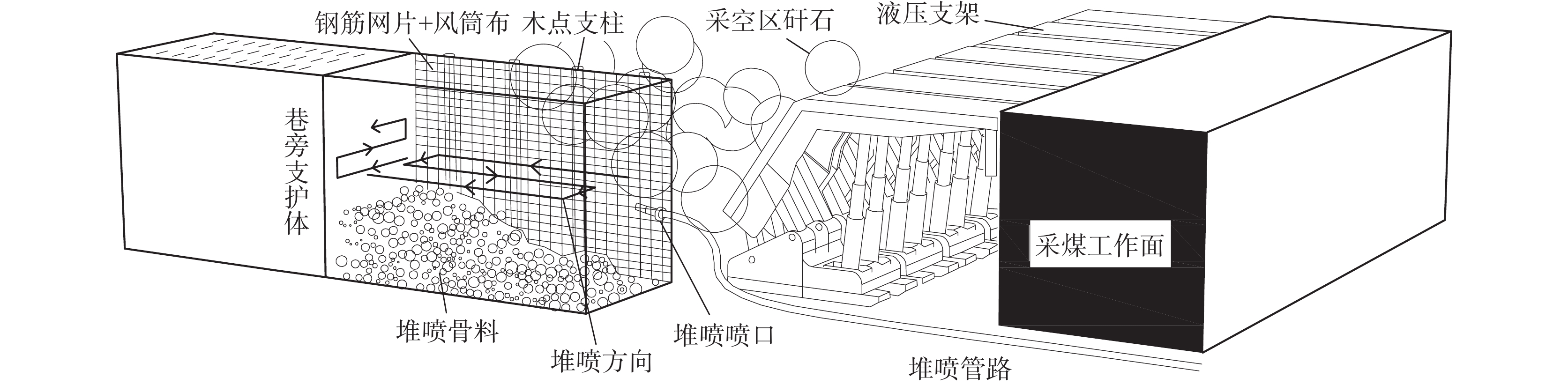
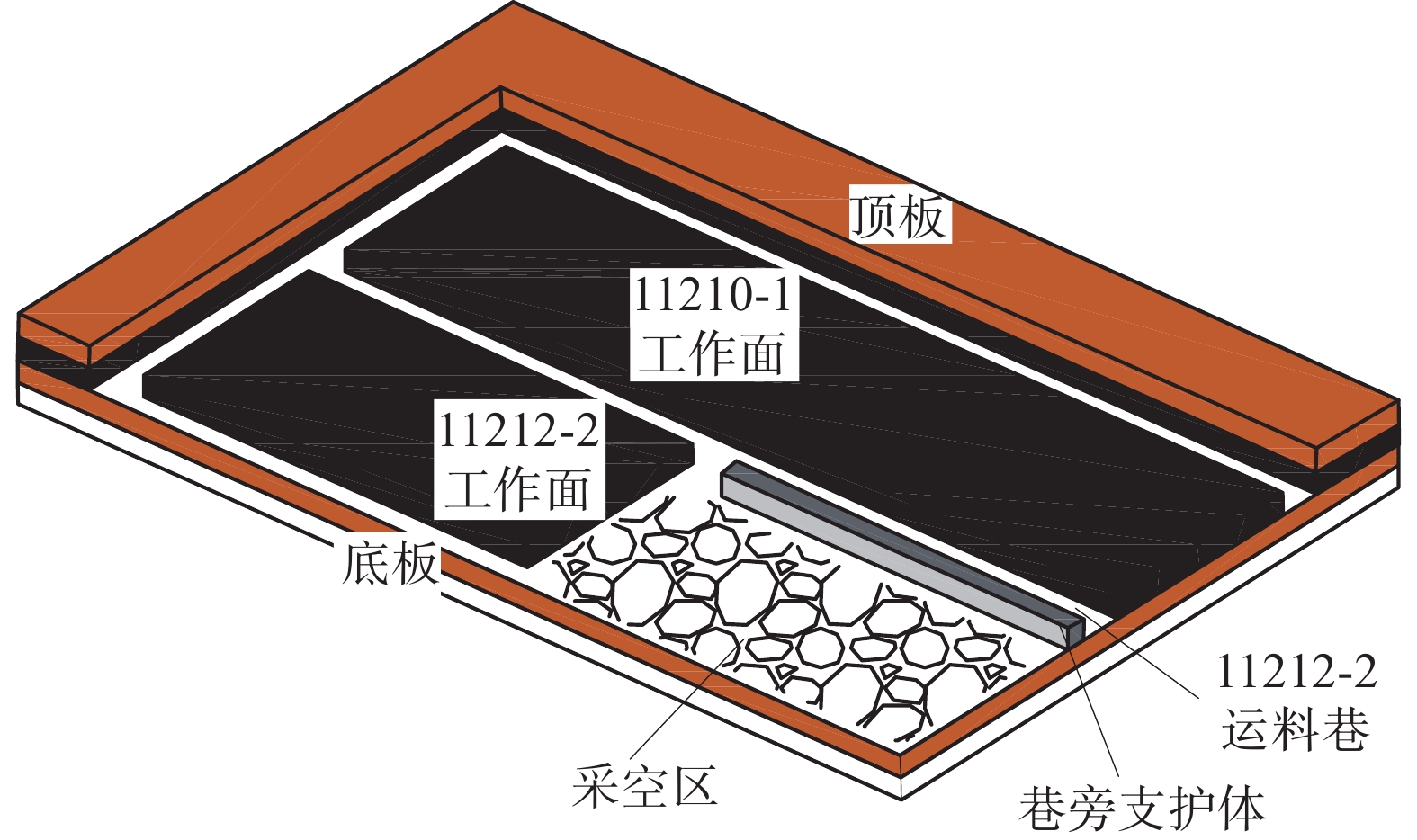
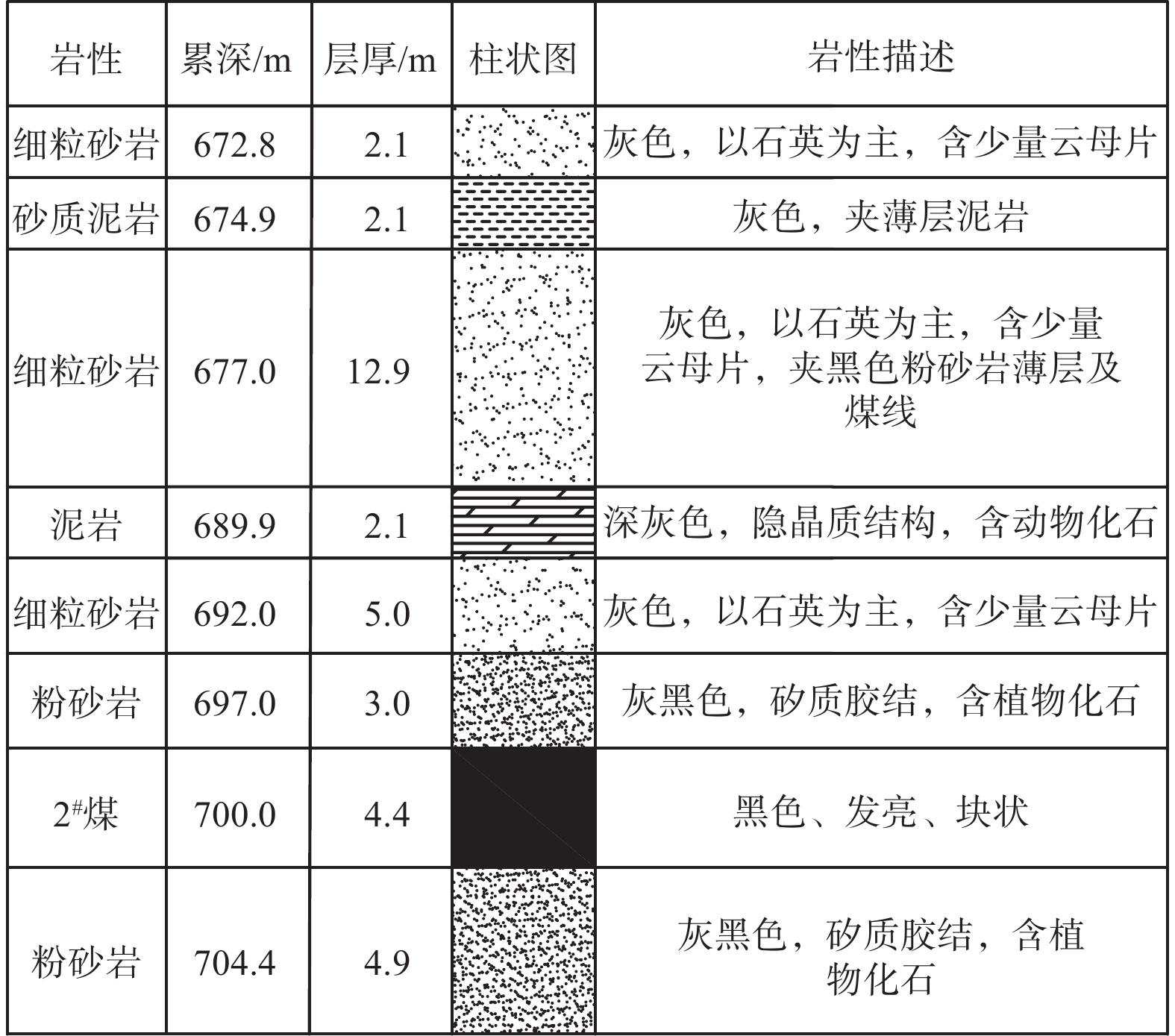
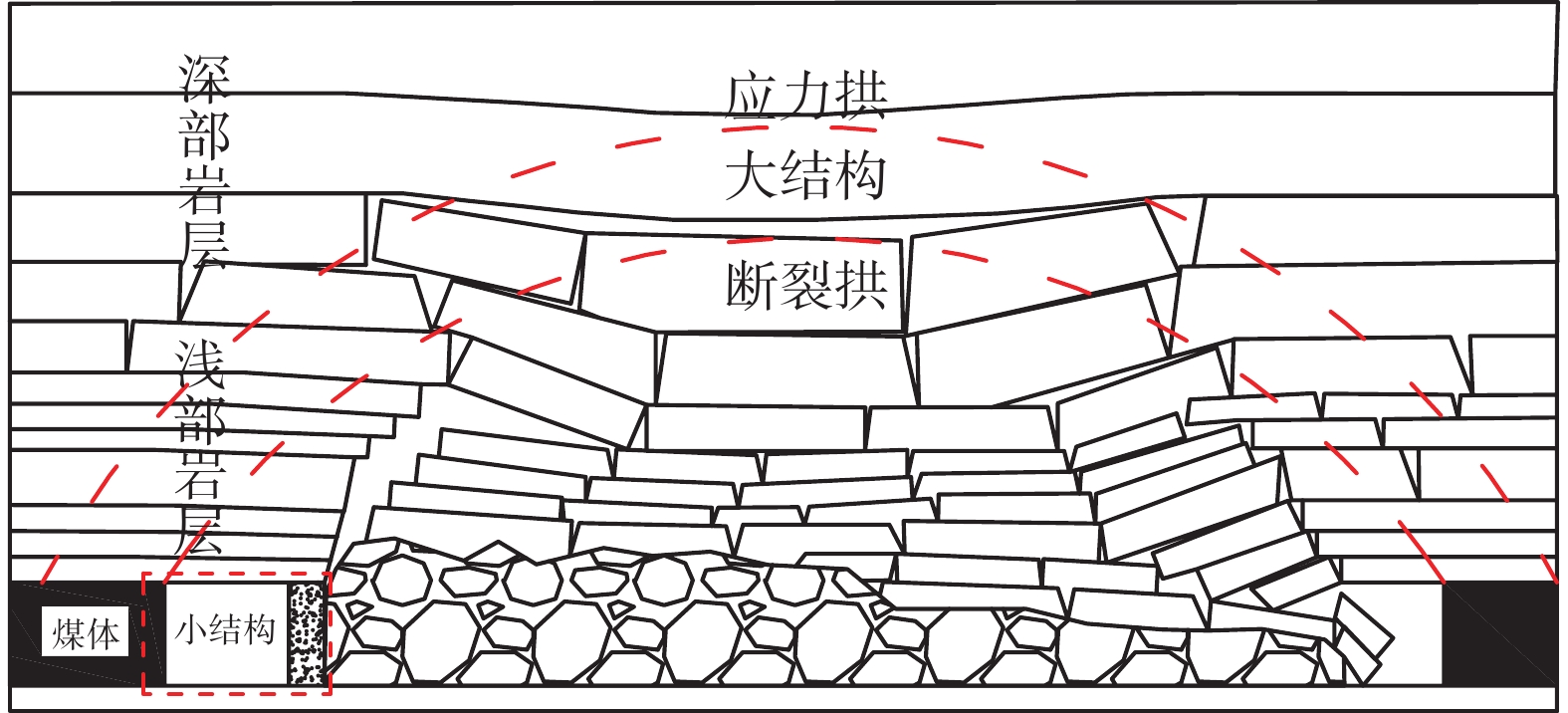
Stability analysis of roadside support body for gob-side entry retaining by heap spraying technology
-
摘要:
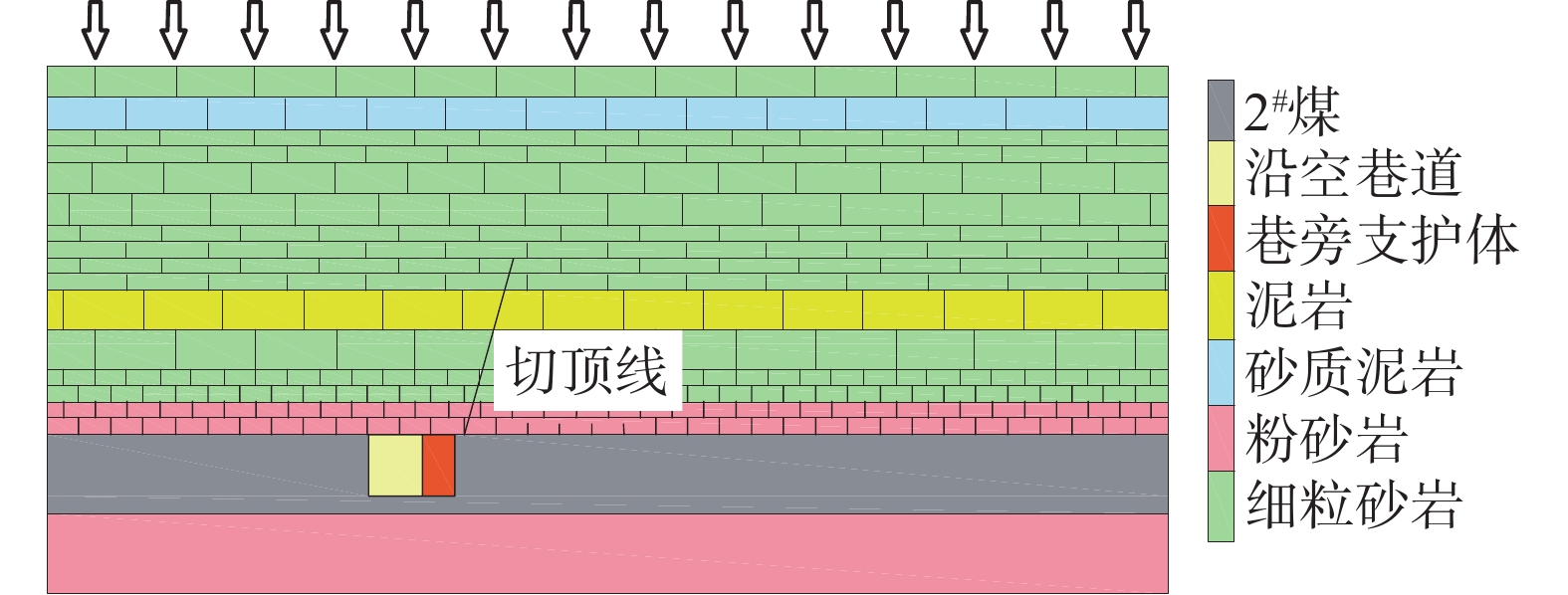
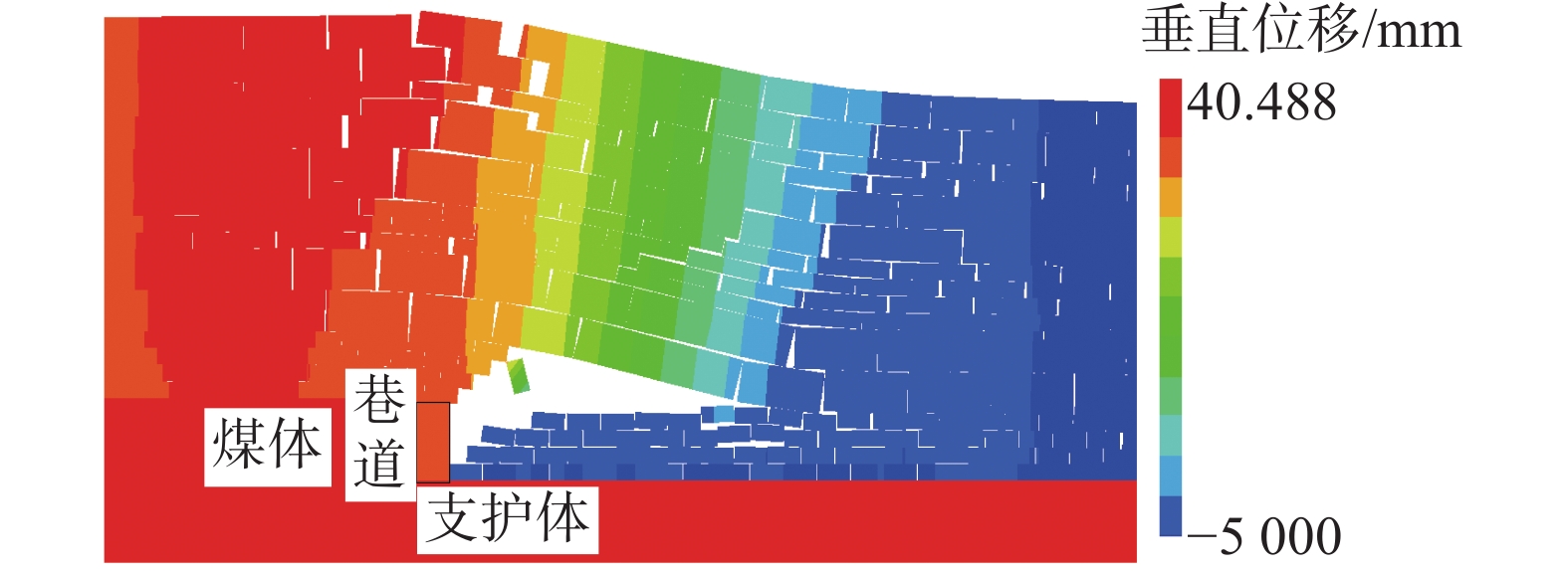
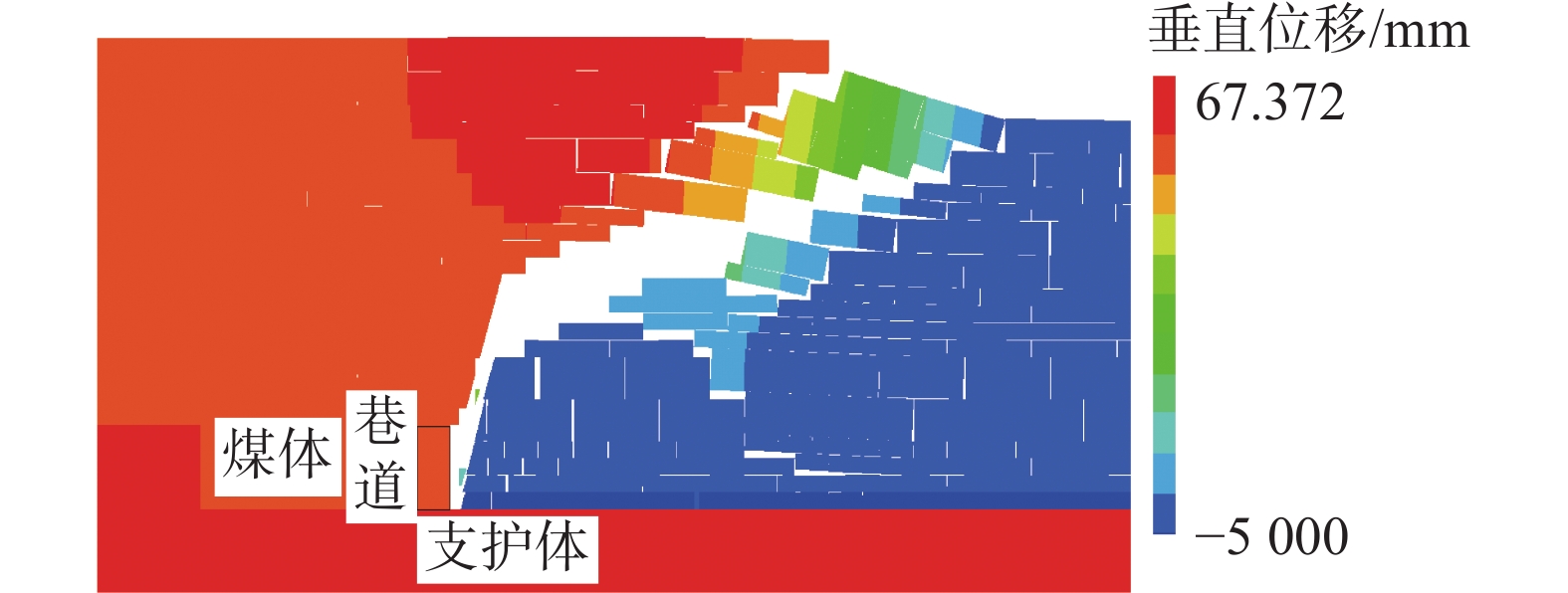
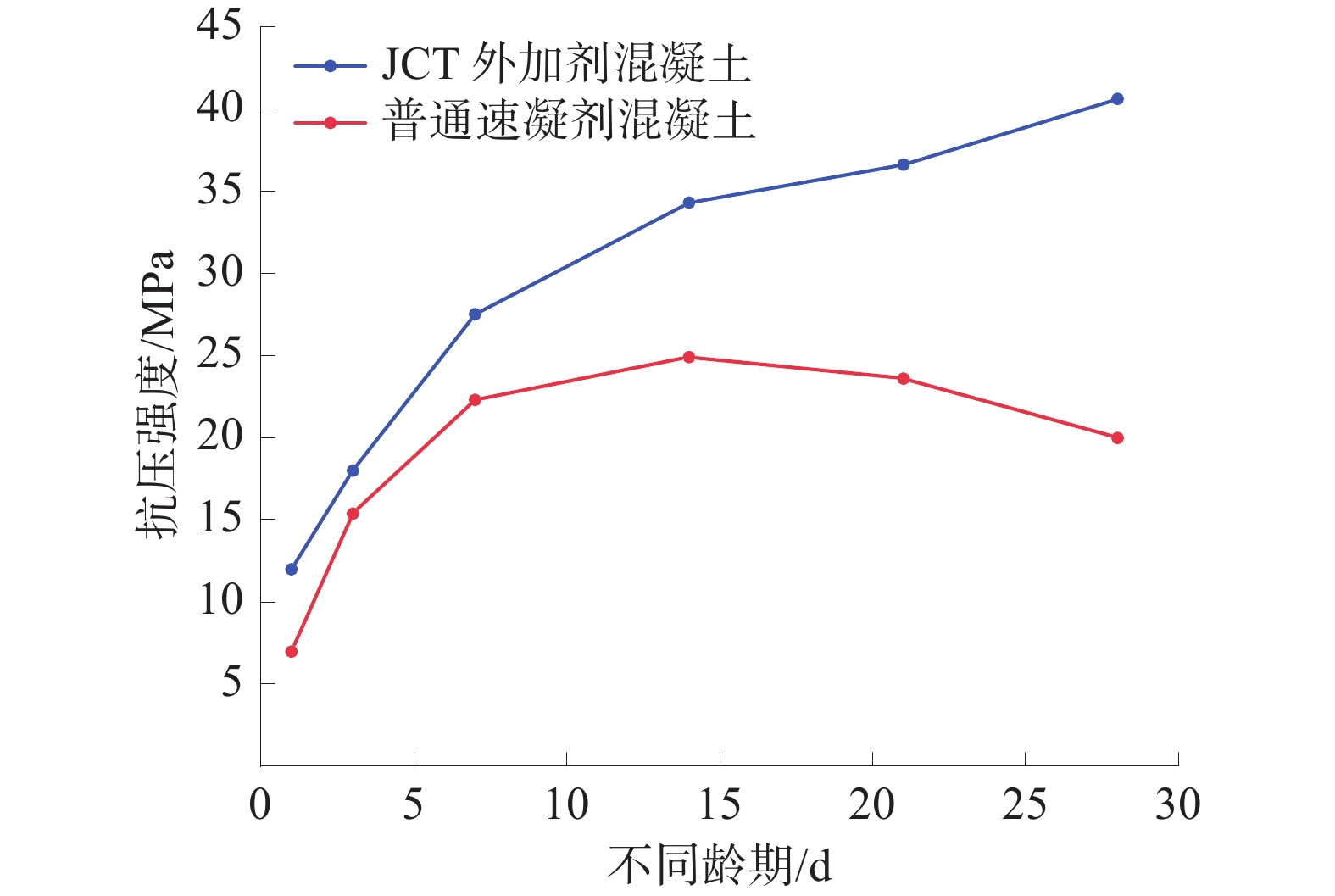
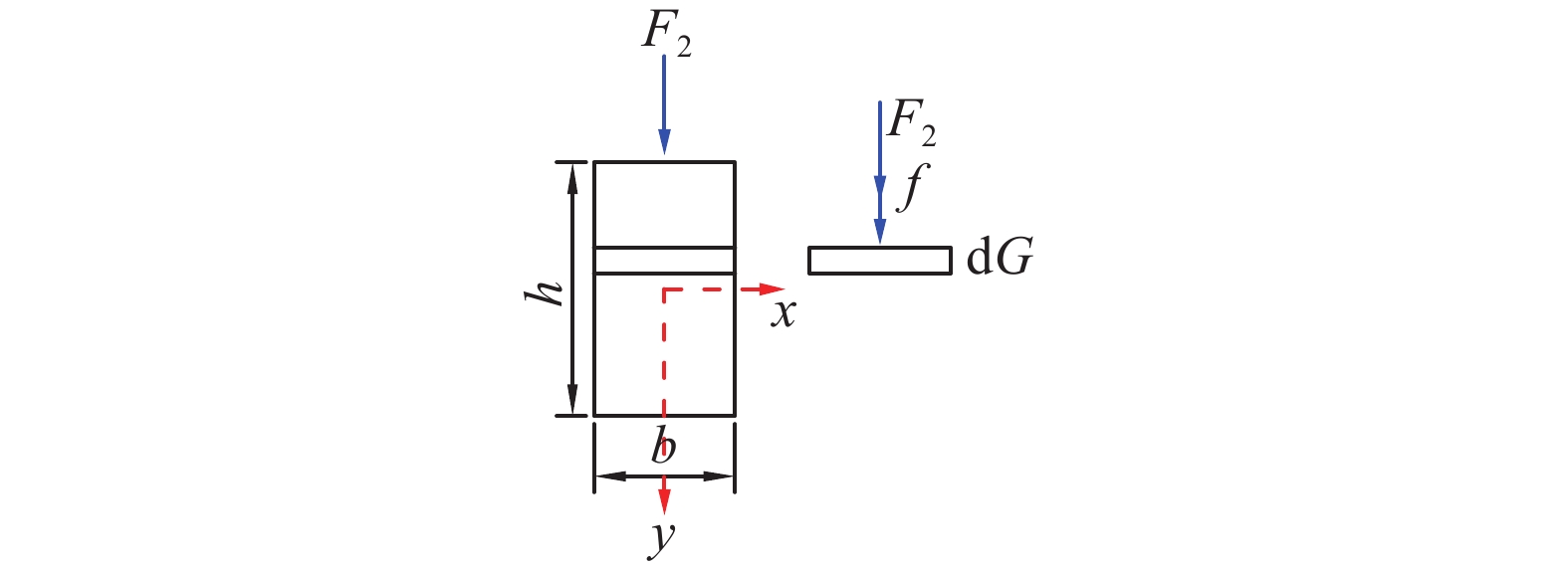
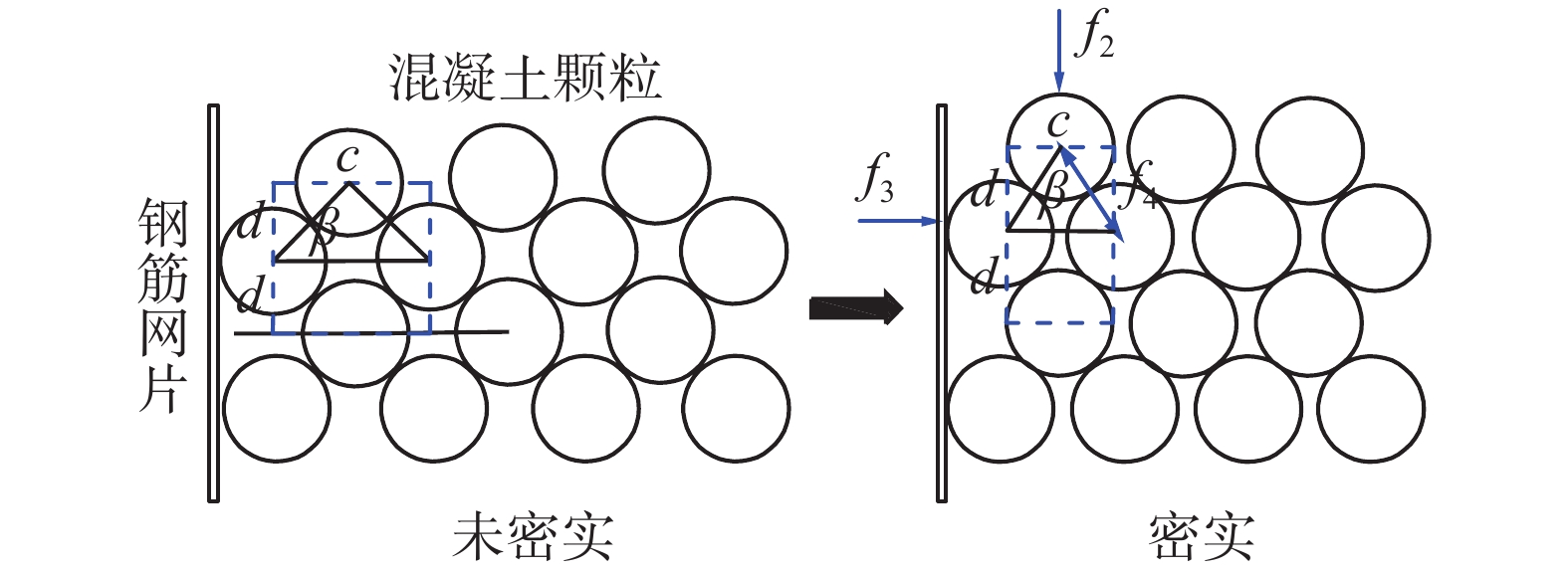
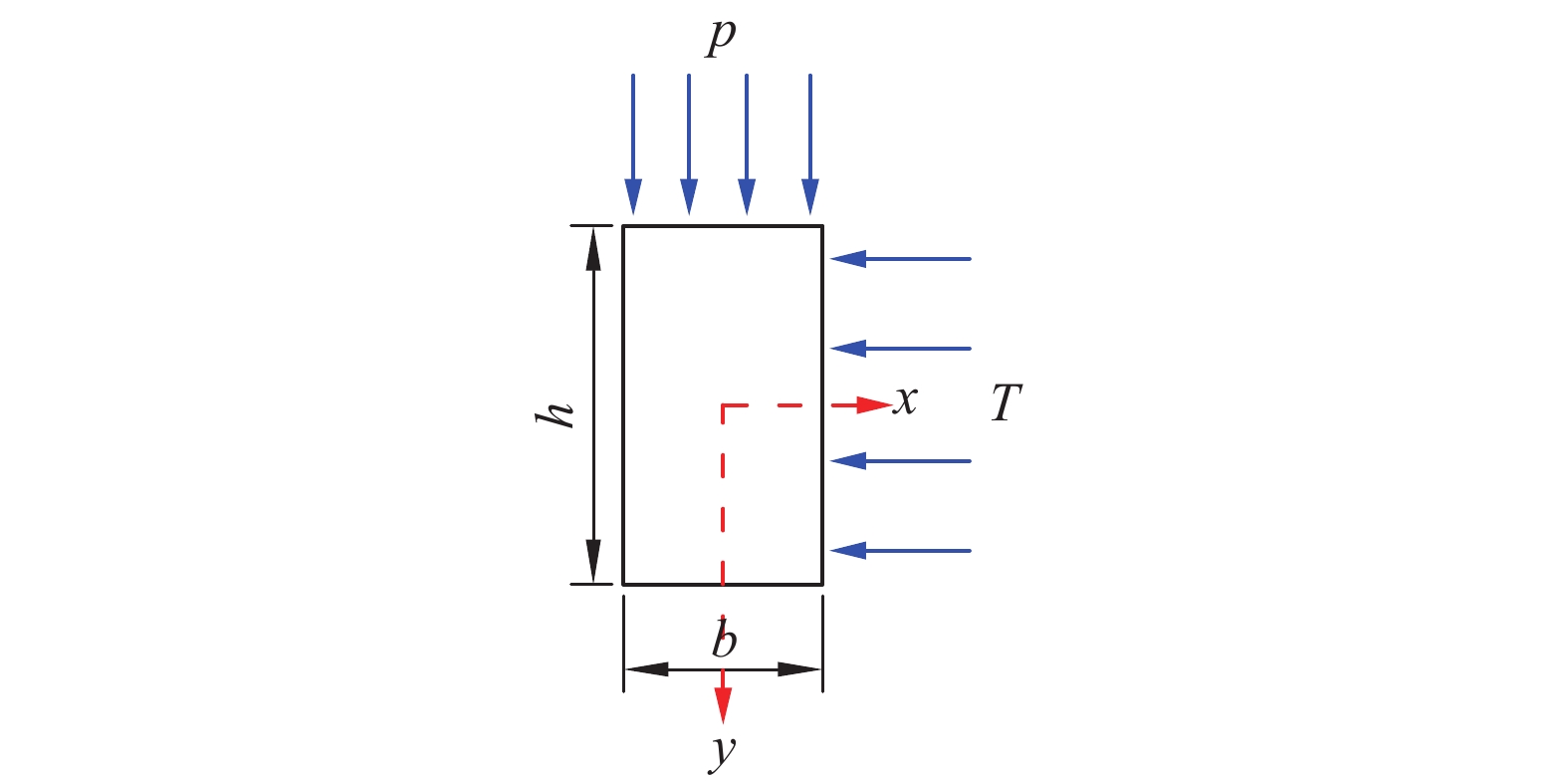
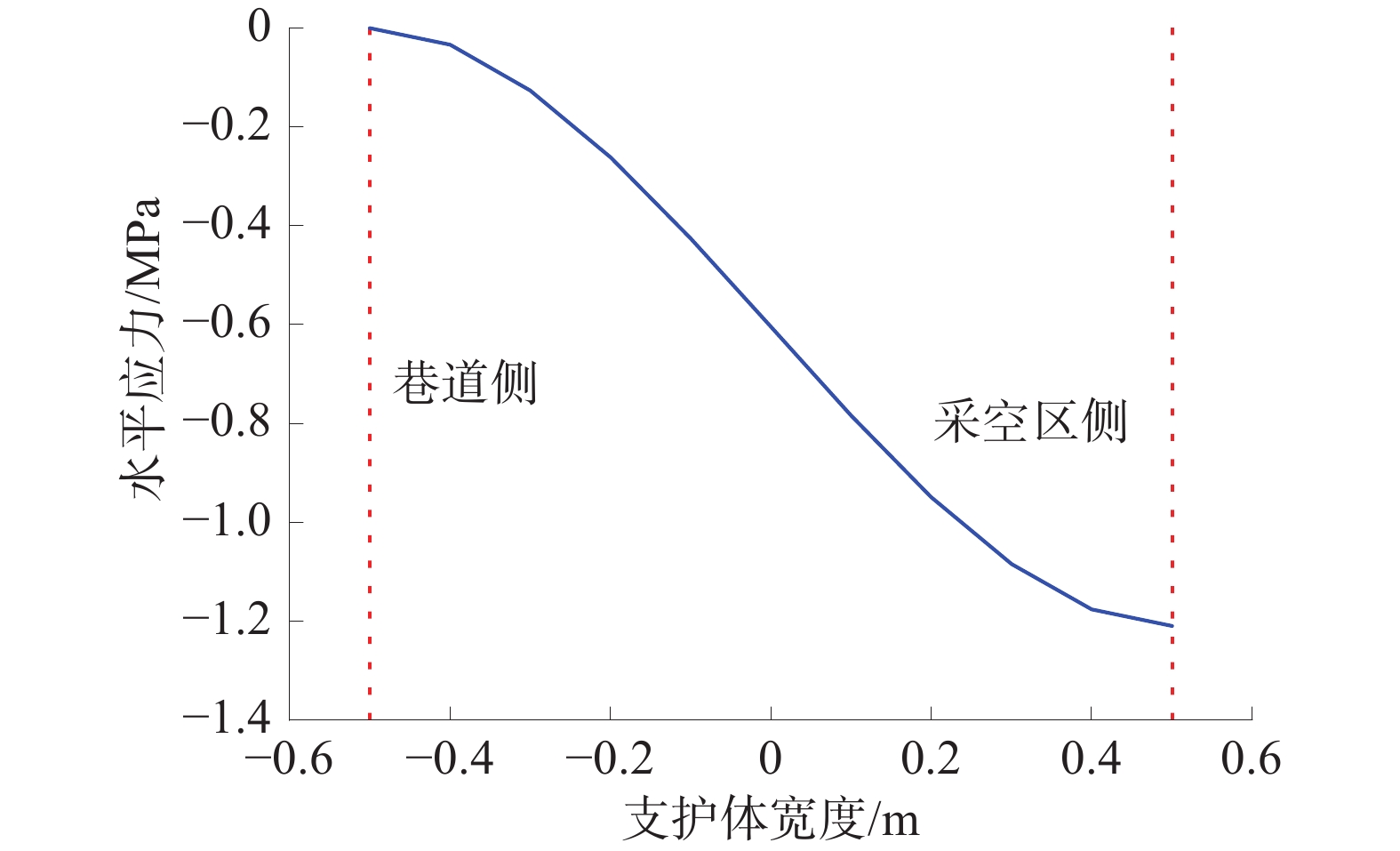
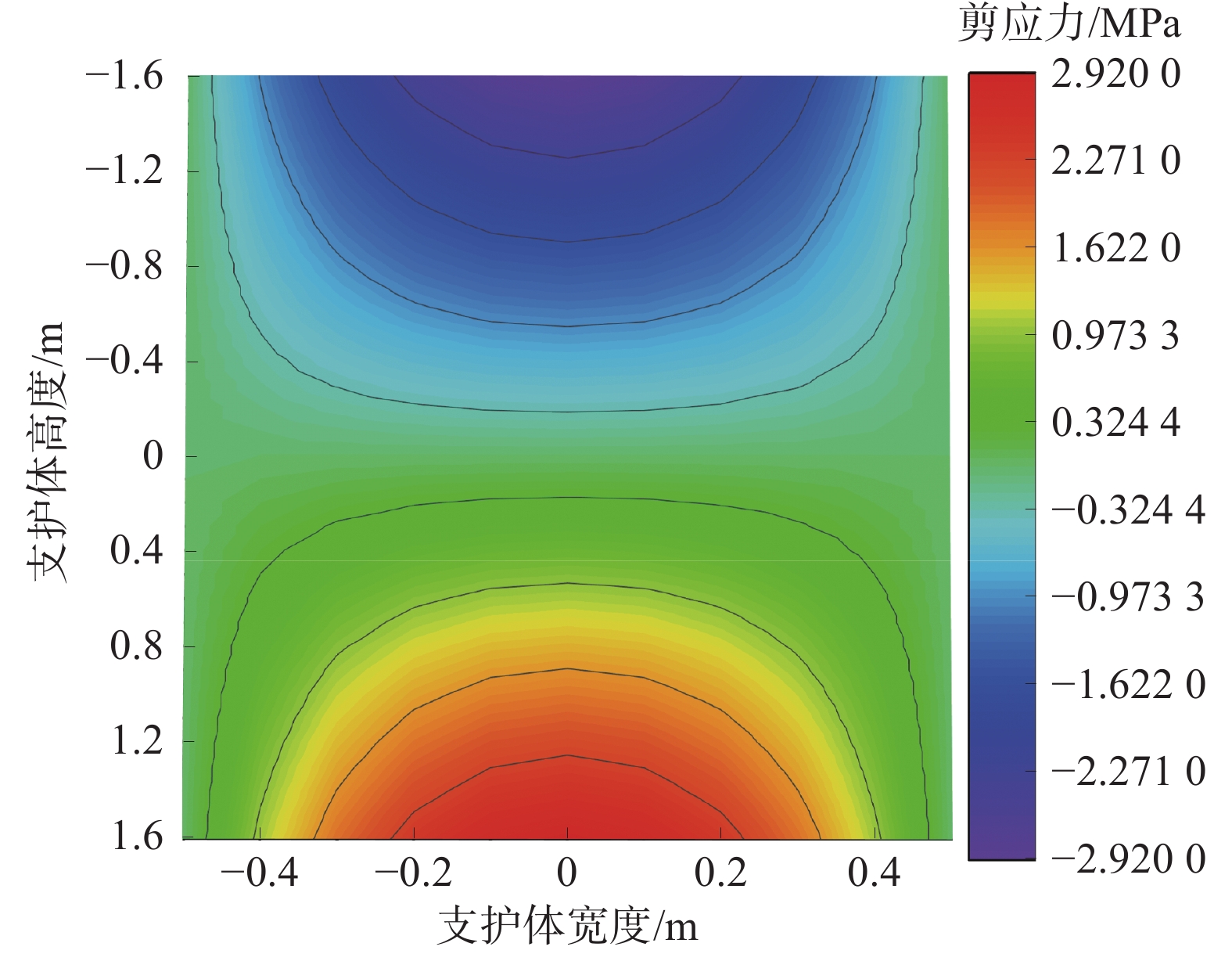
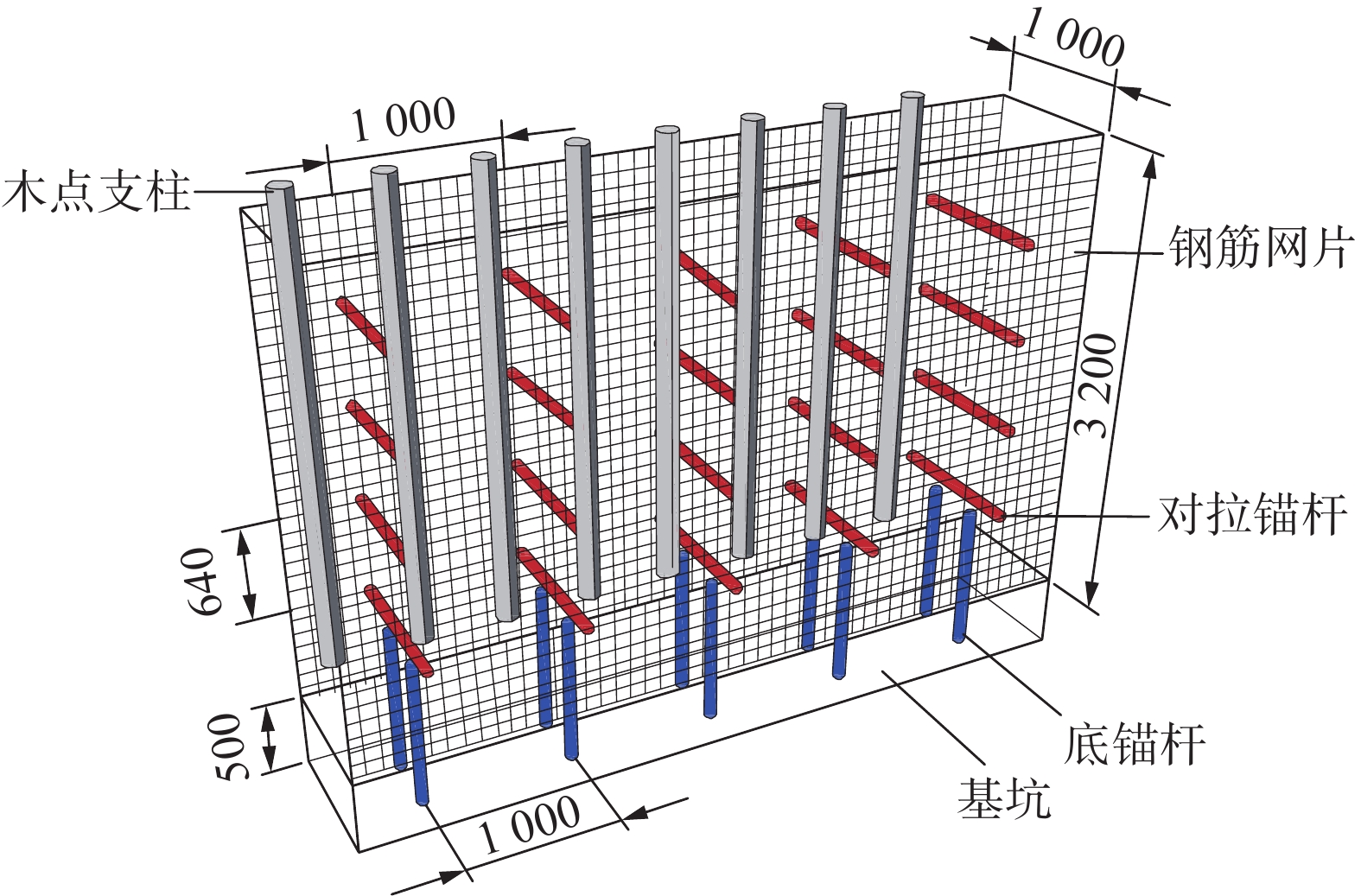
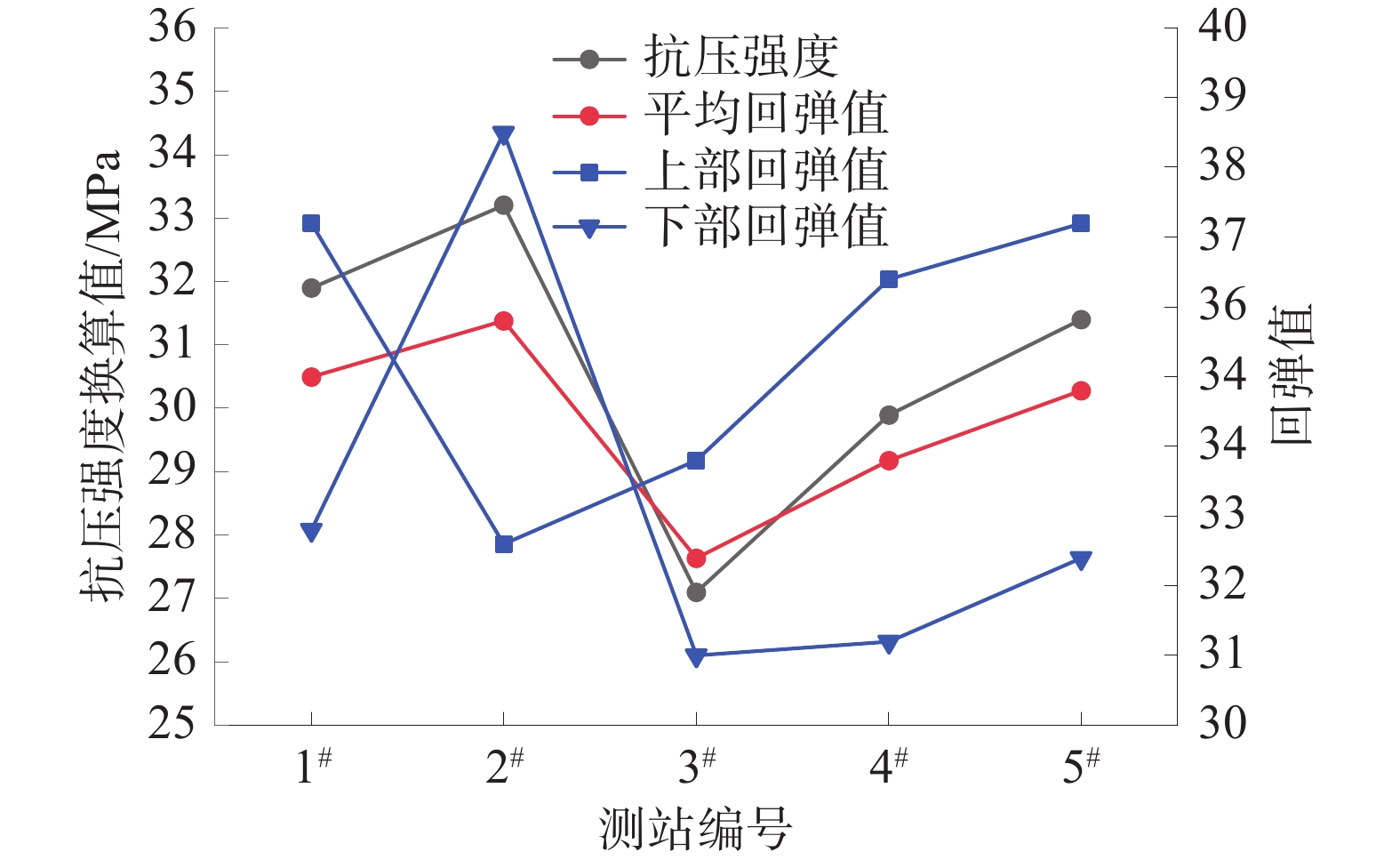
为研究堆喷工艺对沿空留巷的适应性,基于11212-2工作面沿空留巷的工程实际,运用数值模拟、物理试验、理论分析的方法,对堆喷工艺巷旁支护体进行了研究。结果表明:切顶条件下,支护体顶板围岩破断特征呈倒梯形,力学模型计算得到的支护体支护阻力为4.16 MPa;数值模拟说明切顶条件下,顶板围岩垮落充分,支护体上部围岩破断边缘类似倒梯形,验证了前面分析的合理性;堆喷工艺混凝土材料具有早强性,1 d强度达到12 MPa,增阻速度快,28 d达到40.6 MPa,最终强度高并且没有强度损失;前期支护体容易发生横向变形,内置钢筋网片结构后,计算减少78%横向变形;后期支护体存在拉压应力区和剪应力区,容易发生破坏,设计内置对拉钢筋,底部施加锚杆。
Abstract:In order to study the adaptability of heap spraying technology to gob-side entry retaining, based on the engineering practice of gob-side entry retaining in 11212-2 working face, the support body beside the gob-side entry of the heap spraying technology was studied by means of numerical simulation, physical test and theoretical analysis. The results are as follows: under the condition of roof cutting, the fracture characteristic of the surrounding rock on the roof of the support body is an inverted trapezoid. The support resistance of the support body calcucated by a mechaincal model is 4.16 MPa. The numerical simulation shows that under the condition of roof cutting, the surrounding rock of the roof collapses sufficiently, and the broken edge of the surrounding rock on the upper part of the support body is similar to an inverted trapezoid, which verifies the rationality of the previous analysis. The sprayed concrete material has early strength, the 1 d strength reaches 12 MPa, the resistance increase speed is fast, and the 28 d strength reaches 40.6 MPa, the final strength is high and there is no strength loss. In the early stage, the support body is prone to lateral deformation. After the steel mesh structure is built in, the lateral deformation is reduced by 78%. In the later stage, there are tension-compression stress areas and shear stress areas in the support body, which are prone to damage. The design has built-in tension steel bars and bolts are applied at the bottom.
-
煤矿粉尘是煤矿开采、运输及储存过程中伴随煤和岩石破碎而产生的混合性粉尘,主要含有煤尘、岩尘以及少量其他物质[1]。煤矿粉尘可分为呼吸性粉尘和非呼吸性粉尘。一般说来,小于5 μm的尘粒能到达并沉积于肺泡中,故称为呼吸性粉尘,是引起尘肺的主要尘粒[2-3]。在《国家职业病防治规划(2016—2020年)》《安全生产“十三五”规划》及《“健康中国2030”规划纲要》中,粉尘职业危害防治已被列入国家战略与重大需求[4]。口罩等防护用具作为煤矿环境劳动者个体防护的最后一道防线,其滤料的研发具有重要的研究意义。
防护用器具对气溶胶的过滤理论以纤维层空气过滤理论为基础,经过十几年的发展,纤维过滤理论已逐渐趋于成熟[5]。纤维过滤过程中,捕集颗粒物的过滤作用有:扩散效应、拦截效应、惯性效应、重力效应、和静电吸附[6]。与传统过滤介质相比,静电纺丝制备的纳米纤维膜具有优异的过滤性能、纤维直径小、孔隙率高、体积比显著的表面积压降[7-8]。目前,许多种高分子量聚合物,包括聚丙烯腈(PAN)、聚苯乙烯(PS)、聚乙烯醇(PVA)和聚丙烯(PP)等[9],已通过静电纺丝加工成纳米纤维,用于空气过滤器。聚对苯二甲酸乙二酯(PET)是世界上规模最大、应用最广泛的合成纤维,是由对苯二甲酸(TA)和乙二醇(EG)脱水酯化得到的半结晶热塑性饱和聚酯[10-12]。虽然静电纺丝技术已有多年历史,但其在聚酯方面的应用还比较少。李静等[13]运用PET与含氟基团改性的SiO2共混进行静电纺丝,构建具有微纳复合结构的低表面能表面,具有优良的超疏水性;ZANDER等[14]使用塑料瓶回收并重新聚合PET,但所制备电纺过滤膜对500 nm以下的颗粒去除效果微乎其微。因此,亟须制备一种对粉尘同时具备高过滤效率和低阻力的滤料。此外,作为一种个体防护材料,呼吸过程中细菌的繁殖对人类健康有很大的影响,当前很少将抗菌性静电纺丝纳米纤维膜作为煤矿井下个体防护材料。为此,以静电纺丝技术为基础,将聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯和银纳米颗粒共混,以制备煤矿粉尘个体防护滤料(PET/Ag);利用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)对纤维形貌、分布以及表面孔隙进行表征,利用X射线光电子能谱(XPS)对纤维表面的化学性质及组成进行分析;实验研究了PET/Ag纳米纤维膜作为个体防护材料的可行性,测试了其纤维膜的防水透湿性能、过滤性能以及抗菌性能。
1. 制备方法及实验测试
1)试剂。选用的试剂为:聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯(PET,99%)、二氯甲烷(DCM,99.5%,化学纯)、三氟乙酸(TFA,分析纯)、AgNO3溶液(0.1 mol/L)、N,N-二甲基甲酰胺(DMF,99.5%,分析纯)、聚乙烯吡咯烷酮(PVP,分析纯)。
2)纳米纤维膜的制备。将PET颗粒溶解于三氟乙酸和二氯甲烷的混合溶剂中(V(TFA)∶V(DCM)=4∶1),在室温下搅拌溶解成均一的PET纺丝溶液。通过液相还原法[15]制备银纳米粒子(AgNPs)。在pH=8的条件下,DMF作为还原剂,聚乙烯吡咯烷酮(PVP)作为保护剂,在DMF中煮沸AgNO3制备银纳米颗粒。将纳米银在去离子水中超声溶解1 h,与PET颗粒共混制备纺丝液,纳米银的含量为0.4%,然后在室温下磁力搅拌10 h,获得质量分数分别为8%、10%、12%的均一纺丝溶液。使用HZ-12静电纺丝机进行纳米纤维膜的制备。将制备的纺丝溶液置于5 mL注射器中,并使用注射泵以1 mL/h的速率推出。针头与20 kV高压电源相连。在静电纺丝过程中,针头与收集器之间的距离保持在15 cm,滚筒转速为100 r/min,温度保持在(25±2)℃,相对湿度为(35±5)%。控制纺丝时间为1、2、3 h,得到不同厚度的PET/Ag纳米纤维膜。
3)性能表征。通过扫描电子显微镜(SEM)(JSM-6360LV)观察纳米纤维膜的形态。将待测样品用导电胶带粘贴在样品台上,经喷金处理后,放入扫描电镜样品室,在10 kV加速电压下,观察纤维膜的微观形貌。在SEM图像中选择100根纳米纤维,使用图像处理软件(Image-Pro Plus)绘制纤维直径分布直方图,并计算纳米纤维平均直径;通过射线光电子能谱(XPS)(ESCALAB 250)测定电子的结合能,对纤维膜样品表面的化学性质及组成进行分析,了解其元素组成。通过水接触角测试仪(Dataphysics DCAT21)在室温和45%湿度条件下进行测试,水滴在纤维膜表面稳定后测定其接触角大小。
4)透湿性能测试。使用WPT-301水蒸气透过率测试仪测量材料的润湿性。在38 ℃、20% RH的条件下对每个样品进行3次重复测量。水蒸气透过率(WVP)由式(1)计算:
$$ {\mathrm{WVP}} = \frac{{\Delta w}}{t} \cdot \frac{x}{{A \cdot \Delta p}} $$ (1) 式中:Δw为质量变化,g;t为时间;x为膜的厚度,m;A为膜样品面积,m2;Δp 为38 ℃下通过膜的蒸汽压差,kPa。
5)过滤性能测试。使用LZC-K1型滤料综合测试仪对纳米纤维膜进行过滤性能测试,该仪器在计算纤维膜的过滤效率的同时还可通过传感器得出气流时的压阻值。过滤效率和品质因子由式(2)和式(3)计算。所得数据为3次测量的平均值和标准偏差。
$$ \eta = \frac{{N_1 - N_2}}{{N_1}} \times 100\% $$ (2) $$ {\mathrm{QF}} = \frac{{ - \ln (1 - \eta )}}{{\Delta p_1}} $$ (3) 式中:η为过滤效率;N1、N2分别为在通过纳米纤维膜之前和之后的气溶胶颗粒的数量;QF为品质因子;Δp1为相应压阻值。
6)抑菌性能测试。选择大肠杆菌(ATCC 25922)和金黄色葡萄球菌(ATCC 25923)作为实验微生物。首先,将制备的营养肉汁琼脂倒在无菌培养皿上,待其凝固,将大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌培养液(各0.5 mL)均匀涂在琼脂平板上;然后将纤维膜均匀切割成直径为1 cm的圆形,将掺杂AgNPs的样品和对照样品(PET膜)轻轻地放置在固化琼脂板上;最后将培养板在37 ℃下培养18 h,通过1个清晰的细菌抑菌圈直径来鉴定和评估抗菌活性,所得抑菌圈直径由图像处理软件进行量化。实验重复进行3次。
2. 实验结果讨论
2.1 纳米纤维膜的形态与结构
不同质量分数纺丝液所纺PET/Ag纳米纤维膜的SEM电镜图片如图1所示;通过射线光电子能谱(XPS)测定电子的结合能对PET和PET/Ag纳米纤维膜表面的元素组成进行分析得出的结果如图2所示。
由图1可知:通过调节纺丝液的质量分数,可以精确地控制纳米纤维膜的纤维径,而纤维直径的形态几乎不受影响,纤维间自由搭接,没有出现粘连现象,纤维间空隙较小,孔隙数目多,结构明显,单个纤维粗细均匀,没有出现串珠结构,纤维间无规则交织排列在一起,形成错综排列的网状结构[16-17]。纤维直径分布图显示了随机选取的100根纤维的直径大小分布,在1 mL/h的纺丝速率下,纳米纤维平均直径从质量分数8%时的298 nm增加到质量分数10%时的424 nm,到12%时的836 nm。纺丝液质量分数为8%的纤维膜的直径较小,主要集中在250~300 nm,纤维间空隙较小;纺丝液质量分数为10%的纤维膜的直径主要集中在400~450 nm;纺丝液质量分数为12%纤维膜的直径较大,主要集中在700~800 nm,纤维间空隙也相对较大。
由图2可以看出:PET纳米纤维膜表面的主要由C、O元素的峰非常明显,峰值分别对应284.6、531.5 eV;而PET/Ag的测试结果在284.6、367.8、531.5 eV处观察到3个峰,分别对应于C、Ag和O元素的峰, 367.8 eV处峰的出现说明Ag+还原成AgNPs并成功负载到PET膜上。相比之下,没有AgNPs负载的PET膜中没有出现Ag 3d峰。
2.2 纳米纤维膜的疏水性表征
质量分数为8%、10%、12%的PET/Ag纺丝液纺丝2 h后纤维膜表面水接触角变化情况如图3所示。
由图3可知:对不同质量分数的PET/Ag膜,水接触角可以在较长时间内保持不变,表现为较好的疏水性;质量分数为8%、10%、12%PET/Ag纤维膜表面水接触角分别为133.88°、131.51°、132.04°。水接触角测试结果表明PET/Ag 膜具有较强的疏水性。
2.3 透湿性分析
随着电纺时间的增加,PET/Ag纤维无规则交织排布,纤维的密集度不断增加,纤维间的空气流通通道愈加曲折,孔隙则不断减小[18]。不同质量分数的纺丝液在不同纺丝时间下纳米纤维膜的水蒸气透过量如图4所示。
纺丝液质量分数影响纤维直径大小,纺丝时间影响纳米纤维膜的厚度,而纤维直径和厚度都影响了纳米纤维膜的水蒸气流通路径。随着纺丝液质量分数的增加,PET/Ag纳米纤维膜的水蒸气透过量呈增加趋势,这可能是由于纺丝液质量分数影响了纤维直径的大小,较大的纤维直径有利于形成较大的孔隙,使水蒸气流通更加通畅;随着纺丝时间的增加,PET/Ag纳米纤维膜的水蒸气透过量呈减小趋势,这可能是由于纺丝时间影响了纳米纤维膜的厚度,较大的厚度会使纤维间孔隙通路变长,水蒸气流通路径更加曲折,阻力更大[19]。从PET/Ag纳米纤维膜的透湿性能来看,纺丝液质量分数为12%、纺丝1 h的纳米纤维膜透湿性最好,高达
9727.55 g/(m2·d),纺丝液浓度为8%、纺丝3 h的纳米纤维膜透湿性最差,为2069.82 g/(m2·d)。2.4 过滤性能测试分析
煤矿中大多数煤尘颗粒的直径在1~10 μm之间,LZC-K1型滤料综合测试仪能够产生粒径范围为0.3~10 μm的NaCl气溶胶颗粒,具有更强的穿透性[20-21]。因此,以NaCl颗粒作为测试介质,在85 L/min空气流量下更严苛地反映滤料的过滤效率。实验分别测试的不同纺丝时间下的PET/Ag纳米纤维膜对空气中颗粒物的过滤效果如图5所示;不同纺丝时间下的PET/Ag纳米纤维膜在过滤过程中的压阻值如图6所示。
由图5可以看出:纺丝液质量分数越高,PET/Ag纳米纤维膜的过滤效率越好,且随着纺丝时间的延长,不同质量分数的纺丝液所纺纳米纤维膜的颗粒物过滤效率呈增加趋势;其中,纺丝液质量分数为10%和12%的PET/Ag纳米纤维膜在纺丝3 h后的过滤效率都可达99.99%,纺丝液质量分数为8%的PET/Ag纳米纤维膜过滤效率为98.75%。结果表明:在一定时间内,增加纺丝时间,纳米纤维膜不断堆积,厚度随之增加,纤维之间气流通道更加曲折,纤维膜对颗粒物的过滤效果有所提升。因此,通过控制静电纺丝时间可以得到不同厚度,对颗粒物有不同过滤效果的材料。
由图6可以看出:纺丝液质量分数越高,PET/Ag纳米纤维膜的压阻值越高,且随着纺丝时间的延长,不同纺丝液浓度所纺纳米纤维膜的压阻值呈增加趋势;当纺丝时间为1 h时,8%、10%、12% PET纤维膜的压阻分别为78.2、85.1、90.2 Pa;当纺丝时间增加到3 h时,3种PET/Ag纳米纤维膜的压阻值分别为159.3、175.6、200.1 Pa。
结合不同PET/Ag纳米纤维膜的过滤效率,通过公式计算相对应的品质因子。通过计算可知:纺丝液质量分数为12%,纺丝时间为3 h时,PET/Ag纳米纤维膜的品质因子最低,为0.013 Pa−1;纺丝液质量分数为10%,纺丝时间为2 h时,PET/Ag纳米纤维膜的品质因子最高,为0.041 Pa−1,该条件下纳米纤维膜的水蒸气透过量为同时7 101.37 g/(m2·d),透湿性较好。
纺丝液质量分数为10%,纺丝时间为2 h时PET/Ag纳米纤维膜在15~85 L/min不同空气流量下的过滤效率、压阻和品质因子见表1。
表 1 不同空气流量下PET/Ag纳米纤维膜的过滤效率、压阻和品质因子Table 1. Filtration efficiency, pressure drop and quality factor of PET/Ag nanofiber membrane under different air flow conditions空气流量/(L·min−1) 过滤效率/% 压阻/Pa 品质因数/Pa−1 15 99.99 32.5 0.084 30 99.42 49.8 0.075 45 98.19 60.6 0.069 60 96.78 89.4 0.056 85 95.14 90.7 0.041 由表1可以看出:随着空气流量增加,流速增大,纳米纤维对颗粒物的拦截、扩散作用减弱,纳米纤维膜的过滤效率逐渐降低;并且流速增强时压力差随之增大,压阻随之升高,品质因子也呈降低趋势,综合性能随流量的增加表现得越来越差,即流量越大,口罩的防护性能和舒适性均随流量增加而变差。
2.5 抑菌性能分析
利用琼脂扩散法评价所制备滤料对微生物的作用效果如图7所示。
由图7(a)可以看出,在37 ℃下培养18 h后,PET纳米纤维膜对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌没有显示出任何抗菌活性,说明PET膜不具备抗菌性能。由图7(b)可以看出共混静电纺丝法制备的PET/Ag纳米纤维膜对2种细菌都显示出明显的抗菌活性,其中,对大肠杆菌的抑菌区直径最大,为18.12 mm,对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑菌区为13.25 mm;这可能是由于金黄色葡萄球菌的细胞壁较厚,蛋白质含量较少,因此其抑菌区直径要比大肠杆菌小。结果表明:PET/Ag纳米纤维膜对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌细菌都具备明显的抗菌活性,作为空气过滤材料能够有效抑制细菌繁殖,在个人防护领域具有广阔的应用前景。
3. 结 语
1)SEM图显示,PET/Ag电纺纤维较细,纤维形貌良好,纤维之间无规则排列在一起,没有出现粘连现象,纤维膜孔隙结构明显,单个纤维粗细均匀,没有出现串珠结构。通过调节纺丝液的质量分数,可以精确地控制纳米纤维膜的纤维直径,而纤维直径的形态几乎不受影响,纤维间自由搭接无规则交织排列在一起,形成错综排列的网状结构。XPS表明Ag+还原成AgNPs并成功负载到PET膜上。
2)水接触角测量表明PET/Ag纳米纤维膜表现为较好的疏水性。从PET/Ag纳米纤维膜的透湿性能来看,纺丝液质量分数和纺丝时间都影响了纳米纤维膜的水蒸气流通路径。纺丝液质量分数为12%、纺丝1 h的纳米纤维膜透湿性最好,高达9 727.55 g/(m2·d)。
3)增加纺丝时间,纳米纤维膜不断堆积,厚度随之增加,纤维之间气流通道更加曲折,纤维膜对颗粒物的过滤效果有所提升。因此,通过控制静电纺丝时间可以得到不同厚度,对颗粒物有不同过滤效果的材料。
4)随空气流量从15 L/min增加到85 L/min, PET/Ag纳米纤维对颗粒物的拦截、扩散作用减弱,纳米纤维膜的过滤效率逐渐降低。并且流速增强时压力差增大,压阻随之升高,综合性能随流量的增加表现得越来越差。
5)PET/Ag纳米纤维膜对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌细菌都具备明显的抗菌活性,作为空气过滤材料能够有效抑制细菌繁殖,在个人防护领域具有广阔的应用前景。
-
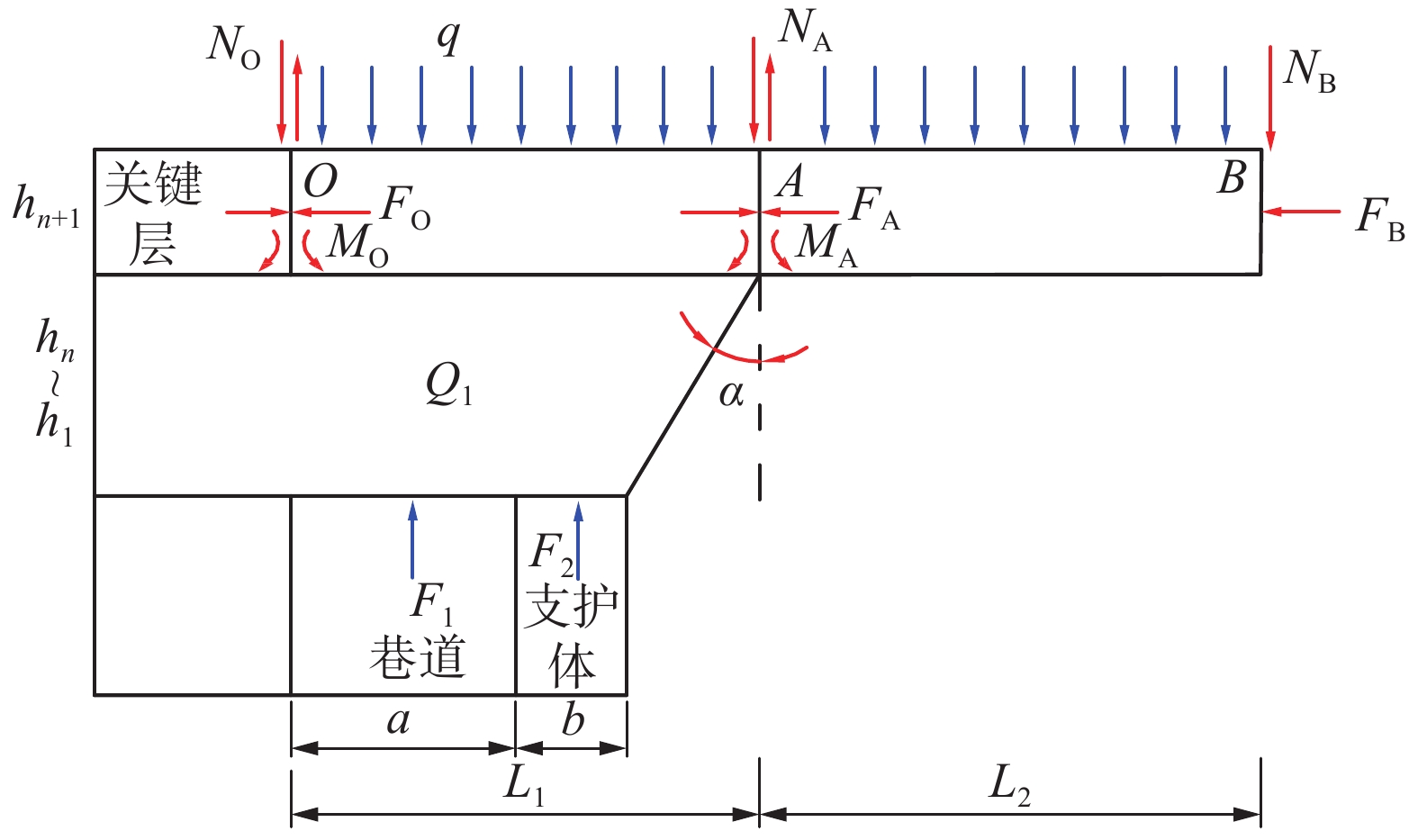
表 1 岩层节理面参数
Table 1 Rock joint surface parameters
岩性 法向刚度/
GPa切向刚度/
GPa内摩擦角/
(°)黏聚力/
MPa抗拉强度/
MPa2#煤 1.62 0.61 20 1.12 1.10 泥岩 3.00 1.20 21 2.40 1.60 砂质泥岩 3.20 1.60 23 2.24 1.92 粉砂岩 4.10 2.00 24 2.08 1.82 细粒砂岩 4.40 2.60 27 2.24 2.48 -
[1] 杨继元,陶志勇,王晓利,等. 榆家梁煤矿沿空留巷装备及工艺[J]. 陕西煤炭,2014,33(4):74−76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-749X.2014.04.025 YANG Jiyuan, TAO Zhiyong, WANG Xiaoli, et al. The equipment and technology of gob-side entry retaining in Yujialiang Coal Mine[J]. Shaanxi Coal, 2014, 33(4): 74−76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-749X.2014.04.025
[2] 惠兴田,李伟. 预支撑袋铸混凝土沿空留巷技术研究[J]. 矿业安全与环保,2015,42(5):58−62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4495.2015.05.015 HUI Xingtian, LI Wei. Study on gob-side entry retaining technology of bag-casting concrete with pre-support[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection, 2015, 42(5): 58−62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4495.2015.05.015
[3] 黄万朋,高延法,文志杰,等. 钢管混凝土支柱巷旁支护沿空留巷技术研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2015,44(4):604-611. HUANG Wanpeng, GAO Yanfa, WEN Zhijie, et al. Technology of gob-side entry retaining using concrete filled steel tubular column as roadside supporting[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2015, 44(4): 604-611.
[4] 王军,高延法,何晓升,等. 沿空留巷巷旁支护参数分析与钢管混凝土墩柱支护技术研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2015,32(6):943−949. doi: 10.13545/j.cnki.jmse.2015.06.012 WANG Jun, GAO Yanfa, HE Xiaosheng, et al. The analysis of roadside supporting parameters and the support technology in the concrete filled steel tubular column in goaf-side entry retaining[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2015, 32(6): 943−949. doi: 10.13545/j.cnki.jmse.2015.06.012
[5] LUAN H, JIANG Y, LIN H, et al. Development of a new gob-side entry-retaining approach and its application[J]. Sustainability, 2018, 10(2): 1−15. doi: 10.3390/su10020470
[6] NING J, WANG J, BU T, et al. An innovative support structure for gob-side entry retention in steep coal seam mining[J]. Minerals, 2017, 7(5): 75. doi: 10.3390/min7050075
[7] 张泽瑞. 高地应力下沿空留巷巷旁支护高延性混凝土材料研究[D]. 太原:太原理工大学,2021. [8] 李化敏. 沿空留巷顶板岩层控制设计[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2000(5):651−654. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2000.05.023 LI Huamin. Control design of roof rocks for gob-side en-try[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2000(5): 651−654. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2000.05.023
[9] 李迎富,华心祝. 沿空留巷上覆岩层关键块稳定性力学分析及巷旁充填体宽度确定[J]. 岩土力学,2012,33(4):1134−1140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2012.04.026 LI Yingfu, HUA Xinzhu. Mechanical analysis of stability of key blocks of overlying strata for gob-side entry retaining and calculating width of roadside backfill[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(4): 1134−1140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2012.04.026
[10] 漆泰岳,郭育光,侯朝炯. 沿空留巷整体浇注护巷带适应性研究[J]. 煤炭学报,1999(3):34−38. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.1999.03.008 QI Taiyue, GUO Yuguang, HOU Chaojiong. Study on the adaptability for the pack-fillings of the gob-side entry retaining[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 1999(3): 34−38. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.1999.03.008
[11] 韩昌良,张农,王晓卿,等. 沿空留巷砌块式墙体结构承载特性及应用研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2013,30(5):673−678. HAN Changliang, ZHANG Nong, WANG Xiaoqing, et al. Bearing behavior of block wall structure in gob-side entry retaining and its application[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2013, 30(5): 673−678.
[12] 冯国瑞,任玉琦,王朋飞,等. 厚煤层综放沿空留巷巷旁充填体应力分布及变形特征研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2019,36(6):1109−1119. FENG Guorui, REN Yuqi, WANG Pengfei, et al. Stress distribution and deformation characteristics of road side backfill body for gob-side entry of fully-mechanized caving in thick coal seam[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2019, 36(6): 1109−1119.
[13] 王晓卿,张农,阚甲广,等. 大尺度混凝土巷旁墙体开裂机理及控制对策[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2017,46(2):237−243. doi: 10.13247/j.cnki.jcumt.000639 WANG Xiaoqing, ZHANG Nong, KAN Jiaguang, et al. Cracking mechanism and control strategy of concrete roadside wall with large scale[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 2017, 46(2): 237−243. doi: 10.13247/j.cnki.jcumt.000639
[14] 郝兵元,任兴云,李铁良,等. 一种用于煤矿井下的堆喷混凝土快速筑墙方法:CN108825301B[P]. 2020-07-03. [15] 李迎富,华心祝. 沿空留巷围岩结构稳定性力学分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2017,42(9):2262−2269. LI Yingfu, HUA Xinzhu. Mechanical analysis on the stability of surrounding rock structure of gob-side entry retaining[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2017, 42(9): 2262−2269.
[16] 秦义岭. 固体充填沿空留巷巷旁支护体稳定性及注浆加固研究[D]. 邯郸:河北工程大学,2021. [17] 李迎富,华心祝,蔡瑞春. 沿空留巷关键块的稳定性力学分析及工程应用[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2012,29(3):357−364. LI Yingfu, HUA Xinzhu, CAI Ruichun. Mechanics analysis on the stability of key block in the gob-side entry retaining and engineering application[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2012, 29(3): 357−364.
[18] 胡明明,周辉,张勇慧,等. 宽断面预留墩柱沿空留巷墩柱支护阻力计算研究[J]. 岩土力学,2018,39(11):4218−4225. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2017.0332 HU Mingming, ZHOU Hui, ZHANG Yonghui, et al. Analysis of supporting resistance of reserved pier column for gob-side entry retaining in wide roadway[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(11): 4218−4225. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2017.0332
[19] 周保精,徐金海,倪海敏. 小宽高比充填体沿空留巷稳定性研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2010,35(S1):33−37. ZHOU Baojing, XU Jinhai, NI Haimin. The small asp-ect ratio backfill gob-side entry retaining stability[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2010, 35(S1): 33−37.
[20] 龚鹏. 深部大采高矸石充填综采沿空留巷围岩变形机理及应用[D]. 徐州:中国矿业大学,2018.




 下载:
下载: