Experimental study on relationship between surface fracture distribution and gas adsorption as well as emission characteristics of outburst coal seam
-
摘要:
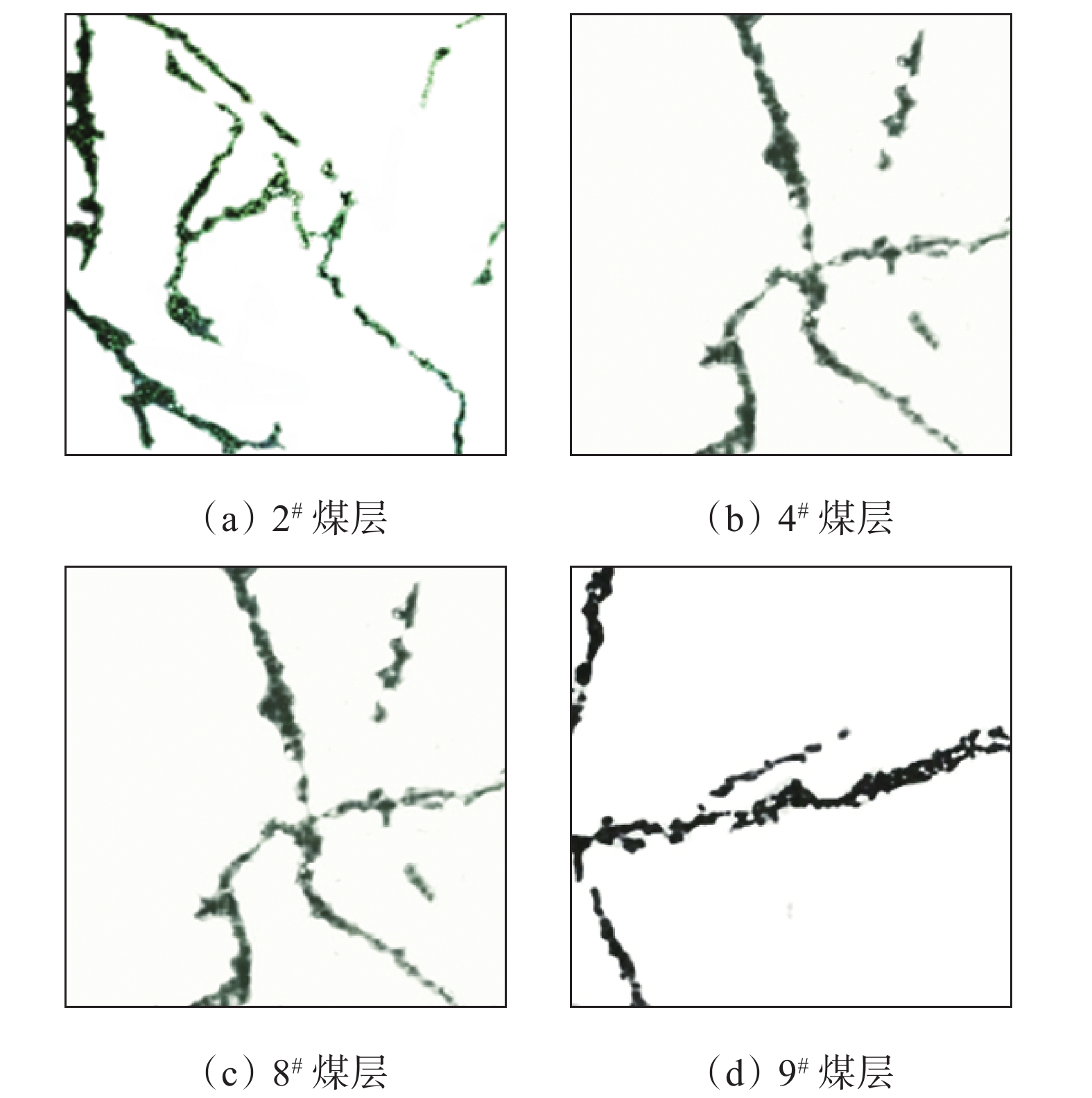
瓦斯吸附、放散特性对于煤与瓦斯突出灾害预测、检验与防治十分重要,且与煤体裂隙结构特征密切相关。选取东曲煤矿2#、4#、8#和9#煤层的煤体试样,利用分形维数表征煤体表面裂隙特征,研究了煤体裂隙分布与瓦斯吸附、放散特性参数之间的关系。结果表明:基于分形理论求解了煤体表面裂隙分布的分形维数,取值范围为1.4~1.5,原生裂隙发育程度为9#煤层>4#煤层>8#煤层>2#煤层;通过瓦斯吸附、放散实验测试分析了煤体等温吸附常数及瓦斯放散初速度,吸附常数a取值范围为34.180~36.920 m3/t,瓦斯放散初速度取值范围为12~18 mmHg,上述参数的大小顺序与分形维数值一致。统计分析了东曲煤矿煤体分形维数与瓦斯吸附、放散特性参数的相关性,结果表明二者呈显著正相关性,分形维数能够表征该煤矿煤体瓦斯吸附与放散的特性与能力。
Abstract:Gas absorption and emission characteristics are very important for the prediction, inspection and prevention of coal and gas outburst disasters, which are related to the structural distribution characteristics of coal fractures closely. In this paper, the coal samples of No.2, No.4, No.8 and No.9 coal seams in Dongqu Coal Mine are selected, and the fractal dimension is used to quantitatively characterize the distribution of coal surface fractures. The relationship is studied between the characteristic parameters of fracture distribution and gas absorption and emission. The results show that the fractal dimension parameters of the fracture distribution on the coal surface are solved by fitting based on the fractal theory. The value range of the fractal dimension parameters is 1.4-1.5, and the development degree of primary fractures is No.9 coal seam>No.4 coal seam>No.8 coal seam>No.2 coal seam. The isothermal adsorption constants of coal and the initial velocity of gas emission are analyzed through the gas adsorption and emission experiment. The value range of adsorption constants a is 34.180-36.920 m3/t, while the value range of initial velocity of gas emission is 12-18 mL/s, which is consistent with the fractal dimension value. The correlation between fractal dimension parameters and gas adsorption and emission parameters of coal in Dongqu Coal Mine are statistically analyzed. It shows that there is a significant positive correlation between them. The fractal dimension value can characterize the values and capabilities of gas adsorption and emission of coal in this coal mine.
-
煤层气是一种储存于煤层中的非常规天然气,我国煤层气资源量十分丰富,大致与陆上常规天然气相当[1]。开发和利用煤层气对于促进我国能源转型以及保护环境具有十分重要的意义。然而,煤岩性质硬脆、机械强度低,受成岩作用、构造作用以及后期工程作业的影响,煤岩结构极易破坏失稳,形成大量煤粉[2]。在煤层气井排采过程中,煤粉随流体运移是其固有属性,难以避免。煤粉一旦侵入支撑裂缝和井筒内,不但会伤害支撑裂缝渗透率,还会引发卡泵、埋泵事故,导致频繁修井作业,影响排采连续性和稳定性[3-4]。修井作业时排采的中断将使得大量悬浮煤粉滞留于支撑裂缝内,进一步伤害支撑裂缝渗透率[5-6]。
目前,众多学者围绕排采中断−恢复事件对支撑裂缝内煤粉运移的影响已开展了大量研究。曹代勇等[7]实验对比了排采中断前和恢复后的支撑裂缝内煤粉产出情况,结果表明,当驱替中断而重新恢复后,由于流速的瞬间增大,煤粉产出量较中断前有所增大;刘岩等[8-9]对比了间歇流和连续流条件下支撑裂缝内煤粉运移及其诱发渗透率伤害情况,结果表明,间歇流条件下的煤粉产出量小于连续流条件下的煤粉产出量,且间歇流诱发的支撑裂缝渗透率伤害率高于连续流条件下的伤害率;张惜图等[10]开展了排采中断−恢复事件对支撑裂缝内煤粉运移的影响实验,结果表明,由于中断期间煤粉的大量滞留,恢复后的支撑裂缝渗透率难以达到中断前水平。目前,相关研究尚存在以下问题:①现有研究中采用的中断后恢复模式均为一级恢复模式,而实际生产过程中多为逐级恢复模式,不同恢复模式下支撑裂缝内煤粉运移规律有何差异还尚未明确;②现有研究开展的中断−恢复实验均针对的是单相流排水阶段(固−液两相流条件),而关于气−水合采阶段(气−液−固三相流条件)的研究还鲜有报道。
鉴于此,针对固−液两相流和气−液−固三相流2种流型,开展了排采中断后恢复模式对支撑裂缝内煤粉运移的影响实验,对比了一级恢复模式和逐级恢复模式下支撑裂缝的渗透率演化规律,并探讨了排采恢复模式对支撑裂缝内煤粉运移的控制作用机制;研究成果可为优化单相流排水阶段以及气−水合采阶段排采中断后的合理恢复方式,以解除煤粉滞留诱发的支撑裂缝渗透率伤害。
1. 实验材料与方法
1.1 样品制备
选用潞安矿区古城矿山西组3号煤层为研究对象。3号煤工业分析及显微组分分析结果见表1,XRD全岩矿物及黏土矿物分析结果见表2。
表 1 古城矿3号煤工业分析及显微组分分析结果Table 1. Results of proximate and maceral component analysis of No. 3 coal in Gucheng Mine水分/
%灰分/
%挥发分/
%固定碳/
%镜质组
反射率/%镜质组/
%惰质组/
%壳质组/
%1.25 9.38 11.16 78.21 2.11 88.41 11.59 — 表 2 古城矿3号煤XRD全岩矿物及黏土矿物分析结果Table 2. XRD results of whole rock mineral and clay mineral of No. 3 coal in Gucheng Mine全岩矿物质量分数/% 黏土矿物质量分数/% 方解石 白云石 黏土 有机质 伊利石 高岭石 0.13 0.23 7.47 92.17 43 57 将现场获取的煤块采用行星球磨机研磨至细微颗粒,用于制备煤粉。鉴于现场煤层气井排出煤粉的粒径范围以小于100 μm为主[11],通过振动筛筛析出粒径小于80 μm的煤粉。实验选用的支撑剂类型为标准石英砂,其粒径范围为0.425~0.850 mm,SiO2质量分数大于99.8%,支撑剂的类型及粒径均为现场压裂常用[8-9]。基于激光粒度分析仪,煤粉的粒度分布特征参数d10、d50、d90(即累计粒度分布百分数为10%、50%、90%时对应的粒径)分别为4.94、30.87、70.13 μm,而标准石英砂的粒度分布特征参数d10、d50、d90分别为553.51、668.45、795.91 μm。
实验设定的煤粉−支撑剂粒级匹配关系可保证煤粉顺利通过支撑裂缝。实验用的背景流体为质量分数为2%的KCl溶液,由去离子水和分析纯级KCl配置而成,并通过0.1 mol/L的HCl和0.1 mol/L的NaOH将溶液pH调节至7.0左右。实验设定的背景溶液电化学条件可满足煤粉在支撑剂表面上有利黏附。鉴于现场煤层气井产出煤粉的质量分数通常介于0.64%~3.71% [5-6,12],以质量分数为2%的KCl溶液为基液,选用粒径小于80 μm的煤粉,配制质量分数为1%的煤粉悬浮液。
1.2 实验装置及流程
支撑裂缝内固−液及气−液−固多相流驱替实验装置流程图如图1所示。
实验装置主要包括流体注入系统、支撑裂缝模拟单元、压力传感器、气−液分离器、馏分收集器、温度控制系统、数据采集系统等。流体注入系统由注射泵、搅拌容器、气瓶以及气体流量控制器构成,搅拌容器用于配置煤粉悬浮液,并经驱替泵实现煤粉悬浮液的恒流注入,而气瓶和气体流量控制器组合用于实现气体的恒流注入;支撑裂缝模拟单元为装填有支撑剂的不锈钢腔体,不锈钢腔体尺寸为50 mm×20 mm×10 mm;2个压力传感器用于监测支撑裂缝模拟单元的进出口压力差,并通过达西定律计算支撑裂缝渗透率;气−液分离器用于分离产出的气相和液相,而馏分收集器用于连续收集产出液相;温度控制系统为恒温箱,实验温度设定为30 ℃。基于上述系统,开展固−液两相流以及气−液−固三相流条件下的排采中断−恢复模拟实验。
1.2.1 固−液两相流条件下实验流程
1)将支撑剂充填至支撑裂缝模拟单元腔体内,并保证支撑剂均匀、密实充填,待支撑裂缝模拟单元充填满后(支撑剂用量约15.5 g),用盖板进行压实、密封,并对模拟单元抽真空饱和质量分数为2%的KCl溶液。
2)开启注射泵,在流量为10 mL/min下,向支撑裂缝内连续注入煤粉悬浮液,注入时间约为40 min,期间连续监测支撑裂缝两端压差Δp,并通过达西定律计算支撑裂缝渗透率k。
3)关闭注射泵,模拟排采中断过程,中断时间为2 h。
4)开启注射泵,在流量为10 mL/min下,向支撑裂缝内注入质量分数为2%的KCl溶液,以模拟一级恢复模式,注入时间约20 min,期间连续监测支撑裂缝两端压差Δp,并计算支撑裂缝渗透率k。
5)重复上述步骤,并将步骤4)中流量加载模式更改为2→5→7→10 mL/min逐级加载模式,各流量阶段的驱替时间约为5 min,期间连续监测支撑裂缝两端压差Δp,并计算支撑裂缝渗透率k。
1.2.2 气−液−固三相流条件下实验流程
1)将支撑剂充填至支撑裂缝模拟单元腔体内,并保证支撑剂均匀、密实充填,待支撑裂缝模拟单元充填满后,用盖板进行压实、密封,并对模拟单元抽真空饱和质量分数为2%的KCl溶液。
2)同时开启注射泵和气瓶,向支撑裂缝内注入煤粉悬浮液和氮气,液相流量qw和气相流量qg均为10 mL/min,注入时间约为30 min,连续监测驱替压差Δp,计算支撑裂缝气相渗透率kg与液相渗透率kw。
3)同时关闭注射泵和气瓶,模拟排采中断过程,中断时间为2 h。
4)同时开启注射泵和气瓶,在qw=qg=10 mL/min(10∶10)条件下向支撑裂缝内注入2% KCl溶液和氮气,模拟一级恢复模式,注入时间约为20 min,连续监驱替压差Δp,计算支撑裂缝气相渗透率kg与液相渗透率kw。
5)重复上述步骤,将步骤4)中的流量加载模式更改为逐级加载模式,各流量加载阶段的气/液流量比保持不变,即qw=qg=5 mL/min(5∶5)→qw=qg=7 mL/min(7∶7) →qw=qg=10 mL/min(10∶10),每个流量加载阶段的驱替时间均约为6 min,期间连续监测驱替压差Δp,并计算支撑裂缝气相渗透率kg与液相渗透率kw。
2. 实验结果
2.1 固−液两相流实验结果
在固−液两相流条件下,排采中断−恢复事件导致支撑裂缝两端压差Δp和渗透率比k/k0(k0为初始渗透率)演化曲线如图2所示。
由图2可知:在一级恢复模式下,驱替恢复后的支撑裂缝两端压差较中断前存在明显降低,鉴于恢复后和中断前流量均为10 mL/min,表明一级恢复模式使得支撑裂缝内煤粉发生了大规模运移产出,从而对支撑裂缝起到明显的疏通作用;在逐级恢复模式下,当流量恢复至10 mL/min时,支撑裂缝两端压差较中断前存在明显增大,表明逐级恢复模式并未使滞留煤粉发生明显的运移产出,其对煤粉疏通作用有限。
由渗透率演化结果可知:在一级恢复模式下,支撑裂缝渗透率提升至中断前水平之上,渗透率增幅为47.7%;而在逐级恢复模式下,尽管各恢复阶段的支撑裂缝渗透率均比上一阶段有所改善,但最终渗透率并未恢复至中断前水平,渗透率降幅为25.4%。在驱替恢复前,支撑裂缝内滞留煤粉由中断前的旧滞留煤粉以及中断期间的新滞留煤粉2部分构成。在一级恢复模式下,支撑裂缝渗透率得到了明显提升,表明一级恢复模式不但能有效清除中断期间的新滞留煤粉,而且对中断前的旧滞留煤粉也具有一定清除作用,从而大幅改善支撑裂缝渗透率;然而,在逐级恢复模式下,支撑裂缝渗透率存在明显降低,表明该恢复模式并不能完全清除中断期间的新滞留煤粉,新滞留煤粉导致了支撑裂缝渗透率降低。因此,在单相流排水阶段,为更好地抑制排采中断诱发支撑裂缝内煤粉滞留伤害,应采用一级恢复模式进行排采恢复,即尽可能快地将排采强度恢复至中断前水平。
2.2 气−液−固三相流实验结果
在气−固−液三相流条件下,排采中断−恢复导致支撑裂缝两端压差Δp以及气相渗透率比kg/kg0(kg0为初始气相渗透率)和液相渗透率比kw/kw0(kw0为初始液相渗透率)演化曲线如图3所示。
与固−液两相流条件下不同,在一级恢复模式和逐级恢复模式下,驱替恢复后的支撑裂缝两端压差均小于中断前水平,且一级恢复模式下的驱替压差降幅要大于逐级恢复模式,表明在气−固−液三相流条件下,一级恢复模式和逐级恢复模式对支撑裂缝内滞留煤粉均有明显的疏通作用,但一级恢复模式的疏通作用要强于逐级恢复模式。此外,在气−固−液三相流条件下,驱替恢复过程中驱替压差为缓慢降低过程;而在固−液两相流条件下,驱替压差为突然降低过程,表明气−固−液三相流场的扰动对煤粉疏通作用为渐进行为,而固−液两相流场的扰动对煤粉的疏通作用却为瞬间行为。
由渗透率演化结果可知:一级恢复模式和逐级恢复模式均能使得支撑裂缝气、液相渗透率恢复至中断前水平之上,一级恢复模式下最终气、液相渗透率较中断前增幅分别为115%和47.3%;而在逐级恢复模式下,最终气、液相渗透率较中断前增幅仅分别为38.6%和17.1%,均小于一级恢复模式下的气、液相渗透率增幅,且各恢复阶段的渗透率与上一阶段相比均无明显变化。在气−固−液三相流条件下,一级恢复模式和逐级恢复模式对支撑裂缝的气、液相渗透率均有不同程度的改善作用,可知2种恢复模式均能有效清除中断期间的新滞留煤粉,且对中断前的旧滞留煤粉也具有一定清除作用。鉴于一级恢复模式对支撑裂缝的气、液相渗透率改善效果更好,在气−水合采阶段,为更好地抑制排采中断事件诱发的支撑裂缝内煤粉滞留伤害,同样应采用一级恢复模式进行排采恢复。
3. 讨 论
3.1 支撑裂缝内煤粉滞留机理
在固−液两相流和气−固−液三相流条件下,由于流场特征及相间作用机制的差异,支撑裂缝内煤粉滞留机理也存在明显不同,固−液和气−液−固多相流条件下支撑裂缝内煤粉滞留机理示意如图4所示。
由图4可知,在固−液两相流条件下,悬浮煤粉通过水动力、重力和布朗力的综合作用,最终黏附于固–液界面(壁面)上,是导致支撑裂缝内煤粉滞留的根本原因 [13]。然而,在气−固−液三相流条件下,支撑裂缝处于非饱和条件,气相的介入将导致煤粉运移变得更加复杂,此时煤粉除了与固–液界面作用外,还将与气–液界面发生相互作用。根据毛细力学理论,当悬浮煤粉与气–液界面接触时,煤粉将受到气–液界面施加的毛细力作用(又称液桥力,由毛管压力和Laplace附加压力构成),该力通常远大于固–液界面施加的黏附力[14-15]。众多研究表明,在气−固−液三相流条件下,固相颗粒更易被气–液界面捕获,并在界面处聚集成团,是三相流条件下多孔介质内颗粒滞留的主要形式[16-17]。由实验结果可知:在固−液两相流条件下逐级恢复模式导致支撑裂缝渗透率较中断前明显降低;而在气−固−液三相流条件下却导致气、液相渗透率比中断前有所提升。固–液两相流和气–液–固三相流条件下支撑裂缝内煤粉滞留形式的显著差异,是导致相同恢复模式下支撑裂缝渗透率改善效果不同的主要原因。
3.2 恢复事件诱发煤粉运移机理
不同排采阶段流速骤变对支撑裂缝内煤粉运移影响机理示意如图5所示。
在固−液两相流条件下,支撑裂缝内流速的突然增加,将导致流速剖面由抛物性型向非抛物型转变,使得壁面处的流体剪应力(τ=dv/dy,式中:τ为流体剪应力;v为流速;y为与壁面的间距)增加,从而增强煤粉受到的水动力作用,促使煤粉的运移产出;且流速的增幅越大,壁面黏附煤粉受到的水动力作用(流体剪应力)就越强,从而促进更多的煤粉运移产出[18-20]。
在气−固−液三相流条件下,支撑裂缝内煤粉主要滞留于非移动气泡/气−液界面处,在气液比不变的情况下,流速的突然增大将使得气泡受到的水动力作用增强,从而导致气泡尺寸和形态发生改变[21-22]。首先,由于流速的增大,气泡间的相对速度增加,导致气泡发生碰撞的频率增加,从而使气泡更易聚集形成更大的气泡或气泡群;其次,由于流速的增大,气泡受到的水动力作用更强,气泡更易发生形态改变,变得更加扁平或拉长。气泡形态和尺寸的改变,将导致支撑裂缝内气−液界面发生扰动,使得部分非移动气−液界面转变为移动气−液界面,从而携带煤粉运移产出;且支撑裂缝内流速的增幅越大,气−液界面的扰动就越强,促进更多的非移动气−液界面变为移动气−液界面,并携带更多的煤粉运移产出。
由此可知,无论在固−液两相流以及气−液−固三相流条件下,由于一级恢复模式的流速增幅要大于逐级恢复模式的流速增幅,故一级恢复模式更易诱发支撑裂缝内滞留煤粉运移产出,即对支撑裂缝渗透率的改善幅度就越大。
4. 结 语
1)在固−液两相流和气−液−固三相流条件下,一级和逐级恢复模式对支撑裂缝内煤粉运移的影响均存在明显差异,在固−液两相流条件下,一级恢复模式使得支撑裂缝渗透率较中断前存在明显的增大,而逐级恢复模式却导致支撑裂缝渗透率较中断前明显降低,在气−固−液三相流条件下,一级和逐级恢复模式对支撑裂缝的气、液相渗透率均有不同程度的改善,但一级恢复模式改善效果更好。
2)在固−液两相流和气−液−固三相流条件下,支撑裂缝内煤粉滞留形式主要分别为固−液界面和气−液界面黏附,其差异性是导致相同恢复模式下渗透率改善效果不同的主要原因,流速突然增大将导致壁面剪应力和气−液界面扰动效应增强,促进煤粉运移产出,由于一级恢复模式的流速增幅较逐级恢复模式更大,其诱发的壁面剪应力和气−液界面扰动更强,故对煤粉促排效应就越强,渗透率改善效果越好。
3)无论在固−液两相流和气−液−固三相流条件下,一级恢复模式对支撑裂缝导流能力的改善作用均强于逐级恢复模式,为有效解除排采中断事件对支撑裂缝渗透率的负面影响,在单相流排水阶段和气−水合采阶段排采中断后均应采用一级恢复模式,即尽可能快地将排采强度恢复至中断前水平。
4)在气−液−固三相流条件下,受不同气/液比的影响,气−液相流型会发生明显变化(泡状流、段塞流、环状流等),进而影响固相颗粒的赋存运移形态。仅针对气液比为1∶1的情形,探究了排采中断后恢复模式对支撑裂缝内煤粉运移的影响规律,后续亟待开展不同气/液比条件下的排采中断−恢复模拟实验,系统揭示三相流条件下排采中断后恢复模式对支撑裂缝内煤粉运移的影响规律。
-
表 1 煤样基本参数
Table 1 Basic parameters of coal samples
煤层 试样来源 水分/% 灰分/% 挥发分/% 坚固性
系数2# 12610运输巷 0.74 12.48 18.25 0.33 4# 24808轨道巷距巷道口46 m 0.52 7.94 17.75 0.49 8# 18414回风专用巷 0.85 13.58 14.55 0.34 9# 28210底抽巷向里620 m 0.83 11.06 14.47 0.67 表 2 各煤样吸附常数统计结果
Table 2 Statistical results of adsorption constants of coal samples
煤层 a/(m3·t−1) b/MPa−1 R2 2# 34.188 0.631 0.993 4# 36.350 0.552 0.997 8# 34.423 0.662 0.994 9# 36.914 0.513 0.999 表 3 各煤样瓦斯放散初速度
Table 3 Initial velocity of gas emission of each coal sample
煤层 瓦斯放散初速度/mmHg 2# 12 4# 16 8# 15 9# 18 注:1 mmHg=133.3224 Pa。 -
[1] 王恩元,张国锐,张超林,等. 我国煤与瓦斯突出防治理论技术研究进展与展望[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(1):297−322. WANG Enyuan, ZHANG Guorui, ZHANG Chaolin, et al. Research progress and prospect on theory and technology for coal and gas outburst control and protection in China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(1): 297−322.
[2] 蒋静宇,程远平,张硕. 低阶煤孔隙结构定量表征及瓦斯吸附放散特性[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(10):3221−3233. JIANG Jingyu, CHENG Yuanping, ZHANG Shuo. Quantitative characterization of pore structure and gas adsorption and diffusion properties of low-rank coal[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(10): 3221−3233.
[3] WANG Z Y, CHENG Y P, QI Y X, et al. Experimental study of pore structure and fractal characteristics of pulverized intact coal and tectonic coal by low temperature nitrogen adsorption[J]. Powder Technology, 2019, 350: 15−25. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2019.03.030
[4] MOHANTY M M, PALK B. Sorption behavior of coal for implication in coal bed methane an overview[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2017, 27(2): 307−314. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2017.01.014
[5] BARRER R M. Diffusion in and through solids[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1951.
[6] 张群,杨锡禄. 平衡水分条件下煤对甲烷的等温吸附特性研究[J]. 煤炭学报,1999(6):566−570. ZHANG Qun, YANG Xilu. Isothermal adsorption of coals on methane under equilibrium moisture[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 1999(6): 566−570.
[7] 王恩元,何学秋. 瓦斯气体在煤体中的吸附过程及其动力学机理[J]. 江苏煤炭,1996(3):17−19. [8] 李一波,郑万成,王凤双. 煤样粒径对煤吸附常数及瓦斯放散初速度的影响[J]. 煤矿安全,2013,44(1):5−8. doi: 10.13347/j.cnki.mkaq.2013.01.010 LI Yibo, ZHENG Wancheng, WANG Fengshuang. The effect of coal sample particle size on coal adsorption constants and initial speed of methane diffusing[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2013, 44(1): 5−8. doi: 10.13347/j.cnki.mkaq.2013.01.010
[9] 李志强,王司建,刘彦伟,等. 基于动扩散系数新扩散模型的构造煤瓦斯扩散机理[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2015,44(5):836−842. LI Zhiqiang, WANG Sijian, LIU Yanwei, et al. Mechanism of gas diffusion in tectonic coal based on a diffusion model with dynamic diffusion coefficient[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2015, 44(5): 836−842.
[10] 贾东旭,孙景来. 不同变质程度煤体破碎度对瓦斯放散初速度的影响[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2013,41(8):68−70. doi: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2013.08.021 JIA Dongxu, SUN Jinglai. Fragmentation of different metamorphic degree coal affected toinitial velocity of gas emission[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2013, 41(8): 68−70. doi: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2013.08.021
[11] 李成武,薛洪来,刘文彪. 承压煤体瓦斯解吸-扩散特性实验研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(3):717−723. LI Chengwu, XUE Honglai, LIU Wenbiao. Experimental study on gas diffusion in coal under stress[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2018, 43(3): 717−723.
[12] SI L L, ZHANG H T, WEI J P, et al. Modeling and experiment for effective diffusion coefficient of gas in water-saturated coal[J]. Fuel, 2021, 284: 118887. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.118887
[13] LIU X F, WANG L K, KONG X G, et al. Role of pore irregularity in methane desorption capacity of coking coal[J]. Fuel, 2022, 314: 123037. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.123037
[14] 张强. 变质程度对突出煤体瓦斯吸附/解吸特性影响研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2018. [15] 安丰华,贾宏福,刘军. 煤孔隙特征对瓦斯放散初速度影响研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(9):82−87. doi: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2021.09.012 AN Fenghua, JIA Hongfu, LIU Jun. Study on influence of coal pore characteristics on initial velocity of gas emission[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49(9): 82−87. doi: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2021.09.012
[16] 郝从猛. 下向钻孔机械破煤造穴快速卸压增透机制及瓦斯抽采技术研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2021. [17] 宋孝忠. 烟煤显微组分组图像自动识别技术研究及应用[D]. 北京: 煤炭科学研究总院, 2020. [18] JU Y, REN Z Y, ZHENG J T, et al. Quantitative visualization methods for continuous evolution of three-dimensional discontinuous structures and stress field in subsurface rock mass induced by excavation and construction-An overview[J]. Engineering Geology, 2020, 265: 105443. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105443
[19] 李学龙. 裂隙煤岩动态破裂行为与冲击失稳机制研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2017.



 下载:
下载: