1)采用位移控制模式,加载速率设定为0.002 mm/s,对3类圆柱形煤试件进行单轴压缩试验,每种煤试件进行3组试验,获得3类煤体的准静态平均单轴抗压强度值。
2)对3类圆柱形煤试件进行单轴压缩变上限应力循环加卸载试验,采用载荷控制模式,加载速率设定为0.04 kN/s,即约0.02 MPa/s;启始载荷加载至圆柱形煤试件单轴抗压强度的50%,再按照相同速率将载荷卸载至0,此为第1个加卸载循环;第2次循环中加载的上限峰值在第1次循环加载上限基础上增加1 kN,即约增加0.5 MPa,再将该载荷完全卸载;按照此规律,后1次循环内加载阶段均比前1次增加1 kN,实现递增变上限应力加卸载循环;依照该步骤进行5次变上限加卸载,完成循环加卸载后将煤试件加载至完全破坏,同时采用光纤光栅测定以上试验过程中煤试件的轴向应变,3类圆柱形煤试件各进行2组变上限循环加卸载试验。
1.3.2 准静态煤体I型断裂韧度(KIC)测定试验
准静态煤体I型断裂韧度(KIC)测定试验步骤如下:
1)将3类煤体I型单边缺口梁试件置于三点弯曲加载框架中,将底部支撑辊轮分别调整至距煤试件边界20 mm位置,同时在预置裂纹尖端位置粘贴光纤光栅,测定试验过程中裂纹尖端张开位移(CTOD)变化。
2)将三点弯曲加载框架整体置于岩石压力机加载平台上,启用位移控制模式,加载速率设定为0.002 mm/s,沿着煤体I型单边缺口梁试件对称中线施加载荷,使得煤试件沿预置裂纹处发生I型断裂,每种类型煤试件进行2组试验。
1.3.3 冲击载荷作用下煤试件动态I型断裂试验
冲击载荷作用下3类煤试件动态I型断裂试验具体步骤如下:
1)将I型单边缺口梁煤试件置于SHPB试验系统内经过改进的三点弯曲入射杆与输出杆之间,并使得三者端面中心线对齐。
2)将动态应变片粘贴在入射杆和输出杆中间部位,以监测试验过程中产生应变信号及应力波;同时将3条光纤光栅粘贴在煤试件预置裂纹尖端前位置,以监测冲击载荷下煤试件预置裂纹尖端动态张开位移(CTOD)变化过程。试验最终选用0.6 MPa冲击气压进行动力学试验,每种类型煤试件进行2组有效试验。
1.4 试验结果
布尔台煤矿煤样平均单轴抗压强度为10.46 MPa,平均弹性模量为1.07 GPa;雨田煤矿煤样平均单轴抗压强度为12.85 MPa,平均弹性模量为1.25 GPa;屯宝煤矿煤样平均单轴抗压强度为14.75 MPa,平均弹性模量为1.37 GPa。3类煤样的平均I型平均断裂韧度值KIC分别为0.249、0.291、0.347 MPa·m1/2;I型断裂能分别为18.11、18.21、18.52 N/m。3类煤体准静态I型断裂相关试验结果见表2。
表 2 3类煤样I型断裂参数Table 2. Type I fracture parameters of three coal samples煤样来源 煤试件编号 峰值载荷/N KIC/(MPa·m1/2) GF/(N·m−1) 试验值 平均值 试验值 平均值 布尔台
煤矿Kb-1 810.5 0.264 0.249 57.21 53.17 Kb-2 720.7 0.234 49.13 雨田煤矿 Ky-1 967.1 0.315 0.291 63.37 58.46 Ky-2 819.2 0.267 53.55 屯宝煤矿 Kt-1 1150.6 0.375 0.347 80.12 72.98 Kt-2 980.4 0.319 65.84 2. 试验结果分析
2.1 循环加卸载条件下煤体力学特性
3类煤样圆柱形试件的变上限循环加载试验典型应力-应变曲线如图3。
3类煤试件初始受到较低应力加载过程中,试验线呈现下凹形式,煤体试件处于压密阶段,这是由于较低的载荷作用使煤试件内部原生微裂隙及微孔隙反复压缩闭合[19-20]。后续该试验进入变上限循环加卸载阶段,每一次循环内卸载完成后,3类煤试件应变并未完全恢复至该循环初始加载时的应变水平,即形成了滞回现象,这是由于煤试件中存在的各类微缺陷,在循环加卸荷载的作用下,将发生微裂隙开启与闭合、裂纹面间摩擦作用、裂纹尖端附近区域塑性变形以及微孔隙压缩变形等一系列非线性不可逆行为[21-22],这些行为将消耗掉一部分能量,加载曲线与卸载曲线之间所包络的面积即为耗散应变能。完成循环加卸载应力再次增加后,应力-应变曲线近似线性关系,直至达到峰值载荷,煤试件产生宏观裂纹,随着载荷持续施加煤体试件最终发生破坏。3类煤样中布尔台矿煤样应力-应变曲线压实下凹程度及持续范围较之其他2类煤样更大,同时其每一级变上限加卸载循环滞回曲线范围相较于其他2种煤试件也有显著增大,这表明与其他2类煤样相比,布尔台矿煤样内所包含的原始缺陷更多,使得每一次循环加卸载中消耗的能量相对增加,表现为循环中滞回应变值增大。此外,经过变上限循环作用后屯宝矿煤样试件的峰值应力普遍高于其他2类煤试件的峰值应力,布尔台矿煤样圆柱形试件达到峰值应力时的应变值大于其他2类煤试件的峰值应变,说明载荷施加过程中布尔台矿煤试件发生了更多的塑性应变。
2.2 煤体I型断裂特性
3类煤样I型单边缺口梁试件典型应力p与裂纹尖端张开位移CTOD的三点弯曲试验全过程变化曲线如图4。
试验初期在较低载荷作用下,3类煤试件试验曲线呈下凹形态,表明煤试件中保留有较多的微缺陷,在三点弯曲轴向压缩载荷作用下,煤体内部微缺陷被逐步压密,该阶段为被压密过程,其中布尔台矿煤样I型单边缺口梁试件的压密阶段持续范围大于其他2类煤样,说明该煤样中微缺陷数量更多。随着载荷增加,3类煤试件试验曲线进入线性变形阶段;当载荷接近峰值时,p-CTOD试验曲线斜率逐渐降低,表明煤试件进入塑性变形阶段。达到峰值载荷时,煤试件中沿着预置裂纹尖端发生新的宏观断裂,3类煤体中屯宝煤矿煤的I型单边缺口梁试件三点弯曲试验峰值载荷最高(达到1065 N),雨田矿煤试件次之(893 N),布尔台煤试件峰值载荷最低(765 N)。通过该I型单边缺口梁试件可获得煤体I型断裂韧度值,具体计算公式如下[23]:
$$ {K_{{\text{IC}}}} = \frac{{3{p_{\max }}S\sqrt a }}{{2{H^2}B}}{F_i}(a/H) $$ (1) $$\begin{split} &\begin{gathered} {F_i}(a/H) = \\ \frac{{1.99 - \left( {a/H} \right)\left( {1 - a/H} \right)\left[ {2.15 - 3.93\left( {a/H} \right) + 2.7{{\left( {a/H} \right)}^2}} \right]}}{{\left( {1 + 2a/H} \right){{\left( {1 - a/H} \right)}^{3/2}}}} \end{gathered}\\[-6pt]& \end{split}$$ (2) 式中:KIC为煤体I型断裂韧度,MPa·m1/2;pmax为I型单边缺口梁试件三点弯曲试验峰值载荷N;a为I型单边缺口梁试件的预置裂纹长度,mm;H 为试件高度,mm;B 为试件厚度,mm;S为I型单边缺口梁试件的跨度,mm。
3类煤样中,屯宝矿煤试件KIC值最大,试验平均值达到0.347 MPa·m1/2。达到峰值载荷后持续对煤试件施加应力,布尔台矿煤试件峰后存在一定程度的应力软化现象,表明该煤样存在韧性断裂行为;而其他2类煤试件峰后应力软化行为并不明显,表现为脆性断裂行为。
三点弯曲试验测得的I型单边缺口梁煤试件载荷p与法向位移(挠度)δ关系曲线如图5。
3类煤试件p-δ曲线变化规律与p-CTOD试验曲线变化规律类似,加载初期三者均存在压实阶段,随着载荷不断增加,试验曲线逐渐经历线性阶段及塑性变形阶段;达到峰值载荷时,煤试件出现新的宏观裂纹,雨田矿煤试件与屯宝矿煤试件符合脆性断裂特征,布尔台矿煤试件试验曲线出现应力软化,表现出一定程度的韧性断裂特征。通过I型单边缺口梁三点弯曲试验,确定了3类煤样的I型断裂能GF,计算公式[24]如下;
$$ {G_{\text{F}}} = \dfrac{{{W_{\rm{A}}} + \dfrac{1}{2}mg{\delta _{{\rm{max}}}}}}{{{A_0}}} $$ (3) 式中:WA为p-δ试验曲线下包络的面积,mm2;m为煤试件质量;g为重力加速度,取 9.81 m/s2;δmax 为梁试件破坏时的挠度,mm;A0为潜在断裂区的面积,mm2,即B×(H-a)。
计算结果见表2。
3类煤体中,屯宝矿煤样具有最高的断裂能,达到72.98 N/m,意味着使其形成新的裂纹面将会消耗更多的能量。
2.3 煤体I型动态断裂行为特性
通过冲击压头改良后的SHPB试验系统,对上述3类煤样进行I型动态断裂力学试验,冲击动力气压设定为0.6 MPa,冲击载荷作用下以上3类煤体I型单边缺口梁试件的P-CTOD曲线如图6。
由图6可以看出,3类煤试件的动态I型断裂试验结果与准静态试验结果存在明显差异。3类煤体I型单边缺口梁试件在冲击载荷作用初始阶段,p-CTOD曲线斜率陡增,三点弯曲载荷增加速度明显,与静载荷加载相比,不存在显著的煤体压实阶段,尤其对于布尔台矿煤试件,该现象尤为明显。在冲击载荷持续作用下,煤试件迅速进入线性变形阶段;随着冲击载荷的进一步增加,当p值约达到峰值载荷的约75%时,应力增长速率减缓,煤试件进入塑性变形阶段,直至煤试件发生宏观断裂。3类煤样试件冲击载荷作用下平均极限载荷分别为1055.7 、1277.2、1619.6 N,平均I型断裂韧度分别为0.344、0.416、0.527 MPa·m1/2,较之静载荷作用下3类煤体I型断裂韧度值,分别提高了1.38、1.43、1.52倍。
此外,临近冲击破坏时,在屯宝矿煤体I型单边缺口梁试件主体断裂的同时有较多的碎块从煤试件主体中崩离,表现出较为明显的动力学破坏特征。冲击载荷作用下布尔台矿煤体I型单边缺口梁试件整体发生断裂,伴有少量煤体碎屑崩落。屯宝矿煤体的I型单边缺口梁试件以动态宏观断裂破坏为主,并未有尺寸较大的煤屑崩出;表明不同类型煤体在冲击载荷作用下的动态断裂破坏形式不同。
3. 讨 论
3.1 循环载荷作用下煤体应变能变化规律
煤样变上限应力循环加卸载过程各应变能示意图如图7。
假定该试验过程不与外界发生热交换;以第n级循环加卸载为例,该循环加载过程中输入能Uin n为加载阶段应力-应变曲线下所包络的面积,弹性应变能Ue n为该循环内卸载阶段曲线下的面积值,该循环内耗散应变能Ud n为上述Uin n与Ue n的差值。具体计算公式如下:
$$ {U_{{\text{in}}}^{{n}}}{\text{ = }}\int_{{\varepsilon _{{n}}}}^{\varepsilon _n^{\rm{L}}} {\sigma {\text{d}}\varepsilon } $$ (4) $$ {U_{\text{e}}^{{n}}}{\text{ = }}\int_{\varepsilon _n^{\rm{U}}}^{{\varepsilon _{{n}}}} {\sigma {\text{d}}\varepsilon } $$ (5) $$ {U_{\text{d}}^{{n}}}{\text{ = }}{U_{{\text{in}}}^{{n}}} - {U_{\text{e}}^{{n}}} $$ (6) 式中:εL n为第n次循环中初始加载时刻的应变值;εU n为第n次卸载完全后的应变值;εn为第n次循环加载中峰值载荷时刻的应变值。
由试验结果可知,随着循环荷载的增加,3类煤试件耗散应变能Ud n逐渐变大,说明煤体中不可逆应变逐步增加。同时,3类煤样变应力上限循环加卸载过程中的Un e与Un in之间存在近似线性函数关系,其统一表达公式为:Un e=1.032Un in−5.536,拟合优度分别为0.997。
3.2 冲击倾向性对煤体动态断裂行为特性影响
通过剩余弹性能指数CEF对以上3类煤体的冲击倾向性进行定量化分析。根据剩余弹性能指数CEF定义[9]:当CEF<15 kJ/m3时,表示该煤体无冲击倾向性;当15 kJ/m3<CEF< 30 kJ/m3时,代表该煤样具有弱冲击倾向性;当CEF>30 kJ/m3时,表明该煤样具有强冲击倾向性。CEF具体计算公式如下:
$$ C_{{\rm{EF}}}^{}{\text{ = }}{U_{\rm{e}}^{\text{c}}} - {U_{\text{d}}^{\text{p}}} $$ (7) 式中:Ue c为峰值载荷前的弹性应变能,即峰值载荷前煤试件中累积的弹性能;Ud p为峰后破坏(残余)应变能,即峰后残余应变曲线下的面积值。
计算3类煤试件Uc e时,可将各类煤试件峰前曲线下包络的面积带入前述所建立3类煤样的Un e与Un in关系方程中计算得到;经过计算,布尔台矿煤试件平均CEF值为25.35 kJ/m3,表明该类煤体具有弱冲击倾向性;雨田矿煤试件平均CEF值为30.34 kJ/m3,表示该类煤体具有强冲击倾向性;屯宝矿煤试件平均CEF值为33.26 kJ/m3,表明该类煤样具有更高的强冲击倾向性。
煤体剩余弹性能CEF与3类I型单边缺口梁煤试件经过冲击载荷作用后KIC增大倍数关系曲线如图8。
由图8可知:该增量将静态载荷作用下3类煤试件KIC值作为比较基准对于CEF分别为25.35、30.34、33.26 kJ/m3的煤体;经过冲击载荷试验后,其动态I型断裂韧度KIC分别增大1.32、1.40、1.45倍,其动态弹性模量分别增大了1.38、1.43、1.52倍;即随着CEF的增加,煤体动态KIC增长倍数逐渐增大,表明煤体冲击倾向性将直接影响其动态断裂力学相应,煤体冲击倾向性越大,其动态断裂参数较静力学状态下断裂参数提高越多。
3.3 煤体动态断裂分形特征
冲击载荷作用下,煤试件预置裂纹尖端附近微裂纹萌生,煤试件内逐渐形成裂缝网络,随着动载荷进一步施加,宏观裂缝交错出现,直至煤试件发生破碎。分形理论[25]已经被广泛地用来描述煤岩体断裂破碎复杂特征,断裂越复杂说明试样破碎得越剧烈。针对煤岩体材料破碎分形计算过程为[26]:
$$ k{\text{ = }}{{M\left( R \right)} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{M\left( R \right)} {{M_{\rm{T}}}}}} \right. } {{M_{\rm{T}}}}} = {\left( {{R \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {R {{R_{\text{m}}}}}} \right. } {{R_{\text{m}}}}}} \right)^\alpha } $$ (8) $$ N = C{R^{{{ - }}D}} $$ (9) 式中:k 为R尺寸以下煤体碎块的质量分数;R为破碎煤块的等效直径;M(R)为等效直径小于R的累积煤体碎块质量;MT为煤体碎块的总质量;Rm为最大煤体碎块的等效直径大小;α为碎块分散参量;N 为特征尺度不小于R的煤体碎块数目;C为关系常数;D为碎块分布的分形维数。
煤样碎块数量与碎块质量M的增量关系为:
$$ {\text{d}}M = {R^3}{\text{d}}N $$ (10) 将式(8)与式(9)分别求导与式(10)联立得到:
$$ D = 3 - \alpha $$ (11) 假设经过冲击载荷作用后煤样碎块密度仍然不变,通过1、3、5、10、15、20 mm 6组标准筛,将煤样破碎块体分为<1~3、<3~5、<5~10、<10~15、<15~20、>20 mm 6个尺寸等级。通过高精度电子天平量得以上每一级筛分出的冲击断裂后崩裂的煤试件破碎块体质量,将冲击破碎的煤样按块度与质量关系进行分形计算,根据破碎块度分析结果,可求得3类煤样的煤体破碎块度分形维数分别为1.21、1.29、1.40。
3类煤体剩余弹性能指数CEF与煤体冲击破碎后分形维数关系曲线如图9。随着煤体冲击倾向程度的增加,动载荷作用后煤体破碎分形维数随之增大,表明煤体受冲击后断裂崩解的更加复杂破碎,动态断裂响应变得更加显著。
4. 结 语
1)经过变上限循环加卸载试验,随着循环荷载的增加,3类煤试件耗散应变能Ud n逐渐变大,说明煤体中不可逆应变逐步增加。同时,3类煤样变应力上限循环加卸载过程中的Un e与Un in之间存在近似线性函数关系,其统一表达公式为:Un e=1.032Un in−5.536。
2)测定3类煤样的煤体静态I型断裂韧度值KIC值分别为0.249、0.291、0.347 MPa·m1/2,I型断裂能分别为53.17、53.17、72.98 N/m,经过冲击载荷作用下平均I型断裂韧度分别为0.344、0.416、0.527 MPa·m1/2,布尔台矿煤试件峰后存在一定程度的应力软化现象,表明该煤样存在韧性断裂行为;而其他2类煤试件峰后应力软化行为并不明显,表现为脆性断裂行为。
3)剩余弹性能指数CEF分别为25.35、30.34 、33.26 kJ/m3的煤体,经过冲击载荷试验后,其动态I型断裂韧度KIC分别增大1.32、1.40、1.45倍,即随着CEF的增加,煤体动态KIC增长倍数逐渐增大,表明煤体冲击倾向性将直接影响其动态断裂力学响应,煤体冲击倾向性越大,其动态断裂参数较静力学状态下断裂参数提高越多。
4)3类煤样的煤体动态断裂破碎分形维数分别为1.21、1.29、1.40,随着煤体冲击倾向程度的增加,动载荷作用后煤体破碎分形维数随之增大,表明煤体受冲击后断裂崩解的更加复杂破碎,动态断裂响应变得更加显著。
-
表 1 粉煤灰掺比试验设计表
Table 1 Fly ash ratio test design table
粉煤灰掺
比比例/%混合灰密度/
(g·cm−3)水灰比 浆液总
质量/g水/
g水泥/
g粉煤灰/
g混合浆
液比重10 3.01 0.781 36 3 000 1 316 1 516 168 1.6 20 2.93 0.756 27 3 000 1 292 1 367 342 30 2.85 0.731 18 3 000 1 267 1 213 520 40 2.78 0.706 09 3 000 1 242 1 055 703 50 2.71 0.681 00 3 000 1 216 892 892 10 3.01 1.004 03 3 000 1 503 1 347 150 1.5 20 2.93 0.975 81 3 000 1 482 1 215 304 30 2.85 0.947 58 3 000 1 460 1 078 462 40 2.78 0.919 35 3 000 1 437 938 625 50 2.71 0.891 13 3 000 1 414 793 793 表 2 J11孔基岩风氧化带取心试样
Table 2 Core samples for bedrock wind oxidation zone in well J11
样品标号 采样深度/m 岩性 圆柱体抗压强度/MPa 修正系数 修正后圆柱体抗压强度/MPa 备注 1−01 270.18~270.31 泥岩 — — — 一压就碎 1−02 271.22~271.37 泥岩 3.12 0.97 3.03 — 2−01 275.91~276.07 细粒砂岩 5.16 0.82 4.23 — 2−02 276.2~276.36 细粒砂岩 3.65 0.93 3.39 — 3−01 277.51~277.68 泥岩 — — — 样品破碎 3−02 278.52~278.82 泥岩 10.09 1.10 11.10 — 3−03 278.27~278.42 泥岩 5.98 0.97 5.80 — -
[1] 范立民,马雄德. 浅埋煤层矿井突水溃沙灾害研究进展[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2016,44(1):8−12. FAN Limin, MA Xiongde. Research progress of water inrush hazard in shallow buried coal seam mine[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2016, 44(1): 8−12.
[2] 郭龙辉,程桦,彭世龙,等. 厚松散层薄基岩开采覆岩离层裂隙演变与下沉分形特征研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2020,51(9):59−64. GUO Longhui, CHENG Hua, PENG Shilong, et al. Study on evolution and subsidence fractal characteristics of overlying strata in thick loose layers and thin bedrocks[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2020, 51(9): 59−64.
[3] LI C C. Field observations of rock bolts in high stress rock masses[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2010, 43(4): 491−496. doi: 10.1007/s00603-009-0067-8
[4] MORTAZAVI A, MAADIKHAH A. An investigation of the effects of important grouting and rock parameters on the grouting process[J]. Geomechanics and Geoengineering, 2016, 11(3): 1−17.
[5] BOBET A, EINSTEIN H H. Tunnel reinforcement with rock bolts[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2011, 26(1): 100−123. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2010.06.006
[6] 沈君,刘保国,陈景,等. 辉绿岩裂隙注浆体力学特性试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020,39(S1):2804−2817. SHEN Jun, LIU Baoguo, CHEN Jing, et al. Experimental study on mechanical properties of diabase fracture grouting[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(S1): 2804−2817.
[7] 王晓蕾,熊祖强,袁印,等. 破碎围岩无机材料注浆加固机理及其应用研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2022,18(1):112−119. WANG Xiaolei, XIONG Zuqiang, YUAN Yin, et al. Research and application of reinforcement mechanism of inorganic materials in broken rock[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2022, 18(1): 112−119.
[8] 陈安生,陈柯,吴义. 饱和松散砂层中挖孔桩双液注浆截水帷幕的实施[J]. 工业建筑,2013,43(7):150−154. CHEN Ansheng, CHEN Ke, WU Yi. Experimental study on two-shot grouting for waterproof curtain of man-hole-pile in saturated loose sand layer[J]. Industrial Construction, 2013, 43(7): 150−154.
[9] 张民庆,张文强,孙国庆. 注浆效果检查评定技术与应用实例[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2006(S2):3909−3918. ZHANG Minqing, ZHANG Wenqiang, SUN Guoqing. Evaluation technique of grouting effect and its application to engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006(S2): 3909−3918.
[10] 刘洋,王春刚,梁向阳,等. 等巴拉素煤矿强富水煤层注浆改造设计[J]. 煤矿安全,2020,51(2):146−151. LIU Yang, WANG Chungang, LIANG Xiangyang, et al. Grouting reconstruction design of strong water-rich coal seam in Balasu Coal Mine[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2020, 51(2): 146−151.
[11] 谢聪. 朱仙庄煤矿“四含”砂砾层劈裂注浆浆液扩散规律研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2019. [12] 李存禄,余大有,翁洪周,等. 厚松散层地面高压注浆参数现场试验确定方法[J]. 煤炭工程,2021,53(1):65−70. LI Cunlu, YU Dayou, WENG Hongzhou, et al. Parameters determination for ground high pressure grouting in thick alluvium through field test[J]. Coal Engineering, 2021, 53(1): 65−70.
[13] 范吉宏,戴德胜,周均民,等. 深厚松散层地面注浆压力与扩散半径确定方法[J]. 建井技术,2020,41(6):18−23. FAN Jihong, DAI Desheng, ZHOU Junming, et al. Method to define pressure and diffusion radius of grouting at surface ground of deep and thick loose strata[J]. Mine Construction Technology, 2020, 41(6): 18−23.
[14] 刘天航. 五沟煤矿1010工作面松散含水层注浆改造可行性研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽建筑大学, 2020. [15] 刘孝孔,绪瑞华,赵艳鹏,等. 厚松散层邻近既有立井井筒地面注浆地层加固技术[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2022(7):127−134. LIU Xiaokong, XU Ruihua, ZHAO Yanpeng, et al. Ground grouting stratum reinforcement technology for thick loose layer adjacent to existing shaft[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2022(7): 127−134.
[16] 张华磊,涂敏,程桦,等. 薄基岩采场覆岩破断机理及风氧化带整体注浆加固技术[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(8):2126−2132. ZHANG Hualei, TU Min, CHENG Hua, et al. Breaking mechanism of overlying strata under thick unconsolidated layers and integrated grouting reinforcement technology for wind oxidation zone[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2018, 43(8): 2126−2132.
[17] 袁克阔,李雄伟,徐拴海,等. 巨厚富水松散砂层溃砂灾害现状与注浆固沙技术研究及应用[J]. 水利与建筑工程学报,2017,15(4):32−38. YUAN Kekuo, LI Xiongwei, XU Shuanhai, et al. Underground grouting-reconstruction technology for thick water-rich sand layer and its engineering practice[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering, 2017, 15(4): 32−38.
[18] 余岩,王传兵,徐燕飞,等. 工作面上覆风化带岩层地面注浆加固效果分析[J]. 煤炭工程,2021,53(5):68−73. YU Yan, WANG Chuanbing, XU Yanfei, et al. Effect of ground grouting on overlying weathered zone of working face[J]. Coal Engineering, 2021, 53(5): 68−73.
[19] 方杰,李全生,杜文凤,等. 神东矿区浅埋深薄基岩上覆厚松散层水害治理[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2016,44(4):94−97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2016.04.018 FANG Jie, LI Quansheng, DU Wenfeng, et al. Water disaster control in overlying thick loose layer on bedrock in Shendong coal mining area[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2016, 44(4): 94−97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2016.04.018
[20] 王振荣. 厚松散含水层煤层开采突水溃沙防治技术[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2016,44(8):46−51. WANG Zhenrong. Water inrush and sand inrush prevention and control technology for coal mining in seam with thick and loose aquifer[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2016, 44(8): 46−51.
[21] 国家安全生产监督管理总局, 国家煤矿安全监察局. 煤矿防治水细则[M]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社, 2018. -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 张宏升,张国强,李波. 煤矿采空区积水形成机制与处置技术研究. 煤炭技术. 2025(01): 185-189 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李晓超. 瞬变电磁探测技术在煤矿防水工作中的应用研究. 凿岩机械气动工具. 2025(01): 178-180 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王健. 井下储水采空区多应力监测预警分析. 煤矿机电. 2024(06): 38-42 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: