Study on strata behavior and overburden activity law of 10 million ton super long working face in medium thick coal seam
-
摘要:
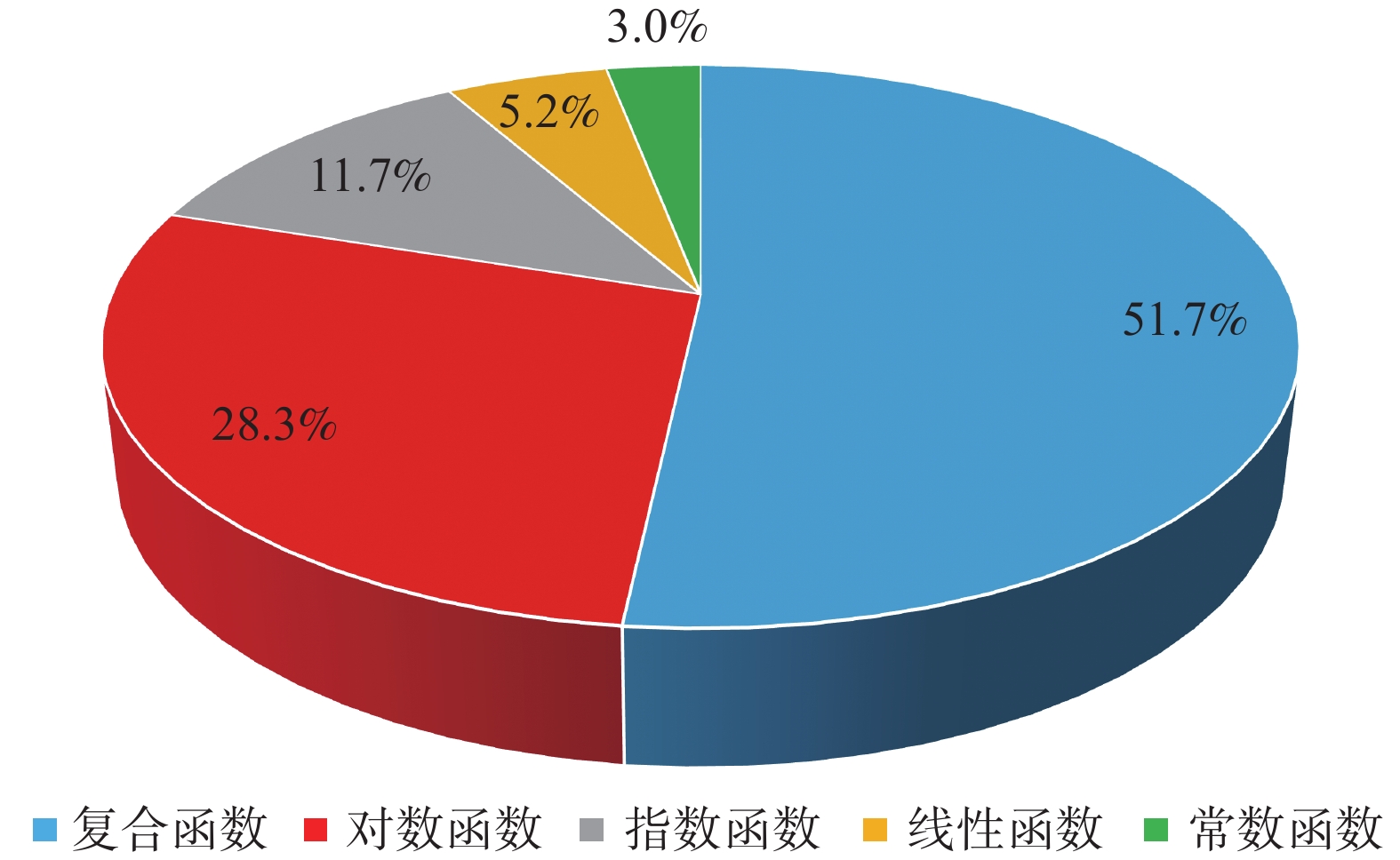
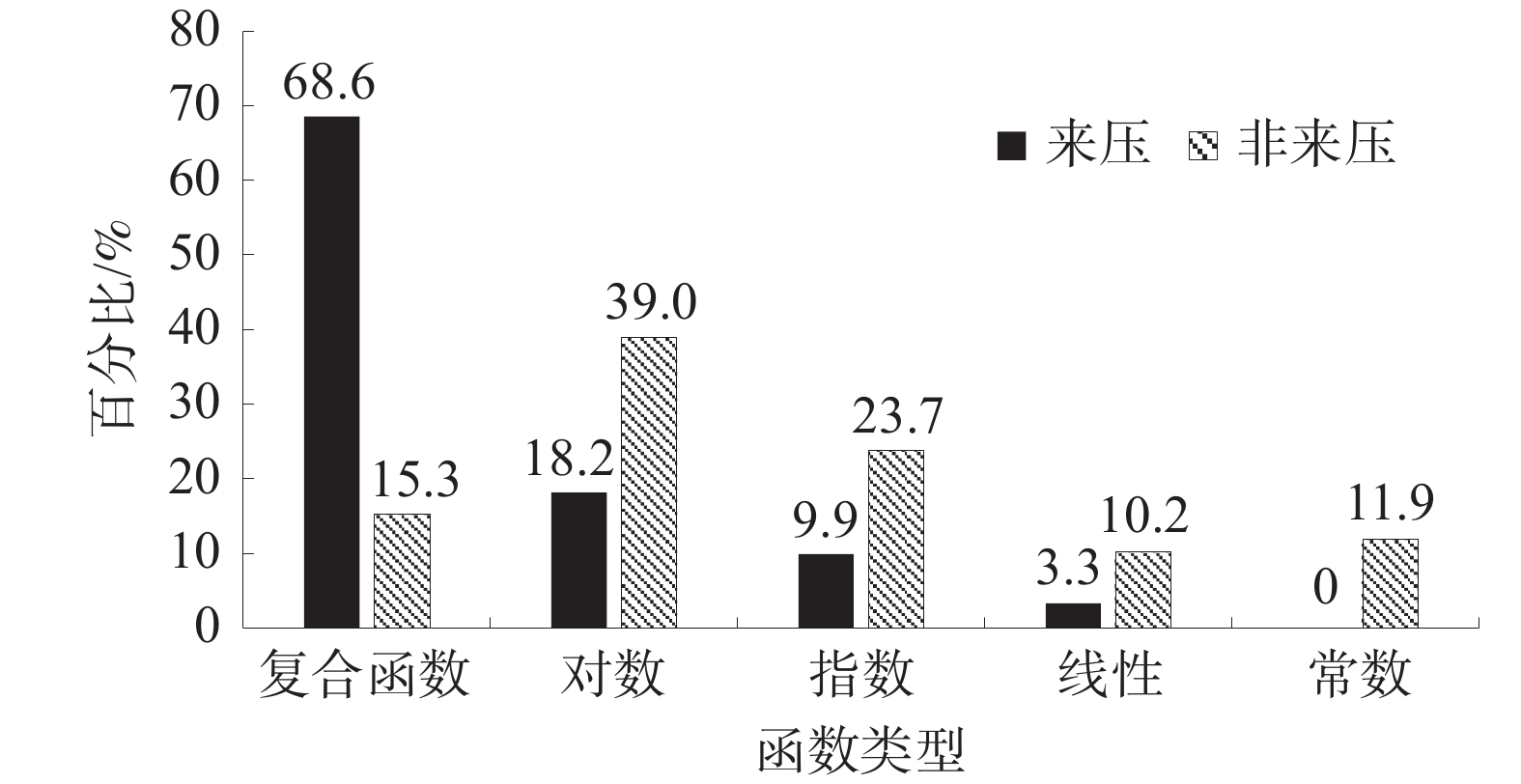
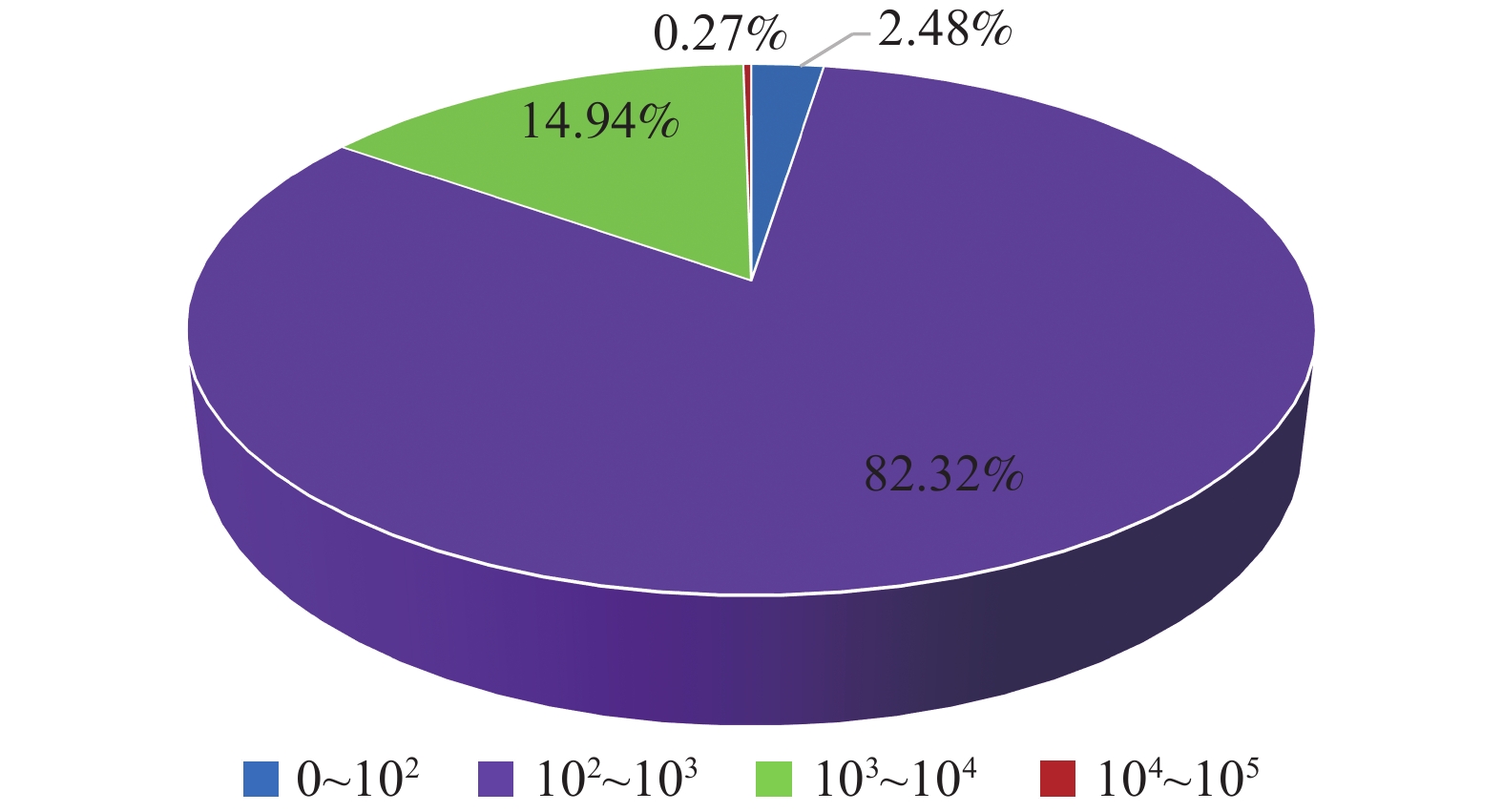
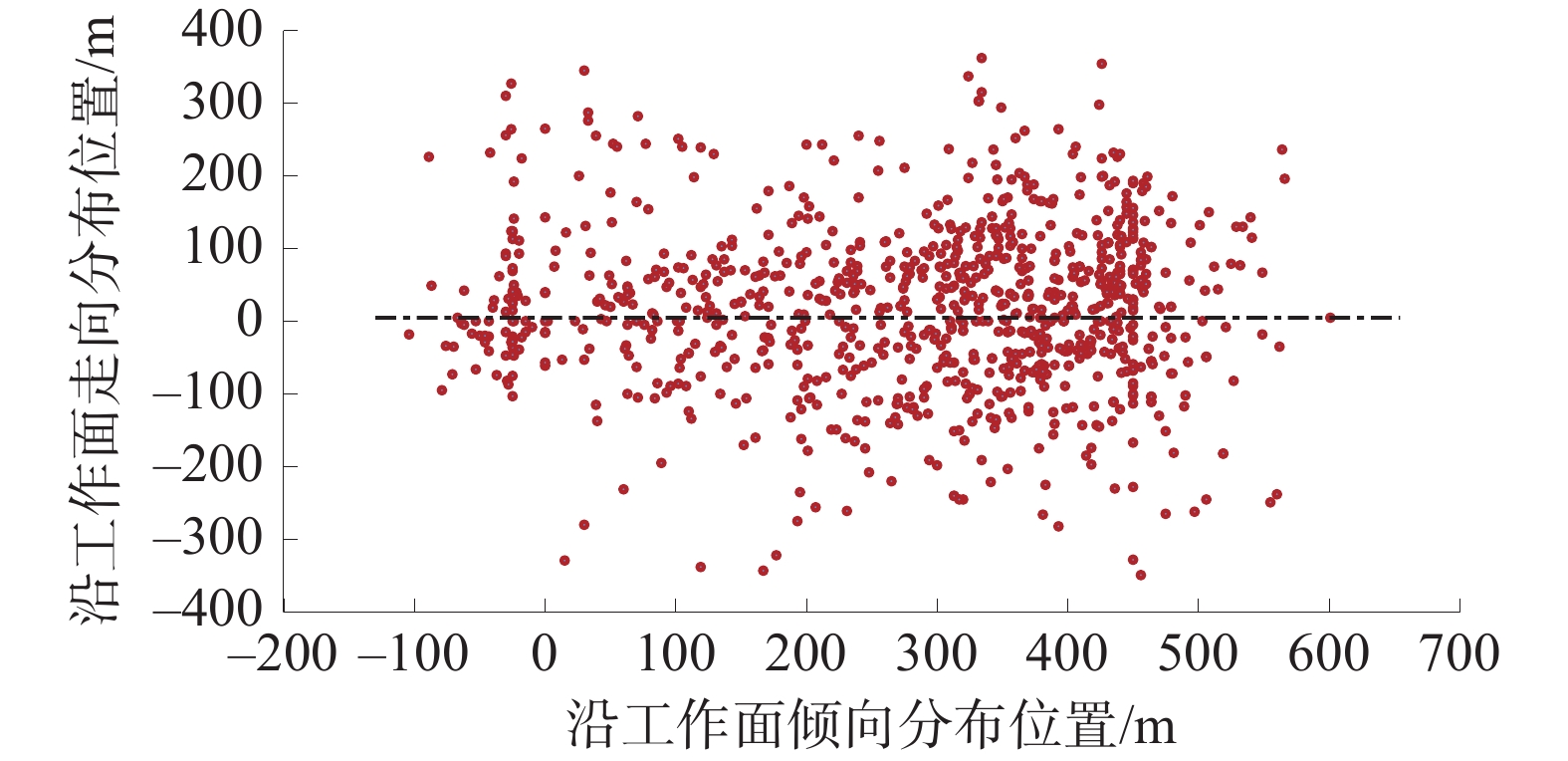
为探究综采工作面长度显著加长后工作面矿压显现和顶板活动的新特点,以国内首个中厚煤层千万吨级450 m超长工作面为工程背景,基于支架压力和微震实时监测手段,全面分析了超长工作面支架阻力分布、增阻特性和覆岩破断微震能量分布特征。研究结果表明:综采工作面长度由300 m加长为450 m后,支架阻力沿倾向分布特征由单峰状转变为双峰状,工作面支架支护强度平均增大约7%,工作面加长后,工作面矿压显现强度整体增强;超长工作面来压期间支架增阻形式主要为“对数−指数”复合函数型增阻,呈现先快、中缓、最后短时急速增阻的特点,超长工作面大截深开采是造成采煤循环末期支架快速增阻的主要诱因,在顶板状态不稳的情况下,应适当减小采煤机截深并提高支护质量;工作面覆岩破断微震事件的发生能量小、频次低,主要活跃在工作面后方40 m至前方80 m范围,微震事件分布特征表明超长工作面顶板垮落及时,无长距离悬顶现象,不易造成强动载事件,在垂直方向微震事件主要分布在垂高25 m以下顶板,厚度17.82 m的细粒砂岩基本顶是造成工作面矿压显现的主导岩层,高位岩层破断对工作面矿压显现影响较小。
Abstract:In order to explore the new characteristics of the mine pressure behavior and roof activity of the working face after the length of the fully mechanized coal mining face has been significantly extended, taking the first 450 m super long working face in the medium thick coal seam in China as the engineering background, based on the support pressure and micro-seismic real-time monitoring means, the support resistance distribution, resistance increase characteristics and micro-seismic energy distribution characteristics of super long working face are comprehensively analyzed. The research results show that after the length of the fully mechanized mining face is lengthened from 300 m to 450 m, the distribution characteristics of the support resistance along the dip change from single peak to double peak, the support strength of the working face increases by an average of about 7%, and after the working face is lengthened, the ground pressure intensities of the working face is enhanced as a whole. The resistance increase of the support during the weighting period of the super long working face is mainly in the form of “logarithmic−exponential” composite function, which is characterized by rapid resistance increase at the beginning, slow resistance increase in the middle, and rapid resistance increase in the last short time. The large cutting depth mining of super long working face is the main inducement for the rapid increase of support resistance at the end of coal mining cycle. The cutting depth of the shearer should be appropriately reduced and the support quality should be improved when the roof state is unstable. The energy and frequency of micro-seismic events of overburden breaking in the working face are small and low, and they are mainly active in the range of 40 m behind the working face to 80 m in front of it. The distribution characteristics of micro-seismic events show that the roof of the super long working face can collapse in time, and there is no long-distance hanging phenomenon, which is not easy to cause strong dynamic load events. In the vertical direction, the micro-seismic events are mainly distributed in the roof below 25 m in vertical height. The basic roof of fine sandstone with a thickness of 17.82 m is the leading rock stratum that causes the mine pressure behavior of the working face. The breakage of the high level rock stratum has little impact on the mine pressure behavior of the working face.
-
随着我国采煤技术由传统采煤向机械化、自动化采煤转变,煤炭的开采效率得到了极大的提高,但随之而来的是采煤工作面产尘量急剧增大。粉尘危害被认为是矿井安全生产的重大挑战之一。粉尘爆炸会严重威胁矿井生产安全,粉尘还会诱发矿工尘肺病[1-3]。因此,厘清回采工作面粉尘的空间分布特征及运移规律至关重要。许多国内外专家学者已经展开了大量关于煤矿粉尘运移规律的研究。WANG等[4]根据气固两相流理论,研究了粉尘运移规律与气流之间的关系,发现粉尘运移分布主要受风流影响;周刚等[5]利用Fluent软件对走向长度为15 m的综放工作面粉尘浓度分布进行了数值模拟,并根据模拟结果指导喷雾降尘装置的优化设计;刘毅等[6]采用流体力学软件Fluent对开滦集团唐山矿走向长度为54 m的工作面粉尘浓度分布进行了数值模拟,得出模拟结果与实测数据相吻合。
目前,国内外学者针对粉尘运移规律方面的研究已经取得了丰硕的成果[7-15]。但针对多尘源、长距离工作面粉尘运移规律的研究却稍显不足,并且对于三维空间内粉尘质量浓度分布缺乏系统的统计分析。基于此,以柠条塔煤矿走向长280 m的N1219工作面为工程背景,利用流体力学等数值方法建立数学模型,使用Solid Works结构设计软件建立工作面及采空区的三维物理模型,并运用Fluent软件通过气固双向耦合的方法,系统地研究采煤机割煤尘源、移架尘源、通风携尘尘源产生的呼尘在综采工作面走向、倾向、高度3个方向不采取任何防尘措施情况下的粉尘质量浓度和粒径分布规律。
1. 风流−粉尘数学模型
为简化综采工作面的气体流动模型,采用定常的不可压缩、绝热流动假设。选用标准k-ε湍流模型来描述气体流动,并使用欧拉模型来模拟风流。对于粉尘颗粒的建模,采用拉格朗日模型,并使用欧拉−拉格朗日离散相模型来描述粉尘颗粒在气流中的运动[16-23]。
连续性方程:
$$ \frac{{\partial \left( {\rho {u_x}} \right)}}{{\partial x}} + \frac{{\partial \left( {\rho {u_y}} \right)}}{{\partial y}} + \frac{{\partial \left( {\rho {u_{\textit{z}}}} \right)}}{{\partial {\textit{z}}}} = 0 $$ (1) 式中:$\rho $为流体密度,kg/m3;$ u_{x} $、$ u_{y} $、$ u_{{\textit{z}}} $为流速分量,m/s;$ x $、$ y $、$ {\textit{z}} $为长度变量,m。
湍流脉动动能方程($ {k} $方程):
$$ \;\;\; \frac{{\partial \left( {{\rho _{\text{1}}}k} \right)}}{{\partial t}} + \frac{{\partial \left( {{\rho _{\text{1}}}k{u_i}} \right)}}{{\partial {x_i}}} = \frac{\partial }{{\partial {x_j}}}\left[ {\left[ {\mu + \frac{{{\mu _{\mathrm{t}}}}}{{{\sigma _{\mathrm{k}}}}}} \right] \frac{{\partial k}}{{\partial {x_{{j}}}}}} \right] + {G_{\mathrm{k}}} - {\rho _{\text{1}}}\varepsilon $$ (2) 式中:${\rho _{{1}}}$为气体密度,kg/m3;$ {k} $为湍动能,m2/s2;t为时间,s;$ u_{i} $为连续相在$ i $方向上的速度分量,m/s;$ x_{i} $、$ x_{j} $分别为$ x $、$ y $方向上的坐标($ i $≠$ j $),m;$ \mu $为层流黏性系数,Pa·s;$ \mu_{{\mathrm{t}}} $为湍流黏性系数,Pa·s;$ \sigma_{{\mathrm{k}}} $为经验常数,取值为1.30;${G_{\mathrm{k}}}$为湍动能由于平均速度梯度引起的产生项,kg/(s3·m);$ {\varepsilon} $为湍动能耗散率,m2/s3。
湍流脉动动能耗散率方程($\varepsilon $方程):
$$ \begin{split}& \begin{gathered} \frac{{\partial \left( {{\rho _{\text{1}}}\varepsilon } \right)}}{{\partial t}} + \frac{{\partial \left( {{\rho _{\text{1}}}\varepsilon {u_i}} \right)}}{{\partial {x_i}}} = \frac{\partial }{{\partial {x_j}}}\left[ {\left[ {\mu + \frac{{{\mu _{\mathrm{t}}}}}{{{\sigma _{\text{ε} }}}}} \right] \frac{{\partial \varepsilon }}{{\partial {x_j}}}} \right] +\\ \frac{{{C_{1\text{ε} }}\varepsilon }}{k}{G_k} - \frac{{{C_{2\text{ε} }}{\varepsilon ^2}}}{k}{\rho _{\text{1}}} \end{gathered}\\[-15pt]& \end{split} $$ (3) 式中:$ \sigma_{{\text{ε} }} $为经验常数,取值为1.00;$ C_{1{\text{ε} }} $、$ C_{2{\text{ε} }} $为湍流耗散率输运方程常数,取值分别为1.44、1.92。
$$ {G_{\mathrm{k}}} = {\mu _{\mathrm{t}}} \left[ {\frac{{{\partial _{{u_i}}}}}{{{\partial _{{x_j}}}}} + \frac{{{\partial _{{u_j}}}}}{{{\partial _{{x_i}}}}}} \right] \frac{{{\partial _{{u_i}}}}}{{{\partial _{{x_j}}}}} $$ (4) 式中:$ u_{i} $、$ u_{j} $分别为连续相在$ i $、$ j $方向上的速度分量($ i $≠$ j $),m/s。
在Fluent软件中,使用DPM模型来模拟气固两相流。在综采工作面空间内,粉尘颗粒所受作用力的平衡方程如下:
$$ m_{\mathrm{p}}=\frac{\mathrm{d}u_{\mathrm{p}}}{\mathrm{d}t}=\Sigma F $$ (5) 式中:${m_{\mathrm{p}}}$为粉尘颗粒质量,mg;${u_{\mathrm{p}}}$为粉尘颗粒运动的速度,m/s;$\sum F$为粉尘颗粒所受外力的总和,N。
2. 风流−粉尘物理模型
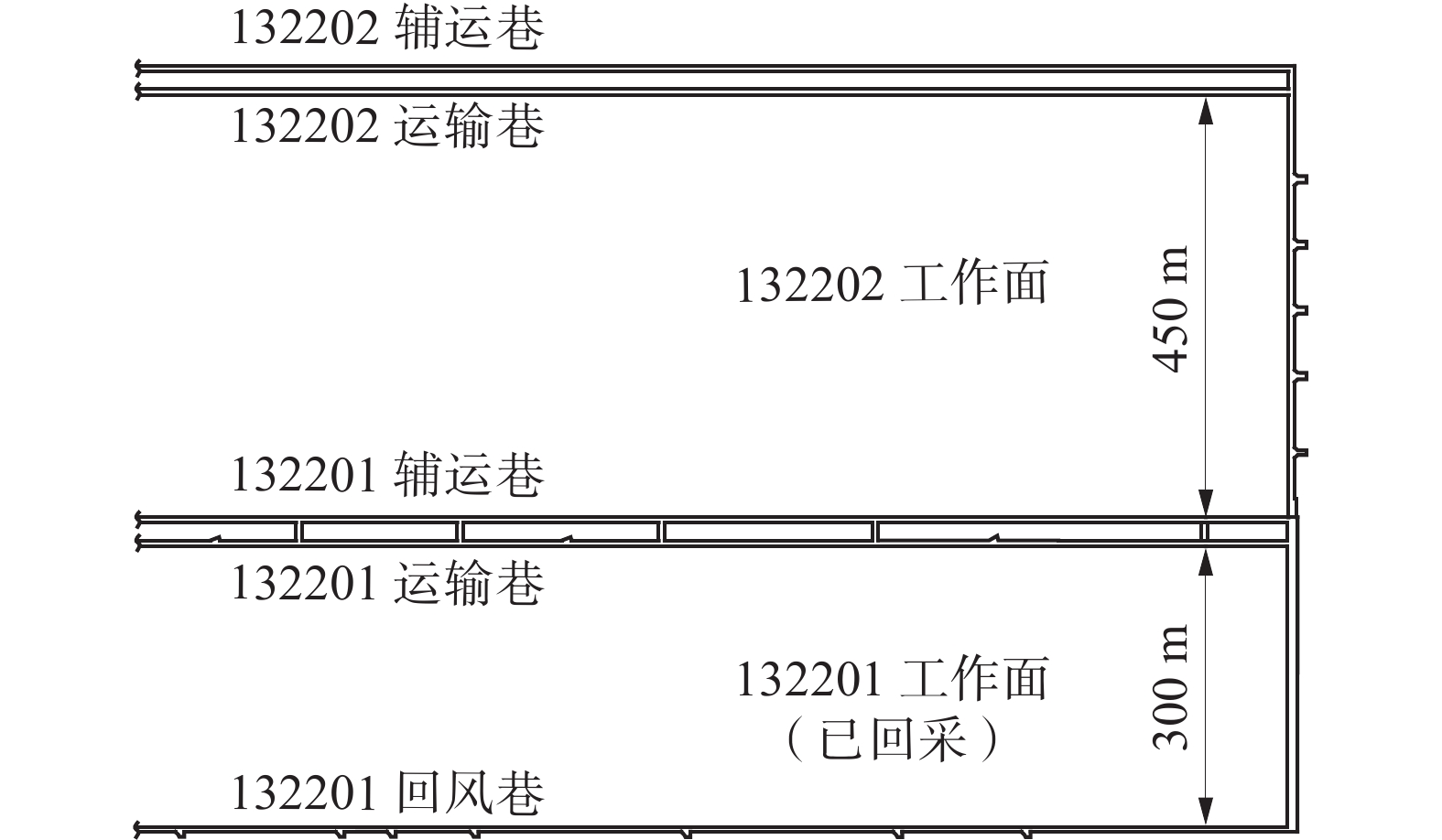
根据柠条塔煤矿N1219工作面和采空区的实际情况,采用Solid Works软件构建数值模拟的几何模型。综采工作面及采空区物理模型如图1所示,综采工作面物理模型如图2所示。
根据三维直角坐标系对N1219工作面开采模型进行构建,原点为回风巷与采空区的交界点,设置在采空区底板处,规定x、y、z方向分别为走向、倾向、高度方向。传统综采工作面采用“U”型通风方式。几何模型包括:采空区、综采工作面、采煤机、液压支架、电缆槽、进回风巷道6部分。采空区尺寸为500 m×280 m×45 m(长×宽×高),采空区包括垮落带(高15 m)和裂隙带(高30 m)。工作面作业空间尺寸为280 m×8 m×4 m(长×宽×高),按工作面长度分为移架完成区(42 m)和移架未完成区(238 m),移架未完成区内包括采煤区(70 m)和未采区(170 m),空间内有通风携尘、移架、采煤机滚筒割煤3个尘源。将采煤机机身简化为长方体,滚筒简化为1个圆柱,布置于距进风巷70 m处。两侧的进风巷和回风巷尺寸都为20 m×6 m×4 m(长×宽×高)。根据建立的几何模型生成四面体网格,共划分11 448 300个节点,2 705 172个单元。
3. 边界条件设定
3.1 连续相边界条件设定
连续相边界条件设置见表1[24-29]。在流场模型中,k-ε流场模型能模拟射流撞击、分离流等复杂流动,k-ω流场模型对于壁面边界层、自由剪切流的模拟效果较好。由于在该模拟中风流在流动中受工作面和采空区空隙率、渗透率等因素的影响,流动紊乱,属于完全湍流的复杂流动,更适配于k-ε模型。
表 1 连续相边界条件设置Table 1. Continuous phase boundary condition setting项目 名称 设置情况 求解器设置 求解器通用项 基于压力 稳态 绝对速度 重力/(m·s−2) −9.81 空气参数 密度/(kg·m−3) 1.225 黏度/(kg·m−1·s−1) 1.79×10−5 温度/ K 298 流场模型 黏性湍流模型 标准k-ε 边界条件 入口边界类型 速度入口 入流速度/(m·s−1) 1.5 湍流强度/% 3.2 水力直径/ m 4 出口边界类型 自由出流 壁面剪切条件 无滑移 3.2 离散相边界条件设定
离散相边界条件设置见表2。使用滤膜法测定尘源粉尘浓度,进而计算尘源质量流率。滤膜法测尘原理:使用抽气机将一定体积的含尘空气在一定时间内通过已知质量的滤膜,由于滤膜将粉尘截留,通过测量滤膜前后质量差就可以计算出粉尘浓度。
表 2 离散相边界条件设置Table 2. Discrete phase boundary condition setting项目 名称 设置情况 离散相参数 与连续相作用 On 相间耦合频率 10 曳力定律 球形 尘源参数 射流类型 面尘源 射流源 滚筒/移架处顶板/风流入口 喷射速度方向 尘源面法线方向 初始速度/(m·s−1) 1.5 质量流率/(kg·s−1) 0.003/ 0.0002 /0.0001 离散相材料 高挥发分煤 粒径分布 罗森−拉姆勒法则 最大粒径/µm 8 中位径/µm 5 最小粒径/µm 2 分布指数 1.3 湍流扩散模型 随机轨道模型 物理模型 粗糙壁面模型 壁面设置 底板 捕捉 其余 反弹 综采工作面的产尘包括全尘(包括呼尘和非呼尘)和呼尘,不同粒径粉尘之间的相互作用对呼尘分布会产生一定影响。因此,设定粉尘粒径为2~8 µm,包含粒径为2~5 µm的呼尘和2~8 µm的全尘。
4. 数值模拟结果
4.1 呼吸带风速
工作面呼吸带高度(z=1.5 m)[30]风速分布云图如图3所示,工作面呼吸带高度(z=1.5 m)湍流动能分布云图如图4所示。
由图3(a)可知,风流由进风巷涌入工作面时,由于风流通过转角风速方向发生很大改变,导致湍流较强,工作面液压支架侧风速较高,同时在内侧形成一条低风速带;在采空区侧,由于近工作面空间顶板垮落不充分,空隙率较大,存在由工作面向采空区漏风现象。随后由于工作面空间增大,风速降低至0.8 m/s。在采煤机附近,由于采煤机体型较大,导致工作面有效截面积变小,且风速受后滚筒扰动,增大至1.2 m/s。此后工作面基本不存在遮挡物,风流相对平稳,保持在0.8 m/s左右。风流在人行道至煤壁方向呈现出规律的由小变大现象。这是因为风流在采煤区受到采煤机影响后向支架侧运移,但因为液压支架分布较密,对风流产生一定的阻碍作用,导致风流发生横向偏移,再次运移至煤壁方向。在回风巷处截面减小,风速逐渐增大至1.7 m/s。总体来看,工作面风流从进风巷到回风巷呈现出“先减小后增大”的趋势。由图3(b)发现,工作面和采空区存在风流交换现象,在采空区侧形成一块低风速区域。
由图4可知,进回风巷和支架侧湍流动能高于采煤机侧。湍流动能是指流体湍流运动所具有的能量,是湍流状态下分布于各个时空尺度范围内的动能和压力能的总和。湍流动能值反映了湍流运动的强度和规模大小。支架侧湍流动能高,说明风流动能大、流动紊乱,一方面是由于进回风巷道处风流改向造成的,另一方面是因为支架侧与采空区风流交换的影响。采煤机侧湍流动能小,风流流动相对稳定。
4.2 呼吸带粉尘质量浓度
截取工作面呼吸带高度(z=1.5 m)对粉尘质量浓度进行分析,工作面粉尘质量浓度分布云图如图5所示。
通风携带的粉尘受湍流影响运移到液压支架侧,被高风速裹挟着运动,难以沉降,浓度较高,而采煤机侧风速较低,粉尘容易沉降,浓度较低。进入采煤机所在区域,采煤机后滚筒截煤产生的粉尘开始沿着风流运移,至前滚筒与其产生的粉尘混合,使得采煤机下风侧粉尘质量浓度陡然增至
1200 mg/m3,形成1条长约200 m的粉尘带,粉尘平均质量浓度约700 mg/m3。移架时,由于液压支架对粉尘的阻挡作用,且支架侧湍流动能大,风流流动紊乱,粉尘不易沉降,形成1条长220 m的粉尘带,粉尘平均质量浓度约12 mg/m3。在采煤机下风侧,煤壁侧粉尘质量浓度较高,支架侧粉尘质量浓度较低。在回风巷口,由于巷道截面减小,导致风速增大,粉尘质量浓度升至350 mg/m3。4.3 工作面呼尘粒径分布规律
工作面采煤机侧与支架侧呼尘粒径分布如图6所示。
由图6可知,采煤机侧呼尘粒径普遍高于液压支架侧。风流携带呼尘粒径大小可以反映风流的搬运能力,支架侧风流向采空区存在漏风情况,部分风量损失,风流的搬运能力减弱,携带呼尘粒径较小,在2.7~4 µm之间。粉尘粒径跨度区间较大,且存在波动,这是因为支架侧风流受液压支架遮挡,且与采空区存在风流交换,致其分布较为紊乱,风流的湍流动能大。采煤机侧风量损失小,且湍流动能低,风流流动平稳,搬运能力强,携带呼尘粒径较大,平均粒径在3.25 µm。
4.4 呼尘在工作面走向方向质量浓度分布规律
不同尘源工作面走向方向呼尘质量浓度如图7所示。各尘源沿工作面走向方向的呼尘质量浓度均取呼吸带高度的呼尘质量浓度。
由图7(a)、图7(b)可知,前后滚筒割煤产生呼尘在工作面走向方向质量浓度相似,且远高于移架产尘和通风携带呼尘的质量浓度。前后滚筒割煤产生的呼尘质量浓度随距进风巷距离的增加有明显的下降趋势,但最低仍在100 mg/m3左右。图7(a)和图7(b)的起点为采煤机滚筒处,距进风巷70 m,采煤机在切割煤壁时煤块被粉碎会产生大量粉尘,是工作面最大的产尘点。后续呼尘随风流在工作面空间扩散开来,呼尘质量浓度降低,在距进风巷120 m处下降缓慢,这是因为从该处工作面无遮挡物,风流相对稳定。距进风巷70~120 m区间为滚筒割煤产生呼尘质量浓度的快速下降区段,距进风巷120~280 m区间为呼尘质量浓度的缓慢下降区段。由于快速下降区段呼尘质量浓度较高,后续采用降尘措施时,可在快速下降区段架设湿式挡尘帘,由水幕与滤网组成,可有效阻隔工作面形成高质量浓度粉尘。
由图7(c)可知,移架产生的呼尘沿工作面走向方向质量浓度总体上也呈下降趋势,但在距进风巷125、150、225 m处存在波动,这是因为支架侧风流与采空区存在交换,湍流动能大,加之风流被支架反弹,分布较为紊乱,导致这几处呼尘质量浓度存在上升趋势。
由图7(d)可知,在工作面走向方向,通风携带的呼尘在进风和回风两处(距进风巷0~20 m和260~275 m区段)质量浓度较高,在其余位置分布相对均匀。这是因为在进回风巷道处,风流通过转角,风流方向发生大幅度偏转,形成湍流区,所以进回风巷风流携带的呼尘受湍流影响部分扩散到了液压支架侧。另外,通风携尘尘源呼尘释放量最低,且相当一部分呼尘扩散至采空区,剩余呼尘随风流均匀分布在工作面区域,所以走向方向呼尘质量浓度分布相对平稳。
4.5 呼尘在工作面倾向方向质量浓度分布规律
以三维坐标中心为原点,y轴方向为正方向,截取若干横截面研究不同尘源呼尘质量浓度分布规律。不同尘源工作面倾向方向呼尘质量浓度图如图8所示。
由图8(a)、图8(b)可知,前后滚筒割煤产生的呼尘质量浓度分布相似,距煤壁距离增加,呼尘质量浓度呈递减趋势,这是由于滚筒尘源靠近煤壁,近煤壁处呼尘质量浓度最高,呼尘受风流影响在工作面发生横向运移,质量浓度逐渐递减。滚筒割煤产生的呼尘质量浓度在距煤壁4~5 m处递减至0 mg/m3,说明在工作面空间内,滚筒割煤产生呼尘影响的区域集中在近煤壁区域。距煤壁1~4 m区段为滚筒割煤产生的呼尘质量浓度递减段,4~8 m区段为其归零段。在递减段内,越靠近进风巷,截面初始呼尘质量浓度越高,随距煤壁距离增加递减速率加快。在归零段,呼尘质量浓度经过递减段的降低,各截面呼尘质量浓度为0。因此,工作面内靠近煤壁区域是粉尘防治的重点区域。
由图8(c)可以看出,在距煤壁1~4 m区段,除了靠近回风巷的y=4 m、y=40 m截面,其余截面呼尘质量浓度为0。说明移架产生的呼尘主要分布在液压支架侧,只在靠近回风巷时,向煤壁侧有所扩散,且越靠近回风巷,向煤壁侧扩散越强烈。这是因为靠近回风巷时,液压支架侧向采空区漏风增加,部分呼尘向煤壁侧偏移。
由图8(d)可知,除了进回风巷两截面y=0 m、y=280 m外,其余截面呼尘分布均匀。进风巷处截面y=280 m湍流动能大,呼尘分布两边高中间低,回风巷处截面y=0处,煤壁侧呼尘质量浓度远高于支架侧,说明此处呼尘发生横向运移。
4.6 呼尘在工作面高度方向质量浓度分布规律
不同尘源工作面高度方向呼尘质量浓度如图9所示。
由图9(a)可知,在靠近前滚筒割煤尘源截面y=180 m、y=210 m处,呼尘主要分布在巷道2~4 m的高度区间。这是因为采煤机的前滚筒位置靠上,与煤层顶板相切,煤体被切割后,呼尘顺着风流从煤层顶板处开始扩散。在其余工作面截面处,呼尘质量浓度在高度方向分布均匀。
由图9(b)可知,各个截面的呼尘质量浓度随工作面高度的增加都呈下降趋势。因为采煤机后滚筒与煤层底板相切,后滚筒割煤尘源释放的粉尘位于底板附近区域,在工作面走向方向随风流部分扩散至中上层空间。
由图9(c)可知,移架产生的呼尘质量浓度沿工作面高度分布情况与后滚筒基本相反。移架尘源位于工作面顶板,呼尘质量浓度在近顶板空间较高,在工作面走向方向随风流部分扩散至工作面底部空间。
由图9(d)可知,截面y=0、y=280 m处,呼尘质量浓度在工作面高度方向分布规律性不明显,这是因为在进回风巷处湍流动能大,风流流向紊乱,呼尘呈不规则分布。在剩余截面呼尘在工作面高度方向分布均匀。
综上可知,综采工作面呼尘分布特点如下:①采煤机侧呼尘粒径普遍高于液压支架侧;②滚筒割煤尘源呼尘质量浓度在工作面走向方向随距进风巷距离增加有明显的下降趋势,在工作面倾向方向呼尘集中在近煤壁区域;③在y=80~280 m区段,移架产生的呼尘全部集中在液压支架侧。
5. 降尘措施及建议
1)设置湿式挡尘帘。采煤机割煤尘源在近煤壁区域产生高质量浓度呼尘,根据这一规律,可以在煤壁处设置由水幕和滤网组成的湿式挡尘帘。它的工作原理是利用水的表面张力,使由水幕喷出的液滴在滤网上形成水膜,用以捕捉工作面形成的高浓度呼尘。此外,在喷雾水中添加表面活性剂或采用磁化水,有效降低水的表面张力,提高捕尘能力。
2)安设喷雾引射除尘装置。相较于采煤机割煤产尘,移架产尘的主要分布区域为液压支架侧,可在液压支架间安设喷雾引射除尘装置。装置启动后,在其内部产生的负压可从吸尘口吸入移架粉尘,粉尘在装置内会与水雾颗粒不断发生碰撞、结合,导致其自重增加,在被喷出装置后会很快沉降下来。
3)选用合适的喷嘴型号及喷雾压力。当喷出液滴的粒径与呼尘粒径相似时,液滴的捕尘效果最好。由于采煤机侧呼尘粒径普遍高于液压支架侧,在选用喷嘴型号及喷雾压力时,应在采煤机侧喷出较大粒径的雾滴,与呼尘粒径相匹配。
6. 结 论
1)采煤机侧呼尘粒径普遍高于液压支架侧。支架侧风流向采空区存在漏风情况,风流的搬运能力减弱,携带呼尘粒径较小。
2)滚筒割煤尘源呼尘在工作面走向方向上呈现出快速递减和缓慢递减2个阶段;在工作面倾向方向上,距煤壁越远,滚筒割煤尘源呼尘质量浓度越低,在距煤壁4~5 m处呼尘质量浓度递减至0。
3)在y=80~280 m区段,移架产生的呼尘全部集中在液压支架侧。
4)在y=40~240 m区段,通风携带的呼尘质量浓度在工作面高度方向分布均匀。
-
表 1 ZY16000/18/32D中部液压支架技术特征表
Table 1 Technical characteristics of ZY16000/18/32D middle hydraulic support
序号 技术指标 技术参数 1 支架种类 双柱掩护式 2 支护高度/mm 1 800~3 200 3 支架中心距/mm 2 050 4 初撑力/kN 13 572(p=25.2 MPa) 5 工作阻力/kN 16 000(p=44.2 MPa) 6 移架步距/mm 1 050 7 最大控顶距/mm 7 050 表 2 ZY12000/17/32D中部液压支架技术特征表
Table 2 Technical characteristics of ZY12000/17/32D middle hydraulic support
序号 技术指标 技术参数 1 支架种类 双柱掩护式 2 支护高度/mm 1 700~3 200 3 支架中心距/mm 1 750 4 初撑力/kN 10 390(p=25.2 MPa) 5 工作阻力/kN 12 000(p=43.3 MPa) 6 移架步距/mm 800 7 最大控顶距/mm 6 180 表 3 工作面周期来压和非来压期间支架增阻情况统计
Table 3 Statistics of support resistance increase during periodic weighting and non periodic weighting of working face
时期 平均增阻量/kN 循环增阻速率/
(kN·min−1)最大增阻速率/
(kN·min−1)来压期间 4 420 8~162.5/68 68~1 573/354 非来压期间 2 314 0~160/47 36~415/208 -
[1] 王国法,庞义辉,任怀伟. 煤矿智能化开采模式与技术路径[J]. 采矿与岩层控制工程学报,2020,2(1):1−15. WANG Guofa, PANG Yihui, REN Huaiwei. Intelligent coal mining pattern and technological path[J]. Journal of Mining and Strata Control Engineering, 2020, 2(1): 1−15.
[2] 丁彦雄,张金虎,李明忠,等. 中厚煤层超长工作面大中心距超强力液压支架优化设计[J]. 煤炭技术,2022,41(6):168−170. DING Yanxiong, ZHANG Jinhu, LI Mingzhong, et al. Optimal design of super strong hydraulic support with large center distance in super long working face of medium thick coal seam[J]. Coal Technology, 2022, 41(6): 168−170.
[3] 张金虎,李明忠,胡健,等. 超长工作面布置方式优化设计与设备选型配套[J]. 煤炭工程,2021,53(7):7−10. ZHANG Jinhu, LI Mingzhong, HU Jian, et al. Optimized design of super-long working face layout and the equipment selection and matching[J]. Coal Engineering, 2021, 53(7): 7−10.
[4] 缪协兴,钱鸣高. 超长综放工作面覆岩关键层破断特征及对采场矿压的影响[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2003,22(1):45−47. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2003.01.008 MIAO Xiexing, QIAN Minggao. Broken feature of key strata and its influence on rock pressure in super-length fully-mechanized coal face[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2003, 22(1): 45−47. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2003.01.008
[5] 王国法,张金虎,徐亚军,等. 深井厚煤层长工作面支护应力特性及分区协同控制技术[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(3):763−773. WANG Guofa, ZHANG Jinhu, XU Yajun, et al. Supporting stress characteristics and zonal cooperative control technology of long working face in deep thick coal seam[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(3): 763−773.
[6] 王家臣,杨胜利,杨宝贵,等. 深井超长工作面基本顶分区破断模型与支架阻力分布特征[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(1):54−63. WANG Jiachen, YANG Shengli, YANG Baogui, et al. Roof sub-regional fracturing and support resistance distribution in deep longwall face with ultra-large length[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2019, 44(1): 54−63.
[7] 王家臣,王兆会,杨杰,等. 千米深井超长工作面采动应力旋转特征及应用[J]. 煤炭学报,2020,45(3):876−888. WANG Jiachen, WANG Zhaohui, YANG Jie, et al. Mining-induced stress rotation and its application in longwall face with large length in kilometer deep coal mine[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(3): 876−888.
[8] 王兆会,孙文超,水艳婷,等. 千米深井超长工作面采动应力旋转轨迹及其推进方向效应[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(2):634−650. WANG Zhaohui, SUN Wenchao, SHUI Yanting, et al. Mining induced stress rotation trace and its sensitivity to face advance direction in kilometer deep longwall panel with large face length[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(2): 634−650.
[9] 宋选民, 顾铁凤, 闫志海. 浅埋煤层大采高工作面长度增加对矿压显现的影响规律研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 26( S2): 4007-4012. SONG Xuanmin, GU Tiefeng, YAN Zhihai. Effects of increasing working face’s length on underground pressure behaviors of mining super-high faces under shallow coal seam[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(S2): 4007-4012.
[10] 赵雁海,宋选民. 浅埋超长工作面裂隙梁铰拱结构稳定性分析及数值模拟研究[J]. 岩土力学,2016,37(1):203−209. ZHAO Haiyan, SONG Xuanmin. Stability analysis and numerical simulation of hinged arch structure for fractured beam in super-long mining workface under shallow seam[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2016, 37(1): 203−209.
[11] 刘长友, 黄炳香, 孟祥军, 等. 超长孤岛综放工作面支承压力分布规律研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 26(S1): 2761-2766. LIU Changyou, HUANG Bingxiang, MENG Xiangjun, et al. Research on abutment pressure distribution law of overlength isolated fully-mechanized top coal caving face[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(S1): 2761-2766.
[12] 范志忠,付书俊,潘黎明. 深部超长孤岛工作面覆岩垮落结构特征研究[J]. 煤炭工程,2020,52(2):86−90. FAN Zhizhong, FU Shujun, PAN Liming. Study on caving structure characteristics of overlying strata in deep super long island working face[J]. Coal Engineering, 2020, 52(2): 86−90.
[13] 付书俊,范志忠,张雪峰,等. 超长工作面异常矿压显现与瓦斯涌出关系研究[J]. 煤炭工程,2019,51(5):139−142. FU Shujun, FAN Zhizhong, ZHANG Xuefeng, et al. Study on the relation between abnormal mine pressure behavior and gas emission in super-long working face[J]. Coal Engineering, 2019, 51(5): 139−142.
[14] 王庆雄,鞠金峰. 450 m 超长综采工作面矿压显现规律研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2014,42(3):125−128. WANG Qingxiong, JU Jinfeng. Study on mine strata pressure behavior law of 450 m ultra long fully-mechanized coal mining face[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2014, 42(3): 125−128.
[15] 宋立兵,王庆雄. 国内首个450 m 超长综采工作面安全开采技术研究[J]. 煤炭工程,2014,46(3):45−47. doi: 10.11799/ce201403015 SONG Libing, WANG Qingxiong. Study on safety mining technology of China first 450 m ultra long fully mechanized coal mining face[J]. Coal Engineering, 2014, 46(3): 45−47. doi: 10.11799/ce201403015
[16] 丁国利,鲁喜辉,武少国,等. 深埋超长综采工作面矿压规律及支架适应性研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(3):43−48. doi: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2021.03.004 DING Guoli, LU Xihui, WU Shaoguo, et al. Study on ground pressure law and support adaptability of deep-buried and ultra-long fully-mechanized longwall mining face[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49(3): 43−48. doi: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2021.03.004
[17] 车禹恒,朱志洁. 特厚煤层工作面长度对矿压显现的影响[J]. 矿业安全与环保,2016,43(3):81−85. CHE Yuheng, ZHU Zhijie. Influence of length of working face in extra-thick coal seam on strata behaviors[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection, 2016, 43(3): 81−85.
[18] 金圣宝,王爱午,黄志栋,等. 朔南矿区特厚煤层超长综放工作面矿压显现规律研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2019,50(12):203−207. doi: 10.13347/j.cnki.mkaq.2019.12.045 JIN Shengbao, WANG Aiwu, HUANG Zhidong, et al. Study on strata behavior law of fully mechanized caving face in super-long and thick coal seam in southern Shuozhou Mining Area[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2019, 50(12): 203−207. doi: 10.13347/j.cnki.mkaq.2019.12.045
[19] 刘一扬,史光亮,张光磊,等. 工作面倾向覆岩垮落形态的面长效应及力链拱特征研究[J]. 煤矿安全,2021,52(5):242−249. doi: 10.13347/j.cnki.mkaq.2021.05.043 LIU Yiyang, SHI Guangliang, ZHANG Guanglei, et al. Study on effect of working face length on overburden caving form and force chain arch characteristics[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021, 52(5): 242−249. doi: 10.13347/j.cnki.mkaq.2021.05.043
[20] 张昆. 黄陵二号煤矿超长工作面矿压规律分析[J]. 陕西煤炭,2021,40(3):72−74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-749X.2021.03.016 ZHANG Kun. Analysis on ground pressure law of super long working face in Huangling No.2 Coal Mine[J]. Shaanxi Coal, 2021, 40(3): 72−74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-749X.2021.03.016
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 魏启明,胡亚军,张海龙,杨宗泉,王虎,刘玉德. 煤层群下煤层开采工作面矿压显现规律研究. 当代化工研究. 2025(01): 43-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 安伟岗,陆星,白贝贝. 煤矿综采工作面增面设备安装及施工技术研究. 设备管理与维修. 2025(04): 97-99 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 武瑞成. 厚煤层综放开采矿压显现异常治理研究. 内蒙古煤炭经济. 2024(04): 67-69 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 尚立斌. 阳泉矿区大埋深超长工作面装备适应性研究. 煤炭技术. 2024(06): 217-219 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 孙俊明,侯增平,徐宏强. 超长工作面液压支架关键参数设计及效益分析. 陕西煤炭. 2024(08): 72-77 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 李尚国. 超长工作面采空区分段阻隔自燃防治研究. 煤炭与化工. 2024(11): 121-124 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 薛丁才. 煤矿120210工作面矿压监测及采煤工艺优化分析. 山西冶金. 2024(11): 205-207 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: