Gas content prediction simulation of unsaturated low coalification coal cores
-
摘要:
为对比分析长焰煤储层煤心现场解吸动态与数值模拟解吸动态,实测了新疆某井长焰煤煤心现场含气量,构建了吸附气欠饱和储层煤心数值模型,并基于此分析了损失气量计算方法。结果表明:构建的吸附气欠饱和煤心(吸附气饱和度54.77%、77.51%、99.79%)数值模型计算的损失气量、解吸气量和残余气量与现场测试相应结果接近(误差<10.12%),可近似反映欠饱和储层煤心含气量构成;对于构建的含气饱和(吸附气饱和与游离气饱和)储层煤心数值模型,损失气时间与解吸时间和的平方根与解吸初期累计解吸气量回归分析预测损失气量误差较大,已不适用;相同损失气时间下,饱和煤心损失气占比(18.64%)高于吸附气欠饱和煤心损失气占比(11.95%),饱和煤心解吸气占比(80.90%)低于吸附气欠饱和煤心解吸气占比(87.32%),饱和煤心残余气占比(0.46%)低于吸附气欠饱和煤心残余气占比(0.63%)。
Abstract:In order to compare and analyze the on-site desorption performance and numerical simulation desorption performance of low coalification reservoir coal core, the on-site gas content of coal core of a coalbed methane (CBM) well in Xinjiang was measured, and a numerical model of coal core in undersaturated reservoir with adsorbed gas is established, and based on this, the loss gas content calculation method was analyzed. The results show that the loss gas, desorption gas and residual gas contents calculated by the desorption numerical model of the unsaturated coal core (adsorbed gas saturation 54.77%, 77.51%, and 99.79%, respectively) were close to the corresponding results measured in the field (error<10.12%), which could reflect the gas content composition of the unsaturated coal core. For the coal core numerical model of gas bearing saturated reservoir (both adsorbed gas and free gas are saturated), the regression analysis method of the square root of the sum of gas loss time and desorption time and the cumulative desorption gas volume at the initial stage of desorption had a large error in predicting the loss gas content, which was no longer applicable. Under the same gas loss time condition, the proportion of loss gas content of saturated coal core (18.64%) was higher than that of unsaturated coal core (11.95%), the proportion of desorption gas of oversaturated coal core (80.90%) was lower than that of unsaturated coal core (87.32%), and the proportion of residual gas of oversaturated coal core (0.46%) was lower than that of unsaturated coal core (0.63%).
-
Keywords:
- coalbed methane /
- gas content /
- low coalification coal /
- loss gas content /
- coal core
-
煤储层含气量是煤层气资源勘探测试的关键参数[1-4],也是表征煤储层开发潜力和确保矿井瓦斯安全的关键参数之一[4-11];煤储层含气量测试可为煤层气资源量、储量估算和煤层气开发设计提供重要依据[4]。煤储层含气量测值的不准确性是导致煤层气资源计算出现差异的重要原因[12]。现阶段,我国煤炭资源勘探和煤层气资源勘探开发煤层含气量测试方法主要采用GB/T19559—2021《煤层气含量测定方法》提供的解吸法及其矫正计算方法[13-17],其中损失气量计算采用最初10个地面实测解吸气量数据,由损失气时间与解吸时间和的平方根与累计解吸气量之间线性关系倒推零时间解吸气量得出。
应用上述方法,多年来我国在多个煤层气勘探开发区块获取了大量含气量数据。然而,目前煤层含气量计算仍有以下不足:吸附气欠饱和储层现场含气量测试的可靠性缺乏数值模拟验证,特别是损失气量估算的准确程度尚未有数值模型验证;另外,上述方法对含气饱和储层(吸附气、游离气均饱和,下同)含气量测试的准确性尚不清楚,饱和储层煤心含气量测试过程模拟尚未开展。基于此,选取新疆低煤化煤(本次为长焰煤)煤心为研究对象,构建了储层煤心含气量解吸-扩散数值模型,并通过模型计算分析了吸附气欠饱和与含气饱和储层煤心解吸动态,对比分析了数值模型与现场测试损失气量、解吸气量、残余气量构成的差异性,以期为我国低煤化储层煤层气勘探提供含气性分析新思路。
1. 测试方法
1.1 现场含气量相关测试
按照GB/T 19559—2021《煤层气含量测定方法》国家标准提供的方法,开展自然煤心采样,记录采样及装样时间,开展自然解吸气量连续测试和残余气测试;根据GB/T 19560—2008《煤的高压等温吸附试验方法》、GB/T 212—2008《煤的工业分析方法》等开展煤等温吸附实验和工业分析。现场煤心采样及上述相关工作开展于新疆某长焰煤储层煤层气开发先导试验区,煤心样品为长焰煤(属于低煤化度煤),且煤心对应的实测含气饱和度分别为54.77%、77.51%、99.79%。工业分析及煤岩组分分析成果见表1。
表 1 煤心工业分析及煤岩组分分析成果Table 1. Coal core industrial analysis and coal rock composition analysis results样品编号 直径/mm 长度/cm 宏观煤岩类型 平均镜质组最大反射率/% 水分/% 灰分/% 挥发分/% 镜质组组分/% 惰质组组分/% 壳质组组分/% BF-1 63.0 26.8 半亮煤 0.60 0.90 11.77 43.79 84.2 14.8 1.0 BF-2 60.1 30.0 半亮煤 0.61 0.86 22.08 40.45 79.6 19.4 1.0 BF-3 61.0 34.0 半亮煤 0.67 1.12 13.40 37.17 78.6 25.5 1.0 1.2 储层煤心含气量测试数值模拟流程
1.2.1 假设条件
煤是一种复杂的多孔介质,为了方便求解,通常对煤心样品做出以下假设:①煤屑由球形颗粒组成;②煤颗粒为均质、各向同性体;③CH4解吸-扩散遵从连续性原理;④扩散系数与浓度、时间和坐标无关;⑤煤屑瓦斯解吸为等温条件下的解吸过程;⑥煤心含气量测试过程中孔隙度不变。
1.2.2 控制方程
单位体积吸附气欠饱和储层煤心基质CH4质量可表述为(CH4全部吸附在煤基质表面,在储层压力条件下吸附解吸平衡,孔隙表面外不含游离CH4):
$$ {m}_{\mathrm{m}\mathrm{u}}={\varphi }_{\mathrm{u}\mathrm{n}}(1-{\phi }_{\mathrm{m}})\left(\dfrac{100-{M}_{\mathrm{a}\mathrm{d}}-{A}_{\mathrm{a}\mathrm{d}}}{100}\right)\dfrac{{V}_{\mathrm{L}}{p}_{\mathrm{m}}}{{p}_{\mathrm{m}}+{p}_{\mathrm{L}}}{\rho }_{\mathrm{c}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{l}}{\rho }_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{c}} $$ 式中:mmu为单位体积煤基质中赋存的瓦斯质量,g;φun为欠饱和储层含气饱和度,%;ϕm为基质孔隙度;Mad为空气干燥基水分含量,%;Aad为空气干燥基灰分产率,%;VL为朗缪尔体积,单分子层最大的吸附量,cm3/g;pm为基质孔隙中的CH4压力,MPa;pL为朗缪尔压力,吸附量为最大吸附量1/2时间的吸附平衡压力,MPa;ρcoal为煤视密度,kg/m3;ρsc为标准状态下的CH4密度,g/cm3。
煤心解吸至大气环境控制方程:
$$\begin{array}{c} \dfrac{\partial p}{\partial t}\left({\varphi }_{{\mathrm{un}}}\left(1-{\phi }_{{\mathrm{m}}}\right)\left(\dfrac{100-{{M}}_{\mathrm{a}\mathrm{d}}-{{A}}_{\mathrm{a}\mathrm{d}}}{100}\right)\dfrac{{V}_{{\mathrm{L}}}{p}_{{\mathrm{L}}}}{{\left(p+{p}_{{\mathrm{L}}}\right)}^{2}}{\rho }_{{\mathrm{coal}}}\dfrac{{M}_{{\mathrm{c}}}}{{V}_{{\mathrm{M}}}}\right)=\\ \nabla \left(\dfrac{{M}_{{\mathrm{c}}}}{RT}D\nabla p\right) \end{array} $$ 式中:t为时间,s;p为煤心孔隙气体压力,MPa;Mc为甲烷分子摩尔质量,kg/mol;VM为CH4分子摩尔体积,m3/mol;R为理想气体常数,J/(mol·K);T为煤层温度,K;D为扩散系数,10−9 m2/s。
单位体积饱和储层煤心基质CH4质量可表述为(CH4在煤基质表面吸附饱和,且在储层压力条件下游离CH4充满孔隙):
$$ \begin{array}{c} {m}_{{\mathrm{mo}}}=(1-{\phi }_{{\mathrm{m}}})\left(\dfrac{100-{{M}}_{\mathrm{a}\mathrm{d}}-{{A}}_{\mathrm{a}\mathrm{d}}}{100}\right)\dfrac{{V}_{{\mathrm{L}}}{p}_{{\mathrm{m}}}}{{p}_{{\mathrm{m}}}+{p}_{{\mathrm{L}}}}{\rho }_{{\mathrm{coal}}}{\rho }_{{\mathrm{sc}}}+\\ {\phi }_{{\mathrm{m}}}\dfrac{{M}_{{\mathrm{c}}}}{RT}{p}_{{\mathrm{m}}} \end{array} $$ 式中:mmo为初始条件下单位体积饱和储层煤心基质CH4质量,g。
饱和储层煤心含气饱和度:
$$ {\varphi }_{{\mathrm{m}}}=\dfrac{{m}_{{\mathrm{mo}}}}{(1-{\phi }_{{\mathrm{m}}})\left(\dfrac{100-{{M}}_{\mathrm{a}\mathrm{d}}-{{A}}_{\mathrm{a}\mathrm{d}}}{100}\right)\dfrac{{V}_{{\mathrm{L}}}{p}_{0}}{{p}_{0}+{p}_{{\mathrm{L}}}}{\rho }_{{\mathrm{coal}}}{\rho }_{{\mathrm{sc}}}} $$ 煤心扩散、解吸控制方程:
$$ \begin{array}{c} \dfrac{\partial p}{\partial t}\left(\left(1 - {\phi }_{{\mathrm{m}}}\right)\left(\dfrac{100 - {{M}}_{\mathrm{a}\mathrm{d}} - {{A}}_{\mathrm{d}}}{100}\right)\dfrac{{V}_{{\mathrm{L}}}{p}_{{\mathrm{L}}}}{{\left(p + {p}_{{\mathrm{L}}}\right)}^{2}}{\rho }_{{\mathrm{coal}}}\dfrac{{M}_{{\mathrm{c}}}}{{V}_{{\mathrm{M}}}} + {\phi }_{{\mathrm{m}}}\dfrac{{M}_{{\mathrm{c}}}}{RT}\right) =\\ \nabla \left(\dfrac{{M}_{{\mathrm{c}}}}{RT}D\nabla p\right) \end{array} $$ 1.2.3 几何模型和边界条件
几何模型为实际圆柱体煤心物理模型,几何尺寸与现场测量一致;初始煤心各点孔隙压力为根据煤层气井试井储层压力推算得出,由于解吸时煤心已与大气接触,认为边界条件煤心柱面和断面表面压力为大气压力0.1 MPa。煤心几何模型如图1。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 欠饱和储层煤心自然解吸测试与数值模拟
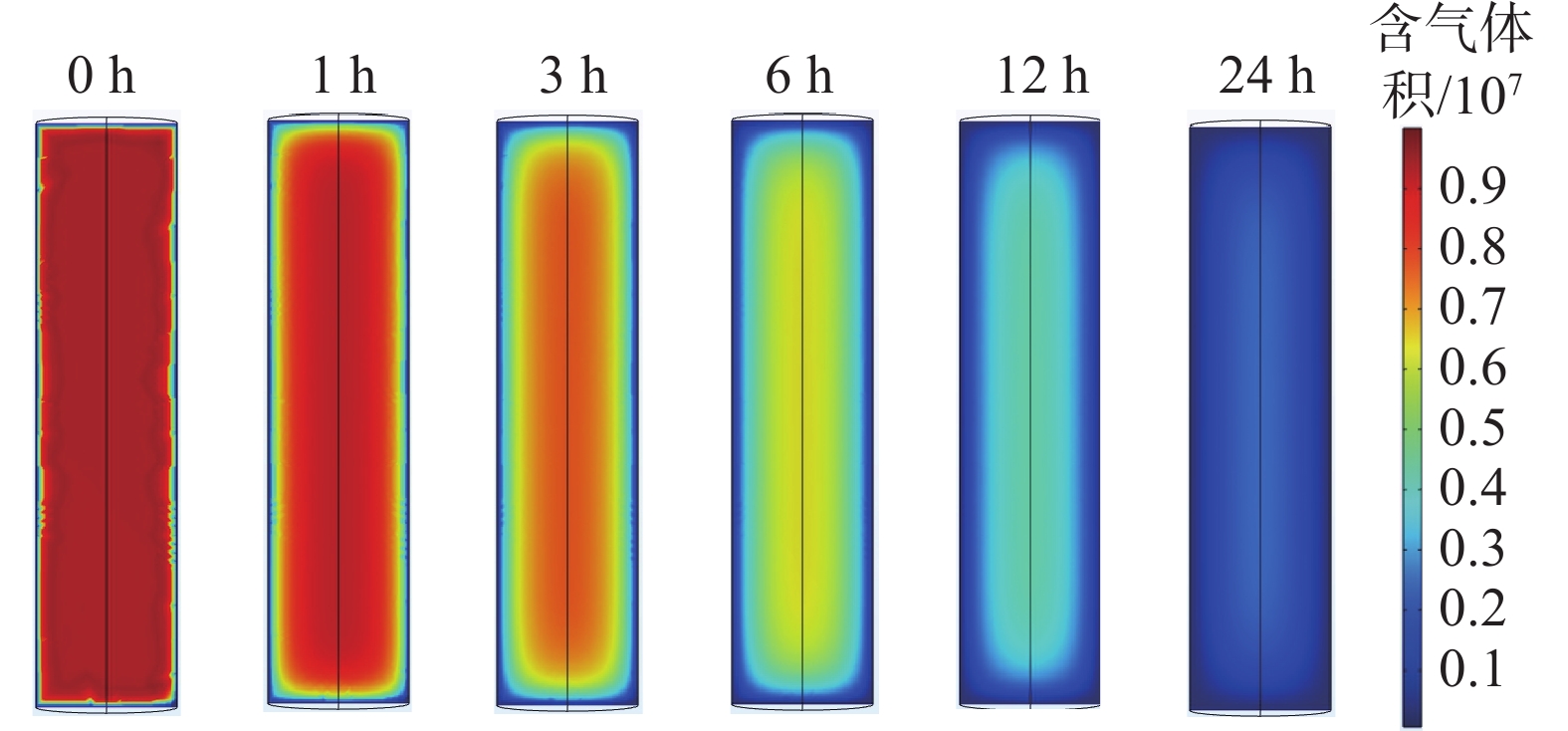
采用与煤心参数近似数据开展模拟并拟合解吸体积曲线,还原现场解吸参数和煤样特性参数。储层煤心参数实测值与拟合值对比见表2,煤心xy中心截面单位体积煤心含气性变化如图2。BF-1煤心累计解吸体积与解吸时间关系如图3。
表 2 储层煤心参数实测值与拟合值对比Table 2. Comparison between measured values and fitting values of coal core parameters of reservoir参数 实测值(BF1/BF2/BF3) 拟合值(BF1/BF2/BF3) 误差率/%
(BF1/BF2/BF3)储层压力/ MPa 9.88/9.25/8.96 9.88/9.25/8.96 0/0/0 兰氏压力/ MPa 1.92/2.05/1.65 1.92/2.05/1.65 0/0/0 兰氏体积/
(cm3·g−1)19.23/22.05/15.40 18.60/20.10/13.80 3.28/8.84/10.39 水分含量
(空干基)/%0.90/0.86/1.12 0.93/0.93/1.08 3.33/8.14/3.57 灰分产率
(干燥基)/%11.77/22.08/13.40 11.72/23.18/14.20 0.42/4.98/5.97 煤心密度/
(g· cm−3)1.36/1.44/1.44 1.36/1.44/1.44 0/0/0 孔隙度 0.10/0.09/0.08 0.10/0.08/0.072 0/11.1/10.0 扩散系数/
10−9(m2·s−1)4×10−9/—/— 3.70/1.00/0.80 7.50/—/— 含气
饱和度/%54.77/77.51/99.79 54.77/77.51/99.79 0/0/0 由图2可知:解吸开始24 h,含气量快速下降,各时刻煤心中心位置含气量最高而边缘最低。
由图3可知:BF-1扣除损失气时间拟合累计解吸气量(6 427.66 cm3)与现场煤心累计解吸气量(6 346.73 cm3)接近,相差2.00%;未扣损失气时间模拟累计解吸量(7 361.4 cm3)大于上述二者,显示损失气的存在;同理,BF-2和BF-3也有类似结果。
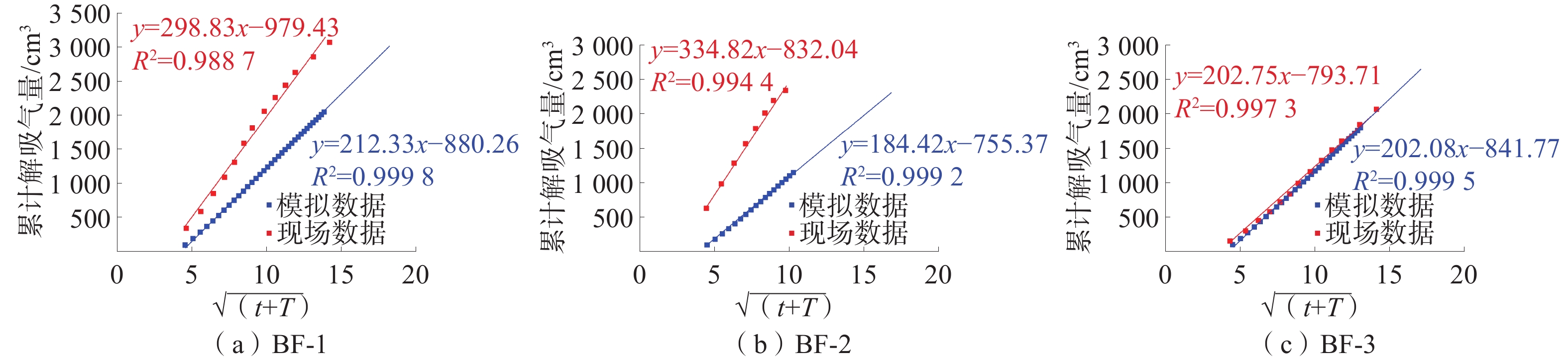
吸附气饱和储层煤心现场解吸与数值模拟含气量构成对比见表3,BF-1、BF-2、BF-3煤心损失气时间(T)与解吸时间(t)和的平方根和解吸初期累计解吸气量回归关系如图4。
表 3 吸附气饱和储层煤心现场解吸与数值模拟含气量构成对比Table 3. Comparison of adsorbed gas saturated reservoirs between on-site desorption and numerical simulation of cores样品 含气饱和度/% 含气量构成 实测体积/cm3 占比/实测/% 拟合体积/cm3 占比(拟合)/% 实测-拟合误差/% BF-1 54.77 损失气 979.43 13.28 880.26 11.95 10.12 解吸气 6 346.73 86.06 6427.66 87.32 2.00 残余气 48.43 0.66 46.24 0.63 4.52 总含气量 7 374.59 100.00 7361.40 100.00 0.18 BF-2 77.51 损失气 823.04 7.80 755.37 7.03 8.22 解吸气 9680.43 91.78 9937.60 92.52 2.66 残余气 43.88 0.42 47.89 0.45 9.14 总含气量 10290.96 100.00 10740.86 100.00 1.83 BF-3 99.79 损失气 793.71 6.36 841.77 6.75 6.06 解吸气 11638.39 93.26 11575.20 92.84 0.54 残余气 47.56 0.38 50.32 0.40 5.80 总含气量 12479.66 100.00 12467.29 100.00 0.10 对于BF-1煤心,现场测试BF-1煤心损失气量结果为979.43 cm3,与数值模拟结果前15 min解吸气量(880.26 cm3)(图4(a))接近。现场BF-1煤心解吸气量和残余气量与数值模型计算的解吸气量和残余气量也较接近。
BF-2和BF-3煤心现场测试煤心损失气量结果分别为823.04、793.71 cm3,略低于与数值模拟结果前15 min解吸气量(952.40、1015.80 cm3) (图4(b)、图4(c)),说明吸附气饱和度较高煤心解吸初期损失气量时间平方根法计算结果可能略偏小。这可能是吸附气饱和度较高,煤心内CH4浓度高,扩散作用更显著导致。用损失气时间与解吸时间和的平方根与解吸初期累计解吸气量的线性回归关系计算BF-2和BF-3煤心损失气量,发现基于数值模拟计算的损失气量结果(755.37、841.77 cm3)与基于现场实测的损失气量计算结果(832.04、793.71 cm3)较为接近。说明基于数值模拟数据利用时间平方根法计算的损失气量与实测时间平方根法估算的损失气量较为接近。
现场实测BF-1、BF-2和BF-3煤心解吸气量和残余气量与数值模型计算出的解吸气量和残余气量也较为接近,误差不超过10.12%(表3)。说明数值模型可以近似反映吸附气欠饱和储层煤心真实解吸过程和损失气量、解吸气量、残余气量特征。
2.2 饱和储层煤心含气量测试与数值模拟
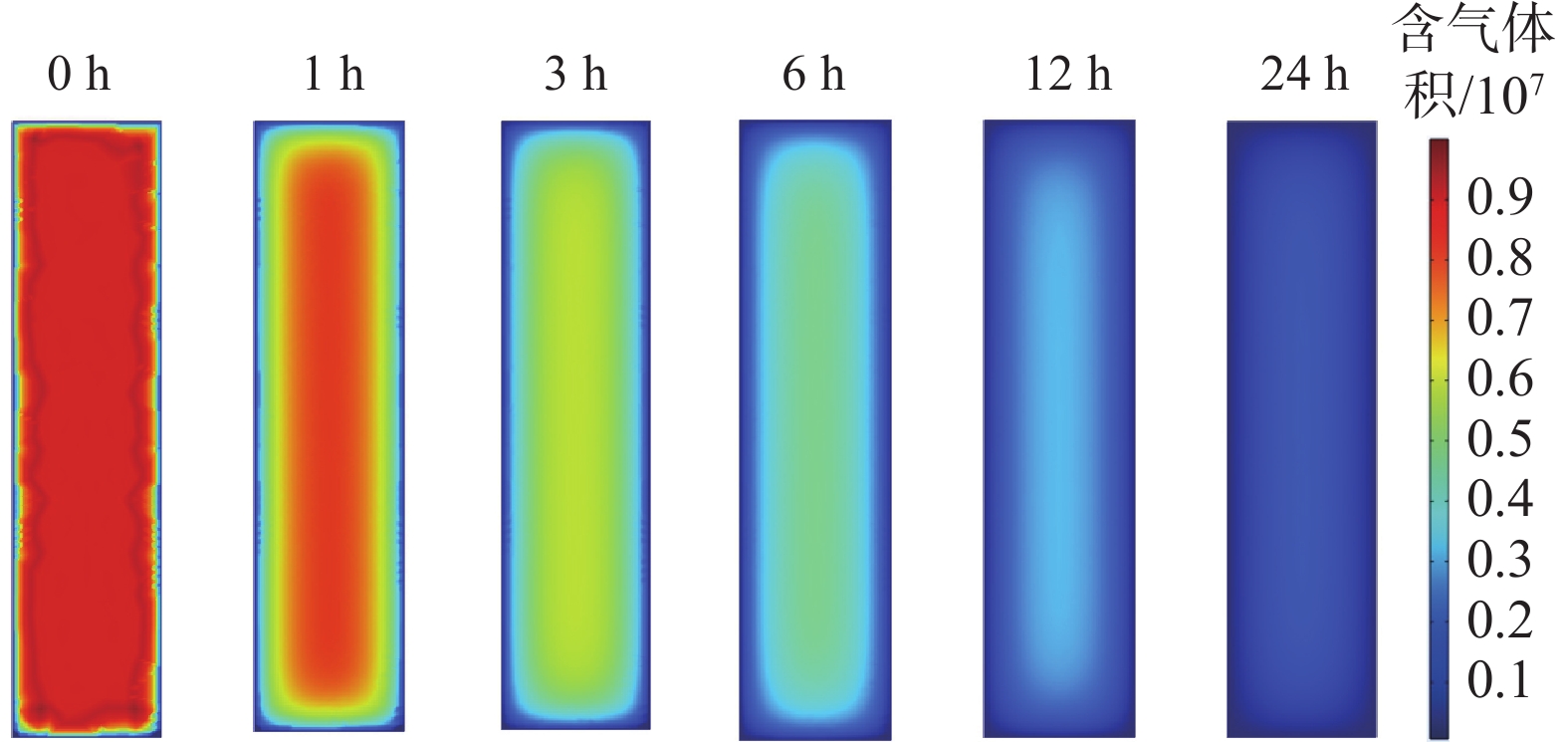
以BF-1煤心为例,采用现场实测参数数据(表2),假设煤心处于饱和状态(即吸附气饱和、游离气在储层压力条件下充满孔隙也达到饱和状态),对现阶段现场含气量测试难度较大的含气饱和煤心解吸-扩散过程进行模拟。含气饱和煤心xy中心截面各位置单位体积煤心含气性变化如图5。
由图5可知:解吸前24 h煤心含气量快速下降,各时刻煤心中心位置含气量最高而煤心边缘含气量最低。
损失气时间与解吸时间和的平方根和累计解吸气量的线性回归关系如图6。饱和储层煤心解吸-扩散数值模拟含气量构成预测见表4。
表 4 饱和储层煤心解吸-扩散数值模拟含气量构成预测Table 4. Prediction of gas content composition of coal core desorption-diffusion numerical simulation in saturated core含气量构成 预测体积/cm3 占比/% 损失气 3 792.50 18.64 解吸气 16 460.70 80.90 残余气 93.51 0.46 总含气量 20 346.71 100.00 数值模拟显示,损失气时间内(15 min)假设的饱和煤心解吸-扩散气量达到4 441.3 cm3,相同损失气时间的情况下,约为相应吸附气欠饱和储层煤心此时间段解吸气量(即本例损失气量)的4倍。
损失气时间与解吸时间和的平方根与解吸初期累计解吸气量的线性回归关系截距为正数(R2=0.9988),暗示采用解吸时间平方根与解吸初期累计解吸气量线性回归方法并不适用于饱和煤心损失气量的估算;采用解吸时间平方根与解吸初期累计解吸气量多项式回归方法,计算得煤心损失气量仅为433.11 cm3(R2=0.9988),甚至小于吸附气欠饱和储层煤心损失气量估算值,说明基于时间平方根与累计解吸气量的相关性分析方法可能无法准确估算损失气量。同时测试初期时间平方根与累计解吸气量的回归关系(图6蓝色标记)和损失气时间与累计气量的回归关系(图6红色标记,实测测不出部分)也存在较大差异,说明饱和煤心损失气时间解吸-扩散规律较为复杂,常规回归分析法可能难以实现对损失气量的准确估算。
由表4可知:饱和煤心损失气、解吸气、残余气占比分别为18.64%、80.90%、0.46%,其损失气占比高于吸附气欠饱和煤心损失气占比、解吸气占比低于吸附气欠饱和煤心解吸气占比。
数值模型可以近似反映吸附气欠饱和储层煤心真实解吸过程和损失气量、解吸气量、残余气量特征。目前,含气量现场测试手段很难达到对饱和煤心含气量的准确测试和估算,希望通过数值模拟为含气饱和煤心含气量分析提供思路。
3. 结 语
1)构建的吸附气欠饱和煤心解吸数值模型计算的损失气量、解吸气量和残余气量与现场测试相应结果接近(误差<10.12%),可近似反映吸附气欠饱和储层煤心含气量构成。
2)对于构建的含气饱和储层煤心数值模型,损失气时间与解吸时间和的平方根与解吸初期累计解吸气量的回归分析法预测损失气量误差较大。饱和煤心损失气时间解吸-扩散规律较为复杂,常规回归分析可能难以实现对损失气的准确估算。
3)相同损失气时间条件下,本例饱和煤心损失气总含气量占比(18.64%)高于吸附气欠饱和煤心损失气占比(11.95%),饱和煤心解吸气占比(80.90%)低于吸附气欠饱和煤心解吸气占比(87.32%),饱和煤心残余气占比(0.46%)低于吸附气欠饱和煤心残余气占比(0.63%)。
-
表 1 煤心工业分析及煤岩组分分析成果
Table 1 Coal core industrial analysis and coal rock composition analysis results
样品编号 直径/mm 长度/cm 宏观煤岩类型 平均镜质组最大反射率/% 水分/% 灰分/% 挥发分/% 镜质组组分/% 惰质组组分/% 壳质组组分/% BF-1 63.0 26.8 半亮煤 0.60 0.90 11.77 43.79 84.2 14.8 1.0 BF-2 60.1 30.0 半亮煤 0.61 0.86 22.08 40.45 79.6 19.4 1.0 BF-3 61.0 34.0 半亮煤 0.67 1.12 13.40 37.17 78.6 25.5 1.0 表 2 储层煤心参数实测值与拟合值对比
Table 2 Comparison between measured values and fitting values of coal core parameters of reservoir
参数 实测值(BF1/BF2/BF3) 拟合值(BF1/BF2/BF3) 误差率/%
(BF1/BF2/BF3)储层压力/ MPa 9.88/9.25/8.96 9.88/9.25/8.96 0/0/0 兰氏压力/ MPa 1.92/2.05/1.65 1.92/2.05/1.65 0/0/0 兰氏体积/
(cm3·g−1)19.23/22.05/15.40 18.60/20.10/13.80 3.28/8.84/10.39 水分含量
(空干基)/%0.90/0.86/1.12 0.93/0.93/1.08 3.33/8.14/3.57 灰分产率
(干燥基)/%11.77/22.08/13.40 11.72/23.18/14.20 0.42/4.98/5.97 煤心密度/
(g· cm−3)1.36/1.44/1.44 1.36/1.44/1.44 0/0/0 孔隙度 0.10/0.09/0.08 0.10/0.08/0.072 0/11.1/10.0 扩散系数/
10−9(m2·s−1)4×10−9/—/— 3.70/1.00/0.80 7.50/—/— 含气
饱和度/%54.77/77.51/99.79 54.77/77.51/99.79 0/0/0 表 3 吸附气饱和储层煤心现场解吸与数值模拟含气量构成对比
Table 3 Comparison of adsorbed gas saturated reservoirs between on-site desorption and numerical simulation of cores
样品 含气饱和度/% 含气量构成 实测体积/cm3 占比/实测/% 拟合体积/cm3 占比(拟合)/% 实测-拟合误差/% BF-1 54.77 损失气 979.43 13.28 880.26 11.95 10.12 解吸气 6 346.73 86.06 6427.66 87.32 2.00 残余气 48.43 0.66 46.24 0.63 4.52 总含气量 7 374.59 100.00 7361.40 100.00 0.18 BF-2 77.51 损失气 823.04 7.80 755.37 7.03 8.22 解吸气 9680.43 91.78 9937.60 92.52 2.66 残余气 43.88 0.42 47.89 0.45 9.14 总含气量 10290.96 100.00 10740.86 100.00 1.83 BF-3 99.79 损失气 793.71 6.36 841.77 6.75 6.06 解吸气 11638.39 93.26 11575.20 92.84 0.54 残余气 47.56 0.38 50.32 0.40 5.80 总含气量 12479.66 100.00 12467.29 100.00 0.10 表 4 饱和储层煤心解吸-扩散数值模拟含气量构成预测
Table 4 Prediction of gas content composition of coal core desorption-diffusion numerical simulation in saturated core
含气量构成 预测体积/cm3 占比/% 损失气 3 792.50 18.64 解吸气 16 460.70 80.90 残余气 93.51 0.46 总含气量 20 346.71 100.00 -
[1] 赵丽娟,秦勇,林玉成. 煤层含气量与埋深关系异常及其地质控制因素[J]. 煤炭学报,2010,35(7):179−181. ZHAO Lijuan, QIN Yong, LIN Yucheng. Abnormal relation and its geological controls of coalbed methane content to buried depth of coal seams[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2010, 35(7): 179−181.
[2] 彭苏萍,杜文凤,殷裁云,等. 基于AVO反演技术的煤层含气量预测[J]. 煤炭学报,2014,39(9):1792−1796. PENG Suping, DU Wenfeng, YIN Caiyun, et al. Coal-bed gas content prediction based on AVO inversion[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2014, 39(9): 1792−1796.
[3] 傅雪海,简阔,丁永明,等. 低煤化储层三相态含气量模拟研究[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2015:139-142. [4] 傅雪海,张小东,韦重韬. 煤层含气量的测试、模拟与预测研究进展[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2021,50(1):13−31. FU Xuehai, ZHANG Xiaodong, WEI Chongtao. Review of research on testing, simulation and prediction of coalbed methane content[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2021, 50(1): 13−31.
[5] 秦勇. 中国煤层气成藏作用研究进展与述评[J]. 高校地质学报,2012,18(3):405−418. QIN Yong. Advances and reviews on coalbed methane reservoir formation in China[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2012, 18(3): 405−418.
[6] 孙粉锦,王勃,李梦溪,等. 沁水盆地南部煤层气富集高产主控地质因素[J]. 石油学报,2014,35(6):1070−1079. SUN Fenjin, WANG Bo, LI Mengxi, et al. Major geological factors controlling the enrichment and high yield of coalbed methane in the southern Qinshui Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2014, 35(6): 1070−1079.
[7] 葛燕燕,秦勇,傅雪海,等. 不同粒径煤样常压与带压解吸对比实验研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2015,44(4):673−678. GE Yanyan, QIN Yong, FU Xuehai, et al. Comparative experimental study of atmospheric pressure desorption and methane pressure desorption among coal samples of different particle sizes[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2015, 44(4): 673−678.
[8] 匡立春,温声明,李树新,等. 低煤阶煤层气成藏机制与勘探突破-以吐哈—三塘湖盆地为例[J]. 天然气工业,2022,42(6):33−42. KUANG Lichun, WEN Shengming, LI Shuxin, et al. Accumulation mechanism and exploration breakthrough of low-rank CBM in the Tuha-Santanghu Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(6): 33−42.
[9] 柴建禄. 基于梳状定向钻孔的碎软煤层瓦斯含量测定取样技术[J]. 煤矿安全,2022,53(6):96−100. CHAI Jianlu. Sampling technology for measuring gas content in broken soft coal seam based on comb-shaped directional borehole[J]. Safty in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(6): 96−100.
[10] 周福宝,康建宏,王有湃,等. 煤层瓦斯含量井下一站式自动化精准测定方法[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(8):2873−2882. ZHOU Fubao, KANG Jianhong, WANG Youpai, et al. Method of underground integrated automatic and accurate determination of coalbed gas content[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(8): 2873−2882.
[11] 张羽,郝富昌. 基于瓦斯解吸规律的掘进落煤瓦斯涌出量预测[J]. 煤矿安全,2021,52(4):20−24. ZHANG Yu, HAO Fuchang. Prediction of gas emission from landing coal during driving based on gas desorption law[J]. Safty in Coal Mines, 2021, 52(4): 20−24.
[12] 冯三利,胡爱梅,霍永忠,等. 美国低阶煤煤层气资源勘探开发新进展[J]. 天然气工业,2003,23(2):124−126. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2003.02.041 [13] 张群,范章群. 煤层气损失气含量模拟试验及结果分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2009,34(12):1649−1654. ZHANG Qun, FAN Zhangqun. Simulation experiment and result analysis on lost gas content of coalbed methane[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2009, 34(12): 1649−1654.
[14] 李忠城,唐书恒,吴敏杰,等. 煤层气损失气量计算的全脱分析法[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2013,41(1):20−24. LI Zhongcheng, TANG Shuheng, WU Minjie, et al. A new method for calculation of lost coalbed methane[J]. Coal Geology and Exploration, 2013, 41(1): 20−24.
[15] 周敏. 煤层气USBM含气量测试过程中损失气量的物理模拟实验及校正方法研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2014:35-59. [16] 苗杰,倪小明,曹运兴,等. 低阶煤含气量修正数学模型及应用[J]. 煤矿安全,2017,48(2):153−155. MIAO Jie, NI Xiaoming, CAO Yunxing, et al. Modified mathematical model of low rank coal gas content and its application[J]. Safty in Coal Mines, 2017, 48(2): 153−155.
[17] 赵晓莉,张遂安. 利用排采数据校正煤层含气量[J]. 科学技术与工程,2014,14(10):137−139. ZHAO Xiaoli, ZHANG Suian. Gas content calibration through production data[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2014, 14(10): 137−139.



 下载:
下载: